Abstract
The comprehensive application of ecosystem service value (ESV) and ecological risk index (ERI) assessment can provide better decision support for regional ecological environment protection. Based on the remote sensing image data of Wuhu city of 1995, 2005 and 2016, the paper analyzed the spatial-temporal evolution of ESV and ERI in Wuhu city and its associated characteristics using an ESV, ERI assessments and a bivariate spatial autocorrelation method. The results showed that (1) the total ESV of Wuhu city continued to decline from 1995 to 2016, with a decrease of US$ 363.664 million. The total ESV per unit area of the sampling plot decreased, and the high-value was mainly distributed in areas within 5–10 km along the Yangtze River floodplain. (2) Wuhu city was mainly dominated by a relatively low ERI and medium ERI from 1995 to 2016. The high-value areas were mainly distributed in the mainstream of the Yangtze River, and the overall ERI improved. (3) There was a positive spatial correlation between the total ESV per unit area and ERI in Wuhu city, and these areas were mainly distributed in the Yangtze River mainstream region. According to this research, it is necessary to pay attention to the protection of wetland and forest landscapes, strengthen wetland ecological protection based on the Yangtze River and protect and restore natural mountain forests, all of which play important roles in improving the ecosystem service function of Wuhu city and protecting the ecological environment of the Yangtze River. We should act on that knowledge, and produce effective environmental regulations and habitat restoration efforts that improve the ESV and reduce the ERI. The findings of the study can serve as a reference for the management and protection of ecological environments in river-crossing cities.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem services are the direct or indirect benefits obtained by humans from an ecosystem, and these services support survival and development and have great value for human well-being [1,2,3,4,5]. Ecosystem services include provisioning services, regulating services, supporting services and cultural services [6]. The value assessment of ecosystems is an important basis of ecological environmental protection, ecological function zoning and ecological compensation decisions [7,8]. At present, the evaluation methods used to determine ecosystem service value (ESV) mainly include the method based on the equivalent factor of unit area value [1,2,9] and the method based on the price of unit service function [10]. The former is more intuitive and easier to use, with a lower data demand, and it is especially suitable for the evaluation of ESV at regional and global scales [2,11]. The use of ESV to monetize different services generated by different ecological processes in a region can effectively link ecological processes with human well-being. Thus, the value of ecosystem services in a region reflects the health of the ecosystem and is one of the important indicators used to measure regional ecological security [12].
Ecological risk index (ERI) assessment is a scientific tool used to guide the decision-making process that underpins ecosystem-based management and prioritization of risk factors for management [13,14]. Landscape ecological risk refers to the adverse consequences that may result from the interaction between landscape pattern and ecological process under the influence of natural or human factors. This concept focuses on the coupling relationship between landscape pattern and ecological process and pays more attention to the spatial-temporal heterogeneity and scale effect of risk, and it is committed to realizing the comprehensive characterization and spatial visualization of multi-source risks [15,16]. In terms of risk receptors, one or more landscapes in specific regions and cities are taken as risk complexes to reflect the impact of landscape patterns and their evolution on ecological processes and ecological health [17]. The evaluation methods mainly include the landscape index method and the risk “source-sink” method [18]. ERI assessments can provide decision-making basis for regional comprehensive risk prevention and effectively guide the optimization and management of regional landscape patterns [14,19].
ESV and ERI are important types of ecological environment assessments. Their comprehensive application can better link between human well-being and ecological environment change, and provide better decision support for regional ecological environment protection [20]. At present, research on ESV and ERI is gradually shifting from independent analysis to correlation analysis. Chen et al. [21] incorporated ecosystem services into the ecological risk assessment system, reconstructed the spatial map of China’s terrestrial ecosystem services by using ArcGIS and remote sensing technology, and provided a quantitative description and spatial distribution of China’s terrestrial ecological risk pattern based on ecosystem services by using an ecological risk analysis model. Cao et al. [17] believed that ecosystem services built a bridge for the connection and communication between ecosystems and human welfare in landscape ecological risk assessments, and this connection helps promote the study of the coupled human-earth system relationship. Additionally, these authors built a landscape ecological risk assessment framework based on ecosystem services: Ecosystem service based landscape ecological risk assessment (ESRISK). Liao et al. [22] took the expansion of developed areas as a risk source and regional ecosystem services, such as soil conservation, soil erosion, and water conservation, as risk receptors, to evaluate the comprehensive ecological risk of Xiamen city. Dong et al. [23] established an ecological risk assessment framework based on the formation, change, risk and management of ecosystem services and evaluated the ecological risks and changes in the Ganzi region in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River Basin. Nevertheless, researches on the correlation between ESV and ERI mostly focus on the ecological risk assessments that are based on ecosystem services, and the spatial distribution and correlation of ESV and ERI in the same region and the same period need to be discussed further.
