Cardiac Amyloidosis Therapy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Supportive Care
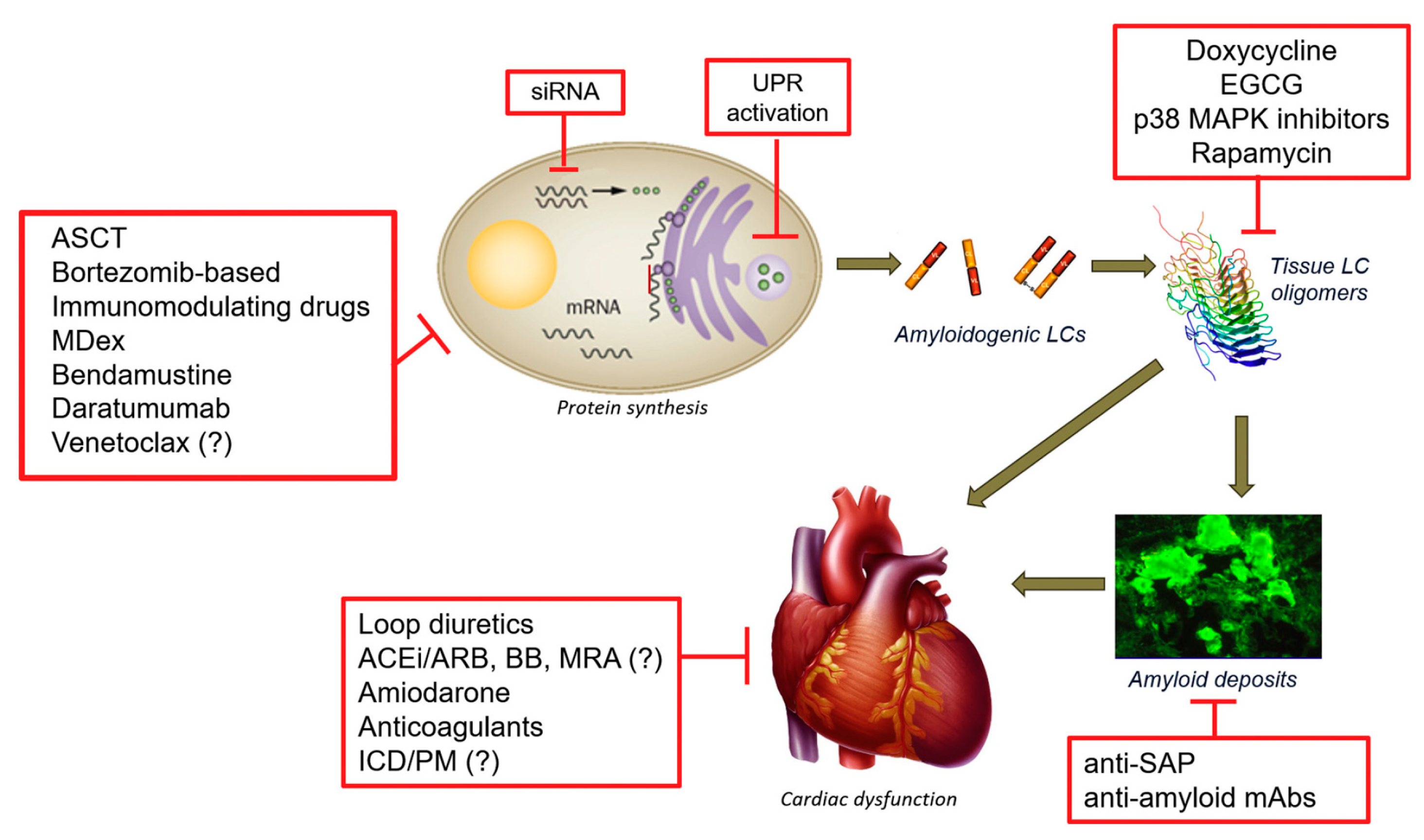
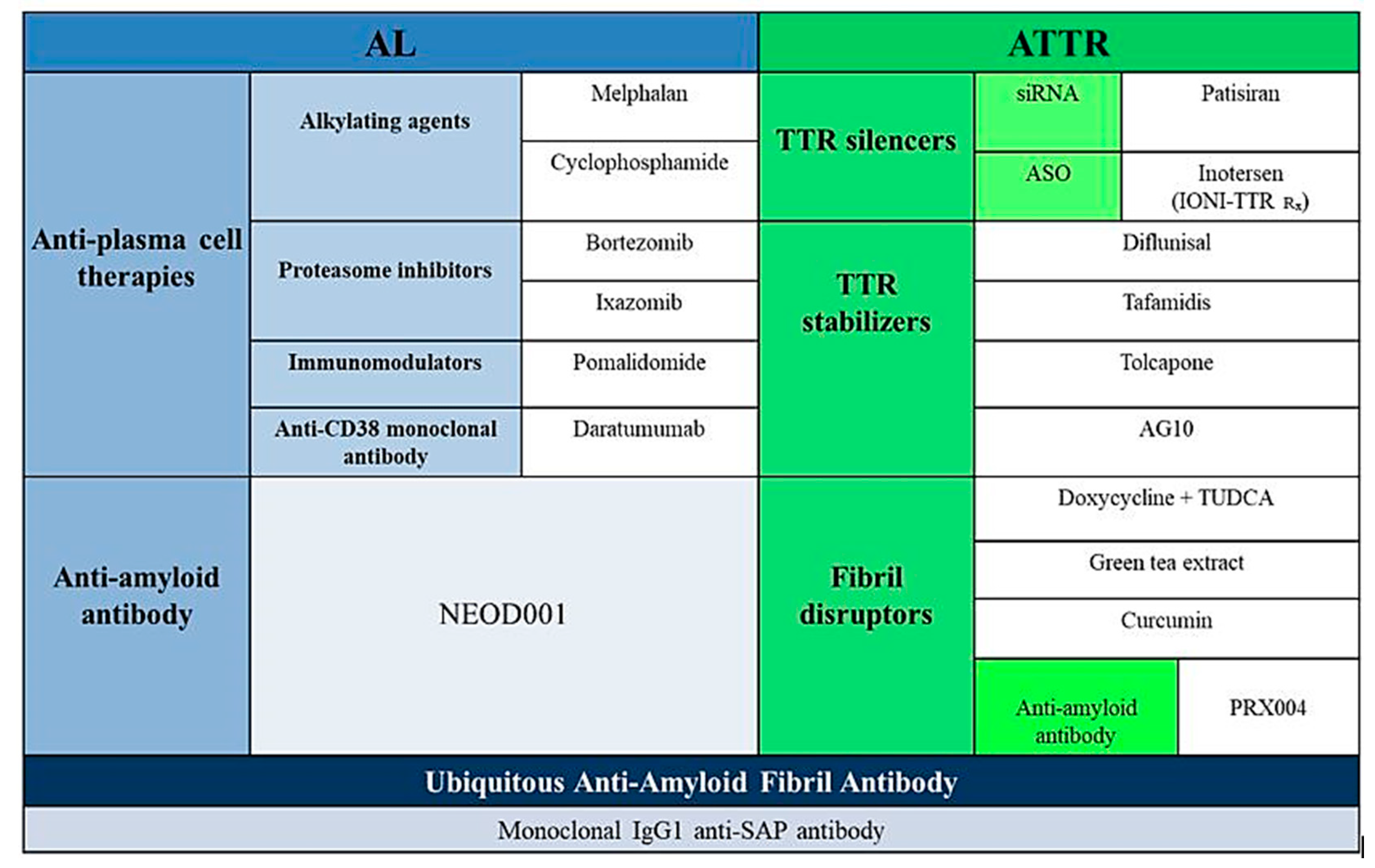
2.1. Light Chain Amyloidosis (AL)
2.1.1. Classical Therapies Targeting the Plasma Cells
2.1.2. Alternative Strategies Targeting the Plasma Cell
2.1.3. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Light Chain Aggregation
2.1.4. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Amyloid Deposits
3. TTR Amyloidosis
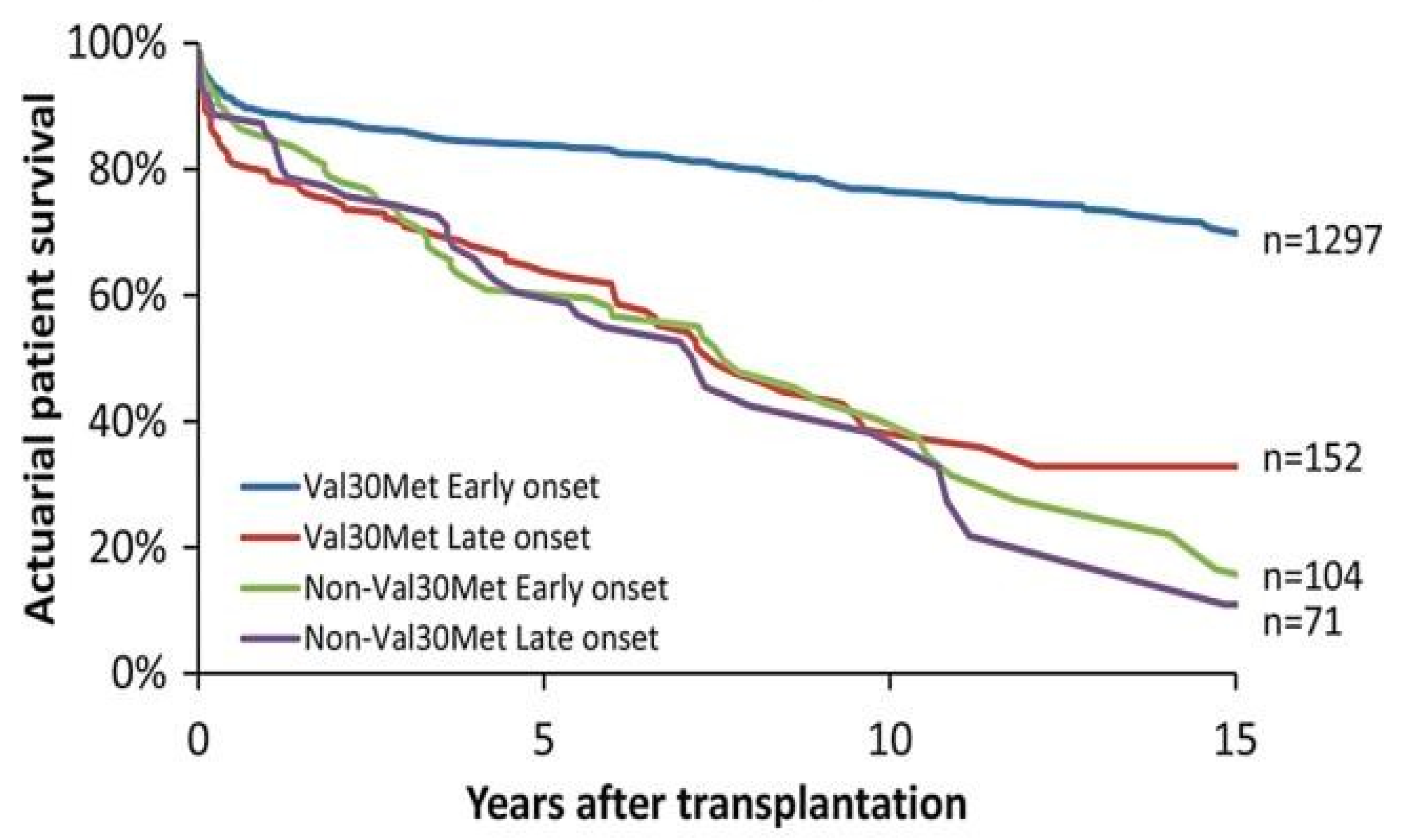
3.1. Liver Transplantation
3.2. Heart Transplantation
3.3. Specific Pharmacological Treatment
3.3.1. Inhibition of TTR Gene Expression
3.3.2. Tetramer Stabilization
3.3.3. Degradation and Reabsorption of Amyloid Fibres
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleszewski, J.J. Cardiac amyloidosis: Pathology, nomenclature, and typing. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quock, T.P.; Yan, T.; Chang, E.; Guthrie, S.; Broder, M.S. Epidemiology of AL amyloidosis: A real-world study using US claims data. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrey, S.W.; Cha, K.; Anderson, J.; Chamarthi, B.; Reisinger, J.; Skinner, M.; Falk, R.H. The clinical features of immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) amyloidosis with heart involvement. QJM 1998, 91, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Buda, G.; Fontana, M.; Barison, A.; Vergaro, G.; Emdin, M.; Merlini, G. Therapies for cardiac light chain amyloidosis: An update. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 271, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, M.; Dispenzieri, A. Natural history and therapy of AL cardiac amyloidosis. Heart Fail Rev. 2015, 20, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, A.; Drachman, B.M.; Judge, D.; Maurer, M.S. Natural history and therapy of TTR-cardiac amyloidosis: Emerging disease-modifying therapies from organ transplantation to stabilizer and silencer drugs. Heart Fail Rev. 2015, 20, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinow, A.; Skinner, M.; Cohen, A.S. Digoxin sensitivity in amyloid cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1981, 63, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassid, Y.J. Cardiac amyloidosis. Two cases with digitalis sensitivity. Ann. Intern. Med. 1961, 55, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Caetano, F.; Almeida, I.; Paiva, L.; Gomes, P.; Mota, P.; Trigo, J.; Botelho, A.; do Carmo Cachulo, M.; Alves, J.; et al. Diagnostic approach to cardiac amyloidosis: A case report. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2016, 35, 305-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Benson, M.D.; Dyck, P.J.; Grogan, M.; Coelho, T.; Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Plante-Bordeneuve, V.; Schmidt, H.H.J.; Merlini, G. Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy of Transthyretin Amyloidosis. J Am. Coll Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristen, A.V.; Dengler, T.J.; Hegenbart, U.; Schonland, S.O.; Goldschmidt, H.; Sack, F.U.; Voss, F.; Becker, R.; Katus, H.A.; Bauer, A. Prophylactic implantation of cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with severe cardiac amyloidosis and high risk for sudden cardiac death. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhoble, A.; Khasnis, A.; Olomu, A.; Thakur, R. Cardiac amyloidosis treated with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator and subcutaneous array lead system: Report of a case and literature review. Clin. Cardiol. 2009, 32, E63–E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algalarrondo, V.; Dinanian, S.; Juin, C.; Chemla, D.; Bennani, S.L.; Sebag, C.; Planté, V.; Le Guludec, D.; Samuel, D.; Adams, D.; et al. Prophylactic pacemaker implantation in familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, O.K.; Ruberg, F.L. Cardiac amyloidosis: An update on pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gameren, I.I. Novel treatments for systemic amyloidosis. Int. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 4, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.W.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.E.; Lenihan, D.J. Emerging Therapeutics for the Treatment of Light Chain and Transthyretin Amyloidosis. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Recent advances in the management of AL Amyloidosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Perfetti, V.; Obici, L.; Caccialanza, R.; Semino, A.; Adami, F.; Cavallero, G.; Rustichelli, R.; Virga, G.; Merlini, G. Association of melphalan and high-dose dexamethasone is effective and well tolerated in patients with AL (primary) amyloidosis who are ineligible for stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004, 103, 2936–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, R.D.; Majeed, U.; Sher, T. Antibody-based immunotherapy for treatment of immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.D.; Landau, H.; Scott, E.C.; Liedtke, M.; Kaufman, J.L.; Rosenzweig, M.; Gasparetto, C.; Vesole, D.H.; Sanchorawala, V.; Lentzsch, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of