Abstract
We propose in this paper a two-phase approach that decomposes the process of solving the three-dimensional single Container Loading Problem (CLP) into subsequent tasks: (i) the generation of blocks of boxes and (ii) the loading of blocks into the container. The first phase is deterministic, and it is performed by means of constructive algorithms from the literature. The second phase is non-deterministic, and it is performed with the use of Generate-and-Solve (GS), a problem-independent hybrid optimization framework based on problem instance reduction that combines a metaheuristic with an exact solver. Computational experiments performed on benchmark instances indicate that our approach presents competitive results compared to those found by state-of-the-art algorithms, particularly for problem instances consisting of a few types of boxes. In fact, we present new best solutions for classical instances from groups BR1 and BR2.
1. Introduction
Cutting and Packing (C&P) problems are combinatorial optimization problems that focus on the optimal use of existing resources (e.g., wood, glass, or even space), thus being often encountered in manufacturing industries. In a nutshell, cutting problems consist of cutting one or more large objects into small items, while packing problems consist of packing small items into one or more large objects.
In this paper, we investigate a particular C&P problem commonly referred to as the single container loading problem, a three-dimensional single large object placement problem [1]. The CLP is defined as follows: Consider a collection of boxes grouped into m types. Each box type has a length , a width , a height , a volume , and a quantity of boxes available to be loaded. Consider also a container with L, W, and H as its length, width, and height, respectively. The objective is to load—orthogonally and without overlapping—boxes inside the container with the aim of maximizing the volume utilization of the three-dimensional space. In this work, we consider the following additional constraints:
- Orientation constraint: In principle, a box can be loaded in up to six orientations. However, in practice, some of them may be prohibited.
- Stability constraint: Boxes that are not loaded directly on the container floor must be fully supported by top surfaces of one or more boxes.
An example of container loading is presented in Figure 1. Some other requirements may appear in real-world applications, such as load bearing strength, weight distribution/limit, and cargo priority. See [2] for an extensive review on CLP constraints.
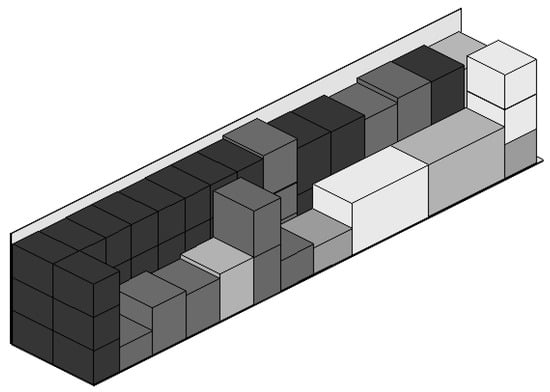
Figure 1.
A container loading pattern with orientation and stability constraints.
The CLP is strictly NP-Hard [3], and therefore, exact methods can effectively solve only small size instances. To deal with larger ones, heuristics are the current alternative. In a recent paper [4], CLP heuristics were categorized into three, not necessarily disjoint, groups:
- Conventional heuristics, which take advantage of the specific problem structure. A classical example is the wall-building procedure of George and Robinson [5], where the loading is made layer-by-layer across the depth of the container. Other examples of problem-dependent techniques applied to solve the CLP can be found in [6,7,8].
- Metaheuristics, which have been extensively applied to the CLP. Parreño et al. [9], for instance, conceived of a constructive procedure based on maximal-space representation. Insertion and deletion shifts directly affecting the container layout were used in a variable neighborhood search to improve partial solutions. Further studies include co-evolutionary computation techniques (e.g., Genetic Algorithms (GAs) [10,11]), trajectory-based methods (e.g., simulated annealing [12], the greedy randomized adaptive search procedure [13], and tabu search [14]), and swarm intelligence systems (e.g., bee colony algorithm [15]).
- Tree search methods, which have produced good-quality solutions to the CLP. Fanslau and Bortfeldt [4], for instance, proposed a tree search method that keeps a list of empty spaces to be filled by blocks of boxes. Similar contributions can be found in [16,17,18,19].
