Abstract
The importance of reducing food loss and waste (FLW) has recently been emphasized at a European level with the amendment to the European Waste Framework Directive, according to which the effective reduction of food waste can be carried out by adopting a circularity approach that facilitates the transition to more sustainable management of materials. Likewise, the importance of concentrating on FLW produced within specific food supply chains has emerged as an effective starting point for quantifying the overall amount of wastage produced, emphasizing possible prevention actions as well as re-using and valorising waste. From this perspective, our study focuses on the tomato-sauce supply chain with a threefold aim. Firstly, to quantify the amount of FLW generated along the tomato-sauce supply chain from cultivation to retail; secondly, to understand the most important related causes; and thirdly, to assess if and to what extent FLW can be reused according to the Circular Economy (CE) approach. By adopting the Food Loss and Waste Accounting and Reporting Standard, the analyses focused on the production of the Barilla Tomato and Basil sauce in Italy, as well as the related inventory. It was revealed that this supply chain can be considered an example of a true circular economy, in which almost nothing is lost because more than 85% of the total FLW are valorized into alternative sectors or activities.
1. Introduction
Food loss and waste (FLW) is a global concern that is mining the world’s sustainability. According to the Food and Agriculture Organizaation (FAO), one third of the food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted at some point during the food supply chain (FSC) [1], causing severe environmental, economic and social impacts [2,3,4]. Indeed, if food waste could be represented by a country, this would be the third largest global greenhouse gas emitter after China and USA [3]. According to research in the EU-28 Countries, food waste could increase to 126 million tons per year by 2020 if no further counter measures are implemented [5]. This scenario is not in line with the ambitious Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 12.3 set by the United Nations and signed by 193 heads of state, which states that “by 2030, nations will halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses” [6] (p. 27). Indeed, as it has been shown that tackling FLW could help in reaching not only SDG #12.3, but also many others, such as zero hunger or climate action [7], to ensure global sustainable development, it is fundamental to implement as many initiatives as possible against the phenomenon.
According to the definition given by the FAO (2011), for food loss (FL) we intend to mean food that is intended for human consumption, but for any reason is discarded during the first stages of the food supply chain (FSC), that is from the agricultural phase up to the transformation and transport phases [1]. These losses are usually managed by food producers and/or farmers, which is why their involvement in assessing and tackling FL is fundamental in achieving SDG 12.3 and in pursuing sustainable growth. In contrast, for food waste (FW), we specifically intend to mean food that is lost during the last phases of the FSC, namely the distribution and consumption phases [1,8]. A recent study [9] highlighted that, in 2017, only 25% of the world’s major food manufacturing companies had measured FLW within their operations, and among these companies, just 20 percent had established FLW reduction targets and initiatives.
Although the European Commission emphasizes the importance of assessing and managing FLW under a Circular Economy (CE) approach [10], up to now, few academics and practitioners have focused their activities on highlighting how FLW can be reused and redistributed using a closed-loop perspective, instead of the old linear input–output process where ultimately FLW goes to landfill and is not reused in other processes. Therefore, with the aim of filling this literature and managerial gap, in this paper we will focus on FLW under a circular economy framework, by examining the amount of FLW along the different life cycle phases of tomato sauce production, and how it is possible to valorise the majority of them into alternative sectors or activities. Indeed, based on an exploratory case study of the Barilla Company, the global pasta and sauces market leader, we intend to analyse the FLW amounts of Barilla Tomato and Basil sauce, and its causes along the entire life cycle, from field to fork, and show that most FLW that occurs in this supply chain could be reused in by-products, or donated to people in need according to a CE perspective.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. In Section 2 we review the literature of tomato sauce FLW management under the CE framework. In Section 3, the selection of methodology used for assessing FLW is carried out and the Food Loss and Waste Accounting and Reporting Standard, developed by [11], is presented. In the same section, the details of the case study, i.e., the Barilla Tomato and Basil sauce case, are described by illustrating the definition of terms and their application to the studied tomato supply chain. In Section 4, the inventory results are presented in terms of loss and waste generated in each stage of the sauce supply chain by providing the specific amount of FLW generated in each stage and focusing on the main underlying causes and destinations. In Section 5, we discuss the results obtained, while in Section 6 some concluding remarks and future research directions are drawn.
