Abstract
Information technology advancements integrated with the e-commerce supply chain allow participants in the business process to effectively work with large volumes of data and control transactions. To improve the profitability and competitiveness of e-commerce companies, a blockchain solution was incorporated into the global B2B (Business-to-Business) supply chain. This technology simplified the transaction process by providing all participants in the sustainable B2B buying process with the same data about the trade. Overall, the use of blockchain improved the efficiency of logistics and digital documentation which reached 74% and 75%, respectively. The main advantage of using blockchain is that it creates a decentralized database that is secure. In addition, it increases the speed of payment and the reliability and transparency of data transfer. Further research may focus on the use of blockchain in green logistics to improve environmental sustainability in the e-commerce supply chain.
1. Introduction
In today’s world, e-commerce is essential to competitiveness and contributes benefits to many companies. For instance, switching to sustainable B2B (business-to-business) e-commerce facilitates the development of online trading applications and enables companies to meet the demands of more customers that are not necessarily their target audience [1,2]. In China, B2B platforms tend to work with banks providing supply chain finance to enhance trade and identify potential audiences [3,4]. The major problems of e-commerce development in China are associated with:
- -
- wrong or poor-quality product delivery and, consequently, truthfulness in dealings with suppliers [5];
- -
- regional instability [6];
- -
- ineffective management of integrity in business [7].
Previously, China experienced problems, due to the loose regulation of e-commerce [8], which were partly eliminated with the adoption of new e-commerce laws in 2017 and 2019 [9].
In turbulent economic conditions, it is not easy to quickly receive funds through traditional channels. Supply chain financing is a series of practices and technologies that support financial processes in the supply chain “from start to finish”. One of the functions of supply chain financing is to coordinate the design of trade finance instruments with the actual movement of goods and payments along the supply chain [10]. Supply chain financing not only agrees well with the growth of open account trading, but also maximizes efficiency through the introduction of improved information technology (IT)—for example, managed supply chain monitoring. Thus, more efficient supply chain management through online data management platforms has reduced corporate inventory and led to the principle of product delivery exactly on time [11].
While buyers and suppliers can finance their own supply chains, supply chain financing services reduce both the cost of capital and the risk of such transactions, allowing customers to lower their working capital requirements and improve their ability to raise capital [12]. The advantage for customers is accompanied by significant benefits for banks and other financial intermediaries, as they can:
- -
- increase revenues by financing working capital in the supply chain for their customers;
- -
- participate in the entire supply chain;
- -
- sell additional products and services (such as steadily promoting their currency exchange services) to other operators in the supply chain and thus increase their customer base.
The financial interests of buyers and suppliers are often opposed. The buyer is interested in making the payment as late as possible, and the supplier is interested in receiving it as soon as possible. The de facto purpose of supply chain financing is to satisfy these conflicting interests and offer a range of solutions to prevent risks and optimize working capital and liquidity in local and international supply chains [13]. Some products are offered directly to suppliers, others through buyers. Thus, financing of receivables can occur both for suppliers and for buyers.
In the first case (financing for suppliers), receivables arise after invoicing by the supplier. Such debts may be sold to a service provider in the field of financing receivables which purchases debts at a discount in relation to their nominal value and in exchange assumes the risk of non-payment of the full cost of goods or services. There are various types of services in the field of financing receivables—factoring, forfaiting, discounting of accounts—but they all comply with the same fundamental principle. Suppliers refuse part of the transaction amount in exchange for confidence and timely payment which allows them to manage cash flows more efficiently [14]. Thanks to this, they get access to financing on more favorable terms than with unsecured lending which is often the only alternative.
In the case of debt financing for buyers, it must be understood that buyers are also interested in the stable financial position of suppliers. If suppliers are not sure about the timeliness of payment for goods and services and have only unreliable and expensive financing options, then prices for goods and services may be higher [15]. Moreover, the sustainability of the entire supply chain may be at risk if the supplier fails to fulfill the order. Decisions related to the so-called “approved payables” allow suppliers to take advantage of the stable financial position of larger buyers [16]. As suppliers invoice buyers, they upload invoices to a special platform also used by buyers. The buyer agrees to pay the invoice when he/she makes sure that the ordered goods or services meet the specifications of the order. At this point, the funding organization may assume the risk of non-payment by the buyer and provide financing to the invoicing provider. The transaction-financing organization carries out a risk-adjusted assessment for a large (and usually more reliable) buyer, so the supplier receives financing on more favorable terms [17].
For the further development of national economy, China needs to address the social responsibility of players dominating the e-commerce market, enhancing their internal integrity [18]. Companies making use of eco-commerce, user generated content, and after-sales services gain competitive advantages over those companies that ignore these benefits. The above leverages have incredible power to create demand for specific products, provide better B2B market experience, and expand the group of customers [19]. This poses a new challenge to e-commerce, since more customers mean more risks including privacy and security ones.