Despite this general classification, it has been proven to be pertinent to combine distinct optimization techniques to exploit their main advantages simultaneously (e.g., a metaheuristic with an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) solver), which has been referred to as hybrid metaheuristics [20,21]. Some authors prefer to refer to heuristic algorithms particularly made by the interoperation of metaheuristics and mathematic programming techniques as matheuristics [22]. In this paper, we propose a two-phase approach to tackle the CLP, motivated by a general idea of decomposing the CLP into two subproblems [11,23], namely a three-dimensional problem of generating blocks of boxes and a two-dimensional problem of loading blocks on the floor of the container. In our proposal, the three-dimensional problem is solved by means of constructive algorithms from the literature, and the two-dimensional problem is solved by means of a hybrid metaheuristic. Computational experiments performed on weakly-heterogeneous benchmark instances (with a few types of boxes) show that our approach competes with state-of-the-art CLP algorithms.
The remainder of this work is organized as follows. In Section 2, we describe our algorithm. In Section 3, we provide computational experiments on benchmark instances from the literature and present a discussion of the results. Finally, in Section 4, we close the paper with some conclusions and future perspectives.
2. Block-Loading Hybrid Metaheuristic
Our Block-Loading Hybrid Metaheuristic (BLHM) algorithm is segmented into two subsequent phases: block generation and block loading. On the one hand, the block generation phase is very fast and completely deterministic. Constructive algorithms from the literature [7] perform this task. On the other hand, the block loading phase is non-deterministic. It comprises the generate-and-solve methodology [24,25,26], a problem-independent hybrid optimization framework characterized by the interoperation of a metaheuristic with an ILP solver. In what follows, we describe how BLHM works to address the CLP.
2.1. Block Generation
Some CLP algorithms [4,7,8] have received notoriety for loading cuboid blocks of boxes instead of single boxes, thus being properly classified as block-building approaches. By definition, a block is a set of boxes placed compactly inside its Minimum Bounding Cuboid (MBC) [7]. Existing research classifies blocks into two types: simple blocks and guillotine blocks. Simple blocks consist of identical boxes, in the same spatial orientation and occupying the total volume of their respective MBCs. A pseudocode [7] to generate simple blocks is presented in Algorithm 1, which roughly produces valid blocks with boxes in a row, boxes in a column, and boxes in a stack, all of them of the same type, as illustrated in Figure 2.
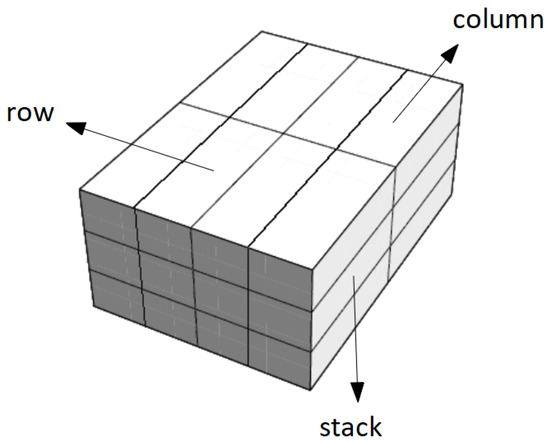
Figure 2.
A simple block with four boxes in a row, two boxes in a column, and three boxes in a stack.
| Algorithm 1 Generating simple blocks (adapted from the original paper [7]). |
| Input: A container with dimensions L, W, and H and a collection of boxes grouped into types. Each type t has a length , a width , a height , and a quantity of boxes available to be loaded. Output: Set B of simple blocks.
|
Conversely, guillotine blocks consist of multiple types of boxes possibly placed in different spatial orientations. A pseudocode to generate guillotine blocks, proposed by Zhu and Lim [7], is given in Algorithm 2. B, , and denote, respectively, the set of blocks generated so far, the set of blocks generated in the previous iteration, and the set of blocks generated in the current generation. Given one block from B and another block from , guillotine blocks are generated by combining the two blocks along the length, width, or height direction of the container, as illustrated in Figure 3.