2. Managing Tomato Sauce FLW under the Circular Economy Framework: A Literature Review
The agri-food sector is recognized as a major sector of greenhouse gas emissions. Indeed, according to a recent study, agriculture itself contributes to 24% of global greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) [12]. The environmental impacts associated with the agri-food chain are mainly due to resource exploitation, land degradation, GHG emissions, and, no less important, waste generation [13]. Many studies have been developed in order to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture, for example, using a life cycle assessment methodology for some specific supply chains [14,15]. However, since 2015 when the European Commission added FLW reduction to its Circular Economy Package [10], scant research has been put forward in order to analyse waste generation along specific supply chains and its possible reuse under the CE lens. Indeed, according to some studies, managing FLW in a sustainable way is a key factor to more sustainable societies [16,17] and communities [18]. Some studies highlighted nutrient and energy retrieval against mere food waste disposal [5,19], which would not only lead to financial paybacks for the food manufacturers but would also bring environmental savings. Indeed, reducing the exploitation of natural resources would help lower GHGs associated with FLW as well as other pollutants [17,20].
Moreover, if we consider the SDGs achievement, the CE framework has been proven to be an enabler of the 2030 Agenda [21], and, as stated during the 2018 High-Level Political Forum, it is fundamental for the SDG 12 achievement (Sustainable Consumption and Production), and especially for the FLW management. However, up to now, the link between the CE framework and the SDGs achievement has been underestimated by both researchers and practitioners [22].
Over the last 150 years, the world economy has been based on the linear input–output process that has been demonstrated to no longer be sustainable from both an economic, environmental and societal point of view [23]. As stated before, recently the EU, along with several other countries like Japan, Canada and China, promoted an alternative economic growth based on a cyclical flow process that ensures a more sustainable development, which is the CE model [10,21,23,24].
As stated by Korhonen et al. (2018) [25], the CE framework “emphasizes product, component and material reuse, remanufacturing, refurbishment, repair, cascading and upgrading, as well as solar, wind, biomass and waste-derived energy utilization throughout the product value chain and cradle-to-cradle life cycle” (p. 37). In sum, the CE promotes all the actions put forward by the industries in order to reuse and recycle materials along the FSC [26]. The CE highlights the relevance of reducing waste (including FLW) by transforming it into a material good that can be used as a new manufacturing input or as a raw material in alternative industrial processes, such as feeding animals or energy recovery [21,27]. Therefore, the CE can supply several options for reusing inputs and by-products in closed-loop systems [28]. Bearing in mind the CE concept, it is necessary that surplus food management follows the so called “waste management hierarchy” [16,29]. That is, as for FLW, the first action that business must take into account is to prevent its generation. After its minimization, a second-best option for inevitable FLW is its reuse, firstly for human consumption, and secondly for animal feeding. The third option is represented by the possibility of recycling for (i) industrial usage, (ii) anaerobic digestion, (iii) composting and (iv) combustion for energy recovery; to finish, landfilling represents the last available option. Therefore, according to the CE perspective, waste management should not only focus on waste prevention, but because some types of FLW are inevitable, managers should put forward actions to reuse and/or recycle it to make renewable energy and/or other by-products [30,31]. Considering food donation, it is important to note that the EU is also committed to encouraging waste reduction and implementing food redistribution to people in need, according to the waste hierarchy framework and CE concept [32]. Considering this aspect, as the Barilla Center for Food and Nutrition (BCFN) Foundation highlighted, our world is facing a large paradox of excess food and access to food. On one hand, one third of the global food production is lost or wasted, but on the other hand, according to FAO, 821 million people are suffering hunger. Furthermore, food insecurity is not just present in developing countries, but is also an important issue in developed countries. According to a recent study [33] in Europe, approximately 43.6 million people are food-insecure.
As stated before, if we consider FLW literature under the CE framework, much has to be done. Indeed, one recent study emphasized pasta production as a good example of a CE approach requiring the need for looking at other supply chains in order to verify whether other food products can be outlined under a CE perspective [34]. Ingrao et al. (2018) [16] focused only on energy recovery from unavoidable FLW, while other studies focused on implementing food sharing models in order to reduce FW without explicitly drawing on a CE framework [35,36], or just focusing on FW reduction for food manufacturing companies under the FW hierarchy [37]. Moreover, many of these studies focused on consumer and retail FW and did not take FL into consideration.
Concerning tomato waste, up to now there are no studies that specifically quantify its amount along the FSC. One study focused on tomato pomace, a by-product of the tomato industry process, and its valorisation, but did not highlight it under a CE approach nor measure its quantity [38].
