Abstract
Grassland is an important ecosystem; the spatiotemporal evolution trend of grassland and its impacts on climatic factors play an irreplaceable role in maintaining regional sustainable development and ecological balance. In this paper, based on the remote sensing images of 1990, 2000, 2010, 2020, and 3S technology, we use the methods of dynamic rate and transfer matrix to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution trend of the northern Songnen Plain (China). The method of grey correlation is used to analyze the impact of climate factors on it. The results showed that the grassland changed dramatically and unevenly across the three periods of 1990–2000, 2000–2010, and 2010–2020, with the biggest change in the last period. The internal conversion of grassland mainly occurred between H-grassland (high coverage grassland) and M-grassland (medium coverage grassland), while the transformation rarely occurred in L-grassland (low coverage grassland) due to its small area. There has been a transfer-in from cultivated land, woodland, and unused land to H-grassland and M-grassland. The grassland transfer-out was mainly from H-grassland and M-grassland to cultivated land and unused land. What’s more, the transformation mainly occurred in Daqing City, Suihua City, Qiqihar city, as well as occurring in the west of Harbin and the southwest of Heihe city. Climate change has exacerbated the reduction of grassland areas. In summary, the spatiotemporal change rates of grassland area in the north of Songnen Plain initially showed a mild decrease and were then followed by a rapid decrease. Climate factors were of great significance to the spatiotemporal changes of grassland, and precipitation had a greater impact on the reduction of grassland. The results can provide meaningful information for grassland change, grassland protection, and management in the northern Songnen Plain.
1. Introduction
Grassland is one of the largest terrestrial ecosystems on earth, accounting for 41.7% of the total land area in China [1], which plays an important role in the global carbon cycle and climate response [2]. Specifically, it can regulate the climate, improve soil fertility, prevent wind, fix sand, conserve soil and water, purify the air, and beautify the environment. China has nearly 40,000 million hectares of grassland, more than three times of China’s farmland area [3], for which China is the country with the largest grassland in the world. The impact of drought climate as well as human activities has resulted in China’s grassland suffering the world’s most serious degradation, which is mainly manifested in area reduction, coverage reduction, and serious salinization. Grassland protection thus becomes an important part of ecological civilization construction.
Studies home and abroad have shown that current research on the characteristics of grassland mainly focuses on the spatiotemporal changes and driving mechanism of grassland [4], or its impact on ecological services [5,6]. As one of the commonly used methods in the spatiotemporal of grassland changes research, remote sensing is suitable for large-scale grassland monitoring. Scholars have extracted some indicators from remote sensing images, such as NDVI, NPP, and have characterized grassland degradation by analyzing the spatiotemporal changes of grassland degradation indicators. Some researchers have found that with the help of soil indicators, such as SOM and SOC, and remote sensing images, the spatiotemporal distribution can be retrieved and the relevant factors can be analyzed [7,8]. The scope of spatiotemporal changes is mainly concentrated on the national [9], regional [10,11], and urban [12] scales. The transfer matrix method, ecological model, kernel density [13], and other methods are often used to describe the spatiotemporal changes of grassland.
As a typical ecologically fragile area, the northern Songnen Plain has been studied by many scholars who mainly focus on the reduction and fragmentation of grasslands [14], the response of grassland change to carbon storage [15,16], and the impact of human activities on grassland changes [17]. However, human activities and climate factors are the main causes of grassland change, but climate change is the main cause of grassland degradation [9,18,19]. At present, there are few studies on the impact of climate change on grassland in the northern Songnen Plain. Therefore, it is of great significance to analyze the spatiotemporal variation and analyze the impact of climate factors on the northern Songnen Plain, thus providing reference to the degradation and regeneration of grassland, as well as offering basic data for the exploration of grassland ecological protection, and providing advice to the ecologically vulnerable areas in the northern Songnen Plain.