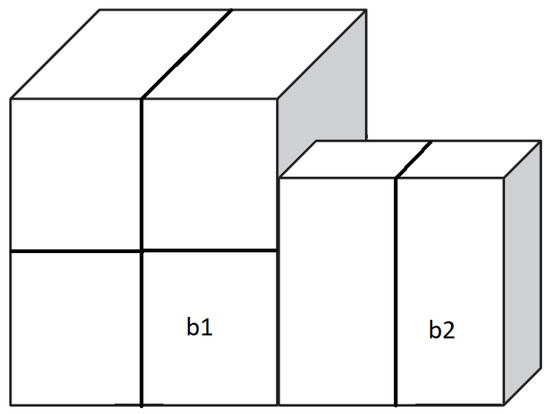
Figure 3.
A guillotine block obtained from the combination of two simple blocks.
| Algorithm 2 Generating guillotine blocks (adapted from the original paper [7]). |
| Input: Set B of simple blocks (see Algorithm 1). Output: Extended set B of guillotine blocks.
|
Fully-Supported Blocks (FSBs) [7] are blocks complying with the stability constraint. They are generated handling an attribute called packing area, which is the rectangular region on the top face of the block that is fully covered by top faces of boxes belonging to its MBC. Obviously, simple blocks are FSBs. Guillotine FSBs are generated according to some rules. For instance, let and be two guillotine FSBs with packing area and , respectively. Such blocks can be combined along the length (resp. width) direction if and only if they have the same height (i.e., ) and the sum of the lengths (resp. widths) of their packing areas spans the entire length (resp. width) of their MBCs, i.e., (resp. ). When and are combined along the length (resp. width) direction, the resultant packing area of the new FSB is given by (resp. ) and (resp. ). Another scenario arises when combining and along the height direction. One can place on the top face of block if and only if the base area of fits entirely into . Then, the packing area of the resultant FSB is equivalent to . See [4,7,27] for illustrations of the concepts related to blocks of boxes.
The first phase of our BLHM uses Algorithms 1 and 2 to generate FSBs. Let B be the set of FSBs obtained after running such algorithms. We now resort to an evaluation function to identify promising FSBs belonging to B. An FSB , , is assumed to be promising if and only if:
where is the volume of boxes in ; is the volume of the virtual space occupied by , calculated as the product of the base area of its MBC by the height of the container (instead of the height of its MBC, since in the next phase, we just place FSBs on the floor of the container); and is a parameter in the real interval . Note that when is near one, only promising FSBs with small residual spaces are considered to the next phase. In this way, we reject FSBs that present a considerable volume not occupied by boxes and FSBs that are too low in relation to the height of the container, as illustrated in Figure 4. In what follows, we refer to as the set of promising FSBs.
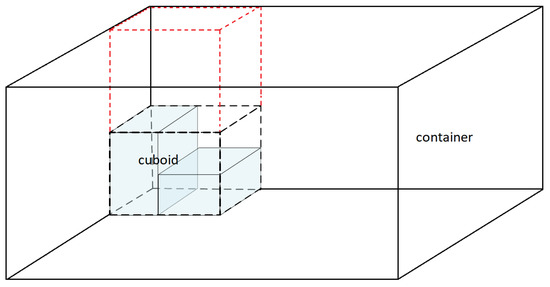
Figure 4.
A representation of a guillotine block, its MBC, and the residual space on top of it.
2.2. Block Loading
In the second phase of our BLHM algorithm, we use the GS hybrid framework. In the sequence, we first present an ILP model to the problem of loading FSBs on the container floor and then propose an application of the GS framework to the problem.
2.2.1. ILP Model
Loading FSBs on the container floor is a two-dimensional C&P problem. We implement a well-known ILP model for orthogonal two-dimensional C&P problems [28]. Let be a binary decision variable standing for the decision of whether or not to load an FSB of type i at coordinate of the container floor.