The e-commerce firms often choose to ensure confidentiality and cybersecurity on their own by relying on new privacy trends such as artificial intelligence [20]. For instance, the first Chinese e-commerce platform, Alibaba, makes use of specially created AI algorithms to fulfil the need for greater transparency about cyber risk [21]. China’s integration into the global e-commerce ecosystem requires multilevel trade platforms to be effective in managing big data, ensuring its reliability and building security around it. However, having a global e-commerce platform running is not enough. Companies need to modernize their cultural values to meet Western-style democracy and enable efficient communication with foreign customers [22].
In China, social media has permeated throughout the end-to-end customer journey. For instance, Chinese customers tend to use social media to discover new brands and products [23]. In this light, social media may serve as a breeding ground for sustainable B2B e-commerce in China.
This work aimed to identify trends in supply chain financing in China’s B2B e-commerce. Findings may be used by regional e-commerce policy makers in China. The relevance of the study lies in the fact that China’s national economy needs to be transformed and its e-commerce supply chains require greater transparency in data processing. Once these requirements are met, e-commerce companies will reach higher competitiveness on the global market.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. B2B E-Commerce Supply Chain Financing
To integrate supply chain financing with B2B e-commerce operations in the Chinese market, various e-commerce platforms with different ways of business boosting, resource management, and data protection were examined. In 2017, the number of China’s B2B e-commerce websites reached several thousand, and B2B transactions reached over 2.5 trillion US dollars in value. In 2020, China’s supply chain finance sector is projected to reach approximately 15 trillion yuan [24]. Alibaba leads China’s B2B e-commerce market, providing different kinds of supply chain finance, i.e., loans provided using one’s own funds, such as Taobao and Ali small loans, and loans offered in collaboration with the Bank of China [4].
Among major challenges that arise when scaling B2B e-commerce internationally, Chinese economists distinguish a big data challenge and a customer loyalty challenge [25]. Handling large volumes of data on trade is contributive to earning the loyalty of customers for the B2B platform and allows reaching effective management and decision-making. Effective supply chain management helps companies to be more competitive in the e-commerce market [26]. At the same time, e-commerce suppliers have an operational request for the implementation of tools and solutions to gain greater control over the movement and storage of data, goods, and services [27].
Companies with insufficient working capital can access more by applying for an extension of payment terms [28], and supply chain finance providers enable this to happen while offering a loan with an interest rate that is lower than that normally issued by the bank [29]. Extension of the payment terms is an important option in short-term financing [30]. Companies can also finance from both the bank and the supplier at the same time in a dual financing mode. However, it is not proven which method of financing is preferable [31,32]. The Chinese B2B e-commerce market seems to need a supply chain based on the blockchain model to track shipments. A blockchain technology embedded in B2B platforms enables cloud storage of documents and ensures security of data transfer during transactions. A blockchain also contains records of transactions made on the blockchain and allows all participants within the supply chain to access these records (Figure 1).
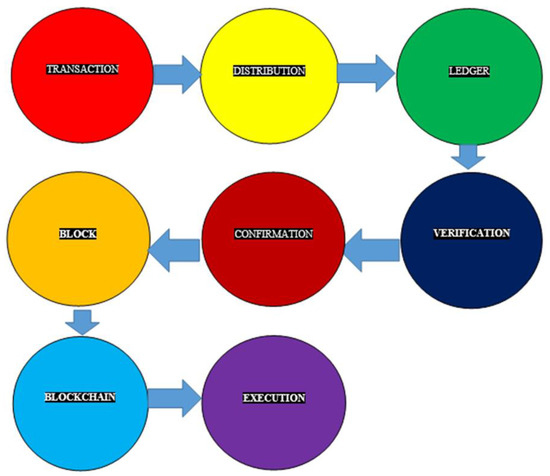
Figure 1.
Blockchain in the supply chain.
2.2. Blockchain as a Way to Create a Network of Market Participants
Blockchain platforms use cryptography and a set of public/private keys to ensure data security, and anyone involved in the supply chain may use these keys to manage or check with supply chain operations using information blocks protected from unauthorized access [33]. A similar system was first designed for the bitcoin cryptocurrency [34]. A blockchain network is a transparent and decentralized database. It can be used both for financing and for managing digital items, encouraging customers from different countries to enter the B2B supply chain [35].
