Abstract
This paper introduces energy consumption and carbon emission into the analysis framework of the green productivity of tourism. By comparing and analyzing the two main methods used to evaluate the energy consumption and carbon emission estimations of tourism, namely, the “top-down” and “bottom-up” method, and considering the availability of data, the “bottom-up” method was adopted to evaluate the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the Yangtze River Economic Zone (YREZ). Then, using the Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) index in the super-efficiency data envelopment analysis (DEA) model, the green productivity of the tourism in 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ from 2006 to 2015 was measured. The empirical results show that: (1) The energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ have increased steadily over the past 10 years, which has caused a certain degree of pollution to the environment, indicating that tourism is no longer a “smoke-free industry”; (2) there are significant provincial differences between the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ, with Shanghai always ranking first, while Guizhou and Yunnan ranks last, which represents that the tourism economic development level is positively correlated with the tourism energy consumption and carbon emissions; (3) the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ shows a fluctuating increasing trend in the past 10 years, and technological progress has become the main reason for its growth in green productivity; and (4) the green productivity of tourism in 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ can be divided into three types: Progressive type of tourism green development, stagnant type of tourism green development, and declining type of tourism green development. Consequently, different types of provinces should explore effective dependency paths based on their own conditions.
1. Introduction
The YREZ is an important link between the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, which covers more than 20% of the land area in China, and the proportion of GDP and population in this area is more than 40% of the whole country. Furthermore, there are unique and abundant human tourism resources and natural tourism resources along the Yangtze River [1]. However, for a long time, the rapid growth and continuous expansion of the economic scale of tourism in the YREZ have been heavily dependent on the input of resource elements, resulting in a series of issues, such as high resource consumption, low development and utilization rates, low economic output, environmental pollution, and ecological destruction, which have seriously affected the quality and efficiency of green tourism development [2]. Therefore, tourism in the YREZ needs to be changed from extensive to intensive, and from quantity expansion to quality improvement [3]. In 2014, the State Council promulgated the guiding opinion on relying on the golden waterway to promote the development of the YREZ [4], and put forward the idea of creating tourist cities along the Yangtze River, opening high-quality tourist routes, speeding up the development of characteristic tourism, and promoting the transformation and upgrading of tourism. Therefore, through the study of green productivity of tourism in the YREZ, we can determine the contribution of green tourism elements’ input into the provinces and cities along the Yangtze River, and reveal the inherent law of the green development, transformation, upgrading, and balanced development of tourism, which is expected to provide some theoretical guidance and decision-making reference for exploring the way to improve green productivity of tourism in the YREZ, and provide new ideas for the creation of the International Golden Tourism Belt and the growth of the green tourism economy [1,3].
Total factor productivity (TFP), also called system productivity, refers to “the efficiency of production activities in a certain period of time”. It is a productivity index that is used to measure the total output of per unit of total input, that is, the ratio of total output to total factor input [5]. TFP can reflect the growth trend of high-end production factors, such as technology, management, and knowledge, and their contribution to economic development. Their growth rate is often regarded as an indicator of scientific and technological progress. However, if the constraints on resources and the environment are ignored, the productivity measurement will be deviant. The green total factor productivity (GTFP) is lower than the traditional TFP [6]. Compared with TFP, GTFP integrates resources and the environment into the measurement framework, and is known as actual, environmentally-sensitive, or green TFP [7]. It regards environment pollution as the input factor [8], or regards environment pollution as the non-expected output [9], or constructs the environmental comprehensive index to transfer the output into green output [10]. In recent years, GTFP, as an important indicator of the quality of regional economic growth and environmental management efficiency, has been widely researched by scholars. At present, scholars have carried out systematic studies on industrial green productivity [7,11,12,13], agricultural green productivity [14,15], manufacturing green productivity [16], and so on, especially in the field of industrial research. In the field of tourism, some scholars regard carbon emission efficiency as an important indicator to measure the GTFP of tourism [17]. However, most of these studies only take traditional capital and labor factors as input indicators to measure the TFP of tourism, and less consideration is given to the resources and environment factors that are closely related to the sustainable development of tourism [18]. In fact, based on the accurate measurement of the GTFP of tourism, the technological progress efficiency can be improved, which provides a strong basis for the formulation of sustainable policies of tourism development [19]. However, there is insufficient attention on GTFP of tourism in the YREZ, and there is also a lack of research on the development strategies to promote the optimization and transformation of its tourism structure, while the path design and institutional innovation to enhance productivity are also relatively scarce; only a few studies have discussed the GTFP of tourism [3] and their study area is a coastal area. In view of the regional characteristics of the development of tourism green industry efficiency, this paper measures the evolution and development of green tourism industry efficiency in the YREZ, and puts forward a targeted promotion strategy. It is conducive to the healthy development of the tourism economy in the YREZ. Moreover, it enriches the theory of green tourism efficiency, and has great significance as a reference for the study of green tourism efficiency in other provinces and cities both in China and internationally.