The elements j and k belong, respectively, to the following discretization sets:
To avoid overlapping of FSBs, the incidence matrix is defined as:
which is computed a priori for each FSB of type i, for each coordinate , and for each coordinate . Finally, the ILP model is defined as follows:
The objective function (1) maximizes the volume of loaded FSBs inside the container. Constraints (2) avoid overlapping of FSBs in any feasible solution. Let represent the quantity of boxes of type t in an FSB of type i. Constraints (3) impose that, for each box type t, the quantity of loaded boxes of this type must not exceed the number of boxes available. Finally, Constraints (4) specify the domain of variables. The ILP model (1)–(4) contains variables and constraints. Since the product may be too large for practical instances of this problem, the number of constraints and variables can easily reach the order of millions, which discourages the straightforward use of classical ILP techniques.
2.2.2. Generate-and-Solve
ILP solvers are very effective at coping with combinatorial optimization problems up to a certain problem-specific instance size. Recently, approaches based on problem instance reduction [29], such as generate-and-solve [24,25,30], construct, merge, solve and adapt [31], and column reduction methods [32], have shown that, when a problem instance is too large to be directly solved by an ILP solver, it might be possible to reduce the problem instance in a way such that it can be effectively solved by the ILP solver and it still contains high-quality solutions to the original problem instance.
The GS hybrid optimization framework has been introduced to cope with hard combinatorial optimization problems, such as those of the C&P family. The framework prescribes the integration of two distinct conceptual components: the Generator of Reduced Instances (GRI) and the Solver of Reduced Instances (SRI), as depicted in Figure 5.
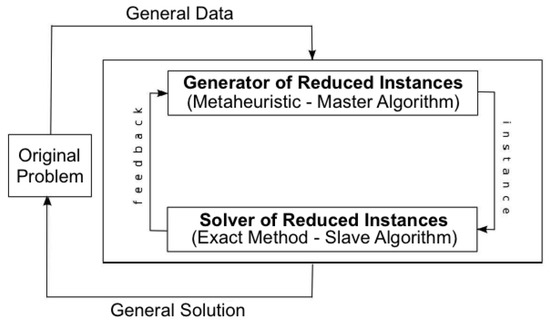
Figure 5.
The generate-and-solve hybrid framework.
An exact method (e.g., ILP solver) encapsulated in the SRI component is in charge of solving reduced instances (i.e., subproblems) of the original problem that still preserve its conceptual structure. Thus, a feasible solution to a given subproblem will also be a feasible solution to the original problem. At a higher level, a metaheuristic (e.g., GA) works on the complementary optimization problem of generating reduced instances, which, when submitted to the SRI, produce feasible solutions whose objective function values can be used as a figure of merit (fitness) of the associated subproblems, thus guiding the search process. The interaction between GRI and SRI proceeds until a given stopping condition is satisfied. The best solution obtained by the solver to any of the subproblems generated by the metaheuristic is deemed to be the final solution.
2.2.3. Random Key Genetic Algorithm
One can generate reduced instances of the block loading problem by removing some of the types of FSBs and/or some of the elements of the discretization sets from the ILP model (1)–(4). In our implementation, the GRI runs a Random Key Genetic Algorithm (RKGA) [33]. Individuals are represented by chromosomes (of random keys) with a size equal to , as shown in Figure 6.
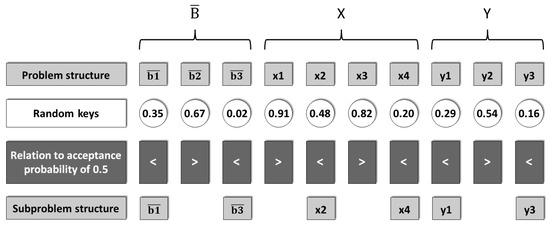
Figure 6.
Chromosome of random keys.
In this representation, each allele of the encoding scheme denotes the decision of counting (or not) on the presence of an element in the reduced instance. Let , , and be the probability of acceptance related to , X, and Y, respectively. If an allele , with , then the corresponding FSB will be a candidate FSB to be loaded on the container floor by the SRI. This insight is also applied to the discretization sets, i.e., if an allele , with (resp. , with ), then the corresponding element of X (resp. Y) will take part of the reduced instance. As an example in Figure 6, FSBs and take part in the subproblem to be solved by the SRI, since their alleles (or random keys) are less than the acceptance probability of 0.5. Regarding the discretization sets, elements , , , and take part of the reduced instance. Therefore, and may be possibly loaded at coordinates , , , and .