A blockchain network lacks a centralized server, and participants engaged in B2B trade have equal rights in tracking and updating information about shipping. This method allows creating a network of market participants, from consumers to suppliers, without involving an intermediary while adding additional value to B2B market platforms. A B2B blockchain solution makes it possible to track shipments and changes in the location of items and their integrity 24 hours after these items acquire new statuses and ensures the maintenance of complete electronic documentation in each supply chain. To optimize supply chains, blockchain may be used in inventory management, ensuring accounting and planning of assets and customer transactions. This results in a sustainable B2B supply chain system. Thus, the use of blockchain will improve productivity, reduce time spent on the process control, boost competitiveness, and provide B2B companies with additional profit.
2.3. Base of Practical Research and Its Design
This study was based on the supply chain of China’s largest e-commerce B2B market player, Alibaba. Quantitative data for the calculations were taken from the company’s open reporting for 2019. The research design consisted of carrying out procedures and calculations to assess the effectiveness of Alibaba’s supply chain and financing after the introduction of blockchain technology. The effectiveness was evaluated based on the following indicators:
- Logistics Efficiency:
- Logistics Efficiency (El) = Items Delivered with Incidents (Ndl) × Accurate deliveries (Nl)
- Digital Documentation Efficiency:
- Digital Documentation Efficiency (Eed) = Documentation Defects (Ned) × Data Transmission Speed (Ns)
- Overall Supply Chain Efficiency:
- Overall Supply Chain Efficiency = El × Eed
3. Results
A B2B blockchain model designed for the improvement of Alibaba’s supply chain provides for the efficiency of logistics and digital documentation measured by the following formulas:
- Logistics Efficiency (El) = 0.8 × 0.92 = 0.74 (1)
- Digital Documentation Efficiency (Eed) = 0.82 × 0.91 = 0.75 (2)
- Overall Supply Chain Efficiency (Esch) = 0.74 × 0.75 = 0.56 (3)
The above calculations conclude that with blockchain, logistics efficiency will be 74%, at a rate of 65% according to References [36,37], while the efficiency of digital documentation will be 75%, with an efficiency rate of 70% according to References [38,39]. This proves the feasibility of the blockchain model.
As part of the financing process, companies create and distribute many copies of relevant documentation. A typical delivery involves the exchange of more than 30 documents—some with a few changes and versions. Such a complex architecture often leads to delays, duplication errors, loss of time because of approval processes, and even fraud. Using the blockchain network, financing chain partners can reduce the time required to provide documentation, reduce the delays associated with approval processes, and eliminate duplication of documents. It will also help reduce conflicts, avoid fines, and better manage costs. Thus, through blockchain, Alibaba will be able to achieve “programmed trust” of the chain’s participants, both to Alibaba as a platform and to other participants in the chain.
In addition, Alibaba will receive additional benefits to enhance the financial stability of the company:
- (1)
- The blockchain registry will work as a recording system. Alibaba’s platform will thus become a single reliable source for both suppliers and buyers. Such a platform will provide automatic tracking of movement of money and goods along the supply chain and record of each change;
- (2)
- All participants in the chain will be known and registered in the blockchain network. All users will have access to this information. The supply chain financing process will become more efficient, as all interested parties will be able to notice and eliminate the problems of interaction and management;
- (3)
- All direct participants in the management, organization, control, and implementation of processes related to the movement of money and goods along the chain will gain access to data on the blockchain and the right to change them;
- (4)
- Evidence and securities obtained for operations, for example, a “bill of lading”, will be digitized and recorded which will create conditions for the prevention of illegal seizure of property rights;
- (5)
- The platform interface will be adaptive for the user which will allow the platform to subscribe to external events and transactions related to the financing chain of interest, for example, for events such as “money sent” or “money received”.
Thus, in the current conditions, the introduction of blockchain technology in supply chain financing of Alibaba’s B2B commerce platform will allow for:
- -
- strengthening the company’s competitive position in the market;
- -
- improving existing operational processes;
- -
- forming a new “standard of work” in the industry (since most of the operations go through Alibaba);
- -
- forming additional intangible competitive advantages of the company in the market through increased user trust in the company.
The latter will cause a further increase in consumer loyalty to the company and, as a result, strengthen the stability of company’s processes in the market.
4. Discussion
Many global companies have postponed the digitization of paper processes because of concerns that the costs of digitization will not justify the benefits. Therefore, financial chains are still largely dependent on physical signatures and printed documents which require the personal presence of personnel at various facilities to ensure continuity of operations. Paper operations reduce transparency and increase risks during periods of disruption, reducing the ability of firms to respond quickly to changing circumstances. According to the Global Competitiveness Report 2019 [40], governments and firms with powerful digital infrastructures already cope with the current crisis far better than those without such tools.
However, resistance to the transition to digital technology is associated not only with costs, as the report says. Companies are worried that transparency without strong data privacy might jeopardize their business advantage [41]. They fear losing control over access to confidential information about their internal operations, prices, and sources.
