Abstract
An in-depth understanding of the dominant factors controlling soil respiration is important to accurately estimate carbon cycling in forest ecosystems. However, information on variations in soil respiration at different soil depths and the influencing factors in forest is limited. This study examined the variations in soil respiration at two soil depths (0–10 and 10–20 cm) as well as the effects of soil temperature, soil water content, litter removal, and root cutting on soil respiration in three typical forest types (i.e., Pinus tabulaeformis Carrière, Platycladus orientalis (L.) Franco, and Quercus variabilis Bl.) in the mountainous area of north China from March 2013 to October 2014. The obtained results show that soil respiration exhibited strong seasonal variation and decreased with soil depth. Soil respiration was exponentially correlated to soil temperature, and soil respiration increased with soil water content until reaching threshold values (19.97% for P. tabulaeformis, 16.65% for P. orientalis, and 16.90% for Q. variabilis), followed by a decrease. Furthermore, interactions of soil temperature and water content significantly affected soil respiration at different soil depths of forest types, accounting for 68.9% to 82.6% of the seasonal variation in soil respiration. In addition to soil temperature and water content, aboveground litter and plant roots affected soil respiration differently. In the three forest types, soil respiration at two soil depths decreased by 22.97% to 29.76% after litter removal, and by 44.84% to 53.76% after root cutting. The differences in soil respiration reduction between the two soil depths are largely attributed to variations in substrate availability (e.g., soil organic content) and soil carbon input (e.g., litter and fine root biomass). The obtained findings indicate that soil respiration varies at different soil depths, and suggest that in addition to soil temperature and water content, soil carbon input and dissolved organic substances may exert a strong effect on forest soil respiration.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of industrialization and the continuous growth of its population, China has become one of the world’s largest emitters of greenhouse gases [1]. The increase of CO2 concentration can directly break the dynamic balance of the carbon cycle and cause ecological and environmental problems, such as global warming [2]. As the second largest contributor of CO2 flux between terrestrial ecosystems and the atmosphere, soil respiration plays an important role in global carbon cycling [3,4]. On a global scale, approximately 60% to 90% of the total ecosystem respiration originates from soil, which is 11 times higher than the fossil fuel combustion [5]. Consequently, even a slight variation in soil respiration can significantly influence both the atmospheric CO2 concentration and carbon cycling [2,6]. Accurately predicting soil respiration and identifying the driving environmental factors are therefore of considerable importance to improve carbon cycle models and evaluate the potential effects of global warming on terrestrial ecosystems.
Soil respiration is a complex process involving both autotrophic root respiration and heterotrophic microbial respiration [7], and it is affected by a multitude of biotic and abiotic factors, such as soil temperature, soil water content, distribution of fine roots, substrate availability, and plant productivity. Among these factors, both soil temperature and water content have been recognized as the main factors that control soil respiration [8]. These influence soil respiration by promoting litter decomposition and root activities as well as by altering both plant productivity and substrate supply [9,10]. Soil microclimate differences in general, and soil temperature in particular, result in different soil respiration rates across ecosystems [11]. At the ecosystem scale, a large portion of the observed soil respiration variation can be explained by differences of soil temperature and moisture [12,13,14]. Other factors may potentially strongly affect soil respiration. An increasing body of evidence indicates that soil respiration is partially derived from soil organic carbon, and results in the direct dependence of soil respiration on aboveground litter fall and plant roots [15]. Thus, factors ranging from soil microclimate to litter fall and plant roots can explain the variations in soil respiration. Differentiating individual from interactive effects of these factors on the variability of soil respiration is of considerable importance toward an understanding of carbon cycling in response to future climate change [7,10].