The initial population contains p chromosomes, whose alleles are randomly generated in the real interval . After an individual is translated to its ILP formulation and solved by means of an ILP solver, its fitness value is computed. Note that, if a chromosome includes all FSBs and coordinates, the original problem will be generated. However, it is very likely that the corresponding ILP model cannot be handled by the ILP solver. The population is then partitioned into two groups: a small group of elite individuals whose corresponding reduced instances present the best fitness values (i.e., objective function values) and the remaining set of non-elite individuals.
To evolve the population, a new generation must be produced. First, all elite individuals are carried over from generation g to generation . Then, RKGA implements mutation by introducing mutants into the population. Mutants are vectors of random keys generated as elements of the initial population. Finally, discounting elite individuals and mutants, offspring individuals are produced through mating to complete p individuals that will make up the population of generation . Mating (crossover) is performed as in [34]. Given two parents A and B randomly selected from the current population and a user-chosen probability that an offspring inherits the allele of A, for each allele (where n is the number of genes), the child either takes the value of the allele of A with probability or the corresponding allele of B with probability .
3. Computational Experiments
Experiments were performed on a PC Intel Pentium i7, 8 × 3.60 GHz, 16 GB DDR3 RAM under Linux Ubuntu 14.05 LTS. We used CPLEX 12.7 and Java concert technology as underlying solver of the SRI. The time limit for each instance was set to 3600 seconds. The GRI ran an RKGA implemented in Java.
3.1. Control Parameters and Calibration
We conducted preliminary experiments to figure out the best input values for BLHM. To identify promising FSBs, we set . Concerning the RKGA, we set individuals, , and . To control the duration of the optimization process, the maximum number of generations was set to 400, while the total time to stop was set to 3600 seconds. If the best fitness value did not change in 15 consecutive generations, a new population consisting of the two best individuals and random ones was generated. The acceptance probabilities were set to , , and , for . The CPLEX time limit of 60 seconds was set to solve each subproblem.
3.2. Numerical Results
To evaluate the potentialities behind our BLHM algorithm, computational experiments were performed over difficult benchmark instances proposed by Bischoff and Ratcliff [6], which can be accessed via OR-Library [35]. Instances can be either weakly heterogeneous (few types of boxes, each one with many units available) or strongly heterogeneous (many types of boxes, each one with few units available). We decided to conduct our analysis only on weakly-heterogeneous datasets BR1 and BR2, which contain three and five types of boxes, respectively, after preliminary tests showed that the required computation time would be considerably high to compete with alternative approaches for strongly-heterogeneous instances.
We present results in Table 1 and Table 2 (BR1) and Table 3 and Table 4 (BR2). In these tables, for each instance, we present the volume utilization achieved by well-known state-of-the-art approaches enforcing orientation and stability constraints: the Container Loading by TRee Search (CLTRS) of Fanslau and Bortfeldt [4], the Iterative-Doubling-Greedy Lookahead Tree Search (ID-GLTS) of Zhu and Lim [7], and the Beam Search (BSG-VCS) of Araya, Guerrero, and Nuñes [36] with a new heuristic function for selecting boxes. To the best of our knowledge, BSG-VCS has reported the best results to date. It is important to stress that CLTRS, ID-GLTS, and BSG-VCS have a maximum runtime of 500 s for each instance. The columns related to BLHM show, for each instance, the average (avg.) and the best (best) solution values found by our algorithm over 10 runs. We indicate by bold font the best solution found among the four CLP algorithms. To compare the algorithms, since BLHM is non-deterministic, we consider its average value (and denote by * in the case that the best solution of BLHM is better than the solutions found by the other algorithms).

Table 1.
Results for group BR1.

Table 2.
Results for group BR1 (cont.).

Table 3.
Results for group BR2.

Table 4.
Results for group BR2 (cont.).
