Abstract
Background and Aims: There is still uncertainty about the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous compared to intravenous administration of biologics for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remission. Methods: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we searched Cochrane, PubMed, SCOPUS, CINHAL, and preprint archives for trials that compared the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous and intravenous biologics for the induction and maintenance of IBD remission. Meta-analysis was carried out with a subgroup analysis for Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC), heterogeneity using I2, and publication bias using funnel plots. Results: A total of 14 randomized controlled trials, 9 on CD, 4 on UC, and 1 with data on both were included Subcutaneous, compared to intravenous administration, was less efficacious for the induction of remission; overall (OR 0.68, 95%CI 0.35–1.31, I2 = 83%), worse in UC (OR 0.35, 95%CI 0.07–1.79, I2 = 91.2%), and showed similar efficacy in CD (OR 0.97, 95%CI 0.73–1.30, I2 = 0%). For the maintenance of remission, subcutaneous biologics were almost similar to intravenous biologics; overall (OR 0.97, 95%CI 0.63–1.49, I2 = 57.1%), with less efficacy in UC (OR 0.82, 95%CI 0.54–1.23, I2 = 52%), but superior efficacy in CD (OR 1.81, 95%CI 1.09–3.01, I2 = 0%). Subcutaneous, compared to intravenous biologics, showed slightly higher odds of treatment discontinuation (OR 1.32, 95%CI 1.02–1.71, I2 = 14.2%), worse in UC (OR 1.52, 95%CI 1.17–1.98, I2 = 13%), and was similar to intravenous for CD (OR 1.03, 95%CI 0.65–1.62, I2 = 0%). Conclusion: Subcutaneous administration has lower efficacy for the induction of remission but can achieve almost similar efficacy and safety in maintaining remission in IBD. Subcutaneous injection has better efficacy and safety in CD than in UC.
1. Introduction
The global prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and its two main subtypes, ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD), is increasing in step with the rapid epidemiological transition occurring in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC) [1]. Between 1990 and 2019, the number of people affected by IBD increased from 3.3 to 4.9 million, highlighting the growing disease burden of IBD globally [2]. IBD has a significant impact on the health-related and social quality of life of affected individuals, which includes recurring disease activity, extraintestinal manifestations, decreased social functioning and productivity, and has been linked to colonic cancer [3,4,5]. Despite the availability of immune and disease-modulating agents, a significant proportion of individuals do not maintain clinical remission from symptoms [6,7]. The impact of IBD is worsened in individuals with severe phenotypes of IBD [8], and treatment options for individuals with difficult-to-treat IBD remain limited [9].
Treatment of IBD has targeted the resolution of clinical symptoms, such as diarrhea and extraintestinal manifestations [6,7]. However, remission is not maintained in a significant proportion of people [9,10], and some treatments such as corticosteroids, have harmful side effects. Biologic therapies such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), have expanded the available tools for achieving IBD remission [11,12]. Since the introduction of Infliximab, many biologics targeting IBD-relevant proteins have been approved and utilized for the treatment of IBD, such as Natalizumab, Risankizumab, and Vedolizumab [13,14].
Biologics are active proteins and therefore have been traditionally administered using the intravenous route [15,16]. Advantages of intravenous administration of biologics include quicker drug effect, better control of dosages, continuous drug administration, larger dose infusion, and allows drug administration in patients who are unable to take drugs via oral and other routes [17]. Recent advances have resulted in formulations of biologics that can be delivered via subcutaneous injections [16]. The introduction of subcutaneous anti-TNF-α biologics, including the groundbreaking CT-P13 subcutaneous formulation of infliximab, has significantly expanded treatment options for patients undergoing monoclonal antibody therapies [18]. This route enhances patient adherence and lowers treatment costs, as it allows self-administration, improves patient mobility, reduces hospital stay, reduces overall costs, and enables the administration of biologics in patients with poor venous access [17]. Additionally, subcutaneous injections typically take minutes compared to the hours needed for intravenous infusions, which make it a compelling and efficient alternative, favored by both patients and healthcare providers [19,20].
Several trials have compared the efficacy and safety of subcutaneously administered biologics to that of the intravenous route, with varying results [20,21,22]. Lower efficacy has been generally observed when subcutaneous biologics were used for the induction of remission [21,23]. However, some trials have demonstrated equivalence [24,25], while others have demonstrated that subcutaneous biologics can surpass intravenous biologics in inducing remission in CD [26]. A different scenario has been observed when subcutaneous biologics were used for maintaining IBD remission. Several trials have shown superiority of subcutaneous biologics, but some trials have shown that subcutaneous biologics were inferior, especially for UC [20,22]. One meta-analysis showed that patients can be switched from intravenous Infliximab to subcutaneous Infliximab after three months without loss of efficacy and without increased side effects [27]. However, this meta-analysis examined switching only and included observational studies [27]. A recent network meta-analysis showed that subcutaneous administration of Infliximab and Vedolizumab was potentially better than either oral or intravenous routes, although the evidence is based on indirect comparisons with very few studies for each outcome [28]. The previous meta-analyses have been limited to either studying the efficacy of switching [27] or comparisons with placebo or indirect comparisons between subcutaneous and intravenous routes [28]. Further, there is little evidence about the efficacy of subcutaneous compared to intravenous for other biologics apart from the first-line biologics such as Infliximab. Given the increasing number of biologics available, there is a need to assess their efficacy between subcutaneous and intravenous routes to enable clinicians to make informed choices with their patients. In this meta-analysis, we compared the safety and efficacy of the subcutaneous route of administration of biologics compared to the intravenous route.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
This research is a systematic review and meta-analysis and follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [29]. The protocol for this study is registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) (CRD42024484820).
2.2. Data Sources
We conducted a comprehensive search of electronic databases, including Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), PubMed, Scopus, Cumulated Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), and the databases of preprints (medRXIV), clinicaltrials.org, Google Scholar, and references search. This search covered databases up to 5 March 2024, with no language restrictions. The search was conducted during November 2023, using a search strategy (Supplementary Document S2), and updated during March 2024.