There is an inherent compromise between transparency and confidentiality. A completely transparent system allows anyone to see any part of the information, i.e., confidentiality is not provided. Similarly, a fully private system does not provide any transparency. However, the system can provide guaranteed confidentiality without leakage of information about the status of each individual participant. Confidentiality in the public system can be achieved using cryptographic methods, but it usually comes at the expense of lower efficiency. Using an open or closed blockchain makes sense when several mutually distrusting entities want to interact and change the state of the system and do not want to use a trusted third party [42].
The clearest example in the context of the Chinese market is the precedent of 2019. Standard Chartered (a banking and financial company) completed its first blockchain-driven supply chain finance deal in partnership with Linklogis (a Chinese supply chain finance provider). The firms agreed to cooperate in expanding the visibility of the bank’s supply chain as well as in support of China’s sustainable economic growth and innovation [43]. By using blockchain algorithms, the parties sought to increase transparency and optimize the cost of access to credit for suppliers as part of a Chinese project known as Digital Guangdong. Digital Guangdong is a joint venture of Tencent, China Unicom, China Telecom, and China Mobile, and has developed more than 700 digital government services and applications and processed over 200 million transactions for Guangdong residents. The vision of Digital Guangdong was declared to increase the competitiveness of the companies involved in the project.
One of the main advantages of blockchain technology comes from the ability to speed up processes and reduce transaction complexity and risk. New benefits will arise as this technology can be integrated with outdated IT, legal regulations, and existing assets such as currencies, stocks, bonds, etc. Therefore, existing financial services can be strengthened by blockchain systems that offer potentially lower costs for financial institutions, better products, and faster time to market [44].
Transformations in the B2B e-commerce market allow a global economic growth [45]. The occurrence of various transaction management methods requires the global economy to improve its institutional framework [46].
In 2020, China ranked first in the world e-commerce ranking, followed by the USA, UK, Japan, Germany, France, South Korea, Canada, Russia, and Brazil (Figure 2).
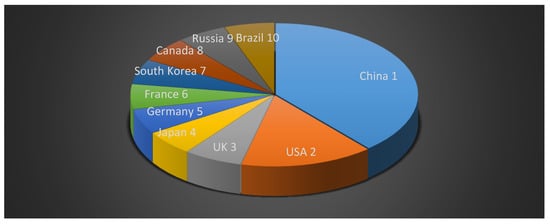
Figure 2.
World e-commerce ranking 2020. Source: developed by the authors based on data from Statista [47,48].
The global B2B e-commerce GMV (gross merchandise volume) grew from 6449 billion US dollars in 2014 to 7661 billion US dollars in 2017 (Figure 3).
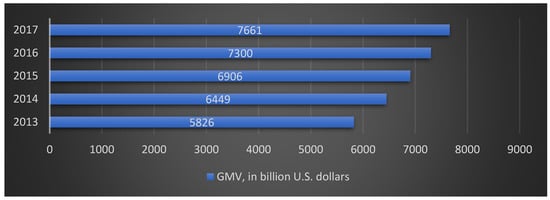
Figure 3.
Gross merchandise value (GMV) of B2B world e-commerce. Source: developed by the authors based on data from Statista [47,48].
Alibaba customers can receive loans on the OneTouch platform for up to two million US dollars and 120 days of any current account transactions from Ant Financial Services payment system operator via MyBank online bank under the e-Credit Line program in partnership with Bank of China and Sinosure. Meanwhile, Alibaba suppliers themselves can provide customers with a choice in lending banks where their credit history and business activity are monitored over the past 6 months from the date of applying for borrowed funds through their trading records on the OneTouch platform. Due to the difficulty of obtaining loans in China, an online Mybank was created, 30% of which is owned by Ant Financial. Credit funds are credited to the seller’s online account in Alipay. Alipay is key driver of Alibaba’s success. Unlike Alipay, PayPal pays the seller before delivery. A “third-party payment decision” is “escrow” in common law, where an obligation to a third party is fulfilled [49,50,51]. Alipay is known for risk minimization, while China’s banking system is associated with monopoly.
Alibaba owns 33% of Ant Financial’s shares, which allows Mybank to improve customer communications. Ant Financial is a diversified, large financial organization among the top 10 banking groups in the world (Table 1) alongside Ping An. These banking groups are all driven by market capitalization and available services. Sinosure is China’s export credit agency working through commercial banks. Sinosure provides export credit insurance and financial leasing to increase creditworthiness and the ability to repurchase at a set price [52].

Table 1.
Bank ranking. Source: developed by the authors based on data from Disruptive finance [53].
