Abstract
With the inclusion of new members, understanding about evolutionary mechanisms and processes by which members of the proposed order, Megavirales, have evolved has become a key area of interest. The central role of gene acquisition has been shown in previous studies. However, the major drawback in gene acquisition studies is the focus on few MV families or putative families with large variation in their genetic structure. Thus, here we have tried to develop a methodology by which we can detect horizontal gene transfers (HGTs), taking into consideration orthologous groups of distantly related Megavirale families. Here, we report an automated workflow MimiLook, prepared as a Perl command line program, that deduces orthologous groups (OGs) from ORFomes of Megavirales and constructs phylogenetic trees by performing alignment generation, alignment editing and protein-protein BLAST (BLASTP) searching across the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant (nr) protein sequence database. Finally, this tool detects statistically validated events of gene acquisitions with the help of the T-REX algorithm by comparing individual gene tree with NCBI species tree. In between the steps, the workflow decides about handling paralogs, filtering outputs, identifying Megavirale specific OGs, detection of HGTs, along with retrieval of information about those OGs that are monophyletic with organisms from cellular domains of life. By implementing MimiLook, we noticed that nine percent of Megavirale gene families (i.e., OGs) have been acquired by HGT, 80% OGs were Megaviralespecific and eight percent were found to be sharing common ancestry with members of cellular domains (Eukaryote, Bacteria, Archaea, Phages or other viruses) and three percent were ambivalent. The results are briefly discussed to emphasize methodology. Also, MimiLook is relevant for detecting evolutionary scenarios in other targeted phyla with user defined modifications. It can be accessed at following link 10.6084/m9.figshare.4653622.
1. Introduction
Ever since the finding of the first giant amoeba virus Mimivirus [1,2], a thrust has been seen among researchers to understand the evolutionary mechanisms underlying their origin. With the discovery of new giant viruses in environmental samples over the past decade, representatives of new or putative new viral families namely Marseilleviruses, Pandoraviruses, Pithoviruses, Faustoviruses and Mollivirus [3,4,5,6,7] have been proposed to be included into a new order, Megavirales, together with viruses already classified in viral families Ascoviridae, Asfarviridae, Iridoviridae, Phycodnaviridae, and Poxviridae, and formerly known as nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDVs). Members of the proposed order Megavirales have various genome sizes and infect a wide range of eukaryotic hosts [8,9,10]. This genome size variation (ranging from 100 kb to 2550 kb) has kept researchers questioning about their origin and evolution as these viruses challenge the established description of viruses and viral diversity. Certainly, they share a common ancestor, virion architectures and major functional features, as evident from the results of phylogenetic and phyletic analyses [10]. To explain this variation, several hypotheses have been put forward that postulate that either Megavirales were derived from a cellular ancestor after going through the process of genome degradation and adaptation [11,12], or, through expansion of viral genomes by acquisition of genes by the process of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Regarding the latter case, the role of HGT in genome expansion cannot be discarded. However, genes transfer studies done so far have been more focused on understanding the evolution of a few Megavirale families (Phycodnaviridae and Mimiviridae) in particular, because of their genome variation and availability of several sequenced genomes. Apart from this, several studies have pointed out that the process of gene duplications [20,21], in addition to spreading of mobile genetic elements as introns or DNA transposons belonging to Polinton/virophage superfamily [22,23], can be evolutionary forces guiding the Megavirale genomic evolution.
Horizontal gene transfer involves a direct transfer of genetic material from one lineage to another. Main approaches used for detection of HGT in silico depend upon the analysis of sequence composition [24,25,26] or upon phylogenetic methods. Phylogenetic methods enable detection of gene transfers either (i) by reconstructing the gene tree and comparing it with the reference species tree, often via statistical analysis like bipartitions, quartet bipartitions, etc. [27,28]; or (ii) by examining gene history, through phyletic profiles [29]. Several algorithms like LatTrans [30], HorizStory [31], Efficient Evaluation of Edit Paths [32] and PhyloNet package including RIATA-HGT [33] and T-REX [34] are available to detect HGT events.