2. Study Area, Study Methods and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
The YREZ refers to the economic development circle along the Yangtze River, covering 11 provinces and cities, including Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, and Yunnan, which spans eastern, central, and western China. It connects the east with the west, and links the region to rivers and seas (Figure 1). The YREZ Strategy is important for the development of the country. Its development philosophy is to “take great protection and not engage in large-scale development”. It emphasizes the coordination of economic development and ecological protection, and industrial development should be based on the premise of protecting the ecology and take the path of green, low-carbon, and sustainable development. The quality level of scenic spots in China is divided into five levels. From high to low, the order is: AAAAA, AAAA, AAA, AA, and A-level scenic spots [20]. Tourism is an important industry in the YREZ, which is large and has good development vitality. The number of A-level scenic spots in the YREZ is 3602, accounting for 40.23% of the national A-level scenic spots; the number of tourists is 4.929 billion, accounting for 46.50% of the national tourism; the total tourism revenue accounts for 44.21% of the total tourism revenue in the country, with the total tourism revenue in 2015 reaching 506.2597 billion RMB, accounting for 18.08% of the GDP of the YREZ, which contributed greatly to the economic development of the YREZ [21]. As an important part of the industrial development in the YREZ and the development of national tourism, tourism should also be combined with the concept of green development. The green production efficiency of the tourism industry should be improved, and the active role of the tourism industry in protecting the ecology and reducing pollution should be considered, which is regarded as an important engine for the green development of the YREZ.
Figure 1.
Yangtze River Economic Zone location map.
2.2. Study Methods
Green productivity considers energy consumption as an input, and carbon emission is considered as an undesirable output [22], while governments at all levels have not directly calculated the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry. Both the domestic and foreign literature estimate the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry [23]. Therefore, in this study, the “bottom up” method is used to estimate the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry in the YREZ. Then, the super-efficiency DEA model and ML index are applied to measure the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ. Finally, the characteristics of the evolution of green productivity in the YREZ are analyzed.
2.2.1. “Bottom up” Method
There are two main methods for estimating the energy consumption and carbon emissions in the tourism industry: Top-down and bottom-up. The top-down method is mainly based on the use of national tourism satellite accounts [24,25], or is based on national economic accounting and uses the input-output model to estimate the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry [26,27]. The bottom-up method divides the tourism industry into the three categories of tourism transportation, accommodation, and tourism activities, and the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry are estimated based on tourists’ consumption of these three categories [28,29]. Among them, tourism activities refer to people’s short-term departure from their usual environment for leisure, business, and other purposes, travel to other places, and stopovers in the area [30]. The top-down method and the bottom-up method have similar estimates of the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry [31]. According to the availability of data, the bottom-up method is selected to estimate the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the tourism industry in the YREZ. The equation is expressed as follows:
In Equation (1), Ct refers to the energy consumption/carbon emissions of the tourism industry; CTt is used as the energy consumption/carbon emissions of tourism transport; CHt indicates the energy consumption/carbon emissions of tourism accommodation; and CRt refers to the energy consumption/carbon emissions of tourism activities.
The estimated equation of CTt for the energy consumption/carbon emissions of tourism traffic is expressed as follows:
In Equation (2), Qit represents the passenger turnover of the ith transportation (including railway, highway, water transport, and aviation); and fi is the proportion of tourists in the passenger turnover of the ith transportation. According to the study of Wang Kai et al., the fi of railway, highway, water transport, and aviation are 31.6%, 13.8%, 10.6%, and 64.7%, respectively [32]; ai refers to the energy consumption coefficient/carbon emissions factor of the ith transportation. Because of the difference in the classification of tourism traffic and the value of energy consumption coefficient/carbon emission factors at home and abroad, this paper mainly refers to domestic research. The energy consumption coefficients of railway, highway, and aviation are 1 MJ/pkm, 1.8 MJ/pkm, and 2 MJ/pkm, respectively [33]. Since the value of the energy consumption coefficient of water transport is not found in domestic research, the water transport energy consumption coefficient is 2.4 MJ/pkm according to the study of Becken and Patterson [31]. The carbon emission factors of railway, highway, water transport, and aviation are taken as 27 g/pkm, 133 g/pkm, 106 g/pkm, and 137 g/pkm, respectively [32].
The estimated equation of CTt for the energy consumption/carbon emissions of tourism accommodation is expressed as follows:
In Equation (3), Nt refers to the number of room beds; lt is the room occupancy rate; T represents the number of days in a year (the general value is 365 days); and β is the energy consumption coefficient/carbon emissions factor of tourism accommodation. Due to the differences in the value of the energy consumption factor/carbon emissions factor among various scholars, this paper mainly refers to the research of domestic scholars. The energy consumption coefficient of tourism accommodation is 155 MJ/bed night [33], and the carbon emissions factor is 245.8 g/pkm [32].
