Abstract
Monitoring the living and production standards of resettlers due to hydraulic engineering is at the core of the evaluation of the effectiveness of resettlement and providing post-relocation support. In the past two decades, 0.196 million individuals were relocated outside of the reservoir area (out-resettlers) because of the construction of Three Gorges Dam. In 2019, large-scale tracking and monitoring of resettlers in 1371 households in 122 villages and 12 provinces was conducted by using the methods of stratified sampling, equidistant random sampling, and simple random sampling. The status of out-resettlers from the Three Gorges Reservoir area was compared with that of local residents in resettlement areas and nearby-resettlers based on the production–living–social security–social integration–satisfaction perspective. The results show that the living and production conditions of out-resettlers have significantly improved, and their income and consumption were positively correlated with the development level of the resettlement area. More than 90% of out-resettlers have adapted to local languages, cultural customs, and living habits. Out-resettlers have the highest satisfaction with infrastructure construction and public service facilities, at more than 90%, and the lowest satisfaction with the availability of arable land, at approximately 80%. This study can provide a reference for follow-up work on the Three Gorges Project.
1. Introduction
The demand for energy has increased dramatically with the rapid growth of the global economy. Hydropower, as a renewable energy source, causes less pollution in the environment and will become an essential source of low-carbon power generation in response to climate pledges and the goal of decreasing greenhouse gas emissions in the power sector [1,2]. Hydroelectric energy requires the construction of dams, which can lead to massive reservoir resettlement. There are no reliable global data on involuntary resettlement as a result of development. The World Bank estimated that in the 1990s, around 100 million people were displaced by hydropower, transportation, and urban projects, with an average of 10 million relocated each year. From 2001 to 2010, this number increased to 15 million each year, for a total of 150 million. It was estimated that 20 million people would be displaced yearly between 2011 and 2020 [3,4]. There is a risk of sliding into poverty if resettlement livelihoods are not recovered and resettlement is not handled appropriately [5,6,7]. According to Cernea, the vast majority of involuntary resettlers as a result of development in India are living in poverty [8]. This has happened not only in developing countries but also in developed countries [9,10]. For example, the Tennessee Valley Comprehensive Development Projects in the United States once displaced 12,000 households [11].
In terms of the internal dynamics, population removal can be divided into active and passive resettlement, or “voluntary” and “involuntary” resettlement. Voluntary resettlement refers to people migrating independently after weighing the economic, social, environmental, and other benefits of their original location and places where they could emigrate in order to achieve goals or avoid risks. For example, people migrate to developed cities or countries for their own development. Involuntary resettlement refers to the migration decision being forced on people due to external reasons when they have no intention to migrate, such as resettlement caused by reservoir, transportation, urban infrastructure, and other projects. Compared with voluntary resettlement, involuntary resettlement involves no rational thinking or willingness to relocate and lacks subjective adaptation and the motivation to integrate in the society and environment in the new location [12]. Reservoir resettlement is a kind of involuntary resettlement. After resettlement, the original lifestyle of resettlers was destroyed, and as a consequence of poverty caused by forced migration, not only are their economic activities and income interrupted, and food, clothing, housing, and transportation not guaranteed, but also, necessary public services such as medical treatment and education may be lost, and they are marginalized by the social mainstream and can even become refugees [13].
The focus of involuntary resettlement policy prior to the 1980s was relief and compensation, which was exclusively focused on the living conditions of the displaced population while ignoring the growth of production. Resettlers had a hard time supporting themselves, because their livelihoods were dependent on government assistance [14]. In 1980, the first resettlement policy, “Social Problems Caused by Involuntary Resettlement in World Bank-Funded Projects”, was developed and published by the World Bank. It promoted the policy of “land-for-land” and the rehabilitation of economic and social infrastructure [15]. Cernea proposed the Impoverishment Risks and Reconstruction Model (IRR) in 1997, focusing on three main concepts of risk, poverty, and reconstruction. This model pointed out eight major risks faced by resettlers after project relocation: loss of land, unemployment, loss of homes, marginalization, increased incidence of disease and mortality, food insecurity, loss of access to public infrastructure, and disintegration of social organization. The evaluation model included prediction, diagnosis, problem-solving, and research functions, as well as proposing measures to avoid risks and rebuild livelihoods [8]. Michael studied the impact of the construction of the Xiaolangdi Project on the production and income of involuntary resettlers. He proposed that avoiding land loss, having unemployment insurance, reducing the low-income proportion, and developing sufficiently detailed plans to deal with different rural economies should be the focus of agricultural resettlement in China [16]. Gu thought that the income of resettlers was the most significant societal factor and used a multiple linear regression model to analyze the influencing factors. The results showed that the amount of education had no significant effect, family upbringing had a negative effect, the average age of the labor force had a V-shaped relationship with income, and there was a significant positive correlation between immigration policy and government subsidy [17]. Involuntary resettlement faces disadvantageous situations such as reduction in land area, loss of production sites, and worker stoppage or unemployment. Resettlers cannot legitimately share the benefits of water resource development and may even slip into poverty, and they must rely on the implementation of resettlement policies and their own resilience to restore productive living standards [18].
By 2020, China had constructed a total of 98,566 reservoirs [19], and approximately 26 million people were relocated due to development [20]. The monitoring and evaluation of involuntary resettlement originated in China [21]. The Chinese government issued a document called “Opinions on Improving Post-Relocation Support Policies for Large and Medium-Sized Reservoirs” in 2006 that demanded the construction of a monitoring and assessment framework for the implementation of post-support policy. Chen monitored and evaluated the implementation effect of post-relocation support through a questionnaire survey and interviews on resettlement due to the large and medium-sized reservoirs in Luxi County, Yunnan Province, China. The results showed that the production and living conditions of the poor resettlers in the Luxi County reservoir area and resettlement area had improved [22]. Zuo summarized the monitoring and evaluation of post-relocation support for reservoir resettlement from 2008 to 2011 and found that support policies, collection and management of funds for poverty alleviation, and implementation of support policies were the main contents. A monitoring and evaluation index system was also established [23]. Early evaluations of the effects of resettlement assistance tended to focus on production and living standards and economic evaluations [24,25]. With the need for sustainable development, there are new requirements for evaluating the effects of resettlement assistance, and more attention should be paid to the long-term livelihood and sustainable development of resettlers [26]. The government and researchers should focus on objective evaluation indicators from the viewpoint of observers, such as monthly salary, as well as subjective and descriptive indicators from the viewpoint of resettlers, such as those related to satisfaction [27]. Nowadays, the connotation of quality of life has gradually diverged from physiology to include physiology, psychology, and society, and its rise is related to social development and improvement in living standards [28]. Objective living conditions and subjective feelings are indispensable aspects of quality of life. The quality of life of reservoir migrants can be seen as the value orientation of the support effect. If only the subjective well-being of migrants is taken into consideration, it is difficult to accurately and quantitatively reflect the support effect. On the contrary, if researchers only focus on the objective living conditions of migrants, it is easy to ignore their needs and lose the focus of support.
