Abstract
Plant nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) concentrations and ratios serve as critical indicators of nutrient constraints in coastal ecosystems. However, the response of leaf–soil N-P-K stoichiometry in tropical coastal shelterbelt forests to seasonal rainfall variations remains poorly understood. This study measured total N, P, and K contents in leaves and soils of three typical tropical coastal shelterbelt forests in Wenchang, China—Casuarina equisetifolia L., Cocos nucifera L., and Pinus elliottii × caribaea—during August 2022 (wet season) and February 2023 (dry season). Key findings are as follows: (1) All three forests exhibited low N-P-K contents in both leaves and soils, with significant stand-specific variations. Soil N:P ratios were consistently below 14, indicating chronic N limitation for plant growth. (2) Wet seasons significantly altered leaf–soil N-P-K contents and stoichiometric ratios. (3) Leaf and soil stoichiometric traits exhibited strong correlations, but these relationships diverged under seasonal transitions. (4) Shifts from wet to dry seasons increased the sensitivity of N-P-K stoichiometric homeostasis, reflecting weakened nutrient buffering capacity. This study reveals stand-specific nutrient cycling patterns in tropical coastal shelterbelts, with seasonal rainfall modulating soil–leaf nutrient coupling and stoichiometric stability. These findings provide a theoretical basis for optimizing nutrient management and species configuration in tropical coastal ecosystems under climate variability.
1. Introduction
Ecological stoichiometry is an important approach for exploring the balance of major elements and material cycling among the components of an ecosystem, reflecting the dynamic balance between energy and chemical elements [1,2,3]. It centers on the dynamic balance between elements, their interactions, and plant nutrient requirements [1,4]. Among essential nutrients, N, P, and K are particularly crucial for plant growth and development. Nitrogen is a basic component of proteins and nucleic acids and the fundamental element for chlorophyll molecules, plant hormones, and a number of coenzymes. Phosphorus plays structural and functional roles in the photosynthetic carbon cycle as nucleic acids, membrane lipids, energy metabolites and active intermediates, and is also involved in signal transduction. Potassium, as the most abundant cation in plant cells, is essential for a series of physiological processes, including osmoregulation, stomatal motility and protein biosynthesis [5]. Previous studies have shown that, in terrestrial ecosystems, aboveground plants are closely linked to belowground soil [6,7,8]. On one hand, soil is the direct source of plant nutrients, as plants utilize their roots to establish extensive contact surfaces for material exchange between plants and soil [9]. On the other hand, as an important ecological factor for plants, soil significantly affects plant growth through its physical and chemical properties [10]. Therefore, analyzing the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of nutrients between plants and soil in ecosystems is important and helps in elucidating the correlation between plants and nutrients in soil, as well as the relationship between constraints and equilibrium.
The ability of organisms to maintain a relatively stable chemical composition in response to changes in the external environment over a long period of time is known as eco-stoichiometric homeostasis, which also reflects the physiological and biochemical adaptations of plants to environmental changes [11]. Leaves are an important organ for photosynthesis in plants, and they have higher and more stable N, P, and K contents compared to other organs [12]. Elemental ratios characterizing plant homeostasis are mainly related to the contents and ratios of key nutrients in plants [13]. For instance, N:P ratios in leaves can reflect the growth rate, nutrient limitation status, and ecosystem productivity level of plants [14]. Under different conditions, plants adapt to environmental changes by optimizing their nutrient uptake and utilization strategies through N:P ratio adjustments [15].
Over the past two decades, ecological stoichiometry and stoichiometric homeostasis have been extensively researched. Many studies have focused on the relationship between plants and soil nutrients in temperate and subtropical regions, as well as plant adaptation to soil water and salt changes [16,17,18,19,20,21]. However, research in tropical regions has been limited, and most studies have been conducted on natural forests and grasslands rather than coastal shelterbelts. Additionally, most of these studies were conducted on single forests, with only a few studies considering different forests [8]. As a key factor influencing plant growth cycle and soil nutrient availability [22,23,24], seasonal variations in rainfall induce modifications of N, P, and K contents and the stoichiometric characteristics of plants [25]. Therefore, to achieve a deep understanding of the nutrient cycling mechanism of forest ecosystems, it is of great significance to study the effects of seasonal variations in rainfall on N, P, and K contents in plants and their stoichiometric characteristics. In this manner, the interrelationship between plants and soil nutrients can be determined and a basis for forest management and protection can be established.
The coastal shelterbelt in Wenchang, China is a typical tropical coastal ecosystem, with unique ecological functions and significant values. However, in recent years, the rates of soil and water erosion and vegetation degradation have increased due to severe climate events, such as typhoons, and human activities, leading to a significant decline in ecological function and stability [26]. The coastal shelterbelt in this region has a significant effect on biological diversity and ecosystem stabilization. However, the effects of seasonal changes in rainfall on the N, P, and K stoichiometric characteristics of leaves and soil of the coastal shelterbelt remain unclear. Therefore, this study investigated the N, P, and K stoichiometric characteristics of leaves and soil in three tropical coastal shelterbelt forests (Casuarina equisetifolia L. forest, Cocos nucifera L. forest, Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest) in Wenchang, China in wet and dry seasons. This study aims to address the following questions: (1) How do the N, P, and K contents and their ratios in leaves and soils of the three tropical coastal shelterbelt forests vary with seasonal rainfall changes? (2) What are the limiting nutrients for plant growth in these three tropical coastal shelterbelt forests? (3) Is there a leaf–soil coupling of nutrient elements in these three tropical coastal shelterbelt forests? (4) What are the homeostatic characteristics of leaf–soil nutrient systems in these forests, and how do they shift in response to seasonal rainfall variations? The findings will provide references for understanding nutrient cycling and ecological processes in tropical coastal shelterbelt ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in Wenchang, China (108°21′ E–111°03′ E, 19°20′ N-20°10′ N), which lies in the northeastern part of Hainan. Located to the east of the South China Sea, it has a tropical oceanic monsoon climate, characterized by an annual average temperature of 23.9 °C and an annual average rainfall of 1850 mm. The wet season is mainly concentrated from May to October, which accounts for more than 80% of the annual rainfall, and the dry season is from November to the next April. The parent materials of soil are coastal sediments [27]. The primary forest types in the coastal shelterbelt of the study area are Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera forest, and Pinus elliottii × caribaea [28].