Members of the proposed order Megavirales have been shown over the past decade to be very common in our environment [35,36] and giant viruses were also detected in humans and suspected to be potential human pathogens [37,38,39]. Therefore, the need for understanding the major evolutionary forces guiding the evolution of Megavirale genomes and their gene history is growing, which makes it necessary to adopt some systematic searching for identifying the role of reticulate evolutionary events like HGT in evolution of distantly related Megavirale families. We herein describe an automated phylogenetic analysis workflow, MimiLook, that depends on the use of stringent filters to search systematically for probable instances of HGT in Megavirales. The workflow scripted in Perl connects existing programs to automate mining of conserved orthologous sequences among a designated number of Megavirale ORFomes, followed by a Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) search to retrieve sequences of cellular domains of life that are homologous to these Megavirale clusters. The BLAST results are then subjected to alignment generation and phylogenetic tree (both gene tree and species tree) construction. Phylogenetic trees were then queried in T-REX [34] algorithm for detection of HGT instances. A reference Megavirale family tree was constructed from the orthologous groups’ information and various evolutionary scenarios are then mapped to this reference tree. Along with detection of HGT, the output of the workflow reveals various information about orthologous groups (OGs), such as which are Megavirale-specific and OGs which form monophyletic clades with other cellular domains of life. Some of the identified transfers are in accordance with previous analyses [40]. The results are discussed in brief to give more emphasis on development of strategy and methodology which is our main aim to present here.
2. A General Overview of Workflow
Our workflow inputs whole ORFomes in FASTA format (user-defined) and executes the following basic steps in sequential order: orthologous cluster identification, reference species tree construction, selection of representative sequence from cluster, searching for homologs of the representative sequence using protein-protein BLAST (BLASTP) in local database, filtering of the blast hits, retrieval of taxonomic lineage information, coding BLAST hits with taxonomy identifier (TaxID), alignment generation from filtered BLAST output, maximum likelihood (ML) tree generation from alignment, preparation of species tree for each gene tree, and finally, detection of HGT event (Figure 1). Some steps in the workflow involve automated curation and filtering of dataset for ease of use and understanding, which will be discussed in following paragraphs. The Megavirale family tree (reference tree) was constructed from resulting species tree and OGs are tagged on the tree manually, along with their evolutionary scenarios. The phylogenetic trees of each OG in Newick format are visualized using a Python script in Environment for Tree Exploration (ETE) phylogeny.
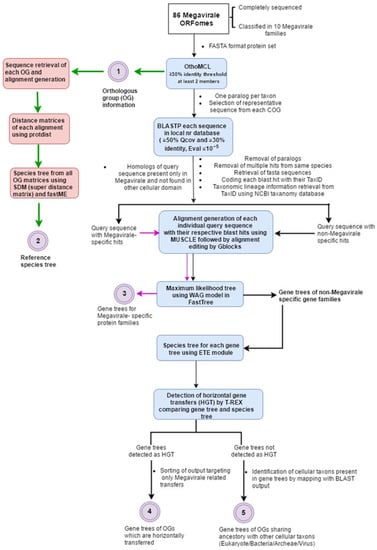
Figure 1.
Depiction of workflow followed in MimiLook. Square colored boxes (in blue) indicate the calling of external executable algorithms in workflow. The bulleted text at each arrow and squared box without color indicates the steps which are written in Perl in this workflow. Colored circles with numbering are the outputs in each step of workflow (description of output labeled corresponding to them).
2.1. Complete ORFomes
The ORFomes for 86 completely sequenced members of 10 families (3 ascoviruses, 1 asfarvirus, 1 faustovirus, 16 iridoviruses, 3 marseilleviruses, 5 mimiviruses, 2 pandoraviruses, 18 phycodnaviruses, 1 pithovirus and 36 poxviruses) within the order Megavirales were downloaded from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The details regarding NCBI accession numbers and download link for these genomes are provided in Table S1.
