The Viruses Editorial Office wishes to notify its readers of corrections in [1].
The authors refer to [2], writing that the experiments were done using 126 mM/kg/day for mouse treatment without side effects. The correct dose used in [2] was 126 µmol/kg/day.
On page 6235, the last sentence of the first paragraph should read: “These data are in line with published reports on the absence of significant toxicity caused by the inhibitor at the concentration below 75–100 M in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK), human hepato cellular carcinoma cells (HUH), HepG2 cells or ex vivo in human peripheral blood monocytes [13], as well as in a mouse model where NHC was provided up to 126 µmol per kilogram of body weight during five consecutive days without any measurable side effects [13]”.
The original Figure 3 was in French and has been replaced by the following:
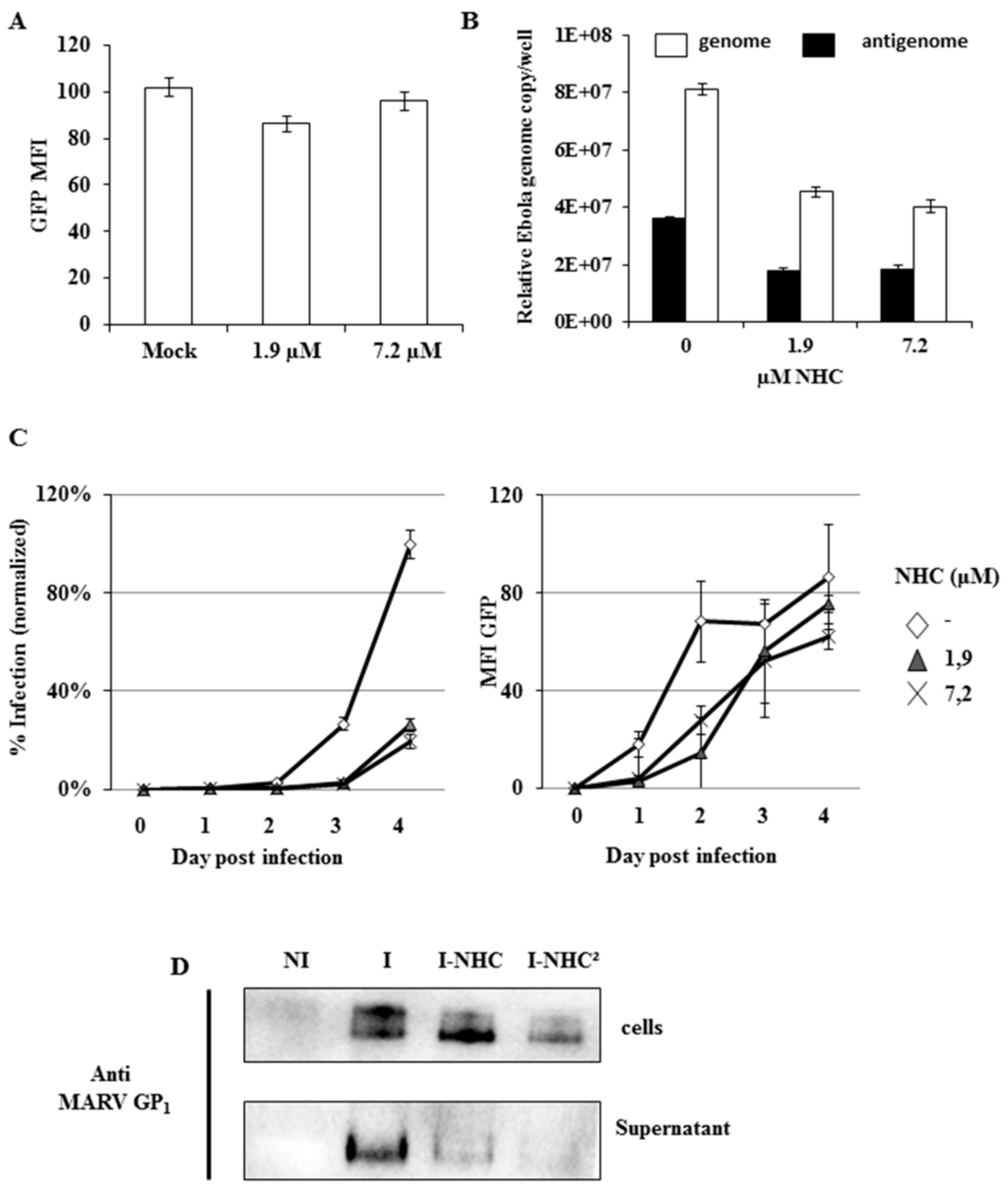
The manuscript will be updated and the original will remain available on the article webpage. The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused.
References
- Reynard, O.; Nguyen, X.-N.; Alazard-Dany, N.; Barateau, V.; Cimarelli, A.; Volchkov, V.E. Identification of a New Ribonucleoside Inhibitor of Ebola Virus Replication. Viruses 2015, 7, 6233–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuyver, L.J.; Whitaker, T.; McBrayer, T.R.; Hernandez-Santiago, B.I.; Lostia, S.; Tharnish, P.M.; Ramesh, M.; Chu, C.K.; Jordan, R.; Shi, J.; et al. Ribonucleoside analogue that blocks replication of bovine viral diarrhea and hepatitis C viruses in culture. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).