2.3. Search Terms
2.3.1. Search Terms for Monoclonal Antibody Therapies
“Infliximab” OR “IFX” OR “CT-P13” OR “monoclonal antibody” OR “Remicade” OR “Renflexis” OR “Inflectra” OR “infliximab-dyyb” OR “infliximab-abda” OR “MAb cA2” OR “Monoclonal Antibody cA2” OR “Anti-TNF-α biologics” OR “Biologics” OR “Adalimumab” OR “Golimumab” OR “Adalimumab-atto” OR “Adalimumab-adbm” OR “Amjevita” OR “Cyltezo” OR “D2E7 Antibody” OR “Humira” OR “Anti-TNF-α therapy” OR “Ustekinumab” OR “Stelara” OR “Wezlana” OR “CNTO-1275” OR “CNTO1275” OR “anti-IL-12” OR “anti-IL-23” OR “Vedolizumab” OR “Guselkumab” OR “Risankizumab”.
2.3.2. Search Terms for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
“Inflammatory Bowel Diseases” OR “IBD” OR “Crohn’s disease” OR “Crohn disease” OR “CD” OR “Ulcerative Colitis” OR “UC” OR “Colitis” OR “Crohn” OR “Granulomatous colitis” OR “Granulomatous enteritis” OR “Regional enteritis” OR “Regional ileitis” OR “Regional ileitides” OR “Terminal ileitis” OR “Ileocolitis” OR “Cleron disease” OR “Enteritis regional” OR “Regional enterocolitis” OR “Chronic colitis” OR “Chronic inflammation of the bowel” OR “Intermediate Colitis”.
2.3.3. Search Terms for Route of Administration
“Subcutaneous” OR “SC” OR “SQ” OR “SubQ” OR “Sub-Q” OR “Subcut” OR “SubC” OR “Subcu” OR “Hypodermic” OR “Hypodermal” OR “Intracutaneous” OR “Intravenous” OR “Drip” OR “Endovenous” OR “IV” OR “Venous” OR “Infusion”.
2.4. Procedure for Selection of Studies
The study records obtained from the literature search were imported into EndNote 20 software for de-duplication. Subsequently, the study records were uploaded to the Rayyan systematic review management website (https://www.rayyan.ai/ (accessed on 17 July 2024)) for screening using the title and abstract. The preliminarily included study records were retrieved in full-text and evaluated manually for eligibility by two independent investigators. In cases of disagreement, a third investigator was consulted to make the final decision.
2.5. Eligibility
Studies were eligible for inclusion if they were RCTs evaluating the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous compared to intravenous biologic therapies in adult or pediatric participants with IBD. We excluded observational studies, trials where the comparator was placebo, as well as those in which both the induction and maintenance phases used the same route of administration without a direct comparison between subcutaneous and intravenous biologic therapies. This approach was adopted to ensure that only studies providing a direct, head-to-head comparison between subcutaneous and intravenous administration were included.
2.6. Outcomes
The primary efficacy outcomes were overall induction and maintenance of remission, with the latter defined by the Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) as asymptomatic remission <150 for CD or Mayo score of ≤2 with no subscore >1 for UC [30,31]. Endoscopic remission for UC was defined as endoscopy subscore of zero [32]. Improvement in endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as endoscopy subscore ≤1 [33]. Endoscopic remission for CD was defined as Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD) of 0–2. Endoscopic response was defined as ≥ 50% reduction from baseline in SES-CD [34]. The primary safety outcome was the adverse events. The secondary efficacy outcomes were IBD-related quality of life (IBDQ), hospitalization, and all-cause mortality. The secondary safety endpoints were treatment discontinuation and serious adverse events.
2.7. Data Extraction
Data were extracted from the included studies on Microsoft Excel. Eight authors (NA, RI, HA, K-HA, M-AA, N-AA, W-NA, YA) independently extracted data on the study characteristics including study design, date, location, number of participants, and selected demographic characteristics (e.g., age, gender, race, comorbidities, type, and severity of IBD). Data regarding the treatment regimen included the drugs used, the dosage, and the treatment duration. Data on the study outcome included the number of individuals in the subcutaneous and intravenous groups with induced remission, the number of participants in the subcutaneous and intravenous groups with maintained remission, the number of individuals that developed at least one adverse event, and the number of individuals that developed at least one serious adverse event, death, or treatment discontinuation.
2.8. Assessing Quality of Included Studies
The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Methodological Standard for Epidemiological Research (MASTER) scale, comprising 7 standards subdivided into 36 safeguards [35].
2.9. Data Synthesis
Characteristics of the included studies were displayed in the tables and narratively described. Meta-analysis was carried out for the induction, maintenance of remission, IBDQ, mortality, and safety using the bias adjusted inverse variance heterogeneity (quality-effects) model [36], with overall and separate analyses for the two subtypes of IBD, i.e., CD and UC. Study level unadjusted odds ratios (OR) and their 95%CIs were recalculated for each of the binary outcomes and then synthesized to compute the overall effects. The quality effects model was also used to synthesize weighted mean differences (WMD) from mean IBDQ scores from the included studies. The quality-effects model modifies variance weights using quality scores from the studies, therefore incorporating study quality in the synthesis. Sensitivity analysis was conducted to re-analyze data using the quality-effects model [37]. We used Stata version 18 (College Station, TX, USA) with the metan package for the meta-analysis and reported exact p values throughout. We used the I2 statistic, Cochran’s Q p-value, and tau2 to quantify heterogeneity and I2 values of 25%, 50%, and 75% were assigned into low, moderate, and high inconsistency categories, respectively [38,39]. We investigated publication bias using Doi plots and the LFK index [40], in addition to funnel plots and Egger regression [41]. GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations) was used to assess the quality of evidence of each outcome, overall and for each disease (CD and UC).
2.10. Ethics
This systematic review utilized published data, therefore there was no need for ethical approval.
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
A total of 6311 studies were identified through the search. After eliminating duplicates and a manual screening process based on title and abstract, 37 studies underwent full-text screening. Out of these, 23 studies were excluded for the reasons indicated in Figure 1. After the full-text screening, most of the studies were excluded because they did not compare the administration routes (n = 8). Ultimately, 14 trials were included [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,45,46,47,48], 7 of them were included in the induction analysis [21,23,24,25,26,44,46], and 7 studies were included in the maintenance analysis [20,21,22,23,45,47,48]. Also, 13 RCTs [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,45,47,48] were included in the analysis of adverse events, 12 trials were included in the serious adverse events [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,47,48], and 11 trials in the treatment discontinuation analysis [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,44,45,47,48].