2.2. Detection of Orthologous Groups
Complete ORFomes were queried in OrthoMCL [41] to retrieve orthologous protein groups with ≥30% identity and Expect (E) value of less than 0.00001 as thresholds. Only groups with members longer than 50 amino acids and at least two members were considered for further analysis. OrthoMCL is based upon all-against-all BLASTP algorithm [42] and Markov Cluster algorithm [43] that allows simultaneous classification of global relationships in a similarity space. OrthoMCL creates a similarity matrix from E-values and then clusters homologous proteins into related groups. The main parameter that influences the size of a cluster is the inflation parameter. A lower inflation parameter represents a more lenient clustering parameter (fewer clusters with more proteins) and a higher inflation parameter represents a more stringent clustering parameter (more clusters with fewer proteins). The inflation index of 1.5 was used to regulate cluster tightness (granularity), and the resulting clusters of orthologous groups were analyzed further (output 1).
Orthologous group information (output 1, Tables S1 and S2) was used to construct the reference Megavirale family tree using distance super-matrix approach. Amino acid sequences of each OG were retrieved from ORFome sets and they were further subjected to alignment generation using MUSCLE [44] followed by distance matrices generation by deploying ‘protdist’ program from Phylip package [45]. The computational efficiency and ease of use of distance-based tree reconstruction methods make them an attractive option for large data sets, where they can provide a snapshot of the underlying evolutionary relationships quickly and easily. A species tree was constructed from all gene matrices using the super distance matrix (SDM) approach—method weighted by alignment lengths [46]. A balanced minimum evolution tree was inferred from the resulting distance supermatrix by FastME (fast minimum evolution) [47], using NNI (nearest neighbor interchange), SPR (sub-tree pruning and grafting), and TBR (Tree Bifurcation and Reconnection) tree topology refinement (output 2). Further, Megavirale family tree topology was inferred from species tree and used as a reference tree for tagging various evolutionary scenarios (see Section 2.6). Many OGs will have multiple sequences for some proteins from same ORFomes, due to paralogy. In some analyses (e.g., gene family studies), paralogous sequences are informative, but, in this study, only one paralog per taxon is used to build the alignment for HGT detection in major orthologous groups. In these cases of two copies of orthologous genes in the same genome, we included the paralog with the best bit score in the corresponding cluster. After removal of paralogs from the OGs, we selected the representative sequence from each cluster—longest sequence in cluster was selected to increase the phylogenetic spread of homologs in non-redundant (nr) database—and carried out BLASTP search to detect homologs.
2.3. Search for Homologs and Curation of Blast Output
BLASTP [42] was used against local nr database (last accessed on 14 January 2016) to find potential homologs of each representative sequence (scoring matrix BLOSUM62, word size 3, low complexity region filtered out). An E-value cutoff equal to or less than 10−5 was set to filter out possible contaminants from blast output and hits below the threshold of 50% query size (coverage) plus 30% identity were further discarded. Since, we took one representative from each cluster, other sequences present in OG were automatically re-picked from nr database. A tabular output is generated with taxonomic lineage information of each significant hit (information such as TaxID, species name, etc., were retrieved). BLAST is currently the most common way of assessing homologous sequences, however, it can return identical hits (such as highly similar sequences from different strains of same species, allelic variations, paralogs, etc.) that do not add information to the analysis but instead make the final analysis more time-consuming.
Thus, to make BLAST tabular output more feasible and easy to use, we removed such sequences from the Blast output file. From hits of each queried sequence, paralogs from same species were removed by selecting the hit with the best bit score. Also, hits from different strains of same species were removed and one with the best bit score was selected. Amino acid sequences of significant hits were retrieved in FASTA format using blastdbcmd utility from nr database for each OG and taxonomic lineage information was extracted using corresponding TaxID. For keeping track of the names in this large dataset, we complimented the FASTA headers with their TaxIDs; thus, each OG had their unique homologous protein set in FASTA format coded with their TaxIDs. An annotation file in tabular format was prepared manually containing the TaxID of all Megavirale members retrieved from NCBI (both used and unused in dataset of our analysis; phages were excluded). Further, from homologous protein sets, those which contain Megavirale-specific hits and those containing non-specific Megavirale hits were separated, by comparing them with the annotation file. Both protein sets were used for further assessment in our workflow.