Therefore, it is essential to understand the quantity of tomato left along the FSC, why this occurs, and, when there are inevitable losses, to see if it is possible to minimize them through reuse and/or recycling, in line with the CE approach. In line with this, the correct and sustainable implementation of waste management practices, established according to the waste hierarchy and CE approach, can help companies give FLW a second life and to use them as secondary raw materials and energy [39]. Therefore, the main research questions that this study seeks to answer are: (i) how much tomato is wasted along the FSC to produce a tomato sauce?, (ii) what are the main causes leading to tomato losses and waste along the FSC?, (ii) could this FLW be reused according to the CE approach?
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The Selection of Methodology
FLW accounting is a central element for policy design and interventions [40]. From this perspective, the importance of collecting, describing and analysing FLW produced in the various FSC phases has recently emerged, mainly focusing on tomatoes and tomato-derived products as this vegetable is widely used in large parts of the world, both fresh and processed [41]. In addition to this issue, both the prevention and the re-use of generated waste are crucial for a more effective and efficient use of natural resources and for a greater alignment with a sustainable production system.
In our research, focusing on the Tomato and Basil sauce produced by Barilla we firstly selected the methodology (see [40] for a detailed explanation of existing methods for quantifying FLW) that best fits with our goals. Indeed, “clearly defining the aim of the study is the first step towards an effective design and a proper choice of the quantification method” [40].
Bearing in mind the research questions of our study and the possible theoretical and applied contributions of our paper, the reference standard we selected for our analysis was the global Food Loss and Waste Accounting and Reporting Standard (from now on referred to as the FLW Standard), which is a “global standard providing requirements and guidance for quantifying and reporting on the weight of food and/or associated inedible parts removed from the food supply chain—commonly referred to as “food loss and waste” [11] (page 11). This was introduced to help countries, cities, companies, and other entities develop inventories of how much FLW is generated and where it goes (destinations). The FLW Standard is designed to account for the fact that different organizations will have different reasons for quantifying FLW [11] and the differences can therefore reflect different definitions of what constitutes FLW.
The implementation of a FLW inventory according to the FLW standard foresees the following five mandatory requirements that apply to all entities regardless of their situations:
- “Define goals”: the entity who wants to implement the inventory should clarify why it is quantifying FLW and it may refer to food security, economic performance, environmental impact or combinations of these elements.
- “Review accounting and reporting principles”: as specified in the FLW protocol the basic principles for accounting and reporting (i.e., relevance, completeness, consistency, transparency and accuracy) must be fulfilled for guiding the implementation of the standard.
- “Establish scope”: this step specifically requires defining the timeframe, material type(s), destination(s), and boundaries addressed by the implemented FLW inventory.
- “Decide how to quantify FLW”: the FLW standard requires a decision to undertake a new calculation of the amount of FLW or to use existing data as well as to select the quantification method(s) to use in implementing the FLW inventory.
- “Calculate inventory results”: once the data have been collected and analysed, inventory results can be calculated according to the guidance provided by the FLW standard.
In addition to these steps, there are three additional conditional steps focusing on the data collection process (data gathering and uncertainty), as well as on the performance review (carrying out an internal or external assurance process to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the FLW inventory) [11].
Focusing on step III, in order to complete this step, there are the following four mandatory dimensions that must be defined:
1. Timeframe: the specification of the period of time for which the inventory results are reported by including starting and ending dates;
2. Material type: the distinction of material types removed from the process by distinguishing into “food” and “inedible parts”, where food refers to any substance (whether processed, semi-processed or raw) that is intended for human consumption, while the term “inedible parts” refers to components associated with food that are not intended to be consumed by humans. More specifically, in any inventory aimed at quantifying FLW, it is required that materials removed from the studied FSC should be distinguished into food only, inedible parts or both.
3. Destination: where material removed from the food supply chain is directed. As specified, the possible destination must be selected among the following ten possible destinations: animal feed; bio-based materials/biochemical processing; codigestion/anaerobic digestion; composting/aerobic processes; controlled combustion; land application; landfill; not harvested/plowed-in; refuse/discards/litter; sewer/wastewater treatment.
4. Boundaries: defined by specifying:
- (a)
- The food category: this describes the specific type of food included in reported FLW by using the categories in the Codex General Standard for Food Additives (GSFA) system or the United Nations Centrale Production Classification (CPC). Moreover, for more detailed information, codes from the Global Product Category (GPC) and United Nations Standard Products and Service Code (UNSPSC) can be used. It is worth noting that the information specified as “food category” differs from “material type”, in which it is specified for each stage whether FLW is composed of “food – edible parts” and/or “associated inedible parts” removed from the FSC.