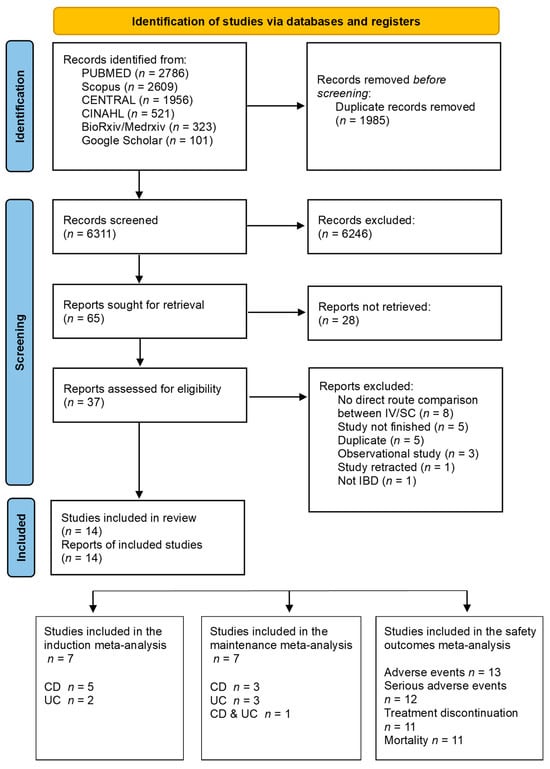
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram.
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
The 14 selected RCTs [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] involved 4209 participants from a total of 43 countries with most studies from Canada, Germany, and the United States. Nine trials focused on CD [23,25,26,42,43,44,45,46,47], four trials focused on UC [21,22,24,48] and one trial on both diseases [20]. All trials included adult participants aged 18 to 85 years with moderate-to-severe IBD, except for two trials on Risankizumab [42,43], which included both pediatric and adult participants, with ages ranging from 16 to 80 years. The characteristics of the included studies are in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies.
3.3. Assessment of Quality of Included Studies
The examination of the study quality revealed that most of the included trials obtained MASTER scale scores ranging from 30 to 35 out of 36, with an average of 33, signifying an overall high quality of evidence (Figure 2 and Supplementary Table S1). The equal recruitment domain was met by all but one study [23], due to participant exclusion after the study commencement. Similarly, the temporal precedence domains were met by all of the studies except one cross-over trial [44]. All of the trials were multicenter trials and therefore failed the safeguard of equal care delivery in the MASTER scale.

Figure 2.
Quality assessment of included trials. NB: Quality assessment of included trials [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] using seven domains. Equal Recruitment (blue) has 4 safeguards; Equal Retention (orange) has 5 safeguards; Equal Ascertainment (gray) has 7 safeguards; Equal Implantation (yellow) has 6 safeguards; Equal Prognosis (sky blue) has 6 safeguards; Sufficient Analysis (green) has 3 safeguards; Temporal Precedence has 5 safeguards (dark blue).
3.4. Induction of Remission
Seven RCTs [21,23,24,25,26,44,46] compared subcutaneous to intravenous biologics for the induction of remission. Overall, the odds of inducing remission were reduced by almost one-half in the subcutaneous group compared to the intravenous group (OR 0.68, 95%CI 0.35–1.31), with high heterogeneity (I2 = 83%), and minor asymmetry (Supplementary Figure S1), suggesting no concerns with publication bias. The results were consistent after sensitivity analysis using leave-one-out (Supplementary Figure S2). When the data were analyzed according to the drug mechanism of action, subcutaneous biologics showed a trend towards being superior to intravenous biologics for TNF-alpha inhibitors (OR 1.27, 95%CI (0.85–1.89), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.620, n = 2 studies), while subcutaneous showed a trend towards being inferior to intravenous biologics for interleukin 12/23 inhibitors (OR 0.77, 95%CI (0.53–1.12), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.972, n = 4 studies) and for the combination of integrin and TNF-alpha inhibitors (OR 0.23, 95%CI (0.15–1.35), I2 = 0.0%, p < 0.00, n = 1 study) (Supplementary Table S2). For CD, synthesis of the five trials, three on subcutaneous Ustekinumab [23,25,44], one on subcutaneous Brazikumab [26], and one on subcutaneous Adalimumab [46], showed similar odds of induction of remission compared to intravenous routes (OR 0.97 95%CI 0.73–1.30, I2 = 0%). Of the two trials for UC induction, one showed [21] greatly reduced efficacy for subcutaneous Etrolizumab versus intravenous Infliximab (OR 0.23, 95%CI 0.15–0.35), while the other study [24] showed almost similar odds of induction of remission when subcutaneous Golimumab was compared to intravenous Guselkumab (OR 1.07, 95%CI 0.48–2.36) (Figure 3). The summary GRADE rating for this outcome was of moderate certainty evidence for the overall synthesis due to high heterogeneity, moderate certainty for CD, and moderate certainty for UC (Supplementary Table S3).
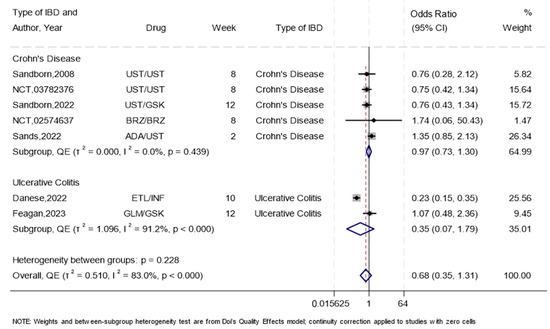
Figure 3.
The efficacy of subcutaneous compared to intravenous biologics for the induction of remission using a forest plot. NB: This forest plot shows the overall analysis for the odds of inducing remission using the subcutaneous compared to the intravenous route in seven trials [21,23,24,25,26,44,46]. Abbreviations: Ustekinumab (UST), Guselkumab (GSK), Brazikumab (BRZ), Etrolizumab (ETL), Infliximab (INF), Golimumab (GLM), Adalimumab (ADA). The figure includes a line of no effect (vertical black line), meta-analytical estimates with confidence intervals (blue diamonds), study weights (gray boxes), study effect sizes (black dots), confidence intervals for study effect sizes (horizontal black lines), and a line representing the overall odds ratio (red dotted line).
