Abstract
Rare-earth-based AB2-type compounds with Laves phase structure are readily subject to hydrogen-induced amorphization and disproportionation upon hydrogenation. In this work, we conducted the Sc alloying on Y0.95Ni2 to improve its hydrogen storage properties. The results show that the amorphization degree of Y0.95Ni2 deepens with the increasing hydrogenation time, pressure, and temperature. The Y(Sc)0.95Ni2 ternary compounds show a significant improvement in reversibility and dehydriding thermodynamics due to the reduced atomic radius ratio RA/RB and cell volume. Hydrogen-induced amorphization is fully eliminated in the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2. The Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 delivers a reversible hydrogen storage capacity of 0.94 wt.% and the dissociation pressure of 0.095 MPa at the minimum dehydrogenation temperature of 100 °C.
1. Introduction
Numerous intermetallic compounds in the formula of ABn, in which A is the strong hydride-forming elements and B is weak hydride-forming elements, have been considered to be a potential hydrogen storage medium for either gaseous or electrochemical applications [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Among them, AB2-type intermetallic compounds possess higher theoretical specific capacity than the most widely used AB5-type rare-earth compounds. Zr-based and Ti-based compounds with cubic MgCu2-type (C15) or hexagonal MgZn2-type (C14) structure could store more than 2.0 wt.% hydrogen [7,8,9]. However, the rare-earth-based AB2-type compounds have rarely been considered for reversible hydrogen storage because of the hydrogen-induced amorphization (HIA) and phase disproportionation (HID) upon hydrogenation [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. For example, the YFe2 with cubic C15 structure would experience four steps of structural change in the hydrogenation: the formation of crystalline hydride YFe2Hx, the transformation of crystalline YFe2Hx to non-crystalline YFe2Hx, precipitation of YH3 from non-crystalline hydride, and the decomposition into YH3 and α-Fe [18].
The HIA and HID mechanisms of several representative rare-earth-based AB2-type compounds have been comprehensively investigated in early studies by Aoki et al. [19,20]. The hydrogenation pressure, time, and temperature dependence has been demonstrated. For example, the structural change of DyNi2 during hydrogen absorption is dependent on the pressure. The decomposition phases DyNi5 and DyH3 were finally obtained above 2.0 MPa hydrogen [21]. The occurrence of HIA and HID means the structural instability of AB2-type compounds, especially as hydrogen atoms enter the tetrahedral interstices and cause the lattice expansion. The structural stability of rare-earth-based AB2-type compounds is closely related to the atomic radius ratio RA/RB of the constituting A and B elements. The ideal RA/RB value for the cubic Laves phase structure is 1.225 [22], and the larger the RA/RB deviation from the value of 1.225, the more unstable Laves phase structure. Aoki et al. proposed a critical RA/RB value of 1.37 as the judgment factor of HIA by summarizing a large variety of AB2-type hydrogen storage compounds [20]. Since rare-earth elements possess a relatively large atomic radius, most rare-earth-based AB2-type compounds have a RA/RB value exceeding 1.37 and, thus, are readily subject to HIA.
Rare-earth-based compounds form the largest subset of the AB2-type Laves phase compounds [23], and their potential for hydrogen storage is worthy of more exploration to overcome the HIA problem by compositional and structural modification. Our previous studies show that the B-side substitution with Al and the A-side alloying with Zr could effectively inhibit the HIA and achieve reversible hydrogen storage [24,25,26,27]. The YFe1.7Al0.3 delivers a reversible hydrogen storage capacity of 1.38 wt.%, but the complete hydrogen desorption must be conducted in a dynamic vacuum at 200 °C [24]. The Zr alloying could realize the reversible hydrogen absorption with the elevated dissociation pressure of YFe2 because of the reduced cell volume [25]. Zhang et al. [28] reported that the pseudo-binary Sm1.25Mg0.75Ni4 compound could reversibly absorb and desorb ca. 0.95 wt.% hydrogen without the occurrence of HIA at 25 °C.
