Abstract
Urban greenspace planning plays a crucial role in improving the quality of human settlements and the living standard of citizens. Urban public greenspace (UPGS) is an important part of urban greenspaces. Existing literature rarely includes a scientific evaluation of greenspace plans (including of UPGS) and plan implementation effects. To bridge this gap, this study evaluated and monitored the UPGS plan enacted in 2010 in Kunming, China. Object-based image classification and visual interpretation of satellite images and Google Earth imagery were used to quantify the different periods of UPGS implementation. Six indicators and monitoring at four classic sites were applied to explore the change at two scales (overall scale and district scale) for monitoring the UPGS plan execution. The results showed that UPGS structure greatly improved after plan implementation. However, UPGS provision per capita has not reached the level of greenspace planning and the connectivity was poor. Significant implementation inequalities existed in each district and implementation has lagged behind schedule. This study contributes to a better understanding of greenspace planning and urban planning in general, which can help improve future planning and planning decisions.
1. Introduction
Contemporary urbanization differs markedly from historical patterns of urban growth in terms of scale, rate, location, and form, especially in developing countries [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The pressure of urban development results in the destruction of extensive greenspaces that provide a variety of environmental, economic, and social benefits for urban citizens [7]. The environmental benefits include offsetting carbon emissions [8], removing air pollutants and reducing noise, absorbing rainwater, regulating the microclimate [9,10,11], and maintaining biodiversity [12,13,14,15]. Other benefits of green space include esthetic, recreational, and relaxation opportunities [16,17], as well as increased property values [18,19,20,21] and protected public health [22,23]. Additionally, current research has shown that urban greenspaces are becoming a good measure for the sustainability of a city [18,24,25], so that the importance of urban greenspaces in an urban ecosystem is being increasingly recognized [24]. In this context, more attention has recently been paid in most developing countries to urban green space planning for enhancing citizens’ quality of life, and greenspace planning should be an integral component of any urban development or remodeling endeavor [25,26]. Urban public greenspace (UPGS) is an important part of the urban greenspace system, and also plays a major role in cities by providing aesthetic and recreational opportunities and improving physical and psychological well-being of citizens [16,27,28,29,30,31].
At present, the research into green space is mainly focused on urban green space planning based on the evaluation [32], adaptation and mitigation of climate change [33], environmental purification and improvement of air quality [7], urban rainwater management [34,35], ecosystem services and social well-being [36,37], and biodiversity conservation in foreign countries [14,15]. In China, scholars mainly focus on the theoretical framework, introduction of domestic and foreign practice cases, identification and extraction of green space, green space landscape design, and rainwater management [38].Urban greenspace planning is a passive or active strategy adopted by highly urbanized countries and regions to cope with urban problems. Since the mid-19th century, European and North American countries have widely incorporated UPGS (e.g., green belt, green heart, green corridor, greenway, ecological network, and ecological infrastructure) into urban planning [39]. In China, urban greenspace planning is an indispensable part of urban planning through which to protect the public interest, maintain fairness, and improve the living environment by the rational layout of UPGS and public infrastructure [25], and a series of relevant laws and regulations have been successively promulgated to promote its significance [25,40].
However, many problems still challenge urban green space planning practices, especially in Chinese cities [40,41,42]. First, high efficiency and high precision survey methods (e.g., 3S) are lacking in the greenspace research about inner cities because the time-consuming traditional research methods require a significant amount of labor [43]. Second, the intention of greenspace planning has been to satisfy rigid indices (the per capita park area, the green space ratio, and the green coverage ratio) at a whole-city level based on incomplete and one-sided information while ignoring the uniformity of layout [44,45,46]. For example, some studies have reported a serious shortage of UPGS area on a per capita basis in downtown zones of large cities [47,48]. Furthermore, the plan’s implementation effect often deviates from the original goal due to rapid urban expansion and decisions by policy makers [25]. Currently, planning evaluation, as an important part of optimizing the planning formulation and implementation mechanism, has gained a clear legal status. However, most of the planning implementation evaluation remains in the static and passive terminal evaluation; dynamic and real-time process evaluation is seldom carried out [49,50,51]. Some major cities (e.g., Shanghai and Beijing) have tried to establish a comprehensive planning evaluation system in the overall urban planning evaluation, but there is still a shortage of quantitative evaluation methods for the spatial effect of the planning, and little attention has been paid to the evaluation of the effectiveness and consistency of special planning (e.g., green space system planning) and urban public facilities (e.g., public green space [46].
Kunming, the capital city of Yunnan Province in southwest China, was used as a case study to evaluate the UPGS plan within Kunming’s current green space planning, which was ongoing for 9 years as of 2019, and to assess whether the plan had encountered the common problems that plague greenspace plans in China (e.g., uneven layout patterns and planning implementation lag). The research was accomplished by quantifying the different periods (initial status in 2010, midterm-plan implementation in 2015, current plan implementation in 2019, and projected status in 2020) of UPGS implementation in the tricyclic metropolitan area (populated areas) of Kunming city. To address the research question, we defined the following research objectives: (1) developing and testing methods for evaluating and monitoring UPGS planning; (2) assessing the UPGS plan effect and implementation against the initial UPGS (2010), the actual midterm-UPGS (2015) and the actual status (2019) with appropriate indicators at two scales (the entire area within the “3rd Ring Road” and four different administrative districts); and (3) checking the local implementation of the plan with image contrast analysis at sites.
2. Study Area
The study area was the central portion of Kunming City (102°10′–103°40′ E, 24°23′–26°33′ N; 1890 m elevation), which is the capital and only mega-city of Yunnan Province in southwestern China. Kunming is located in central Yunnan Province and encompasses a total area of about 21,000 km2, which is a typical example of where local authorities have paid special consideration to urban greenspace. Due to the successful declaration of Kunming as a “National Garden City” in 2010 and “National Forest City” in 2013, the importance of urban green spaces is increasingly recognized in urban ecosystems. Various campaigns and activities were therefore implemented from 2006 to 2010 to allocate more green areas and corridors within urban areas, resulting in a significant plan called Green Space System Planning of Kunming 2010–2020 [52]. This plan was developed through a special planning action under the master plan during the period 2008–2020 of Kunming City and is a guiding document for the development and construction of greening in Kunming. The ultimate goal of the plan is to build Kunming City into a plateau lake eco-city that incorporates forestry, landscape design, environmental protection, and sustainable development.
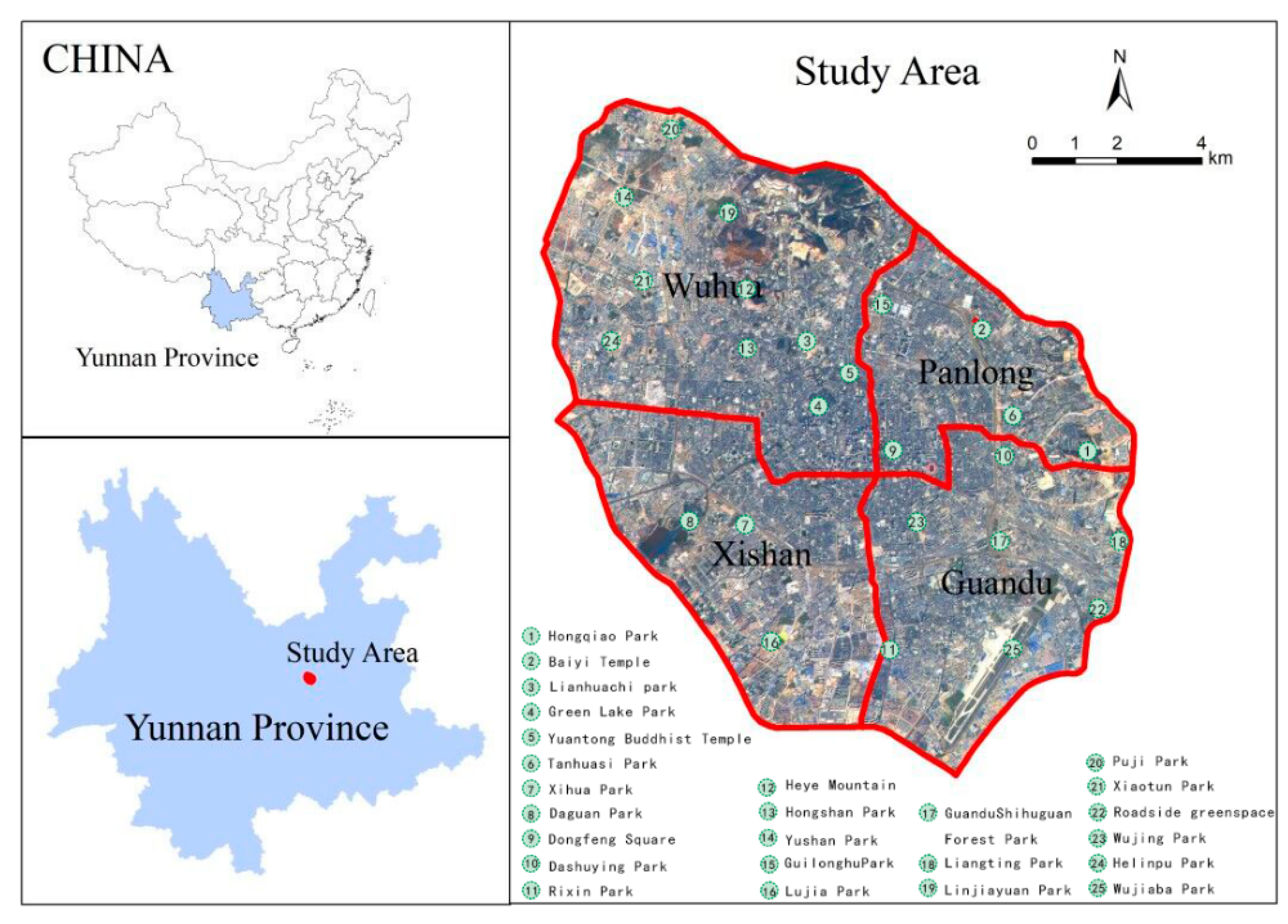
The city’s high population growth rate has resulted in 6 million permanent residents living in a small mountain city environment. The main urban areas are concentrated within a tricyclic road network (consisting of three main “ring roads”) and are densely populated (>10,000 people per km2). The study area covers 144 km2 and includes the administrative divisions of Wuhua District, Panlong District, Guandu District, and Xishan District (Figure 1).
