Nusinersen Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Retrospective Multicenter Study of Pediatric and Adult Patients in Kuwait
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Nusinersen Treatment
2.3. Functional and Safety Assessments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
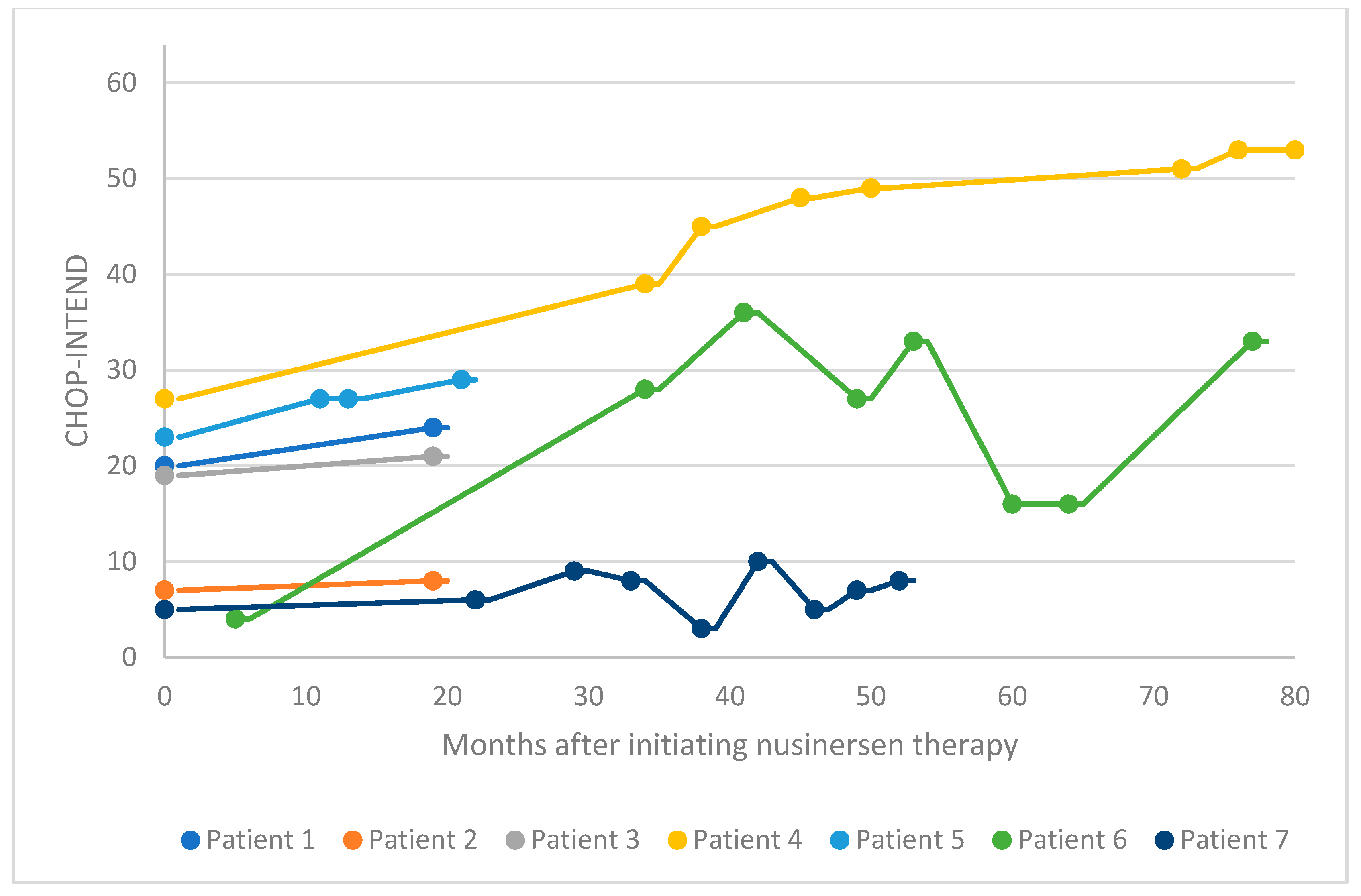
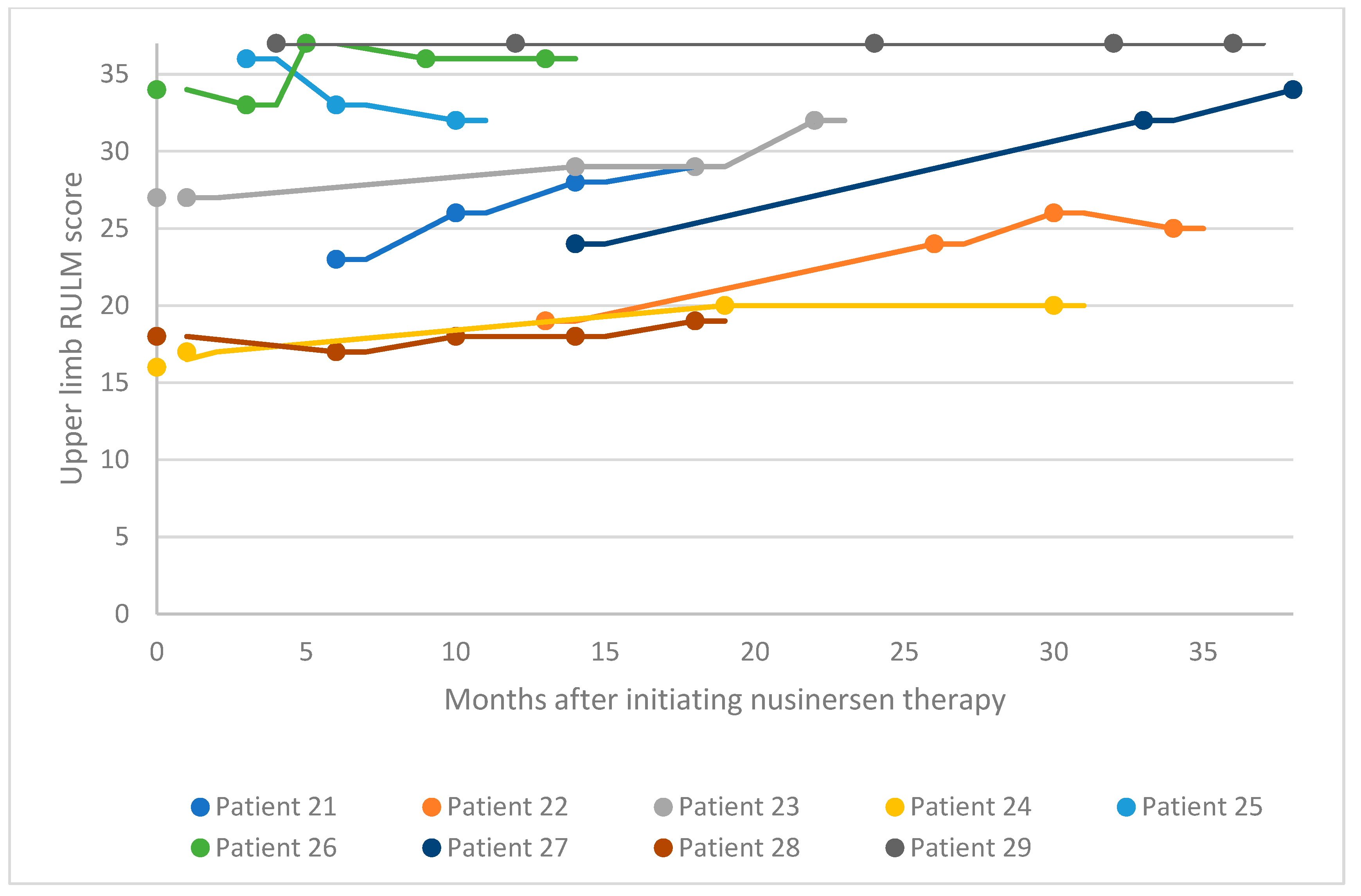
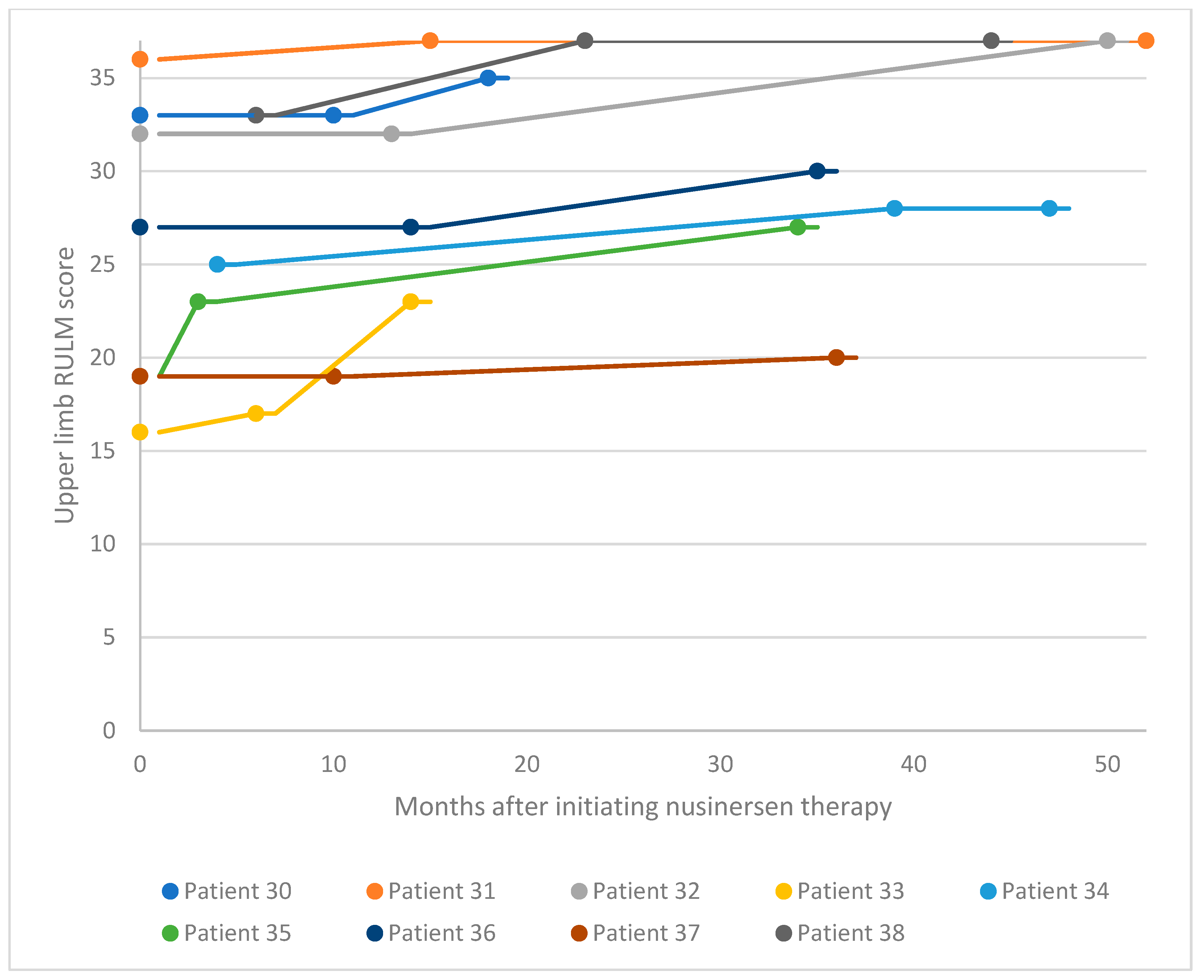
3.2. Functional Motor Studies
3.3. Clinical Presentations and Motor Milestones
3.4. Safety Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, W.D.; Kassar, D.; Kissel, J.T. Spinal muscular atrophy: Diagnosis and management in a new therapeutic era. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaart, I.E.C.; Robertson, A.; Wilson, I.J.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Cameron, S.; Jones, C.C.; Cook, S.F.; Lochmuller, H. Prevalence, incidence and carrier frequency of 5q-linked spinal muscular atrophy—A literature review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rajeh, S.; Bademosi, O.; Gascon, G.G.; Stumpf, D. Werdnig Hoffman’s disease (spinal muscular atrophy type I): A clinical study of 25 Saudi nationals in Al-Khobar. Ann. Saudi Med. 1992, 12, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al Rajeh, S.; Bademosi, O.; Ismail, H.; Awada, A.; Dawodu, A.; al-Freihi, H.; Assuhaimi, S.; Borollosi, M.; al-Shammasi, S. A community survey of neurological disorders in Saudi Arabia: The Thugbah study. Neuroepidemiology 1993, 12, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, A.; Bappal, B.; Al-Shaikh, H.; Al-Khusaibi, S.; Mohammed, A.J. Common autosomal recessive diseases in Oman derived from a hospital-based registry. Community Genet. 2005, 8, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al-Gazali, L.I.; Dawodu, A.H.; Sabarinathan, K.; Varghese, M. The profile of major congenital abnormalities in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) population. J. Med. Genet. 1995, 32, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.G.; Ibrahim, K.; Elsaid, M.F.; Mohamed, R.B.; Abeidah, M.I.A.; Al Rawwas, A.O.; Elshafey, K.; Almulla, H.; El-Akouri, K.; Almulla, M.; et al. Gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy: The Qatari experience. Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jumah, M.; Al Rajeh, S.; Eyaid, W.; Al-Jedai, A.; Al Mudaiheem, H.; Al Shehri, A.; Hussein, M.; Al Abdulkareem, I. Spinal muscular atrophy carrier frequency in Saudi Arabia. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2022, 10, e2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, C.C.; McGovern, V.L.; Murray, J.D.; Gombash, S.E.; Zaworski, P.G.; Foust, K.D.; Janssen, P.M.; Burghes, A.H. Low levels of Survival Motor Neuron protein are sufficient for normal muscle function in the SMNDelta7 mouse model of SMA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6160–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, T.W.; Leach, M.E.; Finanger, E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. In GeneReviews((R)); Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; Clevelandclinic: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, S.J.; Kissel, J.T. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Vajsar, J.; Day, J.W.; Montes, J.; De Vivo, D.C.; Yamashita, M.; Rigo, F.; Hung, G.; Schneider, E.; et al. Treatment of infantile-onset spinal muscular atrophy with nusinersen: A phase 2, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet 2016, 388, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.; Mercuri, E.; Tiziano, F.D.; Bertini, E. Spinal muscular atrophy. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; McDermott, M.P.; Kaufmann, P.; Darras, B.T.; Chung, W.K.; Sproule, D.M.; Kang, P.B.; Foley, A.R.; Yang, M.L.; Martens, W.B.; et al. Observational study of spinal muscular atrophy type I and implications for clinical trials. Neurology 2014, 83, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepers, S.; van den Berg, L.H.; Brugman, F.; Scheffer, H.; Ruiterkamp-Versteeg, M.; van Engelen, B.G.; Faber, C.G.; de Visser, M.; van der Pol, W.L.; Wokke, J.H. A natural history study of late onset spinal muscular atrophy types 3b and 4. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.W.Y.; Carey, K.A.; D’Silva, A.; Vucic, S.; Kiernan, M.C.; Kasparian, N.A.; Farrar, M.A. Health, wellbeing and lived experiences of adults with SMA: A scoping systematic review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, S.; Burglen, L.; Reboullet, S.; Clermont, O.; Burlet, P.; Viollet, L.; Benichou, B.; Cruaud, C.; Millasseau, P.; Zeviani, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 1995, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslesh, T.; Yokota, T. Restoring SMN Expression: An Overview of the Therapeutic Developments for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Cells 2022, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, S.; Burlet, P.; Liu, Q.; Bertrandy, S.; Clermont, O.; Munnich, A.; Dreyfuss, G.; Melki, J. Correlation between severity and SMN protein level in spinal muscular atrophy. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldkotter, M.; Schwarzer, V.; Wirth, R.; Wienker, T.F.; Wirth, B. Quantitative analyses of SMN1 and SMN2 based on real-time lightCycler PCR: Fast and highly reliable carrier testing and prediction of severity of spinal muscular atrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Wu, A. Clinical Outcome of Adult Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patients Treated with Nusinersen: A Case Series Review. Perm. J. 2020, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechtsen, S.S.; Born, A.P.; Boesen, M.S. Nusinersen treatment of spinal muscular atrophy—A systematic review. Dan. Med. J. 2020, 67, A02200100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Connolly, A.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Day, J.W.; Campbell, C.; Connolly, A.M.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Saito, K.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Later-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cintas, P. Current treatments of spinal muscular atrophy in adults. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 179, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacCannell, D.; Berger, Z.; East, L.; Mercuri, E.; Kirschner, J.; Muntoni, F.; Farrar, M.A.; Peng, J.; Zhou, J.; Nestorov, I.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics-based recommendations for a single delayed or missed dose of nusinersen. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2021, 31, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanzman, A.M.; Mazzone, E.; Main, M.; Pelliccioni, M.; Wood, J.; Swoboda, K.J.; Scott, C.; Pane, M.; Messina, S.; Bertini, E.; et al. The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND): Test development and reliability. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2010, 20, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagen, J.M.; Glanzman, A.M.; McDermott, M.P.; Ryan, P.A.; Flickinger, J.; Quigley, J.; Riley, S.; Sanborn, E.; Irvine, C.; Martens, W.B.; et al. An expanded version of the Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale for SMA II and III patients. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2007, 17, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, E.S.; Mayhew, A.; Montes, J.; Ramsey, D.; Fanelli, L.; Young, S.D.; Salazar, R.; De Sanctis, R.; Pasternak, A.; Glanzman, A.; et al. Revised upper limb module for spinal muscular atrophy: Development of a new module. Muscle Nerve 2017, 55, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusakowska, A.; Wojcik, A.; Fraczek, A.; Aragon-Gawinska, K.; Potulska-Chromik, A.; Baranowski, P.; Nowak, R.; Rosiak, G.; Milczarek, K.; Konecki, D.; et al. Long-term nusinersen treatment across a wide spectrum of spinal muscular atrophy severity: A real-world experience. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, M.C.; Coratti, G.; Forcina, N.; Mazzone, E.S.; Scoto, M.; Montes, J.; Pasternak, A.; Mayhew, A.; Messina, S.; Sframeli, M.; et al. Content validity and clinical meaningfulness of the HFMSE in spinal muscular atrophy. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, M.C.; Coratti, G.; Mazzone, E.S.; Montes, J.; Scoto, M.; De Sanctis, R.; Main, M.; Mayhew, A.; Muni Lofra, R.; Dunaway Young, S.; et al. Revised upper limb module for spinal muscular atrophy: 12 month changes. Muscle Nerve 2019, 59, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, B.; Bois, J.M.; Bolz, S.; Kizina, K.; Totzeck, A.; Schlag, M.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Hagenacker, T. Minimal clinically important differences in functional motor scores in adults with spinal muscular atrophy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanzman, A.M.; McDermott, M.P.; Montes, J.; Martens, W.B.; Flickinger, J.; Riley, S.; Quigley, J.; Dunaway, S.; O’Hagen, J.; Deng, L.; et al. Validation of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND). Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2011, 23, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenacker, T.; Wurster, C.D.; Gunther, R.; Schreiber-Katz, O.; Osmanovic, A.; Petri, S.; Weiler, M.; Ziegler, A.; Kuttler, J.; Koch, J.C.; et al. Nusinersen in adults with 5q spinal muscular atrophy: A non-interventional, multicentre, observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, D.; Czech, M.; Chudzynska, E.; Kon, B.; Kostera-Pruszczyk, A. Real World Evidence on the Effectiveness of Nusinersen within the National Program to Treat Spinal Muscular Atrophy in Poland. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagae, L.; Proesmans, M.; Van den Hauwe, M.; Vermeulen, F.; De Waele, L.; Boon, M. Respiratory morbidity in patients with spinal muscular atrophy-a changing world in the light of disease-modifying therapies. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1366943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Finkel, R.S.; Muntoni, F.; Wirth, B.; Montes, J.; Main, M.; Mazzone, E.S.; Vitale, M.; Snyder, B.; Quijano-Roy, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of spinal muscular atrophy: Part 1: Recommendations for diagnosis, rehabilitation, orthopedic and nutritional care. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018, 28, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Bertini, E.; Iannaccone, S.T. Childhood spinal muscular atrophy: Controversies and challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, B.; Nonnemacher, M.; Kizina, K.; Bolz, S.; Totzeck, A.; Thimm, A.; Wagner, B.; Deuschl, C.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Hagenacker, T. Nusinersen treatment in adult patients with spinal muscular atrophy: A safety analysis of laboratory parameters. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.; Wolford, C.; McDermott, M.P.; Macpherson, C.E.; Pasternak, A.; Glanzman, A.M.; Martens, W.B.; Kichula, E.; Darras, B.T.; De Vivo, D.C.; et al. Nusinersen Treatment in Adults With Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, e317–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Nusinersen: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinger, F.; Kosel, C.; Pietz, J.; Rating, D. Headache and backache after lumbar puncture in children and adolescents: A prospective study. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darras, B.T.; Farrar, M.A.; Mercuri, E.; Finkel, R.S.; Foster, R.; Hughes, S.G.; Bhan, I.; Farwell, W.; Gheuens, S. An Integrated Safety Analysis of Infants and Children with Symptomatic Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) Treated with Nusinersen in Seven Clinical Trials. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study for Participants with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) Who Previously Participated in Nusinersen (ISIS 396443) Investigational Studies (SHINE). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02594124 (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhu, B.S.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, X.H.; Guo, J.J.; Jin, C.C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Association of copy number of SMN1 and SMN2 with clinical phenotypes in children with spinal muscular atrophy. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2019, 21, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of Patients | Proportion of Female Patients (%) | SMA Type (%) | Number of SMN2 Gene Copies (%) | Proportion with a Family History of SMA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 45 | Type I: 40 | 1: 10 | 50 |
| Type II: 40 | 2: 50 | |||
| Type III: 20 | 3: 10 | |||
| Type IV: 0 | Unknown: 30 |
| Number of Patients | Proportion of Female Patients (%) | SMA Type (%) | Number of SMN2 Gene Copies (%) | Proportion with a Family History of SMA (%) | Proportion with Parental Consanguinity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 28 | Type I: 0 | 2: 17 | 72 | 94 |
| Type II: 11 | 3: 44 | ||||
| Type III: 89 | 4: 11 | ||||
| Type IV: 0 | Unknown: 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlTawari, A.; Zakaria, M.; Kamel, W.A.; Shaalan, N.; Elghazawi, G.A.I.; Ali, M.E.A.; Salota, D.; Attia, A.; Elanany, E.E.A.; Shalaby, O.; et al. Nusinersen Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Retrospective Multicenter Study of Pediatric and Adult Patients in Kuwait. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030047
AlTawari A, Zakaria M, Kamel WA, Shaalan N, Elghazawi GAI, Ali MEA, Salota D, Attia A, Elanany EEA, Shalaby O, et al. Nusinersen Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Retrospective Multicenter Study of Pediatric and Adult Patients in Kuwait. Neurology International. 2024; 16(3):631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlTawari, Asma, Mohammad Zakaria, Walaa A. Kamel, Nayera Shaalan, Gamal Ahmed Ismail Elghazawi, Mohamed Esmat Anwar Ali, Dalia Salota, Amr Attia, Ehab Elsayed Ali Elanany, Osama Shalaby, and et al. 2024. "Nusinersen Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Retrospective Multicenter Study of Pediatric and Adult Patients in Kuwait" Neurology International 16, no. 3: 631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030047
APA StyleAlTawari, A., Zakaria, M., Kamel, W. A., Shaalan, N., Elghazawi, G. A. I., Ali, M. E. A., Salota, D., Attia, A., Elanany, E. E. A., Shalaby, O., Alqallaf, F., Mitic, V., & Bastaki, L. (2024). Nusinersen Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Retrospective Multicenter Study of Pediatric and Adult Patients in Kuwait. Neurology International, 16(3), 631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030047