Regarding the Y0.95Ni2 compound with a C15 superlattice structure, the crystalline hydride Y0.95Ni2H2.6 with a capacity of 1.27 wt.% has been reported, but further increasing the hydrogen capacity would result in amorphization [29]. Zhang et al. reported that the Y0.95Ni2 experienced gradual amorphization during absorption/desorption cycling under gaseous hydrogen at ambient temperature [30]. In this work, we conducted the Sc alloying on Y0.95Ni2 to suppress the HIA because the Sc element has a relatively smaller atomic radius (1.66 Å) than Y (1.78 Å), and, thus, the RA/RB value could be decreased. The effect of Sc content on the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Y–Sc–Ni compounds have been investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
Commercial Y, Sc, and Ni ingots with a purity of 99.9% were used as the starting materials. Y0.95-xScxNi2 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7) alloys were prepared by arc melting under a high purity Argon atmosphere with Y, Sc, and Ni bulks in proper proportion. All samples were remelted four to five times and annealed at 950 °C for 4 days to obtain homogenous composition and structure. The alloys were crushed into powder and sieved by a 200-mesh (~74 um) sieve in the glove box for further measurement.
The composition and microstructure were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Zeiss Supra 40/VP, Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany) equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS). X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were conducted using a PANalytical Empyrean with Cu Ka radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å, PANalytical B.V., Almelo, The Netherlands). Rietveld refinements were conducted by using the Highscore Plus 4.5 software (PANalytical B.V.).
To investigate hydrogen-induced amorphization, the alloy powder was loaded into stainless steel reactors in an Argon-filled glove box. Then, the alloy powder was subjected to a hydrogenation reaction under different hydrogenation conditions: 3 MPa H2-100 °C-2 h, 3 MPa H2-100 °C-24 h, 3 MPa H2-200 °C-2 h, and 5 MPa H2-100 °C-24 h. The hydrogen desorption and crystallization processes of hydrogenated samples were monitored by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, Setaram SENSYS Evolution, SETARAM Instrumentation, Lyon, France) at a heating rate of 5 °C/min.
The measurement of hydrogen storage properties was conducted on an automatic Sieverts-type apparatus (AMC HP2000, Advanced Materials Corporation, Pittsburgh, America). About a 1.3 g sample was put into the sample holder, the hydriding, and dehydriding pressure-composition isotherms (PCI) of Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 compound were measured at different temperature.
3. Results
3.1. Structure of Y(Sc)0.95Ni2 Compounds
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of as-annealed Y0.95-xScxNi2 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7) compounds. The structural parameters of all compounds are refined by the Highscore Plus 4.5 software and summarized in Table 1. For the compounds with the Sc content of 0, 0.1, and 0.3, in addition to the strong Bragg peaks of cubic C15 Laves phase (MgCu2-type structure, space group Fdm), some extra weak Bragg peaks indicate the formation of the C15 superstructure (C15s) with the space group of F3m. The C15s structure of Y0.95Ni2 has a doubled lattice constant of 14.35 Å compared with the C15 structure. The structural refinement by Latroche et al. shows that most atoms in the C15s structure are shifted from the ideal atomic positions expected from the C15 structure [31]. It is noted that the Y vacancies in the 4a site could stabilize the Laves phase structure of nonstoichiometric Y0.95Ni2 with a large RA/RB value of 1.424 [29]. Since the Sc content is larger than 0.3, the weak peaks of the superstructure disappear, implying the transformation from the C15s superstructure to the C15 structure. This transformation should be related to the decrease of the RY/RNi value due to Sc substitution, which results in the decrease of the number of ordered Y vacancies [31]. The Rietveld refinement results indicate that the 4a site occupancy of the Y vacancy for Y0.85Sc0.1Ni2 is 0.421, which decreases to almost zero for the Y0.65Sc0.3Ni2. The Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 has an RA/RB value of 1.353, which is much lower than that of the Y0.95Ni2. Therefore, the ScNi2 phase with the C15 structure is identified for the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 [32]. EDS analysis (Figure 2) shows that the representative compound Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 has a homogeneous microstructure and distribution of Y and Sc elements. Further, the EDS compositions of each Y–Sc–Ni compound is highly consistent with the designed ones, as shown in Table 1.