The estimated equation of CTt for the energy consumption/carbon emissions of tourism activities is expressed as follows:
In Equation (4), Pkt represents the number of tourists of the kth activities (including sightseeing, leisure vacation, visiting relatives and friends, business meetings, and others); and gk is the energy consumption coefficient/carbon emissions factor of the kth activities. Based on the research of domestic scholars, the energy consumption coefficients of tourism, sightseeing, leisure vacation, visiting relatives and friends, business meetings, and others are 8.5 MJ/person, 26.5 MJ/person, 12 MJ/person, 16 MJ/person, and 3.5 MJ/person, respectively, and the carbon emissions factors are 417 g/person, 1670 g/person, 591 g/person, 786 g/person, and 172 g/person, respectively [33].
2.2.2. Super-Efficiency DEA Model and ML Index
Green productivity refers to the economic performance of the industry under environmental constraints. Carbon emission is regarded as an undesired output to estimate the TFP of the industry [34,35]. The DEA model is a method used to evaluate the efficiency of decision-making units with multiple inputs and outputs. It takes the study object as a decision-making unit (DMU) and interprets the efficiency through the input-output ratio of the study object, and then finds out the effective production frontier and the gap between the study object and the effective production frontier, which is used to judge whether the economic study object is effective or not. Its advantage is that the production frontier can be obtained by linear programming without using any function or hypothesis [36]. The super-efficiency DEA model is an important method for measuring green productivity. The degree of relative change of GTFP is obtained by comparing the actual green output level with the frontier level by a directional distance function [37]. The directional distance function (DDF) is used to represent a steady increase of the expected output during production, while minimizing undesired output. That is, under the conditions of the established direction, h = (hy, hz), input, x, and the environmental technology set, P(x), the expected output increases by a certain proportion, while the undesired output maintains a reduction of the same proportion. Assuming that the direction vector of the output expansion is h = (hy, −hz), the output directional distance function can be defined as:
The above formula represents the maximum multiple β of the expansion and contraction of the output vector, (y, z), when moving to the production frontier along the direction, h = (hy, hz), under the condition of the established input, x, and the environmental technology set, P(x).
When using the DEA model to obtain results, scholars mainly use the Malmquist Index and the ML Index. The ML index is actually a modified Malmquist index. The input data of these two indexes is the same, but the output data is different. The traditional Malmquist index is calculated based on the output distance function. It considers the “good output” and does not consider the “bad output” of pollution emissions, while the ML index is calculated based on the directional distance function. It increases the good output while reducing the bad output, which is impossible for the output distance function [10]. The ML index is still effective when considering the negative output caused by carbon emissions. Therefore, the ML Index was chosen to measure the green productivity of tourism (GTFP) in the YREZ. The ML index represents the productivity growth from the period, t, to the period, t + 1. If the ML index is greater than 1, it indicates a productivity growth; if the ML index is less than 1, it indicates a productivity decline; and if the ML index is equal to 1, it indicates no change in productivity. Through the directional distance function, the ML productivity index can be further decomposed into the efficiency improvement index (EFFCH index) and technological progress index (TECH index). The TECH index indicates the moving speed of the production frontier of production technology from the period, t, to the period, t + 1; that is, the degree of innovation of production technology. When the TECH index is greater than 1, the production technology is improved; when the TECH index is less than 1, the production technology is decreased; and when TECH index is equal to 1, the production technology does not change. The EFFCH index measures the degree of the production system’s catch-up for the production possibility boundary from the period, t, to the period, t + 1, which indicates the change in the degree of relative efficiency under the conditions of a constant scale reward and free disposal of factors. When the EFFCH index is greater than 1, the technical efficiency is improved; when the EFFCH index is less than 1, the technical efficiency is decreased; and when the EFFCH index is equal to 1, the technical efficiency does not change. Based on the study of Zhang et al. [38], for any provincial region, I, in the YREZ, the input factor vector (including tourism capital, tourism labor, and tourism energy consumption) is represented by x; y refers to the expected output vector (including operating income, tax, and surcharge of tourism enterprises); z is the undesired output vector (including the carbon emissions of tourism); and h represents the direction vector of the output. Therefore, the ML index from the current year to the next year is:
2.3. Data Sources
Based on the availability and continuity of data, the author selected the data of 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ from 2006 to 2015 as the measurement object. Among them, the tourism traffic indexes, such as passenger turnover of railway, highway, water transport, and aviation, are derived from the China Statistical Yearbook [39] and the statistical yearbooks of the provinces and cities in the YREZ. Some indexes are derived from the China Tourism Statistics Yearbook, including the tourist accommodation indexes, such as the number of beds and the room occupancy rate; the capital input indexes, such as the original cost of the fixed assets of tourism enterprises; the labor input indexes, such as the employees of tourism enterprises; and the expected output indexes, such as the operating income, tax, and surcharge of tourism enterprises [40]. The tourism activities indexes, such as the number of tourists who are sightseeing, on leisure vacation, visiting relatives and friends, and attending business meetings, are estimated according to the Tourism Sampling Survey Data [41]. The data sources of the indicators are shown in Appendix A. Figure 2, and Table 1 and Table 2 are calculated from the source data in the statistical yearbook by formulas.