2.4. Alignment Generation, Alignment Editing and Tree Preparation
Both protein sets (containing amino acid sequences of optimal BLAST hits) were then queried in alignment program MUSCLE [44] to generate the alignment for each orthologous group, which is executed with the program’s default settings. After generation of alignment, Gblocks [48] was used for the removal of poorly aligned positions and highly divergent regions. Maximum likelihood (ML) trees from each such alignment were constructed using FastTree [49] using WAG [50] model of amino acid evolution. FastTree is optimized to work with large dataset and considered to be more accurate than many of other standard ML-based phylogenetic tree construction algorithms such as PhyML 3.0 or RAxML 7 [49,51]. At this stage of workflow, we were able to generate gene trees in Newick format of those OG which are specific (output 3) and non-specific to Megavirales. For further analysis, gene trees generated from non Megavirale-specific protein sets were queried in T-REX for detection of HGT event.
2.5. Detection of Horizontal Gene Transfer Event
Horizontal gene transfer detection by phylogenetic discordance method relies upon comparing gene tree with reference species tree. The trees generated by FastTree algorithm were used as gene trees for this analysis. Species trees were constructed for each gene tree separately. For this, we retrieved the TaxIDs of all the members of each alignment and fetched their common tree from NCBI taxonomy browser using those IDs. Each pair of species and gene tree was then subjected to T-REX [34] algorithm for inferring probable HGTs. T-REX is a suite of phylogenetic tools dedicated for several analyses including in-silico detection of HGT. Given a test and a reference tree, T-REX calculates their proximity by several distance-based measures and predicts minimum-cost scenario HGTs by progressive reconciliation of those trees. T-REX was optimized by taking into account the evolutionary events such as gene duplication, deletion, etc., and was attributed to be faster and more accurate than most of the other currently available tree discordance methods [34]. Further, this algorithm validates HGT by bootstrap and compilation of the consensus and interactive HGT scenarios. The output in text format contains name of the tree in which HGT is identified, donor branch, recipient branch and various statistical values like Robinson foulds distance, least square coefficient and bipartition dissimilarity. Since, our analysis only requires detecting HGTs either from Megavirales to cellular domains or from cellular domains to Megavirales; we modified the T-REX tabular output so that it contains only those types of detections. After curation, output 4 was generated containing the information of horizontally transferred gene families (OGs) with information of putative donor and receptor. Gene trees in which a HGT event was not detected were then further mapped with BLAST tabular output which contains taxonomic lineage information of each homologous hit, by which we are able to extract information about other cellular domains present in tree, thus generating output 5, which include gene trees of those OGs which have common origin with other cellular domains of life.
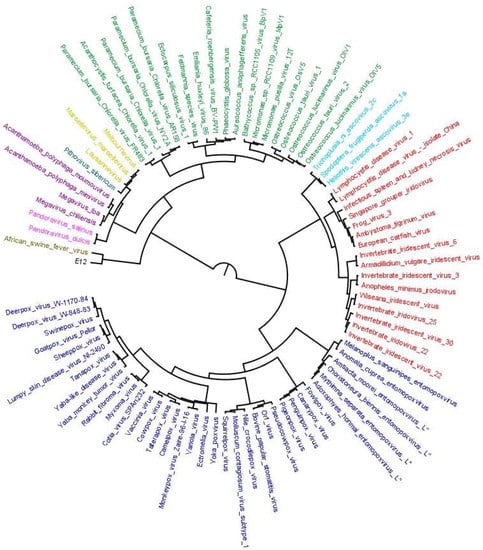
Gene trees which are generated at the end of this workflow (output 3, output 4, output 5) were in Newick format. So, in order to visualize the proper midpoint rooted and color coded phylogenetic trees, a python script was implemented in ETE toolkit [52]. For this purpose, another annotation file was prepared manually from taxonomic lineage information of Blast output. Here, for each taxon present in BLAST output, we prepared a tabular file containing columns with species name; cellular domain—Eukaryote, Bacteria, Archaea, Virus, Phages, Megavirales included in dataset, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) (other Megavirales not included in dataset); group and lineage (highest possible taxonomic level).