To build long-term relations with the USA, Alibaba has signed a contract with Kabbage that enables the group to provide small- and medium-sized businesses with loans in the amount of up to 150 thousand US dollars under the Pay Later program on the conditions of six-month repayment with a rate of 1.25 percent [54]. For residents of companies in Hubei, £10 billion was allocated with a zero-interest rate for the first 90 days and a 20% discount on rates for the remaining nine months [55]. MyBank provides loans at 5.3% per annum [56]. China Construction Bank lends to small businesses at 5.3% per annum in the amount of up to 5 million yuan [57]. The Bank of China has a lending rate of 4.6 percent per annum [58]. Alibaba.com collaborates also with Postal Savings Bank of China, the Bank of China, the Bank of Shanghai, the China Merchants Bank, the Ping An Bank, and the Fuzhou City-based Industrial Bank.
In China, the largest e-commerce platform is Alibaba, while in the USA, this title goes to Amazon (Table 2).

Table 2.
Services of B2B e-commerce platforms. Source: developed by the authors based on data from Chuen and Paul [59].
China’s e-commerce market is set to grow at Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19% by 2021 to reach 840 billion USD dollars (Figure 4).
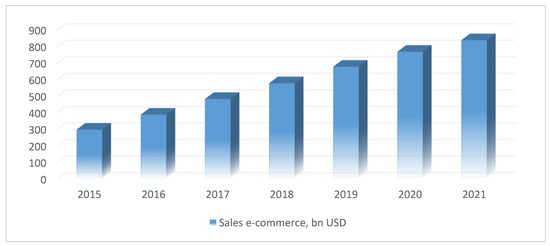
Figure 4.
E-commerce of China. Source: developed by the authors based on data from Chuen and Paul [59].
On the Alibaba platform, a customer can select a supplier by status. Payment through Secure Payment can be made by Alibaba, not the provider. The seller receives money once the item is delivered, which can be returned using the trade assurance service, and the commission for this service is approximately 5% of the order value. The shipping can be carried out with FedEx, EMS, DHL, UPS, and TNT. Platform suppliers also provide large customers with an extra service such as direct ordering and direct procurement. Alibaba provides information about the supplier, founders, and equipment.
Alipay is a key driver of Alibaba’s success. The platform also has intermediary services that allow negotiating with a supplier, placing an order, checking quality, purchasing, and paying for and delivering goods. The platform hosts only suppliers, excluding manufacturers.
Supplier statuses on Alibaba:
- Free member—insecure service;
- Gold supplier—100% guaranteed supplier;
- Assessed supplier—there is a check of all licenses and documents.
Gold suppliers have three tariffs per annum—$6000, $3000, and $1400, depending on the volume of photos on the quantity of goods and personal customer support.
For example, the Yorso24 service receives a percentage of the transaction, while the client pays the site when a profit is earned. The Traderb2b trading platform receives payments from both sellers and buyers who within 8 hours find out the best price for the requested product. Premium service is available on B2B platforms like EC21, TradeIndia, and TradeKey, where buyers are mainly from China, the USA, and the UK. China’s e-commerce supply chains get the most out of the economy unlike developing countries, whose companies have problems with materials management [60]. The fourth party in the e-commerce supply chain is logistics companies.
In China’s B2B e-commerce supply chain, sustainability is among the key challenges [61]. Ant Financial embedded a new blockchain solution in the Ant Blockchain Open Alliance and Double Chain Connection platforms to offer financial services to small- and medium-sized businesses [62]. A global blockchain trend has intangible benefits (trust, transparency, and openness of data) and allows developing sustainability in the e-commerce supply chain beyond China. PepsiCo uses blockchain in the supply chain to promote online advertising and product sales [63].
To take exports/imports in a B2B supply chain into account, a blockchain technology is needed that allows platforms to reduce transaction costs by modifying product quality certification. The vigorously developing e-commerce industry in China demands digitalization of the B2B market and the use of blockchain at all stages of the supply chain. An additional service on the e-commerce blockchain, also known as a smart contract, serves an additional advantage if the terms of delivery have been violated [64,65,66].
Implementation of blockchain in companies conducting international business and, as a result, cross-border e-commerce like Alibaba, will increase the level of customer confidence and the effectiveness of managing large databases in the operational detail of the B2B e-commerce supply chain [67,68]. Trust is an integral part of any highly functional supply chain. Usually, it is established gradually, in the process of successful cooperation between companies and suppliers. When partners in the same chain share data, financial information, and even intellectual property, confidence in mutual honesty (along with contracts and other guarantees) compensates for the risks [69,70,71]. The blockchain provides an overall reliable platform for updating information such as financial stability of suppliers, payment terms, quality standards, prices, delivery requirements, service specifications, and conflict resolution procedures. Using this platform, new suppliers quickly and efficiently integrate into the process, and much less time is spent on a comprehensive legal assessment [72]. Thus, a decentralized blockchain network records and marks each transaction of any member of the supply chain and updates it in real time. A record cannot be changed without the agreement of all participants. The algorithm ensures the reliability of data, prevents fraud and, therefore, is extremely valuable in the B2B market of China [73].