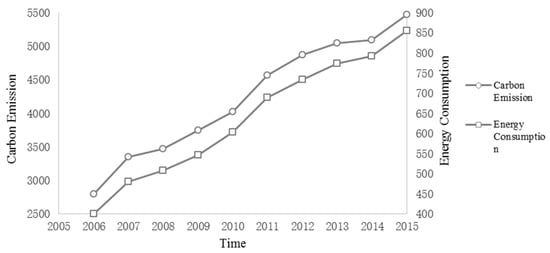
Figure 2.
Energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the Yangtze. River Economic Zone during 2006–2015.

Table 1.
Energy consumption of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the Yangtze. River Economic Zone (MJ).

Table 2.
Carbon emissions of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the Yangtze River. Economic Zone (Ton).
3. Research Process and Results Analysis
3.1. Analysis of the Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions of Tourism in the YREZ
The “bottom-up” method was adopted to evaluate the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ. It was found that the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the entire YREZ have been increasing from 2006 to 2015. By 2015, the energy consumption of tourism in the YREZ reached 854.80 MJ, with an average annual growth rate of 8.78%; and the carbon emissions of tourism reached 5469.48 × 104t, with an average annual growth rate of 7.73% (Figure 2). Over the past 10 years, the annual growth rate of domestic tourism income and inbound tourism income in the YREZ is 20.86% and 10.09%, respectively, which shows that the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ will maintain continuous growth with the development of the tourism economy. However, its growth rate is lower than the growth rate of the tourism economy. Since the carbon emissions and energy consumption of tourism are produced by tourists in the process of satisfying tourism demand, that is, in tourism transportation, tourism accommodation, and tourism activities [28]. Therefore, the fundamental reason for the continuous growth of the carbon emissions and energy consumption of tourism in the YREZ from 2006 to 2015 is the continuous expansion of the tourism scale, that is, the surge in the tourism population.
From comparing and analyzing the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in provinces and cities in the YREZ during 2006–2015 it is evident that the carbon emissions of tourism in the Jiangsu province shows a slight downward trend. However, the overall energy consumption of tourism shows a rising trend. In addition, the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism of the other 10 provinces and cities show an increasing trend over the past 10 years. Except for the sustainable growth of the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in Jiangxi, Chongqing, and Hunan, the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism of the other eight provinces and cities are in a state of fluctuating growth. That is, in a few years, there has been a slight decrease in tourism energy consumption and carbon emissions (Table 1 and Table 2).
Comparing the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism of 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ vertically, the authors find that the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism of these 11 provinces and cities are significantly different and can be roughly divided into four gradients. The first gradient includes Jiangxi, Guizhou, Chongqing, and Yunnan, which have the lowest overall energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism; the second gradient includes Anhui, Hubei, and Hunan, and their energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism are more than the first gradient; the third gradient includes Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Sichuan, and they have more energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism than the provinces and cities of the first and second gradients; Shanghai is in the fourth gradient, with its energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism being far more than the other 10 provinces and cities in the YREZ. Referring to the tourism economic development level of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ, it can be found that the tourism economic development levels of provinces and cities where energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism are in the first and second gradients is lower than that of other provinces and cities. Additionally, the tourism economic development levels of provinces and cities that are in the third and fourth gradients are more than other provinces and cities. This indicates that the carbon emissions and energy consumption of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ are closely related to the tourism economic development level, with a higher tourism economic development level related to a higher energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism. This is mainly because the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ have different tourism consumptions due to the difference in the number of tourists, which leads to a different development of each tourism economy, and different carbon emissions and energy consumption of tourism in the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ. For example, Shanghai has many tourists, a developed tourism economy, and high carbon emissions and energy consumption of tourism, whereas Guizhou is the opposite. (Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3).

Table 3.
Number of tourists of the 11 provinces and cities in the Yangtze River. Economic Zone (Ten thousand person-time).
Previous studies have shown that tourism is not a smokeless industry, and tourist activities generated by tourism development and tourism industry activities that meet the needs of tourists will increase energy consumption and carbon emissions, which results in environmental problems [28,42]. The United Nations World Tourism Organization has stated that carbon emissions from tourism accounts for 4.9% of the total anthropogenic carbon emission in the world, and the impact of carbon emissions is about 14% of the global greenhouse effect [43]. Wang Kai et al. verify that the economic growth of tourism is at the cost of carbon emissions through Granger causality [32]. In terms of time, the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ and its 11 provinces and cities are, overall, increasing; in terms of space, the provinces and cities with a higher tourism economy development level in the YREZ have a higher energy consumption and carbon emissions. These indicate that the tourism economy development in the YREZ will inevitably increase tourism energy consumption and carbon emissions, which is consistent with the findings of scholars at home and abroad on tourism energy consumption and carbon emissions.
