Abstract
Salinization hinders the restoration of vegetation in salt-affected soils by negatively impacting plant growth and development. Halophytes play a key role in the restoration of saline and degraded lands due to unique features explaining their growth aptitude in such extreme ecosystems. Suaeda fruticosa is an euhalophyte well known for its medicinal properties and its potential for saline soil phytoremediation. However, excessive salt accumulation in soil limits the development of this species. Research findings increasingly advocate the use of extremophile rhizosphere bacteria as an effective approach to reclaim salinized soils, in conjunction with their salt-alleviating effect on plants. Here, a pot experiment was conducted to assess the role of a halotolerant plant growth-promoting actinobacterium, Glutamicibacter sp., on the growth, nutritional status, and shoot content of proline, total soluble carbohydrates, and phenolic compounds in the halophyte S. fruticosa grown for 60 d under high salinity (600 mM NaCl). Results showed that inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. significantly promoted the growth of inoculated plants under stress conditions. More specifically, bacterial inoculation increased the shoot concentration of proline, total polyphenols, potassium (K+), nitrogen (N), and K+/Na+ ratio in shoots, while significantly decreasing Na+ concentrations. These mechanisms partly explain S. fruticosa tolerance to high saline concentrations. Our findings provide some mechanistic elements at the ecophysiological level, enabling a better understanding of the crucial role of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) in enhancing halophyte growth and highlight their potential for utilization in restoring vegetation in salt-affected soils.
1. Introduction
Soil salinization is a major ecological constraint affecting plant growth and development, with nearly 10% more salt-affected areas annually in various regions of the world [1,2]. Salt currently affects about 7% of the earth’s land surface, or approximately one billion hectares [3]. At the global level, more than two-thirds of salt-affected soils are found in arid and semi-arid regions, with 64% of them situated in arid deserts and steppes [4]. Moreover, in semi-arid and arid regions, high evaporation rates, coupled with limited ion leaching due to low precipitation, lead to further salt accumulation, making soils in these areas infertile [5]. High salt levels in the soil reduce water availability, disrupt metabolic activities, and affect nutrient balance, osmotic regulation, and hydraulic conductivity, leading to decreased plant growth and development [6].
Halophytes are salt-tolerant plants that survive and thrive in highly saline environments owing to unique physiological and molecular mechanisms [7]. Due to the increase in worldwide soil salinization and their potential as sources of valuable products, the environmental and economic significance of halophytes is currently recognized. Interestingly, the microbiome of halophytic plants plays a key role in enhancing plant adaptation to osmolality fluctuations and in promoting the growth and development of salinity-sensitive plants under salt stress [8]. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) are well known for their ability to enhance plant stress tolerance among the microorganisms that interact with plants [9]. These bacteria, which also display biocontrol properties, are beneficial under environmental stresses by promoting several traits related to plant growth and soil health [10]. PGPRs enhance, for instance, plant growth, either directly or indirectly by producing auxins or siderophores, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase, fixing nitrogen (N2), or by solubilizing phosphate and potassium [9,11]. PGPRs may also enhance the salt tolerance of host plants by modulating photosynthetic efficiency, ion homeostasis, the accumulation of osmotic regulators, the synthesis of secondary metabolites, and gene expression related to plant hormone signaling pathways [12,13,14]. PGPRs have been found to boost plant growth in different halophyte species, such as in Salicornia sp., especially under high salt concentrations [15].
Suaeda fruticosa (Amaranthaceae) is a succulent perennial euhalophyte native to arid and semi-arid salt flats and salt marshes [16]. This species thrives in environments characterized by adequate NaCl salinity, enabling the optimal growth and development of this species [17]. Khan et al. [18] suggested that S. fruticosa growth is maximal at NaCl concentrations ranging from 200 to 400 mol m−3, facilitated by efficient osmotic adjustment, reactive oxygen species (ROS) balancing, and Na+ homeostasis. S. fruticosa is regarded as a valuable cash crop due to its medicinal, nutritional, and economic benefits, as well as its potential for use in the phytoremediation of contaminated soil [2,17,19]. S. fruticosa produces high-quality edible oil with a desaturation content ranging from 70% to 80%. In addition to these practical benefits, S. fruticosa is regarded as a suitable species for investigating plant–microorganism interactions in saline environments, which ameliorates the understanding of how euhalophytes in particular can be so competitive in challenging conditions.