In this study, Landsat images were used as a data source to analyze the spatiotemporal changes and the impact of climate factors on grassland from 1990 to 2020 in the northern Songnen Plain (China). The main goals of this study are as follows:
- (1)
- To reveal the internal conversion characteristics of the grassland;
- (2)
- To analyze the characteristics of grassland transfer-in and transfer-out;
- (3)
- To explore the probable impact of climate factors on the grassland in the northern Songnen Plain (China).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area, situated in the north of Songnen Plain (China), with an area of 13,052,000 ha, including Qiqihar City, Daqing City, Suihua City, West of Harbin City, and Southeast of Heihe City (Figure 1). The study area is adjacent to the north and northeast of the Lesser Hinggan Mountains, to the east and southeast of the Changbai Mountains, and the west and northwest of the Great Hinggan Mountains, and is separated by the Songliao and the Liaohe Plain. The terrain of the study area is generally high in the east, low in the central west. The main soil types in the region are Phaeozems, Chernozems, Arenosols, and Cambisols, as described in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB). It has a temperate continental, semi-humid, and semi-arid monsoon climate according to the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The area is warm and rainy in summer, cold and dry in winter, with an annual average temperature of 4.2 °C, annual average precipitation of 524.5 mm, annual average evaporation of 1586.8 mm, and annual average wind speed of 3.6 m/s [20]. Grassland is one of the most important ecosystems in the northern Songnen Plain, growing with relatively flat terrain.
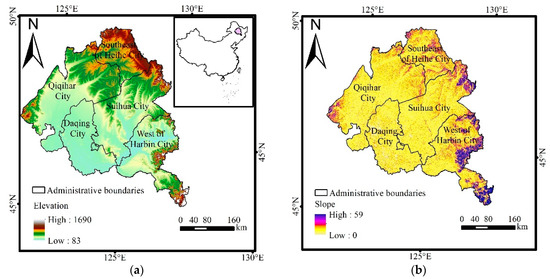
Figure 1.
The location, elevation (a), and slope (b) of the study area.
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
The data sources of land use are LandsatTM5/ETM + 7 remote sensing images from 1990 to 2010 and Landsat8 OLI in 2015. Based on the above sources, the land-use data in 2020 is generated by artificial visual interpretation, which was supported by the “Resource and Environment Science Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences”. According to ArcGIS 10.6 software (ESRI Inc., Redlands, CA, USA), there are six types of land use: cultivated land, woodland, grassland, water land, construction land, and unused land. The secondary classification of grassland is divided into H-grassland (high coverage grassland), M-grassland (medium coverage grassland), and L-grassland (low coverage grassland). H-grassland refers to natural grassland, improved grassland, and mowing land covering more than 50% grassland. Generally, this kind of grassland has good water conditions, and its cover grows densely. M-grassland refers to natural grassland and improved grassland with coverage more than 20–50%, which is deficient in water and sparse in grass cover. L-grassland refers to natural grassland with coverage of 5–20%. This kind of grassland is deficient in water, sparse in grass cover, and poor in animal husbandry utilization conditions. Other data include the administrative boundary of China and the northern Songnen Plain. The temperature and precipitation data come from the daily value data set of China surface climate data (V3.0), China Meteorological Data Service Center (Beijing, China). The meteorological spatial distribution raster map (1 km) is interpolated by the ordinary kriging method. The DEM of the northern Songnen Plain comes from (https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/) in 2009.
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Dynamic Analysis on the Change of Grassland
The land-use dynamic rate is used to analyze the quantity change and change rate of land-use types in the study area over a certain period time [21,22,23]. Its mathematical expression is:
where Ki is the dynamic rate of land use from t1 to t2, and St1, St2 were the number of land-use types in t1, t2.
2.3.2. Analysis of the Transfer Matrix of Land-Use Types
Transfer matrix can describe the quantitative structure characteristics of land-use change and the transfer changes of different types at the beginning and end of a certain period in a region comprehensively and concretely, which has rich statistical significance [24]. In this paper, we use the land-use transfer matrix to study the time change characteristics of grassland in the area. Its mathematical expression is:
where S is the area of land-use types; n is the number of land-use types. In this study, n was 10; i and j are the land-use types at the beginning and the end of the study period, respectively. The transfer matrix of any two periods can be obtained by substituting the maps of land-use types in the two periods using the raster calculator of ArcGIS10.6 software (ESRI Inc., Redlands, CA, USA).