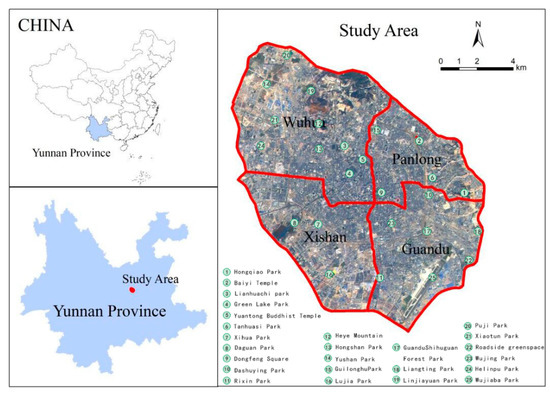
Figure 1.
Location of Kunming City, China and four administration districts encompassed in the study area.
According to Kunming statistical yearbooks [53,54,55], the land area of the four districts was 381.60 km2 (Wuhua), 343.71 km2 (Panlong), 632.92 km2 (Guandu), and 881.32 km2 (Xishan). The permanent population of the four districts was 0.87 million (Wuhua), 0.67 million (Panlong), 0.77 million (Guandu) and 0.72 million (Xishan) in 2010; 0.87 million (Wuhua), 0.83 million (Panlong), 0.87 million (Guandu) and 0.76 million (Xishan) in 2015; and 0.88 million (Wuhua), 0.84 million (Panlong), 0.90 million (Guandu) and 0.79 million (Xishan) in 2018. In terms of real estate investment, Wuhua district had the largest amount in 2010, followed in decreasing order by Xishan district, Panlong district, and Guandu district. After 2015, Guandu district had the largest amount of investment, followed by Xishan district, Guandu district, and Wuhua district.
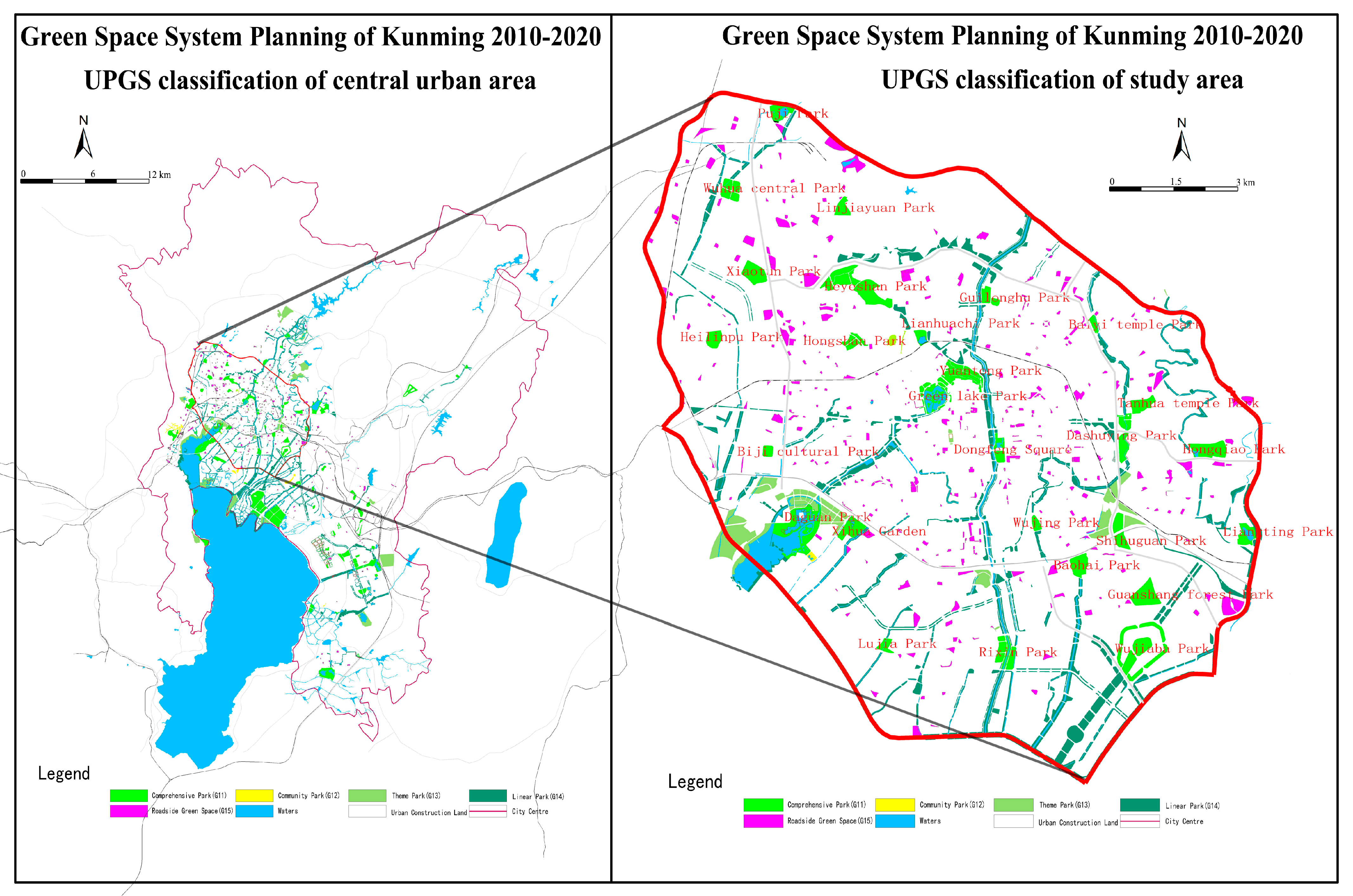
According to the Green Space System Planning of Kunming 2010–2020, the central urban area (including the study area) at the end of the planning period should achieve a 45% greening rate, 50% green coverage, and 6829.6 hm2 of UPGS area (15.88 m2/person). Figure 2 shows the UPGS patterns of the central urban area and the study area.
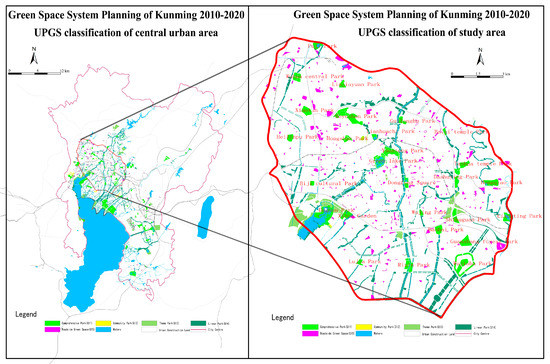
Figure 2.
Illustration of the “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” (highlighting the urban public greenspace (UPGS) classification of the central urban area and study area).
Seventy-nine comprehensive parks, community parks and special parks have been planned for construction in the central urban area, and there currently 25 parks (comprehensive parks, community parks and special parks) in the study area, of which 15 parks are planned for new construction and 10 parks are planned for expansion.
3. Materials and Methods
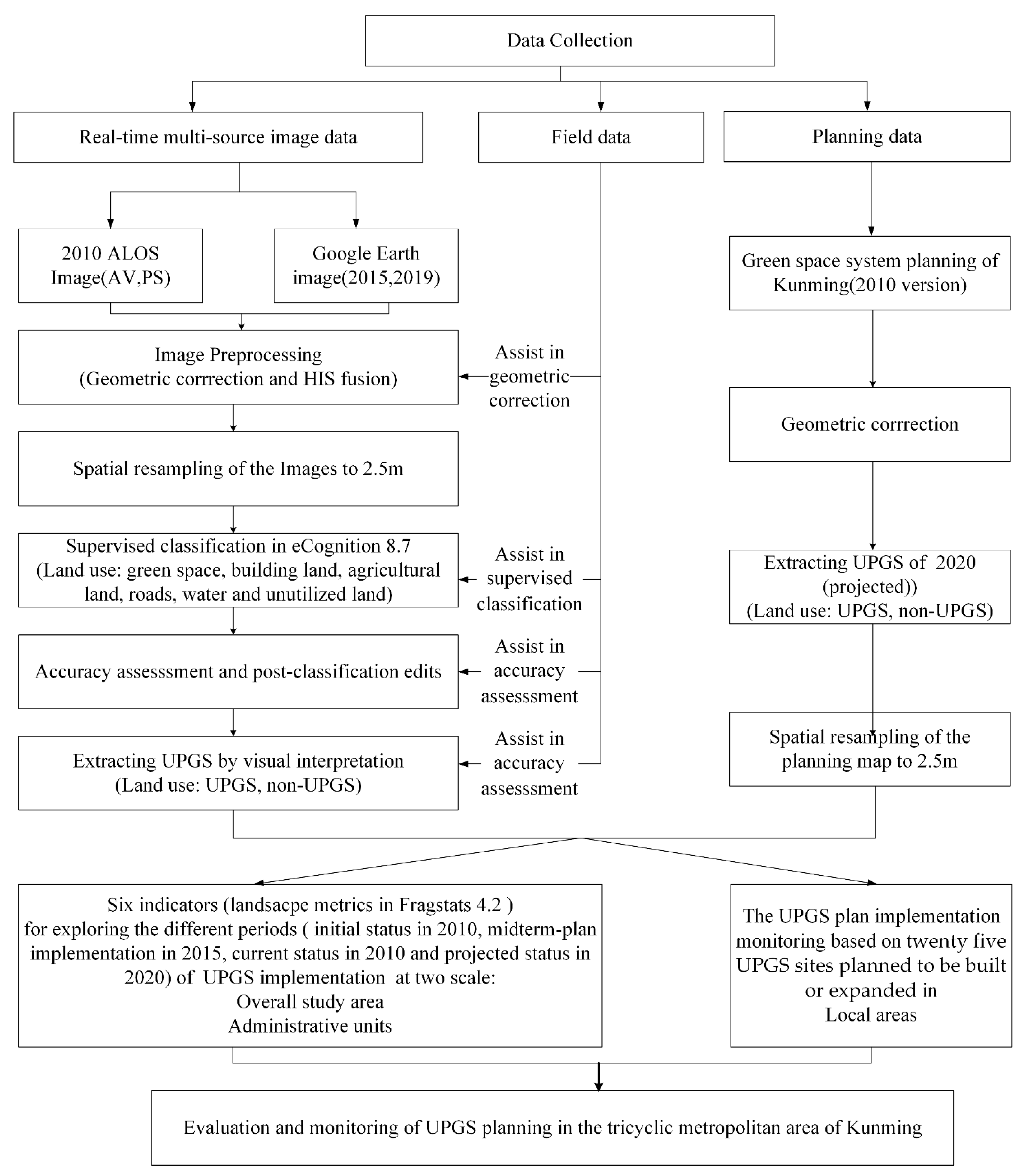
Figure 3 shows the methodological framework for evaluating and monitoring UPGS planning in the study area. The specific processes are elaborated below.