2.2. Sample Site Selection and Setup
In July 2022, three tropical coastal shelterbelt forests (Casuarina equisetifolia forest, Cocos nucifera forest, Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest) around the observation location and research station of the forest ecosystem in Wenchang, China were selected as the study objects. Each forest had a sample area of more than 1 ha and was essentially under the same management method. The specific locations of the forests are shown in Figure 1. In each forest, six 20 × 20 m sample plots were randomly selected. Woody plants with a diameter at breast height greater than 5 cm were surveyed in the sample plots, and the diameter at breast height and the height of trees as well as the understory vegetation cover of the sample plots were recorded. The soil type of the sample plots was also recorded, and the soil physical properties, such as soil bulk weight and soil moisture content, were measured (Table 1).
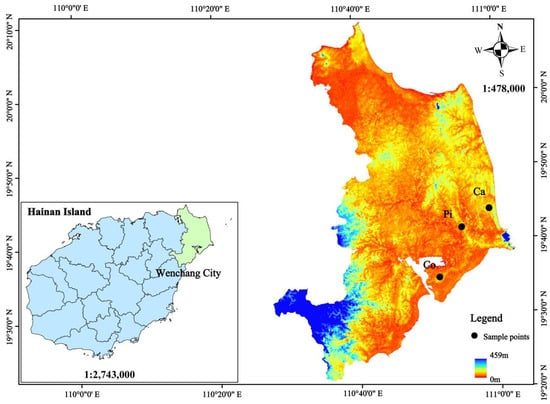
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the study area and sample plot locations. Note: Ca, Co, and Pi are forests of Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera, and Pinus elliottii × caribaea, respectively.

Table 1.
Overview of the three coastal shelterbelt forests.
2.3. Sample Collection and Testing
In August 2022 (wet season) and February 2023 (dry season), five healthy, disease-free standard trees were selected from each sample plot. Using high branch shears, fully matured, sun-exposed, and intact leaves were sampled from the east, south, west, and north orientations of standardized tree crowns. In this manner, a total fresh weight of 80 g per sampling unit was obtained. The collected leaves were cleaned of impurities and mixed, transported to the laboratory, dried at 70 °C to a constant weight, ground through a 100-mesh sieve, and then chemically analyzed. Soil samples were collected at the four corners and the center of each sample plot using a five-point sampling method. After removing the surface litter layer, a soil drill with a diameter of 5 cm was used to extract 0–20 cm of surface soil. The soil was mixed well after removing roots and stones, then placed in self-sealing bags, and labelled for transportation to the laboratory. For the determination of soil nutrients, the soil was filtered through a 100-mesh sieve after drying. Total nitrogen (N) in leaves and soil of plants was determined by the semimicro Kjeldahl method, total phosphorus (P) was determined by the acid dissolution–molybdenum–antimony colorimetric method, and total potassium (K) was determined by the alkaline dissolution–flame photometric method [29].
2.4. Data Analysis
Preliminary data organization and statistical analysis were conducted using EXCEL 2019. Subsequently, one-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) and LSD (Least Significant Difference) multiple comparison tests were performed using SPSS 26.0 to analyze the differences in N, P, and K concentrations and their stoichiometric ratios in leaves and soils among different forest stands and across different rainfall seasons. Additionally, Pearson correlation analysis was conducted using Origin 2021 to examine the relationships between these nutrient indicators within the context of different forest stands and rainfall seasons. The homeostasis index of leaves was calculated using an ecological stoichiometric homeostasis model [30,31]:
Converting Equation (1) to the logarithmic linear form:
where y refers to the N, P, and K contents or stoichiometric ratio in leaves, x refers to the N, P, and K contents or stoichiometric ratio in soil, C is a constant, and H is an index of dynamic equilibrium. When H < 0, H = −H. H is positively correlated with plant homeostasis; larger H values suggest higher stability of the plant. If the regression relationship between lgy and lgx is not significant (p > 0.1), then the plant is considered to be in “absolute homeostasis”. Otherwise (p < 0.1), the data set with H > 0 is defined as follows: H < 0.75 indicates sensitivity, 0.75 < H < 2 indicates weak sensitivity, 2 < H < 4 indicates weak homeostasis, and H > 4 indicates homeostasis.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. N, P, and K Stoichiometric Characteristics in Leaves of the Three Shelterbelt Forests
3.1.1. N, P, and K Contents
Among various forests, the N content in leaves during both wet and dry seasons followed a consistent order: Casuarina equisetifolia > Pinus elliottii × caribaea > Cocos nucifera. During the dry season, measurements showed that Casuarina equisetifolia contained 72.74% and 37.82% more leaf N than Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea, respectively (p < 0.05). This superiority persisted during the wet seasons, with Casuarina equisetifolia exhibiting 29.79% higher N content than Cocos nucifera (p < 0.05), although its 21.03% lead over Pinus elliottii × caribaea did not achieve statistical significance. In contrast, wet season data revealed that Cocos nucifera accumulated 27.13% more foliar P than Pinus elliottii × caribaea and 50.71% more than Casuarina equisetifolia (p < 0.05), while the latter two species maintained comparable P levels (p > 0.05). During the dry seasons, Casuarina equisetifolia exhibited the highest leaf P content, significantly outperforming Cocos nucifera by 24.09% (p < 0.05), and showing a non-significant 7.78% increase compared to Pinus elliottii × caribaea (p > 0.05). Regarding K content, Pinus elliottii × caribaea exhibited the highest leaf K levels during the wet seasons, surpassing Casuarina equisetifolia by 90.35% (p < 0.05) and Cocos nucifera by 35.86% (although this difference was not statistically significant, p > 0.05). However, this pattern reversed in the dry seasons, with Casuarina equisetifolia exhibiting the highest K content—27.79% greater than Pinus elliottii × caribaea (p < 0.05)—while maintaining comparable levels to Cocos nucifera (p > 0.05) (Figure 2). Overall, the leaf N, P, and K contents varied among different forests. The leaf N content of the three shelterbelt forests exhibited a consistent pattern across different wet seasons, with Casuarina equisetifolia consistently showing the highest value.