5. Conclusions
The deep penetration of suppliers to further transform the economy requires new methods of supply chain management and innovative approaches to information technology that is used in e-commerce management. As the digital economy grows, the presence of blockchain in international B2B e-commerce seems relevant from the efficiency point of view, as it improves organizational processes as well as the competitiveness of companies within the industry. Findings show that with blockchain, the efficiency of logistics and digital documentation maintenance is 74% and 75%, respectively, which gives an advantage over traditional materials management systems and improves profitability of B2B market companies in the e-commerce market. The findings allow making more transparent electronic reporting, thereby simplifying the supply chain finance. Further research may focus on exploring the ecosystem of e-commerce platform financing to improve company competitiveness and customer satisfaction. The combination of supply chain finance and logistics platforms ensure an efficient exchange of data between all participants in the transaction.
Academic and practical implications: The development of the blockchain network and the active introduction of blockchain into the corporate world will form such an important information infrastructure of the future which will cover the Internet of Things, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and other new and emerging technologies. In the future, increasing the transparency, traceability, and security of supply chains and their financing can be a breakthrough in the development of much more sustainable economies. All this requires specific calculations of introducing the blockchain into the practice of leading companies of individual niches and industries.
Study limitations: The calculations carried out on the example of Alibaba’s practice were limited by the level of reliability and transparency of the data published in the company’s statements. These calculations also did not take into account the force majeure circumstances caused by the pandemic that has occurred in the global economic environment in 2020.
Future research will focus on the role of blockchain in diversifying the financing risks in the supply chains of global corporations amid the crisis of 2020.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.L. and S.W.; methodology, M.E.; validation, M.J.L., S.W., M.E. and M.U.; formal analysis, M.J.L.; investigation, S.W.; resources, M.E. and M.U.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.J.L.; writing—review and editing, M.E. and M.U.; visualization, S.W. and M.J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The third author M.E. was supported by Tomsk Polytechnic University within the framework of Tomsk Polytechnic University Competitiveness Enhancement Program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khan, A.G. Electronic commerce: A study on benefits and challenges in an emerging economy. GJMBR 2016, 16, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M. Alibaba and the Future of Business. Harv. Bus. Rew. 2018, 96, 88–96. Available online: https://hbr.org/2018/09/alibaba-and-the-future-of-business (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Alibaba.com and 7 Big Chinise Banks Offering Loans to Small Exporter. Alizila. 22 July 2014. Available online: https://www.alizila.com/alibaba-com-and-7-big-chinese-banks-offering-loans-to-small-exporters-2/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Shen, Q. Research on Financial Financing Mode of SME Supply Chain based on B2B E-commerce Platform. In 2018 International Symposium on Social Science and Management Innovation (SSMI 2018); Atlantis Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, S.; Lin, Z. Capturing the essence of word-of-mouth for social commerce: Assessing the quality of online e-commerce reviews by a semi-supervised approach. Decis. Support. Syst. 2013, 56, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panova, Y.; Tan, A.; Hilmola, O.P.; Puvindran, M.H.; Hongsheng, X.; Li, W. Evaluation of e-commerce location and entry to China-implications on shipping and trade. J. Shipp. Trade 2019, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Z. Research on How to Strengthen the Management of Chinese E-Commerce Credit. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 798, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Chang, Y.; Li, Sh.; Li, F. E-Commerce Strategy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, E. China’s New E-Commerce Law: A Step in the Right Direction. China.org.cn. 9 January 2019. Available online: http://www.china.org.cn/opinion/2019-01/09/content_74355741.htm (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Tate, W.; Bals, L.; Ellram, L. Supply Chain Finance: Risk Management, Resilience and Supplier Management; Kogan Page Publishers: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.L.; Wang, Z.X.; Chan, F.T. How important are supply chain collaborative factors in supply chain finance? A view of financial service providers in China. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 219, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsomino, L.M.; de Boer, R.; Steeman, M.; Perego, A. An optimisation strategy for concurrent Supply Chain Finance schemes. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2019, 25, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Jia, F.; Brown, S.; Gong, Y.; Xu, Y. Supply chain finance: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 204, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkakos, S.D.; Serrano, A.; Ellinger, A. Supply chain finance for small and medium sized enterprises: The case of reverse factoring. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Johnson, M. Supply Chain Finance—Some conceptual thoughts reloaded. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.; Hofmann, E. Involving financial service providers in supply chain finance practices. J. Appl. Account. Res. 2017, 18, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvelis, P.; Dong, L.; Turcic, D. Emerging Technology & Advances in Supply Chain Finance & Risk Management; Now Foundations and Trends: Boston, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q. Comprehensive Evaluation of Businesses Strategy and E-Commerce Performance in Smes: A Corporate Social Responsibility Perspective. Int. J. Hybrid. Inf. Technol. 