3.2. Analysis of Green Productivity of Tourism in the YREZ
First, the total energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ can be obtained from Table 1 and Table 2. Then, combined with the four indicators, including the original cost of the fixed assets of tourism enterprises, employees of tourism enterprises, operating income of tourism enterprises, and tax and surcharge of tourism enterprises (in Appendix A), the MATLAB 7.0 software is used to calculate the overall value of the ML index of the GTFP for the nine provinces and two municipalities in the YREZ from 2007 to 2015 (Figure 3). From Figure 3, we can see that the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ shows a trend of growth and decline alternately from 2007 to 2015. However, the ML index values of the green productivity of tourism are all greater than 1, which means that the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ has maintained a sustained growth trend in the past decade [44]. Specifically, in 2015, the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ increased by more than 4.5% compared with 2007, indicating that the green economic performance of tourism in the YREZ has been improved continuously. That is, tourism in the YREZ has obtained better tourism output through lesser energy consumption and carbon emissions during this decade. Green productivity can be decomposed into the EFFCH index and TECH index. The EFFCH index refers to the catch-up degree of technology laggard reaching the best practice boundary, which is called the “catch-up effect”, while the TECH index refers to the progress degree of the technological frontier, and it is called the “growth effect” [45,46]. Using the MATLAB software for programming, the above acquired ML index was decomposed into the EFFCH index and TECH index. Comparing and analyzing the EFFCH index and TECH index of tourism in the YREZ over the past ten years, the author finds that the EFFCH index and TECH index of tourism in the YREZ shows a fluctuating state, and the two indexes showed a distinct differentiation state. The TECH index is greater than 1 and the EFFCH index was mostly less than 1, indicating that, over the past ten years, the technology of tourism in the YREZ has been constantly innovating and progressing. It has achieved a good “growth effect”, while “technical efficiency” has declined, and the “catch-up effect” has weakened. The growth of the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ is mainly due to the increases in technological progress (Figure 3). Therefore, it can be inferred that, because the YREZ adheres to innovation and development, and pays attention to technology investment and research, the efficiency of technological innovation is improved continuously [47]. Technological progress continues to release the growth effect in the process of constant accumulation, digestion, and absorption, while the technological efficiency does not achieve the complete release of the catch-up effect under the squeeze of technological progress. Therefore, technological progress gradually becomes the main driving force for the green growth of tourism in the YREZ in the long run, and the catch-up effect of technological efficiency should continue to be strengthened [44].
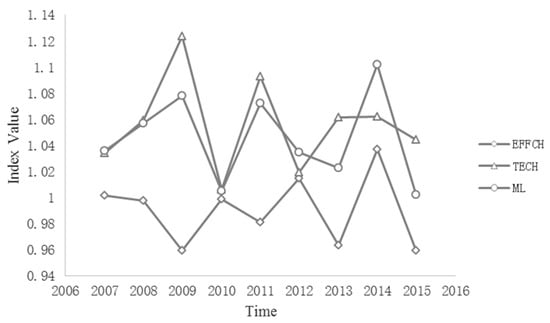
Figure 3.
The Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) index, efficiency improvement index (EFFCH index) and technological progress index (TECH index) in the Yangtze River Economic Zone from 2006 to 2015.
Similar to the total index values of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ obtained above (based on Table 1 and Table 2) and using the MATLAB 7.0 software for programming, the author can also obtain the means of the ML index, EFFCH index, and TECH index of tourism for each province and municipality in the YREZ from 2006 to 2015, as shown in Table 4. Table 1 shows that there are significant differences in the green productivities of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ. They are mainly divided into three types. The first type is the progressive type of tourism green development, that is, the average green productivity of tourism is greater than 1 and the overall green productivity of tourism is increasing [48]. It includes Shanghai, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Sichuan. Jiangxi, Hunan, and Sichuan, which all have rapid green development, and the average growth rate of green productivity of tourism is 10.37, 8.045, and 6.87, respectively. Since the averages of their efficiency improvement indexes and technological progress indexes in Anhui, Jiangxi, Hunan, Chongqing, and Yunnan are greater than 1, the tourism green development in these provinces and city is mainly driven by both the “catch-up effect” and “growth effect”. The averages of the technological progress indexes in Shanghai, Sichuan, and Hubei are more than 1, and the efficiency improvement indexes are less than or equal to 1, indicating that the tourism green development in these provinces and city relies mainly on the “growth effect” brought about by technological progress, while the “catch-up effect”, brought about by efficiency improvement, is basically completed. The second type is the stagnant type of tourism green development, that is, the average green productivity of tourism is equal to 1, and the overall green productivity of tourism is invariant [48]. It includes the Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces. The main reason for the stagnation of the green productivity of tourism of these two provinces is that the “catch-up effect” of tourism of the two provinces has been released completely, while the “growth effect” is not obvious. That is, the two provinces pay less attention to technological innovation and investment into tourism. The third type is the declining type of tourism green development; that is, the average green productivity of tourism is less than 1, and the overall green productivity of tourism is declining. In the YREZ, only the tourism development of the Guizhou Province is declining, and its tourism green productivity has decreased by 4.02%. Although Guizhou attaches importance to the efficiency improvement of tourism green development, it is limited by the concept of development, technological support, social economy, and other factors, so its technology innovation in tourism is lacking [48]. This negates the “catch-up effect” brought by efficiency progress. As a result, its tourism development is blocked. (Table 4).