The Three Gorges Dam was constructed on the Yangtze River over more than 20 years and has reaped enormous benefits [29]. However, millions of residents around reservoirs were resettled because of this project. By December 2009, approximately 1.2964 million individuals had been relocated. There are two kinds of Three Gorges migrants; one is nearby-resettlers who were resettled in the flooded county, and the other is out-resettlers who were resettled out of the flooded county. They have many similarities, but compared with nearby-resettlers, involuntary and forced long-distance migration have meant a lack of psychological preparation for out-resettlers, and profound changes have taken place in their production and living structure, cultural customs, and social environment. The “hometown is difficult to leave” concept is more prominent for out-resettlers, and their social networks are more damaged. Some studies about relocation due to the Three Gorges Project were conducted recently. Brooke conducted a questionnaire survey and in-depth interviews with resettlers due to the Three Gorges Project in 2003 and 2011, analyzed the resettlers’ livelihoods in a longitudinal study, and discovered that the income inequality and food security of the sample group had improved, and their income and happiness had increased [30]. Suo investigated resettlement in the Three Gorges Reservoir area and found that the social and economic aspects of the reservoir area were comprehensively developed in 2007 [31]. The existing research mainly focuses on nearby-resettlers, while out-resettlers have received less attention [32].
In order to objectively analyze and evaluate the quality of life of out-resettlers, determine the problems of resettlement, and put forward proposals, this research selected out-resettlers from the Three Gorges Project as the research object, with 2019 as the monitoring year, and the monitoring scope was resettlement counties (cities, districts), including Shanghai Municipality, Jiangsu Province, Zhejiang Province, Shandong Province, Fujian Province, Guangdong Province, Anhui Province, Jiangxi Province, Hunan Province, Hubei Province, Chongqing Municipality, and Sichuan Province. This research analyzed the resettlement status of out-resettlers from the Three Gorges area in terms of production level, living level, social security, social integration, and satisfaction compared with local residents in the resettlement area and nearby-resettlers in Three Gorges Reservoir area. The results can provide a reference for effectively improving the financial status and maintaining the social security of out-resettlers from the Three Gorges Project.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
The study used data from monitoring and investigation provided by the Three Gorges Project Management Department of the Ministry of Water Resources, and the Statistics Yearbook of China and the Three Gorges Project Reservoir Area and resettlement provinces.
2.2. Investigation Methods
The monitoring and investigation data were primarily obtained through household inquiries (income and consumption), on-site inspections (houses, farmland, durable consumer goods, living environment, etc.), file inspections (five guarantees, household registration book, subsidy issuance book, property right certificate, etc.), case verification, and so on.
2.2.1. Sampling Methods
In order to comprehensively, objectively, and scientifically reflect the production and living standards of out-resettlers, the selection of samples for this survey follows the principles of representativeness, scientificity, applicability, and operability. The details are as follows:
The monitoring samples in the 12 resettlement provinces were selected using the methods of stratified sampling, equidistant random sampling, and simple random sampling. First, considering factors such as the number of resettlers, the degree of economic development, and the stability of petitions, at least two key counties (cities, districts) in each resettlement province (city) were selected as samples. Second, sample villages were selected that represented not less than 10% of the total number of resettlement villages in the county, numbering between 2 and 15. For counties with highly dispersed population distribution, the number of sample villages was appropriately increased until reaching county (city, district) sample size requirements. Third, the sample should be representative and cover the village groups where the Three Gorges resettlement was located. During the selection of sample households, economic income, education level, and consumption ability were fully considered to represent various groups of people with high, medium, and low economic status in the region, and the structure should have a reasonable ratio. Then, 15 to 20 sample households were selected from each village (group), with the total number in each county (city, district) not less than 50 and not more than 70, and the proportions of resettlers and non-resettlers were basically balanced. Finally, there were 24 sample counties (cities, districts), 122 sample villages, and 1371 sample households, totaling 5571 people. Among them, 723 households with 3076 people were from the Three Gorges Reservoir, 316 households with 1279 people were from other large and medium-sized reservoirs, and 332 households with 1192 people were local residents. Considering the randomness of sampling and the universality of sample space, we assumed that the selected samples could reflect out-resettlers to some extent.
2.2.2. Data Analysis Methods
Using the questionnaire and interview data, Excel and MATLAB were used for data processing and interpolation and integral calculation to analyze the resettlement situation of Three Gorges Project out-resettlers and their relationship with the local situation in 2019.
(1) Statistical analysis: A comprehensive statistical analysis of the quality of life of out-resettlers in terms of production level, living level, social security, social integration, and satisfaction was conducted.
(2) Comparative analysis: Through comparisons of the above indicators regarding out-resettlers and local residents in the resettlement area and out-resettlers in different provinces, we analyzed the gaps in the quality of life of out-resettlers in different provinces and the gaps between out-resettlers and local residents.
2.3. Selection of Survey Indicators
With reference to the statistical monitoring indicators for building a well-off society in an all-round way and the household income, consumptions, and living conditions survey plan compiled by the National Bureau of Statistics and other standard systems and technical specifications in China, combined with the tasks and goals of tracking and monitoring the production and living standards of out-resettlers from the Three Gorges area, we set up a corresponding 3-level indicator system for comparison and analysis from 7 aspects: farmland, employment, income, consumption, social security, social integration, and satisfaction. Details are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Indicators regarding out-resettlers used in the investigation.
