Dissolution and Early Hydration Interaction of C3A-C4AF Polyphase in Water and Aqueous Sulfate Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
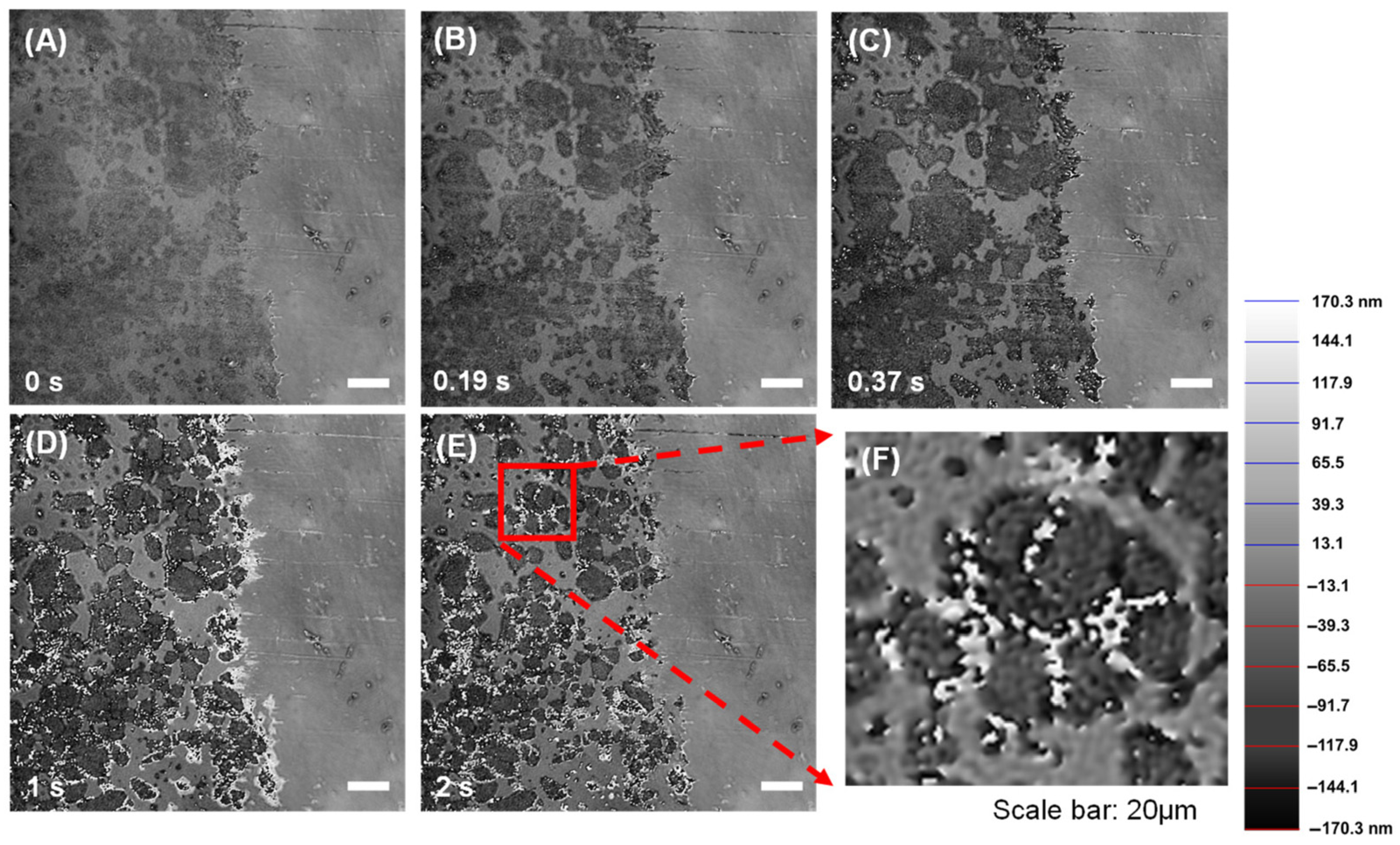
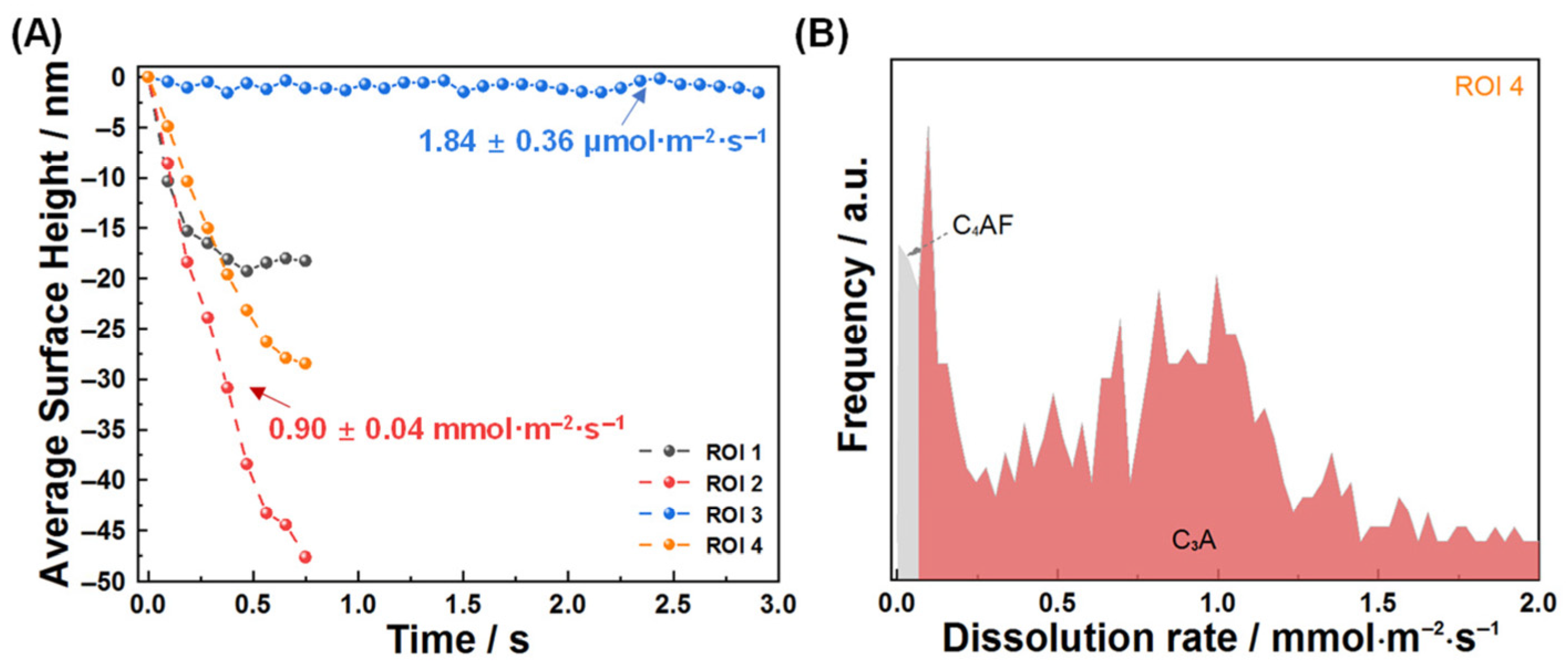
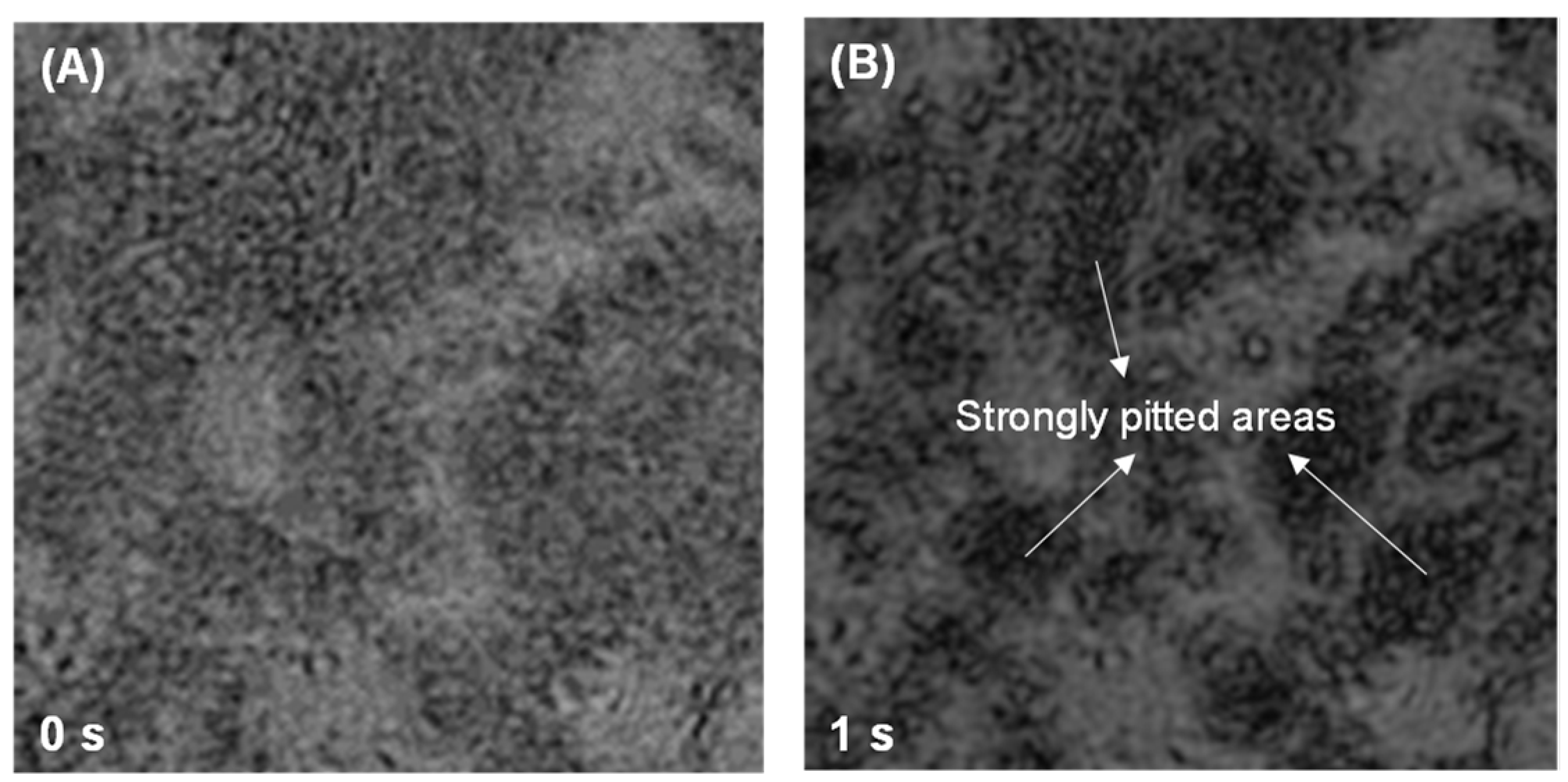
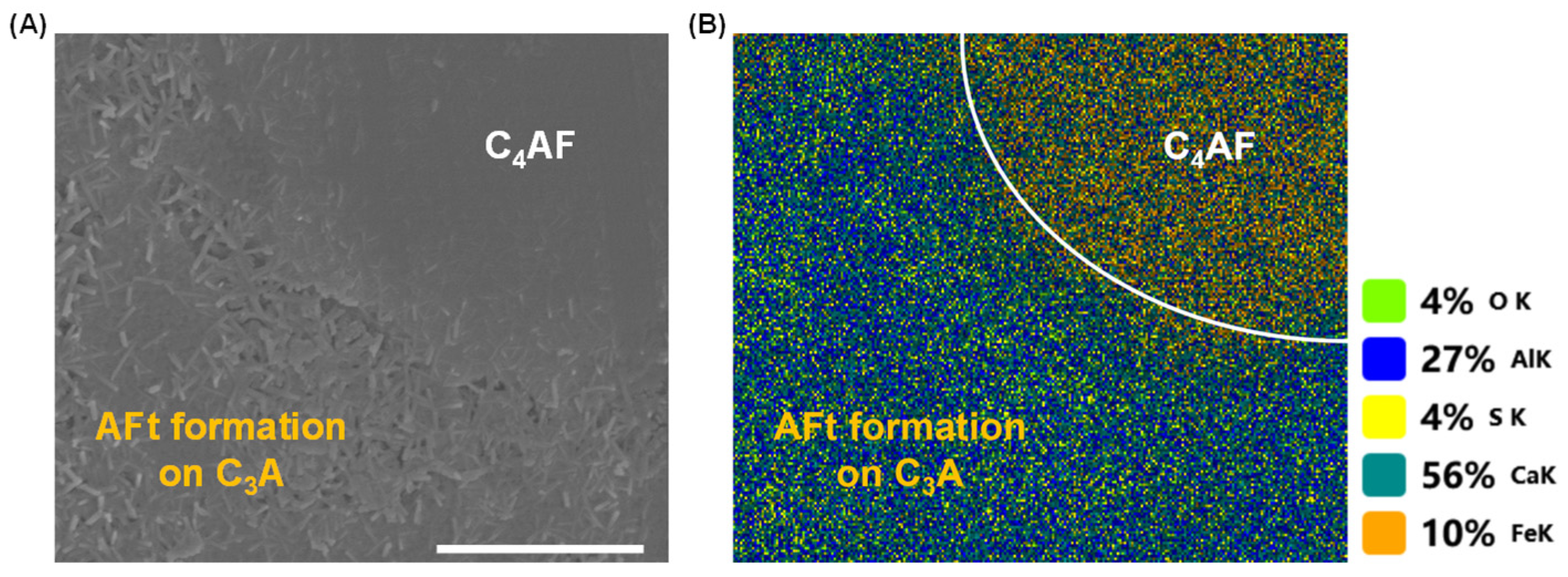
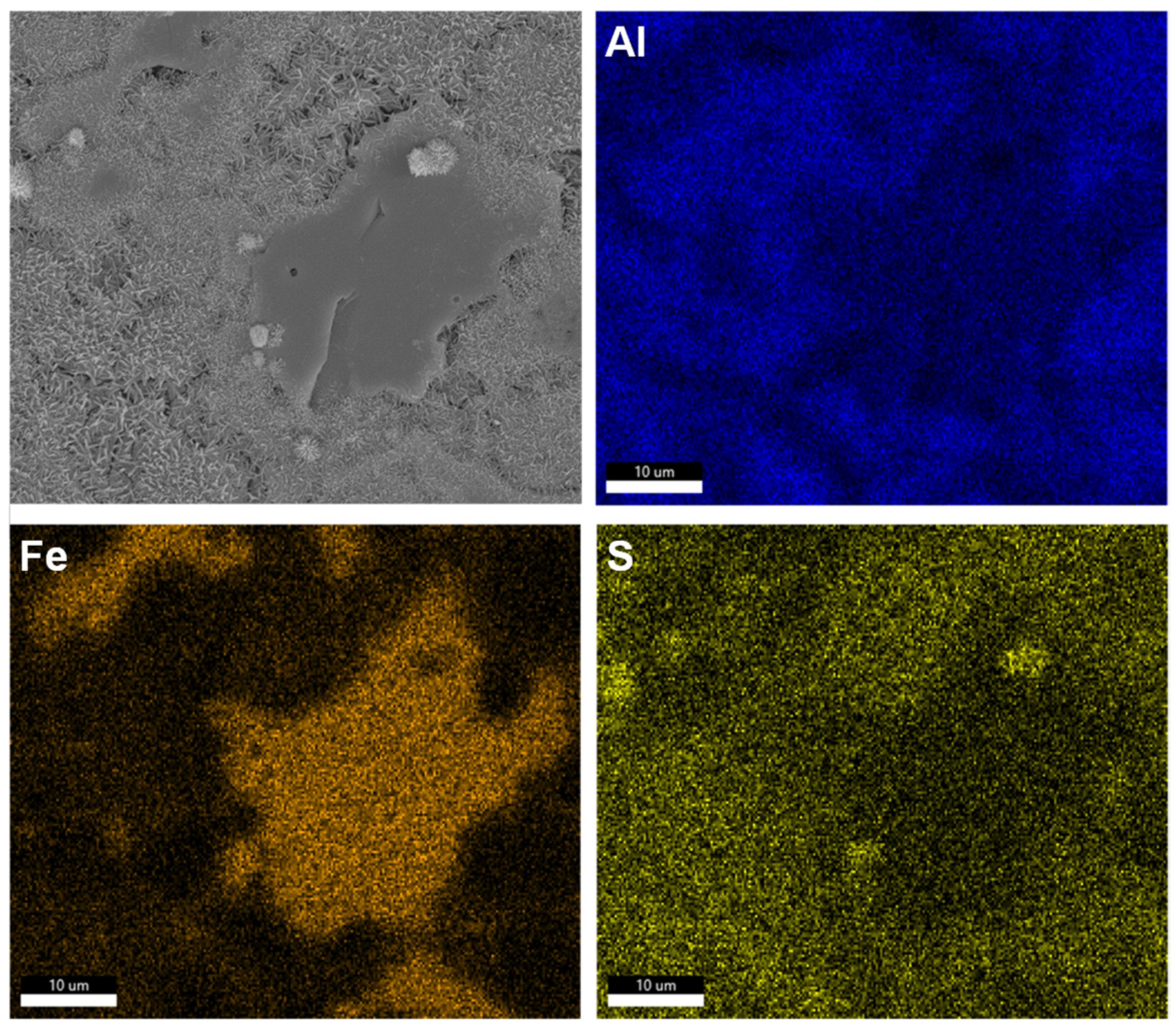
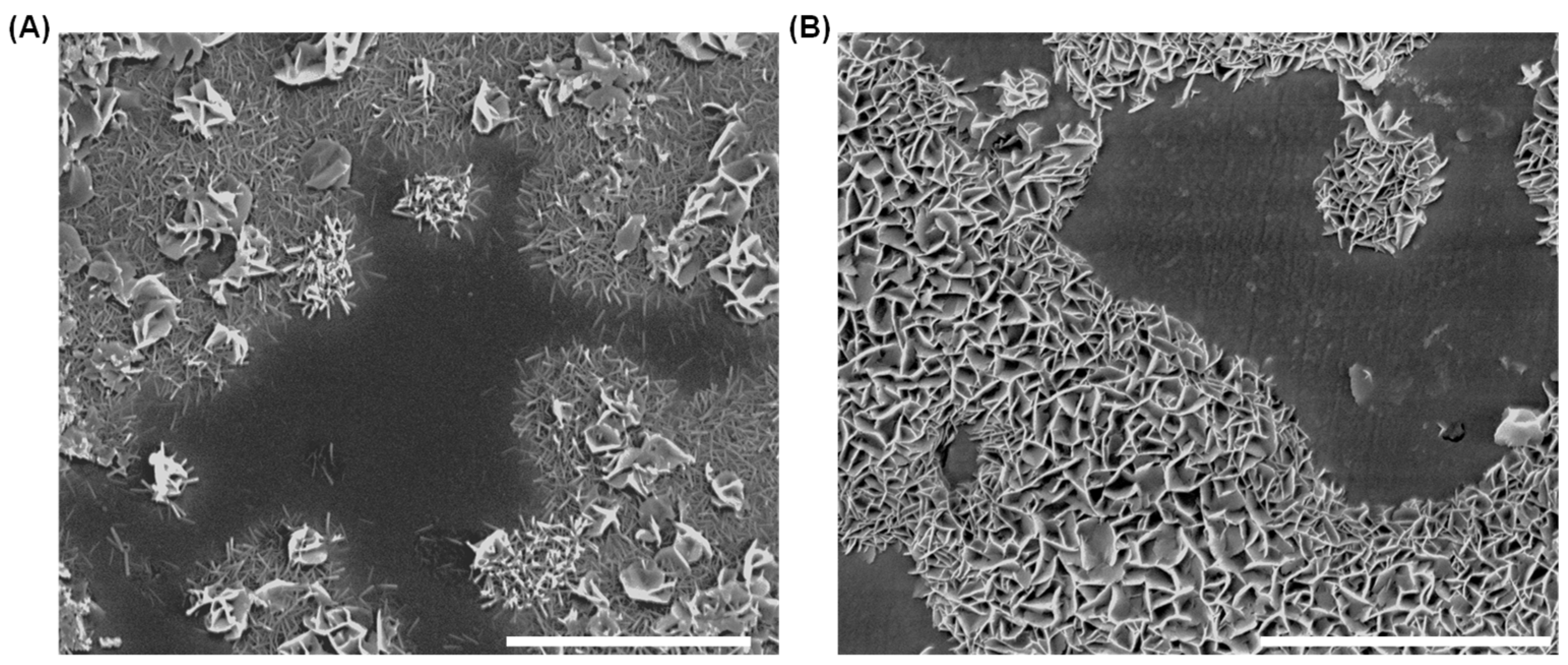
3.1. Dissolution Interaction in Water
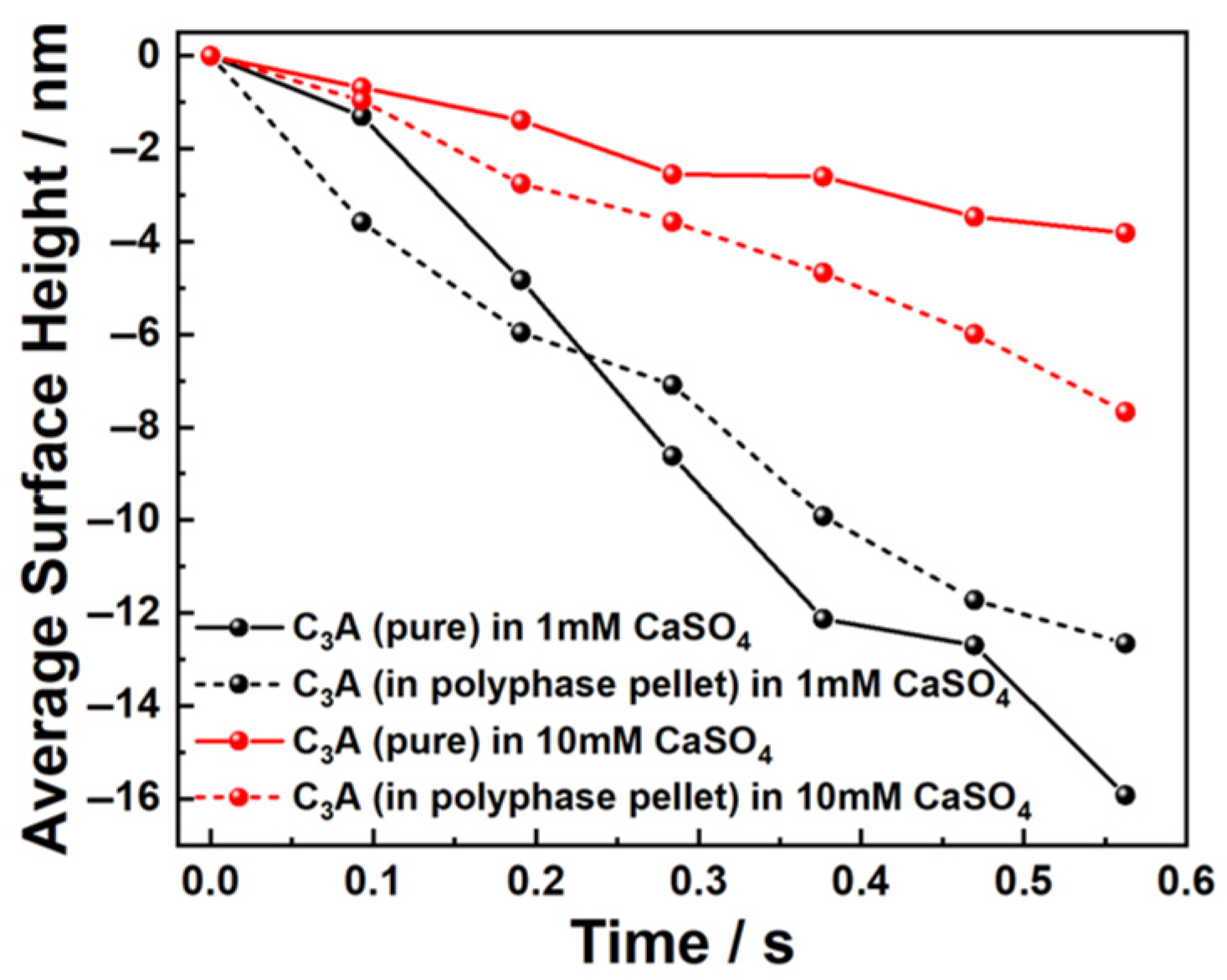
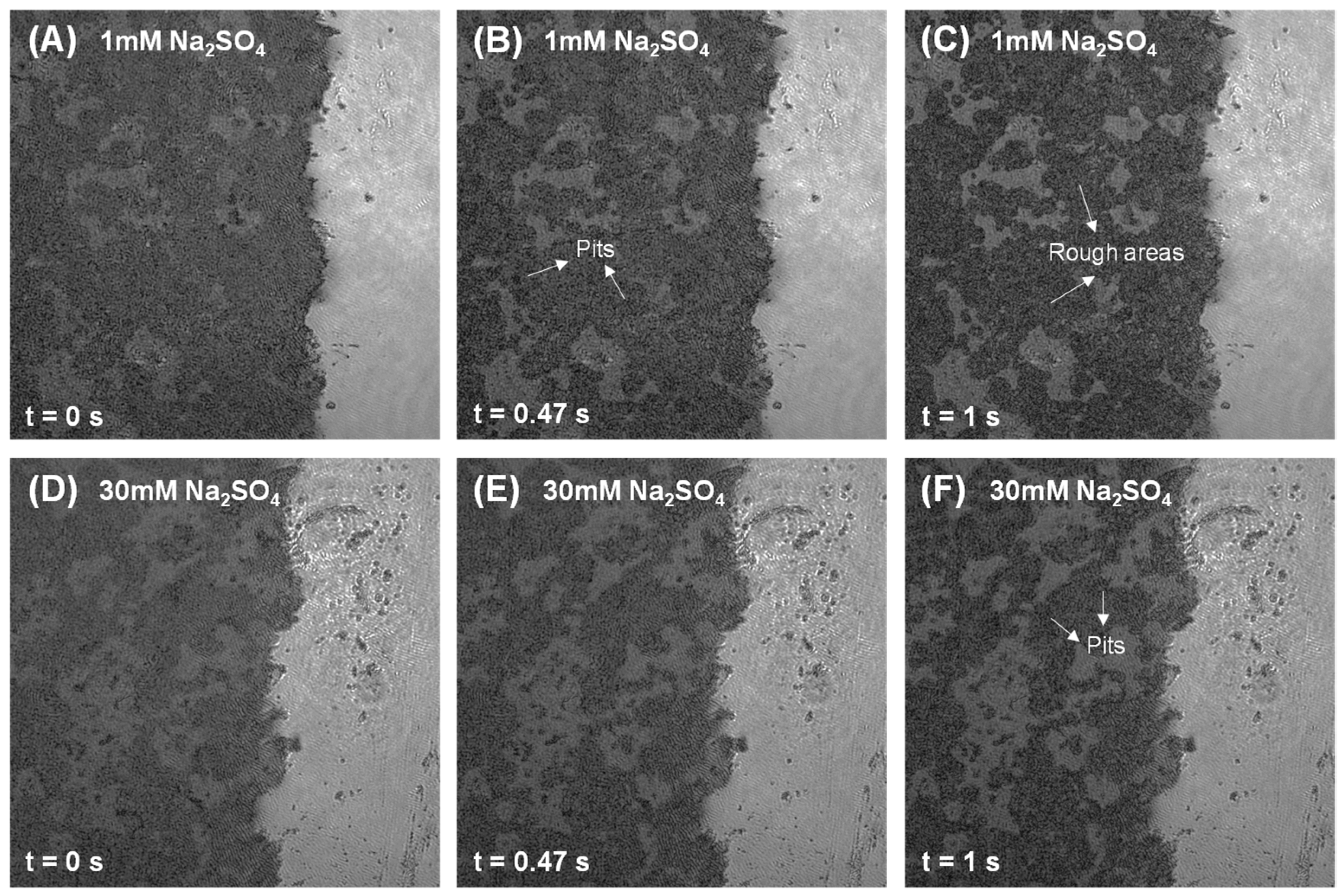
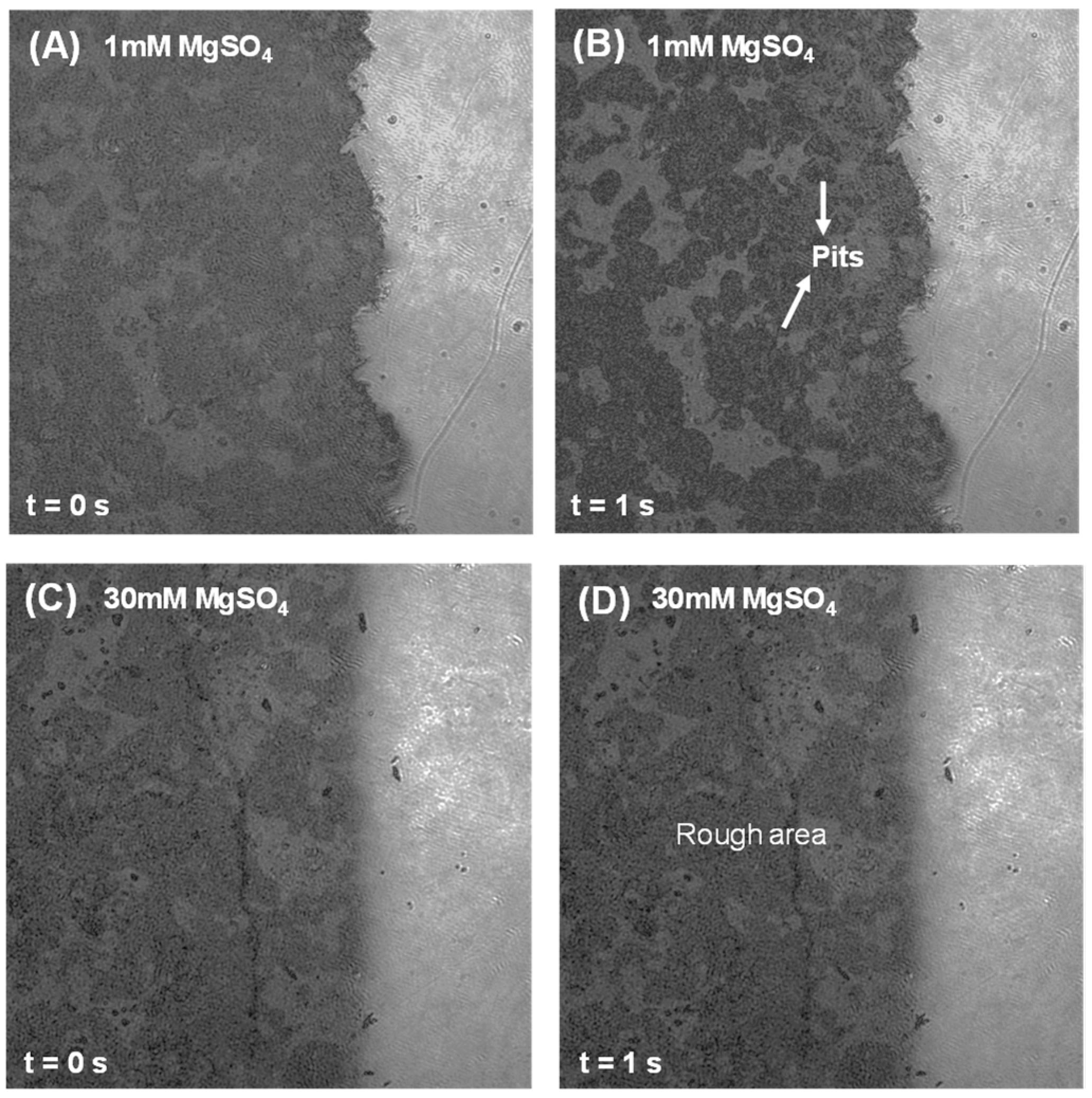
3.2. Dissolution and Early Hydration Interaction in Sulfate Aqueous Solutions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flatt, R.J.; Martys, N.; Bergström, L. The Rheology of Cementitious Materials. MRS Bull. 2004, 29, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Panda, S.K.; Nayak, S. Rheology of Concrete: Critical Review, Recent Advancements, and Future Prospectives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 132007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.; Noman Husain, M.; Chaudhary, S. Factors Affecting the Rheology of Cement-Based Composites: A Review. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 108, e20429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isteri, V.; Ohenoja, K.; Hanein, T.; Kinoshita, H.; Illikainen, M.; Tanskanen, P.; Fabritius, T. The Effect of Fluoride and Iron Content on the Clinkering of Alite-Ye’elimite-Ferrite (AYF) Cement Systems. Front. Built Environ. 