Forests cover extensive areas in terrestrial ecosystems, and significant attention has been focused on the carbon cycle of forest ecosystems due to their potential significance in the global carbon budget and climate change [2,4,16,17]. These ecosystems contain considerable carbon stores belowground, which are released via soil respiration [2,18]. Especially in the mountainous area of north China, where a shortage of water resources has become increasingly severe, soil respiration in the forest ecosystem experiences enormous changes [19]. Litter and root distribution as well as microbial activity respond differently to variations in climatic conditions. In several forest ecosystems, microbial respiration may control soil respiration [20,21]. In other forest ecosystems, root respiration plays a dominant role in the control of soil respiration [7,22]. However, despite several available studies on the response of soil respiration to roots and litter in forest ecosystems, no satisfying consensus has been reached. Additionally, forests influence carbon flux by improving the soil structure, and while soil respiration represents the comprehensive carbon flux from plant biomass and microorganisms at different soil depths, many factors and their interactions influence soil respiration [21,23]. How soil respiration varies at different soil depths and how it responds to influencing factors still remains unclear. Soil microclimate, root distribution, and microbial activity are closely linked to soil depth, which is therefore suitable to investigate long-term impacts of climate and vegetation on soil respiration at different soil depths. Thus, the determining factors that govern the variations in soil respiration at different soil depths are vital not only to understand the soil CO2 efflux dynamics but also the accurate prediction of soil respiration in forests. Furthermore, differences in the magnitude of soil respiration among forest types can greatly influence the net ecosystem exchange of forests under water stress and can also provide a useful reference for local government officials on regional forestation planning. The present study set up litter removal, root cutting, and control treatments. Soil respiration was measured in each of the treatments, along with soil temperature and water content at different soil depths of forests in the mountainous area of north China from 2013 to 2014. We hypothesized that soil temperature and water content, litter, and roots could differently affect the variation of soil respiration at different soil depths of forests. The main objectives of this study were to (1) investigate the dynamics of soil respiration at different soil depths for three forest types, and to (2) identify the contributions of each of these factors to the soil respiration of forest.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
This study was conducted at the Forest Ecosystem Research Station, capital circle, Jiu Feng National Forest Park, northwest Beijing, China (116°28′ E, 39°34′ N) (Figure 1). Forests and landscape are features of the National Park, the topography is high in the west, low in the east, and mountainous, with elevations ranging between 100 and 1153 m above sea level. This park is characterized by a typical warm temperate climate with a hot and wet summer and a cold and dry winter. The mean annual precipitation is 630 mm, of which 70% to 80% occurs during June and August. The mean annual temperature is 11.6 °C, and average November and July temperatures are −5 and 28 °C, respectively. The soil type in this park is leached cinnamon soil with a mean thickness of 52.8 mm. The vegetation is dominated by artificial forests, all of which were planted in the 1960s. The total forest coverage is 85%.
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
Three permanent fixed study plots were set up based on the existence of dominant tree species in the study area, i.e., Pinus tabulaeformis (PT), Platycladus orientalis (PO), and Quercus variabilis (QV). All of the plots had similar climate, topography, and soil type. Detailed information on the three forest plots is summarized in Table 1. Three treatments (natural control, litter removal, and root cutting) were applied to each plot to separate soil respiration between litter and roots. Within each treatment, five subplots (1 × 1 m) were randomly selected and used as independent replicates for soil respiration experiments, which yielded a total of 15 subplots. The control subplots received no further treatments. The litter removal treatment used two layers of nylon screen mesh to build a barrier. The litter was originally removed from the subplots in April 2012 when the barriers were first built, and new litter was regularly removed every two weeks throughout the study period. The root cutting treatment was implemented by digging trenches along the four sides of the subplot to depths of 1 m in April 2012. Then, a tarp sheet was buried in the soil to prevent root extension from the surrounding area to the subplot.

Table 1.
Plot characteristics of the three forest types.
2.2. Measurements of Soil Respiration, Soil Temperature, and Water Content
To investigate soil respiration in these three forest types at different soil depths, a barometric process separation (BaPS) system, a closed-chamber that can hold a maximum of seven soil samples, was used. Soil samples at depths of 0–10 and 10–20 cm were collected using a circular stainless steel auger (with 5.6-cm inner diameter) in each subplot. Three soil samples were taken as replicates at each depth once every month from March 2013 to October 2014. At each sampling date, a total of 90 soil samples (3 treatments × 5 subplots × 2 depth × 3 replicates) were collected, sealed, and returned to the laboratory for analysis.
BaPS is based on the measurement of CO2, O2, and the total gas equilibrium of soil samples within an isothermal, gas-tight, and closed system. For a given soil depth (such as 0–10 cm depth) of every experiment treatment at each sampling date, the measurement group included 15 replicated soil samples (5 subplots × 3 replicates). Every five soil samples were incubated in the BaPS system in a cooling water bath until temperatures reached those measured in the subplot. After temperature equilibration for at least 30 min, the tightness of the system was verified and the air pressure of the closed system was simultaneously measured (if the tightness is good, the change in air pressure in the system is less than 0.8 hPa). Then, the soil water content and other necessary soil parameters were inputted, and incubated for 12 h in the closed system. The incubation time was sufficient to generate significant variations in both the total gas amount as well as the CO2 and O2 concentrations. Via gas equilibrium and inverse equilibrium, the rate of soil respiration can be estimated. The measurement of soil samples for other soil depths and treatments also followed these steps. The unit of soil respiration is μg C·kg−1·h−1, which indicates the production of CO2-C per dry soil weight per hour. The specific theoretical description of BaPS and the relevant calculation processes can be found in [24].