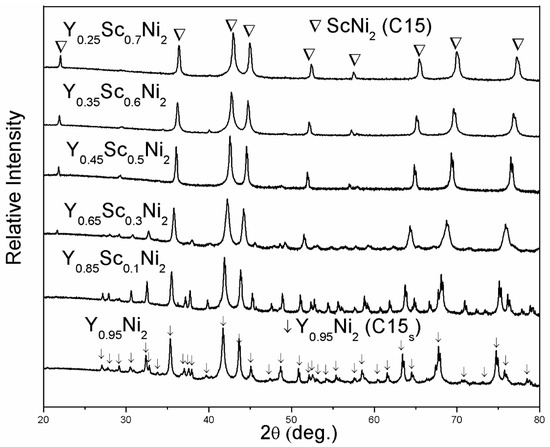
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of as-annealed Y-Sc-Ni compounds.

Table 1.
Structural parameters of Y0.95−xScxNi2 compounds.
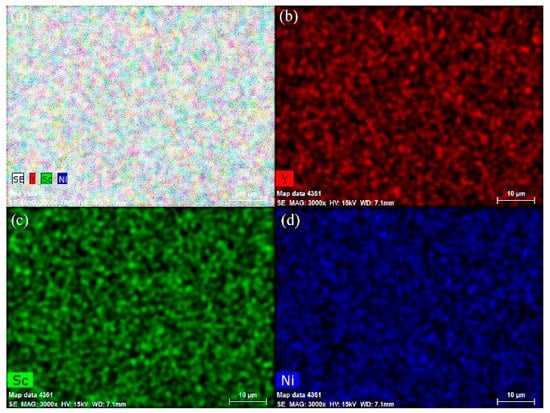
Figure 2.
EDS elemental mapping (a–d) of as-annealed Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2.
3.2. Hydrogen-Induced Amorphization of Y0.95Ni2
The effect of hydrogenation temperature, time, and pressure on the HIA of Y0.95Ni2 is investigated. Figure 3 compares the structures of Y0.95Ni2 hydrogenated under different conditions with the as-annealed Y0.95Ni2. After hydrogenation at 100 °C-3 MPa-2 h, Figure 3b shows that all Bragg peaks shift toward the low angle direction, indicating the formation of crystalline hydride of Y0.95Ni2. The interstitial hydride also adopts the same C15s structure. As shown in Figure 3c,d there exists a broad scattering peak at 30° to 45° in addition to the diffractions of crystalline hydride, indicating the formation of amorphous phase at an elevated temperature of 200 °C or prolonged time of 24 h. It is noted that the present Y2O3 phase may be related to the partial oxidization of Y during the arc-melting or hydrogenation. When hydrogenated at 100 °C-5 MPa-24 h, the hydrogenated product consists of the major amorphous phase, indicating full transformation from crystalline hydride to non-crystalline hydride under the elevated hydrogenation pressure. Hence, it is assumed that the increased hydrogen storage capacity due to the increased hydrogenation temperature, pressure, and time results in the destruction of the Laves phase structure of Y0.95Ni2 hydride, which is in line with other rare-earth RENi2 compounds [14].
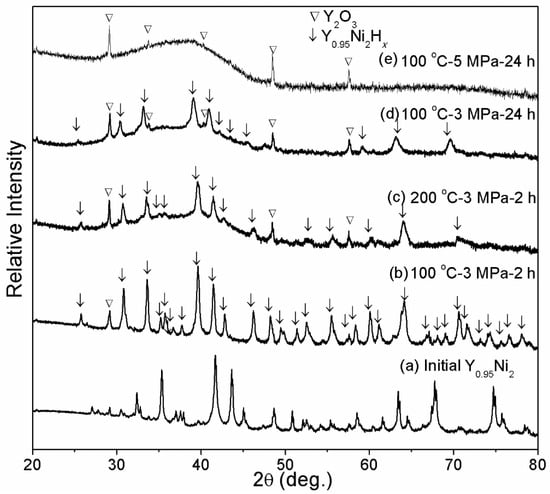
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of Y0.95Ni2 after hydrogenation under different temperatures, hydrogen pressure, and times. (a) Initial Y0.95Ni2; (b) 100 °C-3 MPa-2 h; (c) 100 °C-3 MPa-2 h; (d) 100 °C-3 MPa-24 h; (e) 100 °C-5 MPa-24 h.