3.5. Maintenance of Remission
Seven RCTs [20,21,22,23,45,47,48] measured the maintenance of remission with one study that had both cohorts of IBD. Overall, the subcutaneous route indicated slightly lower odds of maintaining remission (OR 0.97, 95%CI 0.63–1.49) (Figure 4), with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 57.1%), and major asymmetry (Supplementary Figure S3), suggesting some concerns with publication bias. The results were consistent after sensitivity analysis using leave-one-out (Supplementary Figure S2). When the data were analyzed according to the drug mechanism of action, data from two studies suggested that subcutaneous biologics were superior to intravenous biologics for TNF-alpha inhibitors (OR 1.95, 95%CI (1.03–3.66), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.587, n = 2 studies), while there was a trend towards superior efficacy for subcutaneous interleukin inhibitors (OR 1.71, 95%CI (0.92–3.19), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.559, n = 2 studies) and data from one study suggested similar efficacy between the two routes for anti-integrin antibody (OR 1.16, 95%CI (0.60–2.24), I2 = 0.0%, p < 0.00, n = 1 study). However, the subcutaneous route showed a trend towards being inferior to intravenous biologics in regimens which combined TNF-alpha inhibitor and anti-integrin antibody drugs (OR 0.69, 95%CI (0.53–0.90), I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.419, n = 2 studies) (Supplementary Table S2). For CD, synthesis of the four trials, two on subcutaneous Infliximab [20,45], one on subcutaneous Ustekinumab [23], and one on subcutaneous Mirikizumab [47] showed higher odds of maintenance of remission compared to intravenous routes (OR 1.81, 95%CI 1.09–3.01, I2 = 0%). For UC, three trials showed results that suggested either equality or superiorty of subcutaneous compared to intravenous Infliximab [20] (OR 1.86, 95%CI 0.73–4.71), subcutaneous compared to intravenous Vedolizumab [22] (OR 1.16, 95%CI 0.60–2.24), and subcutaneous Etrolizumab compared to intravenous Infliximab (OR 0.81, 95%CI 0.50–1.30) [21]. One trial showed inferiority of subcutaneous Adalimumab compared to intravenous Vedolizumab [48] (OR 0.64, 95%CI 0.46–0.88). The summary GRADE rating for this outcome was of moderate certainty evidence for the overall synthesis due to major asymmetry, moderate certainty for CD, and moderate certainty for UC (Supplementary Table S3).

Figure 4.
The efficacy of subcutaneous compared to intravenous biologics in IBD maintenance of remission using a forest plot. NB: This forest plot shows the overall analysis of the odds of maintaining remission using the subcutaneous route compared to the intravenous route which was reported by seven trials [20,21,22,23,45,47,48]. One trial with two cohorts of individuals (CD, UC). Abbreviations: Ustekinumab (UST), Infliximab (INF), Mirikizumab (MRK), Adalimumab (ADA), Vedolizumab (VDL), Etrolizumab (ETL). The figure includes a line of no effect (vertical black line), meta-analytical estimates with confidence intervals (blue diamonds), study weights (gray boxes), study effect sizes (black dots), confidence intervals for study effect sizes (horizontal black lines), and a line representing the overall odds ratio (red dotted line).
3.6. Endoscopic Remission
Seven RCTs [20,21,22,24,45,47,48] reported endoscopic remission. Overall, subcutaneous administration was associated with 16% lower odds of achieving endoscopic remission compared to intravenous administration with moderate heterogeneity (OR 0.84, 95%CI 0.56–1.26, I2 = 49%) ( Supplementary Figure S4) and major asymmetry suggesting concerns with publication bias (Supplementary Figure S5). In the subgroup analysis of the four trials [21,22,24,48] with data on UC, subcutaneous administration was associated with 28% lower odds of achieving endoscopic remission compared to intravenous administration with low heterogeneity (OR 0.72, 95%CI 0.52–0.99, I2 = 34%). Three trials on CD [20,45,47] indicated that subcutaneous administration had 90% higher odds of achieving endoscopic remission compared to intravenous administration with no-to-low heterogeneity (OR 1.90, 95%CI 0.85–4.26, I2 = 0%). One trial [20] that included both cohorts suggested that subcutaneous administration had 1.66 times the odds of achieving endoscopic remission compared to intravenous administration with no-to-low heterogeneity (OR 1.66, 95%CI 0.72–3.79, I2 = 0%). The summary GRADE rating for this outcome was of moderate certainty evidence, due to major asymmetry. In subgroups, the GRADE rating was of high certainty for CD, and moderate certainty for UC ( Supplementary Table S3).
3.7. Endoscopic Response
Five RCTs reported endoscopic response. Overall, the subcutaneous administration was associated with a 9% reduction in the odds of achieving response compared to intravenous administration (OR 0.91, 95%CI 0.56–1.50, I2 = 36.7%). In subgroup analysis, four trials reported endoscopic response for individuals with CD. The odds suggested that individuals receiving subcutaneous administration had a 1% increase in the odds of achieving endoscopic response compared to those receiving intravenous administration with low heterogeneity (OR 1.01, 95%CI 0.43–2.38, I2 = 48%). One trial [21] reported endoscopic response in UC; the odds suggested a 24% reduction in achieving response with subcutaneous administration compared to the intravenous infusion (OR 0.76, 95%CI 0.49–1.17, I2 = 0%) ( Supplementary Figure S6).
3.8. Any Adverse Events and Serious Adverse Events
A total of 13 trials reported adverse events [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,45,47,48]. The overall effect estimate showed a 7% increase in the odds of adverse events with subcutaneous administration, with low heterogeneity (OR 1.07, 95%CI 0.86–1.34, I2 = 29.6%) ( Supplementary Figure S7). This effect was slightly similar in UC (OR 1.17, 95%CI 0.86–1.59, I2 = 34.1%) and in CD (OR 0.91, 95%CI 0.65–1.27, I2 = 28.9%). A total of 12 RCTs [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,47,48] reported the serious adverse events, nearly the same overall effect was reported (OR 1.12, 95%CI 0.86–1.46, I2 = 0%) ( Supplementary Figure S8). This effect was nearly the same in UC (OR 1.23, 95%CI 0.88–1.73, I2 = 0%) and in CD (OR 0.97, 95%CI 0.61–1.53, I2 = 0%).
