Abstract
In the post-polio eradication era, increasing attention is given to non-polio enteroviruses. Most of the data about enteroviruses in sub-Saharan Africa are related to acute flaccid paralysis surveillance and target the pediatric population. This study aimed to investigate the presence of enterovirus in PLHIV (people living with HIV) and HIV-negative individuals in Ghana. Stool samples from HIV-positive individuals (n = 250) and healthy blood donors (n = 102) attending the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital in Kumasi, Ghana, were screened by real-time PCR for enterovirus. Molecular typing of the VP1 region was performed. Enterovirus-positive samples were tested for norovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus, sapovirus, and cosaviruses. Twenty-six out of 250 HIV-positive subjects (10.4%) and 14 out of 102 HIV-negative individuals (13.7%) were detected enterovirus-positive, not showing a significant different infection rate between the two groups. HIV-negative individuals were infected with Enterovirus C strains only. HIV-positive participants were detected positive for species Enterovirus A, Enterovirus B, and Enterovirus C. Co-infections with other viral enteric pathogens were almost exclusively detected among HIV-positive participants. Overall, the present study provides the first data about enteroviruses within HIV-positive and HIV-negative adults living in Ghana.
1. Introduction
Enteroviruses belong to the family Picornaviridae and are non-enveloped single stranded RNA viruses. So far more than 100 different serotypes have been identified to infect humans and grouped into 4 species (Enterovirus A- Enterovirus D) on the basis of their genetic divergence [1]. Enteroviruses are endemic worldwide and mainly transmitted via the fecal–oral route or by droplets and direct contacts [2]. The most known members of the genus Enterovirus are represented by the three poliovirus types (PV), assigned within the species Enterovirus C. Polioviruses are the etiologic agents of paralytic poliomyelitis, an infectious disease characterized by acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) and whose main target is children under 5 years of age [3]. The success of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) has dramatically reduced the circulation of wild PVs [4]. Since 1988, the number of polio endemic countries has declined from 125 to 3, represented by Nigeria, Pakistan and Afghanistan, with Nigeria being on the verge of being certified as polio free [4,5].
In the post-polio eradication era, increasing attention is given worldwide to the detection and characterization of non-polio enteroviruses [6,7]. Although enterovirus infections are mostly asymptomatic, the available data evidenced a high pathogenic potential. Different non-polio enteroviruses have been isolated from patients affected from AFP in the context of polio surveillance [6]. Other severe clinical forms associated with enteroviruses include aseptic meningitis, myocarditis, encephalitis, and respiratory diseases [8,9]. Age, gender, and host immune status can influence the clinical presentation and severity of infection [10]. Furthermore, emerging enterovirus variants have been recognized worldwide as causes of severe clinical manifestations in both sporadic and epidemic cases [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
In Europe, the non-polio enterovirus network (ENPEN) was recently established, with the aim to collect data on severe enterovirus infections and monitor the circulation of enterovirus types [19].
In sub-Saharan Africa, the limited data about enterovirus infections are mostly related to AFP surveillance [20,21,22]. A previous survey in Côte d’Ivoire evidenced a high variety of enterovirus strains circulating in apparently healthy individuals [23]. A high diversity in enterovirus isolates infecting healthy individuals was also observed in other African countries [24,25].
Malnutrition and inadequate supply of water, sanitation, and hygiene presumably play a crucial role in the spread of this group of viruses [26]. However, few data are available about the presence of enteroviruses in immunocompromised individuals living in these areas, namely PLHIV (people living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus). Chronic meningoencephalitis associated to enterovirus in immunocompromised patients have long been known [27,28,29]. Nevertheless, the potential role of HIV-positive patients as a source of enterovirus infections in tropical areas has been barely examined [30].
As known, the depletion of CD4+ T lymphocytes and the associated impairment of the immune system make HIV patients more vulnerable to acquiring other infections and to developing more severe clinical manifestations [31]. Remarkably, co-infections with enteric parasitic infections are reported to worsen the progression of the HIV infection to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) [32]. On the contrary, a potential beneficial immunomodulatory effect was evidenced in case of co-infection with Helicobacter pylori in HIV-positive persons [33,34]. The impact of enteric viruses in HIV-positive people living in low-income countries is poorly investigated; however, they are considered a relevant cause of morbidity in this group of patients [35]. Furthermore, HIV progression was associated with the expansion of enteric virome [36,37].