Table 4.
Average of the ML index, EFFCH index, and TECH index of the 11 provinces and cities in the Yangtze River Economic Zone.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
4.1. Conclusions
Based on the evaluation of the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ by using the bottom-up method, this paper adds the estimated carbon emissions of tourism to the indicator system of tourism green productivity output as an undesired output, and then uses the Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index method to consider the non-expected output to measure the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ from 2006 to 2015. The conclusions are as follows: (1) The energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism in the YREZ show a steady growth trend in the past ten years, but the growth rate is lower than the speed of the tourism economic development; (2) the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ can be divided into four gradients, among which Guizhou, Chongqing, and Yunnan have lower emissions, and Shanghai always ranks first, which shows that the tourism economy development level and the energy consumption of tourism are positively correlated with carbon emissions; (3) the green productivity of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ can be divided into three types: The provinces and cities that belong to the progressive type of tourism green development mostly driven by the “catch-up effect” and “growth effect”; the stagnant type of tourism green development, such as Jiangsu and Zhejiang, of which the technological innovation investment in tourism is insufficient; and the declining type of tourism green development, such as Guizhou, of which the catch-up effect is weak and the growth effect has not yet been completed; (4) the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ has maintained a growing trend over the past ten years, which is mainly due to the growth effect brought by “technological progress”, and the catch-up effect brought by “efficiency improvement” is not obvious. This conclusion is basically consistent with the existing research results that the main driving force of green productivity in the YREZ is technological progress [49,50]. Since the reform 40 years ago, the evolution characteristics of the driving force of green productivity of tourism in the YREZ is still a key scientific issue worthy of further study. Continuous in-depth study of this problem will help to the explore the regional economic development model of the YREZ. Drawing on the relevant research results [1,51,52], we can infer that, before 1990, the promotion of the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ was mainly based on the “efficiency improvement” brought about by institutional reform and the expansion of the scale; from 1990 to 2005, the promotion of the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ was mainly due to the “efficiency improvement” and “technological progress” brought about by the structural optimization and technology introduction. Since 2006, the promotion of the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ mainly depends on the “technological progress” brought by technology introduction and technological innovation. However, from 1990 to 2005, studies on the promotion of the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ are mostly qualitative and simple, and the dynamic mechanism of the promotion of the green productivity of tourism is not accurately analyzed from the spatio-temporal dimension without the application of a mathematical model.
4.2. Countermeasures and Suggestions
The tourism green development in the YREZ shows a good trend. In particular, the “growth effect” brought about by technological progress has become the key core force to promote the tourism green development in the region, which urges tourism as an important supporting industry to promote the construction of ecological civilization in the region. However, there are still three shortcomings of the tourism green development in the YREZ. First, the development power focuses on “technological progress”, but the role of “efficiency improvement” lags; second, the green development of inter-regional tourism is not balanced; and, third, the problems of tourism green development among different provinces are quite different. In view of this, the following policy recommendations are put forward: (1) Technological progress is key to improving energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions. Therefore, the YREZ should comprehensively promote the construction of “smart tourism”, accelerate the development of green and low carbon tourism products with independent intellectual property by introducing advanced technology at home and abroad, increasing the investment of scientific research funds and promoting the transformation of tourism scientific and technological achievements, continue to increase investment in scientific research funds, and promote the transformation of scientific and technological achievements in tourism. In addition, tourism enterprises should be guided to adopt green and clean production methods to realize technological progress and scientific and technological innovation in tourism; (2) efficiency improvement is an important driving force for promoting tourism green development. The efficiency improvement index of the YREZ has been below 1 over the past 10 years, which indicates that the rationality of the tourism structure in the YREZ has not been effectively improved. Therefore, the YREZ should be guided by the concept of global tourism and tourism based on the creation of regional tourism industry clusters and cross-border integration of tourism and forestry, industry, agriculture, and other industries. A focus on the development of a new, green, environmental protection tourism industry that meets the “good needs of people’s living” is required; (3) strengthening inter-regional cooperation is an important way to realize tourism green development. In view of the large spatial differences in energy consumption, carbon emissions, and the green productivity of tourism of the 11 provinces and cities in the YREZ, the YREZ should promote interregional cooperation and technological exchanges between the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the zone, especially, by being a leader and growth pole of the Yangtze River Delta, and promote the coordinated development of the Triangle of Central China, Chengdu-Chongqing, and Yunnan-Guizhou areas through the diffusion effect, for example, high-quality talents and advanced green technologies in the Yangtze River Delta flow to the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River; and (4) it is an important consideration to improve the green productivity of tourism by adopting different strategies based on their own comparative advantages. The provinces that belong to the progressive type of tourism green development should pay attention to both technological progress and efficiency improvement, continue to strengthen the technological progress by innovation-driven methods, and promote efficiency improvement by optimizing the industrial structure. The provinces that belong to the stagnant type of tourism green development (Zhejiang and Jiangsu) should improve their green development efficiency by giving full use of their economic and social location advantages, using advanced tourism energy technology in Shanghai and other regions as a reference. The provinces that belong to the declining type of tourism green development should change the traditional tourism development mode, and shift the focus of development to the track of introducing advanced technologies to promote tourism green development.