2016, 9, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholin, Zh.; Online Shopping Stimulates Development. E-Commerce is Becoming the Core of China’s Digital Economy. Russian Newspaper. 9 February 2019. Available online: https://rg.ru/2019/09/02/elektronnaia-kommerciia-stanovitsia-iadrom-cifrovoj-ekonomiki-kitaia.html (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Pernot-Leplay, E. Data Privacy Law in China: Comparison with the EU and U.S. Approaches. 2020. Available online: https://epernot.com/data-privacy-law-china-comparison-europe-usa/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Linsey, N. Alibaba Intercepts 2.2 Billion Cyber Attacks on Singles Day. CPO Magazine. 27 November 2019. Available online: https://www.cpomagazine.com/cyber-security/alibaba-intercepts-2-2-billion-cyber-attacks-on-singles-day/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Holmes, K.; Balnaves, M.; Wang, Y. Red Bags and WeChat (Wēixìn): Online collectivism during massive Chinese cultural events. Glob. Med. J. 2015, 9, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- PWC. E-Commerce in China—The Future is Already Here; Total Retail: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.pwccn.com/en/retail-and-consumer/publications/total-retail-2017-china/total-retail-survey-2017-china-cut.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Lahkani, M.J.; Wang, S. Research on the Supply Chain Finance Mode of B2B E-Commerce Platforms in China: A Literature Review; School of Economics and Management, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, R.; Huang, G.Q. E-commerce logistics in supply chain management: Practice perspective. Procedia Cirp 2016, 52, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, X. The role of supply chain finance in third-party logistics industry: A case study from China. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2019, 22, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashina, V.; Scharfstein, D. Bank Lending During the Financial Crisis of 2008. J. Financ. Econ. 2010, 97, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondys, K. Implementation of the Sharing Economy in the B2B Sector. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yang, L. Financing strategy in fresh product supply chains under e-commerce environment. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2020, 39, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Rhee, B.D. Trade credit for supply chain coordination. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 214, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. A model of credit in a capital-constrained distribution channel. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 159, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvelis, P.; Zhao, W. Financing the newsvendor: Supplier vs. bank, and the structure of optimal trade credit contracts. Oper. Res. 2012, 60, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, G. The economics of Bitcoin and similar private digital currencies. J. Financ. Stabil. 2015, 17, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoshi, N. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Bitcoin. 2018. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Mettler, M. Blockchain technology in healthcare: The revolution starts here. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on E-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lukinskiy, V.; Lukinskiy, V.; Merkuryev, Y. Supply chains efficiency increasing based on the modelling of logistics operations. Int. J. Simul. Process. Model. 2017, 12, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, H. Conceptual considerations for real-time supply chain efficiency monitoring. Res. Logist. Prod. 2016, 6, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loklindt, C.; Moeller, M.P.; Kinra, A. How blockchain could be implemented for exchanging documentation in the shipping industry. In International Conference on Dynamics in Logistics; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2018; pp. 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, J.; De Meyer, A.; Marques, A.S.; Pinho, T.M.; Boaventura-Cunha, J.; Van Orshoven, J.; Rosset, C.; Künzi, J.; Kaarle, J.; Nummila, K. Digital technologies for forest supply chain optimization: Existing solutions and future trends. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 1108–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. The Global Competitiveness Report; WEF: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rizal Batubara, F.; Ubacht, J.; Janssen, M. Unraveling Transparency and Accountability in Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research, Dubai, UAE, 8–20 June 2019; pp. 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.K. Blockchain—A financial technology for future sustainable development. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International conference on green technology and sustainable development (GTSD), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 24–25 November 2016; pp. 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lumineau, F.; Wang, W.; Schilke, O. Blockchain Governance—A New Way of Organizing Collaborations? Organ. Sci. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott, A.; Tapscott, D. How blockchain is changing finance. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2017, 1, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Malala, J. Law and Regulation of Mobile Payment Systems: Issues Arising ‘Post’ Financial Inclusion in Kenya; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, L. Transaction costs and environmental policy design. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 88, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global B2B E-Commerce Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV) from 2013 to 2017. Statista. 9 May 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/705606/global-b2b-e-commerce-gmv/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- SMEs B2B E-Commerce Platforms Revenue Change in China 2013–2020. Statista. 6 May 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/302480/china-sme-b2b-e-commerce-revenue-change/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Justia US Law. Division 6. Escrow Agents. Chapter 3. Escrow Regulations. In 2016 California Code. Financial Code—FIN; Government of California: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 17400–17425.