The Yangtze River is the largest river in China and the third largest in the world, with a total length of 6300 km. Its basin is rich in natural resources, and its towns, population and industries are clustered. It occupies an important position in China’s regional development. Wuhu city is an important node area in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River ecological corridor and is located at a typical cross section of the river. The Yangtze River runs from the southwest to the northeast of the city and divides it into two regions: the north side and the south side. Wuhu city has unique geographical, landscape and resource advantages. Within the territory, the Yangtze River coastline spans 194 km. The Yangtze River is not only a lifeline on both sides of Wuhu city but also an artery supporting its economic development. However, with the acceleration of urbanization, the landscape patterns of land-use types along the Yangtze River have undergone profound changes, and the structure and function of the ecosystem have been affected. Based on this typical region, this research uses Wuhu city as the research object, and through the accounting of ESV and ERI, it reveals the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of ESV and ERI in Wuhu city from 1995 to 2016. Then, the paper discusses the spatial-temporal correlation between ESV and ERI using bivariate spatial autocorrelation analysis to provide some references for the improvement of ecosystem service function, regional ecological security, and ecological environment restoration and protection along the Yangtze River in Wuhu city.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Wuhu city is a prefectural-level municipality, encompassing 6026 km2 of urban and rural areas in the south-eastern Anhui province of China and is located along the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Its geographical coordinates are 117°28′–118°43′ E and 30°38′–31°31′ N. To its south are the southern Anhui Mountains, and the Jianghuai Plain is located to the north (Figure 1). Wuhu city has a subtropical humid monsoon climate. Annual average temperature is 15–16 °C. Annual average rainfall is about 1200 mm. Annual frost-free period is approximately 219–240 days. The terrain of the study area is high in the south and low in the north, with varied landforms including plains, hills and low mountains. However, plains are dominant. The city has a network of rivers and lakes. There are more than 50 rivers at all levels and more than 20 lakes in the city. The study area has jurisdiction over Jinghu, Yijiang, Sanshan, Jiujiang and Wuwei, Wuhu, Fanchang and Nanling counties. By the end of 2016, the total population of the study area was 3.876 million, with a GDP of US$ 38.954 billion. The composition of primary, secondary and tertiary industries was 22.8%, 28.2% and 49.0%, respectively. Wuhu city is the economic, cultural, transportation and politics sub-centre of Anhui province. It is a key “open city” along the Yangtze River approved by the State Council, and a core city of the Wan Jiang City Belt to accept the industrial transfer demonstration zone. It is also a member of Nanjing Metropolitan Circle, neighboring Shanghai, Hangzhou and other metropolises. Therefore, it has an excellent geographical location. Additionally, Wuhu is a city with high urbanization rate in the Anhui province, and it is known as “the giant port of the Yangtze River, the backbone of Anhui province”.
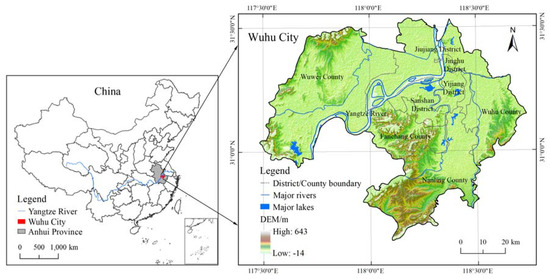
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
Landsat–5 TM in 1995 and 2005 and Landsat–8 OLI in 2016 were used as data sources, and periods without cloud cover were chosen. The time phase was from May to September, which is the peak season of vegetation growth. The data resolution was 30 m, and the data were downloaded from the Geospatial Data Cloud website (http://www.gscloud.cn/). Demographic, social and economic data were retrieved from the official website of the Wuhu government, the Wuhu Municipal Statistics Bureau and the Wuhu Statistical Yearbook (2017). Both Yangtze River vector data and Wuhu city vector data were provided by the Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC) (http://www.resdc.cn).
The three-phase remote sensing images were subjected to band combination, registration, mosaic, image enhancement, geometric clipping and other processing using ENVI 5.3 software; then the images were supervised and classified by the maximum likelihood method. According to the 2017 national standard of the “Current Land Use Classification”, combined with the landscape characteristics of the research area, Google Earth data and our specific research purposes, the landscape was supervised and classified through human–computer interaction visual interpretation and was divided into five types: cultivated land, forest land, wetland, construction land and bare land (Figure 2). The accuracy of the classification results was evaluated by field investigation and the obfuscation matrix method. The overall accuracy of the classification results of three-phase remote sensing images was above 85%, which met the requirement of discrimination error accuracy.
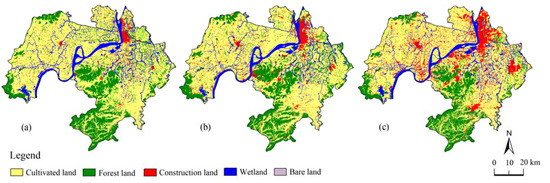
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of the landscape types in Wuhu city for (a) 1995; (b) 2005 and (c) 2016.
By using ArcGIS 10.2 software and considering relevant studies [24,25] and computing efficiency, a 5 km × 5 km grid was used to conduct grid resampling of Wuhu city’s landscape types, and 304 evaluation units were formed. Based on the evaluation unit, the ecosystem service value and landscape ecological risk index were calculated and assigned to the centre point of the evaluation unit; then Kriging interpolation was carried out to analyze the spatial pattern distribution characteristics.
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Calculation of Ecosystem Service Value
The ESV assessment model of Costanza et al. [1] was used to calculate the ESV of Wuhu city in the three periods. The formula is as follows:
where ESV is the total value of ecological services in the research area (US$); n is the number of landscape types; Ck is the value coefficient of ecological services per unit area of the k–type landscape (US$/ha); and Ak is the area (ha) of landscape type k.