- (b)
- Lifecycle stage: this refers to the studied stage (or stages) and for which inventory results are reported. With the aim to identify specific stages, the United Nations International Standard Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) codes are used.
- (c)
- Geography: this refers to the geographic borders within which the reported FLW occurs. In order to identify countries or regions, one or more UN regions or country codes can be used.
- (d)
- Organizational unit: this requires one to specify what organizational units (all sectors, entire company, only selected business units) are involved in the reported FLW.
The inventory fulfilled according to the FLW standard allows an entity to select which combination of material types and destinations it considers to be “food loss and waste” in accordance with the entity’s stated goals. Therefore, the inventory prepares results into a “standard credible, practical, transparent, and internationally consistent basis for entities to account for and report on FLW” [11] (page 5).
3.2. The Studied FSC: The Barilla Tomato and Basil Sauce
This study focuses on the production of Barilla Tomato and Basil sauce and provides evidence, according to the FLW standard, of the amount of FLW generated (quantification expressed in grams), as well as its causes and destinations along the various phases of the supply chain, from cultivation to retail, in accordance with similar studies analysing the life cycle of tomato puree [38].
The studied product (and therefore the related studied production process) is the Barilla Tomato and Basil Sauce in a 400-gram format. In the inventory, whose detailed results are provided in the following subsection, we analysed the FLW concerning the main ingredients used for producing Tomato and Basil sauce, represented by tomato pulp and concentrate, which account for 344 g (86%) of the total final product. On the other hand, the remaining ingredients (56 g) are represented by basil, onions, water, oil, salt, sugar and flavours.
In accordance with step I (defined in the previous sub-section), the aim of this FLW inventory is to quantify FLW in tomato sauce production (pulp and concentrate). The importance of focusing on this specific FSC, which has emerged in the literature, is that tomato production is spread over all continents, with the largest producers being China, India, US, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, Italy, Spain and Brazil [41]. Therefore identifying, describing and reporting best-practice situations and rules for the re-use of edible parts of FLW in secondary destinations within a circular economy perspective can represent an important contribution to the literature as well as a good example to follow in terms of benchmarking for similar companies. The FLW inventory, according to step II, was carried out by referring to the five basic principles of accounting and reporting, as discussed in the previous sub-section.
According to the FLW standard and in order to “establish scope” as required by the third step for implementing the FLW standard, Table 1 shows the details of the mandatory four dimensions (i.e., timeframe, material type, destination and boundaries) required by the FLW standard for describing the inventory.

Table 1.
Barilla 400-gram Tomato and Basil sauce: the inventory components according to the FLW standard.
The inventory results reflect the state in which the FLW was generated (i.e., before water or other condiments are added or before the intrinsic water weight of the FLW is removed). Pre-harvest losses have been excluded from the inventory results because they are not relevant for the purpose of this study.
Focusing on the quantification of the FLW (step IV of implementing the standard), the amount of FLW generated throughout the studied FSC derives from a new calculation. From this perspective, we also referred to the conditional step concerning data gathering, required for assembling the necessary data for FLW quantification. Indeed, by distinguishing data collection for the specific FSC phases, two different sources provided us with the necessary data to complete the FLW inventory: (i) Barilla G. & R. F.lli S.p.A, who collected data and information concerning the processes of cultivation, transport, pulp and concentrate production and factory, and (ii) Last Minute Market (LMM) – Impresa Sociale Srl, accredited spin-off of the University of Bologna, who collected and elaborated data and provided us with data about the distribution phase. Indeed, specifically focusing on distribution, the data were collected by LMM through a survey conducted in six brands of the Italian large-scale distribution. The resulting data refer to 1700 points of sale, representative of the distribution chains located across the Italian territory, from small supermarkets to larger hypermarkets.
It is worth noting that packaging and any other non-FLW material were excluded from the inventory, as suggested by [11], and as carried out in similar studies assessing the environmental impacts of tomato (and related by-products) wastage [41].
4. Results
4.1. Inventory Results
In this section, the inventory results are presented in order to fulfill our first research objective. By focusing on the Barilla Tomato and Basil sauce in the 400-grams format we analyzed the generation of FLW throughout the various phases of FSC, from cultivation to retail. It is worth noting that the ingredients under study are represented by 344 g of sauce, which includes (tomato and concentrate) the main ingredients of the studied product, as clarified in the previous section.