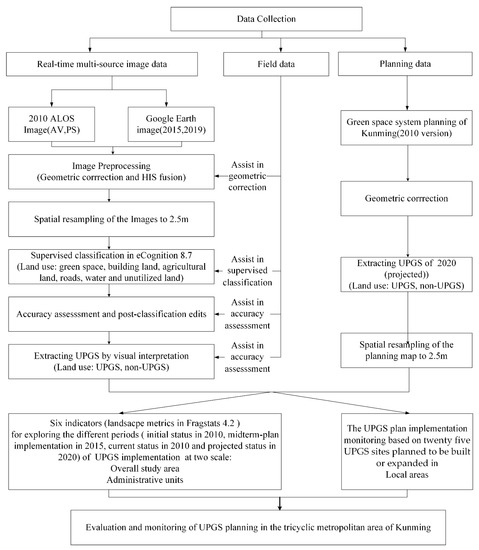
Figure 3.
The methodological framework of the study.
3.1. Data Collection
Data used in this study were derived from Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) imagery, Google Earth (GE) imagery, Kunming green space system plan maps, and field surveys (including the sampling of image interpretation and accuracy evaluation, and the verification of the UPGS sites monitoring). The following cloud-free remotely sensed images were used: ALOS image (sensor AVNIR-2) acquired on 22 March 2010; ALOS image (sensor PRISM) acquired on 22 March 2010; and a GE image acquired on 4 May 2015. The AVNIR-2 (AV) image had a resolution of 10 m in multispectral bands. The PRISM (PS) image had a resolution of 2.5 m in a panchromatic band. The freely accessible GE image was downloaded using the GetScreen software [56] at a resolution of 1.08 m and was used in the study as a direct data resource that has been documented to have great advantages for land use/cover mapping and good spatial characteristics. The green space planning map of the period 2010–2020 from Kunming Planning Bureau [52] was used to extract the UPGS plan map of the period 2010–2020. Field survey data included the ground control points collected using global positioning systems for geo-referencing satellite images and photographs for assisting in image interpretation.
3.2. Data Processing
Images were first geo-referenced to the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system. Six evenly distributed ground control points were selected for geometric correction using a second-order polynomial transformation and the nearest neighborhood resampling method. Then, the intensity-hue-saturation fusion was adopted to integrate the geometric detail of the PS image and the color information of AV image to produce a high-resolution multispectral (MS) image [57,58,59]. To facilitate the landscape metrics analysis, the map of the green space system plan was converted into the shapefile format used in ArcGIS 10.2 software [60,61], and experienced the same geographical processing process. Finally, the MS image, GE image, and the map of green space planning were resampled to a resolution of 2.5 m to achieve matching spatial resolution for all data (Figure 4).
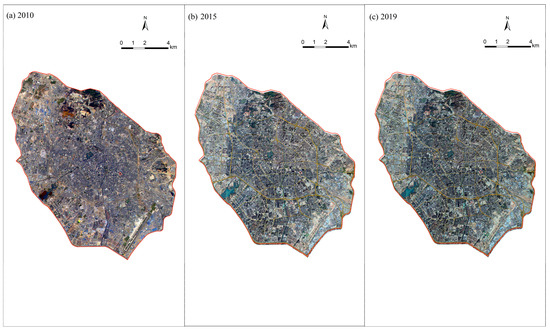
Figure 4.
The image of the ALOS image in 2010 (a), and the Google Earth images in 2015 (b) and 2019 (c).
3.3. Classification and Extraction of UPGS
Object-oriented remote sensing image classification is an effective approach to greenspace information extraction and has been shown to improve land classification accuracy [62,63,64,65]. This technology has a powerful capability in spatial analysis and visualization, and may be an appropriate tool for evaluating Kunming’s UPGS plan. In this study, a hierarchical classification and the neighboring classification rules in eCognition 8.7 [66] were used in the image classification. The land use in the study area was classified into roads, agricultural land, building land, green space, water, and unutilized land [67]. The various types of green space were characterized according to the different surface textures and color information.
Statistical indices of training samples for images were analyzed to ensure that different land use classes could be separated. Moreover, 50 sampling points in the synchronized GE image (2010, 2015, and 2019) for each land-use class were randomly selected to assess the classification accuracy (Figure 4b,c). At the same time, ALOS images (Figure 4a) in 2010, the green space map in 2010, the field survey data, and local knowledge and experience of the study area were used as reference data for the accuracy assessment. Minor adjustments were made to correct the misclassified classes through field verification.
For the classification result, UPGS within the scope of the study area was extracted by visual interpretation. In the end, the study area was classified as UPGS and non-UPGS. In this analysis, 110 polygon samples for each category in the two synchronized GE images were randomly selected to determine the accuracy of visual interpretation. The error matrix analysis of the samples was made for the UPGS after extraction, for which the overall accuracy was 0.98 (2010 image) and 0.99 (2015, 2019) and the overall kappa was 0.89 (2010), 0.95 (2015), and 0.97 (2019). However, for the UPGS map of the period 2010–2020, the attribute of the green space system planning was directly extracted as a shapefile.
3.4. Quantifying UPGS Pattern by Landscape Metrics
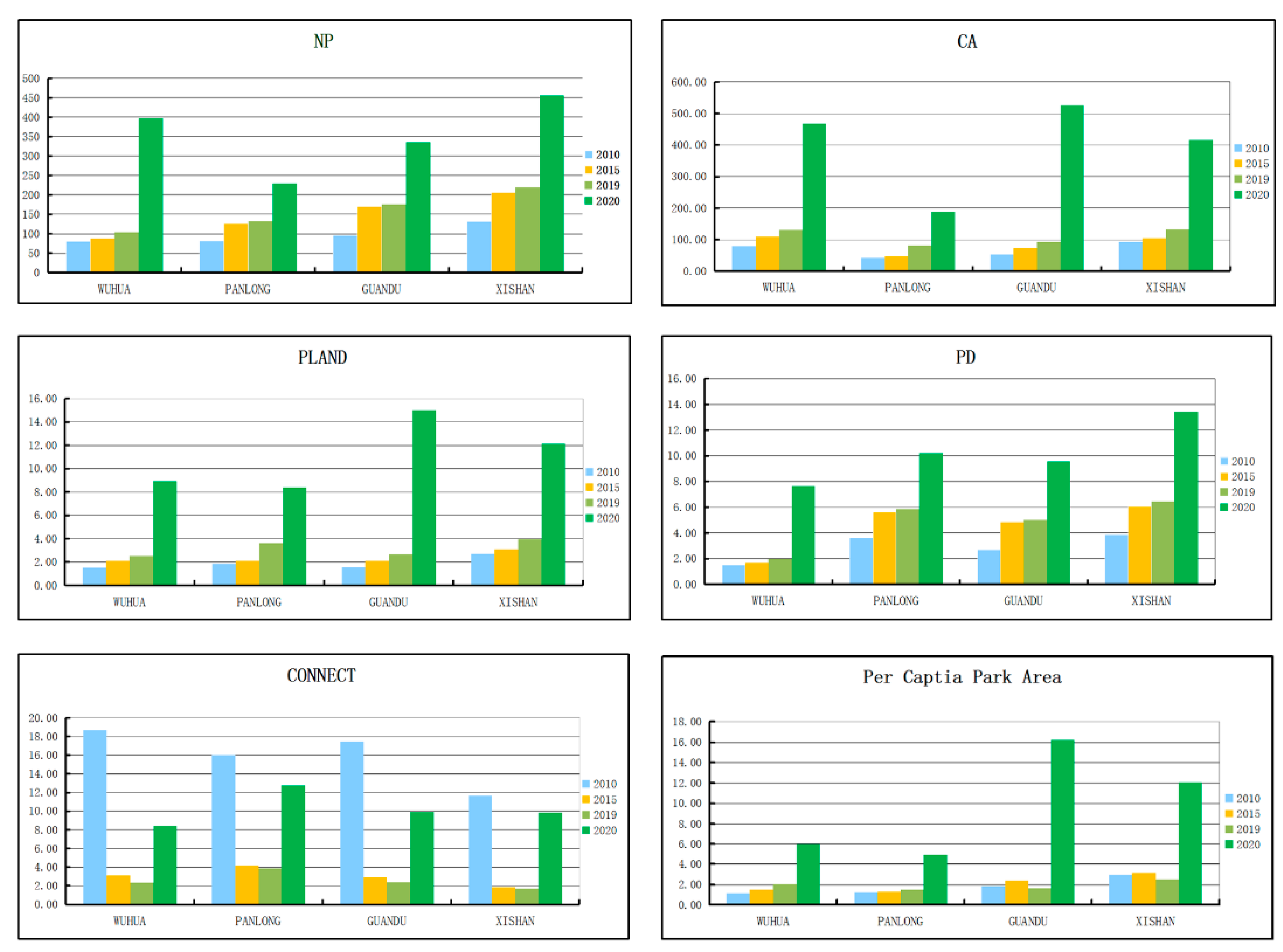
Scholars in the planning field have tried to create effective quantitative evaluation indexes, and these have gradually become an important technical means for the formulation, implementation, and evaluation of urban plans. Additionally, landscape metrics integrated with GIS are useful tools for quantifying spatial land cover characteristics [67]. Kong and Nakagoshi [18] and Rafiee et al. [68] applied landscape metrics for quantifying and capturing changes in green space patterns. Mas et al. [69] analyzed the sensitivity of 85 landscape metrics to different image classification methods. Zhou and Wang [64] and Ghaffari, and Monavari [62] also used common landscape indexes to investigate the dynamic changes green space. M’Ikiugu [70] introduced a process of analyzing and identifying the potential development areas of urban greenspace using landscape metrics. Uuemaa et al. [71] provided an overview of the trends in the usage of landscape metrics as indicators for land use changes, habitat functions (biodiversity, habitats), landscape regulating functions (fire control, microclimate control, etc.), and information functions (landscape aesthetics). The landscape index may be better used to monitor the spatial dynamics of planning implementation. In this study, five classical landscape metrics were selected to quantitatively evaluate the spatial structural effectiveness of UPGS planning at different spatial and temporal scales. The metrics were selected to promote the application of ecological principles to planning practice, and make up for the deficiency of the park area per capita index. Therefore, six indicators (including per capita park area) were selected (Table 1). The classical metrics of patches (NP), class area (CA), percentage of landscape (PLAND), patch density (PD), and CONNECT were analyzed using the FRAGSTATS 4.2 software. NP represents the number of park patches, which quantitatively expresses the intensity of park patches. CA reflects the total area of the UPGS. PLAND describes the relative abundance of UPGS in general. PD is associated with the degree of patch fragmentation in the traditional sense, and is sensitive to the serviceability of UPGS in this study, e.g., the high fragmentation fortunately represents the high radiation capability service of UPGS. CONNECT reflects the connectivity among patches [18,60,62,66]. Per capita park area is a rigid index of urban green space system planning and reflects the per capita provision of park area, in which the population is based on data from 2010, 2015 and 2019, and the Kunming Population Development Plan Outline 2011–2020 [53,54,55,72].