2.4. Overview of Out-Resettlers fromThree Gorges Project
Among the 1.296 million people relocated because of the Three Gorges Project, 0.551 million were relocated to rural areas. Among rural resettlers, 0.355 million individuals were relocated within the Three Gorges Reservoir area (nearby-resettlers), and 0.196 million were relocated outside of the reservoir area (out-resettlers), including in Shanghai Municipality, Jiangsu Province, Zhejiang Province, Shandong Province, Fujian Province, Guangdong Province, Anhui Province, Jiangxi Province, Hunan Province, Hubei Province, Chongqing Municipality, and Sichuan Province. The government implemented a number of resettlement, support, monitoring, and evaluation projects. Among the 0.1962 million out-resettlers, 0.153 million individuals were resettled by the government. Most out-resettlers (0.076 million) were relocated to Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan Provinces, accounting for roughly half of the total resettler population. In terms of living space, a total of 58.54 hm2 of homestead was allotted, with 37,110 newly-built (purchased) houses occupying 49.98 hm2. The per capita housing area of resettlers was 32.66 m2. A total of 10,968.79 hm2 of farmland was allotted for production (Table 2). The remaining 0.046 million resettlers were actively dispersed and relocated across the country to 29 provinces (municipalities and autonomous regions). The relocation regions are shown in Figure 1.

Table 2.
Overview of out-resettlers.
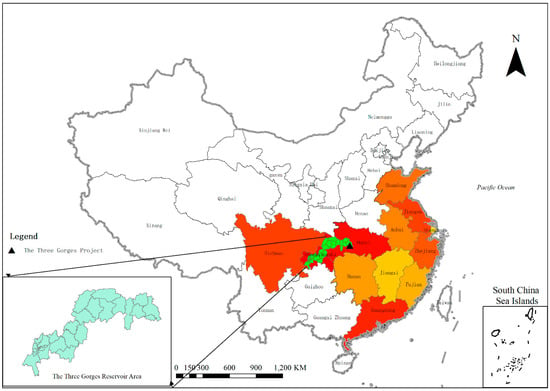
Figure 1.
Distribution of out-resettlers due to Three Gorges Project. Note: Shandong, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Fujian are coastal cities. Source: Completion acceptance report of the Three Gorges Resettlement Project.
The shades of color in Figure 1 represent the numbers of resettlers. It can be clearly seen that the provinces with the largest distribution of resettlers are those near the Three Gorges Project, including Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan. This was mainly because of the policy of initial resettlement. Out-resettlers were first resettled in their own provinces and economically developed provinces, then in neighboring provinces, and then in provinces(cities) along the Yangtze River. The government of the receiving area adopted preferential policies for resettlers and provided support in terms of funds and materials, so as to mobilize their enthusiasm.
3. Results
3.1. Production Conditions
According to the monitoring data, the per capita farmland area was 686.67 m2 for sample households, 646.67 m2 for households of out-resettlers, 653.34 m2 for households of resettlers from other large and medium-sized reservoirs, 846.67 m2 for households of local residents, and 486.67 m2 for nearby-resettlers. From Figure 2, it can be seen that the per capita farmland area for out-resettlers, except in Shanghai and Zhejiang Provinces, was smaller than that of local residents in resettlement counties, while the per capita farmland area for out-resettlers was mostly larger than that of nearby-resettlers. This is mainly because of geographical constraints in the reservoir area creating a contradiction between more people and less land, the per capita arable land area of nearby-resettlers is generally lower than that in plain areas [33,34]. Additionally, out-resettlers can chose locations with rich arable land and resources.
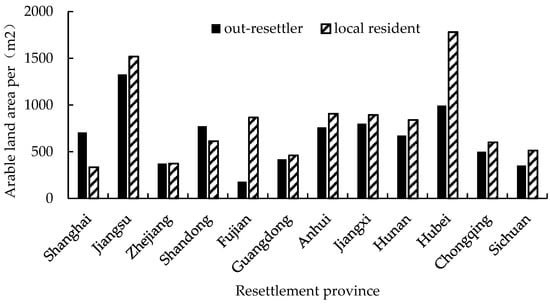
Figure 2.
Per capita cultivated land area of out-resettlers and local residents.
The employment structure and employment rate also affect resettlers’ income and income stability to a certain extent. Table 3 shows the employment of out-resettlers. The employment rate of out-resettlers in Zhejiang and Hubei Provinces was the highest at nearly 90%. The employment rate of out-resettlers in Guangdong Province was the lowest at 58%. In terms of employment structure, generally speaking, non-coastal provinces such as Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Sichuan, and Shandong mainly focus on agricultural production, while coastal provinces such as Shanghai, Jiangsu, Guangdong, and Zhejiang rely on local odd jobs, migrant workers, and stable employees of enterprises and institutions.

Table 3.
Employment of out-resettlers.
3.2. Living Conditions
3.2.1. Income Analysis
Figure 3 shows that the per capita disposable income of out-resettlers’ households in all provinces was higher than that of nearby-resettlers’ households. The per capita disposable income of out-resettlers was the highest in Shanghai Municipality at RMB 34,777, which is 138% higher than that of nearby-resettlers, at RMB 14,627. The per capita disposable income of out-resettlers was the lowest in Jiangxi Province at RMB 14,697, which is higher than that of nearby-resettlers. People’s living standards in the reservoir area have significantly improved after long-term development. However, due to geographic, energy, transportation, and other constraints in the reservoir area, development has been limited, while the relocated provinces of out-resettlers were in good development condition, with accessible transportation and generally complete infrastructure [35]. Out-resettlers were considered in large and medium-sized reservoir resettlement support in follow-up planning of resettlement provinces. The government integrated a variety of resources, solved the issues of economic and social development in the resettlement area, and significantly improved the out-resettlers’ living and working conditions. The economic resilience and development potential of out-resettler households were greatly boosted, and they now have the overall characteristics of realizing employment and entrepreneurship.
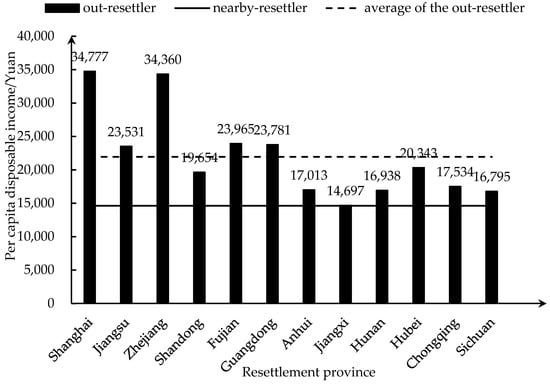
Figure 3.
Per capita disposable income of out-resettlers.
Figure 4 shows relatively high per capita disposable income in the coastal areas, while the income level in central China is relatively low. Correlation analysis was performed between the per capita disposable income of resettlers and the per capita GDP of the resettlement provinces, and the scatter trend line is shown in Figure 5. The Pearson correlation coefficient was 0.88, with correlation significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed), indicating a high correlation between per capita disposable income of out-resettlers and the development degree of resettlement provinces.
