Role of the Host Genetic Susceptibility to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1
Abstract
1. Introduction
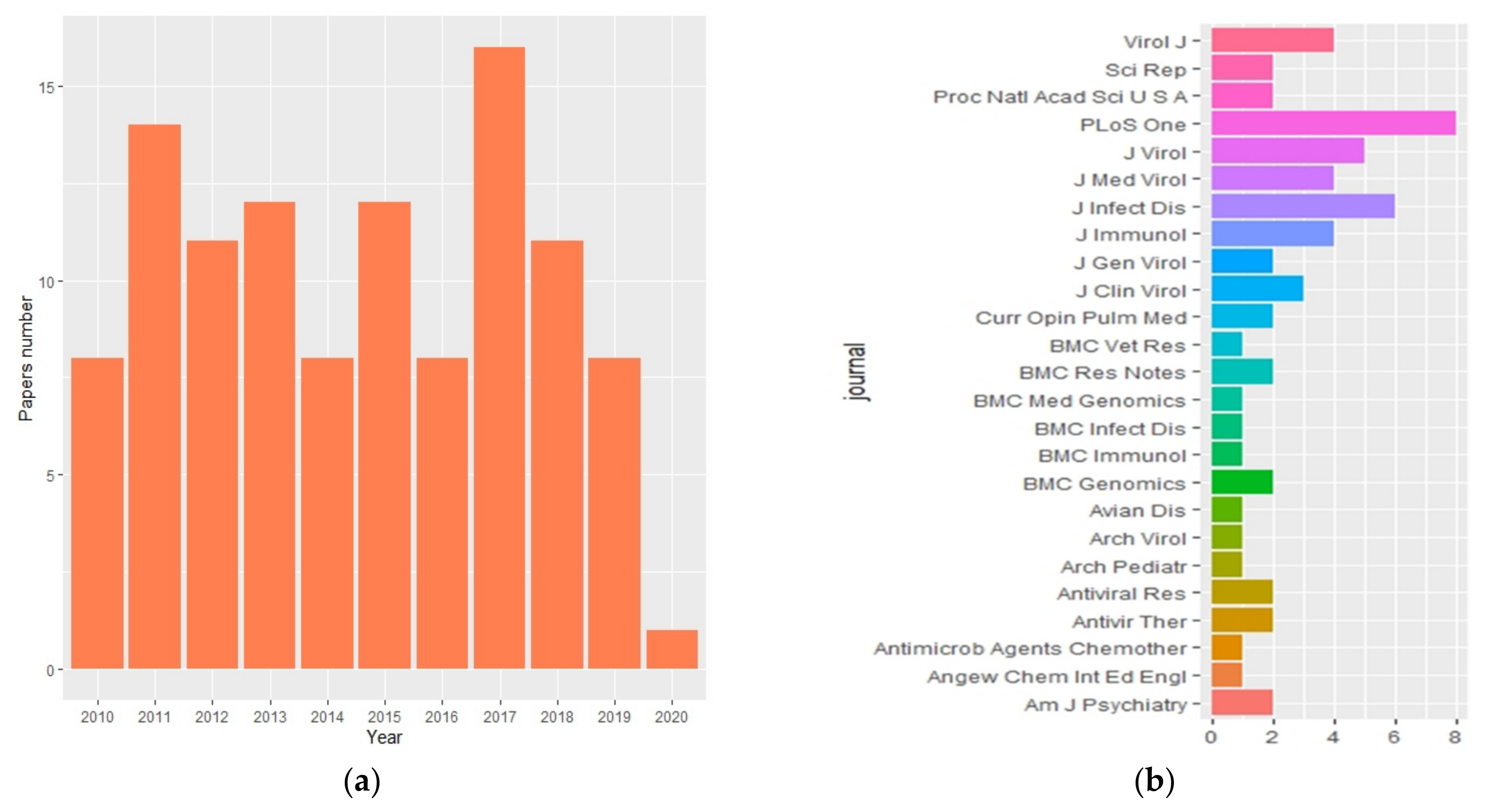
2. Bibliometric Analysis
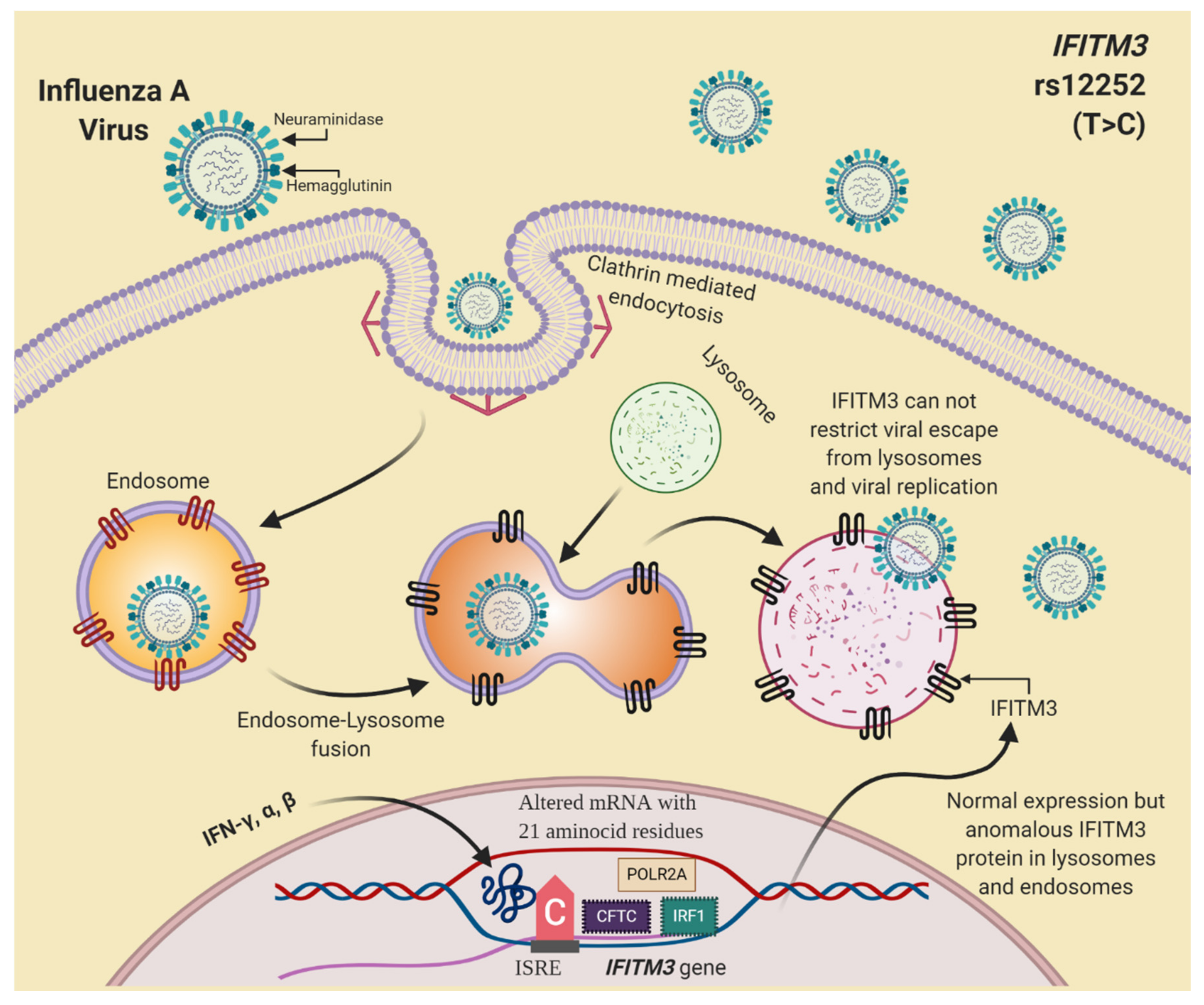
3. Inflammatory Response and IFITM3 Role in Influenza A Virus Infection
4. Genetic Variants and Influenza A H1N1 Virus Infection
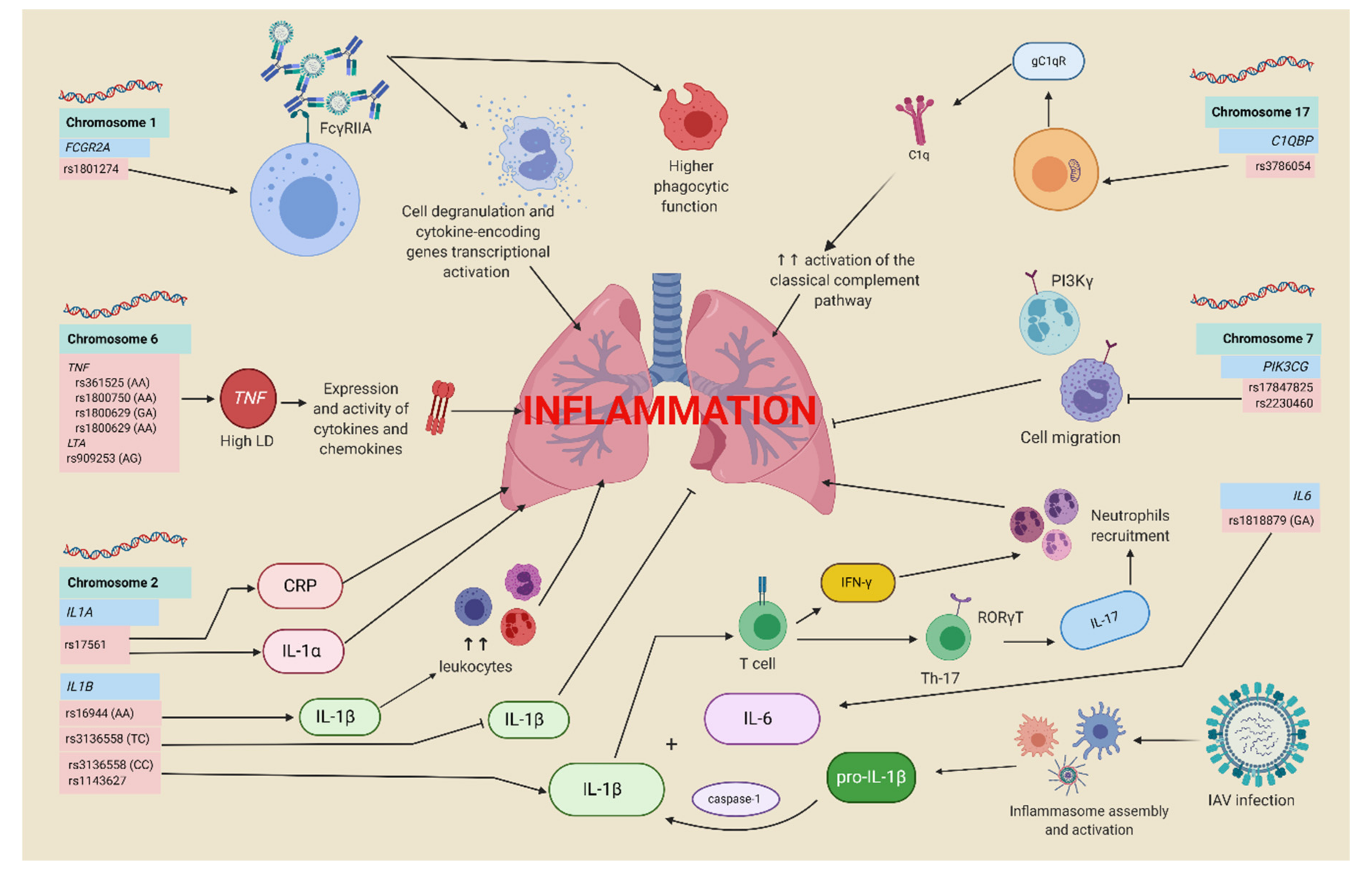
4.1. Polymorphisms in the Complement System and Antibodies-Related Genes
4.2. CD55 and RPAIN Polymorphisms
4.3. Genetic Variants in IFITM3 and Influenza A H1N1
4.4. Inflammatory Response Genes and Influenza A H1N1
4.5. HLA System Genetic Variants and Influenza A H1N1
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.W.; Brandt, C.D.; Arrobio, J.O.; Murphy, B.; Chanock, R.M.; Parrott, R.H. Influenza A and B virus infection in infants and young children during the years 1957–1976. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1979, 109, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, A.S.; Govorkova, E.A.; Webby, R.J.; Ozaki, H.; Peiris, M.; Guan, Y.; Poon, L.; Webster, R.G. Influenza: Emergence and Control. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8951–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, N.-A.M.; Ortega-Sanchez, I.R.; Messonnier, M.L.; Thompson, W.W.; Wortley, P.M.; Weintraub, E.; Bridges, C.B. The annual impact of seasonal influenza in the US: Measuring disease burden and costs. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5086–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.R.; Kedzierska, K.; Van De Sandt, C.E. Back to the Future: Lessons Learned From the 1918 Influenza Pandemic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echevarría-Zuno, S.; Mejía-Aranguré, J.M.; Mar-Obeso, A.J.; Grajales-Muñiz, C.; Robles-Pérez, E.; González-León, M.; Ortega-Alvarez, M.C.; Gonzalez-Bonilla, C.; Rascón-Pacheco, R.A.; Borja-Aburto, V.H. Infection and death from influenza A H1N1 virus in Mexico: A retrospective analysis. Lancet 2009, 374, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cervantes, M.; Venado, A.; Moreno, A.; Pacheco-Domínguez, R.L.; Ortega-Pierres, G. On the spread of the novel influenza A (H1N1) virus in Mexico. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2009, 3, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wong, J.Y.; Kelly, H.; Cheung, C.-M.M.; Shiu, E.Y.; Wu, P.; Ni, M.Y.; Ip, D.K.M.; Cowling, B.J. Hospitalization Fatality Risk of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 182, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalchik, S. The Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Download Content from NCBI Databases [R Package RISmed version 2.1.7]. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/RISmed/index.html (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Package, T.; Clouds, T.W.; Fellows, A.I.; Rcpp, L. Package ‘Wordcloud’. 2018. Available online: https://blogs.ntu.edu.sg/ntulibrary/2019/08/16/free-word-cloud-generators/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. 2015. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(oyulxb452alnt1aej1nfow45))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=2062239 (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Meduri, G.U.; Kohler, G.; Headley, S.; Tolley, E.; Stentz, F.; Postlethwaite, A. Inflammatory cytokines in the BAL of patients with ARDS: Persistent elevation over time predicts poor outcome. Chest 1995, 108, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danis, V.A.; Millington, M.; Hyland, V.J.; Grennan, D. Cytokine production by normal human monocytes: Inter-subject variation and relationship to an IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) gene polymorphism. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 99, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.C.; Kwiatkowski, D. Inherited variability of tumor necrosis factor production and susceptibility to infectious disease. Proc. Assoc. Am. Phys. 1999, 111, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, A.; Baziaka, F.; Tsaganos, T.; Raftogiannis, M.; Koutoukas, P.; Spyridaki, A.; Mouktaroudi, M.; Kotsaki, A.; Savva, A.; Georgitsi, M.; et al. Role of tumor necrosis factor gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in the natural course of 2009 influenza A H1N1 virus infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e204–e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanova, E.N.; Govorin, A.V. TNF-α, IL-10, and eNOS gene polymorphisms in patients with influenza A/H1N1 complicated by pneumonia. Ter. Arkh. 2013, 85, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Walsh, K.B.; Cahalan, S.; Fremgen, D.M.; Roberts, E.; Scott, F.; Martinborough, E.; Peach, R.; Oldstone, M.B.A.; Rosen, H. Endothelial cells are central orchestrators of cytokine amplification during influenza virus infection. Cell 2011, 146, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagau, N.; Slavcovici, A.; Gonganau, D.N.; Oltean, S.; Dirzu, D.S.; Brezoszki, E.S.; Maxim, M.; Ciuce, C.; Mlesnite, M.; Gavrus, R.L.; et al. Clinical aspects and cytokine response in severe H1N1 influenza A virus infection. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reséndiz-Hernández, J.M.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Genetic polymorphisms and their involvement in the regulation of the inflammatory response in asthma and COPD. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Han, Z. The effect of LTA gene polymorphisms on cancer risk: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Sharma, S.; Patibandla, P.K.; Mallick, P.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Pati, S.S.; Mishra, S.K.; Ramteke, B.K.; et al. Polymorphisms of TNF-enhancer and gene for FcγRIIa correlate with the severity of falciparum malaria in the ethnically diverse Indian population. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja-Aburto, V.H.; Chowell, G.; Viboud, C.; Simonsen, L.; Miller, M.A.; Grajales-Muñiz, C.; González-Bonilla, C.R.; Diaz-Quiñones, J.A.; Echevarría-Zuno, S. Epidemiological Characterization of a Fourth Wave of Pandemic A/H1N1 Influenza in Mexico, Winter 2011–2012: Age Shift and Severity. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Estella, A. Cytokine levels in bronchoalveolar lavage and serum in 3 patients with 2009 Influenza A(H1N1)v severe pneumonia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2011, 5, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ocaña, J.; Olivo-Diaz, A.; Salazar-Dominguez, T.; Reyes-Gordillo, J.; Tapia-Aquino, C.; Martínez-Hernández, F.; Manjarrez, M.E.; Antonio-Martinez, M.; Contreras-Molina, A.; Figueroa-Moreno, R.; et al. Plasma cytokine levels and cytokine gene polymorphisms in Mexican patients during the influenza pandemic A(H1N1)pdm09. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pebody, R.; Hardelid, P.; Fleming, D.M.; McMenamin, J.; Andrews, N.; Robertson, C.; Thomas, D.R.; SebastianPillai, P.; Ellis, J.; Carman, W.; et al. Effectiveness of seasonal 2010/11 and pandemic influenza A(H1N1)2009 vaccines in preventing influenza infection in the United Kingdom: Mid-season analysis 2010/11. Eurosurveillance 2011, 16, 19791. [Google Scholar]
- Hardelid, P.; Fleming, D.M.; Mcmenamin, J.; Andrews, N.; Robertson, C.; SebastianPillai, P.; Ellis, J.; Carman, W.; Wreghitt, T.; Watson, J.M.; et al. Effectiveness of pandemic and seasonal influenza vaccine in preventing pandemic influenza A(H1N1)2009 infection in England and Scotland 2009–2010. Eurosurveillance 2011, 16, 19763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga, J.; Torres, M.; Romo, J.; Torres, D.; Jiménez, L.; Ramírez, G.; Cruz, A.; Espinosa, E.; Herrera, T.; Buendía, I.; et al. Inflammatory profiles in severe pneumonia associated with the pandemic influenza A/H1N1 virus isolated in Mexico City. Autoimmunity 2011, 44, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Aoshi, T.; Tanimoto, T.; Kumagai, Y.; Kobiyama, K.; Tougan, T.; Sakurai, K.; Coban, C.; Horii, T.; Akira, S.; et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells delineate immunogenicity of influenza vaccine subtypes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 25ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-I.; Ha, E.; Park, S.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Jang, H.-S.; Bae, J.-H.; Chung, I.-S.; Shin, N.-H.; Song, D.-K. Association of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) promoter polymorphisms with overweight/obesity in a Korean population. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraya, M.U.; Zaighum, F.; Sajjad, N.; Anjum, F.R.; Sakhawat, I.; Rahman, S.U. Web of interferon stimulated antiviral factors to control the influenza A viruses replication. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.-Y.; Segovia, J.A.; Chang, T.-H.; Morris, I.R.; Berton, M.T.; Tessier, P.A.; Tardif, M.R.; Cesaro, A.; Bose, S. DAMP Molecule S100A9 Acts as a Molecular Pattern to Enhance Inflammation during Influenza A Virus Infection: Role of DDX21-TRIF-TLR4-MyD88 Pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Type I Inteferon Gene Induction by the Interferon Regulatory Factor Family of Transcription Factors. Immunity 2006, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Bai, J.; Tian, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, T.; Song, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Construction, expression and antiviral activity analysis of recombinant adenovirus expressing human IFITM3 in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. A New Shield for a Cytokine Storm. Cell 2011, 146, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clark, I.A. The advent of the cytokine storm. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, P.; He, R.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Zhou, L.; Yi, Y.; Wang, F.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. O-GlcNAc transferase promotes influenza A virus-induced cytokine storm by targeting interferon regulatory factor-5. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Wong, C.K.; Hui, D.S.C.; Lee, S.K.W.; Wong, R.Y.K.; Ngai, K.L.K.; Chan, M.C.W.; Chu, Y.J.; Ho, A.W.Y.; Lui, G.C.Y.; et al. Role of human Toll-like receptors in naturally occurring influenza A infections. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; He, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, B.; Huang, L.; Wang, L. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-2 genetic variant rs708035 increases NF-kB activity through promoting TRAF6 ubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12507–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, J.; Van Hoecke, L.; Spitaels, J.; De Vlieger, D.; Kolpe, A.; Saelens, X. Chemical-controlled Activation of Antiviral Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, J.; Hulpiau, P.; Saelens, X. Mx Proteins: Antiviral Gatekeepers That Restrain the Uninvited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, F.; Ebeling, M.; Certa, U. The Small Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Genes and Proteins. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Winkler, C.A.; An, P.; Guo, J.-T. IFITM Genes, Variants, and Their Roles in the Control and Pathogenesis of Viral Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Jeong, M.-J.; Jeong, B.-H. Genetic characteristics and polymorphisms in the chicken interferon-induced transmembrane protein (IFITM3) gene. Vet. Res. Commun. 2019, 43, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Liu, F.; Cuconati, A.; Chang, J.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.-T. Interferon induction of IFITM proteins promotes infection by human coronavirus OC43. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6756–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, E.K.; Randolph, A.G.; Bhangale, T.; Dogra, P.; Ohlson, M.; Oshansky, C.M.; Zamora, A.E.; Shannon, J.P.; Finkelstein, D.; Dressen, A.; et al. SNP-mediated disruption of CTCF binding at the IFITM3 promoter is associated with risk of severe influenza in humans. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brass, A.L.; Huang, I.-C.; Benita, Y.; John, S.P.; Krishnan, M.N.; Feeley, E.M.; Ryan, B.J.; Weyer, J.L.; Van Der Weyden, L.; Fikrig, E.; et al. The IFITM Proteins Mediate Cellular Resistance to Influenza A H1N1 Virus, West Nile Virus, and Dengue Virus. Cell 2009, 139, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, A.; Zhang, L.; McMichael, T.M.; Kenney, A.D.; Chemudupati, M.; Kwiek, J.J.; Liu, S.L.; Yount, J.S. Interferon-induced transmembrane proteins inhibit cell fusion mediated by trophoblast syncytins. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 19844–19851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeley, E.M.; Sims, J.S.; John, S.P.; Chin, C.R.; Pertel, T.; Chen, L.-M.; Gaiha, G.D.; Ryan, B.J.; Donis, R.O.; Elledge, S.J.; et al. IFITM3 Inhibits Influenza A Virus Infection by Preventing Cytosolic Entry. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Pan, Q.; Ding, S.; Rong, L.; Liu, S.-L.; Geng, Y.; Qiao, W.; Liang, C. The N-Terminal Region of IFITM3 Modulates Its Antiviral Activity by Regulating IFITM3 Cellular Localization. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13697–13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, A.D.; McMichael, T.M.; Imas, A.; Chesarino, N.M.; Zhang, L.; Dorn, L.E.; Wu, Q.; Alfaour, O.; Amari, F.; Chen, M.; et al. IFITM3 protects the heart during influenza virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18607–18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, A.; Imas, A.; Rajaram, M.; Yount, J. IFITM3 is cardioprotective during influenza virus infection. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 60. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Public Health Research Agenda for Influenza; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- König, R.; Stertz, S.; Zhou, Y.; Inoue, A.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Alamares, J.G.; Tscherne, D.M.; Ortigoza, M.B.; Liang, Y.; et al. Human host factors required for influenza virus replication. Nature 2010, 463, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs). In Talking Glossary of Genetic Terms. Available online: https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Single-Nucleotide-Polymorphisms (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Iuliano, A.D.; Roguski, K.M.; Chang, H.H.; Muscatello, D.J.; Palekar, R.; Tempia, S.; Cohen, C.; Gran, J.M.; Schanzer, D.; Cowling, B.J.; et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga, J.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Zhao, Y.; Jiménez, L.; Torres, D.; Romo, J.; Ramirez, G.; Cruz, A.; Vargas-Alarcon, G.; Sheu, C.-C.; et al. Genetic variants associated with severe pneumonia in A/H1N1 influenza infection. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalvo, A.C.; Batalle, J.P.; Lopez, M.F.; Krause, J.C.; Klemenc, J.; Hernandez, J.Z.; Maskin, B.; Bugna, J.; Rubinstein, C.; Aguilar, L.; et al. Severe pandemic 2009 H1N1 influenza disease due to pathogenic immune complexes. Nat. Med. 2010, 17, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Schmidt, D.E.; De Haas, M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Genetic Variation in Low-To-Medium-Affinity Fcγ Receptors: Functional Consequences, Disease Associations, and Opportunities for Personalized Medicine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, C.C.; Davila, S.; Breunis, W.B.; Lee, Y.