2.3.3. Grey Correlations Analysis
Grey correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the correlation degree of some impact factors on grassland [25,26]. For this study, the impact factors are temperature and precipitation. The detailed calculation formulas follow. The matrix for impact factors is:
The matrix for the macro behavior is selected as a reference sequence. And the macro behavior for the study is the area of grassland from 1990 to 2020.
Normalization results in a non-dimension matrix.
The correlation coefficient of x0(k) and xi(k) can then be calculated as:
where δ is the recognition coefficient, defined as 0.5.
The grey correlation degree of x0 and xi is calculated as:
Then the correlation of temperature and precipitation with the area of grassland from 1990 to 2020 could be obtained. The greater the φi, the higher the relevance of impact factors is to the reference sequence.
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Variation of Grassland from 1990 to 2020 in the Study Area
Grassland is an important land-use type in the northern Songnen Plain, which is mainly distributed in Daqing City and Qiqihar City (Figure 2). According to the change of land-use types and dynamic rate from 1990 to 2020, grassland has been changing dynamically, accompanied by the unbalanced secondary classification of grassland changes. The dynamic rate of H-grassland is greater than that of M-grassland and L-grassland (Table 1).
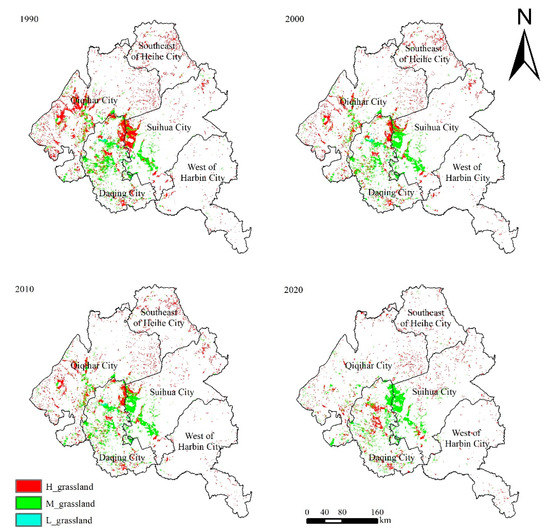
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of Grassland from 1990 to 2020.

Table 1.
The change of land-use types and their dynamic rates in northern Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020.
From 1990 to 2000, the area of H-grassland decreased by 2565 km2, while the area of M-grassland increased by 138 km2, and the area of L-grassland increased by 2 km2. The dynamic rate was −3.07%, 0.25%, and 0.07%, respectively. The total area of grassland decreased, while the dynamic rate of H-grassland was the highest. The decrease field was mainly distributed in Qiqihar City, Daqing City, and Suihua City, while the increased area of M-grassland and L-grassland was mainly distributed in Suihua City.
The next decade saw that the area of H-grassland increased by 27 km2, the area of M-grassland increased by 102 km2, and the area of L-grassland decreased by 2 km2, with the dynamic rate of 0.05%, 0.18%, and −0.07%, respectively. The dynamic rate of L-grassland is the lowest among all land use types, while the dynamic rate of M-grassland is only higher than that of water land. It indicated that though the total grassland area has increased in this period, the change is not obvious. The increased area is mainly conversed from unused land and cultivated land, with the conversion areas of 328 km2 and 259 km2, respectively.
In the last ten years, the area of the secondary classification of grassland decreased to different degrees, including 1635 km2 for H-grassland, 862 km2 for M-grassland, and 29 km2 for L-grassland, with the dynamic rates of −2.81%, −1.47%, and −0.97%, respectively. The decrease of grassland area is distributed throughout the study area, but mainly in the west of the study area.
3.2. Spatial Variation of Grassland from 1990 to 2020 in the Study Area
3.2.1. Characteristics of the Internal Conversion of Grassland
The secondary classification of grassland was H-grassland, M-grassland, and L-grassland. From 1990 to 2000, H-grassland and M-grassland converted between each other, in which the main conversion was from H-grassland to M-grassland, covering an area of 711 km2 and with a conversion ratio of 8.51%. Among all cities, Suihua City ranked first, with a conversion ratio of 96.20% (Table 2).