To estimate the accuracy of soil respiration by BaPS, a concurrent comparative measurement was conducted using an automated soil respiration system (Li-8100, Lincoln, NE, USA) in three forest types. The results showed strong linear correlations between the soil respiration rates measured with both methods, with R2 values of 0.9513 for PT (y = 205.541x + 69.313, n = 21, p < 0.001, where y and x represent soil respiration measured using BaPS and Li-8100, respectively), 0.9524 for PO (y = 91.313x + 103.45, n = 21, p < 0.001), and 0.9229 for QV (y = 112.11x + 86.819, n = 21, p < 0.001). On average, soil respiration measured using the BaPS technique was 8.5% (for PT), 7.9% (for PO), and 10.2% (for QV), which were higher than that measured using Li-8100. Several other studies have also shown that measurements of soil respiration at different soil depths are more suitable using the BaPS technique [24,25]. Therefore, the BaPS technique could be directly used to measure soil respiration at different soil depths in situ in the present study. After measuring soil respiration, soil samples at 0–10- and 10–20-cm depths of each subplot were air-dried to a constant weight for soil organic content (SOC) determination.
Soil temperature and soil water content were continuously measured at 5- and 15-cm depths in each subplot throughout the study. Soil temperature and water content were measured using a Li-Cor thermocouple probe and a soil moisture probe Echo EC-5 (Decagon Devices, Pullman, WA, USA) with an EM50, respectively. Rainfall did not occur during sampling. Only sunny days were selected for sampling to avoid rapid transition of soil respiration.
2.3. Measurements of Litter Cover and Root
To investigate the roles of litter and roots in soil respiration among the three forest types, litter and root biomass were collected at the end of the experiment after soil respiration measurements were completed. The thickness of the litter among the three forest plots was measured using a steel ruler. Litter biomass was harvested on five subplots of 50 × 50 cm in each plot in mid-October 2014, and dried in an oven at 70 °C until a constant weight was reached. The carbon stock in the litter was evaluated from litter mass based on a coefficient of 0.5 [16]. The carbon content in litter samples and SOC in soil samples were estimated using an elemental analyzer (Elementar, Hanau, Germany).
Soil samples were collected every 10 cm to a depth of 60 cm using a soil auger (5 cm diameter) at five locations on each plot in mid-October 2014. Roots were extracted from soil cores by hand, followed by washing and dividing into fine (<2 mm), medium (2–5 mm), and coarse (>5 mm) roots. All live roots were manually separated and dried at 80 °C for 24 h to determine root biomass.
2.4. Data Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the least significant difference (LSD) multiple-comparison test were applied to analyze the differences in soil respiration, litter, and root characteristics at different soil depths. Correlation analyses were used to test the relationships between soil respiration, soil temperature, and soil water content. An exponential function was used to describe the relationship between soil respiration and soil temperature [26]:
where Rs (μg C·kg−1·h−1) represents the measured soil respiration; T (°C) represents the measured soil temperature at depths of 5 and 15 cm; and a and b represent fitted parameters.
Rs = aebT,
The Q10 value was calculated as follows [6]:
where b is obtained from Equation (1).
Q10 = e10b,
A quadratic polynomial model was developed to simulate the response of soil respiration to soil water content. Empirical equations that relate soil respiration to soil temperature and soil water content were established at different soil depths. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 19.0.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Biotic and Abiotic Factors
Both litter thickness and litter biomass varied strongly among the three forest types (Table 2). Carbon content was highest at 718.83 g·kg−1 in the PT plot, followed by the QV plot at 647.28 g·kg−1, and lowest at 539.66 g·kg−1 in the PO plot. Significant differences were found at different soil depths of the three forest types in root biomass (p < 0.001). Root biomass was lowest in the QV plot (640 g·m−2), followed by the PO plot (646 g·m−2), and was highest in the PT plot (805 g·m−2). In these three forest types, fine root (<2 mm) biomass accounted for 53.29% of the total root biomass in the PT plot, whereas the QV plot was dominated by medium root (2–5 mm), and more coarse root biomass (>5mm) was found in the PO plot.

Table 2.
Characteristics of litter thickness and litter and root biomass among forest types.
Changes in soil temperature at 5- and 15-cm depths showed a similar seasonal variation among the three forest types: Maximum temperature was observed in summer, and minimum in winter. However, dynamic changes in soil temperature between both soil depths were different, indicating that the surface soil temperature in spring and summer is higher than the deep soil temperature, while in autumn and winter, it is lower than the deep soil temperature. The mean soil temperatures at the 5-cm depth were 13.64, 11.77, and 12.29 °C whereas those at the 15-cm depth were 13.66, 11.94, and 12.16 °C in the PT, PO, and QV plots, respectively.
Soil water content at the 5-cm depth was slightly lower than that at the 15-cm depth and fluctuated significantly with forest types. Soil water content at the 5-cm depth ranged from 3.8% to 30.7%, 1.2% to 27.4%, and 4.7% to 25.8%, and values at the 15-cm depth ranged from 4.6% to 35.9%, 2.3% to 30.2%, and 5.9% to 28.4% in the PT, PO, and QV plots, respectively.