carfilzomib (CFZ) in previously-treated systemic light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. Blood 2016, 128, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Kortuem, K.M.; Stewart, A.K. Molecular mechanism of action of immune-modulatory drugs thalidomide, lenalidomide and pomalidomide in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Rummel, M.J. Bendamustine: Rebirth of an old drug. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, P.; Schönland, S.; Palladini, G.; Kimmich, C.; Basset, M.; Russo, F.; Foli, A.; Perlini, S.; Bochtler, T.; Ho, A.D.; et al. Response to bendamustine is associated with a survival advantage in a heavily pretreated patients with AL amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2017, 24 (Suppl. S1), 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, G.P.; Schrier, S.L.; Lafayette, R.A.; Arai, S.; Witteles, R.M.; Liedtke, M. Daratumumab yields rapid and deep hematologic responses in patients with heavily pretreated AL amyloidosis. Blood 2017, 137, 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Ramasamy, K. Evolving role of Daratumumab: From backbencher to a frontline agent. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, T.; Colombo, L.; Forloni, G.; Tagliavini, F.; Salmona, M. A new face for old antibiotics: Tetracyclines in treatment of amyloidoses. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5987–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Flynn, K.; Chhabra, S.; Dhakal, B.; Hamadani, M.; Jacobsen, K.; Pasquini, M.; Weihrauch, D.; Hari, P. Rationale and design of DUAL study: Doxycycline to Upgrade response in light chain (AL) amyloidosis (DUAL): A phase 2 pilot study of a two-pronged approach of prolonged doxycycline with plasma cell-directed therapy in the treatment of AL amyloidosis. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2017, 8, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nside Suite for Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03401372 (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Ehrnhoefer, D.E.; Bieschke, J.; Boeddrich, A.; Herbst, M.; Masino, L.; Lurz, R.; Engemann, S.; Pastore, A.; Wanker, E.E. EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Mishra, S.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, J.; Trudeau, K.; Las, G.; Liesa, M.; Shirihai, O.S.; Connors, L.H.; Seldin, D.C.; et al. Lysosomal dysfunction and impaired autophagy underlie the pathogenesis of amyloidogenic light chain-mediated cardiotoxicity. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 9, 1493–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.S.; Hawkins, P.N. Cardiac amyloidosis: Where are we today? J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, K.; Ellmerich, S.; Kahan, M.C.; Tennent, G.A.; Loesch, A.; Gilbertson, J.A.; Hutchinson, W.L.; Mangione, P.P.; Gallimore, J.R.; Millar, D.J.; et al. Antibodies to human serum amyloid P component eliminate visceral amyloid deposits. Nature 2010, 468, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepys, M.B.; Herbert, J.; Hutchinson, W.L.; Tennent, G.A.; Lachmann, H.J.; Gallimore, J.R.; Lovat, L.B.; Bartfai, T.; Alanine, A.; Hertel, C.; et al. Targeted pharmacological depletion of serum amyloid P component for treatment of human amyloidosis. Nature 2002, 417, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericzon, B.G.; Wilczek, H.E.; Larsson, M.; Wijayatunga, P.; Stangou, A.; Pena, J.R.; Furtado, E.; Barroso, E.; Daniel, J.; Samuel, D.; et al. Liver Transplantation for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis: After 20 Years Still the Best Therapeutic Alternative? Transplantation 2015, 99, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liepnieks, J.J.; Zhang, L.Q.; Benson, M.D. Progression of transthyretin amyloid neuropathy after liver transplantation. Neurology 2010, 75, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, G.; Steen, L.; Suhr, O.; Ericzon, B.G.; Groth, C.G.; Andersen, O.; Wallin, B.G.; Seymour, A.; Richardson, S.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. Clinical improvement and amyloid regression after liver transplantation in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Lancet 1993, 341, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, O.B.; Coelho, T.; Buades, J.; Pouget, J.; Conceicao, I.; Berk, J.; Schmidt, H.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Campistol, J.M.; Bettencourt, B.R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of patisiran for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: A phase II multi-dose study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen treatment for patients with Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulawa, C.E.; Connelly, S.; DeVit, M.; Wang, L.; Weigel, C.; Fleming, J.A.; Packman, J.