Table 2.
The Internal Conversion of Grassland.
In the next ten years, there was a significant reduction in the internal conversion of grassland. The conversion from H-grassland to M-grassland was about 26 km2 and H-grassland to M-grassland was 16 km2, which was mainly concentrated in Suihua City, Daqing City, and Qiqihar City. There was no conversion between H-grassland and L-grassland, but little conversion between M-grassland and L-grassland, which covered an area of 3 km2 in Daqing City.
In the last decade, the internal transformation of the secondary grassland classifications all occurred, mainly between H-grassland and M-grassland conversion. The area from H-grassland to M-grassland was 701 km2, with a conversion ratio of 12.06%. M-grassland to H-grassland was 594 km2, with a conversion ratio of 10.15%. The conversion mainly occurred in Daqing City, and also occurred in other cities.
In all the internal transformation of grassland from 1990 to 2020, the transformation from 2010 to 2020 was the most obvious (Figure 3), followed by 1990 to 2000 and 2000 to 2010 ranked the last.
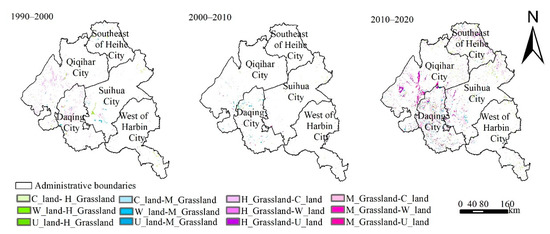
Figure 3.
The characteristics of main land-use types of the spatial grassland conversion from 1990 to 2020 in the study area.
3.2.2. Characteristics of Grassland Transfer-In
The characteristics of grassland transfer-in refer to the increase of grassland area caused by the other five land-use types and transfer into grassland, especially H-grassland and M-grassland in the study area. Of all the cities included, Daqing City, Qiqihar City, and Suihua City changed the most (Figure 4). Based on Table 3, we can see that, from 1990 to 2000, H-grassland mainly converted from woodland and unused land, and the conversion ratio was 0.59%, 1.28%, respectively. Woodland was mainly distributed in the west of Harbin City (56 km2), southwest of Heihe City (49 km2), and Suihua City (30 km2). Unused land was mainly located in Suihua City (87 km2), Qiqihar City (74 km2), and Daqing City (43 km2). The conversion ratio from woodland and unused land to M-grassland was 0.59% and 1.07%, respectively. Woodland was chiefly distributed in Heihe City (17 km2), and unused land was mainly located in Suihua City (99 km2) and Daqing City (49 km2).
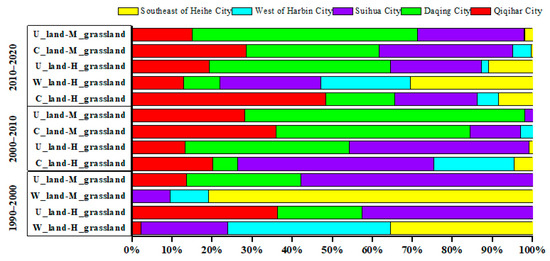
Figure 4.
The ratio of main grassland transfer-in area to total conversion area in every city/%.

Table 3.
Types of Grassland Transfer-In.
From 2000 to 2010, H-grassland and M-grassland mainly came from cultivated land and unused land, and the conversion ratio was 0.24% and 0.71%, respectively. Spatially, cultivated land to H-grassland was mainly found in Suihua City (95 km2), Qiqihar City (39 km2), Harbin (39 km2), and only a small amount distributed in Daqing City and southeast of Heihe City. The unused land was largely distributed in Suihua City (48 km2) and Daqing City (44 km2). The conversion ratio from cultivated land and unused land to M-grassland was 0.08% and 1.37%, respectively. Cultivated land to M-grassland was chiefly distributed in Daqing City (31 km2) and Qiqihar City (23 km2), and unused land was mainly located in Daqing City (144 km2) and Qiqihar City (58 km2).