As a summary result, each 344g of sauce produces 80.5 g of losses and waste (Figure 1), represented by 64.3 g (79.8% of the total FLW) of edible parts because the material type removed from the process is food, referring to any substance whether processed, semi-processed, or raw that is intended for human consumption, and 16.2 g (20.2% of the total FLW) represented by inedible parts, i.e., components associated with a food that, in the studied FSC, are not intended to be consumed by humans.

Figure 1.
Total amount of Food Loss and Waste (FLW) in grams generated during Barilla Tomato and Basil FSC.
From the lifecycle perspective, it is important to analyze the generation of FLW per stage by distinguishing the material types removed from the FSC. According to this, Table 2 shows the specific amount (in grams) of FLW generated in each lifecycle stage, while Figure 2 summarizes the percentage distribution of edible parts removed from each stage.

Table 2.
Barilla 400-gram Tomato and Basil sauce: FLW per lifecycle stage and distinction of material type removed from the FSC (quantities expressed in grams).
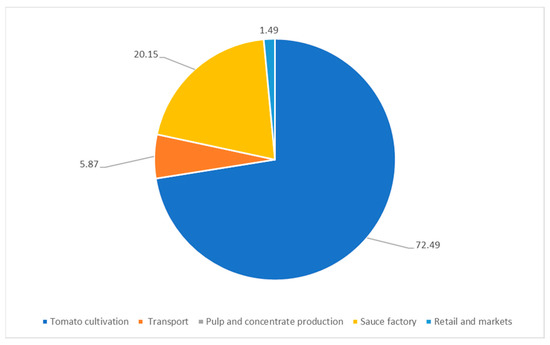
Figure 2.
Total edible FLW per lifecycle stage: percentage values.
Approximately 79.8% of the total FLW (corresponding to 64.27 g) produced during the tomato sauce supply chain, is represented by edible parts and are composed of green, sick, rotten, crushed or broken tomatoes, wrong labelling receipts errors, and problems during tomato sauce stocks, while the remaining part (16.3 g in absolute terms) is represented by inedible parts mainly composed of peels, seeds, and inert waste.
The total amount of inedible parts is created only during the production of pulp and tomato concentrate (lifecycle stage: pulp and concentrate production). On the other hand, by considering the only edible parts of waste (i.e., food only) the stage most responsible in percentage terms is the cultivation stage (the edible parts of FLW produced in this stage account for 72.49% of the total edible parts).
Loss of food in the field accounts for approximately 11% of the total FLW due to the quality selection during the harvesting phase, while during the loading, unloading and transport phases the loss of food amounts to 1%.
During the primary and secondary production stages (pulp and concentrate production + sauce factory), the FLW is limited to 20.1% of the edible parts. More importantly, almost all the FLW of the edible portion during the production stage is used in alternative productions, such as that of animal feed, energy recovery and food banks, as discussed in detail in the following subsection.
4.2. Causes, Allocation and Destinations of FLW
Bearing in mind the second aim of our study and in order to address the causes of FLW during Tomato and Basil sauce supply chain, we firstly identified the types of FLW within each stage, as reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
FLW type and causes.
When considering the total FLW generated during the Barilla Tomato and Basil supply chain, the distinction into causes and lifecycle stages enabled us to highlight that approximately 57.8% of the total FLW is due to “tomato quality standardization” because, in the cultivation phase, unripe and non-quality tomatoes (rotten and diseased) are discarded for the subsequent transition to the tomato sauce production process.
Secondly, approximately 20.2% of the total FLW (8.77 g + 7.46 g= 16.23 g) is concentrated in the pulp and concentrate production. It is important to note that these are “pure” losses because the removed materials are inedible parts consisting of tomato skins, seeds and inert waste. Specifically, on one hand, tomato skins and seeds (8.77 g) derive from the separate-skin sub-phase, as tomatoes, before being transformed into pulp, undergo a process that allows the removal of the seeds, of the consistent green parts and of a good part of the skins. On the other hand, inert waste (7.46 g) is produced during the washing and sorting phase because the machinery separates the inert materials from the tomato that will be transformed into pulp.
Thirdly, approximately 16.7% of the total FLW is generated within the sauce factory (stage). Indeed, by distinguishing the causes, it can be seen that the amount of loss and waste generated in this phase, and represented by edible parts, is due to: (i) breakage and/or incorrect labelling (5.35 g), as remnants of tomato pulp are disposed together with septic sacks or sauce that is disposed of due to broken tears and incorrect labeling; (ii) errors in recipes, e.g., discarded liquid sauce because it is taken away from the tubular pasteurizer, which represents a physiological waste (7.34 g); (iii) stocks (0.46 g) represented by product that remains in stock because it has exceeded the deadline for the sale.