A previous study pointed out that inoculation with the halotolerant strain Glutamicibacter sp. significantly enhanced the salt tolerance of S. fruticosa by boosting the plant’s antioxidative capacity, thereby markedly reducing oxidative stress [20]. The present study aimed to examine the effects of Glutamicibacter sp. on various nutritional and biochemical parameters—such as polyphenols, total soluble sugars (TSSs), and proline in S. fruticosa plants grown under both saline and non-saline conditions.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacterial Inoculation on the Growth of S. fruticosa
As shown in Figure 1a,b, S. fruticosa plants exposed to salt stress (600 mM NaCl) showed 36% and 28% reduction in both shoot length and root length, respectively. Inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. mitigated the adverse effect of salt stress on root length, resulting in an 18% increase, while shoot length remained unaffected. Salinity also significantly reduced plant growth (shoot, root, and whole plant) as well as dry weight production (Figure 1c–e). In contrast, Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation significantly alleviated these effects, leading to an increase (20% to 26%) in shoot dry weight (Figure 1c), root dry weight (Figure 1d), and whole-plant dry weight (Figure 1e), compared to non-inoculated salt-treated plants. Thus, Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation markedly improved the survival and growth of S. fruticosa under high salinity. It is noteworthy that under non-saline conditions, inoculation had no significant effect on overall plant growth, except for root dry weight and shoot length (+18% and +12%, respectively, as compared to non-inoculated plants) (Figure 1a,b).
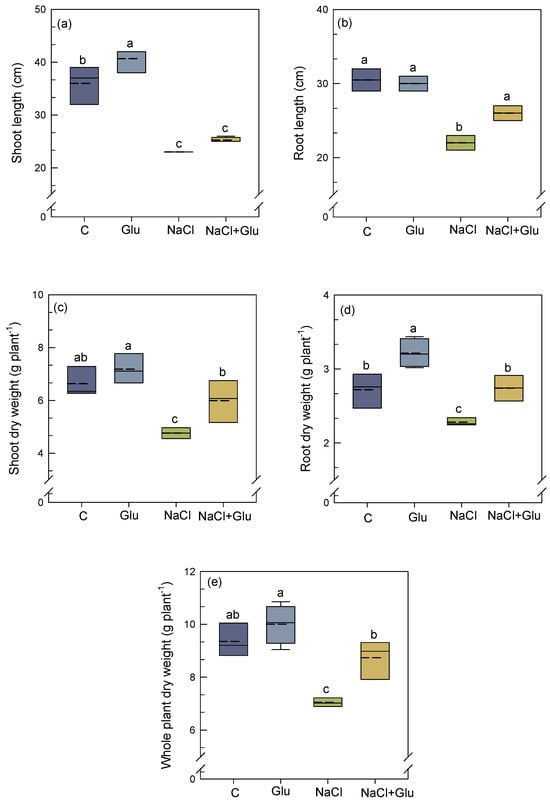
Figure 1.
Effect of Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation on shoot length (a), root length (b), shoot dry weight (c), root dry weight (d), and whole-plant dry weight (e) of S. fruticosa plants under non-saline (0 mM NaCl) and saline (600 mM NaCl) conditions. Values are means of four replicates ± SE, and different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s test. C: control treatment; Glu: Glutamicibacer sp. treatment; NaCl: NaCl treatment; Glu + NaCl: Glutamicibacer sp. + NaCl treatment. The middle line within the boxes represents the median, while the dashed line indicates the mean.
2.2. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacterial Inoculation on Proline, Soluble Sugars, and Polyphenol Contents in S. fruticosa
Shoots of S. fruticosa grown under non-stress conditions and inoculated with Glutamicibacter sp. showed no significant changes in proline and soluble sugar content (Figure 2a,b). However, total polyphenol content significantly increased following inoculation (Figure 2c).
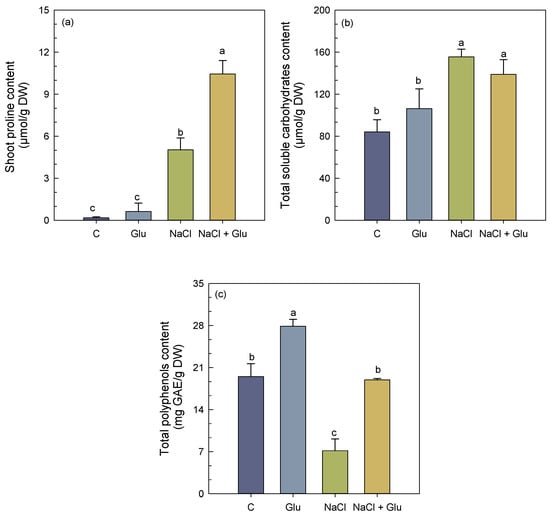
Figure 2.
Effect of Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation on proline content (a), total soluble carbohydrate content (b), and total polyphenol content (c) in the shoots of S. fruticosa plants under non-saline (0 mM NaCl) and saline (600 mM NaCl) conditions. Values are means of four replicates ± SE, and different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s test. C: control treatment; Glu: Glutamicibacer sp. treatment; NaCl: NaCl treatment; Glu + NaCl: Glutamicibacer sp. + NaCl treatment.
Under salt stress conditions, S. fruticosa shoots exhibited a 96% and 58% increase in proline and soluble sugar content, respectively, compared to the control. In contrast, total polyphenol content decreased by 65% under the same conditions. The inoculation of salt-stressed plants with Glutamicibacter sp. also led to a further increase in shoot proline and total polyphenol content by 43% and 61%, respectively, as compared to stressed non-inoculated plants. No significant changes were observed for shoot total soluble sugar content under these conditions.