2.6. Plotting OGs and Evolutionary Scenarios on Reference Megavirale Family Tree
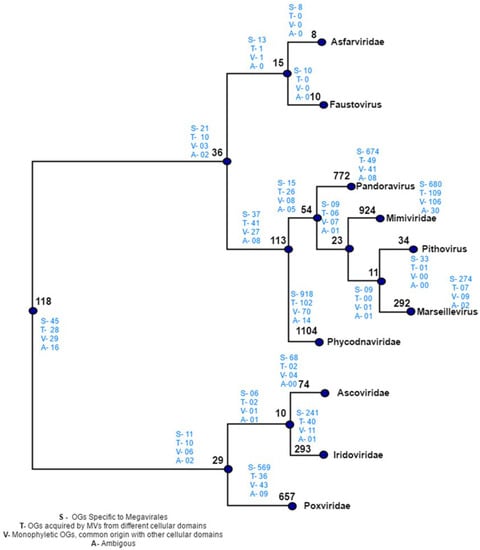
Megavirale family tree topology was inferred from the reference species (output 2). Megavirale family specific OGs were plotted on this family tree considering presence/absence parameter for example, if a particular OG is present in at least one species of Megavirale family, then it is considered to be present in that family. Once the family specific OGs were attributed to their respective nodes, OGs shared between Megavirale families were than tagged on the tree. If a particular shared OG is present in multiple external nodes (family specific nodes), then it is judged to be present in common internal node (Figure S1). Further, evolutionary scenarios detected by our workflow (output 3, output 4 and output 5) were tagged on this tree too. The plotting was done manually using Microsoft Excel spreadsheet utility.
3. Implementation
MimiLook is a Perl (version 5.18.2) command line program developed on a 64-bit Linux architecture, currently running on Ubuntu 14.04.1 LTS. Before its commencement, programs like OrthoMCL [41], Muscle [44], protdist [45], SDM [46], fastME [47], Gblocks [48], FastTree [49], T-REX [34] were installed since the workflow requires calling these algorithms. More details of these programs are available in their respective installation documents. Local blast nr database was downloaded and installed. Also, the workflow requires ETE toolkit [52]. The input for MimiLook is a directory containing ORFomes to be analyzed in FASTA format and the final output is a directory containing gene trees (Newick format), blast tabular output, reference species tree (Newick format) and text file with information of HGT events. By using python script provided for plotting phylogenetic trees (10.6084/m9.figshare.4645273), png format trees were constructed (10.6084/m9.figshare.4645273). This workflow can be accessed from following link (10.6084/m9.figshare.4653622).
5. Discussion and Future Perspective
Several approaches can be considered to detect incidence of HGT [26,27,28], however, the most convincing method to detect HGT uses phylogenetic inference [53]. Highly supported topological incongruence between a strongly supported gene tree and the known species tree can be penuriously explained by a reticulate evolutionary event like HGT [54]. Currently, few algorithms are available to detect HGT [29,30,31,32,33], but no workflow has been devised yet for searching systematically gene acquisition in large dataset of clustered orthologs. MimiLook described here is such an attempt to elucidate the evolutionary scenarios in user specific ORFomes, especially among MVs. It not only detects the instances of gene acquisition, but also allowed us to glance into other evolutionary patterns like phyla specificity and provided information about shared ancestry.