Significant differences of SOC were observed at different soil depths of the three forest types (p < 0.001). The SOC of the PT plot was obviously higher than that of the QV and PO plots, and SOC at the 0–10-cm depth was always higher than that at the 10–20-cm depth in the PT, PO, and QV plots (Figure 2). For the three treatments, SOC was lowest in the litter removal treatment and highest in the natural control treatment (Figure 2).
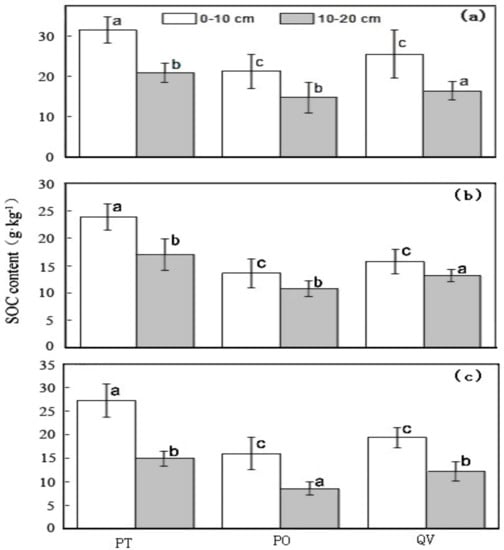
Figure 2.
Organic carbon content of the three treatments at different soil depth of the three forest types (natural control (a), litter removal (b), and root cutting (c)). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences by ANOVA and LSD test at p < 0.001 between soil depths.
3.2. Variation of Soil Respiration at Different Soil Depths of the Three Forest Types
Soil respiration followed similar seasonal variations at different soil depths of the three forest types (Figure 3A). It peaked in summer and decreased to the lowest value in winter, which coincided with the dynamics of the soil temperature. Soil respiration of the three forest types fluctuated sharply between the 0–10- and 10–20-cm depths, and the respiration of the upper soil layer was significantly higher than that of the lower depth (Figure 3B).
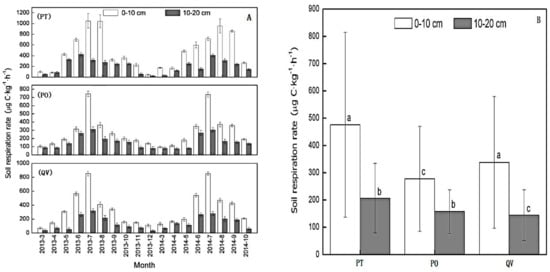
Figure 3.
Dynamic variation (A) and characteristics (B) of soil respiration at different soil depths of the three forest types. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the means. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences by ANOVA and LSD test at p < 0.001 between soil depths.
Significant differences in soil respiration were found at the 0–10-cm and 10–20-cm depths (p < 0.001). The estimated soil respiration at the 0–10-cm depth was highest in the PT plot (475.38 ± 339.27 μg C·kg−1·h−1), followed by the QV plot (337.90 ± 241.62 μg C·kg−1·h−1), and was lowest in the PO plot (277.76 ± 192.56 μg C·kg−1·h−1). At the 10–20-cm soil depth, the mean soil respiration in the PT plot (206.36 μg C·kg−1·h−1) was 23.7% and 29.8% higher than that in the QV and PO plots, respectively.
3.3. Contribution of Litter and Roots to Soil Respiration
Litter removal or root cutting did not modify the seasonal and spatial patterns of soil respiration, which overall corresponded to variations in the natural control. However, soil respiration after litter removal and root cutting decreased considerably at the different soil depths of the three forest types throughout the study (Figure 4A,B). The contribution rates of litter removal to soil respiration at the 10–20-cm depth were lower than that at the 0–10-cm depth, and the percentage of soil respiration reduction in the PT plot was higher than that in both the QV and PO plots (Table 3). In contrast to litter removal, root cutting had a more significant reduction effect on soil respiration, approximately 44.84% to 53.76% of which was explained by root cutting. The response of soil respiration to root cutting varied with soil depths, and the contribution of roots to the upper soil respiration was highest in the PT plot (53.76%), followed by the QV plot (48.26%) and the PO plot (44.84%). The contribution of roots to soil respiration at the 10–20-cm depth was highest in the QV plot (50.29%), followed by the PO plot (49.10%) and the PT plot (45.19%).
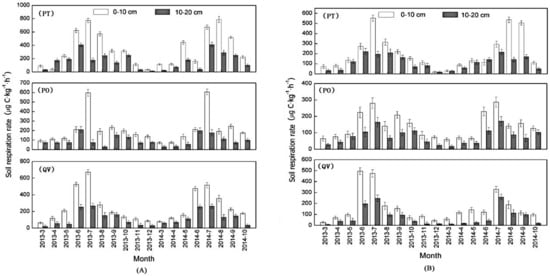
Figure 4.