Table 1.
Landscape metrics used in this study.
3.5. Monitoring the UPGS Plan Implementation in Local Areas
Temporal and spatial monitoring is useful for determining whether a given plan is achieving its goals and targets [51]. The GE images of different historical periods at the local scale can clearly show changes in land use. To test whether there was planning inconsistency in the actual implementation of planning land (e.g., implementation lag), 25 UPGS sites planned to be built or expanded were selected to examine the implementation (Figure 1, Table S1). The GE images for 2010, 2015, and 2019 were used to visually compare the land use change for monitoring the UPGS plan execution.
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation on UPGS Plan at Overall Scale
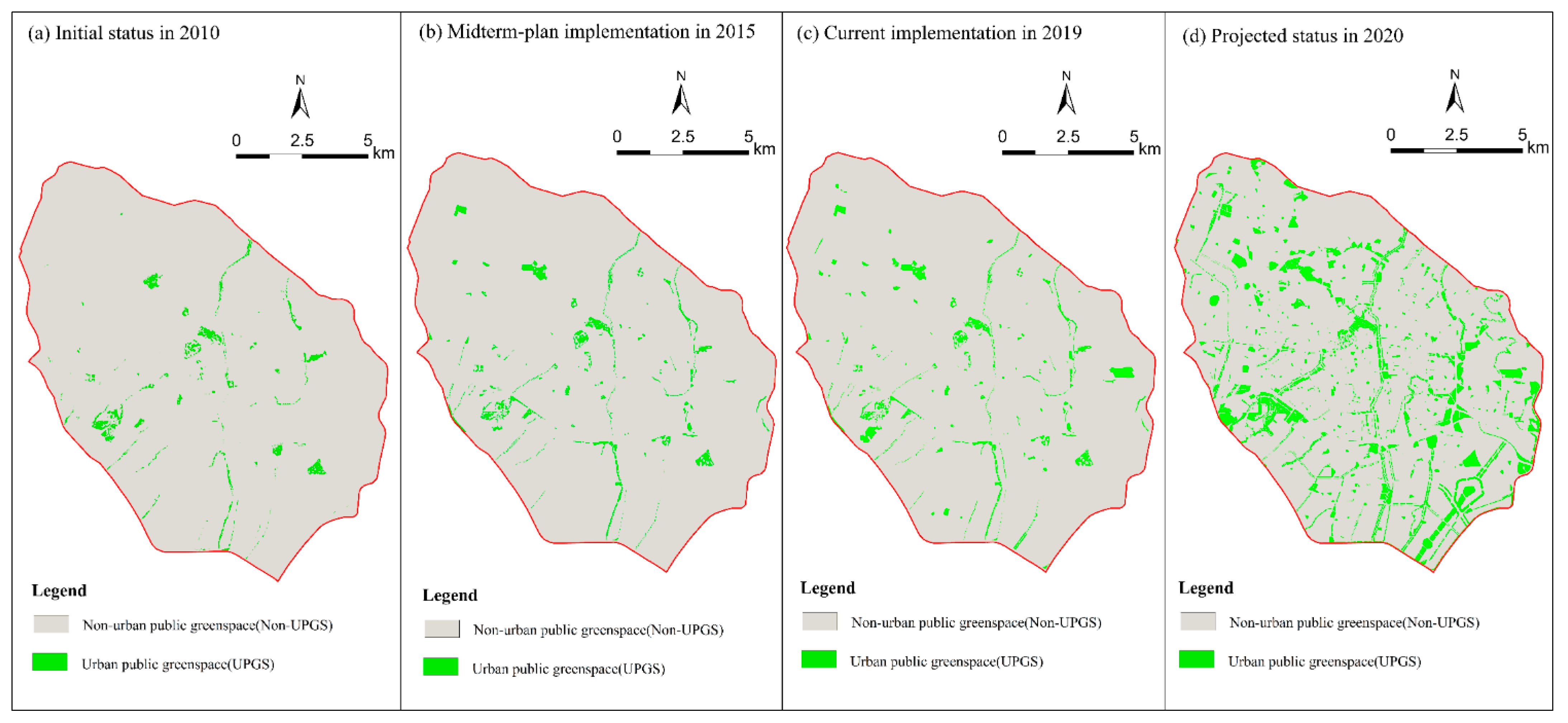
The analysis of the whole study area provided an overall characterization of UPGS composition and configuration during the plan implementation. By comparing the results of the UPGS plan to 2020 with the initial status of 2010, the UPGS pattern at an overall scale was expected to change greatly in the next decade after the implementation of the 2010–2020 plan (Figure 5). Significant increases in value were manifested in all indicators except CONNECT (Table 2). By the end of plan (2020), NP and CA should increase significantly in the entire tricyclic area, resulting in the PD increasing from 2.08 to 9.33, and the PLAND increasing significantly from 1.85% to 11.09%. The per capita park area also should increase from 1.63 m2 to 8.69 m2. However, the CONNECT index is projected to decline from 0.81 to 0.30 due to the emergence of highly fragmented parks. Furthermore, the per capita UPGS is projected to be much lower than the target of 15.88 m2. The per capita index implies that the UPGS supply in the inner-city is offset by the UPGS in surrounding areas.
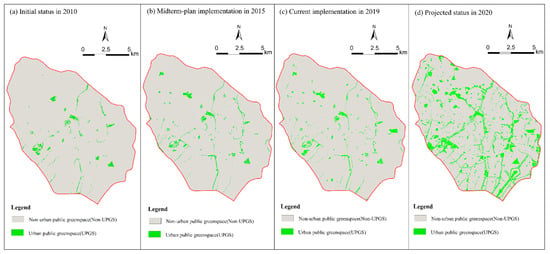
Figure 5.
UPGS in the Kunming study area before and after the implementation of “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020”: initial status in 2010 (a); after midterm-plan implementation in 2015 (b); current plan implementation in 2019 (c); and the projected status in 2020 (d).

Table 2.
UPGS pattern comparison by landscape metrics before and after implementation of the “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020”.
From the perspective of dynamic plan implementation, the actual UPGS pattern following the midterm (2015) and current (2019) plan implementation showed only modest changes (Figure 5) in which each index shifted slightly relatively to its value in 2020 (Table 2). The number of UPGS patches (NP) was 485 in 2015 and 519 in 2019, achieving only 38.70% of the planned. The UPGS area (CA) within the study area reached 1598.82 hm2 at the end of the plan implementation period and 336.56 hm2 in 2015, 438.59 hm2 up to now (only 27.43% of the end goal). The proportion of UPGS (PLAND) was 2.35% in 2015 and 3.05% in 2019, while will be 11.09% for the planned value. Per capita park area shows no sign of continuing increase, as it was 1.90 m2 in 2015 and 1.89 in 2019, which is far below the planned target. CONNECT increased from 0.81 to 0.97 in 2015 and decreased to 0.75 in 2019. Overall, no index reached half of the projected value for 2020. Furthermore, there was a dramatic decline in connectivity, which may have been related to the implementation of linear public spaces (river greening projects).