In Ghana, 300,000 people are estimated to be living with HIV/AIDS and only 70,000 of them are reported to have access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) [38].
The aim of the present study was to analyze and molecularly characterize the spectrum of enteroviruses infecting HIV-positive and HIV-negative adults living in Ghana, in order to evidence if HIV infection was associated with a higher risk for infection with enteroviruses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
The present study comprised participants from an observational cohort study on clinical and sociodemographic determinants of H. pylori infection among HIV-infected and non-infected persons [33,34]. Adult HIV-positive patients from the HIV Outpatient Department of the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital in Kumasi, Ghana, were enrolled between November 2011 and November 2012. Additionally, blood donors from the same hospital were recruited to serve as a HIV-negative control group. From this cohort, we randomly selected HIV-positive patients with CD4+ T cell counts below or more than 200 cells/μL (n= 119 and 131, respectively), and 102 HIV-negative individuals to analyze the prevalence and clinical implications of human enteroviruses.
2.2. Ethics Statement
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Committee on Human Research of the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology in Kumasi, Ghana: HRPE/AP/12/11, and the ethics committee of the Medical Council in Hamburg, Germany: PV3771. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before enrolment in accordance with the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki.
2.3. Specimen Collection, Handling and Storage
Trained study personnel collected demographic and clinical data using a standardized questionnaire. Aliquots of native stool samples were freshly frozen and stored at −80 °C before being transported to Germany on dry ice. Blood samples were collected and the analysis of CD4+ T cell count was performed in Ghana using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Mountain View, California).
2.4. Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction
A 10% suspension of each stool sample was prepared using PBS. Viral nucleic acids were extracted from 700 µL of the stool suspension by using the automated platform VERSANT kPCR Molecular System and the VERSANT Sample Preparation 1.0 Reagents Kit (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Erlangen, Germany) into an elution volume of 100 µl, according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5. Detection of Enteroviruses and Other Viral Enteric Co-Infections
Samples were screened for enteroviruses using the Enterovirus real-time RT-PCR Kit (TaqMan) (AnDiaTec GmbH & Co.KG, Kornwestheim, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Enterovirus-positive samples were screened for the presence of other viral enteric pathogens. Norovirus (NoV), adenovirus (AdV), rotavirus (RV), astrovirus (HAstV), and sapovirus (SaV) were detected using the multiplex FTD Viral gastroenteritis (Fast-Track Diagnostics, Luxembourg), in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Cosaviruses (CoSV) were detected as described by Kapoor et al. [39].
2.6. VP1 Amplification, Sequencing and Molecular Typing
All enterovirus strains were sequenced in the 5′ non-coding region (5′NCR) for enterovirus species assignment. Molecular typing of enterovirus strains was performed using generic and species-specific VP1-primer systems [23,25]. Sequencing was done directly on amplification products using BigDye 3.1 (Applied Biosystems). Assignment to enterovirus types was done using BLAST and the Enterovirus Genotyping Tool [40,41]. Sequences were deposited in GenBank under accession numbers MN812172-MN812201.
In addition to molecular assays, enterovirus-positive stool samples were inoculated to RD-A cells and passaged three times. If CPE was observed, RNA was extracted from 140 µL cell culture supernatant and subjected to enterovirus PCR, targeting the 5′ non-coding region (NCR) and VP1 region. Sequencing was performed to exclude the presence of polioviruses.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using R (version 3.6.1, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Categorical variables were compared using either the χ2 test or the Fisher exact test, as appropriate. Continuous variables were expressed as median (interquartile range, IQR) or mean ± standard deviation (SD) and compared using the Wilcoxon rank sum test or the unpaired Student’s t-test. A multiple linear regression model was used to assess the association between covariates and the continuous outcome CD4+ T cell count cells/μL. Two-sided p-values were presented, and statistical significance was determined at α = 5%.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Enterovirus-positive and Negative Participants
Forty (11.4%) out of 352 stool samples were tested positive for enteroviruses (Table 1). Out of 250 samples of HIV-positive subjects, twenty-six (10.4%) were tested enterovirus-positive, and fourteen out of 102 HIV-negative individuals (13.7%, p = 0.362) were tested enterovirus-positive (Figure 1a). The proportion of HIV infections was not different between enterovirus-positive and enterovirus-negative participants (65.0% vs. 71.8%, respectively). Furthermore, the two groups did not differ regarding the presence of clinical symptoms between enterovirus-positive and enterovirus-negative individuals. Remarkably, within the group of HIV-positive participants, those with an enterovirus infection had significantly higher median CD4+ T cell counts compared to those that were tested enterovirus-negative (416 [IQR 168-535] vs 204 [IQR 78-460] cells/μL, p = 0.017), but did not differ in regard to antiretroviral therapy, intake of antibiotics, or time since diagnosis of HIV (Table S1 and S2). Interestingly, this finding was restricted to HIV-positive subjects and was not observed in participants without HIV infection. On the other hand, HIV-negative adults infected with enterovirus were significantly younger than those without enterovirus infection (28.6 ± 6.4 vs. 33.6 ± 12.9, p = 0.029).