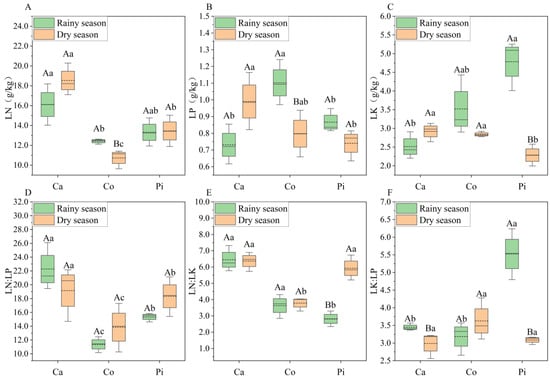
Figure 2.
N, P, and K stoichiometric characteristics in leaves of the three shelterbelt forests. Note: Ca represents Casuarina equisetifolia forest; Co represents Cocos nucifera forest; Pi represents Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences in different seasons (p < 0.05); different lowercase letters indicate significant differences for different forests (p < 0.05). LN, LP, and LK are N, P, and K contents in leaves, respectively. (A–C) represent N, P, and K contents in the leaves of the three forests; (D–F) represent N:P, N:K, and K:P ratios in the leaves of the three forests.
The leaf N, P, and K contents of the three shelterbelt forests exhibited varied responses to seasonal changes. Specifically, during the dry season, Casuarina equisetifolia showed increases in leaf N, P, and K contents by 15.05%, 35.41%, and 16.15%, respectively, although these changes were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). In contrast, Cocos nucifera experienced decreases in leaf N and P contents by 13.55% and 27.59%, respectively, during the dry season (p < 0.05), with a slight, albeit insignificant, decrease in leaf K content (p > 0.05). Notably, Pinus elliottii × caribaea exhibited a significant decrease in leaf K content by 52.25% during the dry season (p < 0.05), while its leaf N and P contents remained relatively stable across the wet and dry seasons (p > 0.05) (Figure 2).
3.1.2. Stoichiometric Ratios of N, P, and K
Across both the wet and dry seasons, the foliar N:P ratios of the three shelterbelt forests consistently adhered to the order: Casuarina equisetifolia > Pinus elliottii × caribaea > Cocos nucifera. Specifically, during the wet seasons, Casuarina equisetifolia exhibited significantly higher N:P ratios by 45.19% and 96.12%, compared to Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Cocos nucifera, respectively (p < 0.05). Conversely, during the dry season, no significant differences were observed among the three forests (p > 0.05). Regarding the N:K ratios, Casuarina equisetifolia dominated during the wet seasons, surpassing Cocos nucifera by 128.79% and Pinus elliottii × caribaea by 77.42% (p < 0.05). No significant difference was noted between Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Cocos nucifera (p > 0.05). In the dry seasons, Casuarina equisetifolia retained its superiority over Cocos nucifera (68.23%, p < 0.05) but its N:K ratio was comparable to that of Pinus elliottii × caribaea (p > 0.05). During the wet seasons, K:P ratios peaked in Pinus elliottii × caribaea, surpassing Casuarina equisetifolia by 60.33% and Cocos nucifera by 75.52% (p < 0.05). No significant difference was found between Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera (p > 0.05). In contrast, during the dry seasons, no interspecific variations were observed in K:P ratios (p > 0.05) (Figure 2). Overall, except for the K:P ratio during the dry seasons, the stoichiometric ratios of leaf N, P, and K in the three shelterbelt forests significantly differed during both the wet and dry seasons. Notably, the leaf N:P ratio of the three shelterbelt forests showed the same size pattern in both seasons, with Casuarina equisetifolia exhibiting the maximum leaf N:P and N:K ratios during both seasons.
The leaf N:P, N:K, and K:P ratios of the three shelterbelt forests differed in response to changes in the wet season. In the Cocos nucifera forest, no statistically significant seasonal differences were observed in the leaf N:P, N:K, or K:P ratios (p > 0.05). Casuarina equisetifolia displayed a significant reduction in leaf K:P ratios during the dry seasons, decreasing by 13.32% (p < 0.05). However, its N:P and N:K ratios showed minimal declines, with non-significant differences (p > 0.05). Conversely, Pinus elliottii × caribaea exhibited contrasting patterns. During the dry seasons, the leaf N:K ratios increased sharply by 110.21% (p < 0.05), while the K:P ratios decreased significantly by 44.11% (p < 0.05). The N:P ratios showed a marginal, non-significant increase (p > 0.05).
3.2. N, P, and K Stoichiometric Characteristics in Soil of the Three Shelterbelt Forests
3.2.1. N, P, and K Contents
Across the three shelterbelt forests, the soil N content of the Casuarina equisetifolia forest consistently ranked the lowest in both the wet and dry seasons. Specifically, during the wet seasons, the soil N content of the Casuarina equisetifolia forest was 41.81% and 39.83% lower than that of the Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Cocos nucifera forests, respectively (p < 0.05). These differences widened to 50.63% and 56.67% during the dry seasons (p < 0.05), while the Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Cocos nucifera forests showed no significant interspecific differences in soil N content in either season (p > 0.05). Regarding P, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest maintained the highest soil concentrations throughout the year. Wet season measurements revealed that the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest had 38.17% and 77.49% higher P levels compared to the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests, respectively (p < 0.05), with no significant difference observed between the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests (p > 0.05). In terms of soil P content during the dry seasons, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest surpassed the Casuarina equisetifolia forest by 25.04% and the Cocos nucifera forest by 53.87% (p < 0.05), while the Casuarina equisetifolia forest exhibited 23.05% higher P levels than the Cocos nucifera forest (p < 0.05). Soil K displayed seasonal reversals in its dynamics. During the wet seasons, the Cocos nucifera forest ranked highest in soil K content, followed by the Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Casuarina equisetifolia forests, although these differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). However, during the dry seasons, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest emerged as the dominant species, with more than two-fold higher soil K content compared to both the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests maintained statistically comparable levels of soil K (p > 0.05) (Figure 3). Overall, there were differences in the three shelterbelt forests except for soil K content during the wet season. The Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest exhibited the highest soil N and P contents during different wet seasons and the highest soil K content during the dry seasons. The Casuarina equisetifolia forest showed the lowest soil N contents and the Cocos nucifera forest showed the lowest soil K contents during different wet seasons.