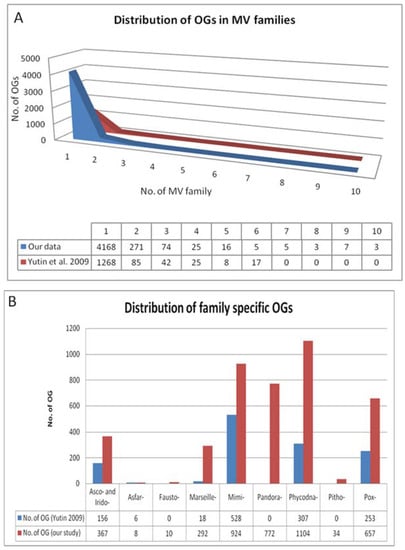
Phylogenetic analysis on orthologous clusters of Megavirales through our automated workflow MimiLook has detected a sizeable number of gene families which can be deduced as being acquired via HGT. Apart from this, we were also able to identify those gene families which are specific only of the order Megavirales and those gene families which share ancestry with cellular organisms (eukaryotes, bacteria, archaea), phages or other viruses. The main focus of this automated workflow is to detect reticulate evolutionary events like HGT by taking into consideration members from all the established or putative families of Megavirales. Interestingly, 129 gene families (OGs) have been found to be horizontally transferred by Megavirales to other organisms by our methodology, some of which are in accordance with what was described in previous studies [40,55,56,57] where acquisition of Megavirale genes by various eukaryotes has been shown. However, phylogenies of few gene families (approximately three percent) are ambivalent, because of a weak phylogenetic signal or complex phylogenetic patterns of transfers. So, in a further study, we could predict an evolutionary model of Megavirales by taking these pit falls in consideration, and the MimiLook has paved us a way for that by clustering distantly related Megavirale families and detecting evolutionary scenarios in orthologous gene families using stringent filters and statistical validation.
Gene families which are predicted as Megavirale-specific (80%) can be checked deeply and might be useful as genetic markers to identify new Megavirale species from environmental genomes and meta-genomes, considering the fact that a large fraction of those gene families are found family specific. By implementing this strategy, we can now have a closer look into this process.
Until recently, the impact of gene accretion in Megavirales was thought to be limited [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. The reasons for this viewpoint included focus on a limited number of ORFomes of few families and the apparent reluctance of large-scale searches for HGT considering all available Megavirale ORFomes. This can be seen as a major shortcoming in interpreting the evolutionary forces guiding evolution of different distantly related families of Megavirales. So far, glancing into the output of MimiLook, the impact of gene accretion in Megavirales appears to be unlimited, which could have a profound effect on their evolution. Thus, our fully automated methodology which was developed here specifically for Megavirales, can give us more precise idea based on a more sensitive strategy about the evolutionary patterns among major families. Most importantly, using this methodology, we were able to infer putative donors and receptors in gene transfers and were able to obtain a more descriptive evolutionary pattern. Another important observation from the output is that some of the putative donors transferring genes are not known to be hosts of Megavirales, nor are they known to interact with them, thus suggesting the possibility of finding new ecological niches of them. Our results that the genomes of Megavirales members harbor many specific genes with no cellular homologs (approximately 80% Megavirale-specific OGs), as well as substantial numbers of genes inferred to have been transferred horizontally (approximately nine percent of OGs) from other cellular organisms, suggest that these viruses are not bags of unused genes taken from various cellular organisms, but, instead they might have acquired genes with a balanced process of genetic exchanges with their environmental interactions.
Although MimiLook was basically designed to detect evolutionary scenarios in Megavirales with an emphasis on reticulate events like HGT, ORFome sets can be selected according to the purpose of study. With little modification, we used this tool for detecting evolutionary scenarios in Mycobacterium species in our laboratory. MimiLook thus can be implemented for user specific sets of species to detect evolutionary events irrespective of a particular domain of life or viral group. Also, at each step, including clustering, alignment generation and editing, tree preparation and detection of HGT, algorithms and parameters can be modified according to the plan of the study.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/9/4/72/s1, Figure S1: Mapping OGs and evolutionary scenarios on reference tree, Figure S2: An example output of statistically validated HGT as predicted by T-REX and then verified by human expertise, Table S1: 86 Megavirale ORFomes used in this study, Table S2: Grouped Megavirale genes in cluster of orthologus groups, Table S3: Presence/absence matrix of orthologus groups in respective Megavirale species, Table S4: Predicted evolutonary scenarios in OGs of Megavirales.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by INFECTIOPOLE-SUD grant to S.J.