4.2. Evaluation of the UPGS Plan at the District Scale
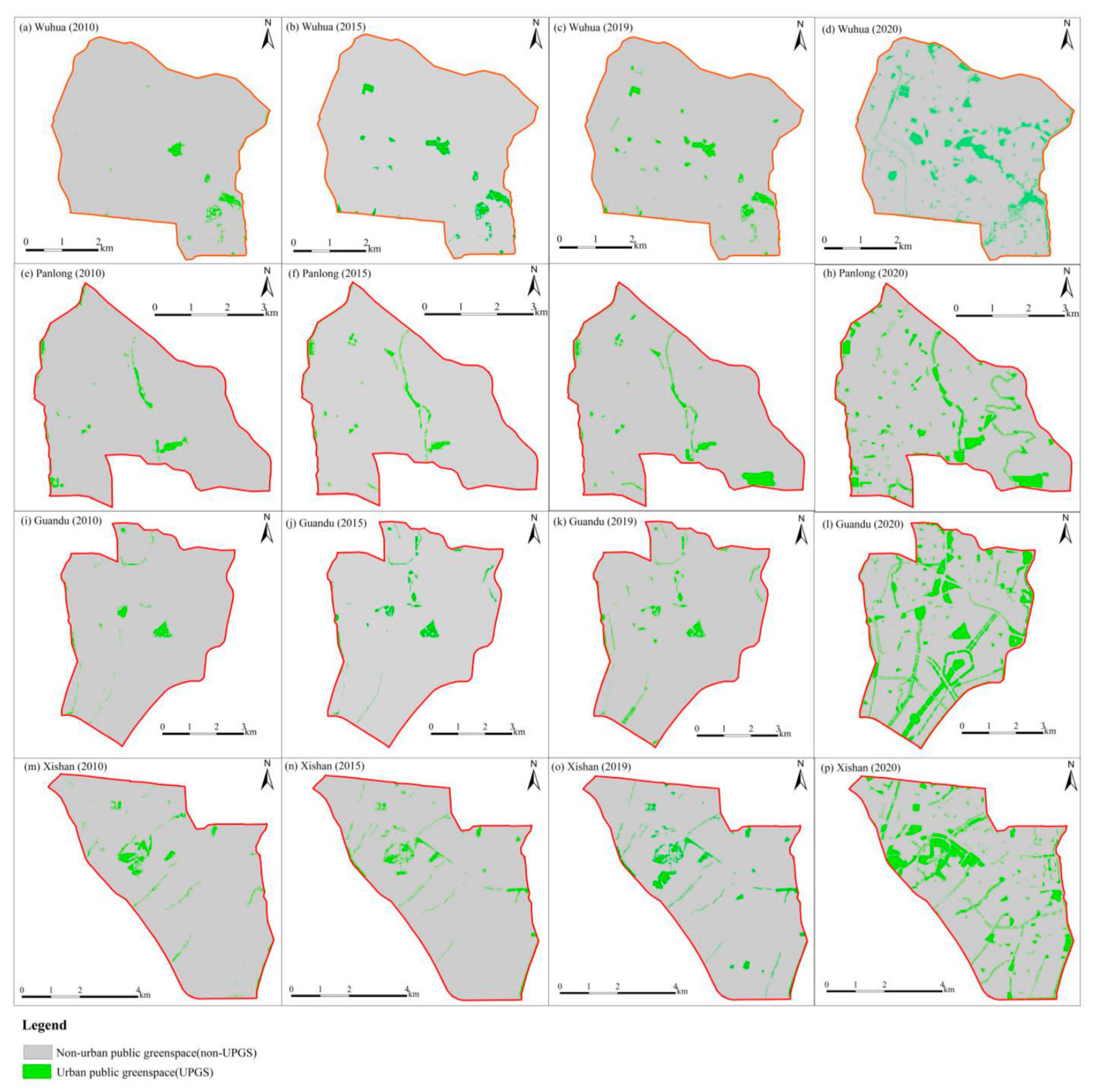
Figure 6 and Figure 7 clearly show that the pattern of UPGS in each district should change greatly after the “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” is fully implemented. It shows the same trend as the overall scale, as all indexes except CONNECT in each administrative district experienced increases between before and after the planning.
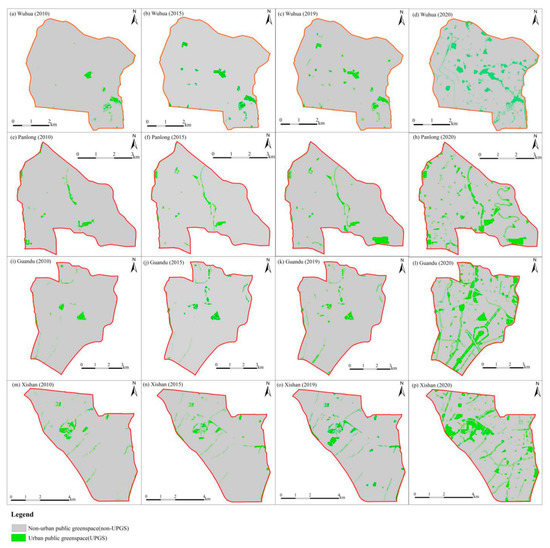
Figure 6.
UPGS in the four districts (Wuhua, Panlong, Guandu, and Xishan) of the study area, before (2010) and following the implementation of “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” as of 2015 (actual midterm status), 2019 (current status) and 2020 (projected).
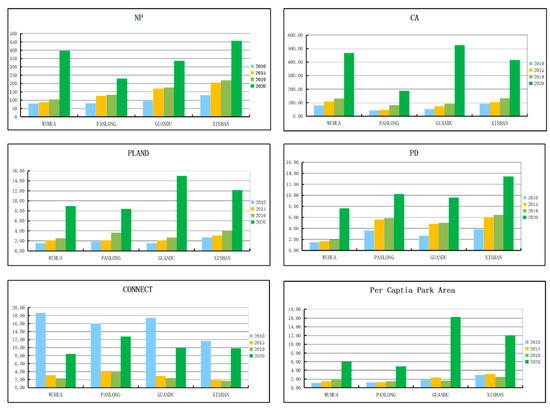
Figure 7.
Landscape metrics of UPGS in the four districts (Wuhua, Panlong, Guandu and Xishan) of the study area before (2010) and following the implementation of “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” as of 2015 (actual midterm status), 2019 (current status) and 2020 (projected).
However, only minor changes of indicators were achieved following the medium term (2015) and current plan implementation (2019). In addition, the CONNECT index in each district showed a consistent declining trend. The value of the NP index showed the pattern of Xishan > Guandu > Panlong > Wuhua in 2015 and 2019, CA showed the pattern of Wuhua > Xishan > Guandu > Panlong in 2015 and 2019, PLAND experienced a maximum value in Xishan, followed by Wuhua and Guandu, and lastly Panlong in 2015, as well as varied in decreasing order as Xishan > Panlong > Guandu> Wuhua in 2019, the metrics of PD and CONNECT in each of the plan implementation times showed the same trend, i.e., Xishan > Panlong > Guandu > Wuhua for PD, Panlong > Guandu > Wuhua > Xishan for CONNECT, the per capita park area index value of Xishan was larger than that of the other districts, and followed a consistent trend: Xishan > Guandu > Wuhua > Panlong in 2015, Xishan > Wuhua > Guandu > Panlong in 2019. From each administrative district perspective, Wuhua maintains the maximum CA and the minimum PD during the implementation of UPGS, and Panlong has the largest value in CONNECT, but the lowest value in CA and per capita park area, whilst Guandu shows a mediocre performance among the four regions, however, Xishan exhibits an absolute superiority in NP, PLAND, PD and per capita park area, and the worst performance in CONNECT. This result is mainly affected by the natural, economic and demographic factors of the four regions, for instance, the existing wetlands in Xishan and forests in Wuhua can contribute to the UPGS area, furthermore, the UPGS pattern was affected by the policy of river greening, which was concentrated in Panlong, which has the highest population density. In general, the landscape metrics identify obvious differences among districts in terms of UPGS patterns at each implementation stage.