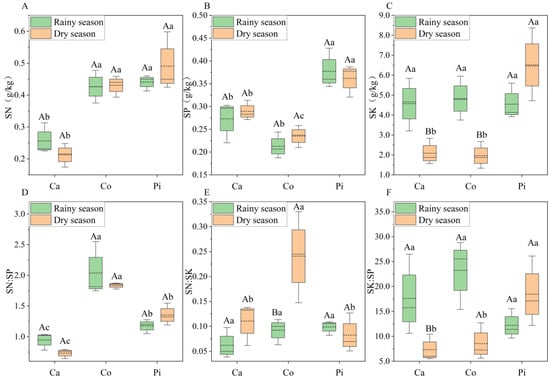
Figure 3.
N, P, and K stoichiometric characteristics in soil of the three shelterbelt forests. Note: Ca represents Casuarina equisetifolia forests; Co represents Cocos nucifera forests; Pi represents Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences during different rainfall seasons (p < 0.05); different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in different forests (p < 0.05). SN, SP, and SK are N, P, and K contents in soil, respectively. (A–C) represent N, P, and K contents in soil of the three forests; (D–F) represent N:P, N:K, and K:P ratios of the three forests.
The Casuarina equisetifolia forest exhibited no statistically significant seasonal variations in soil N and P contents (p > 0.05) but experienced a notable 54.30% decrease in soil K during the dry seasons (p < 0.05). In contrast, the Cocos nucifera forest showed non-significant increases in soil N and P contents during the dry seasons (p > 0.05), whereas soil K experienced a significant decline by 59.42% (p < 0.05). The Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest demonstrated marginal, non-significant increases in soil N and K during the dry seasons (p > 0.05), accompanied by a slight, non-significant decrease in soil P (p > 0.05) (Figure 3). Overall, the soil N and P contents in soil of the three shelterbelt forests were stable during different wet seasons, while the soil K contents of the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests decreased significantly during the dry season.
3.2.2. Stoichiometric Ratios of N, P, and K
During both the rainy and dry seasons, the soil N:P ratios of the three shelter forests exhibited a consistent pattern: Cocos nucifera forest > Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest > Casuarina equisetifolia forest. Specifically, in the rainy season, the Cocos nucifera forest exhibited 73.25% and 115.51% higher N:P ratios compared to the Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Casuarina equisetifolia forests, respectively (p < 0.05), whereas the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest showed a 24.39% higher N:P ratio than the Cocos nucifera forest (p < 0.05). During the dry season, the N:P ratios of the Cocos nucifera forest surpassed those of the Pinus elliottii × caribaea and Casuarina equisetifolia forests by 35.61% and 150.84%, respectively (p < 0.05), with the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest exhibiting an 84.98% higher N:P ratio than the Cocos nucifera forest (p < 0.05). Regarding soil N:K ratios, during the rainy season, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest showed the highest values, followed by the Cocos nucifera forest and then the Casuarina equisetifolia forest, although the differences among these three forests were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). In contrast, during the dry season, the Cocos nucifera forest exhibited the highest N:K ratios, exceeding the Casuarina equisetifolia and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests by 192.17% and 117.59%, respectively (p < 0.05), with no significant difference between the latter two forests (p > 0.05). Regarding soil K:P ratios, during the rainy season, the Cocos nucifera forest further exhibited the highest values, followed by the Casuarina equisetifolia forest and then the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest, with no statistically significant differences among the three forests (p > 0.05). However, during the dry season, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest displayed the highest K:P ratios, surpassing the Cocos nucifera and Casuarina equisetifolia forests by over two-fold (p < 0.05), with no significant difference observed between the latter two forests (p > 0.05) (Figure 3).
The Casuarina equisetifolia forest showed no notable seasonal variations in soil N:P and N:K ratios (p > 0.05); nevertheless, they exhibited a substantial 58.49% decrease in soil K:P ratios during the dry seasons (p < 0.05). Conversely, in the Cocos nucifera forest, soil N:P ratios (p > 0.05) presented a slight, insignificant decline during the dry season. Notably, soil N:K ratios increased significantly by 161.18% (p < 0.05), while K:P ratios decreased markedly by 63.28% (p < 0.05). In the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest, the dry seasons were associated with minor increases in soil N:P and K:P ratios, accompanied by a slight decrease in N:K ratios, although these changes were not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Figure 3). Overall, the soil N:P, N:K, and K:P ratios of different forests exhibited different responses to changes in rainfall seasons, while the soil N:P ratio of different forests remained stable during different rainfall seasons.
3.3. N:P:K Stoichiometric Ratio in Leaves and Soil of the Three Shelterbelt Forests
Pearson correlation analysis was applied for N, P, and K contents in leaves and soil of the three shelterbelt forests and their stoichiometric ratios during the wet and dry seasons. The results showed that the N contents in the leaves and soil of the Cocos nucifera and Casuarina equisetifolia forests had significant positive and negligible correlations during the wet (p < 0.05, same below) and dry seasons (p > 0.05, same below), respectively. The N contents of leaves and soil of the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest had negligible correlations during both the wet and dry seasons. The P contents in the leaves and soil of the Casuarina equisetifolia forest had an extremely significant negative correlation during the dry seasons (p < 0.01, same below), but the correlation was negligible during the wet seasons. The P contents in the leaves and soil of Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea had negligible correlations during both the wet and dry seasons. The K contents in the leaves and soil of Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea had significant positive correlations during both the wet and dry seasons; the K contents in the leaves and soil of the Casuarina equisetifolia forest had negligible correlations during both the wet and dry seasons. During the dry seasons, the N:P ratio in the leaves and soil of the Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera, and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests had an extremely significant positive correlation, significant negative correlation, and a negligible correlation, respectively. During the wet seasons, the N:P ratio in the leaves and soil of Pinus elliottii × caribaea had an extremely significant positive correlation, and those of the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests had negligible correlations. The N:K ratio of the leaves and soil in the Cocos nucifera forest had an extremely significant positive correlation during the wet seasons; in contrast, the N:K ratio of the leaves and soil in the Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera, and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests had extremely significant positive correlations during the dry seasons. The correlations between the N:K ratio of the leaves and soil in the Casuarina equisetifolia and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests were negligible during the wet seasons. The correlation between the K:P ratio of the leaves and soil of the Casuarina equisetifolia forest was extremely significantly negative during the dry seasons; the correlation was extremely significantly positive in the Cocos nucifera forest during the dry seasons; the correlations were negligible in the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests during the wet seasons; it was also negligible in the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest during both the dry and wet seasons (Figure 4).