Fourthly, about 4.7% of the total FLW is generated during the tomato transport phase (following the cultivation) and is due to crushing and therefore to weight loss/drop due to crushing of the tomatoes as the trailer is filled.
Lastly, approximately 1.2% of the total FLW is generated in the retail phase and the cause is the damage. Indeed, tomato-sauce is an easily preserved and long-term product and the main cause of waste in this phase is the breaking or damaging of packaging that makes the sauce unsellable.
Once the cause of FLW during Tomato and Basil sauce production is clarified, a further issue to explore in order to achieve our third aim, and therefore emphasizing possible re-use and valorization of losses and wastage, is the specification of FLW destinations, as required by the FLW standard. The analyses of this specific aspect reveal a good example of a circularity process, where almost nothing is lost. Indeed, although it has emerged that causes of FLW are due to a number of reasons, and the amount of FLW produced from 344 g of pulp and concentrate that are necessary to produce a 400 g bottle of sauce is very low, it is also possible to state that 85.9% of total FLW is valorized into alternative sectors, while only 14.4% is destined for landfill disposal. Considering the specific alternative destinations, 14.5% of total FLW is used for animal feed and care, 57.9% is not harvested, 12.5% is recovered for energy, and 0.7% is used for human consumption, as highlighted in Table 4.

Table 4.
Destination of FLW.
5. Discussion
Food waste is a relevant issue for the world economy, society and environment, that involves all phases of the FSC [40,42]. However, as has emerged in several studies, and also in the recent directives of the European Union, the European Circular Economy Action Plan [10], and the directive amending the European Waste Framework Directive [43], the union between commitment to reduce food waste and the rethinking of business economic models towards a circular economy could be a stimulus to contribute, if not to the solution, to the resizing of this problem. Specifically, as highlighted by the European Waste Frame Directive [43], improving resource use efficiency and ensuring that waste is considered a resource can help reduce the EU’s dependence on imported raw materials and facilitate the transition to more sustainable management of materials and a circular economy model, thus contributing to the aim of smart, sustainable and inclusive growth envisaged by the Europe 2020 strategy. These improvements would also create important opportunities for local economies and stakeholders, while enhancing synergies between the circular economy and policies on energy, climate, agriculture, industry and research, as well as bringing benefits to the environment, in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and being of benefit to the economy.
In our study we focused on the quantification of FLW generated from the tomato sauce industry, from cultivation to retail. To the best of our knowledge, there are no previous studies that have considered the amount of total FLW generated during this specific FSC. In fact, existing studies have focused more on the emissions in specific FSC phases, probably due to “a lack of reliable and accessible information of wastage from some phases but not from others” [41] (page 35).
The analyses of the Barilla Tomato and Basil sauce revealed that this supply chain can be considered an example of a true circular economy, in which almost nothing is lost. This is an important result if read in consideration of the fact that the FSC is considered one of the main drivers behind several major global environmental problems [41].
The total amount of FLW (80.5 g for producing 344 g of pulp and concentrate produced) in the studied supply chain is mainly concentrated in cultivation, transport, pulp and concentrate production, and sauce factory phases (98.8 %, corresponding to 81.1 g), while the distribution (retail) phase covers only 1.2% of the total FLW (0.96 g). However, the most interesting results, emerging from the inventory carried out according to the FLW standard, are represented by the destinations of FLW and therefore the emphasis on a “second-life” of the discarded materials of the Tomato and Basil supply chain. In fact, it is important to stress that more than 85% of the total FLW are valorized in alternative sectors and for scopes other than production, such as animal feed, energy recovery, and donation to people in need. In other words, the circularity approach adopted highlighted how to reuse inevitable waste and if, and what, edible materials removed from the production process can be donated to people in need. Even though food waste is becoming mainstream, and it is a win–win solution that could save money for farmers, food producers, and people, while avoiding unnecessary exploitation of natural resources, the management of surplus food in food manufacturing companies is still under investigated by practitioners and academics.