From 2010 to 2020, the transfer characteristics were more obvious, and all of the other land-use types were transformed into grassland. However, the conversion of H-grassland and M-grassland was more obvious than that of L-grassland. The conversion ratio from cultivated land, woodland, and unused land to H-coverage grassland was 1.93%, 2.26%, and 3.29%, respectively. The conversion areas of cultivated land in Qiqihar City, Suihua City, Daqing City, the southeast of Heihe City, and west of Harbin City were 756 km2, 323 km2, 269 km2, 134 km2, and 83 km2, respectively. Woodland was mainly distributed in Heihe City (150 km2), Suihua City (124 km2), and west of Harbin City (109 km2). Unused land was chiefly located in Suihua City (109 km2) and Daqing City (218 km2). M-grassland was mainly converted from cultivated land and unused land, and the conversion ratio was 1.30% and 4.87%, respectively. The conversion area of cultivated land into M-grassland in Suihua City, Qiqihar City, and Daqing City is 351 km2, 300 km2, and 350 km2, respectively. Unused land into M-grassland is mainly distributed in Daqing City, Suihua City, and Qiqihar City, with an area of 400 km2, 188 km2, and 106 km2, respectively. Because of the small area of L-grassland, the conversion ratio is low.
3.2.3. Characteristics of Grassland Transfer-Out
The characteristics of grassland transfer-out refer to the reduction of grassland area caused by the transformation of grassland into other five land-use types in the study area. From 1990 to 2020, the grassland with H-grassland and M-grassland was mainly converted into cultivated land and unused land (Figure 5).
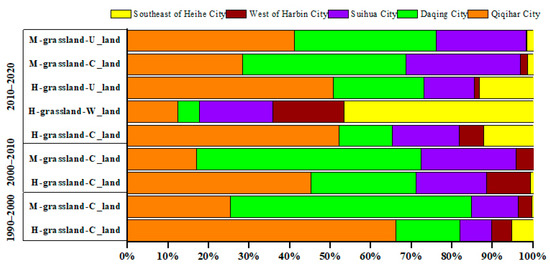
Figure 5.
The ratio of main grassland transfer-out area to total conversion area in every city in percent ages.
From 1990 to 2000, grassland was mainly converted into cultivated land, and the area of H-grassland was 2230 km2 and the conversion ratio was 26.70% (Table 4). The area distributed in Qiqihar was 1472 km2, accounting for 66.10% of the total transfer-out area. The area of M-grassland was 907 km2, with a conversion ratio of 16.16%, mainly concentrated in Daqing City (539 km2), Qiqihar City (230 km2), and Suihua City (104 km2).

Table 4.
Types of grassland transfer-out.
In the next ten years, the proportion of grassland transfer-out was significantly reduced, and mainly transferred into cultivated land. The ratio of H-coverage grassland to cultivated land was 4.66%, and mainly distributed in Qiqihar City (122 km2). The ratio of M-coverage grassland to cultivated land was 2.45%, and mainly distributed in Daqing City (78 km2).
In the last ten years, the grassland transfer-out mainly concentrated in H-grassland and M-grassland. The overall transfer-out ratio of grassland had increased, and the ratio of H-grassland to cultivated land was 40.02%, chiefly located in Qiqihar City, with a transfer area of 1208 km2, accounting for 52.07% of the total transfer-out area. The transfer ratio of woodland was 9.70%, mainly distributed in southeastern Heihe City (262 km2), and the transfer to unused land ratio was 21.60%, mainly distributed in Qiqihar City (636 km2) and Daqing City (280 km2). The ratio from cultivated land to M-grassland land was 26.76%, mainly distributed in Qiqihar City, with the transfer area of 1208 km2, accounting for 52.07% of the total transfer area, while the transfer ratio to unused land was 18.64%, mainly distributed in Qiqihar City (636 km2) and Daqing City (280 km2).