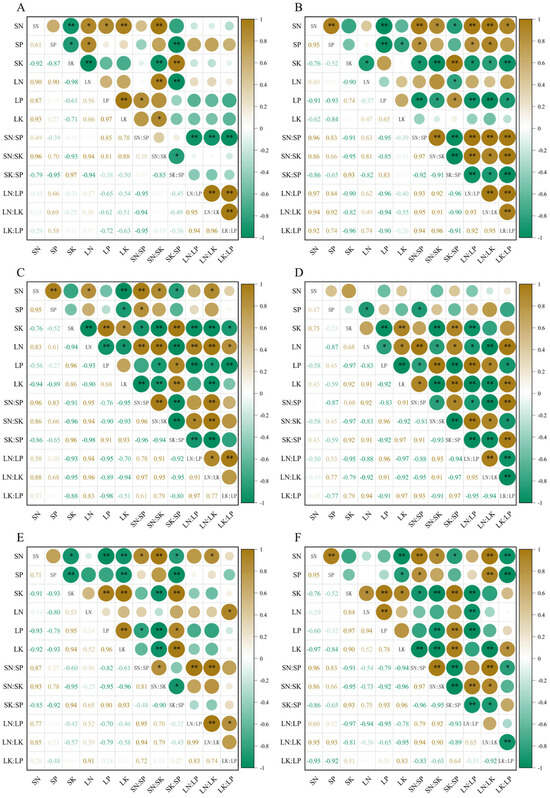
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis of N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric ratios in the leaf–soil continuum of the three shelterbelt forests. Note: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. (A): Casuarina equisetifolia forest during the wet seasons; (B): Casuarina equisetifolia forest during the dry seasons; (C): Cocos nucifera forest during the wet seasons; (D): Cocos nucifera forest during the dry seasons; (E): Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest during the wet seasons; (F): Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest during the dry seasons.
Overall, the N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric ratios in the leaves and soil of the three shelterbelt forests were strongly correlated, but the correlation between them also varied with the change of the wet season. Additionally, the N contents of the leaves and soil in the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest were not significantly correlated during both seasons. The K contents of the leaves and soil in the Casuarina equisetifolia forest were not significantly correlated during both seasons. The P contents of the leaves and soil in the Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests were not significantly correlated during both seasons, and leaves and soil in the Casuarina equisetifolia forest were not significantly correlated during the wet seasons.
3.4. N:P:K Stoichiometric Homeostasis of Leaves of the Three Shelterbelt Forests
In the wet seasons, the leaf N and K contents of Casuarina equisetifolia were weakly sensitive and weakly homeostatic, respectively, while the remaining indicators corresponded to absolute homeostasis; in the dry seasons, the leaf N and K contents of Casuarina equisetifolia corresponded to absolute homeostasis, while its P content and N:P ratio changed from absolute homeostasis to sensitive, and its N:K and K:P ratios changed from absolute homeostasis to homeostasis and weak homeostasis, respectively. In the wet seasons, the leaf N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric ratios of Cocos nucifera corresponded to absolute homeostasis; in the dry seasons, its N and P contents and N:P ratio were sensitive, while its K content and N:K ratio corresponded to homeostasis and weak homeostasis, respectively. In the wet seasons, all parameters (except for leaf N content, which was sensitive) of Pinus elliottii × caribaea corresponded to absolute homeostasis; in the dry seasons, its N content corresponded to absolute homeostasis, while its K content changed from absolute homeostasis to weak homeostasis, and its P content and N:P ratio changed from absolute homeostasis to sensitive (Table 2). Overall, the leaf N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric homeostasis of the three shelterbelt forests were different in different seasons: the leaf N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric homeostasis were higher during the wet seasons than during the dry seasons; the leaf N:P, N:K, and K:P ratios corresponded to absolute homeostasis during the wet seasons.

Table 2.
N, P, and K contents and stoichiometric homeostasis indexes in leaves of the three shelterbelt forests.
4. Discussion
4.1. N, P, and K Stoichiometric Characteristics of Leaves in the Three Shelterbelt Forests
The leaf N, P, and K contents of the three shelterbelt forests are lower than those of plants at the global and national scale during both the rainy and dry seasons [3,32,33]. This is mainly related to the soil parent material and climatic conditions of the study area, and its soil being coastal sedimentary soil, which is usually infertile. Moreover, the nutrients in the soil are more prone to washout and loss because of the high temperature and heavy rainfall, which results in the lower content of soil nutrients in this area and directly limits the ability of plants to absorb N, P, and K from the soil [34]. The leaf N content of the Casuarina equisetifolia forest was the highest among the three shelterbelt forests in both the rainy and dry seasons, which is related to the physiological characteristics of Casuarina equisetifolia. Casuarina equisetifolia can deeply absorb nutrients from the soil through its well-developed roots, convert atmospheric nitrogen into plant-available nitrogen as a nitrogen-fixing tree in symbiosis with rhizobia, and reabsorb nutrients into other organs before leaf senescence. These unique physiological features enable the tree to maintain high N content in leaves in the nutrient-poor coastal sand [35]. The leaf N and P contents of Cocos nucifera forest were significantly higher in the rainy season than in the dry season, and the leaf K content of Pinus elliottii × caribaea was significantly higher in the rainy season than in the dry season. This is because plants grow more vigorously in the rainy season and have a higher demand for nutrients, and absorb more N, P, and K from the soil to meet the demand for growth and development [36]. At the same time, the soil N, P, and K contents are more easily dissolved and released in the rainy season, which also enables the plants to absorb more nutrients, thus increasing the N, P, and K contents in leaves [37]. Nevertheless, compared with the Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests, the Casuarina equisetifolia forest did not show significant changes in its leaf N, P, and K contents during different wet seasons. This is related to the adaptability of Casuarina equisetifolia to environmental changes. Casuarina equisetifolia has a high-water utilization efficiency, maintains normal physiological functions under drought conditions, and is able to adjust its nutrient uptake and utilization strategies in response to changes in environmental conditions. In nutrient-poor environments, it responds by increasing the area of root uptake and improving nutrient uptake efficiency, while in nutrient-rich environments, it maintains nutrient balance by reducing nutrient uptake and increasing nutrient storage [38].