Table 1.
Demographical and clinical characteristics of enterovirus-positive and enterovirus-negative participants.
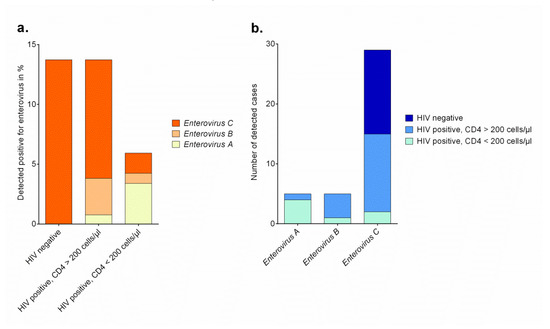
Figure 1.
(a). Absolute numbers of enterovirus strains assigned to species in HIV-positive adults with high and low CD4+ T cell count and HIV-negative persons in Ghana in %. (b). Absolute numbers of enterovirus strains assigned to species detected in adult participants in Ghana.
3.2. Enterovirus Typing
Enterovirus strains were characterized by sequencing the V1 region for type assignment. For strains remaining negative for VP1 amplification, sequencing of the 5′ 5′NCR allowed enterovirus species assignment. Thirty-three strains could be assigned to a type and six could be typed on species level. One real-time RT-PCR positive sample remained negative in the typing PCR assays. The identified enterovirus types were assigned to species Enterovirus A, Enterovirus B and Enterovirus C (Table 2). The presence of polioviruses was also excluded using cell culture assays. Only one stool sample (HP0932) showed CPE in RD-A cells and molecular typing resulted in EV-A76 detection. Remarkably, whereas HIV-negative individuals were infected exclusively with Enterovirus C strains, HIV-positive participants also showed infections with Enterovirus A strains and Enterovirus B strains (Figure 1a,b). None of the 15 HIV-infected participants with Enterovirus C strains detected reported any gastrointestinal complaints and thirteen out of them had CD4+ T cell counts higher than 200 cells/μL (Table 2). In contrast to this, four out of five participants with Enterovirus A strain co-infection had CD4+ T cell counts below 200 cells/μL.

Table 2.
Characteristics, clinical features and enterovirus typing results of enterovirus-positive adults living in Ghana.
3.3. Co-Infection with Other Enteric Viruses
Fifteen (37.5%) out of 40 enterovirus-positive participants were co-infected with additional enteric viruses. Out of them, 10 samples were tested positive for one further viral pathogen and 5 samples for 2 other viruses. AdV and CoSV were the most common co-infections (Table 2). Remarkably, all but one of these infections with additional enteric pathogens were observed in HIV-positive individuals. It is worth noting that four of five co-infections with CoSV in HIV-positive participants were detected in subjects with CD4+ T cell counts below 200 cells/μL (p = 0.02).
3.4. Factors Associated with CD4+ T Cell Count in HIV-Positive Participants With and Without Enterovirus Co-Infection
In the simple linear regression models age, ART-intake and being infected with Enterovirus C strains compared to not carrying enteroviruses were significantly associated with an increased CD4+ T cell count in HIV-positive participants (Table 3). When adjusting for age, sex and ART-intake, detection of Enterovirus C strains was still found to be independently associated with a higher CD4+ T cell count in HIV-positive participants compared to those with an enterovirus-negative status (p = 0.042).

Table 3.
Factors associated with increased CD4+ T cell count in HIV-positive participants with and without enterovirus co-infection.
4. Discussion
Non-polio enteroviruses are recognized worldwide as an emerging cause of different diseases. The outbreaks caused by enteroviruses that affected Europe, America and Asia in the recent years evidenced the high pathogenic potential of this group of viruses [42].