3.3. Hydrogen-Induced Amorphization of Y–Sc–Ni Compounds
Figure 4 shows the XRD patterns of Y0.95−xScxNi2 (x = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7) compounds after hydrogenation at 100 °C-5 MPa-24 h. Like the Y0.95Ni2, the full HIA occurs for the Y0.85Sc0.1Ni2. With the increasing Y content of 0.3–0.6, the Bragg peaks of crystalline hydride with a C15 structure become intensifying, indicating that the HIA is partially suppressed due to the Sc alloying. The absence of the broadening scattering peak and the presence of C15 diffractions indicate that the HIA is fully eliminated in the hydrogenation of Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2. As shown in Table 1, the RA/RB value of Y–Sc–Ni compounds decreases with increasing Sc content, being 1.353 for the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2. This result implies that the Sc alloying could improve the structural stability of Y0.95Ni2, which should be the structural reason for eliminating HIA.
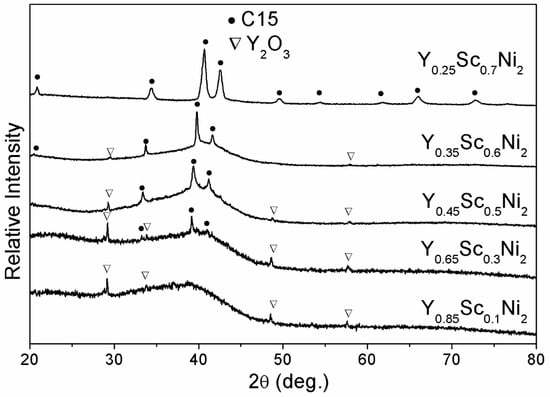
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of Y–Sc–Ni compounds after hydrogenation at 100 °C-5 MPa-24 h.
Figure 5a further shows the DSC profiles of Y–Sc–Ni compounds hydrogenated under 100 °C-5 MPa-24 h. The XRD patterns of DSC samples at specific temperatures are shown in Figure 5b. As shown in Figure 5a, a rather broad endothermic peak is followed by a sharp exothermic peak, which is attributed to the dehydrogenation of non-crystalline hydride and the crystallization of non-crystalline hydride, respectively [33]. This assumption is further confirmed by XRD. At the T1 temperature of the DSC curve of the Y0.95Ni2, no crystalline phase exists in addition to the Y2O3. At the T2 temperature, the presence of YH2 and YNi3 phases indicates the crystallization of non-crystalline hydride and subsequent decomposition. Similar DSC results are also reported for the GdNi2 [34], SmNi2 [35], and YNi2 [36] compounds. With the increasing Sc content, the broad endothermic peak contains a sharp part with an increasing shaded area. The broad endothermic peak below the broken line still corresponds to the hydrogen desorption from noncrystalline hydride, while the sharp endothermic peak with a shaded area is attributed to hydrogen release from the crystalline hydride [33]. In addition, the exothermic peak area and the peak temperature decrease with increasing Sc content. XRD patterns of DSC samples at T3, T4, T5, and T6 also show the weak peaks of YH2 and YNi3 phases, indicating that the amount of non-crystalline hydride decreases with increasing Sc content. For the hydrogenated Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2, the only sizeable endothermic peak in the DSC curve further verifies the elimination of HIA.
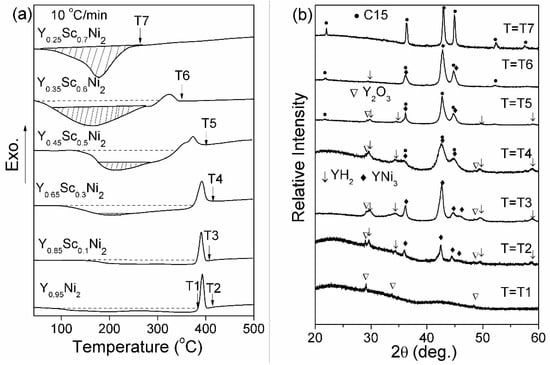
Figure 5.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) profiles of Y–Sc–Ni compounds after hydrogenation at 100 °C-5 MPa-24 h (a) and the corresponding XRD patterns (b).