2.3. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacterial Inoculation on Sodium (Na+) and Potassium (K+) Content in S. fruticosa
Under salt-free conditions, inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. led to a slight increase in shoot Na+ content (Figure 3a). S. fruticosa plants grown under 600 mM NaCl showed a marked accumulation of Na+, reaching +72% and +60%, respectively, in shoots and roots, as compared to the control plants (Figure 3a,b). This trend was concomitant with a strong decrease in shoot K+ content (−62%), whereas no significant changes were observed in roots (Figure 3c,d). Consequently, the shoot and root K+/Na+ ratio decreased (Figure 3e,f). In salt-stressed S. fruticosa plants inoculated with Glutamicibacter sp., shoot Na+ accumulation decreased by 20%, whereas shoot K+ content increased by 45% (Figure 3a–c). No significant changes regarding root Na+ and K+ contents were observed. Furthermore, the K+/Na+ ratio in shoots and roots was significantly increased in inoculated plants under salt stress (Figure 3e,f).
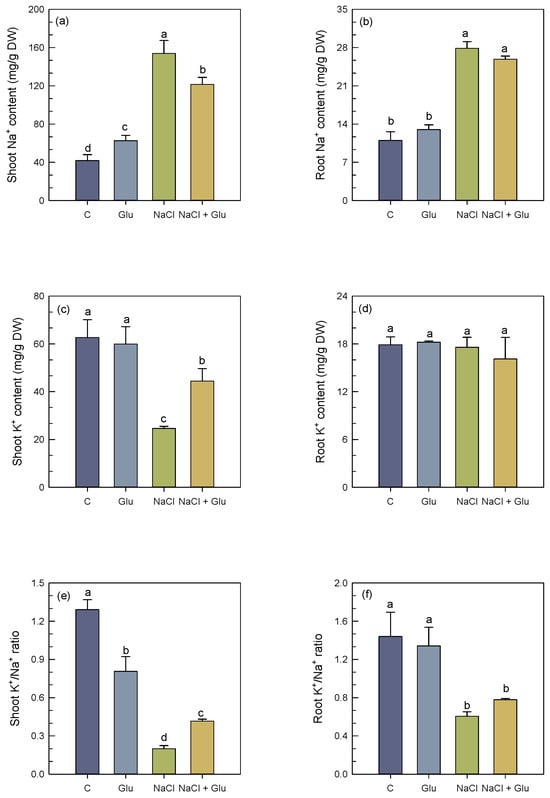
Figure 3.
Effect of Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation on shoot Na+ concentration (a), root Na+ concentration (b), shoot K+ concentration (c), root K+ concentration (d), shoot K+/Na+ ratio (e), and root K+/Na+ ratio (f) of S. fruticosa plants under non-saline (0 mM NaCl) and saline (600 mM NaCl) conditions. Values are means of four replicates ± SE, and different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s test. C: control treatment; Glu: Glutamicibacer sp. treatment; NaCl: NaCl treatment; Glu + NaCl: Glutamicibacer sp. + NaCl treatment.
2.4. Effects of Salt Stress and Bacterial Inoculation on Nitrogen (N) Content in S. fruticose
Under salt-free conditions, S. fruticosa plants inoculated with Glutamicibacter sp. showed a significant increase in root N content, with +20% as compared to non-inoculated control plants (Figure 4b). Salinity treatment did not significantly affect nitrogen levels, neither in shoots nor in roots, when compared to control plants. However, Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation increased shoot N content by 19% (Figure 4a), whereas root content was unchanged as compared to stressed, non-inoculated plants (Figure 4b).
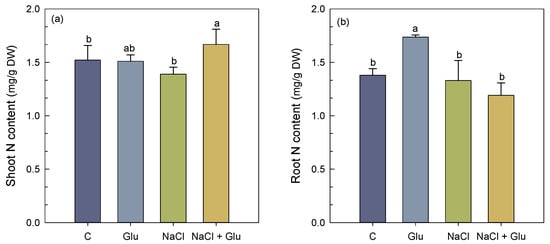
Figure 4.
Effect of Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation on shoot N (a) and root N (b) content of S. fruticosa plants under non-saline (0 mM NaCl) and saline (600 mM NaCl) conditions. Values are means of four replicates ± SE, and different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s test. C: control treatment; Glu: Glutamicibacer sp. treatment; NaCl: NaCl treatment; Glu + NaCl: Glutamicibacer sp. + NaCl treatment.
2.5. Correlation Analysis
A correlation analysis was performed to enhance the precision of data interpretation (Table 1), considering all parameters measured in plants subjected to bacterial inoculation and salt stress. Overall, the findings confirmed that inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. had a beneficial impact, improving S. fruticosa tolerance to salt stress.

Table 1.