2021, 7, 698830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shen, P.; Yang, L.; Rao, M.; Nie, S.; Wang, F. Development of High-Ferrite Cement: Toward Green Cement Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Ouzia, A.; Juilland, P.; Kunhi Mohamed, A. Advances in Understanding Cement Hydration Mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Matschei, T.; Georget, F.; Juilland, P.; Mohamed, A.K. Advances in Hydration and Thermodynamics of Cementitious Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 174, 107332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoleau, L.; Nonat, A. A New View on the Kinetics of Tricalcium Silicate Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, C.; Perfler, L.; Lackner, R. Deconvolution of Main Hydration Kinetic Peaks in Properly Sulfated Portland Cements with Boundary Nucleation and Growth Models and Relation to Early-Age Concrete Strength Development. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bullard, J.W. A Determination of Hydration Mechanisms for Tricalcium Silicate Using a Kinetic Cellular Automaton Model. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.W.; Scherer, G.W.; Thomas, J.J. Time Dependent Driving Forces and the Kinetics of Tricalcium Silicate Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 74, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.W.; Hagedorn, J.; Ley, M.T.; Hu, Q.; Griffin, W.; Terrill, J.E. A Critical Comparison of 3D Experiments and Simulations of Tricalcium Silicate Hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 1453–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quennoz, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Hydration of C3A-Gypsum Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Santacruz, I.; Sanfélix, S.G.; Fauth, F.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Torre, A.G. De Hydration of C 4 AF in the Presence of Other Phases: A Synchrotron X-Ray Powder Diffraction Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Skibsted, J.; Cizer, Ö. A Quantitative Study of the C3A Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.; Matschei, T.; Stephan, D. The Hydration of Tricalcium Aluminate (Ca3Al2O6) in Portland Cement-Related Systems: A Review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 168, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Ling, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, X.; Gu, T.; Liu, H.; Ling, C. New Elucidating into the Microstructural Evolution Mechanisms and Micromechanical Properties of C4AF and Gypsum Synergistic Hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Feng, P.; Liu, Y. Effects of Magnesium and Chloride Ions on the Early-Age Hydration of C3A in the Presence of Gypsum. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 4025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.; Breen, C.; Yarwood, J.; Phipps, J.; Maitland, G. In Situ Raman Analysis of Hydrating C3A and C4AF Pastes in Presence and Absence of Sulphate. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2006, 105, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.; Bénard, A.; El Mrabet, S.; Masion, A.; Moulin, I.; Briois, V.; Olivi, L.; Bottero, J.-Y. Evolution of Iron Speciation during Hydration of C4AF. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K.; Fernández-Carrasco, L.; Flatt, R.J.; Heinz, H. A Force Field for Tricalcium Aluminate to Characterize Surface Properties, Initial Hydration, and Organically Modified Interfaces in Atomic Resolution. Dalt. Trans. 2014, 43, 10602–10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutisya, S.M.; de Almeida, J.M.; Miranda, C.R. Molecular Simulations of Cement Based Materials: A Comparison between First Principles and Classical Force Field Calculations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 138, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Si, W.; Yu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, G.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Molecular Insight into the Initial Hydration of Tricalcium Aluminate. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Shen, D.; Wu, W.; Jin, B.; Wu, S. Hydration Inhibition Mechanism of Gypsum on Tricalcium Aluminate from ReaxFF Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Quantum Chemical Calculation. Mol. Simul. 2021, 47, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axthammer, D.; Lange, T.; Dengler, J.; Gädt, T. Early Hydration and Viscoelastic Properties of Tricalcium Aluminate Pastes Influenced by Soluble Sodium Salts. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 190, 107788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.J.; Geng, G.; Rodriguez, E.D.; da Rosa, P.; Kirchheim, A.P.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Solution Chemistry of Cubic and Orthorhombic Tricalcium Aluminate Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.J.; Geng, G.; Li, J.; Rodríguez, E.D.; Ha, J.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Sposito, G.; Lammers, L.N.; Kirchheim, A.P.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Role of Adsorption Phenomena in Cubic Tricalcium Aluminate Dissolution. Langmuir 2017, 33, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Ren, Q.; He, J.; Jiang, S.; Cheng, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, M. New Understanding of Early Hydration of C4AF under Surface Vitrification. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Feng, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Bullard, J.W. In Situ Nano-Scale Observation of C3A Dissolution in Water. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 132, 106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Feng, P.; Liu, J. Dissolution and Early Hydration of Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite (C4AF) in Water and in Aqueous Sulfate Solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 186, 