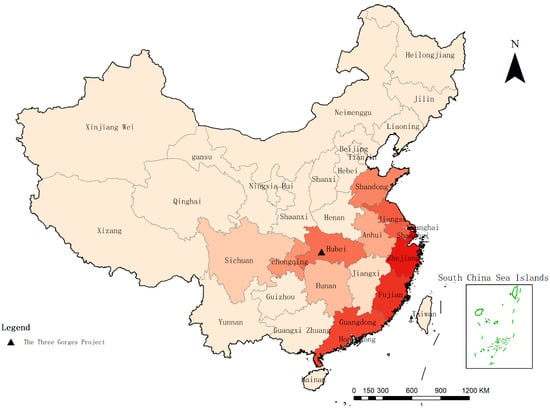
Figure 4.
Distribution of per capita disposable income of out-resettlers.
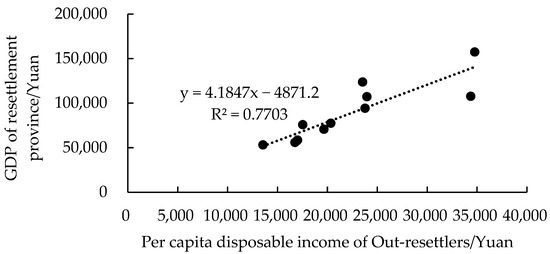
Figure 5.
The relationship between per capita disposable income of out-resettlers and GDP of resettlement provinces.
As shown in Figure 6, a comparison was made between the income of out-resettlers, local residents in the resettlement area, and rural residents of resettlement provinces to further analyze the characteristics of the income level of out-resettlers from the Three Gorges area. The per capita disposable income of out-resettlers in all relocated provinces, except Jiangxi Province, was higher than that of rural residents in the resettlement provinces. The income gap was the largest in Guangdong Province, where the per capita disposable income of out-resettlers was 20.9% higher than the average for local rural residents. According to our research on the industrial structure of Jiangxi Province during the investigation, due to industrial structure changes, the two resettlement counties of Xiajiang and Jingan in Jiangxi Province have ample land capacity, but insufficient development potential, and lack the development of secondary and tertiary industries, which can drive a continuous increase in out-resettlers’ income. The income level in these two counties was lower than the average in Jiangxi Province.
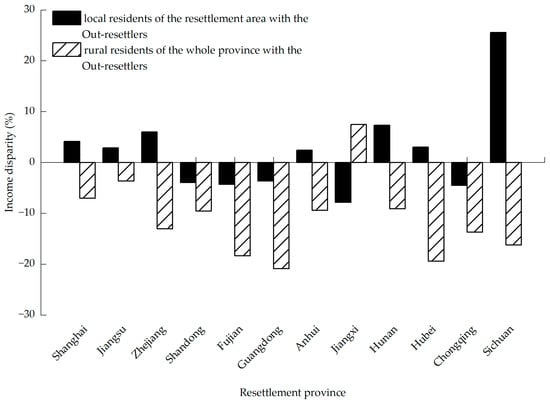
Figure 6.
Gap in per capita income between out-resettlers and local residents. Source: Statistics Yearbook of China.
Per capita disposable income of out-resettlers in most provinces was still lower than the average in resettlement counties. Changes in geography, environment, climate, and society have influenced the income levels of households after resettlers moved into resettlement areas. In the mountainous regions, before resettlement, out-resettlers could earn income from agriculture and ancillary products (tea, fruit, etc.), but after resettlement, such opportunities plummeted. Additionally, the advantages of geography and social connections were no longer present [35]. Out-resettlers typically have less ability to become wealthy and increase their income than local residents, because they lack information resources, employment opportunities, and familiarity with the local environment. Additionally, they have low education levels and their capacity for development is constrained. Generally speaking, the per capita disposable income of out-resettlers is higher than that of residents in resettlement provinces but lower than that of local residents in resettlement counties.
In order to assess the degree of income disparity across various regions within the same project, the Gini coefficient value of out-resettlers from each province was analyzed. The Gini coefficient is a measurement of the degree of unequal distribution in social income and a critical analytical index for assessing the wealth gap. In the study, the Lorenz curve was drawn using MATLAB cubic spline interpolation, and the Gini coefficient value for each province was calculated using an integral method. It is important to note that the Gini coefficient measures unequal distribution of social income rather than fairness. The Lorenz curves are illustrated in Figure 7.
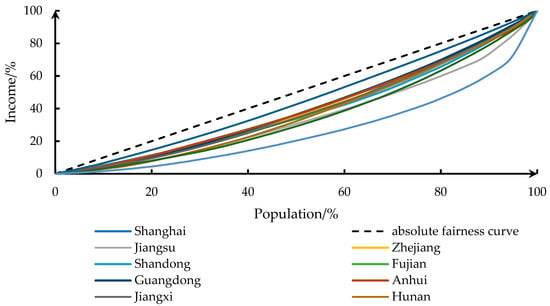
Figure 7.
Lorenz curve of out-resettlers.
Point on the curve in Figure 7 denotes that population has achieved overall income , and the area between the actual income distribution curve and the absolute equality line is designated by the letter . The Gini coefficient value (G) is then calculated using the formula:
The Gini coefficient values for out-resettlers are determined based on this integral [36].
Gini coefficient values ranging from 0.2 to 0.4 are thought to be more reasonable in economics. The distribution is too equal and social growth is unmotivated when the Gini value is less than 0.2, and the distribution is too unequal when the Gini coefficient is more than 0.4, which may cause societal unrest. In most provinces, according to the calculation results, the Gini coefficient of out-resettlers was at a normal level, but in Sichuan Province, it exceeded the unequal threshold of 0.4. Income data analysis reveals that the high Gini coefficient value in Sichuan Province is due to the unusual and unrepresentative data of three sample households with extraordinarily high per capita disposable income. When these three samples are removed from analysis, the Gini coefficient value for Sichuan Province is computed to be 0.369. Table 4 shows lower Gini coefficient values for out-resettlers than resettlement provinces. On the one hand, this is because the sample of out-resettlers represents agricultural resettlement, and the Gini coefficient of resettlement provinces includes both rural and urban residents; on the other hand, it is because of similarities in out-resettlers’ income sources, such as transfer income and direct financial assistance on the basis of our analysis of the income structure of out-resettlers during the survey. The income distribution of the out-resettlers population is roughly equal.

Table 4.
Gini coefficient value of Three Gorges out-resettlers in all provinces.