Pearson’s correlation matrix analyzing the relationships between the control (C) and Glutamicibacter sp. (Glu) treatments under salt-free conditions, as well as NaCl and NaCl + Glu treatments under salt stress conditions, across the various studied parameters.
Under saline conditions, several significant positive correlations were observed between Glutamicibacter sp. inoculation and various growth and physiological parameters, including shoot and root lengths, shoot and root dry weights, whole-plant dry weight, shoot potassium (K+) content, shoot K+/Na+ ratio, shoot nitrogen (N) content, and shoot polyphenol content (Table 1). On the contrary, a negative correlation was found between the inoculation treatment and shoot sodium (Na+) content (Table 1). It should also be emphasized that the results of the correlation analysis were highly consistent with the findings from the trait-by-trait assessments.
3. Discussion
The association of halophytic plants–PGPR native to saline areas is a biological approach of major significance in the context of improving tolerance against environmental stresses [21]. It has been shown that halotolerant PGPRs significantly improve stress tolerance and hence fitness of the host plants [21,22]. In this regard, a beneficial soil bacterium’s role in boosting plant tolerance to abiotic stresses, including salinity, has been highlighted by several reports [23,24,25].
S. fruticosa is a plant that grows naturally in semi-arid ecosystems like sabkhas, where salinity levels are usually higher than those found in seawater [26]. This species is a euhalophyte; i.e., it requires salinity to thrive. It has been documented that S. fruticosa growth is significantly decreased if soil salinity is outside of the optimal range of 200–400 mM NaCl [18]. Plant response to salt stress can be assessed using pertinent physiological parameters like biomass production, water status, plant sodium status, and K+/Na+ ratio [27]. Our present study indicated that S. fruticosa growth was significantly reduced with 600 mM NaCl. However, inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. significantly increased the shoot and root lengths, as well as the dry weights, of S. fruticosa under salt stress, suggesting that this bacterium effectively mitigates the adverse effects of salinity on halophyte growth. These findings further suggest the possibility of using PGPRs to improve the restoration potential of vegetation in salt-affected soils. PGPRs have been shown to improve the halophyte biomass in species such as Salicornia strobilacea [28], Salicornia bigelovii [29], Limonium sinense [30], S. fruticosa [20], and Asteriscus maritimus [31], particularly at high salt concentrations. PGPRs are believed to enhance halophyte growth by boosting nutrient uptake, ionic homeostasis, osmotic adjustment, and antioxidant defenses.
Inoculating S. fruticosa plants with Glutamicibacter sp. also significantly decreased the translocation of Na+ to shoots while increasing K+ uptake as compared to non-inoculated stressed plants, resulting in higher shoot K+/Na+ values, which is indicative of a reduction in ionic stress following plant inoculation. Our findings are consistent with those on the coastal halophyte L. sinense, for which inoculation with the soil bacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola increased K+ uptake and decreased Na+ accumulation under salt stress conditions [30]. The reduction in Na+ influx and the promotion of K+ uptake are important for plant salt tolerance [32].
Although many salt-affected soils are limited in nitrogen and depend on plant-associated diazotrophs as a source of “new” nitrogen, saline areas can still remain productive [33]. Nitrogen (N) is an essential macronutrient for plant growth and productivity. It is necessary for the synthesis of amino acids, which serve as the building blocks of proteins and enzymes involved in various mechanisms that improve plant tolerance to salt stress [34]. Our data show that Glutamicibacter sp. significantly enhanced nitrogen uptake in the shoots of S. fruticosa grown under salt stress conditions. PGPRs are capable of inducing the expression of genes associated with nitrate and ammonium transport, thereby enhancing the uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) [35,36]. With the assistance of HT-PGPR, plants can better absorb nitrogen, enabling them to grow more effectively under salt stress conditions [23]. PGPRs have been demonstrated to improve the uptake of mineral elements in halophytes, a mechanism widely considered essential for enhancing plant tolerance to salt stress. Growth improvement by PGPRs is always associated with an increase in available nutrient elements (K and N). Therefore, halotolerant PGPR strains can be used as biofertilizers to improve halophyte development under salinity stress conditions.