-C.; Shimizu, C.; Wright, V.J.; Yeung, R.S.M.; Tan, D.E.K.; Sim, K.S.; Wang, J.J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies FCGR2A as a susceptibility locus for Kawasaki disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.R.; Stuart, S.G.; Kimberly, R.P.; Ory, P.A.; Goldstein, I.M. A single amino acid distinguishes the high-responder from the low-responder form of Fc receptor II on human monocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 21, 1911–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzopoulou, F.; Gioula, G.; Kioumis, I.; Chatzidimitriou, D.; Exindari, M. Identification of complement-related host genetic risk factors associated with influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 outcome: Challenges ahead. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.L.; Zhanga, W.; Lu, P.D.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Peerschke, E.I.; Ghebrehiwetab, B. The C1q-Binding Cell Membrane Proteins cC1q-R and gC1q-R Are Released from Activated Cells: Subcellular Distribution and Immunochemical Characterization. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 84, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Z.; Huang, S.-D.; Ji, C.-N.; Pang, R.-Y.; Xie, Y.; Xue, J.-L. Identification, Expression Pattern, and Subcellular Location of Human RIP Isoforms. DNA Cell Biol. 2005, 24, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Cao, B.; Ke, C.; Lu, H.; Hu, Y.; Tam, C.H.T.; Ma, R.C.W.; Guan, D.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; et al. IFITM3, TLR3, and CD55 Gene SNPs and Cumulative Genetic Risks for Severe Outcomes in Chinese Patients With H7N9/H1N1pdm09 Influenza. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; To, K.K.-W.; Dong, H.; Cheng, Z.-S.; Lau, C.C.-Y.; Poon, V.K.M.; Fan, Y.-H.; Song, Y.-Q.; Tse, H.; Chan, K.-H.; et al. A Functional Variation in CD55 Increases the Severity of 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Influenza A Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Etxebarria, K.; Bracho, M.A.; Galán, J.C.; Pumarola, T.; Castilla, J.; De Lejarazu, R.O.; Rodríguez-Domínguez, M.; Quintela, I.; Bonet, N.; García-Garcerà, M.; et al. No major host genetic risk factor contributed to A(H1N1)2009 influenza severity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Sánchez-Velar, N.; Catrina, I.E.; Kittler, E.L.W.; Udofia, E.B.; Zapp, M.L. The cellular HIV-1 Rev cofactor hRIP is required for viral replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4027–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.E.; Talon, J.; Palese, P. The influenza virus NEP (NS2 protein) mediates the nuclear export of viral ribonucleoproteins. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellington, D.; Laurenson-Schafer, H.; Abdel-Haq, A.; Dong, T. IFITM3: How genetics influence influenza infection demographically. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Correia, V.; Antunes, L.; Faria, R.; Ferrão, J.; Faustino, P.; Nunes, B.; Maltez, F.; Lavinha, J.; De Andrade, H.R. Population genetics of IFITM3 in Portugal and Central Africa reveals a potential modifier of influenza severity. Immunogenetics 2018, 70, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, A.R.; Clare, S.; Pertel, T.; John, S.P.; Wash, R.S.; Smith, S.E.; Chin, C.R.; Feeley, E.M.; Sims, J.S.; Adams, D.J.; et al. IFITM3 restricts the morbidity and mortality associated with influenza. Nature 2012, 484, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, A.A.; Roy, N.; Porrot, F.; Billet, A.; Casartelli, N.; Yount, J.S.; Liang, C.; Schwartz, O. Natural mutations in IFITM 3 modulate post-translational regulation and toggle antiviral specificity. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tan, B.; Zhou, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Shao, C.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Xia, H.; et al. Interferon-Inducible Transmembrane Protein 3 Genetic Variant rs12252 and Influenza Susceptibility and Severity: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rodríguez, M.; Herrera-Ramos, E.; Solé-Violán, J.; Ruíz-Hernández, J.J.; Borderías, L.; Horcajada, J.P.; Lerma-Chippirraz, E.; Rajas, O.; Briones, M.; Pérez-González, M.C.; et al. IFITM3 and severe influenza virus infection. No evidence of genetic association. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensembl Genome Browser 99. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/index.html (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- López-Jiménez, J.J.; Peña-Iñiguez, D.I.; Fletes-Rayas, A.L.; Flores-Martínez, S.E.; Sánchez-Corona, J.; Rosales-Gomez, R.C.; Montoya-Fuentes, H. Distribution of IFITM3 polymorphism (dbSNP: rs12252) in mestizo populations in four states of Mexico. Int. J. Immunogenetics 2018, 45, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.G.; Symons, J.A.; McDowell, T.L.; McDevitt, H.O.; Duff, G.W. Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansa, R.; Anton, A.; Ramirez, P.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Banner, D.; Pumarola, T.; Xu, L.; Blanco, J.; Ran, L.; Lopez-Campos, G.; et al. Direct association between pharyngeal viral secretion and host cytokine response in severe pandemic influenza. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Ortiz de Lejarazu, R.; Pumarola, T.; Rello, J.; Almansa, R.; Ramírez, P.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Varillas, D.; Gallegos, M.C.; Serón, C.; et al. Th1 and Th17 hypercytokinemia as early host response signature in severe pandemic influenza. Crit. Care. 2009, 13, R201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betakova, T.; Kostrabova, A.; Lachova, V.; Turianova, L. Cytokines Induced During Influenza Virus Infection. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.W.; Hung, I.F.N.; Li, I.W.S.; Lee, K.; Koo, C.; Yan, W.; Liu, R.; Ho, K.Y.; Chu, K.H.; Watt, C.L.; et al. Delayed Clearance of Viral Load and Marked Cytokine Activation in Severe Cases of Pandemic H1N1 2009 Influenza Virus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.D.; Simmons, C.P.; Thanh, T.T.; Hien, V.M.; Smith, G.J.D.; Chau, T.N.B.; Hoang, D.M.; Chau, N.V.V.; Khanh, T.H.; Dong, V.C.; et al. Fatal outcome of human influenza A (H5N1) is associated with high viral load and hypercytokinemia. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Belser, J.A.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Gustin, K.M.; Veguilla, V.; Katz, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M. A(H7N9) Virus Results in Early Induction of Proinflammatory Cytokine Responses in both Human Lung Epithelial and Endothelial Cells and Shows Increased Human Adaptation Compared with Avian H5N1 Virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Guan, W.; Cao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Host immunological response and factors associated with clinical outcome in patients with the novel influenza A H7N9 infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O493–O500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfán-Valencia, R. Factor de necrosis tumoral: Actividad biológica en neumopatías intersticiales. Rev. Inst. Nal. Enf. Resp. Mex. 2002, 15, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Buendía-Roldán, I.; Santiago-Ruiz, L.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Mejía, M.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Benítez-Valdez, G.; Selman, M.; Falfán-Valencia, R. A major genetic determinant of autoimmune diseases is associated with the presence of autoantibodies in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1901380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Galicia-Negrete, G.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Escobar-Morales, A.J.; Abarca-Rojano, E.; Del Angel-Pablo, A.D.; Castillejos-López, M.D.J.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Single Nucleotide and Copy-Number Variants in IL4 and IL13 Are Not Associated with Asthma Susceptibility or Inflammatory Markers: A Case-Control Study in a Mexican-Mestizo Population. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Gallegos, M.A.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Partida-Zavala, N.; Hernández-Zenteno, R.; Flores-Trujillo, F.; García-Gómez, L.; Hernández-Pérez, A.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Genetic variants in IL17A and serum levels of IL-17A are associated with COPD related to tobacco smoking and biomass burning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rubio, G.; Córdoba-Lanús, E.; Cupertino, P.; Cartujano-Barrera, F.; Campos, M.A.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Role of Genetic Susceptibility in Nicotine Addiction and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2019, 71, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón-Romero, G.F.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ramírez-Jiménez, F.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Merino-Camacho, C.R.; Falfán-Valencia, R.; Teran, L.M. IL10 rs1800872 Is Associated with Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Exacerbated Respiratory Disease in Mexican-Mestizo Patients. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Hernández-Zenteno, R.; Del Angel-Pablo, A.D.; Pérez-Rodríguez, M.E.; Salazar, A.M.; Abarca-Rojano, E.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Effect of SNPs in HSP Family Genes, Variation in the mRNA and Intracellular Hsp Levels in COPD Secondary to Tobacco Smoking and Biomass-Burning Smoke. Front. Genet. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rood, M.J.; Van Krugten, M.V.; Zanelli, E.; Van Der Linden, M.W.; Keijsers, V.; Schreuder, G.M.T.; Verduyn, W.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; De Vries, R.R.P.; Breedveld, F.C.; et al. TNF-308A and HLA-DR3 alleles contribute independently to susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, J.; Vargas-Alarcon, G.; Hernández-Pacheco, G.; Portal-Celhay, C.