According to the determination of ESV equivalent per unit area of China’s terrestrial ecosystem by Xie et al. [9,26], and combined with the landscape utilization types and research needs of Wuhu city, the value equivalent was adjusted (Table 1). In this paper, the landscape type of Wuhu city corresponds to the ecosystem type, in which the equivalent of cultivated land and forest land corresponds to the value of farmland and forest, respectively. The wetlands in this paper include river channels, lakes, reservoirs, ponds, beaches and marshes; thus, the equivalent value of wetlands is the mean value of the equivalent value of wetlands and river systems. Bare land takes the equivalent of desert in terms of ecosystem type. Construction land causes great damage to the natural ecological environment, and only the positive utility of ecosystem services is calculated in this paper. Thus, the ESV of construction land is not calculated [27,28]. The average annual grain yield of Wuhu city in 2016 was 6564.39 kg/ha (data from the Wuhu Statistical Yearbook (2017)), and the average grain price in 2016 was 0.394 US$/kg (data from the China Grain Network http://www.cngrain. com/). Based on the research results of Xie et al. [9], that is, “the equivalent economic value of one ecological service is equal to 1/7 of the average market value of the average grain yield per unit area in the research area in that year”, the economic value of the equivalent factor of ESV in Wuhu city was 369.435 US$/ha. Finally, according to “the value coefficient of ecosystem services per unit area of terrestrial ecosystem = equivalent × unit equivalent value” [9], the value coefficient of ecosystem services per unit area of different ecosystems in Wuhu city could be calculated (Table 1).

Table 1.
The ESV coefficients per unit area of different landscape types in Wuhu city.
2.3.2. Calculation of Ecological Risk
The magnitude of landscape ecological risk depends on the intensity of the external disturbance and internal resistance of the landscape ecosystem in the study area [29]. Based on the relationship between the landscape pattern of ecosystems and ecological risk and referring to the existing research results, the landscape fragmentation index, landscape isolation index, landscape dominance index, landscape disturbance index, landscape vulnerability index and landscape loss index were used to construct the landscape ecological risk index model [30,31]. The formulas are as follows:
where ERIk is the ecological risk value of sampling plot k; Aki is the area of type i in sampling plot k, and Ak is the area of sampling plot k; Ri is the landscape loss index (measuring the ecosystem loss caused by external disturbance [25]); m is the number of landscape types in the sampling plot; Si is the landscape disturbance index; and Fi is the landscape vulnerability index. The calculation formulas and ecological significance of each parameter are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Calculation methods of landscape indices.
2.3.3. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Model
The spatial autocorrelation model can reflect the degree of correlation of a certain factor in the spatial position, and the model is divided into global spatial autocorrelation and local spatial autocorrelation and is described by Moran’s I and Local Moran’s I [34,35]. The Moran’s I value is expressed as follows:
where , , Yi and Yj denote the actual attribute values in sampling plots i and j, respectively, and n is the number of sampling plots (this paper is divided into 304 sampling plots). Wij is a weight matrix based on spatial adjacency.
On the basis of Moran’s I index, relevant scholars [36,37] extended the bivariate global autocorrelation and local autocorrelation, providing a method for revealing the correlation of the spatial distribution of different elements. The formula is as follows:
where ; ; is the value of attribute l of sampling plot p; is the value of attribute m of sampling plot q; and are the average values of attributes l and m, respectively; and and are the variances of attributes l and m, respectively.
In this paper, based on the bivariate spatial autocorrelation model, the Moran scatter plot and spatial correlation local index (LISA) were used for spatial autocorrelation analysis. The spatial distribution relationship was divided into 4 clustering types, high and high clustering (H–H), high and low clustering (H–L), low and high clustering (L–H) and low and low clustering (L–L), to explore the spatial correlation characteristics of ecosystem services and ecological risks [38,39]. The calculations were performed using GeoDa 1.14.0 software.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic Analysis of Ecosystem Service Value
3.1.1. Changes in Various and Individual Ecological Services Value
In 1995, 2005 and 2016, the largest proportion of area in Wuhu city is cultivated land (>57.90%), followed by forest land (>17.80%) and wetland (>9.80%). During the last 20 years, the prominent feature of landscape type change was the significant reduction of the area of cultivated land and forest land, which was mainly converted into construction land. Construction land expanded rapidly. Due to the massive mining of mountain mineral resources, the vegetation covering the mountain was seriously damaged, especially in Shijian town of Wuwei county on the north bank of the Yangtze River, and in Digang, Xingang, Suncun and other places in Fanchang county on the south bank of the Yangtze River. This turned what was once a mountain with dense vegetation into bare land. The wetland area experienced an overall decrease, and the reason for this change was cultivated land and construction land encroachment into wetland (Table 3, and Figure 2).

Table 3.
The area and proportion of each landscape type in Wuhu city from 1995 to 2016.
The calculation results and changes in ESV in Wuhu city from 1995 to 2016 are shown in Table 4 and Table 5. During the last 20 years, the total ESV of Wuhu city decreased by US$ 363.66 million, with a change rate of −10.87%, due to the significant reduction of cultivated land, forest land and wetland. In terms of the ESV of each landscape type, the contribution rate of wetland to ESV was very high, followed by forest land and cultivated land. From 1995 to 2005, the ESV of bare land showed an increasing trend, while the ESVs of the other landscape types showed decreasing trends, among which the ESV of wetland had the largest change, with a decrease of US$ 118.41 million. From 2005 to 2016, the ESV of wetland and bare land increased, while that of cultivated land and forest land decreased. The ESV of forest land changed the most, with a decrease of US$ 178.30 million and a change rate of −17.08%. From 1995 to 2016, the ESV of forest land changed the most, with a decrease of US$ 209.28 million and a change rate of −19.47%. In terms of the value structure function of ecosystem services, the ESV changes of various service functions in Wuhu city from 1995 to 2016 were obvious, showing downward trends, but the degrees of decrease were different. The proportion of ESV of each single service function, from large to small, was as follows: waste treatment > water conservation > climate regulation > soil conservation > biodiversity conservation > gas regulation > aesthetic landscape > food production > raw materials. Among them, the functional value of waste treatment was the highest, accounting for 21.97% of the total ESV, followed by the functional values of water conservation (20.06%), climate regulation (14.00%), soil conservation (12.46%) and biodiversity conservation (9.52%). The functional value of raw materials was the lowest, accounting for only 4.19% of the total ESV. Overall, the ratio of regulating service function value was the highest and the change was the largest in Wuhu city. In other words, regulating service is a sensitive factor affecting the regional ESV.