4.3. Research Prospect
In this paper, the energy consumption and carbon emissions of tourism were added to the measurement system of the green productivity of tourism, in which energy consumption is regarded as the input variable and carbon emissions are regarded as the non-expected output. The measurement of the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ is more scientific and reasonable. It provides a new research idea for the measurement of TFP of tourism. In addition, it expands the research scope of the green productivity of tourism, and realizes the transfer from the national and provincial perspectives to the inter-basin economic region. However, due to the limited space, this paper has not conducted an in-depth study on the factors affecting the green development efficiency of tourism, and location transportation, consumption level, environmental regulation, resource endowment, and technical conditions that are all important factors affecting the green development efficiency of tourism. In addition, this study on the green productivity of tourism in the YREZ is limited to the span of 10 years from 2006 to 2015. The evolution characteristics of the driving force of the green productivity of tourism have not been analyzed for a longer time span, which has influenced the research depth to some extent. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct further study on the internal mechanism of the green development efficiency of tourism by constructing the influence factor model of the green development efficiency of tourism from different angles.
Author Contributions
G.L. and P.S. are responsible for research design, data collection and analysis; G.L., P.S. and Y.Z. jointly wrote this paper; F.H. and X.L. provide guidance and suggestions. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41501145) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41501191).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and members of the editorial team for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
The data sources of the indicators.
Table A1.
The data sources of the indicators.
| Index Factor | Unit | Data Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a passenger turnover of transportation (including railway, highway, water transport and aviation) | 100 million passenger-km | CSY, PSY |
| 2 | a number of room beds | Bed | CTSY |
| 3 | a room occupancy rate | % | CTSY |
| 4 | a number of tourism activities (including sightseeing, leisure vacation, visiting relatives and friends, business meetings and others) | 10,000 Person-times | TSSD |
| 5 | a original cost of fixed assets of tourism enterprises | 1000 RMB | CTSY |
| 6 | a employees of tourism enterprises | Person | CTSY |
| 7 | a operating income of tourism enterprises | 1000 RMB | CTSY |
| 8 | a tax and surcharge of tourism enterprises | 1000 RMB | CTSY |
| 9 | b energy consumption | MJ | CSY, PSY, CTSY, TSSD |
| 10 | b carbon emission | Ton | CSY, PSY, CTSY, TSSD |
Note: a = data for these indicators can be directly obtained; b = data for these indicators need to be calculated; CSY = “China Statistical Yearbook, 2005–2016” [39]; CTSY = “China Tourism Statistical Yearbook, 2005–2016” [40]; PSY = data from provincial statistical yearbook (11 provinces or cities); TSSD = Tourism Sampling Survey Data [41].
References
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.C. A study on the measurement of tourism efficiency and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River Economic Zone. East China Econ. Manag. 2016, 30, 66–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, N. Temporal and spatial evolution, influencing factors and forming mechanisms of tourism efficiency in Chinese coastal areas based on DEA-Malmquist model. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 2381–2393. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.F. Analyzing variation and convergence of green total factor productivity of Tourism: An empirical study based on the Chinese coastal areas. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2017, 33, 867–872. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- State Council. The Guiding Opinion on Relying on the Golden Waterway to Promote the Development of the Yangtze River Economic Zone. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2014-09/25/content_9092.htm (accessed on 15 June 2018). (In Chinese)
- Zuo, B.; Bao, J.G. Tourism total factor productivity and its regional variation in China from 1992 to 2005. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y. Green industrial revolution in China: A perspective from the change of environmental total factor productivity. Econ. Res. J. 2010, 11, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Jane, G. ‘Green’ productivity growth in China’s industrial economy. Energy Econ. 2014, 44, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, T.J.; Rao, D.S.P. Total factor productivity growth in agriculture: A malmquist index analysis of 93 countries, 1980–2000. Agric. Econ. 2005, 32, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.G.; Zheng, J.H.; Gao, Y.N.; Zhang, N.; Xu, H.P. The ranking of provincial technical efficiency considering environmental factors (1999–2005). Economics 2008, 7, 933–960. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Lan, Q.X.; Gao, M.; Sun, Y.W. Green total factor productivity growth and its determinants in China’s industrial economy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.G.; Lin, J.; Zhu, J.M. Green total factor productivity of hog breeding in China: Application of SE-SBM model and grey relation matrix. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Osei, E.; Yu, M. Sustainable development of China’s industrial economy: An empirical study of the period 2001–2011. Sustainability 2018, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Koike, A.; Wang, J.J. Assessing total factor productivity and efficiency change for farms participating in grain for green program in China: A case study from Ansai, loess plateau. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.G.; Kim, T.H. Analysis of carbon productivity in Korea agriculture. Korean J. Agric. Econ. 2014, 55, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J. Measuring green productivity growth for China’s manufacturing sectors: 1991–2000. Asian Econ. J. 2007, 21, 425–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Huang, Z.F.; Cao, F.D. Spatial pattern of carbon emission efficiency and its influencing factors of Chinese tourism. J. Ecol. 2015, 35, 7150–7160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L. An empirical study on difference and convergence of total factor productivity of Chinese tourism. Tour. Trib. 2013, 28, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Halkos, G.E.; Tzeremes, N.G. A conditional directional distance function approach for measuring regional environmental efficiency: Evidence from UK regions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 227, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Tourism Bureau. Classification and Evaluation of Quality Level of Scenic Spots; China Tourism Press: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese)
