Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Exacerbates Colitis Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
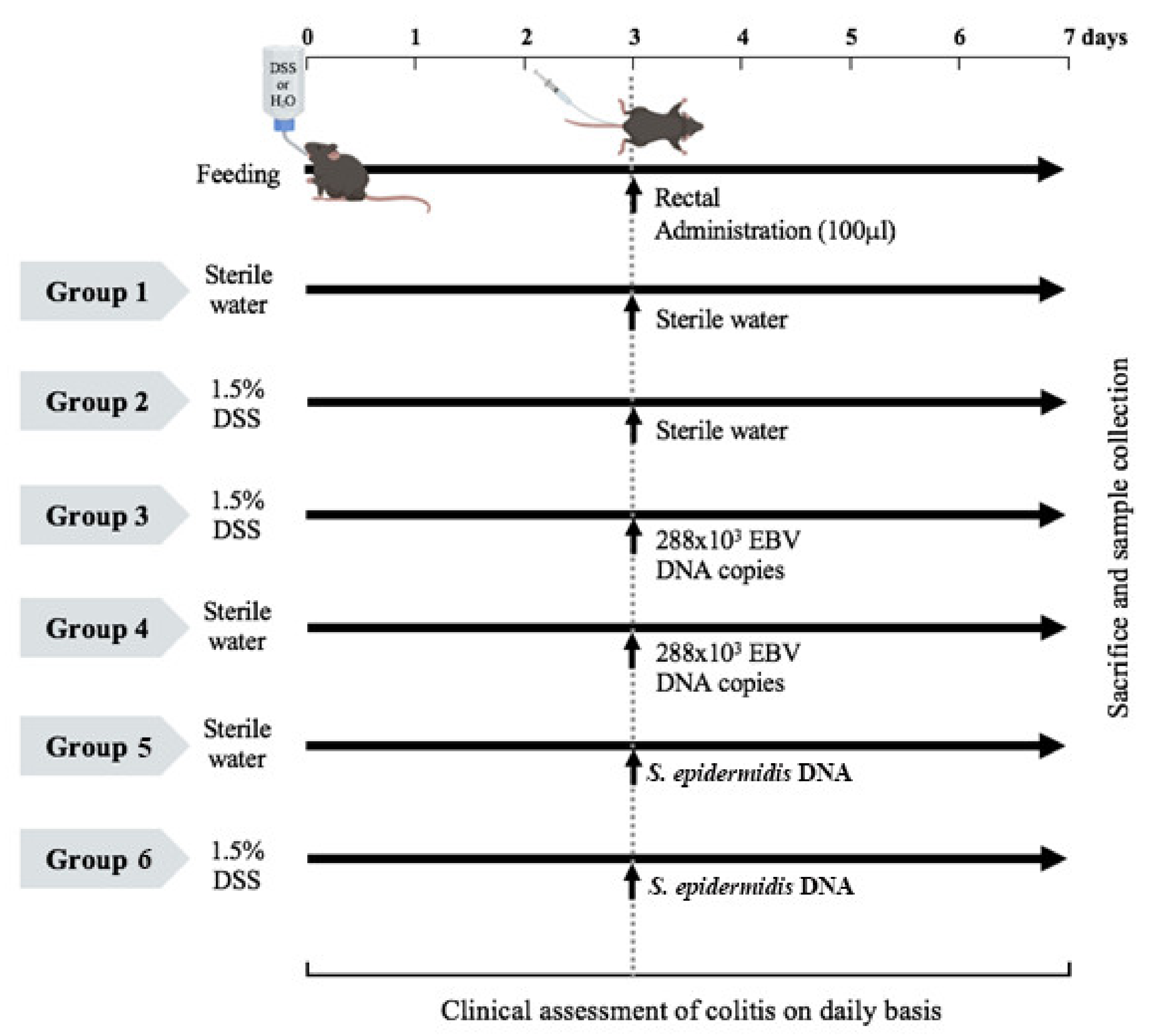
2.1. Induction of Acute DSS Colitis in C57BL/6J Mice and Treatment Administration
2.2. Mouse Monitoring and Assessment
2.3. Expression Studies
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
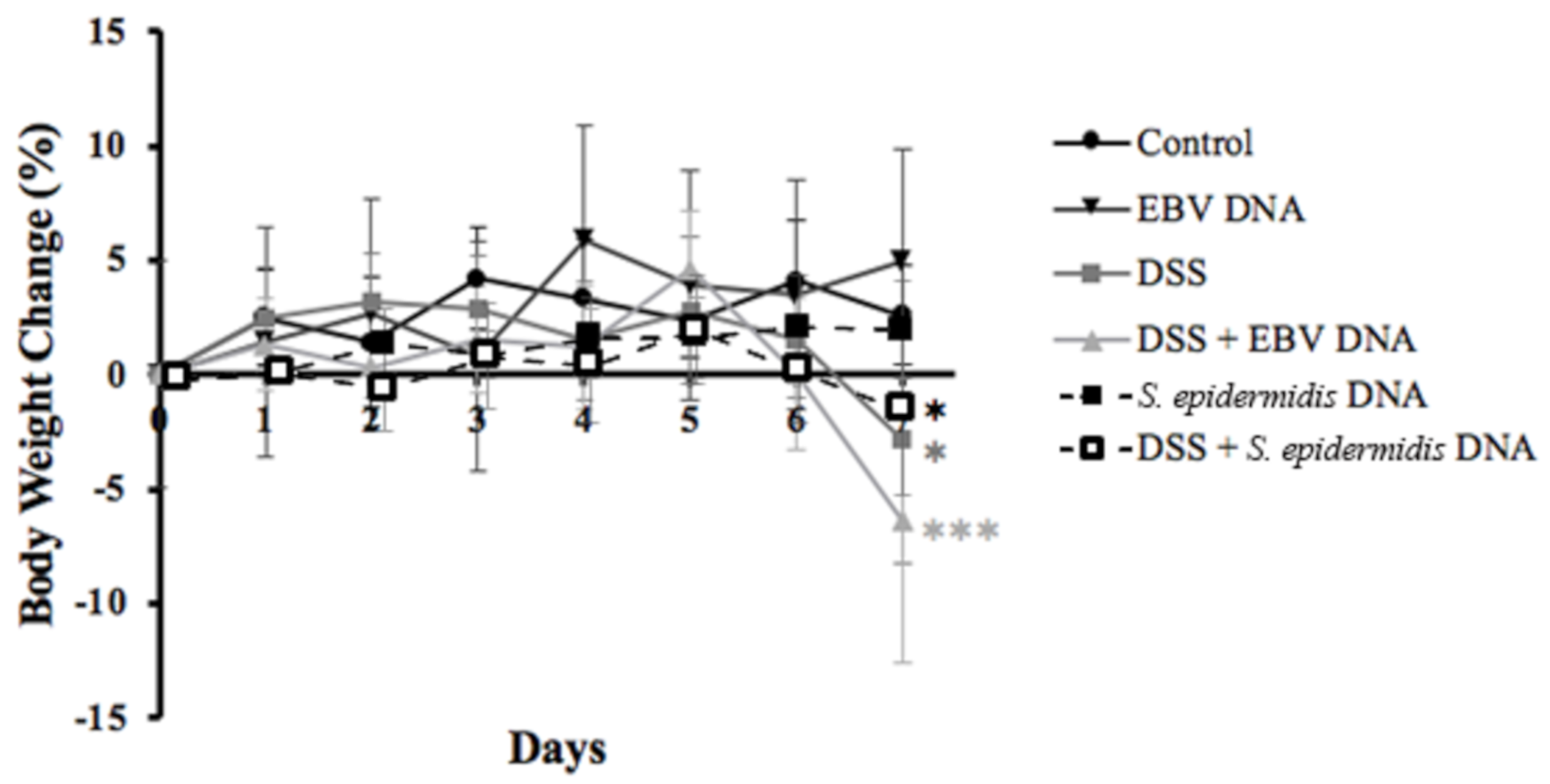
3.1. Increased Body Weight Loss in the EBV DNA-Treated Mouse Colitis Model
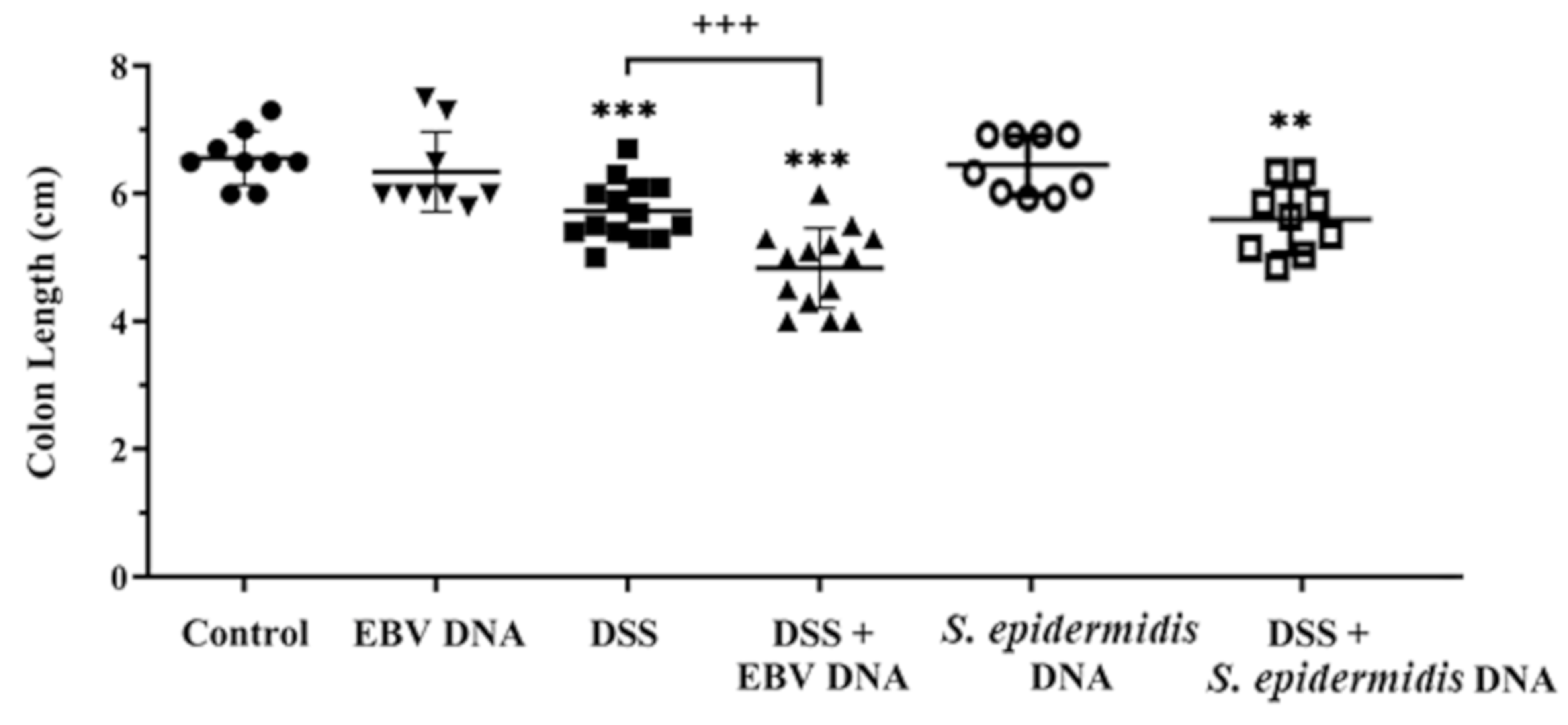
3.2. Enhanced Colon Shortening in the EBV DNA-Treated Mouse Colitis Model
3.3. Exacerbated Disease Activity in the EBV DNA-Treated Mouse Colitis Model
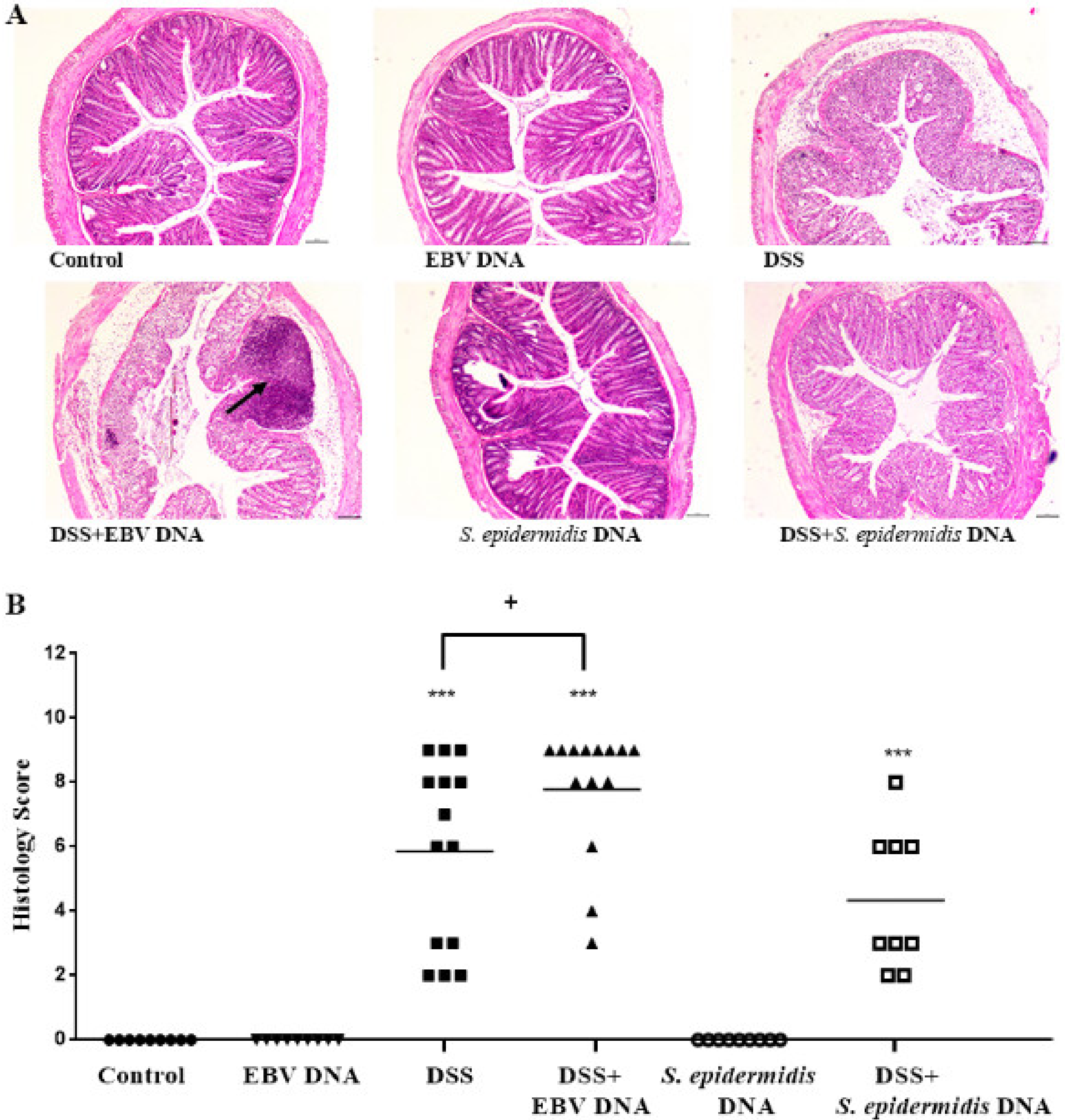
3.4. EBV DNA Administration Aggravates Histological Damage in the Colitis Model
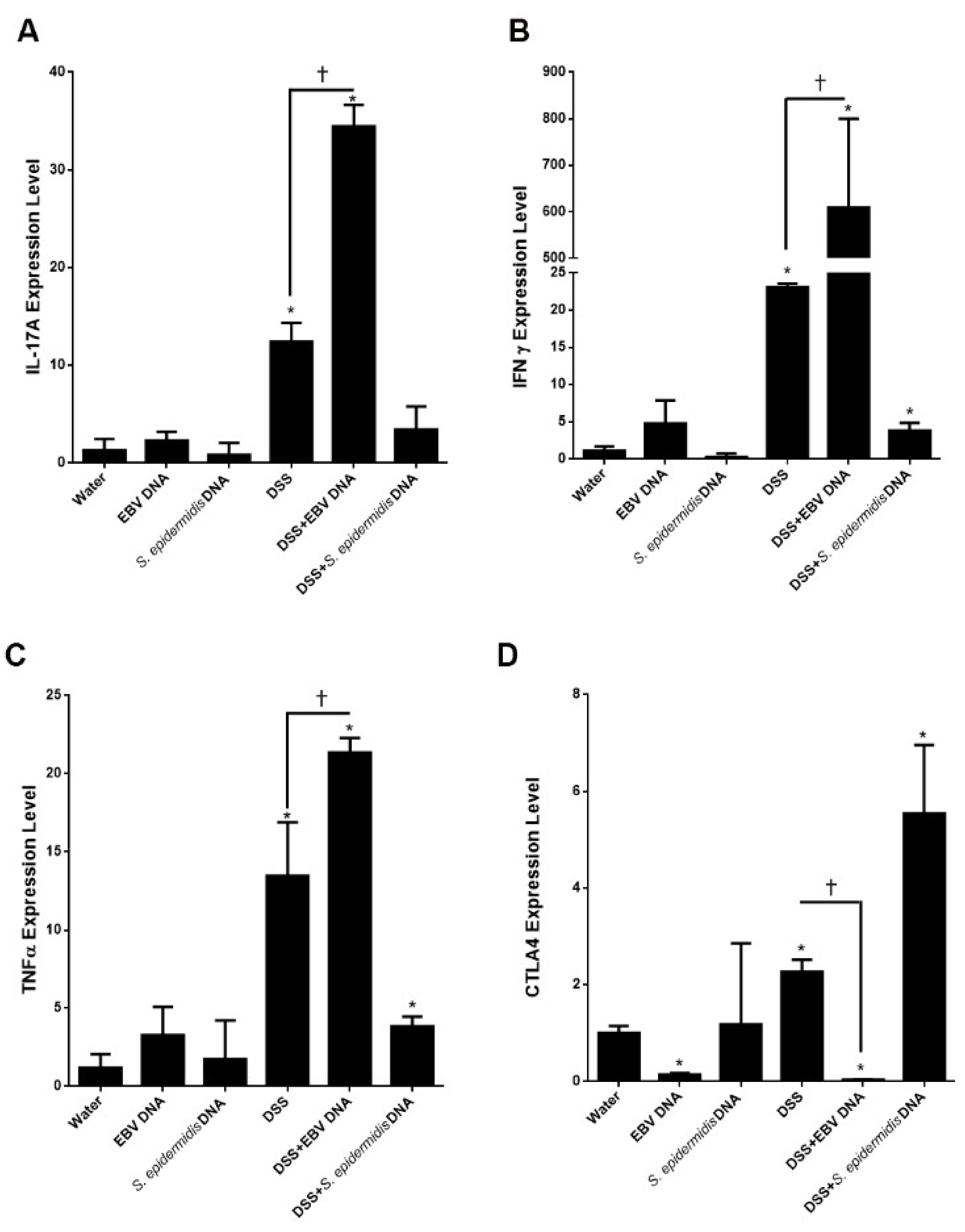
3.5. EBV DNA Enhances the Expression of Proinflammatory Mediators in the Colitis Model
3.6. Enhanced Expression of Endosomal TLRs in EBV DNA-Treated Colitis Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaplan, G. The global burden of IBD: From 2015 to 2025. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, P. The classification of viruses infecting the respiratory tract. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2003, 4, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinde, B. Herpesviruses: Latency and reactivation—Viral strategies and host response. J. Oral Microbiol. 