4.3. Visual Monitoring of UPGS Plan Implementation at the Local Scale
To monitor the implementation of the “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” at the local scale, the real-time visual monitoring of GE images from 2010, 2015, and 2019 for these UPGS planned to be built or expanded were examined. This study carried out the dynamic supervision of 25 UPGS, showing three kinds of implementation phenomena for the UPGS plan.
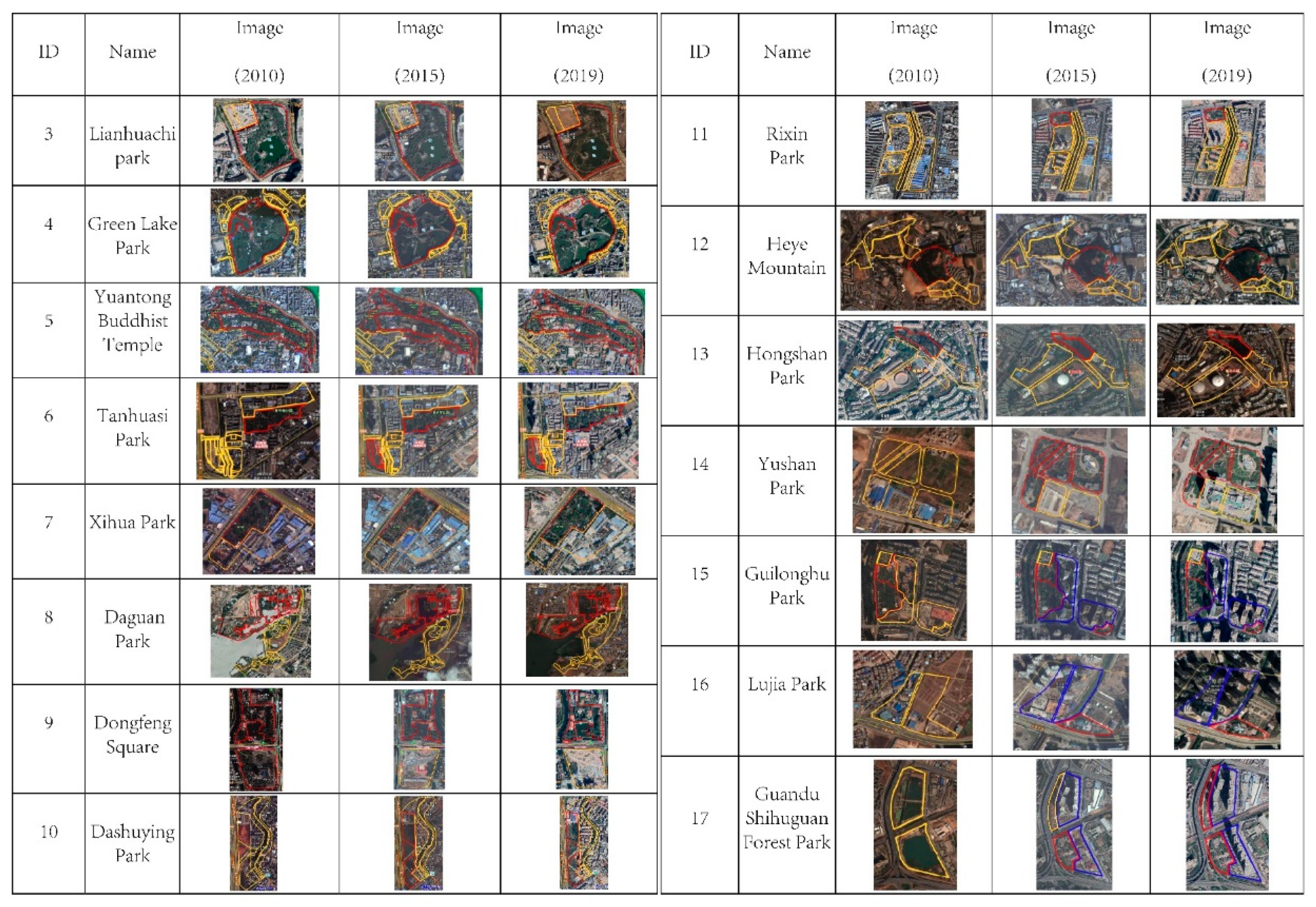
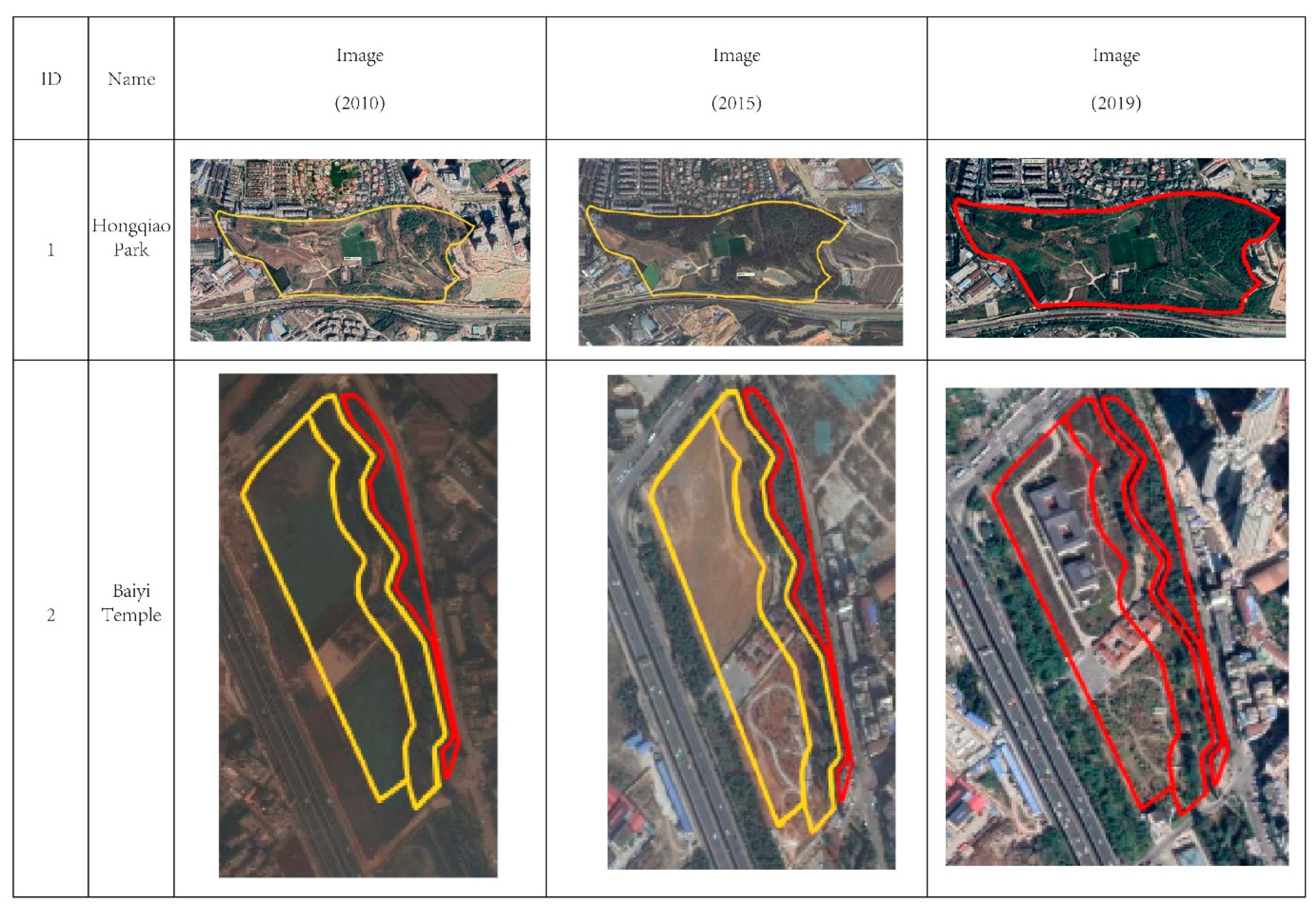
The first phenomenon is full implementation. According to the images of initial status (2010), after midterm-plan implementation (2015) and current plan implementation (2019), two of the 25 UPGS were fully implemented in 2019, namely Hongqiao Park and Baiyi Temple. Hongqiao Park experienced the process of none implementation in 2010 and partial implementation in 2015 to full implementation in 2019, while Baiyi Temple went through a process of partial implementation in 2010 and 2015 before full implementation in 2019 (Figure 8).
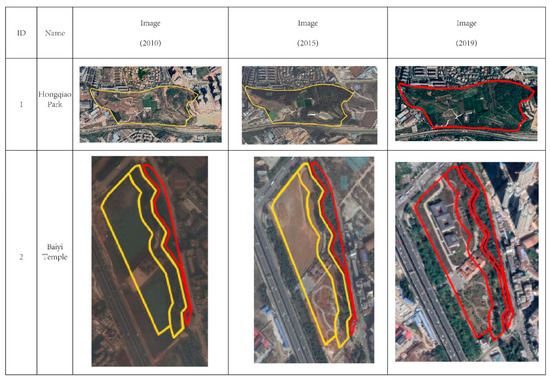
Figure 8.
The UPGS of full implementation (red line means implemented, yellow line means not implemented).
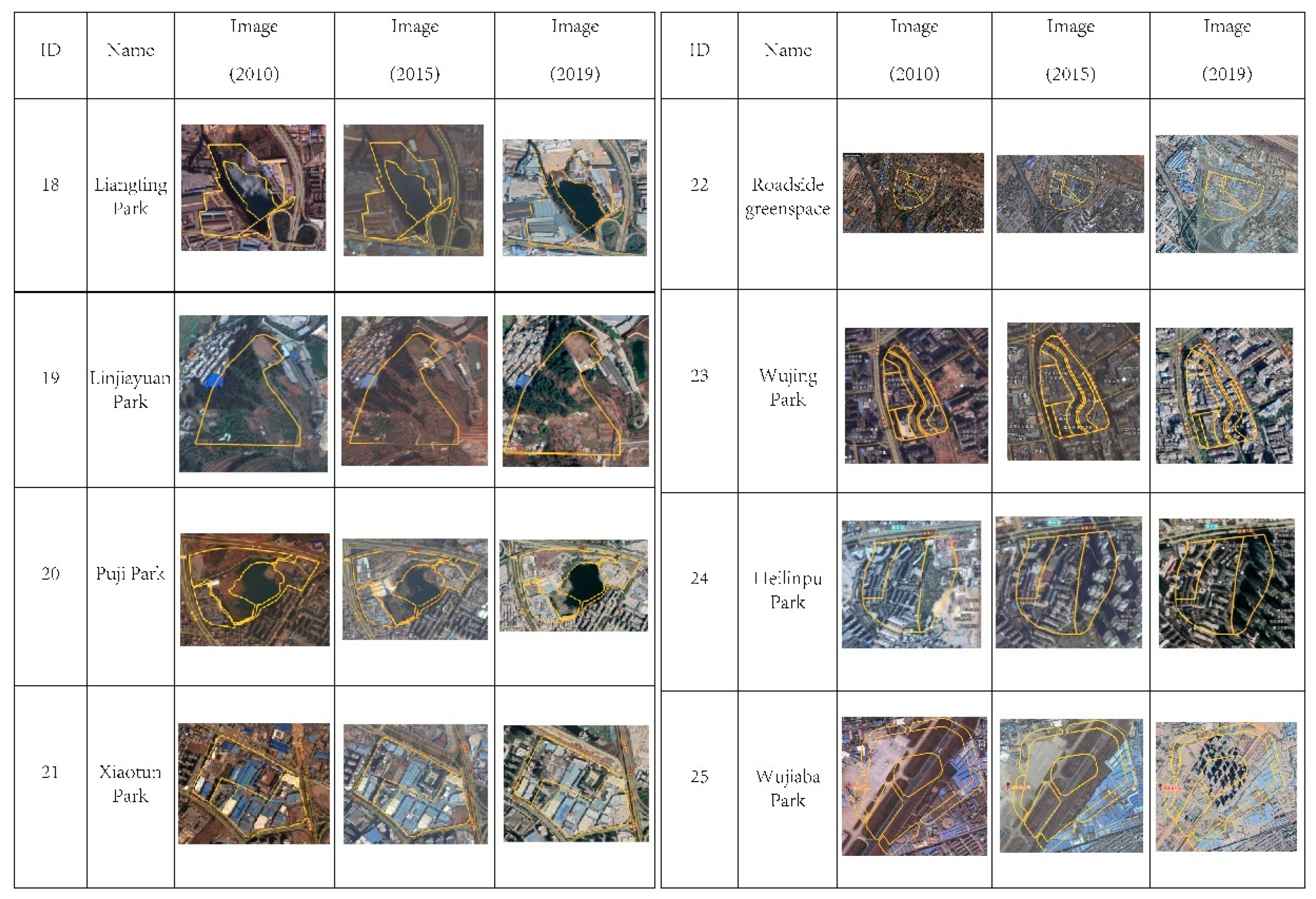
The second phenomenon is partial implementation. Fifteen UPGSs showed this pattern by comparing the images in three periods, Most of them were in this state with partial implementation, and delayed implementation for the rest, such as Lianhuachi park, Green Lake Park, Yuantong Buddhist Temple, Tanhuasi Park, Xihua Park, Daguan Park, Dongfeng square, Dashuying Park, Heye Mountain, Hongshan Park, Yushan Park and Rixin Park. However, three sites presented another status with partial implementation, and new housing estates for the rest. For example, most of the Guilonghu park consisted of real estate development projects (as of 2015 and 2019), and another part consisted of small gardens with water (Figure 9(15)); the Shihuguan park was composed of two brownfield sites in 2010 (Figure 9(17)), and was also to become the planned urban park. In 2019, only two small sites were transformed into UPGS; the other sites were also replaced by a local housing estate project (Figure 9(17)).

Figure 9.
The UPGS of partial implementation (the red line means implemented; the yellow line means not implemented; and the blue line means changing the nature of land use).