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K.; Granados, J. Tumor necrosis factor-α promoter polymorphisms in Mexican patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Genes Immunol. 2001, 2, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Morales, S.; Velázquez-Cruz, R.; Ramírez-Bello, J.; Bonilla-González, E.; Romero-Hidalgo, S.; Escamilla-Guerrero, G.; Cuevas, F.; Espinosa-Rosales, F.; Martínez-Aguilar, N.E.; Gómez-Vera, J.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is a common genetic risk factor for asthma, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosu1. Hum. Immunol. 2009, 70, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, C.G.; Pandey, J.P.; Dooley, M.A.; Treadwell, E.L.; Clair, E.S.; Gilkeson, G.S.; A Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Cooper, G.S. Genetic polymorphisms in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and TNF-β in a population-based study of systemic lupus erythematosus: Associations and interaction with the interleukin-1α-889 C/T polymorphism. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fernández-Mestre, M.; Gendzekhadze, K.; Rivas-Vetencourt, P.; Layrisse, Z. TNF-alpha-308A allele, a possible severity risk factor of hemorrhagic manifestation in dengue fever patients. Tissue Antigens 2004, 64, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagarasu, K.; Mulay, A.; Singh, R.; Gavade, V.; Shah, P.; Cecilia, D. Association of HLA-DRB1 and TNF genotypes with dengue hemorrhagic fever. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Trejo, A.R.; Falcón-Lezama, J.A.; Juárez-Palma, L.; Granados, J.; Zúñiga-Ramos, J.; Rangel, H.; Barquera, R.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Ramos, C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter polymorphisms in Mexican patients with dengue fever. Acta Trop. 2011, 120, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Wong, Y.K.; Chang, K.W.; Chang, H.C.; Liu, H.F.; Lee, Y.J. Tumor necrosis factor-α promoter polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2005, 34, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmy, I.A.F.; Balasubramanian, S.P.; Wilson, A.G.; Stephenson, T.J.; Cox, A.; Brown, N.J.; Reed, M.W.R. Role of tumour necrosis factor gene polymorphisms (-308 and -238) in breast cancer susceptibility and severity. Breast Cancer Res. 2004, 6, R395–R400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.M.; Lee, Y.L.; Chiou, H.L.; Chen, W.; Chang, G.C.; Chou, M.C.; Lin, L.Y. Association of TNF-α polymorphism with susceptibility to and severity of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 52, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-García, G.; Falfán-Valencia, R.; García-Ramírez, R.A.; Camarena, Á.; Ramirez-Venegas, A.; Castillejos-López, M.; Pérez-Rodríguez, M.; González-Bonilla, C.; Grajales-Muñíz, C.; Borja-Aburto, V.; et al. Pandemic influenza A/H1N1 virus infection and TNF, LTA, IL1B, IL6, IL8, and CCL polymorphisms in Mexican population: A case-control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ramirez, R.A.; Ramirez-Venegas, A.; Quintana-Carrillo, R.; Camarena, Á.E.; Falfán-Valencia, R.; Mejía-Aranguré, J.M. TNF, IL6, and IL1B Polymorphisms Are Associated with Severe Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection in the Mexican Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.M.; Hassanein, O.M.; Hassan, N.H.A. Influenza A (H1N1) virus infection and TNF-308, IL6, and IL8 polymorphisms in Egyptian population: A case-control study. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2019, 80, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, Z.; Bankura, B.; Pattanayak, A.K.; Sengupta, D.; Sengupta, M.; Saha, M.L.; Panda, C.K.; Das, M. Association of Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha genetic polymorphisms with gastric cancer in India. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2018, 59, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carrillo, D.N.; Garza-González, E.; Betancourt-Linares, R.; Mónico-Manzano, T.; Antúnez-Rivera, C.; Román-Román, A.; Flores-Alfaro, E.; Illades-Aguiar, B.; Fernández-Tilapa, G. Association of IL1B -511C/-31T haplotype and Helicobacter pylori vacA genotypes with gastric ulcer and chronic gastritis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cai, H.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Yin, W.; Dong, G.; Kuai, J.; He, Y.; Jia, J. Association Between IL-1β Polymorphisms and Gastritis Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz, M.; Namdari, H.; Farahmand, M.; Mehrbod, P.; Mokhtari-Azad, T.; Rezaei, F. Association of polymorphisms in inflammatory cytokines encoding genes with severe cases of influenza A/H1N1 and B in an Iranian population. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Nie, G.; Meng, Z.; Mao, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, G. Genetic variants in IL1A and IL1B contribute to the susceptibility to 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus. BMC Immunol. 2013, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IL1B Interleukin 1 Beta [Homo Sapiens (Human)]; Gene 3553; NCBI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021.