We begin the discussions on experimental analysis by stating that there is not a particular algorithm that stands out from the others for all instances. Taking as the reference group BR1, for instance, BLHM found new best solutions for 24 (out of 100) instances. The average solution obtained by CLTRS, ID-GLTS, BSG-VCS, and BLHM was 94.51, 94.40, 94.74, and 92.97 (considering the average column), respectively. For BR1-043, the result of 83.98 obtained by BLHM was very small when compared to the best one, namely 96.18. We believe this is due to the small number of FSBs generated in the first phase of BLHM.
Concerning group BR2, BLHM obtained the best solutions for seven (out of 100) instances. The average solution of CLTRS, ID-GLTS, BSG-VCS, and BLHM was 94.73, 94.85, 95.38, and 92.52 (considering the average column), respectively. It is important to note that the efficiency of BLHM decreased as the heterogeneity of the instances increased.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we presented a two-phase approach to tackle the container loading problem. The idea behind our algorithm is to decompose the CLP into two subproblems, namely a three-dimensional problem of generating a set of blocks of boxes and a two-dimensional problem of loading a subset of blocks on the container floor. Constructive algorithms conducted the former task, while the generate-and-solve hybrid framework dealt with the latter one. Computational experiments performed on weakly-heterogeneous datasets showed that our algorithm found new best solutions for 31 (out of 200) instances of groups BR1 and BR2. Its performance however deteriorated as the number of types of boxes increases. As future work, we intend to explore other CLP constraints, e.g., load bearing strength and weight distribution, and to investigate other strategies to compare eventually our results to methods more advantageous in solving strongly-heterogeneous problems [37]. Future studies might cover solving the multi-container loading problem [38] and ship loading problem [39] by modifying our suggested method. Another perspective is to study the application of the GS hybrid framework to classical combinatorial optimization problems.
Author Contributions
P.R.P., R.D.S., and N.N. contributed equally to the conceptualization and methodology of the work. R.D.S. was particularly in charge of coding the algorithm and performing the experiments. R.D.S. and N.N. drafted the article. All authors have done critical revision of the manuscript and final approval of the version together.
Funding
This research was funded by CNPq/Brazil Grant Number 305844/2011-3.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge IBM for making CPLEX available to the academic community; and Andreas Bortfeld, Wenbin Zhu, and Ignacio Araya for providing us with detailed results of CLP instances.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BLHM | Block-Loading Hybrid Metaheuristic |
| BS | Beam Search |
| C&P | Cutting-and-Packing |
| CLP | Container Loading Problem |
| CLTRS | Container Loading by TRee Search |
| FSB | Fully-Supported Block |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GRI | Generator of Reduced Instances |
| GS | Generate-and-Solve |
| ID-GLTS | Iterative-Doubling Greedy-Lookahead Tree Search |
| ILP | Integer Linear Programming |
| MBC | Minimum Bounding Cuboid |
| RKGA | Random Key Genetic Algorithm |
| SRI | Solver of Reduced Instances |
References
- Wäscher, G.; Haußner, H.; Schumann, H. An improved typology of cutting and packing problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 183, 1109–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortfeldt, A.; Wäscher, G. Constraints in container loading—A state-of-the-art review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 229, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheithauer, G. Algorithms for the container loading problem. In Operations Research Proceedings 1991; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992; pp. 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Fanslau, T.; Bortfeldt, A. A tree search algorithm for solving the container loading problem. INFORMS J. Comput. 2010, 22, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.A.; Robinson, D.F. A heuristic for packing boxes into a container. Comput. Oper. Res. 1980, 7, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, E.E.; Ratcliff, M. Issues in the development of approaches to container loading. Omega 1995, 23, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lim, A. A new iterative-doubling Greedy–Lookahead algorithm for the single container loading problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 222, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, I.; Riff, M.C. A beam search approach to the container loading problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 43, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreño, F.; Alvarez-Valdés, R.; Oliveira, J.; Tamarit, J.M. Neighborhood structures for the container loading problem: A VNS implementation. J. Heuristics 2010, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.F.; Resende, M.G. A parallel multi-population biased random-key genetic algorithm for a container loading problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, H.; Bortfeldt, A. A genetic algorithm for solving the container loading problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 1997, 4, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, D.; Bortfeldt, A.; Gehring, H. A parallel hybrid local search algorithm for the container loading problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2004, 11, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Oliveira, J.F. A GRASP approach to the container-loading problem. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2005, 20, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Dong, Z.; Maple, C.; Keech, M. A novel hybrid tabu search approach to container loading. Comput. Oper. Res. 2011, 38, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, T.; Das, G.S. A hybrid ‘bee(s) algorithm’ for solving container loading problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, R.; Arenales, M. An AND/OR-graph approach to the container loading problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 1994, 1, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eley, M. Solving container loading problems by block arrangement. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 141, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisinger, D. Heuristics for the container loading problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 141, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Huang, W. An efficient placement heuristic for three-dimensional rectangular packing. Comput. Oper. Res. 2011, 38, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raidl, G.R. Decomposition based hybrid metaheuristics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 244, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.; Raidl, G.R. Hybrid Metaheuristics: Powerful Tools for Optimization; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti, M.; Maniezzo, V.; Roffilli, M.; Bolufé Röhler, A. Matheuristics: Optimization, Simulation and Control. In Hybrid Metaheuristics; Blesa, M., Blum, C., Di Gaspero, L., Roli, A., Sampels, M., Schaerf, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 5818, pp. 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Haessler, R.W.; Brian Talbot, F. Load planning for shipments of low density products. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 44, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, N.; Pinheiro, P.; Coelho, A.L. Tackling the Container Loading Problem: A Hybrid Approach Based on Integer Linear Programming and Genetic Algorithms. In Evolutionary Computation in Combinatorial Optimization; Cotta, C., van Hemert, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume Voume 4446, pp. 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Nepomuceno, N.; Pinheiro, P.; Coelho, A.L. A Hybrid Optimization Framework for Cutting and Packing Problems. In Recent Advances in Evolutionary Computation for Combinatorial Optimization; Cotta, C., van Hemert, J., Eds.; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 153, pp. 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, R.; Nepomuceno, N.; Pinheiro, P. The Generate-and-Solve Framework Revisited: Generating by Simulated Annealing. In Evolutionary Computation in Combinatorial Optimization; Middendorf, M., Blum, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 7832, pp. 262–273. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Lim, A.; Zhu, W. A multi-round partial beam search approach for the single container loading problem with shipment priority. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 145, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, J. An exact two-dimensional non-guillotine cutting tree search procedure. Oper. Res. 1985, 33, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.; Raidl, G.R. Hybridization Based on Problem Instance Reduction. In Hybrid Metaheuristics: Powerful Tools for Optimization; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.R.; Coelho, A.L.V.; de Aguiar, A.B.; Bonates, T.O. On the concept of density control and its application to a hybrid optimization framework: Investigation into cutting problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2011, 61, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.; Pinacho, P.; López-Ibáñez, M.; Lozano, J.A. Construct, Merge, Solve & Adapt: A new general algorithm for combinatorial optimization. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 68, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağatay Iris; Pacino, D.; Ropke, S.; Larsen, A. Integrated Berth Allocation and Quay Crane Assignment Problem: Set partitioning models and computational results. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 81, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, J.C. Genetic algorithms and random keys for sequencing and optimization. ORSA J. Comput. 1994, 6, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, W.M.; De Jong, K.A. On the virtues of parameterized uniform crossover. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Genetic Algorithms, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–16 July 1991; pp. 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, J.E. OR-Library: Distributing test problems by electronic mail. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1990, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, I.; Guerrero, K.; Nuñez, E. VCS: A new heuristic function for selecting boxes in the single container loading problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 82, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tan, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X. A tree search algorithm for the container loading problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 75, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhu, W.; Lim, A.; Wei, L. The multiple container loading problem with preference. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 248, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağatay, I.; Christensen, J.; Pacino, D.; Ropke, S. Flexible ship loading problem with transfer vehicle assignment and scheduling. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2018, 111, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).