3.2.2. Consumption Analysis
The level of consumption is a comprehensive indicator that reflects people’s behavior in terms of spending personal income, using and consuming products and services, and constantly updating and improving their own quality. The consumption level of out-resettlers most directly reflects the development speed and real level of people’s wealth. Figure 8 shows that the per capita consumer expenditure for out-resettlers in our sample in 2019 was RMB 14,766, which was 16.9% more than that of nearby-resettler, at RMB 12,628 according to monitoring statistics. Per capita consumption was the highest in Shanghai Municipality at RMB 33,366, which was 226% higher than that in Jiangxi Province. The consumption of out-resettlers was lower than that of local residents in resettlement provinces, except in Jiangsu, Shandong, Fujian, Guangdong, and Chongqing. The largest consumption gap was seen in Hunan Province, with 20% between out-resettlers and local residents. The consumption level of out-resettlers is typically lower than the average level in resettlement areas due to the limitations of economic conditions and values. With the exception of Shandong, Jiangxi, Sichuan, and Chongqing Provinces, the consumption level of out-resettlers in the other resettlement provinces was higher than that of nearby-resettlers. The resettlement provinces with out-resettlers generally were more economically developed and had convenient transportation. Out-resettlers had a richer spiritual life and higher consumer awareness [37]. Generally speaking, the consumption level of out-resettlers was higher than that of nearby-resettlers but lower than that of local residents.
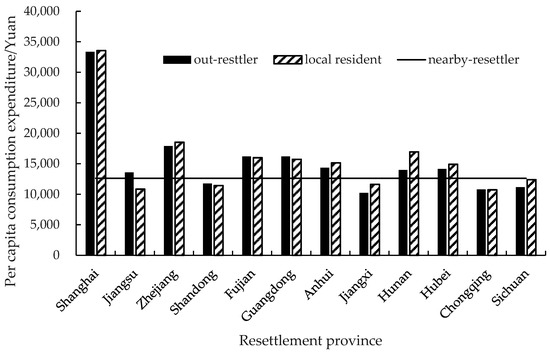
Figure 8.
Per capita consumption expenditure of out-resettlers.
The Pearson correlation coefficient between per capita consumption of out-resettlers and the development degree of the resettlement province was 0.81, with correlation significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed), indicating a high correlation between the per capita consumption of out-resettlers with the development degree of the resettlement provinces (Figure 9).
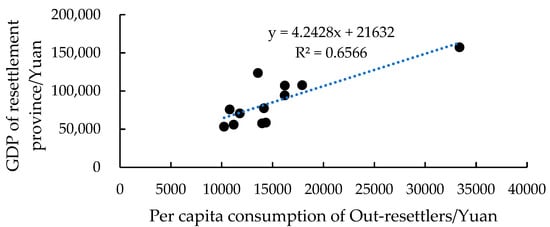
Figure 9.
Relationship between per capita consumption of out-resettlers and GDP of resettlement provinces.
3.2.3. Analysis of Housing Conditions
Housing conditions have a significant positive impact on people’s well-being and represent a major social issue related to people’s livelihoods [38]. The per capita housing area for rural resettlers in the Three Gorges Reservoir area in 2019 was 55.28 m2, 15.12% larger than that of the out-resettlers, with a per capita housing area of 46.92 m2. The per capita housing area for out-resettlers in our samples was typically smaller than that of local residents in resettlement areas (Figure 10).
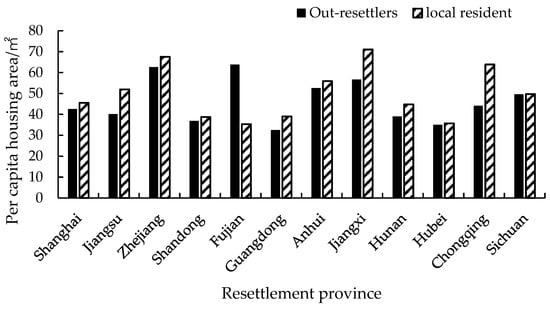
Figure 10.
Per capita housing area for out-resettlers in all provinces.
According to our analysis of migrant housing during the survey, the per capita housing area for out-resettlers complied with the resettlement norms established by the state at the outset of their relocation to various provinces (cities), but it was not particularly large. The per capita housing area increased significantly after resettlement, but centralized resettlement and unified housing arranged by the government remain the primary housing sources for out-resettlers. Their per capita housing area is typically lower than the local average and the average for resettlers in the Three Gorges Reservoir area.
3.3. Social Security Analysis
Among the 3076 out-resettlers sampled, 96.88% participated in medical insurance, slightly less than the sample households of local residents, at 97.57%. The proportion of out-resettlers participating in endowment insurance was relatively low at 71.20%, which was lower than the sample of local residents at 76.51%. Out-resettlers in Sichuan Province had the lowest proportion of participating in endowment insurance at 60.31%. Out-resettlers in Chongqing Province had the lowest proportion of participating in medical insurance at 39.87%. Figure 11 shows that coastal areas such as Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang Provinces have greater participation proportion in medical insurance, in which some cities have 100% coverage. Out-resettlers showed a preference for social security, because their income often increased after relocation, especially when they were resettled to cities with a strong economy.
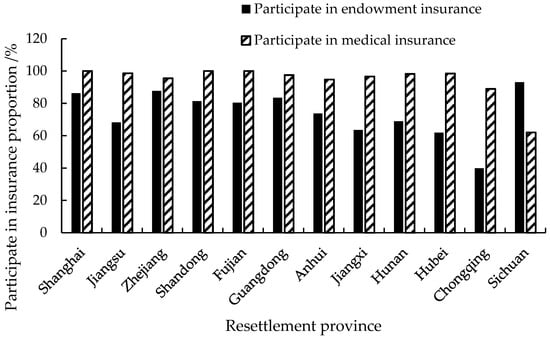
Figure 11.
Social security coverage of out-resettlers.
3.4. Social Integration Analysis
Reservoir resettlement, as involuntary resettlement, is not only an engineering, technical, and economic problem but also a social problem. Every year there are more marriages between out-resettlers and local residents, and resettlers’ willingness to become involved in local governance grows. Some out-resettlers groups have broken away from the policy-dependent way of thinking, evolved in the direction of active enrichment, and have taken the lead in enrichment. Among the sample households of Three Gorges out-resettlers studied, 108 out-resettlers were married to locals, accounting for 3.51% of the total. More than 90% of out-resettlers have adapted to local languages, cultural customs, and living habits. This shows that out-resettlers can be well integrated into resettlement areas.