Table 4.
ESV of different landscape types and changes in Wuhu city from 1995 to 2016.

Table 5.
ESV of various service functions and changes in Wuhu city from 1995 to 2016.
3.1.2. Spatial Pattern of the Total Ecological Service Value per Unit Area
The total ESV per unit area of the sampling plot was divided into 5 grades by the natural break point method: 0.12 × 104 US$/ha < low ESV ≤ 0.39 × 104 US$/ha, 0.39 × 104 US$/ha < relatively low ESV ≤ 0.52 × 104 US$/ha, 0.52 × 104 US$/ha < medium ESV ≤ 0.66 × 104 US$/ha, 0.66 × 104 US$/ha < relatively high ESV ≤ 0.87 × 104 US$/ha, and high ESV > 0.87 × 104 US$/ha. The spatial pattern distribution and area variation of the total ESV per unit area in Wuhu city in the three periods are shown in Figure 3 and Table 6.
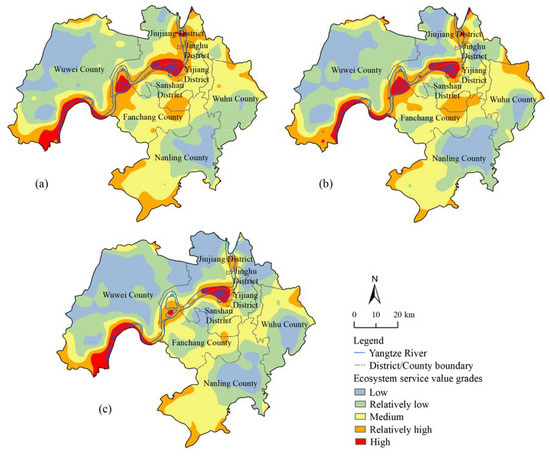
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of total ESV per unit area in Wuhu city for (a) 1995; (b) 2005 and (c) 2016.

Table 6.
Area changes of total ESV per unit area at different grades in Wuhu city.
Table 6 shows that the total ESV per unit area in Wuhu city in 1995 is mainly medium ESV and relatively low ESV, accounting for more than 33%, followed by a relatively high ESV (16.49%), and the high ESV accounted for 4.48%. The high ESV is distributed in the mainstream area of the Yangtze River, including the Longwo Lake area in Sanshan district, the Jiangxinzhou area in the southwest of Jiujiang district and adjacent to Fanchang county, the Tongling Freshwater Dolphin National Nature Reserve in Wuwei county of the Yangtze region, and the Zhusi Lake area in the south of Wuwei county. The relatively high ESV is mainly distributed in the mainstream area of the Yangtze River, that is, the area within 5 km of both sides of the Yangtze River. Its shape is similar to the trend of the Yangtze River, and it is scattered in the southwest of Wuwei county, the southwest and southeast of Nanling county, and the border area between the southeast of the Sanshan district and northeast of Fanchang county. The above areas are all forested vegetation areas, and the ESV is relatively high. In 2005, the areas of high, relatively high, medium and relatively low ESVs in the study area all decreased, while the area of low ESV increased by 534.89 km2 at a rate of 7.53%. In terms of spatial distribution, the riverfront region of Jinghu district changed from a relatively high ESV to a medium ESV. In 2016, the area of relatively high ESV in the study area decreased sharply, accounting for only 8.85%, and high ESV accounted for 3.36%, while low ESV accounted for 28.15%, indicating that the total ESV per unit area of the study area decreased significantly. A large number of wetlands and forest lands were occupied by construction land, and relatively high ESV area sharply reduced, which was distributed in the riverside area of Jiujiang district and the border area between the southeast part of Sanshan district and the northeast part of Fanchang county.
The total ESV per unit area of the sampling plots in Wuhu city continuously decreased from 1995 to 2016, and the high-value areas were all concentrated in the main stream of the Yangtze River, showing a parallel trend with the Yangtze River. Overall, the total per unit area ESV on the south side was higher than that on the north side of the Yangtze River, and this pattern was closely related to the distribution of numerous river and lake systems in the south side of the Yangtze River. There are more than 10 natural lakes in the south side of the Yangtze River, including Longwo Lake, Kui Lake, Lotus Lake, Nantang Lake and Heisha Lake, which have been listed in the Anhui provincial lake protection list. However, the lakes in the north side of the Yangtze River include Zhusi Lake, Luojiatao Lake, Nanhu Lake and Fengsha Lake, which are smaller than those on the southern side of the Yangtze River in terms of both quantity and area.
3.2. Characteristic Analysis of Ecological Risk
Referring to previous relevant studies [32,40], combining the actual situation of the study area and the range of ERI in each sampling plot, ecological risk is divided into 5 grades by the natural break point method using ArcGIS 10.2: 0.013 < low ERI ≤ 0.016, 0.016 < relatively low ERI ≤ 0.019, 0.019 < medium ERI ≤ 0.023, 0.023 < relatively high ERI ≤ 0.030, and high ERI > 0.030 (Figure 4). The spatial pattern distribution and area variation of the ecological risk in Wuhu city in the three periods are shown in Figure 4 and Table 7.