- China Tourism Research Institute (CTRI). China Tourism Development Report 2017; China Tourism Press: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S. A decomposition of total productivity growth: A regional analysis of Indian industrial manufacturing growth. Int. J. Prod. Perform. Manag. 2006, 55, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.T.; Wang, J.C. Greenhouse gas emissions of tourism-based leisure farms in Taiwan. Sustainability 2015, 7, 11032–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perch-Nielsen, S.; Sesartic, A.; Stucki, M. The greenhouse gas intensity of the tourism sector: The case of Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaina-Alves, M.; Moutinho, V.; Rui, C. Change in energy-related CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions in Portuguese tourism: A decomposition analysis from 2000 to 2008. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y. A framework to account for the tourism carbon footprint at island destinations. Tour. Manag. 2014, 45, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y. Decomposition of tourism greenhouse gas emissions: Revealing the dynamics between tourism economic growth, technological efficiency, and carbon emissions. Tour. Manag. 2016, 55, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Peeters, P.; Ceron, J.P.; Dubois, G.; Patterson, T.; Richardson, R. The eco-efficiency of tourism. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 54, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, L.; Forsyth, P.; Spurr, R.; Hoque, S. Estimating the carbon footprint of Australian tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2010, 18, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). Recommendations on Tourism Statistics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Travel and Tourism Statistics, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Becken, S.; Patterson, M.; Viner, D. Measuring national carbon dioxide emissions from tourism as a key step towards achieving sustainable tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2006, 14, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Xi, J.C. Study on the Coupling relationship between tourism economic growth and carbon emission in China. J. Tour. 2014, 29, 24–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.H.; Wu, P. Preliminary estimation of energy consumption and carbon dioxide emission of tourism in China. J. Geogr. 2011, 66, 235–243. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Domazlicky, B.R.; Weber, W.L. The measurement of capital and the measurement of productivity growth and efficiency in state manufacturing. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2014, 29, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.H. A green productivity based process planning system for a machining process. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 5085–5105. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, Y.H.B.; Beasley, J.E. Restricting weight flexibility in data envelopment analysis. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1990, 41, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldamak, A.M.; Zolfaghari, S. Review of efficiency ranking methods in data envelopment analysis. Measurement 2017, 106, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Choi, Y. A note on the evolution of directional distance function and its development in energy and environmental studies 1997–2013. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2015. (In Chinese)
- China National Tourism Administration. China Tourism Statistics Yearbook; China Tourism Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2015. (In Chinese)
- China National Tourism Administration. Tourism Sample Survey Data; China Tourism Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2015. (In Chinese)
- Castellani, V.; Sala, S. Sustainable performance index for tourism policy development. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UN World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). Towards a Low Carbon Travel and Tourism Sector. In Proceedings of the The World Economic Forum, Davos, Switzerland, 28 January–1 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.F. Simulation and prediction of energy saving and emission reduction, and green growth of Chinese industry. Chin. Popul.·Resour. Environ. 2018, 16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Decomposing energy productivity change: A distance function approach. Energy 2007, 32, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, M.; Parikh, J.K. Study of efficiency and productivity growth in opencast and underground coal mining in India: A DEA analysis. Energy Econ. 2002, 24, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Q.; Huang, L.; Wen, C.H. Study on technological innovation and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River Economic Zone. China Soft Sci. 2017, 5, 160–170. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Arabi, B.; Munisamy, S.; Emrouznejad, A.; Shadman, F. Power industry restructuring and eco-efficiency changes: A new slacks-based model in Malmquist–Luenberger index measurement. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.G.; Yuan, B.L. Driving force for the green development of industry in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Reform 2016, 32, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, G.C.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, M.H. Spillover effect and decomposition of green economic performance of the city in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Chin. Popul.·Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 75–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.D.; Huang, Z.F.; Wu, J.; Xu, M. The space-time pattern evolution and its driving mechanism of urban tourism development efficiency: A case study of Pan-Yangtze River Delta. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.M.; Deng, L. An emprical research on the Industrial Structure of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Econ. Prob. 2015, 52, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).