Nutrient utilization efficiency and limiting factors can be further understood by measuring the ratio of N, P, and K in plant leaves [39]. The N:P ratio is an indicator of the extent to which forests are limited by the availability of N and P. N:P < 14 suggests that the plant is limited by N availability, while N:P > 16 suggests that the plant is limited by P availability, and 14 < N:P < 16 suggests that the plant is simultaneously limited by both N and P availability [40]. In this study, the Cocos nucifera forest was N-limited in both the rainy and dry seasons, the Casuarina equisetifolia forest was P-limited in both the rainy and dry seasons, and the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest was N- and P-limited in the rainy season and P-limited in the dry season. Olde Venterink et al. [41] reported that plant growth is K-limited when N:K > 2.1 and K:P < 3.4. In this study, the Cocos nucifera forest during the wet seasons and the Casuarina equisetifolia and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests during the dry seasons were K-limited. This difference is primarily attributable to the nutrient utilization strategies, growth characteristics, and spatial heterogeneity of different tree species in different forests [42].
4.2. N, P, and K Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in the Three Shelterbelt Forests
According to the national soil nutrient content grading standard [43], during both the rainy and dry seasons, the soil N content of the three shelterbelt forests was classified as level 6 (very low), soil P content as level 5 (low), and soil K content as level 6 (very low), except for the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest in the dry season (level 5; low), which is consistent with the results of Xue et al. [34]. This indicates the relative scarcity of soil nutrients in the study area. Among the three shelterbelt forests, the Casuarina equisetifolia forest had a significantly lower soil N content compared to the other two forests. Soil N content has been reported to be often related to the decomposition rate of litter and the nutrient release rate [44]. The Casuarina equisetifolia forest has a slower decomposition rate of litter, and the N released into the soil is reduced. The soil in the Casuarina equisetifolia forest has a relatively loose texture, with poor water and fertilizer holding capacities; consequently, the N content in soil is relatively low [45]. Among the three shelterbelt forests, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest exhibited the highest soil N and P contents during both the rainy and dry seasons, and the highest soil K content during the dry season, which might be related to the spatial heterogeneity of the forests. Compared with other forests, the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest is farther away from the coastline, and the degree of weathering erosion of the soil parent material is lower; thus, the nutrient content of the soil is higher [46]. Additionally, the results of the present study revealed that the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest has the most abundant understory shrub plants, which is conducive to soil microbial activity and nutrient transformation, and more conducive to nutrient accumulation in soil [47]. The soil N and P contents of the three shelterbelt forests did not differ significantly between the rainy and dry seasons, indicating that the soil N and P contents of the three shelterbelt forests were relatively stable during different rainfall seasons. However, the soil K contents of the Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera forests were significantly lower in the dry season than in the rainy season, which might be related to the lower compaction and lower water retention of the soils in these two forests, as well as the form of K in soil.
The stoichiometric ratio of N, P and K in soil can indicate the state of nutrient balance, coordination of nutrient supply, and ecosystem function and stability. In this study, the soil N:P ratio of the three shelterbelt forests ranged from 0.73 to 2.04, which is slightly lower than that of a coastal shelterbelt in Changle, China (2.04–3.11) [48], and significantly lower than the national average (9.3) [49] and the global land average (13.1) [50]. The soil N:P ratio can be used as an indicator to measure nitrogen saturation and has been widely used to determine the critical threshold for nutrient limitation. An N:P ratio less than 14 indicates insufficient nitrogen supply. In this study, the soil N:P ratios of the three shelterbelt forests were all much lower than 14, suggesting insufficient N supply for plant growth. This may be related to the slow decomposition rate of litter, soil nutrient deficiency, and low nutrient availability in the area [48].
4.3. Correlation Analysis of N:P:K Stoichiometric Ratio of Leaves and Soil in the Three Shelterbelt Forests
N, P, and K cycling processes between plants and soil are fundamental components of the ecosystem, and their correlation strongly affects plant growth and development [51]. A strong correlation has been reported between plants and N, P, and K in soil [52,53]. In this study, the P contents of leaves and soil were found to be uncorrelated in the Casuarina equisetifolia forest during the wet seasons and in the Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea forests during both the dry and wet seasons, which is consistent with previous studies [31,54]. In this study, the correlations between N, P, and K and their stoichiometric ratios of leaves and soil in the three shelterbelt forests were not completely consistent, which agrees with the results of numerous studies [25,31]. Furthermore, the N contents of leaves and soil in the Pinus elliottii × caribaea forest were not significantly correlated, and the K contents of leaves and soil in the Casuarina equisetifolia forest were not significantly correlated. This is related to different tree species having developed different nutrient uptake and utilization mechanisms during the long-term evolutionary process [55]. The N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric ratios of leaves and soil in different forests during the wet and dry seasons showed different correlations, which is primarily attributable to the combination of environmental factors and plant physiological mechanisms. During the rainy season, abundant rainfall and sufficient soil moisture favor the uptake and transport of soil N, P, and K by plants. Meanwhile, rainfall and runoff may promote the release and solubilization of soil nutrients, and the rainy season is usually accompanied by higher temperatures, which is conducive to photosynthesis and the metabolism of plants. N, P, and K in plant leaves may be more active and participate in more biochemical reactions. During the dry season, rainfall decreases and soil moisture is insufficient, resulting in limited uptake of nutrients by plants. The release of soil nutrients is also slowed down, the photosynthesis and metabolism of plants are inhibited by the lower temperature, and the activity of N, P, and K in leaves is also reduced [36,56].