Data on enterovirus infections circulating in people living in sub-Saharan Africa are still limited and mostly addressing the pediatric population. Recently, Brouwer et al. detected enteroviruses by real-time RT-PCR in 89.9% of fecal samples collected from a cohort of children ≤ 5 years of age in Malawi, not showing differences in enterovirus detection rates between children with and without severe anemia [43]. So far, no other studies could evidence a comparable high detection rate [44].
In our present cohort 40 out of 352 stool samples were tested positive for enteroviruses, indicating a detection rate of 11.4%. Although apparently modest, this result confirms that enterovirus circulation in Ghana is a phenomenon not limited to childhood, considering that the mean age of participants was 38.2 (± 10.6). Nevertheless, we observed a lower mean age in HIV-negative participants infected with enterovirus compared to those without enterovirus infection in our adult cohort. A recent study reported a similar infection rate in healthy individuals living in Nigeria, including children and adults [25]. Apparently, HIV infection was not shown to be associated with a higher rate of enterovirus infections compared to HIV-negative adults. Previous available data seem to confirm this result regardless of age [45,46].
However, the higher diversity of enteroviruses as well as the detection of rare and zoonotic enterovirus types, mostly in HIV-positive individuals, provide further incentives to understand better the meaning of enterovirus infections within PLHIV.
In our study, the majority of strains were assigned to Enterovirus C (29/39), which is often described as the most common group circulating in sub-Saharan Africa [43,47]. Within this species, CVA20 and EV-C99 were the most common serotypes identified in our cohort. Although both serotypes have been isolated from AFP patients, they have been more commonly identified in apparently healthy individuals [23,25,43,48]. In our cohort, all but one of the HIV-positive individuals infected with these serotypes had a CD4+ T cell count higher than 200 cells/μL. These two serotypes could be detected in both HIV-positive and HIV-negative individuals. On the contrary, the rarely reported EV-C113 was detected in HIV-positive patients only [49].
Interestingly, the detection of enterovirus strains belonging to the species Enterovirus A and Enterovirus B was restricted to HIV-infected participants. In particular, two HIV-positive participants with CD4+ T cell count > 200 cells/µL were detected positive for two rarely described serotypes, namely EV-B106 and EV-B74 [50,51].
The serotype EV-A119 was detected in three female HIV-positive individuals with CD4+ T cell counts below 200 cells/μL and an age of 45 years or higher, whereas EV-A76 was found in a HIV-positive patient with a low CD4+ T cell count and multiple clinical complaints, including cough, gastrointestinal symptoms, and skin rush. Both of them are known for their zoonotic potential and have been isolated in non-human primates in West and Central Africa [52,53,54,55].
The observation that in our cohort only PLHIV were infected with rarely circulating serotypes represents a novel evidence whose meaning needs to be investigated further. The impairment of gastrointestinal immunity induced by HIV might be one possible explanation.
In line with this result, infections with other enteric viral pathogens in addition to infection with enteroviruses could be found almost exclusively in HIV-positive patients.
It is interesting to note that the detection of CoSV infections in enterovirus-positive individuals (6/40, 15%) was rather higher when compared to the limited available data of other cohorts of adults [25]. So far, CoSV infections in adults have been rarely reported worldwide. CoSV were found in one of 1000 adult patients with gastroenteritis in Scotland and in one of 150 stool samples from adults with diarrhea living in Thailand [39,56]. Similar data were obtained from immunocompromised individuals. Among HIV-infected patients, CoSV were detected in one of 154 patients suffering from gastroenteritis in Brazil and in three of 196 patients with and without diarrhea in the Netherlands [57,58]. A case of persistent CoSV infection and chronic diarrhea was also described in a lung transplant recipient [59].
In the present cohort, the almost exclusive detection of other viral enteric agents in enterovirus-positive persons infected with HIV is suggestive of an altered intestinal mucosal immunity affecting this group of patients.
A recent investigation targeting a cohort of Ugandan patients evidenced that advanced HIV/AIDS is associated with the expansion of enteric virome, in particular adenoviruses [36]. Our data confirmed a higher burden, in terms of enterovirus variability and rate of co-infections with other gastrointestinal viruses, among HIV-infected patients compared to HIV-negative individuals. Adenovirus represented the most common viral agent detected as co-infection.