Dynamic variation of soil respiration after litter removal (A, left) and root cutting (B, right) at different soil depths of the three forest types.

Table 3.
Mean (± SD) contribution of litter and roots to soil respiration at different soil depths of the three forest types.
3.4. Relationships among Soil Respiration, Temperature, and Soil Water Content
A significantly exponential function best described the relationship between soil respiration and soil temperature at different soil depths for three forest types (p < 0.001). Soil temperature alone could explain 59.8% to 72.4% of the changes in soil respiration across the three forest types (Table 4). The temperature sensitivity (Q10) of soil respiration not only varied with soil depth but also with forest types. The mean Q10 values at the 5-cm depth were 2.76 ± 0.48, 1.93 ± 0.19, and 2.28 ± 0.24 for PT, PO, and QV, respectively, whereas those at the 15-cm depth were 3.21 ± 0.67, 2.37 ± 0.28, and 2.64 ± 0.41, indicating that Q10 significantly increased with soil depth. Among the three forest types, the mean Q10 values of PT at the 5- and 15-cm depth were higher than those of the QV and PO plots, and PT showed the highest sensitivity of soil respiration in response to temperature at both soil depths. In response to a 10-°C increase in soil temperature, soil respiration increased by 2.76 ± 0.48 (5 cm) and 3.21 ± 0.67 times (15 cm).

Table 4.
Relationship between soil respiration and soil temperature at different soil depths for three forest types.
Soil respiration correlated significantly with soil water content among the three forest types. Based on the quadratic polynomial model, soil respiration in the three forest types tended to increase with soil water content until reaching threshold values (19.97% for PT, 16.65% for PO, and 16.90% for QV), which was followed by a decrease (Figure 5). Soil water content only explained 43.7% to 50.4% of the variance in soil respiration, suggesting that the correlation of soil respiration with soil water content was still weaker than that with soil temperature. Furthermore, soil water content combined with soil temperature significantly influenced the seasonal dynamics of soil respiration at different soil depths for the three forest types, and explained an average of 73.8% of the variation in soil respiration (Table 5). Compared to the soil temperature alone, the combined effects of soil water content and soil temperature on seasonal soil respiration yielded higher R2 values.
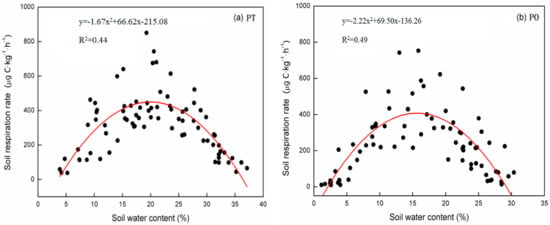
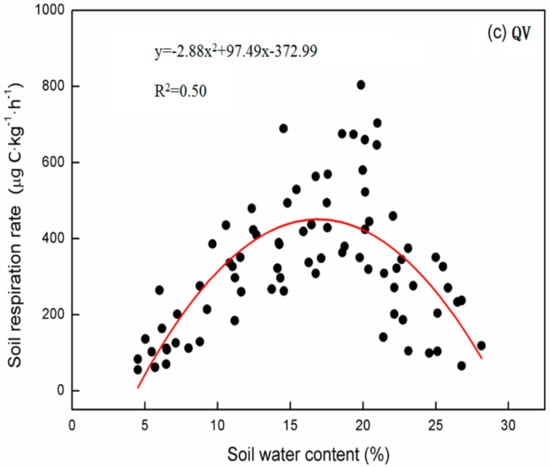
Figure 5.
Relationship between soil respiration and soil water content among the three forest types. (a) PT, Pinus tabulaeformis forest plot; (b) PO, Platycladus orientalis forest plot; (c) QV, Quercus variabilis forest plot.

Table 5.
Regression equation for soil respiration against soil temperature and soil water content at different soil depths for three forest types.
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing Soil Respiration
At the ecosystem scale, soil temperature is considered as the primary control of soil respiration mainly since it influences soil microbial and plant root activities, decomposition of litter and soil organic matter, and plant productivity. This leads to variations in carbon substrate availability for plants and soil [11]. The results of the present study showed a high exponential positive correlation between soil respiration and soil temperature among forests, indicating soil temperature was an important factor for seasonal soil respiration. This result is supported by numerous studies [2,8,23]. However, limitations of other factors (i.e., soil water content, plant biomass, and SOC) may lead to differences in temperature control over soil respiration among forests [10,27]. This study demonstrated that temperature considerably influences the variation in seasonal soil respiration among forest types. Seasonal variation in soil respiration could be explained by variations in soil temperature, which ranged from 59.8% in the PO plot to 72.4% in the PT plot (Table 4). Furthermore, soil respiration had a more significant correlation with soil surface temperature than with temperature at deeper depths, which may result from higher variations in soil temperature at the surface than at deeper soil [28].