4.4. N:P:K Stoichiometric Homeostasis in Leaves and Soil of the Three Shelterbelt Forests
Plants are able to maintain a constant balance of nutrients by regulating their internal stability, which helps them to maintain desired growth levels and adapt to changes in external conditions, such as changes in soil nutrient availability [4]. The homeostasis of N content in the leaves of Pinus elliottii × caribaea was higher than those of Casuarina equisetifolia and Cocos nucifera during both the rainy and dry seasons, suggesting that Pinus elliottii × caribaea tended to utilize N more conservatively and maintained slower growth even under nutrient-poor conditions [31]. In this study, the N:P ratio in the leaves of Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera and Pinus elliottii × caribaea showed absolute homeostasis and sensitivity during the wet and dry seasons, respectively. This may be attributable to the abundant soil moisture during the rainy season and the high solubility of nutrients and their absorption by plant roots. At the same time, the input of nutrients from rainfall may also increase the effectiveness of soil nutrients [57]. Under such environmental conditions, Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera, and Pinus elliottii × caribaea could maintain high nutrient uptake and utilization efficiencies, thus maintaining absolute homeostasis of their leaf N:P ratio. Nevertheless, the case changed during the dry seasons; the homeostasis of their leaf N:P ratio degraded, suggesting that the N:P ratios in leaves were significantly affected by changes in soil nutrients, and their internal stability was reduced. This may be due to the decrease in soil moisture and nutrient availability during the dry season [57], resulting in limited nutrient uptake and utilization by Casuarina equisetifolia, Cocos nucifera, and Pinus elliottii × caribaea. In this case, these trees may not be able to effectively regulate their leaf N:P ratios in order to adapt to the fluctuation of soil nutrients. Overall, the leaf N, P, and K contents and their stoichiometric homeostasis of the three shelterbelt forests were higher in the rainy season than in the dry season. This is primarily attributable to a combination of factors such as sufficient soil moisture, increased microbial activity and adjustment of plant physiological mechanisms during the rainy season [58,59]. These factors jointly promote the uptake and utilization of N, P, and K by plants, thereby increasing the N, P, and K contents in plant leaves and their stoichiometric homeostasis.
5. Conclusions
This study reveals notably low N, P, and K contents in both leaves and soils in three shelterbelt forests, with soil N:P ratios being significantly below 14, indicating insufficient nitrogen supply for plant growth. To address this, future coastal shelterbelt afforestation attempts should incorporate nitrogen-fixing tree species and the application of nitrogen fertilizers. The stoichiometric characteristics of plant leaves in these shelterbelts are strongly influenced by soil properties, and the three forest types exhibit distinct nutrient uptake/utilization mechanisms. Consequently, species-specific management protocols are essential for coastal shelterbelt maintenance. Notably, leaf N, P, and K stoichiometric homeostasis (e.g., N:P, N:K, K:P ratios) is markedly higher during wet seasons, reaching absolute homeostasis. To enhance ecosystem stability, we recommend targeted supplementation of limiting nutrients during the wet season, which is the peak period of nutrient absorption by plants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.N. and Y.C.; methodology, S.N. and Z.C.; investigation, S.N., H.C., Z.L., S.S., X.L. and J.J.; data curation, H.C. and Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.N.; writing—review and editing, Y.C. and Z.C.; project administration, S.N. and Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Hainan Province Department of Science and Technology (Technological Innovation Special Grant for Provincial Research Institutes, No. KYYSLK2023-015).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Elser, J.J.; Hamilton, A. Stoichiometry and the new biology: The future is now. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Peñuelas, J. Recent advances and future research in ecological stoichiometry. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2021, 50, 125611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, E.T. Research status and prospect of efficient utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in plants. Sci. China (Ser. C) 2021, 51, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, J.W.; Bardgett, R.D.; Wilkinson, A.; Jackson, B.G.; Pritchard, W.J.; De Long, J.R.; Oakley, S.; Mason, K.E.; Ostle, N.J.; Johnson, D.; et al. Predicting the structure of soil communities from plant community taxonomy, phylogeny, and traits. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, A.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Ali, A.; Loreau, M.; Mori, A.S.; Reich, P.B.; Jucker, T.; Lin, F.; Ye, J.; Fang, S.; et al. Tree species diversity enhances plant-soil interactions in a temperate forest in northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 491, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Arif, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.X. Patterns and drivers of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry in a novel riparian ecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1354222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Roumet, C.; Comas, L.H.; Weemstra, M.; Bengough, A.G.; Rewald, B.; Bardgett, R.D.; De Deyn, G.B.; Johnson, D.; Klimešová, J.; et al. Root traits as drivers of plant and ecosystem functioning: Current understanding, pitfalls and future research needs. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 1123–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, L.; Castronuovo, D.; Perniola, M.; Scrano, L.; Cicco, N.; Candido, V. The influence of soil physical and chemical properties on saffron (Crocus sativus L.) growth, yield and quality. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.J.; Stelzer, R.S.; Forman, M.R.; Harpole, W.S.; Daufresne, T.; Yoshida, T. Recent advances in ecological stoichiometry: Insights for population and community ecology. Oikos 2005, 109, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, L.Q. Seasonal variations in C/N/P/K stoichiometric characteristics in different plant organs in the various forest types of Sygera Mountain. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1293934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, H.; Li, M.L.; Yu, G.R.; Wilcox, K.; Yu, Q.; He, N.P. stoichiometry in China’s forests: From organs to ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.B.; Niklas, K.J.; Han, W.X.; Kattge, J.; Reich, P.B.; Luo, Y.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Tang, Z.Y.; Hu, H.F.; et al. Global leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry and their scaling exponent. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Fu, F.W.; Li, J.R.; Chen, W.S.; Ding, H.H.; Xiao, S.Y. Stoichiometric characteristics of Abies georgei var. smithii plants in southeast Tibet. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant–microbial–soil organic matter transformations. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Palo, F.; Fornara, D.A. Plant and soil nutrient stoichiometry along primary ecological successions: Is there any link? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lian, C.M.; Gong, L.; Mo, C.N. Leaf stoichiometry of halophyte shrubs and its relationship with soil factors in the Xinjiang Desert. Forests 2022, 13, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Li, T.; Sun, J.K.; Liu, J.H.; Fu, Z.Y. Study on ecological stoichiometry homeostasis characteristics of different halophytes in the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, P.; Gerber, S.; Bhomia, R.K.; King, J.; Osborne, T.Z.; Wright, A.L. Understanding stoichiometric mechanisms of nutrient retention in wetland macrophytes: Stoichiometric homeostasis along a nutrient gradient in a subtropical wetland. Oecologia 2020, 193, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Zhou, J.J.; Lai, S.B.; Jian, C.X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xu, B.C. Species differences in stoichiometric homeostasis affect grassland community stability under N and P addition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 61913–61926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.H.; Laegdsmand, M.; Olesen, J.; Porter, J.R. Effect of soil warming and rainfall patterns on soil N cycling in Northern Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Wang, R.; Gao, J. Precipitation and soil nutrients determine the spatial variability of grassland productivity at large scales in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 996313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Li, Z.G.; Ren, H.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Han, G.D. Effects of simulated precipitation gradients on nutrient resorption in the desert steppe of northern China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1211182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Peng, Q.W.; Li, K.H.; Gong, Y.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Han, W.X. Patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry among leaf, stem and root of desert plants and responses to climate and soil factors in Xinjiang, China. Catena 2021, 199, 105100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Chen, S.L.; Zhong, X.J.; Chen, Q.; Hu, J.; Cheng, W.F. Complex response of beach erosion and restoration to successive typhoons in northeastern Hainan Island. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 39, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Yang, Z.Y.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.H.; Yu, X.B.; Cui, X.B.; Li, R.; Gao, L. Associated Analysis Between Forest Understory Vegetation Diversity and Soft Factors in Hainan Wenchang Coastal Platform. J. Trop. Crops 2015, 36, 2238–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Yang, Z.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Yu, X.B.; Xue, Y.; Wang, X.Y. Interspecific associations of dominant plant populations in secondary forest of Syzygium odoratum in tropical coast. Sci. Silv. Sin. 2017, 53, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, J.; Fink, P.; Goto, A.; Hood, J.M.; Jonas, J.; Kato, S. To be or not to be what you eat: Regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs. Oikos 2010, 119, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.R.; Lu, X.H. Leaf–Soil C: N: P stoichiometry and homeostasis characteristics of plantations in the Yellow River floodplain in western Shandong, China. Forests 2024, 15, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, J.X.; Gao, S.P.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Shen, X.H. Characteristics of leaf element contents for eight nutrients across 660 terrestrial plant species in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, X.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Lin, Z.P. Comparisons of soil chemical properties under four typical forest stands in northeast Hainan. Ecol. Sci. 2014, 33, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.L.; Meng, Q.Q.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.M. Coupling relationship between nitrogen and phosphorus reabsorption and biological nitrogen fixation in leaves of different nitrogen-fixing tree species in coastal sandy land. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 134–138,144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Yan, L.B.; Pi, F.J.; Yu, L.F.; Yuan, C.J.; Shu, L.X. Stoichiometric characteristics and seasonal variation of soils and dominant plant leaves in secondary forest in karst area. J. South. Agric. 2019, 50, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Q.; Fu, D.G.; Wu, X.N.; Zhu, A.Q.; Xu, Z.X. Changes of soil nutrients and stoichiometric characteristics under different vegetation communities in central Yunnan province. Soils 2020, 52, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.F.; Gao, W.; Yin, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.D. Dynamic of transpiration and water use efficiency of Casuarina eguisetfolia in coastline forest. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 10, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.B.; Fang, J.Y. Review on characteristics and main hypotheses of plant ecological stoichiometry. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 682–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, J.T.; Raynal, D.J. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Venterink, H.; Wassen, M.J.; Verkroost, A.; De Ruiter, P. Species richness–productivity patterns differ between N-, P-, and K-limited wetlands. Ecology 2003, 84, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Gou, X.H.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F. Seasonal patterns in the leaf C: N: P stoichiometry of four conifers on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 47, e02632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Soil Census Office. Soil Census Techniques in China; Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, B. Litter decomposition and organic matter turnover in northern forest soils. For. Ecol. Manage. 2000, 133, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.J.; Ye, G.F.; Gao, W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; Li, D. Characteristics of litter decomposition and ecological stoichiometry of different forests on coastal sandy land in Fujian province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.F.; Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, X.P.; Jin, Z.G.; Zhu, J.J. Spatial distribution of soil physical and chemical properties and influencing factors in Changli Gold Coast National Nature Reserve. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2024, 51, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.S.; Song, H.; Yuan, Z.X.; Ni, X.L.; Li, C.X. Changes in soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass after revegetation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Forests 2018, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.T.; Qiu, L.J.; Ge, L.L.; Meng, Q.Q.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.M.; Wang, K.Y.; Dong, Q. Stoichometry of fine roots and topsoil of five plantations in coastal sandy. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2018, 36, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C: N: P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C: N: P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, J.C.; Van Bodegom, P.M.; Witte, J.P.M.; Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Aerts, R. A global study of relationships between leaf traits, climate and soil measures of nutrient fertility. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne Iv, F.; Menge, D.N.L.; Ostling, A.; Hosseini, P. Nutrient recycling affects autotroph and ecosystem stoichiometry. Am. Nat. 2008, 171, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C: N: P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.J.; Sheng, M.Y.; Bai, Y.X.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H.L. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Wan, K.Y. Progress and expectation of the research on plant K efficiency and its evaluation. Soils 2010, 42, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Wang, K.L. Seasonal distribution of soil nutrients and their response to the plant diversity of karst mountain grassland. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.X.; Wu, D.X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.Q. Effect of rainfall pattern change on Stipa grandis seedlings in Inner Mongolia. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2010, 34, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, K. The advances in study on plant photosynthesis and soil respiration of alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.Q.; Wang, S.J. Regulation mechanism of biotic and abiotic factors on the nitrogen mineralization of forest soil. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ. 2021, 38, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).