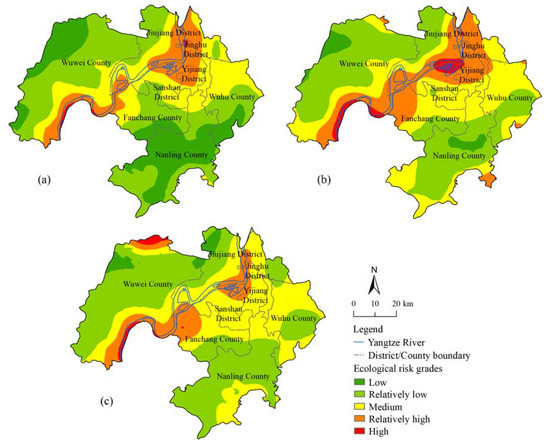
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of ERI of Wuhu city for (a) 1995; (b) 2005 and (c) 2016.

Table 7.
Area changes of ERI at different grades in Wuhu city.
Table 7 shows that Wuhu city was mostly dominated by a relatively low ERI and medium ERI from 1995 to 2016. In the past 20 years, the area of low ERI decreased sharply by 1223.89 km2, from 23.16% in 1995 to 2.83% in 2016, and the area of relatively low ERI and medium ERI increased by 585.45 km2 and 686.72 km2, respectively. Spatially (Figure 4), the ERI of Wuhu city in the three periods used the Yangtze River as the axis, and the south side and north side of the Yangtze River showed a gradient decreasing change with a “low–relatively low–medium–relatively high–high–relatively high–medium–relatively low–low” spatial distribution pattern. In other words, the overall performance of the study area showed that the ecological risk value of the Yangtze River mainstream is relatively high, while the ecological risk of the other regions is relatively low, and the overall ecological risk of the south side of the Yangtze River is higher than that of the north side. This result is because the built-up area of Wuhu city is distributed in the mainstream area of the Yangtze River and is especially concentrated on the south side of the Yangtze River, and because there are many ports, docks, industrial and mining enterprises. This region is an area with concentrated industry and has strong construction and development efforts, a high population density and a high intensity of human interference. Cultivated land and wetlands along the river are vulnerable to damage. Furthermore, due to frequent geological disasters (e.g., floods and landslides) and fragile ecological environments in the Yangtze River mainstream region adjacent to Wuwei county and Fanchang county, the ecological risks near the mainstream Yangtze River are relatively high. However, the areas farther from the Yangtze River have a relatively low intensity of human activities, especially along the southern and south-eastern parts of the south bank of the Yangtze River and along the north-western and south-western parts of the north bank of the Yangtze River. These areas are mostly mountainous and hilly, with high forest coverage and relatively low ERI.
To clearly identify the change in ERI, we constructed a transition matrix of ERIs during 1995–2005, and 2005–2016 (Table 8). From 1995 to 2005, the area converted from low-grade to high-grade risk was 2771.53 km2, accounting for 46.03% of the total study area, while the area converted from high-grade to low-grade risk was 64.55 km2, accounting for 1.07%. These results indicated that the ecological environment in Wuhu city deteriorated from 1995 to 2005, and the ERI showed an increasing trend. Wuhu city was in a stage of rapid urbanization and development from 1995 to 2005. Human activities had a great impact on the regional landscape, and large areas of cultivated land, forest land and wetland were occupied by construction land. Therefore, the fragmentation and separation degree of the landscape increased, the ecological environment was destroyed, and the ERI increased. From 2005 to 2016, the area converted from low-grade to high-grade risk was 484.91 km2, accounting for 8.05% of the total study area, while the area converted from high-grade to low-grade risk was 1611.43 km2, accounting for 26.76%. These results indicated that the overall ERI of Wuhu city decreased from 2005 to 2016. This result was related to the agglomeration and development of construction land and a reduction in fragmentation. Moreover, this result was largely due to the measures taken by the government to strengthen environmental legislation. In 2005, the construction of “Ecological Wuhu” program was fully launched. In 2007, the government issued the decision on “further strengthening environmental protection work”, making environmental protection in Wuhu city the focus of the government’s work. In 2014, Wuhu city started the construction of large-scale ecological green space between urban clusters. Driven by a series of policies, the ecological environment of Wuhu city was greatly improved, and the scope of high-grade ecological risks was narrowed.

Table 8.
Area transition matrixes of ERI grades in Wuhu city (km2).
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Ecosystem Service Value and Ecological Risk
3.3.1. Bivariate Global Spatial Autocorrelation
Using the GeoDa spatial analysis tool, the spatial weight matrix was established to calculate the bivariate spatial autocorrelation index of the total ESV per unit area and ERI in Wuhu city in 1995, 2005 and 2016, and the Moran’s I scatter plot was obtained (Figure 5). According to the images, the scatter points are mainly distributed in the first quadrant (H–H) and the third quadrant (L–L), while the second quadrant (L–H) and the fourth quadrant (H–L) have fewer points, indicating that the total ESV per unit area has a spatial positive correlation with the ERI. The change in scatter point distribution along the trend line showed that the positive correlation was the strongest in 2005, with a Moran index of 0.366619, while the Moran index of 1995 and 2016 was 0.336135 and 0.279746, respectively. This result demonstrated that the positive correlation first increased and then weakened from 1995 to 2016.