- IL1A Interleukin 1 Alpha [Homo Sapiens (Human)]; Gene 3552; NCBI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021.
- Dinarello, C.A. IL-1: Discoveries, controversies and future directions. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.A.; Davis, J.M.; McClellan, J.L.; Carmichael, M.D.; Van Rooijen, N.; Gangemi, J.D. Susceptibility to Infection and Inflammatory Response Following Influenza Virus (H1N1, A/PR/8/34) Challenge: Role of Macrophages. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- rs17561 RefSNP; Report dbSNP; NCBI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2020.
- Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.S. 2009 pandemic influenza A/H1N1. In Environmental Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, I.C.; Scull, M.A.; Moore, C.B.; Holl, E.K.; McElvania-TeKippe, E.; Taxman, D.J.; Guthrie, E.H.; Pickles, R.J.; Ting, J.P.-Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediates In Vivo Innate Immunity to Influenza A Virus through Recognition of Viral RNA. Immunity 2009, 30, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinohe, T.; Pang, I.K.-S.; Iwasaki, A. Influenza virus activates inflammasomes via its intracellular M2 ion channel. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, V.; Ablasser, A.; Charrel-Dennis, M.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Horvath, G.; Caffrey, D.R.; Latz, E.; Fitzgerald, K.A. AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 458, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, T.; Jefford, M.; Luetjens, P.; Hochrein, H.; Masterman, K.-A.; Maliszewski, C.; Shortman, K.; Cebon, J.; Maraskovsky, E. IL-1β Enhances CD40 Ligand-Mediated Cytokine Secretion by Human Dendritic Cells (DC): A Mechanism for T Cell-Independent DC Activation. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Rodriguez, E.V.; Napolitani, G.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F. Interleukins 1β and 6 but not transforming growth factor-β are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogo, L.D.; Rezaei, F.; Marashi, S.M.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Naseri, M.; Ghavami, N.; Mokhtari-Azad, T. Seasonal influenza A/H3N2 virus infection and IL-1Β, IL-10, IL-17, and IL-28 polymorphisms in Iranian population. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 2078–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasaraju, T.; Yang, E.; Samy, R.P.; Ng, H.H.; Poh, W.P.; Liew, A.-A.; Phoon, M.C.; van Rooijen, N.; Chow, V.T. Excessive Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Contribute to Acute Lung Injury of Influenza Pneumonitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Ijiri, S.; Setoguchi, K.; Suga, M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Dietzschold, B.; Maeda, H. Pathogenesis of influenza virus-induced pneumonia: Involvement of both nitric oxide and oxygen radicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2448–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwindinger, W.F.; Robishaw, J.D. Heterotrimeric G-protein βγ-dimers in growth and differentiation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.C.; Tavares, L.P.; Dias, A.C.F.; Kehdy, F.; Alvarado-Arnez, L.E.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; Galvão, I.; Lima, B.H.; Matos, A.R.; Gonçalves, A.P.F.; et al. Phosphatidyl Inositol 3 Kinase-Gamma Balances Antiviral and Inflammatory Responses during Influenza A H1N1 Infection: From Murine Model to Genetic Association in Patients. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Inoko, H.; Kulski, J.K. The HLA genomic loci map: Expression, interaction, diversity and disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 54, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzaraki, V.; Kumar, V.; Wijmenga, C.; Zhernakova, A. The MHC locus and genetic susceptibility to autoimmune and infectious diseases. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Denney, L.; Young, D.; Powell, T.J.; Peng, Y.C.; Li, N.; Yan, H.P.; Wang, D.Y.; Shu, Y.L.; et al. High levels of virus-specific CD4+ T cells predict severe pandemic influenza A virus infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagar, L.E.; Rosella, L.; Crowcroft, N.; Lowcock, B.; Drohomyrecky, P.C.; Foisy, J.; Gubbay, J.; Rebbapragada, A.; Winter, A.L.; Achonu, C.; et al. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity to pandemic H1N1 influenza in a Canadian cohort one year post-pandemic: Implications for vaccination. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Hoa, L.N.M.; Horby, P.; van Doorn, H.R.; Trung, N.V.; Ha, N.H.; Nguyen, T.C.; Vu, D.P.; Nguyen, M.H.; Diep, N.T.N.; et al. Severe pandemic H1N1 2009 infection is associated with transient NK and T deficiency and aberrant CD8 responses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, P.C.; Turner, S.J.; Webby, R.G.; Thomas, P.G. Influenza and the challenge for immunology. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Xu, P.; Lu, Y.; Luo, J.; Nolte, D.L.; Deliberto, T.J.; Duan, M.; et al. Evolutionary Characterization of the Pandemic H1N1/2009 Influenza Virus in Humans Based on Non-Structural Genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garten, R.J.; Davis, C.T.; Russell, C.A.; Shu, B.; Lindstrom, S.; Balish, A.; Sessions, W.M.; Xu, X.; Skepner, E.; Deyde, V.; et al. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 2009, 325, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falfán-Valencia, R.; Narayanankutty, A.; Reséndiz-Hernández, J.M.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Nava-Quiroz, K.J.; Bautista-Félix, N.E.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Castillejos-López, M.D.; Hernández, A. An increased frequency in HLA class I alleles and haplotypes suggests genetic susceptibility to influenza A (H1N1) 2009 pandemic: A case-control study. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, T.; Oshansky, C.M.; Roddam, P.L.; DeVincenzo, J.P.; Caniza, M.A.; Jojic, N.; Mallal, S.; Phillips, E.; James, I.; Halloran, M.E.; et al. HLA targeting efficiency correlates with human T-cell response magnitude and with mortality from influenza A infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13492–13497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, T.; Nolan, D.; James, I.; John, M.; Gaudieri, S.; Phillips, E.; Huang, J.C.; Riadi, G.; Mallal, S.; Jojic, N. Mapping the Landscape of Host-Pathogen Coevolution: HLA Class I Binding and Its Relationship with Evolutionary Conservation in Human and Viral Proteins. J. Virol. 