Two important considerations can be introduced in the light of the analyses conducted and the existing literature review [41]. On one hand, the quantification of the FLW that occurs along the tomato sauce production chain can be of help for prevention where, for example, during the transport phase, the main cause of the removal of tomatoes from the production chain is the crushing of tomatoes and the subsequent loss of raw materials. Here it should be stressed that the re-use in a circular economy perspective is to be considered only as a second-best solution, while prevention should be the first strategy to be adopted. On the other hand, quantifying wastage in the various phases of FSCs is also effective from an environmental perspective because the produced FLW is re-used and valued in other sectors/ activities and does not contribute to increased environmental impacts from wastage.
6. Conclusions
This study focuses on the important supply chain of tomatoes, its food losses and waste along the FSC and its causes, with the aim of providing a comprehensive theoretical and applied framework for assessing/quantifying the FLW and emphasizing its re-use under a circular economy approach. Indeed, the adoption of this perspective that seeks to use all the raw materials and by-products of the process can represent a stimulus for the donation of the part that, if properly and promptly defined, could be suitable for human consumption.
Bearing the above considerations in mind, the overall analysis of the different and various food production chains and the reporting of good practices in the implementation of “circular” production processes can help both academy and companies acquire greater knowledge and familiarity with sustainable circular economy models, as well as with sustainable production (and consumption) models, ultimately reducing the amount of FLW.
Our research reports the inventory results from cultivation to retail. Although the exclusion of the consumption phase may represent a limitation of our analysis, at the same time this lack could represent a future extension of the work and a possible topic of future research, so that the analysis of waste on consumers can focus more on single and specific products, with a more extensive data collection able to provide reliable estimates of waste at a local level (i.e., at a more disaggregated level than the regional or national level).
Finally, further research may add knowledge on other supply chains in order to enforce, adapt and refine methodologies used for quantifying FLW, thus giving effective pictures of this phenomenon. These contributions can help in the reduction of both loss and waste throughout the entire FSC and give the chance for food companies to be one of the big enablers of the UN’s SDG number 12.3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.P.; Data curation, M.G.; Formal analysis, L.S.; Funding acquisition, L.R.; Investigation, L.P. and M.G.; Methodology, L.S. and M.G.; Project administration, L.R.; Supervision, L.S., L.P. and L.R.; Validation, L.R.; Writing – original draft, L.S. and L.P.
Funding
This research was partially funded by Barilla G. & R. F.lli S.p.A. (Supply Chain Group).
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks all those employed in the Supply Chain Group of Barilla G. & R. F.lli S.p.A. for the collaboration in this research and particularly they are grateful to Nicola Cornini for his constant effort and availability.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gustavsson, J.; Cederberg, C.; Sonesson, U. Global Food Losses and Food Waste, Swedish Institute for Food and Biotechnology (SIK); Food and Agriculture Organization of The United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i2697e.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Grizzetti, B.; Pretato, U.; Lassalletta, L.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J. The contribution of food waste to global and European nitrogen pollution. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 33, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food Wastage Footprint: Impacts on Natural Resources; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/018/i3347e/i3347e.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- BCFN-EIU. Fixing Food 2018. 2018. Available online: http://foodsustainability.eiu.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/34/2016/09/FixingFood2018.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Ge, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Anaerobic digestion of food waste e challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations General Assembly. Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations General Assembly: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Principato, L. Food Waste at the Consumer Level. A Comprehensive Literature Review; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Principato, L.; Pratesi, C.A.; Secondi, L. Towards Zero Waste: An Exploratory Study on Restaurant managers. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 74, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champions 12.3. Road Map to Achieving SDG Target 12.3. Available online: https://champions123.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/18_WP_Champions_ProgressUpdate_final.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions Closing the Loop—An EU Action Plan for the Circular Economy 2015; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, C.; Lipinski, B.; Robertson, K.; Dias, D.; Gavilan, I.; Gréverath, P.; Fonseca, J.; Van Otterdijk, R.; Timmermans, T.; Lomax, J.; et al. Food Loss and Waste Accounting and Reporting Standard. Available online: https://www.wri.org/sites/default/files/REP_FLW_Standard.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2019).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cellura, M.; Longo, S.; Mistretta, M. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of protected crops: An Italian case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 28, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.; Vignali, G. Life cycle assessment of a packaged tomato puree: A comparison of environmental impacts produced by different life cycle phases. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 73, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliotis, K.; Detsis, V.; Pappia, C. Life cycle assessment of bean production in the Prespa National Park, Greece. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, C.; Faccilongo, N.; Di Gioia, L.; Messineo, A. Food waste recovery into energy in a circular economy perspective: A comprehensive review of aspects related to plant operation and environmental assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Song, H.B.; Song, Y.; Jeong, I.T.; Kim, J.W. Evaluation of food waste disposal options in terms of global warming and energy recovery: Korea. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Rojas-Downing, M.M.; Zhong, Y.; Saffron, C.M.; Liao, W. Life cycle and economic assessment of anaerobic Co-digestion of dairy manure and food waste. Ind. Biotechnol. 2015, 11, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstad Saraiva Scott, A.; Canovas, A. Current practice, challenges and potential methodological improvements in environmental evaluations of food waste prevention—A discussion paper. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 101, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, M.; Fukushima, K.; Kino-Kimata, N.; Nagao, N.; Niwa, C.; Toda, T. The effects of recycling loops in food waste management in Japan: Based on the environmental and economic evaluation of food recycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacArthur, E.; Zumwinkel, K.; Stuchtey, M.R. Growth within: A circular economy vision for a competitive Europe. Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/publications/EllenMacArthurFoundation_Growth-Within_July15.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIRAIG (International Reference Centre for the Life Cycle of Products, Processes and Services). Circular Economy: A Critical Literature Review of Concepts; Polytechnique Montréal: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggieri, A.; Braccini, A.M.; Poponi, S.; Mosconi, E.M. A meta-model of inter-organisational cooperation for the transition to a circular economy. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; Honkasalo, A.; Seppälä, J. Circular Economy: The Concept and its Limitations. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 143, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Skene, K.; Haynes, K. The Circular Economy: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Concept and Application in a Global Context. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 140, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topi, C.; Bilinska, M. The economic case for the circular economy: From food waste to resource. In Food Waste Reduction and Valorisation—Sustainability Assessment and Policy Analysis, 1st ed.; Morone, P., Papendiek, F., Tartiu, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Venkata Mohan, S.; Annie Modestra, J.; Amulya, K.; Butti, S.K.; Velvizhi, G. A circular bioeconomy with biobased products from CO2 sequestration. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, G.; Woolley, E.; Rahimifard, S.; Colwill, J.; White, R.; Needham, L. A methodology for sustainable management of food waste, waste and biomass valorization. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 8, 2209–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, F.; Porto, S.M.; Chinnici, G.; Cascone, G.; Arcidiacono, C. Assessment of citrus pulp availability for biogas production by using a GIS-based model the case study of an area in southern Italy. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 58, 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Valenti, F.; Porto, S.M.C.; Cascone, G.; Arcidiacono, C. Potential biogas production from agricultural by-products in sicily: A case study of citrus pulp and Olive pomace. J. Agric. Eng. 2017, 48, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, F.-C.; Ingrao, C. Assessment of biowaste losses through unsound waste management practices in rural areas and the role of home composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilini, U. Banking on Food: The State of Food Banks in High-Income Countries; Institute of Development Studies: Brighton, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Principato, L.; Ruini, L.; Guidi, M.; Secondi, L. Adopting the circular economy approach on food loss and waste: The case of Italian pasta production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelini, L.; Principato, L.; Iasevoli, G. Understanding Food Sharing Models to Tackle Sustainability Challenges. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 145, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, S.; Corsini, F.; Gusmerotti, N.M.; Frey, M. Food sharing: Making Sense between New Business Models and Responsible Social Initiatives for Food Waste Prevention. In Economics and Policy of Energy and the Environment; FrancoAngeli: Milano, Italy, 2017; pp. 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrone, P.; Melacini, M.; Perego, A.; Sert, S. Reducing food waste in food manufacturing companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, Z.; Wanga, J.; Gaoa, R.; Yea, F.; Zhaoa, G. Sustainable valorisation of tomato pomace: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Rivero, A.; García-Navarro, J. Best practices for the management of end-of-life gypsum in a circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, S.; Caldeira, C.; Eriksson, M.; Hanssen, O.J.; Hauser, H.E.; van Holsteijn, F.; Liu, G.; Östergren, K.; Parry, A.; Secondi, L.; et al. Food waste accounting methodologies: Challenges, opportunities, and further advancements. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 20, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstad, A.K.; Cánovas, A.; Valle, R. Consideration of food wastage along the supply chain in lifecycle assessments: A mini-review based on the case of tomatoes. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secondi, L.; Principato, L.; Laureti, T. Household food waste behaviour in EU-27 countries: A multilevel analysis. Food Policy 2015, 56, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council, Directive (EU) 2018/851 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 Amending Directive 2008/98/EC on Waste; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).