3.9. Treatment Discontinuation
Overall, 11 RCTs [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,44,45,47,48] reported data on treatment discontinuation. The overall effect estimate showed higher odds of treatment discontinuation with subcutaneous compared to intravenous administration, with no-to-low heterogeneity (OR 1.32, 95%CI 1.02–1.71, I2 = 14.2%) (Figure 5). Subcutaneous administration was worse in UC (OR 1.52, 95%CI 1.17–1.98, I2 = 13%), and similar to intravenous infusion in CD (OR 1.03, 95%CI 0.65–1.62, I2 = 0%). The most common reasons for discontinuation across both groups were due to lack of efficacy and voluntary withdrawal (Supplementary Table S4).
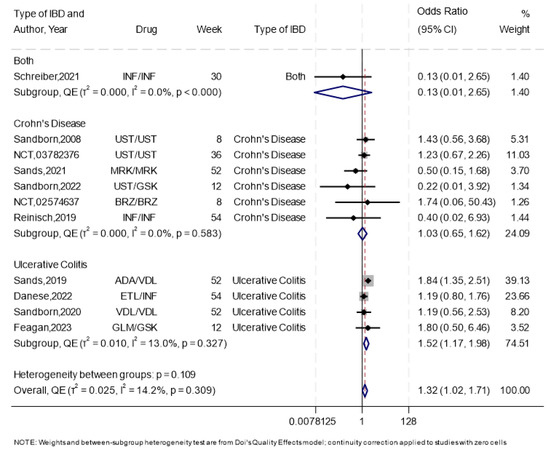
Figure 5.
The forest plot for the overall analysis of treatment discontinuation. NB: This forest plot shows the overall analysis for the odds of treatment discontinuation using the subcutaneous compared to the intravenous route, which was reported by 11 trials [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,44,45,47,48], including 1 study that had both cohorts of patients (CD, UC). The figure includes a line of no effect (vertical black line), meta-analytical estimates with confidence intervals (blue diamonds), study weights (gray boxes), study effect sizes (black dots), confidence intervals for study effect sizes (horizontal black lines), and a line representing the overall odds ratio (red dotted line).
3.10. Quality of Life
Seven trials compared quality of life between subcutaneous to intravenous biologics, with three studies, two on UC [24,48] and one on CD [25], showing that, overall subcutaneous biologics resulted in lower odds of attaining an IBDQ score remission of ≥170 points (OR 0.72, 95%CI 0.57–0.91, I2 = 0%). The remaining four studies [20,21,22,44] reported mean IBDQ scores, with the overall synthesis suggesting a slight difference in mean IBDQ score for subcutaneous compared to intravenous biologics (WMD 0.21, 95%CI −2.78–3.20, I2 = 0%).
3.11. Hospitalization
One RCT [48] reported the number of hospitalizations. The results suggested a slight increase in the odds of hospitalization in the subcutaneous arm compared to the intravenous arm (OR 1.34, 95%CI 0.68–2.66).
3.12. Mortality
Out of the included RCTs, 11 reported the mortality outcome [20,21,22,24,25,26,42,43,44,47,48]. The overall synthesis showed no difference in mortality between the subcutaneous and intravenous routes (OR 0.88, 95%CI 0.31–2.46, I2 = 0%), which was consistent for both CD (OR 1.02, 95%CI 0.24–4.45, I2 = 0%, n = 6 studies) and for UC (OR 0.68, 95%CI 0.13–3.67, I2 = 0%, n = 4 studies) (Supplementary Figure S9).
4. Discussion
In this meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials, overall we found that subcutaneous administration of biologics, compared to intravenous administration, was associated with a lower efficacy when used for induction but comparable to intravenous when used for maintaining IBD remission. However, in individuals with CD, subcutaneous was likely to be as efficacious as intravenous administration for the induction of remission but superior to intravenous administration for the maintenance of remission. In individuals with UC, subcutaneous administration of biologics was inferior to intravenous administration for the induction of remission and almost similar to intravenous administration when used for the maintenance of remission. The two routes of administration showed similar odds of mortality.
We found that subcutaneous administration was associated with an almost 50% reduction in the odds of induction of remission, with worse efficacy for individuals with UC. However, subcutaneous biologics had similar effects compared to intravenous biologics for the induction of CD remission, with moderate certainty GRADE evidence. Existing meta-analyses have not compared subcutaneous to intravenous administration for the induction of IBD remission [27,28]. For CD, three trials [23,25,44] showed that subcutaneous Ustekinumab was almost equivalent to intravenous Ustekinumab [23,44] or Guselkumab [25] with small reductions in the odds of achieving the remission. The other two trials that we included suggested equal or better efficacy for subcutaneous compared to intravenous Brazikumab [26], and subcutaneous Adalimumab compared to intravenous Ustekinumab [46]. Notably, the Brazikumab study was terminated for business reasons. The current European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization Guideline (ECCO) and the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guideline recommend using intravenous Ustekinumab or subcutaneous Adalimumab for inducing remission in naive patients and patients with inadequate response to conventional therapy and/or to anti-TNF therapy [49,50,51]. However, the guidelines do not provide an explicit recommendation about the subcutaneous route of administration of Ustekinumab for the induction of CD remission [49,50,51].
Our findings showed that subcutaneous biologics were less efficacious than intravenous for the induction of UC remission. Of the two trials, subcutaneous Etrolizumab was inferior to intravenous Infliximab [21]. A previous meta-analysis showed no difference between subcutaneous Etrolizumab and intravenous Infliximab, although this was based on indirect comparisons of placebo controlled trials [52]. In the other UC induction trial [24], subcutaneous Golimumab had a similar effect to intravenous Guselkumab, which is a TNF-alpha inhibitor with similar efficacy to Infliximab [53], in inducing remission, which indicates its possible usage in inducing remission in individuals with UC. In the current guidelines [54,55], subcutaneous Golimumab had similar efficacy to intravenous Guselkumab, which is a TNF-alpha inhibitor with similar efficacy to Infliximab [53], in inducing remission, which indicates its possible usage in inducing remission in individuals with UC. The current guidelines [54,55] suggest the use of subcutaneous Golimumab and Adalimumab, and our findings suggest that more trials are needed.