2010, 85, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capittini, C.; Tinelli, C.; Guarene, M.; Pasi, A.; Badulli, C.; Sbarsi, I.; Garlaschelli, F.; Cremaschi, A.L.; Pizzochero, C.; Monti, C.; et al. Possible KIR-driven genetic pressure on the genesis and maintenance of specific HLA-A,B haplotypes as functional genetic blocks. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- La, D.; Czarnecki, C.; El-Gabalawy, H.; Kumar, A.; Meyers, A.F.A.; Bastien, N.; Simonsen, J.N.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. Enrichment of variations in KIR3DL1/s1 and KIR2DL2/L3 among H1N1/09 ICU patients: An exploratory study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Galarza, F.F.; McCabe, A.; Santos, E.J.M.D.; Jones, J.; Takeshita, L.; Ortega-Rivera, N.D.; Del Cid-Pavón, G.M.; Ramsbottom, K.; Ghattaoraya, G.; Alfirevic, A.; et al. Allele frequency net database (AFND) 2020 update: Gold-standard data classification, open access genotype data and new query tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D783–D788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.; Barker, D.J.; Georgiou, X.; Cooper, M.A.; Flicek, P.; Marsh, S.G.E. IPD-IMGT/HLA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D948–D955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Angel-Pablo, A.D.; Juárez-Martín, A.I.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; López-Flores, L.A.; Camarena, A.E.; Falfán-Valencia, R. HLA allele and haplotype frequencies in three urban Mexican populations: Genetic diversity for the approach of genomic medicine. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Tan, S.; Yi, Y.; Wu, B.; Cao, B.; Zhu, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Qi, J.; et al. Cross-Allele Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Responses against 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Influenza A Virus among HLA-A24 and HLA-A3 Supertype-Positive Individuals. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13281–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dutta, M.; Dutta, P.; Medhi, S.; Borkakoty, B.; Biswas, D. Polymorphism of HLA class I and class II alleles in influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infected population of Assam, Northeast India. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Gao, F.; Zhou, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Gao, B.; Tien, P.; Shu, Y.; Iwamoto, A.; et al. Identification and structural definition of H5-specific CTL epitopes restricted by HLA-A*0201 derived from the H5N1 subtype of influenza A viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 91, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrah, T.W.; Goonetilleke, N.; Kopycinski, J.; Deeks, S.G.; Cohen, M.S.; Borrow, P.; McMichael, A.; Brackenridge, S. Reappraisal of the Relationship between the HIV-1-Protective Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism 35 Kilobases Upstream of the HLA-C Gene and Surface HLA-C Expression. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3367–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; August, J.T.; Brusic, V.; Tan, T.W.; Ranganathan, S. In silico characterization of immunogenic epitopes presented by HLA-Cw*0401. Immunome Res. 2007, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Walshe, V.A.; Hattotuwagama, C.K.; Doytchinova, I.A.; Wong, M.; Macdonald, I.K.; Mulder, A.; Claas, F.H.J.; Pellegrino, P.; Turner, J.; Williams, I.; et al. Integrating In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of Peptide Binding Affinity to HLA-Cw*0102: A Bioinformatic Approach to the Prediction of New Epitopes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, E.B.; Grant, E.J.; Wang, Z.; Gras, S.; Tipping, P.; Rossjohn, J.; Miller, A.; Tong, S.Y.C.; Kedzierska, K. Towards identification of immune and genetic correlates of severe influenza disease in Indigenous Australians. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.; Cassidy, S.; Humphreys, L.; Bennett, G.; Hurley, C.K.; Boettcher, B.; McCluskey, J. Evolution in HLA-DRB1 and major histocompatibility complex class II haplotypes of Australian aborigines definition of a new DRB1 allele and distribution of DRB 1 gene frequencies. Hum. Immunol. 1995, 42, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, E.E.; Huda, R.; Scheibel, S.F.; Nichols, J.E.; Mock, D.J.; El-Daher, N.; Domurat, F.M.; Roberts, N.J., Jr. HLA-associated protection of lymphocytes during influenza virus infection. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Gallegos, M.A.; Ruiz-Celis, A.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Bautista-Félix, N.E.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Polymorphisms in Processing and Antigen Presentation-Related Genes and Their Association with Host Susceptibility to Influenza A/H1N1 2009 Pandemic in a Mexican Mestizo Population. Viruses 2020, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Population | rs34481144 G/A, (%) | rs12252 T/C, (%) |
|---|---|---|
| African | 96/4 | 74/26 |
| American | 77/23 | 82/18 |
| East Asian | 99/1 | 47/53 |
| European | 54/46 | 96/4 |
| South Asian | 79/21 | 85/15 |
| All | 82/18 | 76/24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ponce-Gallegos, M.A.; Domínguez-Mazzocco, B.A.; Ponce-Gallegos, J.; García-Ramírez, R.A.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Role of the Host Genetic Susceptibility to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1. Viruses 2021, 13, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020344
Pérez-Rubio G, Ponce-Gallegos MA, Domínguez-Mazzocco BA, Ponce-Gallegos J, García-Ramírez RA, Falfán-Valencia R. Role of the Host Genetic Susceptibility to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1. Viruses. 2021; 13(2):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020344
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Rubio, Gloria, Marco Antonio Ponce-Gallegos, Bruno André Domínguez-Mazzocco, Jaime Ponce-Gallegos, Román Alejandro García-Ramírez, and Ramcés Falfán-Valencia. 2021. "Role of the Host Genetic Susceptibility to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1" Viruses 13, no. 2: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020344
APA StylePérez-Rubio, G., Ponce-Gallegos, M. A., Domínguez-Mazzocco, B. A., Ponce-Gallegos, J., García-Ramírez, R. A., & Falfán-Valencia, R. (2021). Role of the Host Genetic Susceptibility to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1. Viruses, 13(2), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020344