The number of L-grassland is very small due to the small area. The transfer-out area in 2010–2020 was much more than that of the other two periods, while the transfer-out area in 2000–2010 was the least. The transferred grassland is mainly distributed in the west of the study area. Compared with the ratio of grassland transfer-in, the ratio of grassland transfer-out is higher, which indicates that the grassland degradation is prominent.
3.3. The Impact of Climate Factors on Grassland in the Northern Songnen Plain
In this study, the annual mean temperature and precipitation were used to analyze the impact of climate factors on the grassland area from 1990 to 2020 in northern Songnen Plain, China (Figure 6). There was a slow rise from 1990 to 2020. While there was a fluctuation in the mean precipitation, which showed a declined trend from 1990 to 2000, and then increased in the last 20 years.
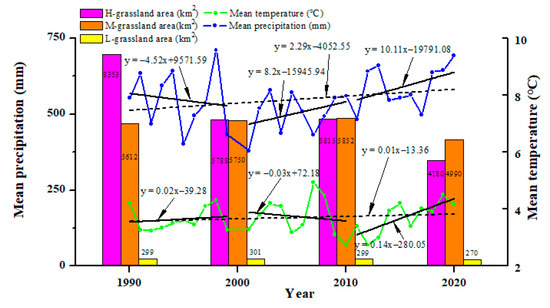
Figure 6.
Time series of the mean temperature, mean precipitation, and grassland area in the study area during 1990–2020.
According to the result of grey correlations (Table 5), the precipitation shows a higher relevance to the grassland area, which means that the grassland area tends to be more sensitive to precipitation than temperature.

Table 5.
Gray correlations of the grassland area with climate factors.
4. Discussion
In this paper, the results can explain the spatiotemporal grassland changes of internal and outside conversion in the northern Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020. The impacts of climate (temperature and precipitation) on grassland spatiotemporal changes under discussion has certain scientific significance for grassland protection and sustainable utilization.
From 1990 to 2020, the temperature tended to increase gradually (Figure 6). The increase of temperature can accelerate the evaporation of soil water, reduce the available water for grass growth, and limit photosynthesis [27]. Schirpke et al. [28] found that accelerating climate change will become the more important driver of changes in mountain grasslands, especially at high altitudes. In our study, the precipitation indicates a higher relevance to the grassland area compared to the temperature (Table 5). The conclusion is consistent with the result obtained by Guo et al. [29]. The precipitation shows an increasing trend from 1990 to 2020 and appropriate precipitation is beneficial to the growth of grassland. However, due to a large fluctuation in precipitation and the frequent occurrence of extreme precipitation events during the study period, the carbon sink capacity of grassland has been seriously affected and the grassland area and productivity are decreased [29]. In general, H-grassland area has decreased over the last 30 years, and M-grassland area shows a fluctuation, but declined on the whole, with L-grassland almost unchanged. From 1990 to 2000, the lessen of grassland especially H-grassland is mainly due to the warm–dry climate resulting from the increasing mean temperature and the decreasing precipitation, which does harm to the growth of grass. In the next ten years, the increasing trend of mean precipitation and decreasing trend of temperature is beneficial to the growth of grass, in order for grassland deterioration to be under control. In the last decennium, the rapid growth of mean temperature aggravated soil salination, which is an important reason for the decrease of grassland area. Furthermore, the sensitivity of grassland to water content and temperature results in the differences between different cities. The low-lying terrain of the northern Songnen Plain (Figure 1, Table 6) is conducive to the formation of a warm and humid climate. Daqing City in particular, with lower elevation and a gentle slope, keeps higher soil moisture and soil temperature, contributing to the growth of vegetation.

Table 6.
The average elevation of each city in Songnen Plain.
However, grassland experienced spatiotemporal change both quantitatively and qualitatively. The studies in the U.S. showed that cropland expansion aggravated grassland losses [30,31]. Meanwhile, the project of returning farmland to grassland and grazing prohibition implemented in 1999 and 2003 in China had greatly contributed to grassland vegetation restoration and forage growth in China. Wang et al. [32] found that grassland coverage increased significantly, and H-grassland had increased from 1.76% to 8.71% in the typical farming-pastoral zone after grazing prohibition. Ecological restoration measures are beneficial to grassland restoration [33].