Osmotic adjustment is a key mechanism for plant adaptation to salt stress, typically achieved through the accumulation of compatible solutes, such as proline and soluble carbohydrates [37]. In our study, salt stress significantly increased the accumulation of both proline and total soluble carbohydrates in S. fruticosa shoots, indicating an active osmotic adjustment response. These nitrogenous compounds play a crucial role in osmoregulation and in protecting plants from damage caused by toxic levels of sodium (Na+) [37]. Compared to salt-stressed non-inoculated plants, inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. led to higher proline content, suggesting that Glutamicibacter sp. contributes to osmotic adjustment under salt stress by stimulating the synthesis or accumulation of osmolytes, thereby helping the plant maintain cellular water potential and protect metabolic functions. Proline, in particular, can accumulate up to high concentrations in the cytoplasm without disrupting cellular structures or metabolic processes. Moreover, it acts as an antioxidant under NaCl stress, thereby reducing oxidative damage in the host plant [38]. Other bacteria, such as halotolerant PGPR strains of Pseudomonas sp. and Bacillus subtilis, have also been shown to increase proline content in salt-stressed halophytic plants like Sulla carnosa after inoculation, highlighting the role of beneficial bacteria in stimulating the accumulation of this compound, which contributes to stress tolerance [39]. Inoculated plants exhibited higher accumulations of total polyphenols in shoots under salt stress conditions. Polyphenols are a group of secondary plant metabolites known to play a significant role in plant responses to abiotic stressors. Recent studies have demonstrated that these compounds mitigate oxidative damage in plant cells caused by reactive oxygen species, thereby preventing the propagation of oxidative chain reactions [40,41]. Our previous data also showed that inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. increased polyphenol content in Phragmites australis under salt stress [20]. Therefore, Glutamicibacter sp. may modulate the biosynthesis of these important secondary metabolites in host plants, contributing to enhanced salt stress tolerance.
Hidri et al. (2022) demonstrated that inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. mitigates the detrimental effects of salinity by enhancing the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, including catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and glutathione reductase (GR). These enzymes collectively contribute to a significant reduction in lipid peroxidation levels in S. fruticosa plants. These findings underscore the role of Glutamicibacter sp. in strengthening the plant’s antioxidant defense system under salt stress. Our current study supports and extends these results by identifying additional physiological changes associated with bacterial inoculation under saline conditions. Specifically, we observed a notable increase in the accumulation of compatible solutes, such as proline, as well as a rise in polyphenol content in S. fruticosa. These compounds are known to contribute to osmotic adjustment and mitigate oxidative stress, indicating that Glutamicibacter sp. promotes salinity tolerance through a dual mechanism involving both metabolic regulation and antioxidant enhancement. Furthermore, Glutamicibacter sp. is capable of producing indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), a key phytohormone involved in plant growth and stress responses [20]. IAA has been shown to regulate antioxidant enzyme activities and support osmotic adjustment under saline conditions [42,43,44]. Collectively, these findings provide strong evidence for the multifaceted role of Glutamicibacter sp. in enhancing salt stress resilience in S. fruticosa.
It is therefore plausible that compounds such as proline, polyphenols, nitrogen (N), and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), whether accumulated in plants as a result of microbial treatment, synthesized by bacteria, or applied exogenously, may contribute to enhanced salt stress tolerance in S. fruticosa. Although the present study did not directly assess the effects of the exogenous application of these compounds, such investigations could provide valuable insights into the physiological and biochemical mechanisms underlying salinity tolerance in this halophytic species. Given the unique adaptive traits of S. fruticosa, the potential effects of exogenous applications remain to be empirically validated.
The ability of these compounds to alleviate salinity stress is well supported by previous studies. For instance, Hosseinifard et al. [45] demonstrated that exogenous proline application enhances osmotic adjustment and stabilizes cellular membranes in halophytes exposed to salt stress. Similarly, Khedr et al. [46] reported that the foliar application of IAA promotes root development and improves water uptake efficiency under saline conditions, thereby enhancing plant growth and resilience. Furthermore, nitrogen supplementation has been shown to support chlorophyll biosynthesis and strengthen antioxidant defenses, leading to improved photosynthetic efficiency and reduced oxidative damage in salt-stressed plants [47]. Polyphenols, owing to their potent antioxidant properties, also play a crucial role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and maintaining redox homeostasis.
Therefore, future studies should focus on evaluating the individual and combined effects of these exogenously applied compounds in S. fruticosa, with particular attention to their influence on physiological and molecular responses under salt stress. Specifically, investigating the direct impact of exogenous IAA applications could offer new insights into hormone-mediated signaling pathways involved in salinity tolerance.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Bacterial Inoculum
S. fruticosa plants were originally collected from the “Enfidha” region (a sabkha area with a semi-arid climate, located 136 km south of Tunis). Young S. fruticosa plants were propagated through cuttings, using 5 cm-long stem segments with leaves taken from these mother plants. These cuttings were cultivated in sterilized soil and then installed in a greenhouse maintained at 25 °C under a 16 h/8 h day/night regime. The properties of the soil used for the growth substrate were as follows: pH of 6.65; containing 0.24 and 0.45 g kg−1 of dry soil of available phosphorus and total nitrogen, respectively, and 0.25, 0.95, 0.65, and 0.05 mEq 100 g−1 of dry soil of sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride, respectively; and 0.05 dS m−1 electrical conductivity.
The plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) strain was Glutamicibacter sp. MK847918, which was obtained from the rhizosphere soil of a salt-impacted region in “Soliman” Sebkha (36°42′03.5″ N, 10°26′00.8″ E), ca. 30 km south of Tunis and characterized by a semi-arid climate. This strain was chosen due to its beneficial properties for plant growth, such as its ability to produce exopolysaccharides (EPSs), siderophores, and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) [20]. Additionally, the bacterial strain was also evaluated for its tolerance to saline conditions [20].
