Human Coronaviruses Do Not Transfer Efficiently between Surfaces in the Absence of Organic Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Viruses
2.2. Surface Preparation
2.3. Determining Limit of Detection
2.3.1. For HCoV-229E and MNV-1
2.3.2. For HCoV-OC43
2.4. Viral Quantification
2.4.1. Plaque Assay for HCoV-229E and MNV-1
2.4.2. TCID50 for HCoV-OC43
2.5. Transfer Experiment
2.5.1. Transfer of Viruses to Surfaces Using Maintenance Media as the Transfer Matrix
2.5.2. Transfer of HCoV-OC43 to Surfaces Using Organic Fecal Material as the Transfer Matrix
2.6. Determining Transfer Efficiency
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Limit of Detection for Swabbing from Stainless Steel and Plastic
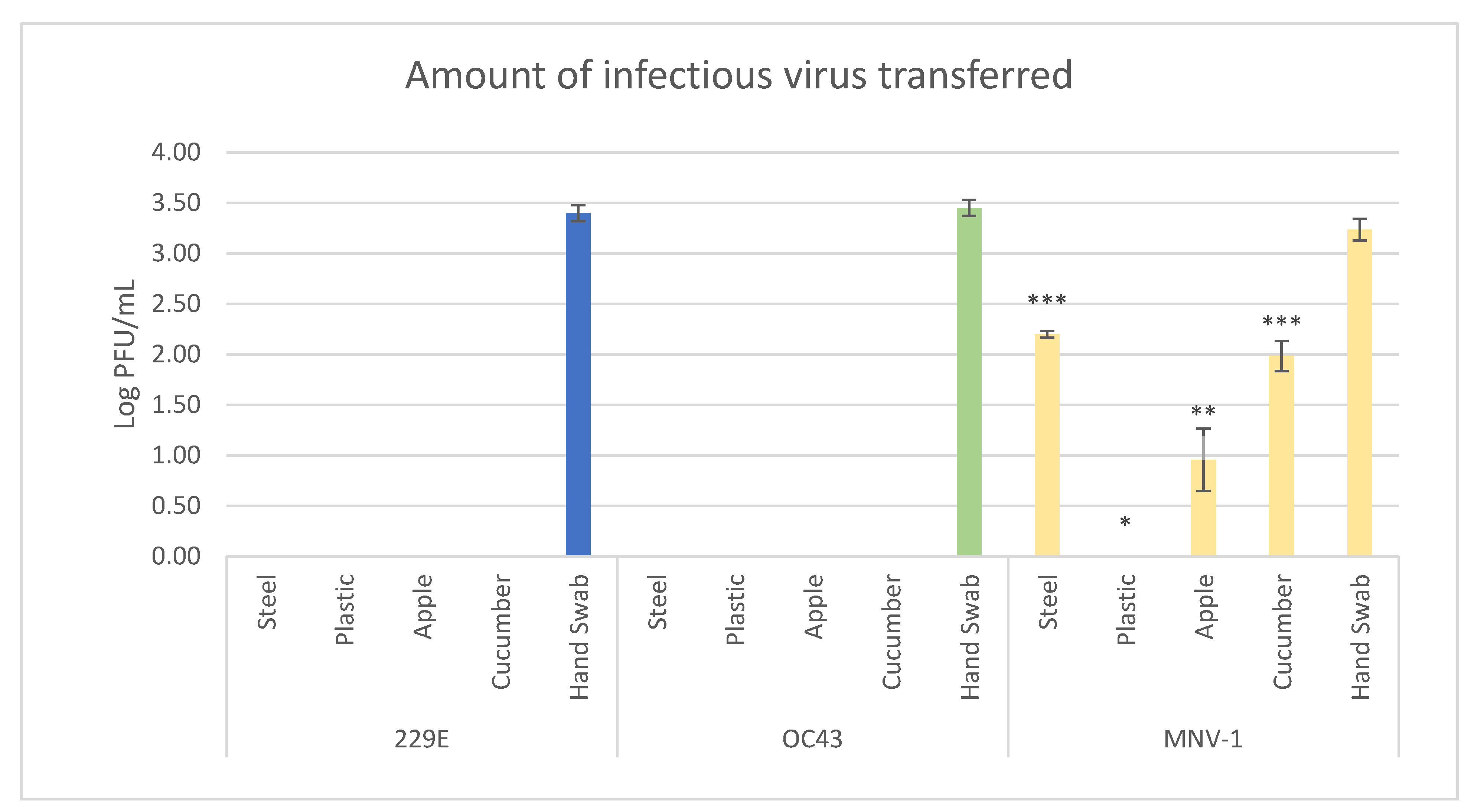
3.2. Viral Transfer Efficiency from Hands to Produce/Surfaces
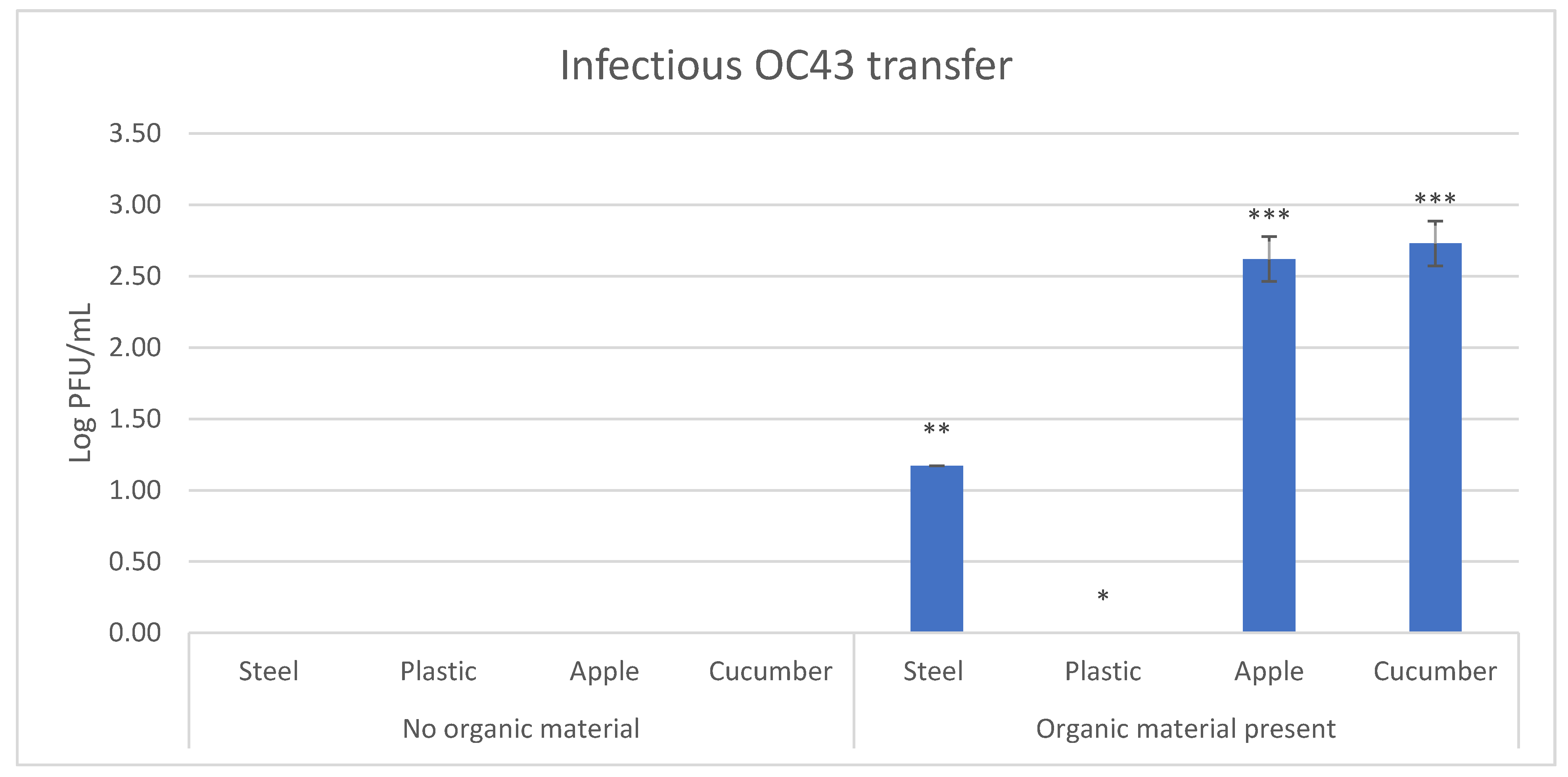
3.3. Effect of Fecal Material on Transfer Efficiency of HCoV-OC43
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, J.C.; Gusmao, T.P.d.L.; Zarzar, A.M.; Leao Filho, J.C.; Barkokebas Santos de Faria, A.; Morais Silva, I.H.; Gueiros, L.A.M.; Robinson, N.A.; Porter, S.; Carvalho, A.D.A.T. Coronaviridae—Old friends, new enemy! Oral Dis. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falahi, S.; Kenarkoohi, A. Transmission routes for SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review of evidence. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 38, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerowitz, E.A.; Richterman, A.; Gandhi, R.T.; Sax, P.E. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Viral, Host, and Environmental Factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboubakr, H.A.; Goyal, S.M. Foodborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is more evident that it has been before. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, E.; Hazeleger, W.C.; Koopmans, M.; Zwietering, M.H.; Duizer, E.; Beumer, R.R. Transfer of noroviruses between fingers and fomites and food products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, G.; Ho, H.J.; Ng, C.G.; Neo, F.J.X.; Win, M.K.; Cui, L.; Leo, Y.S.; Chow, A. An unusual outbreak of rotavirus G8P [8] gastroenteritis in adults in an urban community, Singapore, 2016. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 105, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Y. Transmission of influenza a in a student office based on realistic person-to-person contact and surface touch behaviour. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Brookbank, L.; Ho, A.; Coffey, J.; Brennan, A.B.; Jones, C.J. Surface texture limits transfer of S. aureus, T4 bacteriophage, influenza B virus and human coronavirus. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doremalen, N.; Morris, D.H.; Holbrook, M.G.; Gamble, A.; Williamson, B.N.; Tamin, A.; Harcourt, J.L.; Thronburg, N.J.; Gerber, S.I.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV01. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.W.H.; Chu, J.T.S.; Perera, M.R.A.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Yen, H.-L.; Chan, M.C.W.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondin-Brosseau, M.; Harlow, J.; Doctor, T.; Nasheri, N. Examining the persistence of human coronaviruses on fresh produce. Food Microbiol. 2020, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Sun, W.; Huang, J.; Gamber, M.; Wu, J.; He, G. Indirect virus transmission in cluster of COVID-19 cases, Wenzhou, China, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1343–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Zhao, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; et al. The evidence of indirect transmission of SARS-CoV-2 reported in Guangzhou, China. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.P.; Fuhrmeister, E.R.; Cantrell, M.E.; Pitol, A.K.; Swarthout, J.M.; Powers, J.E.; Nadimpalli, M.L.; Julian, T.R.; Pickering, A.J. Longitudinal monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 RNA on high-touch surfaces in a community setting. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitol, A.K.; Julian, T.R. Community Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by Surfaces: Risks and Risk Reduction Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E. Exaggerated risk of transmission of COVID-19 by fomites. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 892–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felter, C.; Bussemaker, N. Which Countries Are Requiring Face Masks? Available online: https://www.cfr.org/in-brief/which-countries-are-requiring-face-masks (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Bidawid, S.; Malik, N.; Adegbunrin, O.; Sattar, S.A.; Farber, J.M. Norovirus cross-contamination during food handling and interruption of virus transfer by hand antisepsis: Experiments with feline calicivirus as a surrogate. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaelen, K.; Bouwknegt, M.; Carratalà, A.; Lodder-Verschoor, F.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Rutjes, S.A. Virus transfer proportions between gloved fingertips, soft berries, and lettuce, and associated health risks. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidawid, S.; Farber, J.M.; Sattar, S.A. Contamination of foods by food handlers: Experiments on hepatitis A virus transfer to food and its interruption. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2759–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.C.-Y.; Zhang, A.J.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Li, C.; Fan, Z.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Liang, R.; Sridhar, S.; Cai, J.-P.; et al. Oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation establishes subclinical respiratory infection with virus shedding in Golden Syrian hamsters. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Beumer, J.; Van Der Vaart, J.; Knoops, K.; Puschhof, J.; Breugem, T.I.; Ravelli, R.B.G.; Van Schayck, J.P.; Mykytyn, A.Z.; Duimel, H.Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes. Science 2020, 369, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, G.; Chu, H.; Wang, D.; Yan, H.H.N.; Poon, V.K.M.; Wen, L.; Wong, B.H.Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Human intestinal tract serves as an alternative infection route for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobel, Y.R.; Phipps, M.; Zucker, J.; Lebwohl, B.; Wang, T.C.; Sobieszczyk, M.E.; Freedberg, D.E. Gastrointestinal symptoms and coronavirus disease 2019: A case-control study from the United States. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.; Onukogu, I.; Ghanta, S.; Gajendran, M.; Perisetti, A.; Goyal, H.; Aggarwal, A. Gastrointestinal symptoms and outcomes in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Dig. Dis. 2020, 38, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.S.; Hung, I.F.N.; Chan, P.P.Y.; Lung, K.C.; Tso, E.; Liu, R.; Ng, Y.Y.; Chu, M.Y.; Chung, T.W.H.; Tam, A.R.; et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong cohort: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnes, S.L.; Little, Z.R.; Keevil, C.W. Human coronavirus 229E remains infectious on common touch surface materials. MBio 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.X.; Liang, J.Q.; Fung, T.S. Human coronavirus-229E, -OC43, -NL63, and -HKU1. Ref. Modul. Life Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smither, S.J.; Lear-Rooney, C.; Biggins, J.; Pettitt, J.; Lever, M.S.; Olinger, G.G. Comparison of the plaque assay and 50% tissue culture infectious dose assay as methods for measuring filovirus infectivity. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Kalyani, I.H.; Patel, D.R.; Pandya, G.M. Enumeration Techniques of Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) for Oncolytic Virotherapy. J. Anim. Res. 2016, 6, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Project for Statistical Computing The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Cueno, M.E.; Imai, K. Structural Comparison of the SARS CoV 2 Spike Protein Relative to Other Human-Infecting Coronaviruses. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, D.M.; Petric, M.; Skowronski, D.M.; Guasparini, R.; Booth, T.F.; Krajden, M.; McGeer, P.; Bastien, N.; Gustafson, L.; Dubord, J.; et al. An outbreak of human coronavirus OC43 infection and serological cross-reactivity with SARS coronavirus. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 17, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Koerhuis, D.; Van Den Burg, A.C.S.; Rozemuller, E.; Bosch, B.J.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Boons, G.J.; Huizinga, E.G.; et al. Coronavirus hemagglutinin-esterase and spike proteins coevolve for functional balance and optimal virion avidity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25759–25770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontario Ministry of Health. Food Safety: A Guide for Ontario’s Food Handlers. Available online: https://www.health.gov.on.ca/en/pro/programs/publichealth/enviro/docs/training_manual.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Jędruchniewicz, K.; Ok, Y.S.; Oleszczuk, P. COVID-19 discarded disposable gloves as a source and a vector of pollutants in the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, S.A.; Gerba, C.P. Significance of fomites in the spread of respiratory and enteric viral disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azimi, P.; Keshavarz, Z.; Laurent, J.G.C.; Stephens, B.; Allen, J.G. Mechanistic transmission modeling of COVID-19 on the Diamond Princess cruise ship demonstrates the importance of aerosol transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Sridhar, S.; Zhang, R.R.; Chu, H.; Fung, A.Y.F.; Chan, G.; Chan, J.F.W.; To, K.K.W.; Hung, I.F.N.; Cheng, V.C.C.; et al. Factors affecting stability and infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirife, J.; Fontan, C.F. Water activity of fresh foods. J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.U.; Gerba, C.P.; Tamimi, A.H.; Kitajima, M.; Maxwell, S.L.; Rose, J.B. Transfer efficiency of bacteria and viruses from porous and nonporous fomites to fingers under different relative humidity conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5728–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Murallidharan, J.S.; Agrawal, A.; Bhardwaj, R. Why coronavirus survives longer on impermeable than porous surfaces. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lei, W.; Han, W.; Jiang, F.; Liu, W.J.; et al. Cold-chain transportation in the frozen food industry may have caused a recurrence of COVID-19 cases in destination: Successful isolation of SARS-CoV-2 virus from the imported frozen cod package surface. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Virus | Surface | Limit of Detection (PFU) |