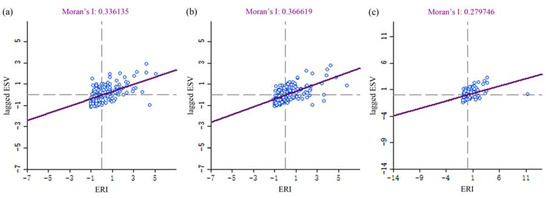
Figure 5.
Moran scatter plots of ERI with total ESV per unit area in Wuhu city for (a) 1995; (b) 2005 and (c) 2016.
In GeoDa, the Monte–Carlo simulation method was used to test the significance of Moran’s I, and the P values of the three periods were all equal to 0.001, indicating that the spatial autocorrelation was significant at the 99.90% confidence level.
3.3.2. Bivariate Local Space Autocorrelation
The local indicators of spatial autocorrelation (LISA) clustering graph is the geographical expression of the regional units that have passed the significance test in the Moran scatter graph [34]. The LISA analysis results are shown in Figure 6. The areas in which the total per unit area ESV and ERI correlation was significant are mainly distributed in the west of Wuwei county, the middle east of Nanling county, the north of Jiujiang district and the mainstream area of the Yangtze River. The areas were divided into 5 patterns: high risk–high value (H–H), low risk–low value (L–L), low risk–high value (L–H), high risk–low value (H–L) and not significant (N–S).
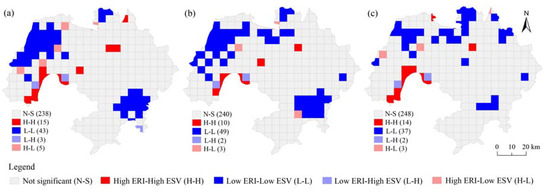
Figure 6.
LISA cluster maps of ERI with total ESV per unit area in Wuhu city for (a) 1995; (b) 2005 and (c) 2016.
In 1995, 2005 and 2016, the area of H–H was 220.15 km2, 120.17 km2 and 189.51 km2, accounting for 3.66%, 2.00% and 3.15% of the total study area, respectively, showing an overall decreasing trend that first decreased and then increased. These sites were mainly distributed in the area within 5–10 km of the mainstream of the Yangtze River, e.g., the area adjacent to the Yangtze River in south-eastern Wuwei county (including the Tongling freshwater dolphin national nature reserve in Wuwei county), the area adjacent to the Yangtze River in western Fanchang county, and the Longwo Lake area in Sanshan district. The above areas all cover large areas of wetlands, which can provide high-value ecosystem services. However, wetlands are faced with high ecological risks due to fragmentation, continuous reductions in area, and encroachment by cultivated land and construction land. At the same time, geological disasters such as floods and landslides occur frequently in Wuwei and Fanchang counties near the Yangtze River. Therefore, in these areas, the ecological environment is fragile, and the ERI level is high.
In 1995, 2005 and 2016, the area of L–L was 980.25 km2, 1114.55 km2 and 775.20 km2, accounting for 16.28%, 18.51% and 12.87% of the total study area, respectively, showing an overall decreasing trend that first increased and then decreased. At the initial stage, the L–L area was mainly concentrated in the west of Wuwei county, the middle east of Nanling county and the northwest of Jiujiang district. The spatial distribution of the L–L area showed a trend ranging from clustered to random from 1995 to 2016, and the L–L area of Wuwei county and Nanling county decreased significantly, while the L–L area of Jiujiang district increased significantly. The main landscape type of the L–L area was cultivated land. Although cultivated land was constantly converted to construction land, the contribution rate of cultivated land’s ESV did not change much. Cultivated land played a relatively stable role in maintaining the total ESV of Wuhu city. Meanwhile, due to the transformation of the regional ecological environment by human activities, the value of ecological services was in a relatively long–term stable state, and the ERI was relatively low.
The area of L–H decreased from 1.04% in 1995 to 0.83% in 2016. It was mainly distributed in the Wuwei county section of the mainstream of the Yangtze River (around the H–H area), namely, in wetland and cultivated land areas. These areas had a relatively high ESV and a relatively stable ERI.
The area of H–L decreased from 1.75% in 1995 to 0.90% in 2016. It was scattered around the L–L zone of Wuwei county and Jiujiang district. The forest land, wetland and cultivated land in these areas were constantly converted into construction land, which decreased the value of regional ecological services and increased the ecological risks.
The area of N–S accounted for 77.27–82.25% of the study area. The main landscape types were cultivated land and construction land that were distributed in a cluster. The distribution of ESV and ERI was approximately average, without obvious high-value centres or low-value centres.
In light of the above, in terms of spatial distribution, the high-value areas of ERI corresponded to the high-value areas of total ESV per unit area, and these areas were mainly along the Yangtze River floodplain, that is, the main concentrated distribution area of wetland landscape. This result indicates that the wetland along the Yangtze River is an area with high ESV, a fragile ecological environment and a high ERI. Therefore, we would recommend strengthening the protection of wetland resources and important wetland landscapes.
4. Discussion
The study area should address the relationship between development and landscape ecological protection, maintain and improve the structure and function of regional ecosystems, and strengthen the continuity of ecosystem patterns. We should strengthen the protection and treatment of natural mountain and mine geological environment. It is necessary to strictly control the exploitation of mineral resources, and promptly take scientific measures to carry out ecological restoration in the mined mountain areas to prevent soil erosion, landslide and other disasters. We would recommend restoring the mountain vegetation and protecting the original natural mountain form to the maximum extent possible. Specifically, we need to strengthen mineral mining control and ecological restoration in Yanqiao town and Shijian town in Wuwei county on the north side of the Yangtze River and in Digang, Xingang and Suncun in Fanchang county on the south side of the Yangtze River.