The third phenomenon is non-implementation. Eight planned parks were investigated and supervised, Five of them showed no change during the three planning implementation points (Figure 10(18)–(22)): for example, the roadside greenspace site in 2010 consisted mainly of village land and farmland; however, as of 2015 and 2019, this site exhibited almost no change and residential land partly without any signs of demolition and construction for UPGS (Figure 10(22)). Three of them illustrate areas planned to partly become non-UPGS area, for instance, Wujiaba park planning was based on transforming the dismantled old airport site, however, the comparison of GE images from 2010 and 2015 shows that this plot has not changed and no progress has been made towards UPGS implementation; in fact, part of the site was changed into real estate construction in 2019 (Figure 10(23)).
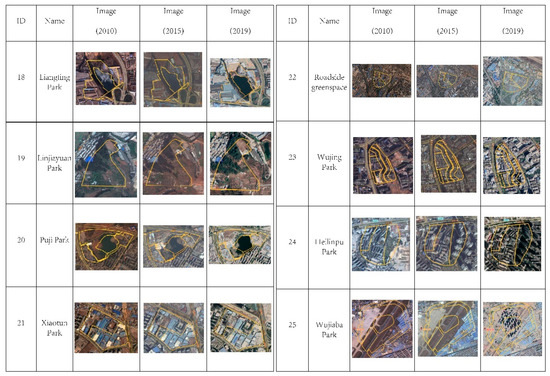
Figure 10.
The UPGS of non-implementation (yellow line means not implemented).
5. Discussion
5.1. Pattern of Planned UPGS
Indicators were used to assess the results of implementing the “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” UPGS in 2010, 2015, and 2019, which were compared for the overall study area and four administrative districts within the study area. For the overall study area, the UPGS pattern was greatly improved after the implementation of the UPGS plan. However, the connectivity was poor and the UPGS provision per capita was still not up to the planned level in Kunming City. The main reason for these deficiencies was the long delay of UPGS implementation and the lack of corridors and/or linear UPGS planning from a landscape ecological perspective. Furthermore, although the UPGS provision per capita in the tricyclic area (with its high density population and relatively limited amount of UPGS) was countervailed by the UPGS in surrounding areas, the effect was not strong enough to achieve the planned per capita UPGS for the study area as a whole. At the district level, imbalances in the UPGS pattern were clear. Xishan District had the maximum values for the indexes NP, PLAND, PD and per capita park area and was identified as the most suitable living district for local residents by having more UPGS. Xishan District was followed in order by Guandu and Wuhua districts. In contrast, Panlong District exhibited inferior values for most of the indicators.
The analysis revealed that Kunming’s 2010–2020 UPGS plan mainly used idle, low-value land for UPGS; thus, the natural resources and development status of districts (e.g., population) were the main factors leading to the quite uneven layout for UPGS in different districts. These natural spaces were planned for UPGS, but only a small amount of this type of land existed in the well development districts of Wuhua and Panlong, both of which had compact land use. Furthermore, in recent years, a series of policies by Kunming governmental authorities have had a great impact on the implementation of the 2010–2020 UPGS plan. Kunming’s efforts to achieve the titles of National Garden City and National Forest City led to a surge in the planned UPGS in the entire study area. The series of initiatives taken by the city’s leadership, such as purifying the river flowing into Dianchi and constructing wetlands, resulted in the emergence of a large number of riverfront parks along the rivers and the wetland park near Dianchi Lake in Xishan District. The completion of the new airport has led to most of the old airport site being planned for park land in Guandu District.
5.2. Implementation Effects of the Plan
The pattern of midterm and current UPGS plan implementation shows that as of 2019, the implementation of the plan was lagging behind schedule. The sites of UPGS planned to be built or expanded at the local level were also used to monitor the UPGS plan implementation and revealed two situations except for full implementation (only two sites) that contradicted the 2010–2020 UPGS plan objectives. One situation illustrated the incomplete implementation of the UPGS plan, mainly due to the adjustment of the plan. The government department introduced the construction method of “property promoting gardens”, in which part of the land used for a UPGS planning project was allocated for real estate development, and part of the income from real estate development was used as the main source of UPGS construction funding, thus reducing the planned UPGS area. The other situation illustrated the complete non-implementation of the UPGS plan, mainly due to the balance of economic interests, which has been lagging behind or even without any changes.
UPGS planning is a competitive process between public interests and economic development, which often conflicts with the goals of different stakeholders. Local governmental authorities pay more attention to economic development than to investment in green infrastructure. Therefore, driven by economic interests, local authorities can suspend or even sacrifice UPGS construction for projects that deliver greater economic benefits. In addition, land ownership and the government’s economic strength can affect the implementation of the UPGS plan. Local authorities encourage developers by granting park development through the method of land use compensation, resulting in a loss of some UPGS planning land.
5.3. Inspiration for the UPGS Plan
Object-based image classification was used to identify existing green space using high-resolution satellite images, achieving credible precision at significant cost savings compared to traditional survey methods. Similarly, the sampling for checking the accuracy of image classification is a new method based on current GE imagery that avoided the labor requirement for field sampling [56].
Compared with the traditional green space system planning implementation, this study selected multivariate metrics and used real-time Google Images and GIS technology to carry out the UPGS implementation evaluation in the time–space dimension, which provides a simple spatial quantitative method for planning implementation [73,74]. The method of mapping and evaluation can be widely applied in other urban planning and research.
However, some challenges remain in the study. At present, the ecosystem services of urban green space for the optimization of urban planning and design is the research hotspot and development trend of urban research [7,75]. At the same time, considering the relationship between the supply and demand of humans, more and more attention is paid to the fairness and inclusiveness of urban green space [76], thus the sustainable development of urban green space is an eternal topic [77]. Although landscape metrics are powerful tools for quantifying landscape structure, uncertainties exist around their interpretation [37,78]. In the future, establishing a standard evaluation system with a comprehensive index is more valuable in guiding the implementation of UPGS planning and construction. Input from industry experts should be incorporated to improve the evaluation system itself, and the ability to track and monitor UPGS plan implementation, which will facilitate the timely optimization of a plan [37]. Furthermore, landscape ecology theory should be applied to the planning and design of UPGS to improve the ecological service functions of UPGS, such as by adding ribbons and wedges of green patches [47].
A UPGS plan can be optimized by evaluating it using landscape metrics from the perspective of landscape ecology in the planning process. Considering that UPGS planning is a spatiotemporal dynamic process, the strategies related to it have been and continue to be difficult to implement due to the complexity of the planning process itself. Therefore, the evaluation of a UPGS plan cannot be confined to only the current planning, but rather should track the whole planning period process so that changes conducive to the effective operation of the plan can be accomplished [64,68]. In addition, urban greenspace planning is an integral part of urban planning and can be considered a special type of planning, which has strong power as a legal mandate, so the evaluation and monitoring of a UPGS plan should be a statutory requirement. At the same time, greenspace development that is connected to the public interest should be identified in future urban plans and should facilitate the uniform distribution of public infrastructure (such as UPGS) at different spatial scales without being limited by factors such as the availability of natural and idle land [75]. Meanwhile, efforts should be implemented to improve public participation in and the transparency of planning.
6. Conclusions
Landscape indicators and high-resolution satellite images were used to evaluate and monitor the UPGS plan implementation in the densely populated tricyclic metropolitan area of Kunming, China. Object-based classification was employed to identify the spatial distribution of UPGS before the implementation of “Green Space Planning of Kunming 2010–2020” (in 2010), after midterm plan implementation (2015), and current implementation (2019). The analysis proved that the object-based classification of high-resolution images possesses great advantages for mapping urban greenspace with credible precision. Classical landscape metrics were applied to quantitatively evaluate the UPGS planning for the study area and the four districts. The higher resolution and multivariate metric analysis can compensate for incomprehensive assessment associated with the use of a single index (e.g., per capita park area) over a large area.
The results showed there has been great improvement in UPGS as a result of the 2010–2020 plan, not only in the overall study area but also in specific administrative districts; however, insufficient per capita UPGS provision and low connectivity document insufficient UPGS implementation and the use of UPGS corridors in the study area. Furthermore, significant UPGS inequalities exist among districts because of local land use policy and natural factors.
This study bridged the gap between greenspace planning and practical implementation. Twenty-five UPGS sites planned to be built or expanded in Google Earth images from 2010, 2015, and 2019 were compared in terms of land-use change to monitor the UPGS plan execution at the local level. The comparison confirmed that the implementation of the plan was lagging behind schedule and indicated that achieving the original goals of the 2010–2020 UPGS plan would be difficult. The imagery comparison also documented that some planned and existing UPGS had been lost to residential construction due to the competing interest of economic development.