2013, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; Gross, A. Persistence of the Epstein–Barr Virus and the Origins of Associated Lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLennan, I.C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Arpin, C. Germinal center development. Immunol. Rev. 1997, 156, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gequelin, L.C.; Riediger, I.N.; Nakatani, S.M.; Biondo, A.W.; Bonfim, C.M. Epstein-Barr virus: General factors, virus-related diseases and measurement of viral load after transplant. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2011, 33, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posnett, D.N. Herpesviruses and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 9, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.L.; Shen, Y.-J.; Morgan, D.R.; Thorne, L.B.; Kenney, S.C.; Dominguez, R.L.; Gulley, M.L. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Is Common in Inflamed Gastrointestinal Mucosa. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakefield, A.J.; Fox, J.D.; Sawyerr, A.M.; Taylor, J.E.; Sweenie, C.H.; Smith, M.; Emery, V.C.; Hudson, M.; Tedder, R.S.; Pounder, R.E. Detection of herpesvirus DNA in the large intestine of patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease using the nested polymerase chain reaction. J. Med. Virol. 1992, 38, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieker, T.; Herbst, H. Distribution and Phenotype of Epstein-Barr Virus-Infected Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, N.; You, P.; Peng, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. The Status of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Intestinal Mucosa of Chinese Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Digestion 2018, 99, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahal, E.A.; Hajjar, H.; Rajeh, M.; Yamout, B.; Abdelnoor, A.M. Epstein-Barr Virus and Human herpes virus 6 Type A DNA Enhance IL-17 Production in Mice. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehab, M.; Sherri, N.; Hussein, H.; Salloum, N.; Rahal, E.A. Endosomal Toll-Like Receptors Mediate Enhancement of Interleukin-17A Production Triggered by Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Mice. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00987-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salloum, N.; Hussein, H.M.; Jammaz, R.; Jiche, S.; Uthman, I.W.; Abdelnoor, A.M.; Rahal, E.A. Epstein-Barr virus DNA modulates regulatory T-cell programming in addition to enhancing interleukin-17A production via Toll-like receptor 9. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherri, N.; Salloum, N.; Mouawad, C.; Haidar-Ahmad, N.; Shirinian, M.; Rahal, E.A. Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Enhances Diptericin Expression and Increases Hemocyte Numbers in Drosophila melanogaster via the Immune Deficiency Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, J.R.; Al Outa, A.; Ghannam, M.; Hussein, H.M.; Shehab, M.; Hasan, Z.A.K.H.; Fayad, A.A.; Shirinian, M.; Rahal, E.A. Drosophila melanogaster as a Model System to Assess the Effect of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA on Inflammatory Gut Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 586930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayasu, I.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yamada, M.; Ohkusa, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Nakaya, R. A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.S.; Murthy, S.N.; Shah, R.S.; Sedergran, D.J. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab. Investig. 1993, 69, 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, H.X.; Liu, J.; Fatima, S.; Lin, C.Y.; Shi, X.K.; Du, B.; Xiao, H.T.; Fan, B.M.; Bian, Z.X. Anti-inflammatory Actions of (+)-3’alpha-Angeloxy-4’-keto-3’,4’-dihydroseselin (Pd-Ib) against Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-T.; Lin, C.; Ho, D.H.H.; Peng, J.; Chen, Y.; Tsang, S.-W.; Wong, M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Zhang, M.; Bian, Z.-X. Inhibitory Effect of the Gallotannin Corilagin on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Murine Ulcerative Colitis. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajib, R.; Janbazian, L.; Rahal, E.; Matar, G.M.; Zaynoun, S.; Kibbi, A.G.; Abdelnoor, A.M. HLA allele associations and V-beta T-lymphocyte expansions in patients with psoriasis, harboring toxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontebasso, A.M.; Shirinian, M.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Bechet, D.; Gayden, T.; Kool, M.; De Jay, N.; Jacob, K.; Gerges, N.; Hutter, B.; et al. Non-random aneuploidy specifies subgroups of pilocytic astrocytoma and correlates with older age. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31844–31856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hleihel, R.; Khoshnood, B.; Dacklin, I.; Omran, H.; Mouawad, C.; Dassouki, Z.; El-Sabban, M.; Shirinian, M.; Grabbe, C.; Bazarbachi, A. The HTLV-1 oncoprotein Tax is modified by the ubiquitin related modifier 1 (Urm1). Retrovirology 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matar, G.M.; Rahal, E. Inhibition of the transcription of the Escherichia coli O157:H7 genes coding for shiga-like toxins and intimin, and its potential use in the treatment of human infection with the bacterium. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2003, 97, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, E.A.; Henricksen, L.A.; Li, Y.; Turchi, J.J.; Pawelczak, K.S.; Dixon, K. ATM mediates repression of DNA end-degradation in an ATP-dependent manner. DNA Repair 2008, 7, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hein, J.; Schellenberg, U.; Bein, G.; Hackstein, H. Quantification of murine IFN-gamma mRNA and protein expression: Impact of real-time kinetic RT-PCR using SYBR green I dye. Scand. J. Immunol. 2001, 54, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-H.; Yeh, S.-L.; Yeh, C.-L. Dietary Supplemental Glutamine Enhances the Percentage of Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Subjected to Hind Limb Ischemia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 3153186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Ke, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Kaplan, H.J.; Shao, H. Regulatory Role of TLR Ligands on the Activation of Autoreactive T Cells by Retinal Astrocytes. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4769–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Mercier, I.; Poujol, D.; Sanlaville, A.; Sisirak, V.; Gobert, M.; Durand, I.; Dubois, B.; Treilleux, I.; Marvel, J.; Vlach, J.; et al. Tumor Promotion by Intratumoral Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Is Reversed by TLR7 Ligand Treatment. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4629–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, L.S. Treg and CTLA-4: Two intertwining pathways to immune tolerance. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 45, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzellos, S.; Farrell, P.J. Epstein-Barr Virus Sequence Variation—Biology and Disease. Pathogens 2012, 1, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussein, H.M.; Rahal, E.A. The role of viral infections in the development of autoimmune diseases. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Rahman, F.Z.; Hayee, B.; Graham, S.J.; Marks, D.J.; Sewell, G.W.; Palmer, C.D.; Wilde, J.; Foxwell, B.M.; Gloger, I.S.; et al. Disordered macrophage cytokine secretion underlies impaired acute inflammation and bacterial clearance in Crohn’s disease. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1883–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, A.L.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Rigby, R.J.; Bell, S.J.; Emmanuel, A.V.; Knight, S.C.; Kamm, M.A.; Stagg, A.J. Characteristics of Intestinal Dendritic Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.P.; Papadakis, K.A. Mechanisms of Disease: Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuss, I.J.; Neurath, M.; Boirivant, M.; Klein, J.S.; de la Motte, C.; Strong, S.A.; Fiocchi, C.; Strober, W. Disparate CD4+ lamina propria (LP) lymphokine secretion profiles in inflammatory bowel disease. Crohn’s disease LP cells manifest increased secretion of IFN-gamma, whereas ulcerative colitis LP cells manifest increased secretion of IL-5. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Fujino, S.; Andoh, A.; Bamba, S.; Ogawa, A.; Hata, K.; Araki, Y.; Bamba, T.; Fujiyama, Y. Increased expression of interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2003, 52, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Z.