The wetland landscape plays a leading role in the change in ESV in Wuhu city and is also the distribution area of high-grade ERI. Therefore, Wuhu city should take the building of a more ecologically-conscious society as an opportunity, which relies on the Yangtze River, lakes, ponds and other wetland resources in the territory, to strengthen the protection of ecological corridors and wetland landscape resources along the Yangtze River. Wuhu city should determine the wetland protection vacancy area based on the existing important wetland landscape. We would recommend establishing a wetland landscape protection system based on wetland nature reserves, wetland parks, and drinking water source protection areas to improve the connectivity of regional wetland landscapes and reduce the interference of human activities with natural wetlands. This approach would not only help improve Wuhu’s ecological environment, ecosystem service function and ecological risk resistance but would also play a very important role in protecting the ecological corridor of the Yangtze River, promoting the sustainable development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and maintaining the ecological security of the Yangtze River Basin.
The spatial autocorrelation between ESV and ERI has a scale effect [41]. In the future, it is necessary to further explore the spatial autocorrelation of ESV and ERI at various scales. In this paper, the total ESV per unit area was used for spatial visualization, which reflected the spatial–temporal distribution characteristics of the total ESV, but the spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of each single ESV were not deeply studied. Exploring the effect of the change in a single ESV on the regional ecological services and ecological risks will also be a worthwhile topic in future research [42,43,44]. Bivariate spatial autocorrelation analysis revealed the positive spatial correlation between ESV and ERI in Wuhu city, which provided a scientific basis for regional landscape layout and ecological environment protection. However, due to the radiation effect of the Yangtze River on both sides of Wuhu city, the location characteristics of different sections of the Yangtze River and the different regional economic conditions may affect the spatial distribution of the ESV and ERI of Wuhu city. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen research on the impact of the Yangtze River radiation effect on the ESV and ERI and its influence on the relationship between them in the future.
As a final note, now that we have the means to identify the priority areas for environmental protection, we should act on that knowledge, and produce effective environmental regulations and habitat restoration efforts that improve the ESV and reduce the ERI.
5. Conclusions
(1) The total ESV of Wuhu city decreased from 1995 to 2016, with a decrease of US$ 363.66 million and a change rate of −10.87%. The main reason for the decrease was the substantial decrease in cultivated land and forest land. Over the past 20 years, all service functions declined. The proportion of ESV of each single service function from large to small was as follows: waste treatment > water conservation > climate regulation > soil conservation > biodiversity conservation > gas regulation > aesthetic landscape > food production > raw materials. The total ESV per unit area of the sampling plots in Wuhu city continuously decreased from 1995 to 2016, and the high-value was mainly concentrated in the areas within 5–10 km from the Yangtze River.
(2) Wuhu city was mostly dominated by a relatively low ERI and medium ERI from 1995 to 2016. Spatially, the high-value areas were mainly distributed in the mainstream of the Yangtze River, and the areas to the south and north of the Yangtze River showed a gradient decreasing change. In other words, the distribution pattern of “low–relatively low–medium–relatively high–high–relatively high–medium–relatively low–low” was presented, and the overall ERI of the south side of the Yangtze River was higher than that of the north side. In terms of risk transfer, the proportion of risk transferred from low-grade to high-grade decreased, while the proportion of risk transferred from high-grade to low-grade increased. This result was largely due to the strong interference of human activities in the process of urbanization and a series of policies and measures to strengthen the construction of ecological green space and ecological environmental protection.
(3) There was a positive spatial correlation between the total ESV per unit area and ERI in Wuhu city, and the main relationships were the H–H correlation and the L–L correlation. From 1995 to 2016, the H–H area showed an overall decreasing trend that first decreased and then increased. These areas were mainly distributed in the Yangtze River mainstream area, e.g., the area adjacent to the Yangtze River in south-eastern Wuwei county (including the Tongling Freshwater Dolphin National Nature Reserve in Wuwei county), the area adjacent to the Yangtze River in western Fanchang county, and the Longwo Lake area in Sanshan district.