The adaptation of out-resettlers to the dialect, cultural customs, and living habits of resettlement areas is shown in Table 5. Overall, in the past 20 years, most out-resettlers have basically adapted to their local living environment through a long period of running-in and coordination between local governments and units. During the investigation, we founded that the third-generation of out-resettlers shares the same dialect and customs as local residents. Interactions and exchanges with local residents are essentially commonplace [39]. The social spheres, social networks, and political standing of out-resettlers are continuously growing and improving. Out-resettlers’ awareness of participating in the management of local affairs has gradually increased, and some advanced out-resettlers representatives have actively participated in public affairs, and have been elected as village leaders, and as members of the County People’s Congress and the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference. However, there are still some first- and second-generation out-resettlers in some areas who have had difficulty adapting to the local language, cultural customs, and living habits of resettlement areas. Additionally, there are regional variations in how people live in various locations. A lack of excitement about learning makes it difficult for out-resettlers to integrate quickly into the community.

Table 5.
Social integration of out-resettlers (%).
3.5. Satisfaction
The satisfaction with resettlement policies; the execution of resettlement support initiatives; the availability of arable land, housing, water and power, and transportation; and other factors (communication, schooling, medical care) regarding out-resettlers from the Three Gorges Project were evaluated in 2019. The satisfaction of out-resettlers is shown in Figure 12.
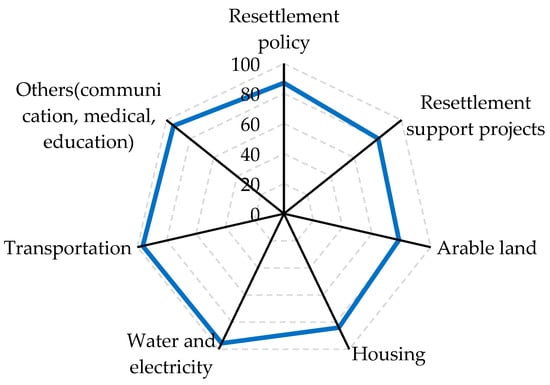
Figure 12.
Satisfaction of out-resettlers.
Generally, out-resettlers from the Three Gorges Project had the highest satisfaction with infrastructure construction and public service facilities in resettlement provinces, such as water and electricity, transportation, communication, medical care, and schooling at 90%; their level of satisfaction with housing conditions was 84.1%; and their level of satisfaction with the conditions of farmed land was the lowest at approximately 80%. This is because prior to being relocated from the reservoir area, the majority of out-resettlers were farmers and depended on agriculture for their livelihood. Despite the fact that all out-resettlers investigated were resettled in rural areas, the province’s industrial structure might be different from their original homeland, creating dissatisfaction among out-resettlers. This demonstrates the continued need to provide homes and arable land for out-resettlers.
It can be seen in Figure 13 that out-resettlers were not satisfied with the conditions of arable land in Fujian, Guangdong Province, and their needs for arable land resources means the government’s assistance measures should be strengthened. On the one hand, the government could directly supply more land resources; on the other hand, it could direct and encourage out-resettlers to work to increase their income and lessen their reliance on land resources and address the issue of a lack in arable land resources. The satisfaction in arable land in Fujian Province was 5%. It appears that all Fujian samples were not satisfied with the availability of arable land. Based on our analysis of the conditions of cultivated land for resettlers during the investigation, we found that the arable land area for sample households in the Fujian Province is small and most of them have been expropriated. Ye’s research showed that the planting structure of out-resettlers in Fujian has changed due to climate change [40]. Navel oranges and mandarin oranges planted in Chongqing before the relocation did not adapt to the hot and humid climate in Fujian. Out-resettlers began to plant bananas, sugar cane, and other crops. However, because they were not familiar with the growth habits of these plants and had not mastered the necessary planting and breeding techniques, the harvest was not good. For the sample households in Fujian Province, this has led to changes in their income structure. Wage income is the main source of income for most of the sample households. In 2019, the per capita wage income of the sample households was RMB 18,152, accounting for 75.7% of their per capita disposable income. As the sample households have few land resources, most out-resettlers have given up traditional agricultural production. There is no agricultural planting income. Family business income mainly comes from secondary and tertiary industries, accounting for 15.1% of per capita disposable income of sample households. From the employment structure in Table 3, it can also be seen that fewer sample households are engaged in agricultural production in Fujian Province.
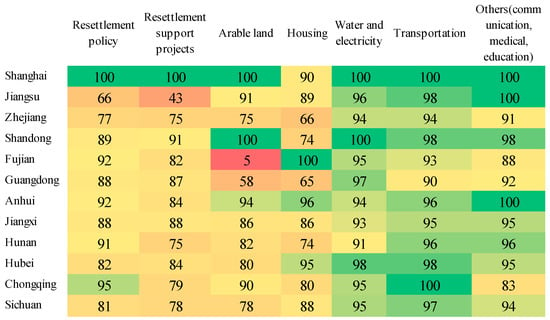
Figure 13.
Satisfaction of out-resettlers in all provinces.
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Employment Structure Affect Resettlement
Some field investigations conducted at the initial stage of the resettlement of out-resettlers found that resettlement at that time was not good; it was easy for them to fall into poverty and they could not adapt well to and integrate into the society in the resettlement area. For example, Ye found that in 2005, 34.5% of the out-resettlers in Xiamen, Fujian Province, were poor, and their income level was lower than that before relocation and far lower than that of rural residents in Xiamen city [40]. In a survey of out-resettlers in Shandong Province in 2009, Xia found that they were not satisfied with their living conditions [41]. However, after more than 10 years of government support and self-development, the survey in this study found that the resettlement of out-resettlers has greatly improved. Through the analysis of the current situation, it can be seen that the production and living conditions of out-resettlers have moved closer to those of local residents, which is as Wang predicted in 2016 [42].
The reason that the status of out-resettlers is moving closer to that of local residents is that the employment structure of out-resettlers has changed. The data show that there is a strong positive correlation between the proportion of stable out-resettler employees in enterprises and institutions and their income. When the data of Zhejiang Province were removed, the correlation coefficient was 0.82 (correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed)). This seems to indicate that the livelihoods of migrant workers who benefit from the resettlement of large private or state-owned enterprises in the province have recovered better. This is consistent with the reasons for the restored livelihoods of Three Gorges immigrants in Badong and Zigui Counties in 2015 given by Brooke [30], causing the high proportion of wage income at 69.35%. The main reason for this phenomenon is the differences in production methods. Compared with the mountainous terrain in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, the areas where most out-resettlers were resettled are developed areas with secondary and tertiary industries as the main industrial structure. The income of nearby-resettlers mainly comes from agricultural production, while that of out-resettlers mainly comes from secondary and tertiary industries. The income of nearby-resettlers (RMB 14,627) is lower than that of out-resettlers (RMB 21,949), and the growth rate is also lower [35,43].