The association of the CD4+ T cell count in HIV-positive individuals with different enterovirus species represents a new aspect of the present study. Rarely reported Enterovirus A infections as well as infections with zoonotic potential types were almost exclusively detected in HIV-positive individuals with an impaired immune system, as indicated by a low CD4+ T cell count.
Contrastingly, the infection with members of Enterovirus C types in HIV-positive participants was independently associated with a higher CD4+ T cell count compared to PLHIV not infected with enteroviruses. So far, Enterovirus C is the only species of human enteroviruses that was not detected in animals, confirming it as highly specific to humans. Considering that Enterovirus C species is more prevalent in healthy people, it might be supposed that members of this group of viruses are able to stably replicate in the human gut, reflecting a favorable health status [60]. On the other hand, the higher CD4+ T cells/μL count detected in HIV+ individuals infected with Enterovirus C strains compared to HIV-positive participants without enterovirus infection might indicate a cell-mediated immune response toward the co-infection.
Another remarkable aspect of this study is represented by the fact that co-infection with CoSV was significantly more common in enterovirus-infected PLHIV with CD4+ T cell counts below 200 cells/μL, indicating the potential role of CoSV as an opportunistic agent.
Overall, the present study provides the first data about enteroviruses and additional enteric co-infections within HIV-positive and HIV-negative adults living in Ghana. Although infections with enteroviruses were not more frequent in PLHIV, a higher diversity of enteroviruses, including rare and zoonotic types, was predominantly detected among HIV-positive individuals with a low CD4+T cell count. Infections with additional enteric viruses were almost exclusively detected among HIV-infected individuals, confirming the detrimental effect of HIV on gut homeostasis. As prolonged enterovirus shedding might be a biomarker for defective immune defenses against enteroviruses, it would be of interest if HIV-positive individuals infected with enterovirus had prolonged shedding of the same serotype in consecutive stool samples. Therefore, further longitudinal studies are required to gain more comprehensive knowledge about the role of such viruses on gut homeostasis.
Surveillance of non-polio enterovirus diversity among distinct patient groups in African countries, including PLHIV, plays an important role in not underestimating this neglected occurrence of EV infections and their potential impact on public health.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/12/2/221/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.D.C., K.W., S.B., F.S.S., T.F., K.A.E.; formal analysis, V.D.C., K.W., K.A.E.; investigation, V.D.C., K.W., E.K., E.H., S.B., A.D., M.W., L.-G.C.; methodology, S.B., K.W., K.A.E.; project administration, A.D.; resources, V.D.C., R.K., R.O.P., B.N.; supervision, F.S.S., R.K., R.O.P., B.N., T.F., A.D.; writing—original draft, V.D.C., K.W., S.B., K.A.E.; writing—review and editing, E.K., E.H., R.K., T.F., R.O.P., B.N, F.S.S., L.-G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Funding
The present study was supported by the Koeln Fortune Program of the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Cologne (Germany), ESTHER Germany, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Project No. 01KA1102).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the patients and medical staff at the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital in Kumasi, Ghana.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Knowles, N.J.; Hovi, T.; Hyypiä, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Simmonds, P.; Skern, T.; Stanway, G.; et al. Picornaviridae; Andrew, M.Q., King, E.L., Michael, J., Adams, E.B., Carstens, S.D., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.I.; Coyne, C.B. Enteroviruses: A Gut-Wrenching Game of Entry, Detection, and Evasion. Viruses 2019, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, P.D. Live attenuated vaccines: Historical successes and current challenges. Virology 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.A.; Ahmed, J.; Datta, S.D.; Burns, C.C.; Quddus, A.; Vertefeuille, J.F.; Wassilak, S.G.F. Progress Toward Polio Eradication-Worldwide, January 2017–March 2019. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, S.; Bhatnagar, P.; Sutter, R.W.; Roesel, S.; Zaffran, M. Global Polio Eradication-Way Ahead. Indian J Pediatr. 2018, 85, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S.; Forgie, S.; Robinson, J. Non-polio Enterovirus detection with acute flaccid paralysis: A systematic review. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. Acute Flaccid Myelitis: Something Old and Something New. MBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, D.; Krogstad, P. Enteroviruses in the early 21st century: New manifestations and challenges. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, H.; Schroten, H.; Tenenbaum, T. Enterovirus Infections of the Central Nervous System in Children: An Update. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebruegge, M.; Curtis, N. Enterovirus infections in neonates. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009, 14, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.A.; Zheng, X.T.; Harris, M.U.; Cadichon, S.B.; Melin-Aldana, H.; Khetsuriani, N.; Oberste, M.S.; Shulman, S.T. Outbreak of life-threatening coxsackievirus B1 myocarditis in neonates. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragstad, K.; Jakobsen, K.; Rojahn, A.E.; Skram, M.K.; Vainio, K.; Holberg-Petersen, M.; Hungnes, O.; Dudman, S.G.; Kran, A.M. High frequency of enterovirus D68 in children hospitalised with respiratory illness in Norway, autumn 2014. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2015, 9, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Chidini, G.; Cinnante, C.; Napolitano, L.; Giannini, A.; Terranova, L.; Niesters, H.; Principi, N.; Calderini, E. Acute flaccid myelitis associated with enterovirus-D68 infection in an otherwise healthy child. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messacar, K.; Asturias, E.J.; Hixon, A.M.; Van Leer-Buter, C.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Tyler, K.L.; Abzug, M.J.; Dominguez, S.R. Enterovirus D68 and acute flaccid myelitis-evaluating the evidence for causality. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e239–e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doitsh, G.; Galloway, N.L.; Geng, X.; Yang, Z.; Monroe, K.M.; Zepeda, O.; Hunt, P.W.; Hatano, H.; Sowinski, S.; Muñoz-Arias, I.; et al. Cell death by pyroptosis drives CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1 infection. Nature 2014, 505, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taravilla, C.N.; Perez-Sebastian, I.; Salido, A.G.; Serrano, C.V.; Extremera, V.C.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Marin, L.L.; Sanz, M.A.; Traba, O.M.S.; Gonzalez, A.S. Enterovirus A71 Infection and Neurologic Disease, Madrid, Spain, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takechi, M.; Fukushima, W.; Nakano, T.; Inui, M.; Ohfuji, S.; Kase, T.; Ito, K.; Kondo, K.; Maeda, A.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Nationwide Survey of Pediatric Inpatients With Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, Herpangina, and Associated Complications During an Epidemic Period in Japan: Estimated Number of Hospitalized Patients and Factors Associated With Severe Cases. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvala, H.; Broberg, E.; Benschop, K.; Berginc, N.; Ladhani, S.; Susi, P.; Christiansen, C.; McKenna, J.; Allen, D.; Makiello, P.; et al. Recommendations for enterovirus diagnostics and characterisation within and beyond Europe. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 101, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momou, K.J.; Akoua-Koffi, C.; Akre, D.S.; Adjogoua, E.V.; Tieoulou, L.; Dosso, M. Detection of enteroviruses in urban wastewater in Yopougon, Abidjan. Pathol. Biol. 2012, 60, e21–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoom, J.K.; Obodai, E.; Barnor, J.S.; Ashun, M.; Arthur-Quarm, J.; Osei-Kwasi, M. Human Enteroviruses isolated during acute flaccid paralysis surveillance in Ghana: Implications for the post eradication era. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2012, 12, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Faleye, T.O.C.; Adewumi, M.O.; Japhet, M.O.; David, O.M.; Oluyege, A.O.; Adeniji, J.A.; Famurewa, O. Non-polio enteroviruses in faeces of children diagnosed with acute flaccid paralysis in Nigeria. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristanziano, V.D.; Bottcher, S.; Diedrich, S.; Timmen-Wego, M.; Knops, E.; Lubke, N.; Kaiser, R.; Pfister, H.; Kabore, Y.; D’Alfonso, R. Detection and characterization of enteroviruses and parechoviruses in healthy people living in the South of Cote d’Ivoire. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 71, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attoh, J.; Obodai, E.; Adiku, T.; Odoom, J.K. Prevalence of human enteroviruses among apparently healthy nursery school children in Accra. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2014, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osundare, F.A.; Opaleye, O.O.; Akindele, A.A.; Adedokun, S.A.; Akanbi, O.A.; Bock, C.T.; Diedrich, S.; Böttcher, S. Detection and Characterization of Human Enteroviruses, Human Cosaviruses, and a New Human Parechovirus Type in Healthy Individuals in Osun State, Nigeria, 2016/2017. Viruses 2019, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristanziano, V.; Timmen-Wego, M.; Lubke, N.; Kaiser, R.; Pfister, H.; Di Cave, D.; Berrilli, F.; Kabore, Y.; D’Alfonso, R. Application of Luminex Gastrointestinal Pathogen Panel to human stool samples from Cote d’Ivoire. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2015, 9, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfert, C.M.; Buckley, R.H.; Mohanakumar, T.; Griffith, J.F.; Katz, S.L.; Whisnant, J.K.; Eggleston, P.A.; Moore, M.; Treadwell, E.; Oxman, M.N.; et al. Persistent and fatal central-nervous-system ECHOvirus infections in patients with agammaglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 296, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, E.; Winkelstein, J.; Webster, A.D. Enteroviral infections in primary immunodeficiency (PID): A survey of morbidity and mortality. J. Infect. 2003, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez, R.; Lastinger, A.M.; Hogg, J.P. Chronic enteroviral meningoencephalitis in a patient on rituximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: A case report and brief literature review. IDCases 2019, 17, e00558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Musoke, R.; Palakudy, T.; D’Agostino, A.; Gray, J. An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection among HIV-1-infected orphans in Nairobi. Aids 2004, 18, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, G.; Alelign, D.; Abossie, A. Prevalence of Opportunistic Intestinal Parasites and Associated Factors among HIV Patients while Receiving ART at Arba Minch Hospital in Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-sectional Study. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2018, 28, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedle, D.; Kumera, G.; Eshete, T.; Ketema, K.; Adugna, H.; Feyera, F. Intestinal parasitic infections and its association with undernutrition and CD4 T cell levels among HIV/AIDS patients on HAART in Butajira, Ethiopia. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2017, 36, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, K.A.; Sarfo, F.S.; Dompreh, A.; Kuffour, E.O.; Geldmacher, C.; Soltau, M.; Schachscheider, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Häussinger, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Coinfection Is Associated With Decreased Markers of Immune Activation in ART-Naive HIV-Positive and in HIV-Negative Individuals in Ghana. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfo, F.S.; Eberhardt, K.A.; Dompreh, A.; Kuffour, E.O.; Soltau, M.; Schachscheider, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Häussinger, D.; Oteng-Seifah, E.E.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Infection Is Associated with Higher CD4 T Cell Counts and Lower HIV-1 Viral Loads in ART-Naïve HIV-Positive Patients in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portes, S.A.R.; Carvalho-Costa, F.A.; Rocha, M.S.; Fumian, T.M.; Maranhao, A.G.; de Assis, R.M.; Xavier, M.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Leite, J.P.G.; Volotao, E.M. Enteric viruses in HIV-1 seropositive and HIV-1 seronegative children with diarrheal diseases in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, C.L.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Zhao, G.; Handley, S.A.; Ghebremichael, M.S.; Lim, E.S.; Lankowski, A.; Baldridge, M.T.; Wilen, C.B.; Flagg, M.; et al. Altered Virome and Bacterial Microbiome in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.A.; Desai, C.; Zhao, G.; Droit, L.; Monaco, C.L.; Schroeder, A.C.; Nkolola, J.P.; Norman, M.E.; Miller, A.D.; Wang, D.; et al. SIV Infection-Mediated Changes in Gastrointestinal Bacterial Microbiome and Virome Are Associated with Immunodeficiency and Prevented by Vaccination. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, K.A.; Okyere, P.; Doku, P.N. An evaluation of a community-based food supplementation for people living with HIV in Ghana: Implications for community-based interventions in Ghana. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Victoria, J.; Simmonds, P.; Slikas, E.; Chieochansin, T.; Naeem, A.; Shaukat, S.; Sharif, S.; Alam, M.M.; Angez, M.; et al. A highly prevalent and genetically diversified Picornaviridae genus in South Asian children. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20482–20487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneman, A.; Vennema, H.; Deforche, K.V.D.; Avoort, H.V.D.; Penaranda, S.; Oberste, M.S.; Vinje, J.; Koopmans, M. An automated genotyping tool for enteroviruses and noroviruses. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 51, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvala, H.; Robertson, I.; McWilliam Leitch, E.C.; Benschop, K.; Wolthers, K.C.