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L.; Foss, T.R.; et al. Tafamidis, a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9629–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Egolum, U.; Parker, S.; Andrews, E.; Ombengi, D.; Ling, H. Tafamidis: A First-in-Class Transthyretin Stabilizer for Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 54, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.S.; Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Melita, H. Cardiac amyloidosis: An underdiagnosed/underappreciated disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 67, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, M.; Aimo, A.; Rapezzi, C.; Fontana, M.; Perfetto, F.; Seferović, P.M.; Barison, A.; Castiglione, V.; Vergaro, G.; Giannoni, A.; et al. Treatment of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis: An update. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Tennent, G.A.; Hutchinson, W.L.; Gallimore, J.R.; Lachmann, H.J.; Goodman, H.J.; Offer, M.; Millar, D.J.; Petrie, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. Sustained pharmacological depletion of serum amyloid P component in patients with systemic amyloidosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.B.; Cookson, L.M.; Barton, S.V.; Liefaard, L.; Lane, T.; Hutt, D.F.; Ritter, J.M.; Fontana, M.; Moon, J.C.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. Repeat doses of antibody to serum amyloid P component clear amyloid deposits in patients with systemic amyloidosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Rappaport, M.; Shimoni, S.; Goland, S.; Voldarsky, I.; Fabricant, Y.; Edri, O.; Cuciuc, V.; Lifshitz, S.; Tshori, S.; et al. A novel monoclonal antibody targeting aggregated transthyretin facilitates its removal and functional recovery in an experimental model. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 41, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iodice, F.; Di Mauro, M.; Migliaccio, M.G.; Iannuzzi, A.; Pacileo, R.; Caiazza, M.; Esposito, A. Cardiac Amyloidosis Therapy: A Systematic Review. Cardiogenetics 2021, 11, 10-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11010002
Iodice F, Di Mauro M, Migliaccio MG, Iannuzzi A, Pacileo R, Caiazza M, Esposito A. Cardiac Amyloidosis Therapy: A Systematic Review. Cardiogenetics. 2021; 11(1):10-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleIodice, Franco, Marco Di Mauro, Marco Giuseppe Migliaccio, Angela Iannuzzi, Roberta Pacileo, Martina Caiazza, and Augusto Esposito. 2021. "Cardiac Amyloidosis Therapy: A Systematic Review" Cardiogenetics 11, no. 1: 10-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11010002
APA StyleIodice, F., Di Mauro, M., Migliaccio, M. G., Iannuzzi, A., Pacileo, R., Caiazza, M., & Esposito, A. (2021). Cardiac Amyloidosis Therapy: A Systematic Review. Cardiogenetics, 11(1), 10-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11010002