Author Contributions
D.R. and P.P. conceived the study; S.J. and P.C. designed the methodology. S.J. performed the experiments; A.P. wrote the Perl scripts; S.J. and P.P. analyzed the data; S.J. and A.P. contributed equally.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- La Scola, B.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Jungang, L.; de Lambellerie, X.; Drancourt, M.; Birtles, R.; Claverie, J.M.; Raoult, D. A giant virus in amoebae. Science 2003, 299, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Abergel, C.; Renesto, P.; Ogata, H.; La Scola, B.; Suzan, M.; Claverie, J.M. The 1.2-megabase genome sequence of Mimivirus. Science 2004, 306, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, M.; Yutin, N.; Pagnier, I.; Barrassi, L.; Fournous, G.; Espinosa, L.; Robert, C.; Azza, S.; Sun, S.; Rossmann, M.G.; et al. Giant Marseillevirus highlights the role of amoebae as a melting pot in emergence of chimeric microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21848–21853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippe, N.; Legendre, M.; Doutre, G.; Couté, Y.; Poirot, O.; Lescot, M.; Arslan, D.; Seltzer, V.; Bertaux, L.; Bruley, C.; et al. Pandoraviruses: Amoeba viruses with genomes up to 2.5 Mb reaching that of parasitic eukaryotes. Science 2013, 341, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, M.; Bartoli, J.; Shmakova, L.; Jeudy, S.; Labadie, K.; Adrait, A.; Lescot, M.; Poirot, O.; Bertaux, L.; Bruley, C.; et al. Thirty-thousand-year-old distant relative of giant icosahedral DNA viruses with a pandoravirus morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014, 111, 4274–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reteno, D.G.; Benamar, S.; Khalil, J.B.; Andreani, J.; Armstrong, N.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Faustovirus, an asfarvirus-related new lineage of giant viruses infecting amoebae. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, M.; Lartigue, A.; Bertaux, L.; Jeudy, S.; Bartoli, J.; Lescot, M.; Alempic, J.M.; Ramus, C.; Bruley, C.; Labadie, K.; et al. In-depth study of Mollivirus sibericum, a new 30,000-y-old giant virus infecting Acanthamoeba. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5327–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Common origin of four diverse families of large eukaryotic DNA viruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11720–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Eukaryotic large nucleo-cytoplasmic DNA viruses: Clusters of orthologous genes and reconstruction of viral genome evolution. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; de Lamballerie, X.; Yutin, N.; Asgari, S.; Bigot, Y.; Bideshi, D.K.; Cheng, X.W.; Federici, B.A.; Van Etten, J.L.; Koonin, E.V.; et al. “Megavirales”, a proposed new order for eukaryotic nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claverie, J.M. Viruses take center stage in cellular evolution. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, D.; Legendre, M.; Seltzer, V.; Abergel, C.; Claverie, J.M. Distant Mimivirus relative with a larger genome highlights the fundamental features of Megaviridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17486–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, D.; López-García, P. Comment on “The 1.2-megabase genome sequence of Mimivirus”. Science 2005, 308, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, L.M.; Balaji, S.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. Evolutionary genomics of nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 156–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filée, J.; Siguier, P.; Chandler, M. I am what I eat and I eat what I am: Acquisition of bacterial genes by giant viruses. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filée, J.; Pouget, N.; Chandler, M. Phylogenetic evidence for extensive lateral acquisition of cellular genes by Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Brochier-Armanet, C. Giant viruses, giant chimeras: The multiple evolutionary histories of Mimivirus genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Mimiviridae: Clusters of orthologous genes, reconstruction of gene repertoire evolution and proposed expansion of the giant virus family. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Origin of giant viruses from smaller DNA viruses not from a fourth domain of cellular life. Virology 2014, 466–467, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhre, K.J. Gene and genome duplication in Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14095–14101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filée, J.; Chandler, M. Convergent mechanisms of genome evolution of large and giant DNA viruses. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnues, C.; la Scola, B.; Yutin, N.; Fournous, G.; Robert, C.; Azza, S.; Jardot, P.; Monteil, S.; Campocasso, A.; Koonin, E.V.; et al. Provirophages and transpovirons as the diverse mobilome of giant viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18078–18083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Koonin, E.V. Polintons: A hotbed of eukaryotic virus, transposon and plasmid evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, S.D.; Berg, O.G. Detection of genes with atypical nucleotide sequence in microbial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschavanne, P.; Giron, A.; Vilain, J.; Dufraigne, C.; Fertil, B. Genomic signature is preserved in short DNA fragments. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering, Arlilngton, VA, USA, 8–10 November 2000; pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dufraigne, C.; Fertil, B.; Lespinats, S.; Giron, A.; Deschavanne, P. Detection and characterization of horizontal transfers in prokaryotes using genomic signature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, H. An approximately unbiased test of phylogenetic tree selection. Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaxybayeva, O.; Gogarten, J.P.; Charlebois, R.L.; Doolittle, W.F.; Papke, R.T. Phylogenetic analyses of cyanobacterial genomes: Quantification of horizontal gene transfer events. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snel, B.; Bork, P.; Huynen, M.A. Genomes in flux: The evolution of archaeal and proteobacterial gene content. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M.; Lagergren, J. Efficient algorithms for lateral gene transfer problems. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual International Conference on Research in Computational Biology; El-Mabrouk, N., Lengauer, T., Sankoff, D., Eds.; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, D.; Charlebois, R.L.; Doolittle, F.; Bapteste, E. Deduction of probable events of lateral gene transfer through comparison of phylogenetic trees by recursive consolidation and rearrangement. BMC Evol. Biol. 2005, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiko, R.G.; Hamilton, N. Phylogenetic identification of lateral genetic transfer events. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Than, C.; Ruths, D.; Nakhleh, L. PhyloNet: A software package for analyzing and reconstructing reticulate evolutionary relationships. BMC Bioinf. 2008, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boc, A.; Diallo, A.B.; Makarenkov, V. T-REX: A web server for inferring, validating and visualizing phylogenetic trees and networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W573–W579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; Raoult, D. Megavirales composing a fourth domain of life: Mimiviridae and Marseilleviridae. In Viruses: Essential Agents of Life; Witzany, I., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 217–244. [Google Scholar]
- Pagnier, I.; Reteno, D.G.; Saadi, H.; Boughalmi, M.; Gaia, M.; Slimani, M.; Ngounga, T.; Bekliz, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; et al. A decade of improvements in Mimiviridae and Marseilleviridae isolation from amoeba. Intervirology 2013, 56, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; La Scola, B.; Birtles, R. The discovery and characterization of Mimivirus, the largest known virus and putative pneumonia agent. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Giant viruses of amoebae as human pathogens. Intervirology 2013, 56, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, L.; Baud, D.; Bertelli, C.; Greub, G. Lausannevirus seroprevalence among asymptomatic young adults. Intervirology 2013, 56, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filée, J. Genomic comparison of closely related giant viruses supports an accordion-like model of evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Stoeckert, J.; Christian, J.; Roos, D.S. OrthoMCL: Identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, S. Graph Clustering by Flow Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP: Phylogenetic inference package, version 3.2. Cladistics 1989, 19, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Criscuolo, A.; Berry, V.; Douzery, E.J.; Gascuel, O. SDM: A fast distance-based approach for (super) tree building in phylogenomics. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O. FastME 2.0: A comprehensive, accurate, and fast distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2798–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Paramvir, S.D.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, S.; Goldman, N. A general empirical model of protein evolution derived from multiple protein families using a maximum-likelihood approach. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Linder, C.R.; Warnow, T. RAxML and FastTree: Comparing two methods for large-scale maximumlLikelihood phylogeny estimation. PLoS ONE 2011, 16, e27731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Serra, F.; Bork, P. ETE3: Reconstruction, analysis and visualization of phylogenomic data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, M.A. On surrogate methods for detecting lateral gene transfer. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 201, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, P.J.; Palmer, J.D. Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filee, J. Multiple occurrences of giant virus core genes acquired by eukaryotic genomes: The visible part of the iceberg? Virology 2014, 466–467, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maumus, F.; Epert, A.; Nogue, F.; Blanc, G. Plant genomes enclose footprints of past infections by giant virus relatives. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 42–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forterre, P. Giant viruses: Conflicts in revisiting the virus concept. Intervirology 2010, 53, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).