There were benefits from the Three Gorges resettlement policy. Benefit-sharing refers to the explicit and formal use of the benefits generated by the development project for resettlement [44]. Resettlers should be able to ‘benefit directly’ from the larger development project and avoid impoverishment [45]. Since 1996, China has withdrawn funds from hydropower revenue to establish a reservoir area resettlement support fund (no more than RMB0.0005 per kilowatt hour of electricity) [46]. In 2006, out-resettlers were included in the management of large and medium-sized reservoir migrants nationwide. In 2006, the State Council revised the Regulation on Land Requisition Compensation and Resettlement for Engineering Construction of Large and Medium Water Conservancy and Hydropower Projects, which clearly stipulates the restoration and reconstruction of the production and living standards of emigrants: “The state implements the policy of development oriented migration, and adopts the method of combining early compensation, subsidies and late support to make the life of migrants reach or exceed the original level”. Therefore, the Regulations on Resettlement for Three Gorges Project Construction of the Yangtze River stipulated that the income from increasing the price of electricity sold by provincial power grid companies within the province and the value-added tax due to the increase in the price of electricity should be included in the later supporting funds [47]. Out-resettlers can obtain long-term support of RMB600 per person per year to improve their quality of life. In addition, the most important aspect is that the Three Gorges resettlement policy has implemented a leadership mechanism for resettlement work based on the province under the unified leadership of the central government. This innovative leadership mechanism for resettlement work, with a clear division of labor and sharing of responsibilities, has greatly boosted the enthusiasm and sense of responsibility in governments at all levels to do a good job in resettlement work, including the national counterpart support for Three Gorges out-resettlers [48]. Although the income of out-resettlers in all provinces and cities is considerable, as mentioned above, the income and resettlement conditions for out-resettlers in developed cities such as Shanghai are good. These differences are related to the region and are the result of the comprehensive effects of the economy, industrial structure, natural and geographical conditions, society, and cultural customs of resettlement sites.
4.2. Contributions and Limitation of the Study
The scale of the Three Gorges Project and the resulting abundant reservoir displacement are rare. Dissimilar to traditional reservoir resettlement, such large-scale, long-distance resettlement not only faces the risk of loss in traditional land area and production sites and worker stoppages and unemployment, it has also faced industrial structure changes, lifestyle changes, and the rebuilding of social relationships. However, according to the results of this study, after more than 10 years of development, the production and living standards of out-resettlers have significantly improved, and they can better integrate into the local society. This result will come as a surprise to those who study dam/development displacement and resettlement.
This study systematically and comprehensively analyzed the resettlement status of out-settlers from the Three Gorges Reservoir area in 2019, adopting a wide and complex monitoring scope. By comparing Three Gorges resettlers and local residents in resettlement areas, the production and living conditions of out-resettlers were objectively evaluated. The results of correlation analysis preliminarily show a positive correlation between the income and consumption of resettlers and the resettlement area. This has certain guiding relevance to the following supporting direction and key points of Three Gorges out-resettlers.
The monitoring year of this study was 2019, and there were no long-term observation data. The study was concerning the resettlement status of resettlers in 2019, and it was not possible to analyze changes in their livelihoods at the time of relocation. It is unfortunate that because of the limitation of the monitoring time point, it was not possible to conduct deep research on the situation before the migration of Three Gorges migrants and compare it with the current production and living conditions in order to analyze and study the problem more intuitively. In the design of the monitoring indicator system, migrants are still regarded as an engineering problem, and more attention is paid to the objective indicators of their production and lives, and a monitoring and evaluation index system for reservoir resettlement has not been studied in combination with indicators of happiness and welfare.
To obtain a long-term sequence of reservoir resettlement information, researchers could establish a long-term monitoring and management system that could be combined with big data and the Internet to reduce the difficulty of monitoring. Then the changes in livelihoods of reservoir resettlers from the time of relocation can be analyzed. In future studies of reservoir resettlement, researchers should monitor the resettlement before relocation, and analyze the influence of the livelihood status of reservoir resettlement before and after relocation. For designing the questionnaire and establishing the evaluation index system of reservoir resettlement, it could be given more comprehensive and scientific indicators by combining the research on happiness and welfare in social science.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically and comprehensively analyzed the resettlement status of the Three Gorges Project out-resettlers in 2019 based on a large-scale investigation. The conclusions are as follows:
Overall, the living conditions of out-resettlers were significantly improved, reaching or exceeding the average level of rural residents in resettlement provinces (cities). However, the contradiction of insufficient space for subsequent development as reflected by resettlement has appeared in individual areas to varying degrees.
The average income of out-resettlers has increased. The degree of economic development in resettlement provinces has a significant impact on the overall income level of out-resettlers. There is a significant positive correlation between the development level of the resettlement province and individuals’ income and consumption. At the same time, the issue of uneven development exists.