4.2. Experimental Design and Conditions
After 30 d of the pre-treatment phase, uniform S. fruticosa plants were chosen and transferred to pots containing 5 kg of sterilized soil. Each plant was inoculated with 1 mL of the bacterial culture (108 CFU mL−1). Then, 7 d following inoculation, plants were watered three times per week with 50 mL of either a 0 mM or 600 mM NaCl solution. To prevent osmotic shock, NaCl was gradually added at five different concentrations (100, 200, 300, 400, and 600 mM) on alternate days. NaCl levels were selected according to Khan et al. [20]. The experiment consisted of a factorial design with two factors (inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. and salinity), resulting in four treatments in total: (1) control plants (C); (2) plants inoculated with Glutamicibacter sp. (Glu); (3) salt stress plants in the absence of Glutamicibacter sp. (NaCl); and (4) salt stress plants in the presence of Glutamicibacter sp. (NaCl + Glu). Each treatment was performed on four S. fruticosa plants.
After 60 d of salt treatment, plants were harvested and separated into shoots and roots following cleaning with distilled water to remove soil particles. Fresh weight (FW, in g) and dry weight (DW, in g) were then determined.
4.3. Determination of Organic Solutes
4.3.1. Proline
Proline content in shoots was determined using the ninhydrin method, as described by Bates et al. [48]. Aqueous sulfosalicylic (3%) was first homogenized with fresh shoot material. After centrifugation at 20,000× g, the samples were incubated with 1 mL of ninhydrin acid and 1 mL of glacial acetic acid and then boiled at 100 °C for 1 h. The reaction was stopped in an ice bath, and proline was extracted with 2 mL of toluene, and absorbance was read at 520 nm. The proline content in each sample was calculated based on a standard curve prepared with L-proline.
4.3.2. Total Soluble Sugars
TSS content was determined following the method of Yemm and Willis [49]. Briefly, 25 mg of plant dry material was homogenized with 80% ethanol solution. The mixture was incubated at 70 °C for 30 min and then centrifuged at 3000× g for 30 min at 25 °C; 0.5 mL of the supernatant was added to 5 mL of freshly prepared throne solution and 2 mL of ethanol (80%), and the mixture was heated in a boiling water bath for 10 min. After cooling, the absorbance was read at 640 nm with a spectrophotometer. TSS was quantified based on a glucose standard curve determined using glucose.
4.3.3. Total Polyphenol
Phenolic compound contents were quantified using the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent, following Singleton and Rosi’s method [50] slightly modified by Dewanto et al. [51]. Shoot dry powder (1 g) was homogenized with 10 mL of pure methanol for 30 min, and the mixture was filtered. Deionized water and Folin–Ciocalteu reagent were added to the sample extracts. After incubating the mixture for 6 min, a 7% sodium carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was adjusted with distilled water. A further 90 min of dark incubation at room temperature was applied, before determining the absorbance was measured at 760 nm. Gallic acid was used to prepare a standard curve, and results were expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram of DW (mg GAE g−1 DW).
4.4. Inorganic Ion Assay
Shoot and root dry powder (30 mg) was mineralized in 30 mL of nitric acid (0.1 N) to extract inorganic ions. Corning 480 flame photometer was used to determine cation contents (Na+ and K+). The Kjeldahl method [52] was used to assay nitrogen.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
The SPSS 20.0 statistical program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used to perform an analysis of variance (ANOVA) on the data, and the means were compared according to Duncan’s test at p < 0.05. Correlation analysis was performed using XLSTAT software v. 2014.
5. Conclusions
Our results demonstrate that inoculation with Glutamicibacter sp. significantly enhanced growth of S. fruticosa under high salt stress, as evidenced by increased shoot and root biomass, higher contents of osmolytes (proline) and polyphenols, and improved shoot nitrogen content. Moreover, Glutamicibacter sp. contributes to maintaining ion homeostasis under saline conditions, thereby strengthening the plant’s overall salt tolerance. Furthermore, Glutamicibacter sp. plays a vital role in mitigating the adverse effects of salinity, enhancing the resilience of halophytic plants, and supporting their use in the restoration of salinized ecosystems. Given these promising effects, future research should investigate the potential of Glutamicibacter sp. to improve growth and stress resilience in non-halophytic crop species cultivated in saline-alkali soils. Such studies could pave the way for sustainable microbial-based strategies for soil remediation and crop productivity in salt-affected regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H., O.M.-B.M. and C.A.; methodology, R.H.; software, R.H.; formal analysis, R.H.; writing—original draft preparation, R.H. and F.B.; writing—review and editing, W.Z. and A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research (LR15CBBC02).
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data can be found in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests. The authors declare that they have no known competing personal relationships or financial interests that could have appeared to impact the work reported in this paper.