-T.; Zhou, R.; Wu, J. Expression and clinical significance of IL-17 and IL-17 receptor in ulcerative colitis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2016, 36, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueber, W.; Sands, B.E.; Lewitzky, S.; Vandemeulebroecke, M.; Reinisch, W.; Higgins, P.D.; Wehkamp, J.; Feagan, B.G.; Yao, M.D.; Karczewski, M.; et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease: Unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut 2012, 61, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.T.; Elson, C.O.; Fouser, L.A.; Kolls, J.K. The Th17 Pathway and Inflammatory Diseases of the Intestines, Lungs, and Skin. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 477–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omenetti, S.; Bussi, C.; Metidji, A.; Iseppon, A.; Lee, S.; Tolaini, M.; Li, Y.; Kelly, G.; Chakravarty, P.; Shoaie, S.; et al. The Intestine Harbors Functionally Distinct Homeostatic Tissue-Resident and Inflammatory Th17 Cells. Immunity 2019, 51, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Gene | Primers | Annealing Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| TLR9 | F: 5 ′-ACTGAGCACCCCTGCTTCTA-3′ R: 5 ′-AGATTAGTCAGCGGCAGGAA-3′ | 60 °C |
| TLR3 | F: 5′-GGTGTTTCCAGACAATTGGCAAG-3′ R: 5′-TGGAGGTTGTTGTAGGAA-AGATCG-3′ | 60 °C |
| TLR7 | F: 5′-CCACAGGCTCACCCATACTTC-3′ R: 5′-GGGATGTCCTAGGTGGTGACA-3′ | 60 °C |
| IL-17A | F: 5′-TTAAGGTTCTCTCCTCTGAA-3′ R: 5′-TAGGGAGCTAAATTATCCAA-3′ | 56 °C |
| CTLA4 | F: 5′-GCCAGTGGTTCCAAAGGTTG-3′ R: 5′-CACTGTGGGACGACACTGAT-3′ | 60.9 °C |