The research results can provide a certain basis for the improvement of ESV, comprehensive risk prevention, and ecological environmental protection along the Yangtze River in Wuhu city. Moreover, the findings in this study can serve as a reference for the management and protection of ecological environments in river-crossing cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.J. and X.T.; methodology, Y.J.; software, Y.J. and W.L.; validation, Y.J., X.T. and W.L.; formal analysis, Y.J.; investigation, Y.J. and W.L.; resources, X.T.; data curation, X.T.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J.; writing—review and editing, X.T.; visualization, Y.J.; supervision, X.T.; funding acquisition, X.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31270746), 2019 Graduate Education Management Project of Agricultural and Forestry Working Committee of Chinese Academic Degree and Graduate Education Association (Grant No. 2019-NLZX-ZD15), Case-Based Construction Project of Professional Degree Postgraduate Courses of Nanjing Forestry University in 2018 (Grant No. 2018AL07) and Higher Education Research Project of Nanjing Forestry University in 2018 (Grant No. 2018B22).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; DeGroot, R.; Farberk, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; DeGroot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s services: Societal dependence on natural ecosystems. Pacific Conserv. Biol. 1997, 6, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bratman, G.N.; Anderson, C.B.; Berman, M.G.; Cochran, B.; de Vries, S.; Flanders, J.; Folke, C.; Frumkin, H.; Gross, J.J.; Hartig, T.; et al. Nature and mental health: An ecosystem service perspective. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, R.S.; Wilson, M.A.; Boumans, R.M.J. A typology for description, classification and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Current State and Trends; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Egoh, B.; Rouget, M.; Reyers, B.; Knight, A. Integrating ecosystem services into conservation assessments: A review. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sven, L.; Carolin, K.; Angela, L.; Ralf, S. Analysis of historic changes in regional ecosystem service provisioning using land use data. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.; Li, S.C. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S.W. Evaluation of economic forest ecosystem services in China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Guo, H.C.; Chuai, X.W.; Dai, C. The impact of land use change on the temporospatial variations of ecosystems services value in China and an optimized land use solution. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, B.K. An examination of ecological risk assessment and management practices. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piet, G.J.; Knights, A.M.; Jongbloed, R.H.; Tamis, J.E.; De Vries, P.; Robinson, L.A. Ecological risk assessments to guide decision-making: Methodology matters. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Dang, W.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Zong, M.L.; Hu, X.X. Review on landscape ecological risk assessment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, M.; Mohammad, A.M.; Shalini, R.; Kumar, J.P. Spatio-temporal variations in landscape ecological risk related to road network in the Central Himalaya. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.W.; Zhang, X.W.; Ma, H.K.; Wu, J.S. Review of landscape ecological risk and an assessment framework based on ecological services: ESRISK. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.S. Ecological risk assessment of land use change in the Poyang Lake eco-economic zone, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrodin, Y.; Boillot, C.; Angerville, R.; Donguy, G.; Emmanuel, E. Ecological risk assessment of urban and industrial systems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5162–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.H.; Caldarone, G.; Duarte, T.K.; Ennaanay, D.; Hannahs, N.; Mendoza, G.; Polasky, S.; Wolny, S.; Daily, G.C. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7565–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, A.L. Ecological risk assessment based on terrestrial ecosystem services in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.F.; Jia, Y.Q.; Tang, L.N.; Huang, Q.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, N.; Hua, L.Z. Assessment of urbanization-induced ecological risks in an area with significant ecosystem services based on land use/cover change scenarios. Int. J. Sust. Dev. World Ecol. 2017, 25, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Xu, W.H.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, L.Q.; Ouyang, Z.Y. A framework for regional ecological risk warning based on ecosystem service approach: A case study in Ganzi, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Wang, D.Y.; Lei, G.P.; Li, H.; Li, W.B. Elevated risk of ecological land and underlying factors associated with rapid urbanization and overprotected agriculture in Northeast China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; You, N.S.; Meng, J.J. Dynamic ecological risk assessment and management of land use in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River based on landscape patterns and spatial statistics. Sustainability 2016, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.M. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Zhao, H.B.; Li, J.F.; Zhu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zeng, J. Land use transitions and the associated impacts on ecosystem services in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China based on the geo-informatic Tupu method. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Changes of ecosystem service values in response to land use/land cover dynamics in Munessa–Shashemene landscape of the Ethiopian highlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Chang, J.; Hu, T.H.; Luo, P.J.; Zhou, H.X. Spatiotemporal variations of land use and landscape ecological risk in a resource-based city, from rapid development to recession. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, J.L.; Lu, W.Y.; Wei, X.L.; Sun, C. Evolution of landscape ecological risk at the optimal scale: A case study of the open coastal wetlands in Jiangsu, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Gong, H.B.; Ye, M.Y.; Shi, X.L.; Wang, L.J.; Liu, R.Q.; Tong, C. Landscape pattern change and ecological risk assessment of the continental coast of the East China Sea. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2018, 37, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.G.; Lin, H.P.; Fu, Z.Y.; Bu, R.C. Regional ecological risk assessment of wetland in the Huanghe River Delta. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2001, 37, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, V.H.; Brown, S.; Haeuber, R.A.; Hobbs, N.T.; Huntly, N.; Naiman, R.J.; Riebsame, W.E.; Turner, M.G.; Valone, T.J. Ecological principles and guidelines for managing the use of land. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 639–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: Distributional issues and an application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartenberg, D. Multivariate spatial correlation: A method for exploratory geographical analysis. Geogr. Anal. 1985, 17, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Smirnov, O. Visualizing multivariate spatial correlation with dynamically linked windows. In New Tools for Spatial Data Analysis, Proceedings of the Specialist Meeting, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 22 June 2002; Anselin, L., Rey, S., Eds.; University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Souris, M.; Bichaud, L. Statistical methods for bivariate spatial analysis in marked points. Examples in spatial epidemiology. Spat. Spatiotemporal Epidemiol. 2011, 2, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.H. The spatial correlation and interaction between manufacturing agglomeration and environmental pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Li, J.L.; Gong, H.B.; Pu, R.L.; Cao, L.D.; Shao, S.Y.; Shi, Z.Q.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, L.J.; Liu, R.Q. Research on land use changes and ecological risk assessment in Yongjiang River Basin in Zhejiang Province, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.; Schwarz, N.; Strohbach, M.; Kroll, F.; Seppelt, R. Synergies, trade-offs, and losses of ecosystem services in urban regions: An integrated multiscale framework applied to the Leipzig-Halle Region, Germany. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasky, S.; Nelson, E.; Pennington, D.; Johnson, K.A. The impact of land-use change on ecosystem services, biodiversity and returns to landowners: A case study in the State of Minnesota. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 48, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Su, C.H.; Martin, F. Linking ecosystem processes and ecosystem services. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2013, 5, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).