References
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, N.; Gao, Z. Suaeda salsa root-associated microorganisms could effectively improve maize growth and resistance under salt stress. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01349-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Rajput, V.D.; Verma, K.K.; Minkina, T.; Ghazaryan, K.; Arora, J. Potential of Suaeda nudiflora and Suaeda fruticosa to adapt to high salinity conditions. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareem, M.; Mahmood, S.; Danish, S.; Iqbal, R.K.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Alharbi, S.A. Influence of indole acetic acid, arginine and mango fruit waste biochar on nutrients, chlorophyll contents and antioxidants of Fenugreek in salt affected soil. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO Global Map of Salt-Affected Soils (GSASmap). 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/gsasmap/en/ (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Minhas, P.S.; Qadir, M. Managing Saline Water for Irrigating Agricultural Crops. In Irrigation Sustainability with Saline and Alkali Waters: Extent, Impacts and Management Guidelines; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 111–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hailu, B.; Mehari, H. Impacts of soil salinity/sodicity on soil-water relations and plant growth in dry land areas: A review. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Zhou, J.; Sui, N. Mechanisms of salt tolerance in halophytes: Current understanding and recent advances. Open Life Sci. 2018, 13, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Glick, B.R. Halotolerant plant growth–promoting bacteria: Prospects for alleviating salinity stress in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 178, 104124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Bibi, H.; Batool, F.; Muhammad, M.; Ullah, S.; Zaman, W.; Abdi, G. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria biochemical pathways and their environmental impact: A review of sustainable farming practices. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 637–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riseh, R.S.; Fathi, F.; Vazvani, M.G.; Tarkka, M.T. Plant Colonization by Biocontrol Bacteria and Improved Plant Health: A Review. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed). 2025, 30, 23223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Rashid, A.A.; Khan, S.N.; Khatun, A.; Karim, M.M.; Prasad, P.V.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Harnessing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, Bacillus subtilis and B. aryabhattai to combat salt stress in rice: A study on the regulation of antioxidant defense, ion homeostasis, and photosynthetic parameters. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1419764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, Y.; Di, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, T.; Shen, S.; Du, N.; Zhang, T.; Dong, Z.; et al. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa HG28-5 improves salt tolerance by regulating Na+/K+ homeostasis and ABA signaling pathway in tomato. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 283, 127707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidri, R.; Metoui-Ben Mahmoud, O.; Debez, A.; Zorrig, W.; Abdelly, C.; Zamarreño, A.M.; García-Mina, J.M.; Azcon, R.; Aroca, R. Dual PGPR-AMF inoculation offsets salinity stress impact on the fodder halophyte Sulla carnosa by concomitantly modulating plant ABA content and leaf antioxidant response. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Haider, F.U.; Liu, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, X. Salt Tolerance Induced by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Is Associated with Modulations of the Photosynthetic Characteristics, Antioxidant System, and Rhizosphere Microbial Diversity in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Agronomy 2025, 15, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaresofla, B.R.; Alikhani, H.A.; Etesami, H.; Khoshkholgh-Sima, N.A. Improved growth and salinity tolerance of the halophyte Salicornia sp. by co–inoculation with endophytic and rhizosphere bacteria. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.; Rasheed, A.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.A.; Nielsen, B.L.; Hameed, A. Maternal salinity improves yield, size and stress tolerance of Suaeda fruticosa seeds. J. Arid Environ. 2020, 12, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, B.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Hussain, T.; Rasool, S.G.; Nielsen, B.L. Thriving under salinity: Growth, ecophysiology and proteomic insights into the Tolerance mechanisms of Obligate Halophyte Suaeda fruticosa. Plants 2024, 13, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ungar, I.A.; Showalter, A.M. The effect of salinity on the growth, water status, and ion content of a leaf succulent perennial halophyte, Suaeda fruticosa (L.) Forssk. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 45, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J.; Ansari, R.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.A. Potential of halophytes as source of edible oil. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidri, R.; Mahmoud, O.M.B.; Zorrig, W.; Mahmoudi, H.; Smaoui, A.; Abdelly, C.; Azcon, R.; Debez, A. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria alleviate high salinity impact on the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa by modulating antioxidant defense and soil biological activity. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 821475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, M.; Ahmad, N.; Nielsen, B.L. Halophilic Plant-Associated Bacteria with plant-growth-promoting potential. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, D.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, J. Insight into bacterial and archaeal community structure of Suaeda altissima and Suaeda dendroides rhizosphere in response to different salinity level. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e01649-23. [Google Scholar]