Soil water content is an important limiting factor for ecosystem processes in regions with water scarcity, and the impact of soil water content on soil respiration is complicated [29], which is possibly confounded with the impact of soil temperature [20,30]. A strong quadratic relationship between soil respiration and soil water content observed in the current study agrees with that observed in previous studies in forest ecosystems [4,10] and in other ecosystems [31]. The lower soil water content may constrain both substrate availability and microbial activity [2,32], thus decreasing soil respiration. Drought stress is gradually relieved with the increase of soil water content, and soil respiration is increased. Soil water content exerted the strongest effects on the seasonal dynamics of soil respiration among forests at the threshold value. Once the soil water content exceeded this threshold, it suppressed oxygen movement and root growth [31], thus reducing soil respiration. In this study, the threshold value was 19.97%, 16.65%, and 16.90% for PT, PO, and QV, respectively. Rey et al. [33] reported that soil water content exerted the highest influence on soil respiration at 20% in a coppice oak forest in central Italy. However, Tang et al. [21] reported that soil respiration declined when soil water content exceeded 25% in an oak-grass ecosystem in California, USA. Differences in the threshold value of soil water content are mainly attributed to species composition, vegetation properties, and soil types [6]. In addition, combining soil water content into soil respiration–temperature models is inadequate for the prediction of soil respiration in these three forest types (Table 5). This implies that other biotic factors, such as root biomass [13], litter input, and carbon substrate supply [10], may greatly affect the seasonal dynamics of soil respiration.
Litter removal and root cutting significantly contributed to the reduction of soil respiration, but their respective contributions differed. The contribution rate of the roots to the reduction in soil respiration was much greater than that of the litter: 48.57% and 26.56%, on average, respectively. Similar results have been reported previously [2,16,22]. The results of the present study, along with the results of previous studies, suggest that soil respiration is positively related to litter and roots, and that root respiration accounts for a large proportion of the total respiration. However, several studies have reported a greater reduction from litter than from roots [34,35]. These conflicting observations are probably the result of differences in the plant species and soil types used in different study areas.
The key mechanism for the litter dependence of soil respiration is that litter can directly influence the aboveground carbon input. According to this study, soil respiration decreased by 22.97% to 29.76% after litter removal, indicating the significance of carbon input from litter on soil respiration. Similarly, plant roots still respired despite the removal of litter. In contrast, the roots contributed more to soil respiration when the latter was reduced 44.84% to 53.76% after root cutting. This is because root cutting not only causes rapid root mortality and decreases plant productivity, but it also hinders subterranean carbon input for microbial decomposition [20,34]. Thus, compared to litter removal, root cutting controlled soil respiration to a higher extent among the three forest types.
In addition, higher soil respiration was observed at the 0–10-cm depth compared to the 10–20-cm depth in all three forest types. This can be attributed to the lower oxygen availability and stronger soil aggregation, which cause slower decomposition of soil carbon in deeper soil [36]. Hence, higher SOC accumulation was detected at the 0–10-cm depth in the three forests. Furthermore, higher root biomass was detected, especially that of fine roots, in the top soil compared to the 10–20-cm depth soil among the forests. Wang et al. [4] demonstrated that higher soil respiration is partially a result of SOC and fine root biomass. This indicates that higher plant biomass productivity will lead to higher soil respiration at different soil depths. Although no significant differences were detected in soil temperature and water content between the 0–10- and 10–20-cm depths among forests, variations in soil temperature and water content at both soil depths may differently affect soil organic matter decomposition, root activities, and plant growth [11,35], which indirectly influences soil respiration. Therefore, the combination of soil temperature, soil water content, and plant biomass production regulates soil respiration in forests.
4.2. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Respiration
The obtained results indicated that Q10 varied from 1.93 to 2.76 and from 2.37 to 3.21 across the three forest types at the 5- and 15-cm depths, respectively, which remained within the previously reported range of 1.8 to 4.1 of forest ecosystems [6]. This not only indicates that deeper soil may enhance the temperature sensitivity of soil respiration but also implies that different soil temperature measurement depths can influence the Q10 estimation. Such variation in Q10 values due to soil depth has also been reported by Peng et al. [5]. Furthermore, as the most widely planted forest types in the study area, PT has the highest Q10 value while the lowest Q10 value was observed for PO. The mechanisms that regulate the variability of Q10 values among forests could be influenced by a variety of factors, such as soil temperature and water content, litter input, root biomass, substrate availability, and microbial population [2,5,20,30]. A recent study demonstrated that variation in the temperature sensitivity of soil respiration reflects the various productivities among different forest types, further suggesting the ecological connection between plant physiology and soil [17,37]. Therefore, rational selection of forest types for afforestation projects is important for future global carbon balance and spatial patterns.