We found that, overall, subcutaneous administration had nearly the same odds of maintaining remission compared to the intravenous route, i.e., only a 3% reduction. For CD, subcutaneous biologics were more efficacious, showing an overall effect of an 81% increase in the odds of maintaining remission, with moderate certainty GRADE evidence. All the four CD trials showed results that suggested equality or superiorty of subcutanaoues regimens of Infliximab [20,45], Ustekinumab [23], and Mirikizumab [47] compared to intravenous regimens. An exsiting meta-analysis showed results that suggested that subcutaneous Infliximab could be better than intravenous Infliximab in maintaining remission, although this was based on indirect comparisons of placebo controlled trials [28]. These findings support current guidelines which recommend subcutaneous Ustekinumab for remission maintenance in CD [50,51], and suggest that other subcutaneous biologics could also be used for maintaining remission in CD.
For UC, subcutaneous administration was associated with an 18% reduction, and the 95%CI suggested no difference between the two routes of administration. Three trials showed results that suggested either equality or superiorty of subcutaneous compared to intravenous Infliximab [20], subcutaneous compared to intravenous Vedolizumab [22], and subcutaneous Etrolizumab compared to intravenous Infliximab [21]. However, one trial showed that subcutaneous Adalimumab was inferior to intravenous Vedolizumab [48]. No existing meta-analyses have compared subcutaneous to intravenous biologics for UC maintenance of remission. The current ACG and ECCO guidelines [54,55] recommend subcutaneous Adalimumab for the maintenance of remission in UC. Our findings suggest that other subcutaneous biologics may provide more options for maintaining remission in UC without a significant loss of efficacy compared to the intravenous biologics.
We found that adverse events were almost similar between subcutaneous and intravenous biologics, with a 7% increase in the odds of adverse events compared to the intravenous route. However, subcutaneous administration was associated with higher odds of discontinuation in UC but not in CD. Although no existing meta-analyses have compared adverse events between the two routes of administration, two network meta-analyses showed that adverse events were comparable between biologics and standard care in UC [56] and CD [12], which suggests that biologics have relatively good safety profiles.
We found no major differences in IBD-related quality of life, hospitalizations, and mortality between subcutaneous and intravenous biologics. Although findings from observational studies suggest an increased risk of opportunistic infections, there is a lack of comparisons between the routes of administrations [57]. Our findings suggest that these two routes of administration may result in similar IBD prognosis, although more trials are required.
One limitation of this study is the inclusion of different biologics in synthesis, although this may not have an impact as this study assessed the efficacy of the route of administration. Some heterogeneity was observed for UC induction and maintenance but not for CD. Furthermore, studies on UC were few for most of the outcomes, suggesting a need for further trials. Some RCTs included different biologics in each arm which may lead to unequal comparisons; however, these trials also reflect choices that clinicians and their patients frequently have to make. Two trials, the ADVANCE [58] and the MOTIVATE [58], have published data on just the intravenous versus placebo comparisons and therefore could not be included in the efficacy outcomes. Another limitation is that most of the studies focused on adult participants and therefore there remains an evidence gap on the comparative efficacy of the two routes of administration of biologics in treating pediatric IBD. A strength of this meta-analysis is the rigorous search and analysis that we carried out. Finally, due to a lack of data from the included studies, we were unable to perform subgroup analyses based on well-established factors that are associated with treatment response. These factors include disease behavior and phenotype, smoking, gender, BMI, prior biologic exposure, treatment-naive status, age at diagnosis, and prior surgical status. Future RCTs should consider reporting stratified analyses on these factors to better understand variations in treatment response.
5. Conclusion
Subcutaneous administration of biologics has lower efficacy for the induction of remission in UC but similar efficacy when used for CD. However, subcutaneous can be used for maintenance of remission for both subtypes of IBD without significant loss of efficacy. There appears to be no difference in prognostic outcomes between the two routes of administration for both CD and UC, but subcutaneous biologics may increase the odds of treatment discontinuation in UC. More studies are required to investigate the efficacy of subcutaneous biologics for both the induction and maintenance of remission in UC.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/gastroent16020012/s1, Figure S1: DOI plot for induction of remission/The Doi plot shows minor asymmetry, confirmed by the LFK index = 1.61. On visual inspection of the funnel plot, the included studies [21,23,24,25,26,44,46] are roughly symmetrical distributed either side of the funnel, indicating symmetry and that publication bias is less likely. Egger’s test p-value was > 0.1 indicating weak evidence against the null hypothesis of asymmetry; Figure S2: Sensitivity analysis for the induction and maintenance of remission/The forest plot shows the Sensitivity analysis for the induction [21,23,24,25,26,44,46] and maintenance [20,21,22,23,45,47,48] of remission to examine the influence of each study on the meta-analytic outcome estimate. The results support those of the main outcome analysis of inducing and maintaining remission; Figure S3: Funnel plot and Doi plot of the maintenance of remission/The Doi plot shows asymmetry, confirmed by the LFK index = 4.54, indicating the presence of publication bias. Visual inspection of the funnel plot illustrates asymmetry of the distribution of the included studies [20,21,22,23,45,47,48] inside the funnel, indicating that publication bias is likely present. Egger’s test p-value was < 0.1 suggesting possible publication bias; Figure S4: Forest plot for endoscopic remission/The forest plot shows the subgroup analysis for the type of inflammatory bowel disease for endoscopic remission. The overall odds suggested that subcutaneous administration was associated with 16% lower odds of achieving endoscopic remission compared to intravenous administration with low heterogeneity (OR = 0.84, 95% CI 0.56–1.26, I2 = 49%); Figure S5: Doi and funnel plots for endoscopic remission/The Doi plot shows major asymmetry, confirmed by the LFK index = 5.16. Visual inspection of the funnel plot illustrates asymmetry of the distribution of the included studies [20,21,22,24,45,47,48] inside the funnel, indicating that publication bias is likely present. The Egger’s test p-value was < 0.1 suggesting possible publication bias; Figure S6: Forest plot for endoscopic response/The forest plot shows the subgroup analysis for the type of inflammatory bowel disease for endoscopic response. The overall odds suggested that subcutaneous administration was associated with 9% lower odds of achieving endoscopic remission compared to intravenous administration with low heterogeneity (OR = 0.91, 95% CI 0.56–1.50, I2 = 36.7%); Figure S7: Forest plot for adverse events analysis/This forest plot shows the analysis of the safety outcome of the development of adverse events in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease using subcutaneous compared to the intravenous biologics [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,45,47,48]; Figure S8: Forest plot for serious adverse events analysis/This forest plot shows the analysis of the safety outcome of the development of serious adverse events in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease using subcutaneous compared to the intravenous biologics [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,42,43,44,47,48]; Figure S9: Forest plot for mortality among both routes/This forest plot shows the analysis of the mortality outcome in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease using biologics with subcutaneous compared to the intravenous route [20,21,22,24,25,26,42,43,44,47,48]. The odds ratio (OR) of 0.88 suggests that the odds of mortality in the subcutaneous group are 12% lower compared to the intravenous group.; Table S1: MASTER scale; Table S2: Subgroups for induction and maintenance of remission; Table S3: GRADE Rating for main outcomes; Table S4: Reasons for treatment discontinuation; Supplementary Document S2: Search Strategy.