- AbuQamar, S.F.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Desoky, E.S.M.; Elrys, A.S.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; El-Tarabily, K.A. Halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria improve soil fertility and plant salinity tolerance for sustainable agriculture—A review. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.R.; Gill, S.P.; Kaundal, A.; Sandhu, D. Strategies for combating plant salinity stress: The potential of plant growth-promoting microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1406913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S.K.; Kashyap, A.S.; Kumar, R.; Gujjar, R.S.; Singh, A.; Manzar, N. Harnessing rhizospheric microbes for eco-friendly and sustainable crop production in saline environments. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houmani, H.; Debez, A.; Slatni, T.; Yousfi, S.; Jellali, N.; M’sehli, W.; Gharsalli, M. Insights into physiological responses of the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa to simultaneous salinity and iron deficiency. Clean—Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, F.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, R.; Mapelli, F.; Rolli, E.; Mosqueira, M.J.; Fusi, M.; Bariselli, P.; Reddy, M.; Cherif, A.; Tsiamis, G.; Borin, S.; et al. Salicornia strobilacea (synonym of Halocnemum strobilaceum) grown under different tidal regimes selects rhizosphere bacteria capable of promoting plant growth. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, Y.; Moreno, M.; Troyo, E. Growth promotion of the seawater-irrigated oilseed halophyte Salicornia bigelovii inoculated with mangrove rhizosphere bacteria and halotolerant Azospirillum spp. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Feng, W.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, T.T.; Xiong, Y.W.; Xing, K. Diversity of bacterial microbiota of coastal halophyte Limonium sinense and amelioration of salinity stress damage by symbiotic plant growth-promoting actinobacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola KLBMP 5180. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01533-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, B.; Aroca, R.; Azcón-Aguilar, C.; Barea, J.M.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M. Importance of native arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation in the halophyte Asteriscus maritimus for successful establishment and growth under saline conditions. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Cuin, T.A. Potassium transport and salt tolerance. Physiol. Plant 2008, 133, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishahi, F.; Alikhani, H.A.; Khoshkholgh-Sima, N.A.; Etesami, H. Mining the roots of various species of the halophyte Suaeda for halotolerant nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacteria with the potential for promoting plant growth. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Nawaz, F.; Shehzad, M.A. Contributions of Nitrogen Metabolic Enzymes in Storage Protein Assimilation and Mineral Accumulation Regulated by Nitrogen and Selenium in Triticum aestivum L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 221, 109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslo, É.; Mara, G. Is PGPR an Alternative for NPK Fertilizers in Sustainable Agriculture? In Microbial Interventions in Agriculture and Environment: Volume 1: Research Trends, Priorities and Prospects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, P.; Zebelo, S.; McNear, D.; Kloepper, J.; Fadamiro, H. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Induce Changes in Arabidopsis thaliana Gene Expression of Nitrate and Ammonium Uptake Genes. J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessini, K.; Issaoui, K.; Ferchichi, S.; Saif, T.; Abdelly, C.; Siddique, K.H.; Cruz, C. Interactive effects of salinity and nitrogen forms on plant growth, photosynthesis and osmotic adjustment in maize. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidri, R.; Barea, J.M.; Mahmoud, O.M.B.; Abdelly, C.; Azcón, R. Impact of microbial inoculation on biomass accumulation by Sulla carnosa provenances, and in regulating nutrition, physiological and antioxidant activities of this species under non-saline and saline conditions. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 201, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamec, D.; Karalija, E.; Šola, I.; Vujčić Bok, V.; Salopek-Sondi, B. The role of polyphenols in abiotic stress response: The influence of molecular structure. Plants 2021, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Zheng, B. The Role of Polyphenols in Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Their Antioxidant Properties to Scavenge Reactive Oxygen Species and Free Radicals. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Latef, A.A.H.; Tahjib-Ul-Arif, M.; Rhaman, M.S. Exogenous auxin-mediated salt stress alleviation in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, C.; Bao, Z.; Xiao, R.; Chen, X.; Xiao, W.; Li, D.; Fu, X.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Auxinalters sodium ion accumulation and nutrient accumulation by playing protective role in salinity challenged strawberry. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 164, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Siddiqi, E.H.; Ahmad, S.; Zeb, U.; Muhammad, I.; Khan, H.; Zhao, G.F.; Li, Z.H. Exogenous application of indole-3-acetic acid to ameliorate salt induced harmful effects on four eggplants (Solanum melongena L.) varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 292, 110662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifard, M.; Stefaniak, S.; Ghorbani Javid, M.; Soltani, E.; Wojtyla, Ł.; Garnczarska, M. Contribution of exogenous proline to abiotic stresses tolerance in plants: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, R.A.; Sorour, S.G.R.; Aboukhadrah, S.H.; El Shafey, N.M.; Abd Elsalam, H.E.; El-Sharnouby, M.E.; El-Tahan, A.M. Alleviation of salinity stress effects on agro-physiological traits of wheat by auxin, glycine betaine, and soil additives. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.; Arafa, S.A. Mitigation of salinity stress in canola plants by sodium nitroprusside application. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. J. Biochem. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rosi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic–phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1956, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouat, A.; Crouzet, C. Notes techniques sur un appareil semi-automatique de dosage de l’azote et de certains composés volatiles. Ann. Agric. 1965, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).