Therefore, this study demonstrated that the common problems that challenged the implementation of many land use plans also exist in Kunming’s 2010–2020 UPGS plan. First, the UPGS plan pattern is uneven at the overall scale and the district scale, and second, there is a serious lag and deviation in the UPGS plan implementation. The evaluation method with 3S technology and landscape metrics is applicable to and should be recommended for use by planners and policymakers in urban planning procedures to select the priority planning scheme. Monitoring the implementation of a UPGS plan should be used to detect the implementation progress to make timely corrections to the implementation process if necessary. Furthermore, the methods used in this study can become the guide and assessment criteria for planning, as they have broader applications for other forms of city planning. This study can be improved by optimizing UPGS layout, which will greatly improve the living environment of local residents by correcting the uneven distribution and insufficient per capita provision of UPGS.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su13073704/s1, Table S1: The information of 25 UPGS sites planned to be built or expanded in the study area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and H.Z.; investigation, M.L. and D.S.; methodology, M.L. and X.L.; software, M.L.; validation, M.L., X.L., D.S. and H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, X.L., D.S. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, M.L. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Youth Program joint in Agriculture of Applied Basic Research Program of Yunnan Province, grant number 2018GF001-099 and supported by the Natural Science Research Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology, grant number 241120200016/3321.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Kunming Planning Bureau for providing Green Space System Planning of Kunming 2010–2020. The authors appreciate International Science Editing for providing language help. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. The research was supported by the Youth Program joint in Agriculture of Applied Basic Research Program of Yunnan Province (2018FG001-099) and the Natural Science Research Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology (241120200016/3321).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Society: Realizing China’s urban dream. Nat. News 2014, 509, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Buyantuev, A.; He, X.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Dawazhaxi; Yang, Z. Urban agglomeration of Kunming and Yuxi cities in Yunnan, China: The relative importance of government policy drivers and environmental constraints. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, C.E.; Hobbs, R.J. Time for a change: Dynamic urban ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzic-Gyurkovich, K. Urban Development and Population Pressure: The Case of Mynówka Królewska Park in Krakow, Poland. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitti, M.; Ferrara, C.; Perini, L.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Long-Term Urban Growth and Land Use Efficiency in Southern Europe: Implications for Sustainable Land Management. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3359–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wei, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Yenneti, K. Urban Land Expansion and Structural Change in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10281–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Kim, G.; Mayer, A.; He, R.; Tian, G. Assessing the Ecosystem Services of Various Types of Urban Green Spaces Based on i-Tree Eco. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisdianto, S.; Udiansyah, B.J. Standing carbon in an urban green space and its contribution to the reduction of the thermal discomfort index: A case study in the City of Banjarbaru, Indonesia. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2012, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.W.; Hauer, R.J.; Werner, L.P. Urban Forestry: Planning and Managing Urban Greenspaces; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alkama, R.; Cescatti, A. Biophysical climate impacts of recent changes in global forest cover. Science 2016, 351, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.-Y.; Kim, J.; Wai, K.O.C.; Samuel, T.A. Urban Green Space Layouts and Urban Heat Island: Case Study on Apartment Complexes in South Korea. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 04018004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.A.; Gaston, K.J. The scaling of green space coverage in European cities. Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-T.; Huang, S.-L. Investigating spatiotemporal patterns of landscape diversity in response to urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 93, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.D.; Byrne, J.A.; Garden, J.G.; Hero, J.-M. Informal urban green space: A trilingual systematic review of its role for biodiversity and trends in the literature. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 883–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schebella, M.; Weber, D.; Schultz, L.; Weinstein, P. The Wellbeing Benefits Associated with Perceived and Measured Biodiversity in Australian Urban Green Spaces. Sustainability 2019, 11, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Jim, C. Assessment and valuation of the ecosystem services provided by urban forests. In Ecology, Planning, and Management of Urban Forests; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- Riechers, M.; Barkmann, J.; Tscharntke, T. Perceptions of cultural ecosystem services from urban green. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Nakagoshi, N. Spatial-temporal gradient analysis of urban green spaces in Jinan, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, H.; Andresen, T.; Monteiro, A. Green structure and planning evolution in Porto. Urban For. Urban Green. 2011, 10, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Peng, J.; Huang, L. Impact of Urban Green Space on Residential Housing Prices: Case Study in Shenzhen. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2015, 141, 05014023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, H. Dynamic and Heterogeneous Demand for Urban Green Space by Urban Residents: Evidence from the Cities in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekkel, E.D.; de Vries, S. Nearby green space and human health: Evaluating accessibility metrics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.C.; Fluehr, J.M.; Mckeon, T.; Branas, C.C. Urban Green Space and Its Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artmann, M.; Bastian, O.; Grunewald, K. Using the Concepts of Green Infrastructure and Ecosystem Services to Specify Leitbilder for Compact and Green Cities—The Example of the Landscape Plan of Dresden (Germany). Sustainability 2017, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J. Analysis of problems in urban green space system planning in China. J. For. Res. 2009, 20, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.; Welivitiya, W.; Nadeeka, P. Urban green spaces analysis for development planning in Colombo, Sri Lanka, utilizing THEOS satellite imagery—A remote sensing and GIS approach. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.A.; McKenzie, T.L.; Sehgal, A.; Williamson, S.; Golinelli, D.; Lurie, N. Contribution of public parks to physical activity. Am. J. Public Health 2007, 97, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczynski, A.T.; Henderson, K.A. Environmental correlates of physical activity: A review of evidence about parks and recreation. Leis. Sci. 2007, 29, 315–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Jeong, S. Assessing the spatial distribution of urban parks using GIS. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 82, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnachie, M.M.; Shackleton, C.M. Public green space inequality in small towns in South Africa. Habitat Int. 2010, 34, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Campbell, L.; Svendsen, E.; Mcmillen, H. Mapping Urban Park Cultural Ecosystem Services: A Comparison of Twitter and Semi-Structured Interview Methods. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Peng, Z. Evaluation and Planning of Urban Green Space Distribution Based on Mobile Phone Data and Two-Step Floating Catchment Area Method. Sustainability 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Y. The role of urban green infrastructure in offsetting carbon emissions in 35 major Chinese cities: A nationwide estimate. Cities 2015, 44, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.M.; Carlos, L.A.; Pablo, B.P.; Pedro, M.V. Viability of Green Roofs as a Flood Mitigation Element in the Central Region of Chile. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher, C.; James, C.; Kelsey, S.; Joshua, P.; Ashlynn, S. The Green Experiment: Cities, Green Stormwater Infrastructure, and Sustainability. Sustainability 2017, 9, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Da Rocha Cecília, G.; Sattler Miguel, A. Improving Acceptance of More Sustainable Technologies: Exploratory Study in Brazil. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2017, 143, 05016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafius, D.R.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Linking ecosystem services, urban form and green space configuration using multivariate landscape metric analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; van den Bosch, C.C.K.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Dong, J. China’s Green Space System Planning: Development, Experiences, and Characteristics. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 60, 127017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega Christine, C.; Nilon Charles, H.; Warren Paige, S. Avian Abundance Patterns in Relation to the Distribution of Small Urban Greenspaces. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2015, 141, A4015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Ding, W. A method for planning mandatory green in China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2011, 35, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the current situation and planning of the greenspace system in huaibei city using GIS based network analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Management and Service Science (MASS’09), Wuhan, China, 20–22 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jim, C.Y.; van den Bosch, C.K.; Chen Wendy, Y. Acute Challenges and Solutions for Urban Forestry in Compact and Densifying Cities. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 04018025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Geng, Y.; Ou, X.; Song, D. Analysis of Urban Public Greenspace Pattern Based on Landscape Metrics in Kunming. In Civil Engineering and Urban Planning IV: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Urban Planning, Beijing, China, 25–27 July 2015; Taylor & Francis Group: London, England, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wüstemann, H.; Kalisch, D.; Kolbe, J. Access to urban green space and environmental inequalities in Germany. Lands. Urban Plan. 2017, 164, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabon, L.; Shih, W.Y. What might ‘just green enough’ urban development mean in the context of climate change adaptation? The case of urban greenspace planning in Taipei Metropolis, Taiwan. World Dev. 2018, 107, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.; Ye, C. Evaluation Index System for Urban Green System Planning. Planners 2019, 35, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Haaland, C.; Bosch, C.K.V.D. Challenges and strategies for urban green-space planning in cities undergoing densification: A review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, N.; Strohbach, M.; Haase, D.; Kronenberg, J. Urban green space availability in European cities. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Mao, Q. Spatio-temporal Evaluation of Urban Planning Implementation. Prog. Geogr. 2011, 30, 967–977. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, D.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Exploration and Reflections on the Implementation Evaluation in the Context of Master Planning Reform. Urban Plan. Forum 2017, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarenhas, A.; Ramos, T.B.; Nunes, L. Developing an integrated approach for the strategic monitoring of regional spatial plans. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunming Planning Bureau. Green Space System Planning of Kunming 2010–2020; Planning Document; Kunming Planning Bureau: Kunming, China, 2010.
- Kunming Statistical Bureau. Kunming Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Kunming Statistical Bureau. Kunming Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Kunming Statistical Bureau. Kunming Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Hu, Q.; Wu, W.; Xia, T.; Yu, Q.; Yang, P.; Li, Z.; Song, Q. Exploring the use of Google Earth imagery and object-based methods in land use/cover mapping. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6026–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, S.; Ghassemian, H. MRI and PET image fusion by combining IHS and retina-inspired models. Inf. Fusion 2010, 11, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Understanding image fusion. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hong, G. An IHS and wavelet integrated approach to improve pan-sharpening visual quality of natural colour IKONOS and QuickBird images. Inf. Fusion 2005, 6, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A. Installing ArcGIS Desktop 10.2.2 on Campus Computers. Heterocycl. Commun. 2014, 10, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, D.J. ArcGIS: General-Purpose GIS Software; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffari, P.O.; Monavari, S.M. Physical development trend and green space destruction in developing cities: A GIS approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2013, 15, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, J.; Bai, C.; Zhao, J.; Ye, F. An object-oriented method for extracting city information based on high spatial resolution remote sensing images. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Technol. 2011, 3, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.-C. Spatial–temporal dynamics of urban green space in response to rapid urbanization and greening policies. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaging, D. eCognition Developer Software: 8.7.1. Reference Book; Trimble Germany GmbH: Raunheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Nakagoshi, N.; James, P. Simulating urban growth processes incorporating a potential model with spatial metrics. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 20, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, R.; Mahiny, A.S.; Khorasani, N. Assessment of changes in urban green spaces of Mashad city using satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.-F.; Gao, Y.; Pacheco, J.A.N. Sensitivity of landscape pattern metrics to classification approaches. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Ikiugu, M.M.; Kinoshita, I.; Tashiro, Y. Urban green space analysis and identification of its potential expansion areas. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 35, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Mander, U.; Marja, R. Trends in the use of landscape spatial metrics as landscape indicators: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunming Government. The Kunming Population Development Plan Outline 2011–2020; Planning Document; Kunming Government: Kunming, China; p. 2011.
- lan, N. Theory and Method of Urban Space System Planning Implementation Evaluation; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Badach, J.; Raszeja, E. Developing a Framework for the Implementation of Landscape and Greenspace Indicators in Sustainable Urban Planning. Waterfront Landscape Management: Case Studies in Gdańsk, Poznań and Bristol. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.W.; An, K. Identifying the Planning Priorities for Green Infrastructure within Urban Environments Using Analytic Hierarchy Process. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Contrary to Common Observations in the West, Urban Park Access Is Only Weakly Related to Neighborhood Socioeconomic Conditions in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titz, A.; Chiotha, S.S. Pathways for Sustainable and Inclusive Cities in Southern and Eastern Africa through Urban Green Infrastructure? Sustainability 2019, 11, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, P.; Xiang, C. Evaluating the effectiveness of landscape configuration metrics from landscape composition metrics. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 13, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).