Author Contributions
N.A.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing, and Project Administration. R.I.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. H.A.-K.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. K.H.A.-A.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. M.A.A.-M.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. N.A.A.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. W.N.A.-M.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. Y.A.-K.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing. M.A.-M.—Methodology, Investigation, and Writing—Review and Editing. S.H.—Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, and Writing—Review and Editing. H.H.F.—Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Data Curation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Review and Editing, and Supervision. T.C.—Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Resources, Software, Methodology, Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, and Guarantor of Review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Qatar National Research Fund, Undergraduate Research Experience Program (UREP) (Grant ID: UREP31-179-3-047). Open Access Funding provided by the Qatar National Library.
Data Availability Statement
This is a meta-analysis. Data are included in primary studies according to policies of parent journals.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our deepest appreciation to the Department of Population Medicine at Qatar University for their continuous help throughout the research process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication. This manuscript has no conflict of interest with Hamad Medical Corporation.
References
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778, Erratum in Lancet 2020, 396, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D. Global, regional and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e065186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Radford, S.J.; McGing, J.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; Moran, G. Systematic review: The impact of inflammatory bowel disease-related fatigue on health-related quality of life. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rogler, G.; Singh, A.; Kavanaugh, A.; Rubin, D.T. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Concepts, Treatment, and Implications for Disease Management. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wan, Q.; Zhao, R.; Xia, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Shen, X.; Wu, X.T. Inflammatory bowel disease and risk of gastric, small bowel and colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis of 26 observational studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 765474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hazel, K.; O’Connor, A. Emerging treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11, 2040622319899297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Shi, H.Y.; Tang, W.; Law, C.C.; Sung, J.J.; Chan, F.K.; Ng, S.C. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Phenotype and Clinical Outcomes of Older-onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parigi, T.L.; D’Amico, F.; Abreu, M.T.; Dignass, A.; Dotan, I.; Magro, F.; Griffiths, A.M.; Jairath, V.; Iacucci, M.; Mantzaris, G.J.; et al. Difficult-to-treat inflammatory bowel disease: Results from an international consensus meeting. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Gulati, A.; Alipour, O.; Shao, L. Relapse From Deep Remission After Therapeutic De-escalation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lasa, J.S.; Olivera, P.A.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Efficacy and safety of biologics and small molecule drugs for patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Murad, M.H.; Fumery, M.; Sedano, R.; Jairath, V.; Panaccione, R.; Sandborn, W.J.; Ma, C. Comparative efficacy and safety of biologic therapies for moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Breedveld, F.C. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Lancet 2000, 355, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; D’Haens, G.; Panés, J.; Kaser, A.; Ferrante, M.; Louis, E.; Franchimont, D.; Dewit, O.; Seidler, U.; et al. Induction therapy with the selective interleukin-23 inhibitor risankizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.F.; Zhu, L.L.; Chen, M.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, H.F.; Feng, X.Q.; Zhu, X.P.; Zhou, Q. The optimal choice of medication administration route regarding intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injection. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2015, 9, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, Z.; Leu, J.H.; Xu, Y.; Nnane, I.; Liva, S.G.; Wang-Lin, S.X.; Kudgus-Lokken, R.; Vermeulen, A.; Ouellet, D. Development of Therapeutic Proteins for a New Subcutaneous Route of Administration After the Establishment of Intravenous Dosages: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 113, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, K.L.; Harder, H.; Fallowfield, L.J.; Jenkins, V.A. Intravenous versus Subcutaneous Drug Administration. Which Do Patients Prefer? A Systematic Review. Patient 2014, 8, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, M. Subcutaneous Infliximab, CT-P13 SC: A Profile of Its Use in the EU. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cock, E.; Pivot, X.; Hauser, N.; Verma, S.; Kritikou, P.; Millar, D.; Knoop, A. A time and motion study of subcutaneous versus intravenous trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schreiber, S.; Ben-Horin, S.; Leszczyszyn, J.; Dudkowiak, R.; Lahat, A.; Gawdis-Wojnarska, B.; Pukitis, A.; Horynski, M.; Farkas, K.; Kierkus, J.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial: Subcutaneous vs. Intravenous Infliximab CT-P13 Maintenance in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2340–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Lukas, M.; Gisbert, J.P.; D’Haens, G.; Hayee, B.; Panaccione, R.; Kim, H.S.; Reinisch, W.; Tyrrell, H.; et al. Etrolizumab versus infliximab for the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (GARDENIA): A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, phase 3 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Baert, F.; Danese, S.; Krznarić, Ž.; Kobayashi, T.; Yao, X.; Chen, J.; Rosario, M.; Bhatia, S.; Kisfalvi, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Vedolizumab Subcutaneous Formulation in a Randomized Trial of Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 562–572.e512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Fedorak, R.N.; Scherl, E.; Fleisher, M.R.; Katz, S.; Johanns, J.; Blank, M.; Rutgeerts, P.; Ustekinumab Crohn’s Disease Study Group. A randomized trial of Ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagan, B.G.; Sands, B.E.; Sandborn, W.J.; Germinaro, M.; Vetter, M.; Shao, J.; Sheng, S.; Johanns, J.; Panés, J.; VEGA Study Group. Guselkumab plus golimumab combination therapy versus guselkumab or golimumab monotherapy in patients with ulcerative colitis (VEGA): A randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 2, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; D’Haens, G.R.; Reinisch, W.; Panés, J.; Chan, D.; Gonzalez, S.; Weisel, K.; Germinaro, M.; Frustaci, M.E.; Yang, Z.; et al. Guselkumab for the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease: Induction Results From the Phase 2 GALAXI-1 Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1650–1664.e165, Erratum in Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1588. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT02574637. Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Brazikumab (MEDI2070) in Participants with Active, Moderate to Severe Crohn’s Disease. ClinicalTrials.gov2021 [Updated 5 May 2021]. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02574637 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Chetwood, J.D.; Tran, Y.; Subramanian, S.; Smith, P.J.; Iborra, M.; Buisson, A.; Paramsothy, S.; Leong, R.W. Intravenous Versus Subcutaneous Infliximab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Bossuyt, P.; Bettenworth, D.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Anjie, S.I.; D’Haens, G.; Saruta, M.; Arkkila, P.; Park, H.; Choi, D.; et al. Comparative Efficacy of Subcutaneous and Intravenous Infliximab and Vedolizumab for Maintenance Treatment of TNF-naive Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 69, 1808–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gajendran, M.; Loganathan, P.; Catinella, A.P.; Hashash, J.G. A comprehensive review and update on Crohn’s disease. Dis. Mon. 2018, 64, 20–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Sands, B.E.; Uddin, S.; Qasim Khan, R.M.; Sagar Mukherjee, R. Clinical Trial Design in Ulcerative Colitis: Interpreting Evolving Endpoints Based on Post Hoc Analyses of the Vedolizumab Phase 3 Trials GEMINI 1 and VISIBLE 1. Crohns Colitis 360 2024, 6, otad076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Viscido, A.; Valvano, M.; Stefanelli, G.; Capannolo, A.; Castellini, C.; Onori, E.; Ciccone, A.; Vernia, F.; Latella, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis: The advantage of endoscopic Mayo score 0 over 1 in patients with ulcerative colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sharara, A.I.; Malaeb, M.; Lenfant, M.; Ferrante, M. Assessment of Endoscopic Disease Activity in Ulcerative Colitis: Is Simplicity the Ultimate Sophistication? Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2022, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vuitton, L.; Marteau, P.; Sandborn, W.J.; Levesque, B.G.; Feagan, B.; Vermeire, S.; Danese, S.; D’Haens, G.; Lowenberg, M.; Khanna, R.; et al. IOIBD technical review on endoscopic indices for Crohn’s disease clinical trials. Gut 2016, 65, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.C.; Glass, K.; Clark, J.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Munn, Z.; Tugwell, P.; Doi, S.A.R. The MethodologicAl STandards for Epidemiological Research (MASTER) scale demonstrated a unified framework for bias assessment. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, S.A.; Thalib, L. A quality-effects model for meta-analysis. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedeker, D.; Gibbons, R.D. A random-effects ordinal regression model for multilevel analysis. Biometrics 1994, 50, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022): Cochrane; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Thompson, S.G. Systematic Review: Why sources of heterogeneity in meta-analysis should be investigated. BMJ 1994, 309, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Furuya-Kanamori, L.; Barendregt, J.J.; Doi, S.A.R. A new improved graphical and quantitative method for detecting bias in meta-analysis. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2018, 16, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- NCT03104413. A Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Risankizumab in Participants with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease Who Failed Prior Biologic Treatment. ClinicalTrial.gov2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03104413 (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- NCT03105128. A Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Risankizumab in Participants with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease. ClinicalTrial.gov2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03105128 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- NCT03782376. A Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of Ustekinumab Re-Induction Therapy in Participants with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease (POWER). ClinicalTrial.gov2018. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03782376 (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Reinisch, W.; Jang, B.I.; Borzan, V.; Lahat, A.; Pukitis, A.; Osipenko, M.; Mostovoy, Y.; Schreiber, S.; Ben-Horin, S.; Lee, S.J.; et al. DOP62 A novel formulation of CT-P13 (infliximab biosimilar) for subcutaneous administration: 1-year result from a Phase I open-label randomised controlled trial in patients with active Crohn’s disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13 (Suppl. S1), S066–S067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, B.E.; Irving, P.M.; Hoops, T.; Izanec, J.L.; Gao, L.L.; Gasink, C.; Greenspan, A.; Allez, M.; Danese, S.; Hanauer, S.B.; et al. Ustekinumab versus adalimumab for induction and maintenance therapy in biologic-naive patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, phase 3b trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 2200–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Kierkus, J.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Fischer, M.; Jairath, V.; Hirai, F.; D’Haens, G.; Belin, R.M.; Miller, D.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Mirikizumab in a Randomized Phase 2 Study of Patients With Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 162, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Danese, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Törüner, M.; Jonaitis, L.; Abhyankar, B.; Chen, J.; Rogers, R.; et al. Vedolizumab versus Adalimumab for Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerstein, J.D.; Ho, E.Y.; Shmidt, E.; Singh, H.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Sultan, S.; Terdiman, J.P.; American Gastroenterological Asso-ciation Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Medical Management of Moderate to Severe Luminal and Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2496–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, G.R.; Loftus, E.V.; Isaacs, K.L.; Regueiro, M.D.; Gerson, L.B.; Sands, B.E. ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Crohn’s Disease in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 481–517, Erratum in Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Bonovas, S.; Doherty, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Raine, T.; Adamina, M.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaghi, E.; Ghasemi-Pirbaluti, M.; Zabihi, M. Etrolizumab versus infliximab in the treatment of induction phase of ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and indirect comparison. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawalec, P.; Pilc, A. An indirect comparison of infliximab versus adalimumab or golimumab for active ulcerative colitis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raine, T.; Bonovas, S.; Burisch, J.; Kucharzik, T.; Adamina, M.; Annese, V.; Bachmann, O.; Bettenworth, D.; Chaparro, M.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Ulcerative Colitis: Medical Treatment. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.T.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Siegel, C.A.; Sauer, B.G.; Long, M.D. ACG Clinical Guideline: Ulcerative Colitis in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 384–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moćko, P.; Kawalec, P.; Pilc, A. Safety Profile of Biologic Drugs in the Therapy of Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annese, V.; Duricova, D.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Jess, T.; Langholz, E. Impact of New Treatments on Hospitalisation, Surgery, Infection, and Mortality in IBD: A Focus Paper by the Epidemiology Committee of ECCO. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haens, G.; Panaccione, R.; Baert, F.; Bossuyt, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Danese, S.; Dubinsky, M.; Feagan, B.G.; Hisamatsu, T.; Lim, A.; et al. Risankizumab as induction therapy for Crohn’s disease: Results from the phase 3 ADVANCE and MOTIVATE induction trials. Lancet 2022, 399, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).