3.4. Hydrogen Storage Properties of Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2
Figure 6a displays the hydriding and dehydriding PCI curves of Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 at different temperatures. There exists a clear plateau region in the hydriding curve, but the dehydriding curve starts to slope. At the midpoint of the PCI curve, the hydriding and dehydriding equilibrium pressures are determined to calculate the enthalpy change ΔH and entropy change ΔS, and the fitted van’t Hoff plots are displayed in Figure 6b. The derived dehydriding ΔH and ΔS for the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 are 35.59 kJ/mol·H2 and 93.83 J/K/mol·H2, respectively. In addition, the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 exhibits a reversible hydrogen storage capacity of 0.94 wt.% at 100 °C, corresponding to the hydride formula Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2H1.92. However, a small amount of hydrogen could not be released at 80 °C, which should be related to the low dissociation pressure. It is strange that, in the present work, the hydride of Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 has a lower capacity than the Y0.95Ni2D2.6 in Reference [29], which may be related to the increased equilibrium hydrogen pressure at a higher testing temperature of 100 °C. It is noted that the Y0.95Ni2D2.6 was determined at ambient temperature and deuterium pressure. As shown in the hydriding kinetic curves at 40 °C in Figure S1, the hydrogen absorption capacity increases and then decreases with Sc content. The Y0.65Sc0.3Ni2 delivers a maximum hydrogen absorption capacity of 1.53 wt. %, corresponding to the hydride formula Y0.65Sc0.3Ni2H2.93. It is noted that the minimum dehydrogenation temperature of the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2 is much lower than that of Y(Zr)Fe2 compounds [24,25,26,27]. Therefore, in addition to the improvement in the reversibility due to the reduced RA/RB, the Sc alloying also shows a significant promoting effect in the hydrogen sorption equilibrium pressure because of the reduced lattice constant.
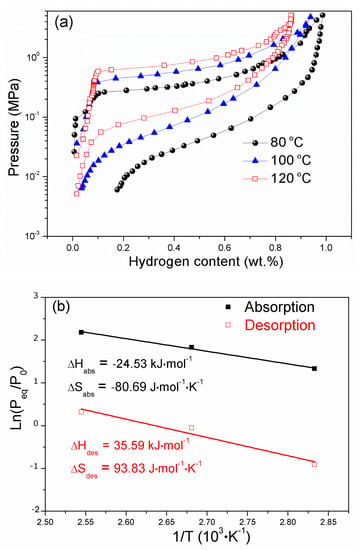
Figure 6.
Hydriding and dehydriding pressure-composition isotherms (PCI) curves (a) and van’t Hoff plots (b) for Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2.
4. Conclusions
The gaseous hydrogen storage reversibility of Y(Sc)0.95Ni2 compounds with different Sc contents has been investigated. The hydrogen-induced amorphization of Y0.95Ni2 is dependent on the hydrogenation pressure, time, and temperature. The Sc alloying could improve structural stability and suppress the hydrogen-induced amorphization. Fully reversible hydrogen storage has been achieved for the Y0.25Sc0.7Ni2, with a reversible capacity of 0.94 wt.% and dissociation pressure of 0.095 MPa at the minimum dehydrogenation temperature of 100 °C. Our work demonstrates the feasibility of rare-earth-based AB2-type compounds for reversible hydrogen storage applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/14/2/276/s1, Figure S1: Hydriding kinetic curves of Y-Sc-Ni compounds with different Sc contentsat 40 °C.
Author Contributions
Data curation, S.Z. and J.L. Formal analysis, S.Z. Funding acquisition, H.W. Investigation, S.Z. Methodology, J.L. Project administration, H.W. Resources, H.W. Supervision, J.L. Writing—original draft, S.Z. Writing—review & editing, H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFB1502105), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1601212, 51871098), the Fund for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51621001), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2016A030312011).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rusman, N.; Dahari, M. A review on the current progress of metal hydrides material for solid-state hydrogen storage applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 12108–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, G. A panoramic overview of hydrogen storage alloys from a gas reaction point of view. J. Alloy. Compd. 1999, 293, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J. The Current Status of Hydrogen Storage Alloy Development for Electrochemical Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 4574–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Progress of hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH rechargeable power batteries in electric vehicles: A review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 200, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Yang, J.; Fetcenko, M. Studies of off-stoichiometric AB2 metal hydride alloy: Part 1. Structural characteristics. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 11137–11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H. Thermodynamic Tuning of Mg-Based Hydrogen Storage Alloys: A Review. Materials 2013, 6, 4654–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovshinsky, S.; Fetcenko, M. Development of high catalytic activity disordered hydrogen-storage alloys for electrochemical application in nickel–metal hydride batterie. Appl. Phys. A 2001, 72, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltiel, D.; Jacob, I.; Davidov, D. Hydrogen absorption and desorption properties of AB2 laves-phase pseudobinary compounds. J. Less Common Met. 1977, 53, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J.; Huang, B.; Fetcenko, M. Studies of off-stoichiometric AB2 metal hydride alloy: Part 2. Hydrogen storage and electrochemical properties. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 11146–11154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Masumoto, T. Hydrogen-induced amorphization of intermetallics. J. Alloy. Compd. 1995, 231, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K. Amorphous phase formation by hydrogen absorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 304–306, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, H.; Iseki, M.; Hirscher, M.; Kronmuller, H. Hydrogen-induced structural changes of RFe2 intermetallic compounds. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 1999, 24, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Aoki, K.; Masumoto, T. Differential thermal analysis of hydrogen-induced amorphization in C15 Laves compounds RCo2. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, A179, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Masumoto, T. Hydrogen induced amorphization in RNi2 laves phases. Scr. Metall. 1987, 21, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterreicher, H.; Clinton, J.; Bittner, H. Hydrides of La-Ni compounds. Mater. Res. Bull. 1976, 11, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Wallace, W. Hydrogen absorption and its effect on structural and magnetic behavior of GdNi2. Solid State Commun. 1977, 24, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, I.; Shaltiel, D. Hydrogen sorption properties of some AB2 Laves phase compounds. J. Less Common Met. 1979, 65, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Li, H.; Dilixiati, M.; Ishikawa, K. Formation of crystalline and amorphous hydrides by hydrogenation of C15 Laves phase YFe2. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Li, H.; Ishikawa, K. Process and mechanism of hydrogen-induced amorphization in C15 Laves phases RFe2. J. Alloy. Compd. 2005, 404, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Li, X.; Masumoto, T. Factors controlling hydrogen-induced amorphization of C15 Laves compounds. Acta Metall. Mater. 1992, 40, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Aoki, K. A study on hydrogen-induced amorphization in C15 Laves phase DyNi2 under different hydrogen pressures. J. Alloy. Compd. 2005, 399, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paufler, P. Early work on Laves phases in East Germany. Intermetallics 2001, 19, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwik, J.; Nenkov, K.; Palewski, T. Effect of Sc on magnetic properties and heat capacity of R1–xScxNi2 (R = Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho) solid solutions: Comparative analysis. Intermetallics 2013, 32, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Reversible hydriding in YFe2–xAlx (x = 0.3, 0.5, 0.7) intermetallic compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 689, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M. Achieving the dehydriding reversibility and elevating the equilibrium pressure of YFe2 alloy by partial Y substitution with Zr. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 14541–14549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Increasing de-/hydriding capacity and equilibrium pressure by designing non-stoichiometry in Al-substituted YFe2 compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 704, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Achieving superior de-/hydrogenation properties of C15 Laves phase Y-Fe-Al alloys by A-side substitution. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 787, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, D. Magnesium effect on hydrogen-induced amorphization of Sm2–xMgxNi4 compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 711, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percheron-Guégan, A.; Paul-Boncour, V.; Latroche, M.; Achard, J. Structure of Y0.95Ni2 and its hydride. J. Less Common Met. 1991, 172, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, G.; Latroche, M.; Percheron-Guégan, A.; Sun, D. Relevance of hydrogen storage properties of ANi3 intermetallics (A = La, Ce, Y) to the ANi2 subunits in their crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 5388–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latroche, M.; Paul-Boncour, V.; Percheron-Guegan, A. Structural Instability in R1–xNi2 Compounds and Their Hydrides (R = Y, Rare Earth). Z. Phys. Chem. 1993, 179, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Li, C.; Guo, C.; Du, Z.; Li, J. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ni–Sc binary system. Calphad 2015, 48, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Masumoto, T. Solid state amorphization of intermetallic compounds by hydrogenation. J. Alloy. Compd. 1993, 194, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Li, X.; Masumoto, T. Differential thermal analysis of hydrogen-induced amorphization in C15 laves compounds GdM2 (M = Fe, Co, Ni). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 133, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadyhay, K.; Aoki, K.; Masumoto, T. The nature of hydrogen induced amorphization of SmNi2 laves compound. Scr. Met. 1987, 21, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, S.; Orimo, S.; Fujii, H. Structural change during amorphization and phase separation processes in the YNi2 H systems. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1996, 60, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).