|---|---|---|
| HCoV-229E | Stainless steel | 53 |
| Plastic | 44 | |
| Apple | 125 | |
| Cucumber | 50 | |
| HCoV-OC43 | Stainless steel | 73 |
| Plastic | 41 | |
| Apple | 10 | |
| Cucumber | 32 | |
| MNV-1 | Stainless steel | 52 |
| Plastic | 30 | |
| Apple | 26 | |
| Cucumber | 63 |
| Virus | Surface | Percent of Samples with Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| HCoV-229E | Stainless steel | 0 |
| Plastic | 0 | |
| Apple | 0 | |
| Cucumber | 0 | |
| HCoV-OC43 | Stainless steel | 0 |
| Plastic | 0 | |
| Apple | 0 | |
| Cucumber | 0 | |
| MNV-1 | Stainless steel | 33 |
| Plastic | 0 | |
| Apple | 50 | |
| Cucumber | 100 |
| Virus | Surface | Percent Transfer Efficiency * |
|---|---|---|
| HCoV-229E | Stainless steel | NT |
| Plastic | NT | |
| Apple | NT | |
| Cucumber | NT | |
| HCoV-OC43 | Stainless steel | NT |
| Plastic | NT | |
| Apple | NT | |
| Cucumber | NT | |
| MNV-1 | Stainless steel | 9.19 ± 0.68 |
| Plastic | NT | |
| Apple | 0.33 ± 0.03 | |
| Cucumber | 5.95 ± 2.05 |
| Transfer | Surface | Percent of Samples with Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| No organic material | Stainless steel | 0 |
| Plastic | 0 | |
| Apple | 0 | |
| Cucumber | 0 | |
| Organic material present | Stainless steel | 16.7 |
| Plastic | 0 | |
| Apple | 100 | |
| Cucumber | 100 |
| Transfer | Surface | Percent Transfer Efficiency * |
|---|---|---|
| No organic material | Stainless steel | NT |
| Plastic | NT | |
| Apple | NT | |
| Cucumber | NT | |
| Organic material present | Stainless steel | 0.52 ± 0.00 |
| Plastic | NT | |
| Apple | 15.51 ± 6.09 | |
| Cucumber | 19.82 ± 6.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dallner, M.; Harlow, J.; Nasheri, N. Human Coronaviruses Do Not Transfer Efficiently between Surfaces in the Absence of Organic Materials. Viruses 2021, 13, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071352
Dallner M, Harlow J, Nasheri N. Human Coronaviruses Do Not Transfer Efficiently between Surfaces in the Absence of Organic Materials. Viruses. 2021; 13(7):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071352
Chicago/Turabian StyleDallner, Matthew, Jennifer Harlow, and Neda Nasheri. 2021. "Human Coronaviruses Do Not Transfer Efficiently between Surfaces in the Absence of Organic Materials" Viruses 13, no. 7: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071352
APA StyleDallner, M., Harlow, J., & Nasheri, N. (2021). Human Coronaviruses Do Not Transfer Efficiently between Surfaces in the Absence of Organic Materials. Viruses, 13(7), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071352