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. Epidemiology and clinical associations of human parechovirus respiratory infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Hansen, C.C.; Midgley, S.E.; Fischer, T.K. Global emergence of enterovirus D68: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e64–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, L.; van der Sanden, S.M.G.; Calis, J.C.J.; Bruning, A.H.L.; Wang, S.; Wildenbeest, J.G.; Rebers, S.P.H.; Phiri, K.S.; Westerhuis, B.M.; van Hensbroek, M.B.; et al. High frequency of Polio-like Enterovirus C strains with differential clustering of CVA-13 and EV-C99 subgenotypes in a cohort of Malawian children. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeuh-Mba, S.A.; Bessaud, M.; Massenet, D.; Joffret, M.L.; Endegue, M.C.; Njouom, R.; Reynes, J.M.; Rousset, D.; Delpeyroux, F. High frequency and diversity of species C enteroviruses in Cameroon and neighboring countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouandjika-Vasilache, I.; Akoua-Koffi, C.; Begaud, E.; Dosseh, A. No evidence of prolonged enterovirus excretion in HIV-seropositive patients. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2005, 10, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetsuriani, N.; Helfand, R.; Pallansch, M.; Kew, O.; Fowlkes, A.; Oberste, M.S.; Tukei, P.; Muli, J.; Makokha, E.; Gary, H. Limited duration of vaccine poliovirus and other enterovirus excretion among human immunodeficiency virus infected children in Kenya. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, J.A.; Oragwa, A.O.; George, U.E.; Ibok, U.I.; Faleye, T.O.C.; Adewumi, M.O. Preponderance of enterovirus C in RD-L20B-cell-culture-negative stool samples from children diagnosed with acute flaccid paralysis in Nigeria. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Cui, H.; Yan, D.; Fan, Q.; Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Ji, T.; et al. Circulation of multiple serotypes of highly divergent enterovirus C in the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region of China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, R.; Haq, S.; Sameroff, S.; Howie, S.R.; Lipkin, W.I. Genomic analysis of coxsackieviruses A1, A19, A22, enteroviruses 113 and 104: Viruses representing two clades with distinct tropism within enterovirus C. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tao, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W. Complete genome characterization of a novel enterovirus type EV-B106 isolated in China, 2012. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sousa, I.P.; Burlandy, F.M.; Tavares, F.N.; da Silva, E.E. Enterovirus B74 associated with hand, foot and mouth disease. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvala, H.; Van Nguyen, D.; McIntyre, C.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Ngole, E.M.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M.; Simmonds, P. Co-circulation of enteroviruses between apes and humans. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayukekbong, J.; Kabayiza, J.C.; Lindh, M.; Nkuo-Akenji, T.; Tah, F.; Bergström, T.; Norder, H. Shift of Enterovirus species among children in Cameroon--identification of a new enterovirus, EV-A119. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeuh-Mba, S.A.; Bessaud, M.; Joffret, M.L.; Endegue Zanga, M.C.; Balanant, J.; Mpoudi Ngole, E.; Njouom, R.; Reynes, J.M.; Delpeyroux, F.; Rousset, D. Characterization of Enteroviruses from non-human primates in cameroon revealed virus types widespread in humans along with candidate new types and species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvala, H.; McIntyre, C.L.; Imai, N.; Clasper, L.; Djoko, C.F.; LeBreton, M.; Vermeulen, M.; Saville, A.; Mutapi, F.; Tamoufé, U.; et al. High seroprevalence of enterovirus infections in apes and old world monkeys. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamrin, P.; Chaimongkol, N.; Malasao, R.; Suantai, B.; Saikhruang, W.; Kongsricharoern, T.; Ukarapol, N.; Okitsu, S.; Shimizu, H.; Hayakawa, S.; et al. Detection and molecular characterization of cosavirus in adults with diarrhea, Thailand. Virus Genes 2012, 44, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöcker, A.; Souza, B.F.; Ribeiro, T.C.; Netto, E.M.; Araujo, L.O.; Corrêa, J.I.; Almeida, P.S.; de Mattos, A.P.; Ribeiro, H.A.C.; Pedral-Sampaio, D.B.; et al. Cosavirus infection in persons with and without gastroenteritis, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Canuti, M.; Deijs, M.; de Vries, M.; Jebbink, M.F.; Rebers, S.; Molenkamp, R.; van Hemert, F.J.; Chung, K.; Cotten, M.; et al. Unexplained diarrhoea in HIV-1 infected individuals. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanini, G.; Rovida, F.; Meloni, F.; Cascina, A.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Piralla, A.; Baldanti, F. Persistent human cosavirus infection in lung transplant recipient, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1667–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Segal, J.P.; Carding, S.R.; Hart, A.L.; Hold, G.L. The gut virome: The ‘missing link’ between gut bacteria and host immunity? Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).