107676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Feng, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Bullard, J.W. Dissolution and Early Hydration of Tricalcium Aluminate in Aqueous Sulfate Solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 137, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaga, A.C. Kinetic Theory in the Earth Sciences; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Feng, P.; Lu, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Bullard, J.W. Solubility of Tricalcium Aluminate from 10 °C to 40 °C. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 162, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quennoz, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Interactions between Alite and C3A-Gypsum Hydrations in Model Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 44, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, F.; Scrivener, K. Factors Influencing the Sulfate Balance in Pure Phase C3S/C3A Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 133, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, F.; Scrivener, K. The Influence of Sulfate Addition on Hydration Kinetics and C-S-H Morphology of C3S and C3S/C3A Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 160, 106930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeluszna, E.; Kotwica, L. New Insights into the Role of Highly Reactive Pozzolans in the Early Hydration Process of C3S and C3A Monitored by Conductometry, Calorimetry, Phase Composition and Microstructure Analyses. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 452, 138950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra, M.; Mazur, A.S. Long-Term Sulfate Resistance of Synthesized Cement Systems with Variable C3A/C4AF Ratio at Low Temperature or Ambient Conditions: Insights into the Crystalline and Amorphous Phase Assemblage. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 160, 106902. [Google Scholar]
- Wesselsky, A.; Jensen, O.M. Synthesis of Pure Portland Cement Phases. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, D.P. Three-Dimensional Computer Simulation of Portland Cement Hydration and Microstructure Development. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Cao, J.; Duan, N. Defects and Their Behaviors in Mineral Dissolution under Water Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayana, N.; Naga Malleswara Rao, B.; Muralidhara Rao, T. Application of Optical Microscopy Techniques for the Evaluation of Raw Materials for Cement and Concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 397, 132425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruffo, M.; Mbogoro, M.M.; Edwards, M.A.; Unwin, P.R. Holistic Approach to Dissolution Kinetics: Linking Direction-Specific Microscopic Fluxes, Local Mass Transport Effects and Global Macroscopic Rates from Gypsum Etch Pit Analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoleau, L.; Schreiner, E.; Nonat, A. Ion-Specific Effects Influencing the Dissolution of Tricalcium Silicate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 59, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, F.; Hu, S.; Lu, Y.; Rao, M.; Mu, Y. Brownmillerite Hydration in the Presence of Gypsum: The Effect of Al/Fe Ratio and Sulfate Ions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 5545–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Snellings, R.; Lothenbach, B. A Practical Guide to Microstructural Analysis of Cementitious Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781498738675. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, S.; Feng, P. Dissolution and Early Hydration Interaction of C3A-C4AF Polyphase in Water and Aqueous Sulfate Solutions. Materials 2025, 18, 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143399
Ye S, Feng P. Dissolution and Early Hydration Interaction of C3A-C4AF Polyphase in Water and Aqueous Sulfate Solutions. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143399
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Shaoxiong, and Pan Feng. 2025. "Dissolution and Early Hydration Interaction of C3A-C4AF Polyphase in Water and Aqueous Sulfate Solutions" Materials 18, no. 14: 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143399
APA StyleYe, S., & Feng, P. (2025). Dissolution and Early Hydration Interaction of C3A-C4AF Polyphase in Water and Aqueous Sulfate Solutions. Materials, 18(14), 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143399