Human activities and climate variation are joint factors contributing to grassland changes. However, besides natural factors such as temperature and precipitation, human factors should also be taken into consideration. Participation of human activities can ensure the sustainability of the land-use system [34]. Aune et al. [35] also found that the implementation of management and conservation measures were the key drivers for the loss of semi-natural grassland in northern Norway. In the future, the quality of the grassland and the effect of human activities on the grassland should be further explored.
5. Conclusions
Taking the northern Songnen Plain in China as the study area, this paper explored the spatiotemporal changes of grassland across the three decades of 1990–2000, 2000–2010, and 2010–2020, and discussed the impact of climate factors on it. The three main conclusions follow.
During the three periods from 1990 to 2020, great changes have taken place in grassland. From 1990 to 2000, the area of grassland decreased obviously, with the dynamic rate of H-grassland the most obvious. From 2000 to 2010, the grassland area changed slowly, and the grassland dynamic rate also changed slowly, with a slight increase in grassland area. However, from 2010 to 2020, the grassland area decreased sharply than that of 1990 to 2000, and the dynamic rate of M-grassland and L-grassland were more visible.
The internal conversion of grassland mainly concentrated between H-grassland and L-grassland, and the change is primarily distributed in Suihua City, Daqing city, and Qiqihar city. Grassland transfer-out was mainly from H-grassland and M-grassland to cultivated land, woodland, and unused land. Grassland transfer-in was largely from woodland and unused land to H-grassland and M-grassland, principally concentrated in Daqing City, Qiqihar city, and Suihua City, as well as distributed in the west of Harbin and the southwest of Heihe City. The changing area of L-grassland was very small.
The impact of precipitation on grassland is greater than that of temperature in the northern Songnen Plain, China.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z.; data curation, L.W. and X.W.; formal analysis, S.Z.; investigation, L.W.; methodology, L.W.; software, L.W.; supervision, S.Z. and X.W.; writing—original draft, L.W. and X.W.; writing—review and editing, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2018–Youth Fund Project (31800538).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qya, B.; Zn, A.; Zeng, T.A. Influencing factors of the grassland ecological compensation policy to herdsmen’s behavioral response: An empirical study in Hexi corridor. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.; Li, L.; Fritz, A. Mapping degraded grassland on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau with multi-temporal Landsat 8 data—Where do the severely degraded areas occur? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 42, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Kawamura, K. Grassland degradation in China: Methods of monitoring, management and restoration. Grassl. Sci. 2010, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Yinglan, A.; Duan, L.; Liu, T. A Spatiotemporal Cross Comparison Framework for the Accuracies of Remotely Sensed Soil Moisture Products in a Climate-Sensitive Grassland Region. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Du, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Cao, G. Alpine grassland management based on ecosystem service relationships on the southern slopes of the Qilian Mountains, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Das, D.; John, R. Grassland vegetation and roads have dominant influence on decadal-scale spatial-temporal patterns of fires in a species-rich protected Terai habitat in northeastern India. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 304, 108411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Li, X.; Dou, H.; Dang, D.; Liu, S. Evaluation of grassland carbon pool based on TECO-R model and climate-driving function: A case study in the Xilingol typical steppe region of Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106508. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, J. Changes of soil organic carbon stocks from the 1980s to 2018 in northern China’s agro-pastoral ecotone. Catena 2020, 194, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Grassland degradation remote sensing monitoring and driving factors quantitative assessment in China from 1982 to 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, R.; Du, H.; Na, L.; Shan, Y.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal changes in the Aeolian desertification of Hulunbuir Grassland and its driving factors in China during 1980–2015. Catena 2019, 182, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Pang, Q.; Ding, J.; Yin, R.; Zhang, Y. The driving factors of mercury storage in the Tibetan grassland soils underlain by permafrost. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265 Pt B, 115079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Bai, L. Grassland degradation and restoration monitoring and driving forces analysis based on long time-series remote sensing data in Xilin Gol League. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Change of Cultivated Land Resources in the Black Soil Region of Heilongjiang Province (China). Sustainability 2018, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Ren, C.; Luo, L.; Yang, T.; Huang, N.; Hu, L.; Yang, H.; et al. Shrinkage and fragmentation of grasslands in the West Songnen Plain, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jie, D.; Ge, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Qiao, Z. Response of phytoliths in Phragmites communis to elevated CO2 concentration in Songnen Grassland, China. Quat. Int. 2014, 321, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Qiang, L.; Jia, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, D. Carbon stocks and storage potential as affected by vegetation in the Songnen grassland of northeast China. Quat. Int. 2013, 306, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yuan, S. The Analysis of Human Factors on Grassland Productivity in Western Songnen Plain. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Linares, D.; Zistl-Schlingmann, M.; Foesel, B.; Dannenmann, M.; Schloter, M. Short term effects of climate change and intensification of management on the abundance of microbes driving nitrogen turnover in montane grassland soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Wen, W.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Li, G.; Wang, H. Effects of grassland degradation and precipitation on carbon storage distributions in a semi-arid temperate grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Oecol. 2017, 85, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahama, Y.; Miyairi, Y.; He, H.; Fu, B.; Echigo, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ikeda, Y. Late Quaternary evolution of the Kumkol Basin at the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau revealed by tectonic geomorphology and the analysis of in situ cosmogenic nuclides. Geomorphology 2019, 329, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.; Hanriot, S.; Queiroz, J.M. Analysis of pulsating phenomena in an ICE intake manifold using lumped parameter and transfer matrix methods. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 178, 108029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, W.; Meng, J. A climate-sensitive transition matrix growth model for uneven-aged mixed-species oak forests in North China. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2020, 2, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doost, M.B.; Kasmaei, H.; Beckwith, A.W. Foldy-Wouthuysen transfer matrix method for Dirac tunneling through monolayer graphene with a mass gap. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 130, 114654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xinliang, X.U.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Rendong, L.I.; Yan, C. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, C.; Dai, J. Prediction of compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete based on gray correlation analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Ge, Y.; Feng, D. The influence of shrinkage-reducing agent solution properties on shrinkage of cementitious composite using grey correlation analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, A.; Cui, X.; Zhao, A. Spatiotemporal variations and its influencing factors of grassland net pri mary productivity in Inner Mongolia, China during the period 2000–2014. J. Arid Environ. 2019, 165, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirpke, U.; Kohler, M.; Leitinger, G.; Fontana, V.; Tasser, E.; Tappeiner, U. Future impacts of changing land-use and climate on ecosystem services of mountain grassland and their resilience. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26 Pt A, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Song, X.; Hu, R.; Cai, S.; Zhu, X.; Hao, Y. Grassland type-dependent spatiotemporal characteristics of productivity in Inner Mongolia and its response to climate factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.A. Agricultural expansion: Land use shell game in the U.S. Northern Plains. Landscape Ecol. 2014, 29, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimberly, M.C.; Janssen, L.L.; Hennessy, D.A.; Luri, M.; Chowdhury, N.M.; Feng, H. Cropland expansion and grassland loss in the eastern Dakotas: New insights from a farm-level survey. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, N.; Cai, D. The effect evaluation of the program of restoring grazing to grasslands in Maqu County. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, P.; Zhao, X.; Feng, W.; Li, Q.; Xue, D.; Dou, J.; Shi, W.; Wei, W.; et al. Impacts of ecological restoration projects on the ecosystem carbon storage of inland river basin in arid area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescia, A.J.; Pons, A.; Lomba, I.; Esteban, C.; Dover, J.W. Reformulating the social-ecological system in a cultural rural mountain landscape in the Picos de Europa region (northern Spain). Landscape Urban Plann. 2008, 88, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, S.; Bryn, A.; Hovstad, K.A. Loss of semi-natural grassland in a boreal landscape: Impacts of agricultural intensification and abandonment. J. Land Use Sci. 2018, 13, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).