- Supreme Court of the United States Journal 2012. Available online: https://www.supremecourt.gov/orders/journal/jnl12.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Yu, Y.; Shen, M. How Consumer Protections are Providing Alibaba’s ‘Open Sesame’ to Steal China’s Consumer Market. In The Foundation for Law, Justice and Society; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; Available online: https://www.fljs.org/sites/www.fljs.org/files/publications/Alibaba%20and%20the%20Threat%20to%20China’s%20Banking%20Sector.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- The Use of Asian Export Credit Financing is an Often Over-Looked Opportunity. Kromann Reumert. May 2017. Available online: https://www.kromannreumert.com/Insights/2017/The-use-of-Asian-export-credit-financing (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Alibaba Becomes Top 10 Global Bank. Disrupt. Financ. 2020. Available online: http://www.disruptivefinance.co.uk/2018/05/26/alibaba-becomes-top-10-global-bank/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Lunden, I. Alibaba Taps Kabbage to Loan up to $150K to SMBs after it Quietly Acquired OpenSky to Ramp in North America. Join Extra Crunch. 2019. Available online: https://techcrunch.com/2019/01/14/alibaba-taps-kabbage-to-loan-up-to-150k-to-smbs-after-it-quietly-acquired-opensky-to-ramp-in-north-america/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- China’s Alibaba Loans Near $3B To Coronavirus-Affected Firms. PYMNTS. 9 May 2020. Available online: https://www.pymnts.com/news/international/2020/chinas-alibaba-loans-near-3b-to-coronavirus-affected-firms/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Jack Ma’s Online Bank Is Leading a Quiet Revolution in Chinese Lending. Fortune. 29 July 2019. Available online: https://fortune.com/2019/07/29/jack-ma-mybank-lending/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Jack Ma’s $290bn Loan Machine Changes Chinese Banking. Bangkok Post. 28 July 2019. Available online: https://www.bangkokpost.com/business/1720991/jack-mas-290bn-loan-machine-changes-chinese-banking (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Jia, C. PBOC to Streamline Lending Interest Rate System. Chinadaily. 2019. Available online: https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201905/22/WS5ce4a5cca3104842260bd080.html (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Chuen, L.D.K.; Paul, S. Ai & Quantum Computing For. Finance & Insurance: Fortunes and Challenges for China and America; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, J.; Wu, T. Factors influencing growth potential of E-commerce in emerging economies: An institution-based N-OLI framework and research propositions. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2015, 57, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P. Integration in Chinese e-commerce and public policy concerns: An analysis of Alibaba Group. TRESP 2017, 3, 68. [Google Scholar]
- The Daughter of the Alibaba Group Introduced a Blockchain Service to Monitor Supply. BitNovosti. 11 March 2019. Available online: https://bitnovosti.com/2019/01/10/dochka-alibaba-group-predstavila-blokchejn-servis-dlya-monitoringa-postavok/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Jiang, G. Blockchain is Key to Realizing the Digital Industrial Revolution. Folksat News. 11 November 2019. Available online: https://forkast.news/blockchain-the-key-to-realizing-the-digital-industrial-revolution/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Kosba, A.; Miller, A.; Shi, E.; Wen, Z.; Papamanthou, C. Hawk: The blockchain model of cryptography and privacy-preserving smart contracts. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2016; pp. 839–858. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, A.S.; Holionko, N.G.; Tverdushka, T.B.; Olejarz, T.; Yakymchuk, A.Y. The Strategic Management in Terms of an Enterprise’s Technological Development. J. Compet. 2019, 11, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myšková, R.; Kuběnka, M. Information sharing in the context of business cooperation—As a source of competitive advantage. J. Int. Stud. 2019, 12, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Popovic, T.; Kraslawski, A.; Barbosa-Póvoa, A.; Carvalho, A. Quantitative indicators for social sustainability assessment of society and product responsibility aspects in supply chains. J. Int. Stud. 2017, 10, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, S.; Goldbach, I.R.; Ślusarczyk, B. Supply chain management in SMEs—Polish and Romanian approach. Econ. Sociol. 2018, 11, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treleaven, P.; Brown, R.G.; Yang, D. Blockchain technology in finance. Computer 2017, 50, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaskova, K.; Kliestik, T.; Kovacova, M. Management of financial risks in Slovak enterprises using regression analysis. Oecon. Copernic. 2018, 9, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakurár, M.; Benedek, S.A.; Popp, J.; Magda, R.; Oláh, J. Trust or doubt: Accuracy of determining factors for supply chain performance. Pol. J. Manag. Stud. 2019, 19, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.R.; Samuelson, L.; Katz, H. How securitization can benefit from blockchain technology. J. Struct. Financ. 2017, 23, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Jian, Z.; ul Haque, A.; Urbański, M.; Nair, S.L.S. Determinants of firm’s export performance in China’s automobile industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).