4.3. Soil Respiration among Forest Types
On a global scale, the annual cumulative CO2 emissions of any type of ecosystem and biome are closely linked to soil respiration [16]. Different vegetation types within the same climatic region have to be considered when estimating soil respiration [38], because the species of vegetation considerably affects carbon distribution pattern, the quality and input of litter, root growth, soil structure, and microclimate, all of which result in significant differences in soil respiration [20,39]. In this study, soil respiration of the QV plot was greater than that of the PO plot, which agrees with the results of previously reported studies [4,40] that indicated higher soil respiration in broadleaved forest versus coniferous forest. However, the PT plot had a significantly higher rate of soil respiration than the QV plot. These differences in soil respiration can be attributed to the combined effects of biotic and abiotic factors. For example, the soil temperature in the PT plot was higher than that in the QV plot (13.64 vs. 12.29 at 5-cm depth; 13.66 vs. 12.16 at 15-cm depth), and the 19.2% higher soil water content in the PT plot likely contributed to the higher rate of soil respiration. Such negligible differences in soil temperature and soil water content are probably not important for other forests but are possibly limiting factors in physiological processes [13] for broadleaved and coniferous forests due to water scarcity in the study region. In addition, the higher SOC and carbon storage in litter and the finer root biomass can further lead to high soil respiration, as other studies [16,20,41] have shown that root biomass and SOC exerted a greater impact on the regulation of soil respiration.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study showed that differences in soil respiration at different soil depths exist in typical forests in the mountainous area of north China. The obtained results indicated that seasonal soil respiration generally decreased with soil depths in three forest types. Through the two soil depths studied, soil temperature is the most predominant factor controlling the seasonal variation of soil respiration, and soil water content is a limiting factor for soil respiration after it reaches the threshold value. The combination of soil temperature and water content could improve soil respiration. In addition to soil microclimate, litter removal and root cutting led to varied reduction of soil respiration. The different contributions of litter and roots to soil respiration across forest types imply that the microbe-driven decomposition is forest-type and soil depth dependent. These findings suggest that both the soil microclimate and forest type contribute to the variation in soil respiration at different soil depths. Furthermore, the differences in soil respiration in the three forest types under the same climatic conditions may largely be attributed to variations in substrate availability (e.g., SOC) and soil carbon input (e.g., fine root biomass). Therefore, combining measurements of soil temperature, water content, and plant productivity enables a better understanding of the mechanisms that underly the soil respiration of forests.
Author Contributions
G.J. conceived and designed the experiment; W.Q. and Z.S. collected data, D.W. analyzed the data and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript; X.Y. provided conceptual and editorial advice and rewrote significant parts of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Financial assistance of this study was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41877073 & 41877152 & 41977149), Research projects on major scientific and technological issues of water conservancy (Basic scientific research on mud-01881913113) and Beijing Municipal Education Commission (CEFF-PXM2019_014207_000099). The authors want to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their support and comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
- IPCC. Climate change. In The Physical Science Basis; Solomon, S., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.X.; Li, R.C.; Li, X.; Tian, L.H. Environmental controls on soil respiration in alpine meadow along a large altitudinal gradient on the central Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2017, 159, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S. Global patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.Z. Soil respiration in six temperate forests in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Piao, S.L.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.Y.; Shen, Z.H. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in different ecosystems in china. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, Y. Spatial and seasonal variations of Q10 determined by soil respiration measurements at a Sierra Nevadan forest. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.W.; Liu, S.R.; Zhu, X.L.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, K. Roles of biotic and abiotic variables in determining spatial variation of soil respiration in secondary oak and planted pine forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Kato, T.; Tang, Y.H. Temperature controls ecosystem CO2 exchange of an alpine meadow on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.Q.; Norby, R.J.; Ledford, J.; Weltzin, J. Responses of soil respiration to elevated CO2, air warming, and changing soil water availability in a model old-field grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 2411–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.S.; Wang, Q.B.; Han, X.G.; Wan, S.Q.; Li, L.H. Temporal and spatial variability and controls of soil respiration in a temperate steppe in northern China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Liu, S.R.; Ge, J.P.; Chu, J.X. Annual and seasonal variations of Q10 soil respiration in the sub-alpine forests of the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søe, A.R.B.; Buchmann, N. Spatial and temporal variations in soil respiration in relation to stand structure and soil parameters in an unmanaged beech forest. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Sun, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yao, L.G.; Hu, Y.X.; Guo, S.L. Contrasting responses of soil respiration and temperature sensitivity to land use types: Cropland vs. apple orchard on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.; Fu, S.L.; Li, Z.; Xia, H.P.; Zhou, L.X. Temperature sensitivity of total soil respiration and its heterotrophic and autotrophic components in six vegetation types of subtropical China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Högberg, P.; Högberg, M.N.; Göttlicher, S.G.; Betson, N.R.; Keel, S.G.; Metcalfe, D.B.; Campbell, C.; Schindlbacher, A.; Hurry, V.; Lundmark, T.; et al. High Temporal Resolution Tracing of Photosynthate Carbon from the Tree Canopy to Forest Soil Microorganisms. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zha, T.G.; Luo, Z.K.; Zheng, J.M. Predicting soil respiration using carbon stock in roots, litter and soil organic matter in forests of Loess Plateau in China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tang, S.; Xiong, L.; Yang, W.Q.; Yin, H.J.; Tu, L.H.; Wu, F.Z.; Chen, L.H.; Tan, B. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in China’s forest ecosystems: Patterns and controls. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 93, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Tan, K.; Nan, H.J.; Ciais, P.; Fang, J.Y.; Wang, T.; Vuichard, N.; Zhu, B. Impacts of climate and CO2 changes on the vegetation growth and carbon balance of Qinghai–Tibetan grasslands over the past five decades. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 98, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Yu, X.X.; Jia, G.D.; Wang, H.N. Sensitivity analysis of runoff to climate variability and land-use changes in the Haihe Basin mountainous area of north China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 269, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Yang, Y.S.; Yang, Z.J.; Chen, G.S.; Xie, J.S.; Guo, J.F.; Zou, S.Q. The dynamic response of soil respiration to land-use changes in subtropical China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Baldocchi, D.D. Spatial-temporal variation in soil respiration in an oak-grass savanna ecosystem in California and its partitioning into autotrophic and heterotrophic components. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Xu, M.; Sun, O.J.; Cui, W.C. Effects of root and litter exclusion on soil CO2, efflux and microbial biomass in wet tropical forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Wang, H.M.; Xu, M.J.; Ma, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Soil organic carbon stocks and CO2, effluxes of native and exotic pine plantations in subtropical China. Catena 2015, 128, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingwersen, J.; Butterbach-bahl, K.; Gasche, R.; Richter, O.; Papen, H. Barometric Process Separation: New Method for Quantifying Nitrification, Denitrification, and Nitrous Oxide Sources in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Huang, Y. Determination of respiration, gross nitrification and denitrification in soil profile using BaPS system. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Q.; Wan, S.Q.; Hui, D.F.; Wallace, L.L. Acclimatization of soil respiration to warming in a tall grass prairie. Nature 2001, 413, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, P.; Kakani, V.G. Confounding Effects of Soil Moisture on the Relationship Between Ecosystem Respiration and Soil Temperature in Switchgrass. Bioenergy Res. 2014, 7, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, M.; Acosta, M.; Marek, M.V.; Kutsch, W.; Janous, D. Dependence of the Q10 values on the depth of the soil temperature measuring point. Plant Soil 2007, 292, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Hu, R.G.; Feng, M.L.; Lin, S.; Malghani, S.; Ali, I.M. Microbial biomass, and dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen strongly affect soil respiration in different land uses: A case study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, S.L.; Liu, Q.F.; Jiang, J.S.; Wang, R.; Li, N.N. Responses of soil respiration to land use conversions in degraded ecosystem of the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Guo, S.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, Q.F.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, N.N.; Li, R.J. Changes in temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in the phases of a three-year crop rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelting, D.L.; Burger, J.A.; Edwards, G.S. Estimating root respiration, microbial respiration in the rhizosphere, and root-free soil respiration in forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Pegoraro, E.; Tedeschi, V.; Deparri, I.; Jarvis, P.; Valentini, R. Annual variation in soil respiration and its components in a coppice oak forest in Central Italy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, N. Biotic and abiotic factors controlling soil respiration rates in Picea abies stands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, D.A.; Feng, W.T.; Zou, X.M. Plant carbon inputs and environmental factors strongly affect soil respiration in a subtropical forest of southwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.W.; Liu, S.R.; Zhu, X.L.; Wang, J.X. Soil carbon stocks and fluxes in a warm-temperate oak chronosequence in China. Plant Soil 2011, 347, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.E.; Adams, M.A. Respiratory quotients and Q10 of soil respiration in sub-alpine Australia reflect influences of vegetation types. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borken, W.; Xu, Y.J.; Davidson, E.A.; Beese, F. Site and temporal variation of soil respiration in European beech, Norway spruce, and Scots pine forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, E.; Steltzer, H.; Berg, S.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Simmons, B.L.; Wall, D.H. Tree Species Traits Influence Soil Physical, Chemical, and Biological Properties in High Elevation Forests. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Tufekciogul, A. Vegetation and soil respiration: Correlations and controls. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, M.; Rodeghiero, M.; Anderson-Dunn, M.; Dore, S.; Gimeno, C.; Drösler, M.; Williams, M.; Ammann, C.; Berninger, F.; Flechard, C.; et al. Soil Respiration in European Grasslands in Relation to Climate and Assimilate Supply. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).