| TNFα | F: 5′-AAATGGGCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTC-3′ R: 5′-CTGCTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC-3′ | 61 °C |
| IFNγ | F: 5′-TGAACGCTACACACTGCATCTTGG-3′ R: 5′-CGACTCCTTTTCCGCTTCCTGAG-3′ | 60 °C |
| β-actin | F: 5′-GGCATTGTTACCAACTGGGACGAC-3′ R: 5′-CCAGAGGCATACAGGGACAGCACAG-3′ | 58.6 °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andari, S.; Hussein, H.; Fadlallah, S.; Jurjus, A.R.; Shirinian, M.; Hashash, J.G.; Rahal, E.A. Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Exacerbates Colitis Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses 2021, 13, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071272
Andari S, Hussein H, Fadlallah S, Jurjus AR, Shirinian M, Hashash JG, Rahal EA. Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Exacerbates Colitis Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses. 2021; 13(7):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071272
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndari, Sirine, Hadi Hussein, Sukayna Fadlallah, Abdo R. Jurjus, Margret Shirinian, Jana G. Hashash, and Elias A. Rahal. 2021. "Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Exacerbates Colitis Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Viruses 13, no. 7: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071272
APA StyleAndari, S., Hussein, H., Fadlallah, S., Jurjus, A. R., Shirinian, M., Hashash, J. G., & Rahal, E. A. (2021). Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Exacerbates Colitis Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses, 13(7), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071272