More than 90% of out-resettlers have adapted to local languages, cultural customs, and living habits. Out-resettlers have the highest satisfaction with infrastructure construction and public service facilities at more than 90%. Their satisfaction with the conditions of arable land is the lowest at approximately 80%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.P. and X.X.; methodology, software, validation, Z.P. and X.G.; formal analysis, Z.P. and X.G.; investigation, W.W., Y.L., X.X., and X.G.; resources, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.P., X.X. and X.G.; writing—review and editing Z.P. and X.G.; visualization, Y.L. supervision, X.X. and X.G.; project administration, X.G. and W.W.; funding acquisition, X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Major Program of National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 19ZDA090).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sepulveda, N.A.; Jenkins, J.D.; de Sisternes, F.J.; Lester, R.K. The Role of Firm Low-Carbon Electricity Resources in Deep Decarbonization of Power Generation. Joule 2018, 2, 2403–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolter, B.; Fellows, G.K.; Rivers, N. The cost effectiveness of new reservoir hydroelectricity: British Columbia’s Site C project. Energy Policy 2022, 169, 113161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Nair, R.; Guoqing, S. Resettlement in Asian Countries: Legislation, Administration and Struggles for Rights; Routledge/Taylor Francis: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cernea, M.M.; Maldonado, J.K. Challenging the Prevailing Paradigm of Displacement and Resettlement; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tortajada, C.; Altinbilek, D.; Biswas, A.K. Impacts of Large Dams: A Global Assessment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hasbullah, M.; Solle, M.S. Dam, project affected families, resettlement. Soc. Inc 2013, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, G.; Dong, Y. Effects of the Post-Relocation Support Policy on Livelihood Capital of the Reservoir Resettlers and Its Implications—A Study in Wujiang Sub-Stream of Yangtze River of China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, M. The risks and reconstruction model for resettling displaced populations. World Dev. 1997, 25, 1569–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Involuntary Resettlement. 2016. Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/521101467989568006/involuntary-resettlement (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Cernea, M.M. Understanding and Preventing Impoverishment from Displacement: Reflections on the State of Knowledge. J. Refug. Stud. 1995, 8, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, P.S. Involuntary resettlement in hydropower projects. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 1994, 19, 189–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengshun, L. The Three Gorges Immigration of China; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jichuan, S.; Shi, G. Economic Analysis on the Poverty Reasons for Reservoir Resettlement. Issues Agric. Econ. 2008, 43–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiwen, Y. Study on Resettlement of Reservoir; China Water&Power Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fujikura, R.; Nakayama, M. Beyond Land-for-Land: Toward a New Paradigm of Resettlement Policy. Asian J. Environ. Disaster Manag. 2017, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.; Mcdonald, B. Involuntary Resettlement, Production and Income: Evidence from Xiaolangdi, PRC. World Dev. 2004, 32, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A. Human Capital, Government Policy and Reservoir Project Resettlement Income. In Proceedings of the The 2nd International Seminar on Computational Intelligence, Engineering and Technology, Shanghai, China, 10 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yao, K.; Liu, B.; Wang, F. A Livelihood Resilience Measurement Framework for Dam-Induced Displacement and Resettlement. Water 2020, 12, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources, People Republic of China. 2020 Statistic Bulletin on China Water Activities. 2020. Available online: http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/202206/t20220615_1579315.html (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Ministry of Water Resources, People Republic of China. Bulletin of First National Census for Water. 2013. Available online: http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/dycqgslpcgb/201701/t20170122_790650.html (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Lian, H.; Shi, G.; Xu, J. A Study on Updating the Model for Monitoring and Evaluation of Involuntary Resettlement Based on the Experience of China. Processes 2022, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Monitoring and evaluation mechanism for the final-period support of reservoir resettlement based on the aim of poverty-relief and development. China Water Resour. 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, P.; Yang, J.S.; Yang, T.; Yun, L.; Li, L.I.; Jiao, L.L. Research on the Monitoring and Evaluation of Later Supporting About Reservoir Resettlement. Yellow River 2011, 33, 141–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tortajada, C.; Altinbilek, D.; Biswas, A.K. Impacts of Large Dams: Issues, Opportunities and Constraints; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilt, B.; Braun, Y.; He, D. Social impacts of large dam projects: A comparison of international case studies and implications for best practice. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S249–S257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D. Discussion on reservoir resettlement planning system considering high-quality development. Yangtze River 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research Group on Index System of People’s Quality of Life. Quality of life indicators in Germany and Sweden. Jiangsu Soc. Sci. 2002, 1, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wan, C.; Tan, J. Comparison of Quality of Life and Subjective Well-being. In Proceedings of the Conference Proceedings of 2012 Asian Chinese Quality of Life Conference and 5th National Quality of Life Conference, Guangzhou, China, 13 September 2012. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Yao, F. Three Gorges Project: Effects of Resettlement on the Environment in the Reservoir Area and Countermeasures. Popul. Environ. 2006, 27, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmsen, B. After the Deluge: A longitudinal study of resettlement at the Three Gorges Dam, China. World Dev. 2016, 84, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Niu, X.; Xie, H. The Three Gorges Project in China. Comprehensive Renewable Energy 2012, 6, 179–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. A Study on the Welfare of the Rural Migrants Induced by Hydroelectric Projects; Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Hubei, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.A.; Xia, L.Z.; Yun-Dong, L.I.; Yang, L.Z.; Dian-Ming, W.U.; Cheng, X.Q. Variation of Population, Arable Land Resources and Ecological Environment in the Area of the Head Part of the Three Gorges Reservoir Based on Migration Investigation. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2010, 26, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqing, L. The reflection and countermeasure of ecological resettlement in Three Gorges reservoir area of Changjiang River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, S1, 521–525. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Na, B. Study on the Employment of Migrants in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area; Minzu University of China: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Fang, Y.; Qiwang, Z. Rediscussion on Statistical Measure on Gini Coefficient. Stat. Decis. 2021, 37, 27–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiajun, X.; Juan, P.; Shi, G. Social integration of Three Gorges immigrants and coastal resettlement areas. J. Econ. Water Resour. 2006, 24, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Shi, Y.C.B. Homeownership and Happiness: Theory and Evidence from China. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 69–82, 160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiumei, T. The survey on the Language Attitude of the Three Gorges Immigrants in Jiangsu Province. Appl. Linguist. 2012, 4, 139. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y. Study on Economic Life of Three Gorges Migration in Xiamen; Xiamen University: Fujian, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yongxia, X. Research on Life Satisfaction of The Three Gorges Rural Reloacted Immigrant; Shandong University: Shandong, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shouwen, W.; Lingyun, L. The Basic Situation, Trend and Countermeasures for Later-period Support of Three Gorges Migrants Underground of the New Normal. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2016, 55, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, J.; Rasul, G.; Liu, S.; Xie, F.; Cao, M.; Liu, E. Household livelihood strategies and dependence on agriculture in the mountainous settlements in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4850–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, D. Advantages and obstacles to retro-fitting benefit: Sharing after development-induced displacement and resettlement. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2021, 39, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. The World Bank Environmental and Social Framework. 2017. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/projects-operations/environmental-and-social-framework/ (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Xiutang, F.; Shirong, L. Reviewing and consideration on reservoir resettlement policy in China. Yangtze River 2007, 38, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W. Stduy on the Evaluation of the Late Stage Support Policy for Large and Medium-Sized Reservoir Resettlement; Xi’an University of Technology: Shanxi, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, W. Chinese Present Age Reservoir Immigrant Policy Comparative Analysis-Take Sanmenxia and Three Gorges Reservoir Immigrant Policy as the Sample; Central China Normal University: Hubei, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).