Abstract
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are becoming one of the key trends in the development of nuclear technology, offering a flexible, safe and cost-effective alternative to large nuclear power plants. This review defines the “driving force” of SMRs as their ability to enhance safety, modular scalability, and fuel sustainability through innovative design and policy integration. It aims to provide a systematic assessment of technological trends, deployment strategies, and fuel innovations that underpin the future of nuclear energy. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the main classes of SMRs, categorised by fuel type and application, ranging from Low-Enriched Uranium (LEU) and High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) reactors to thorium-232, metallic fuel and reprocessed nuclear materials. The key technical advantages of SMRs are discussed—passive safety systems, extended fuel cycles (longer operational periods before refuelling compared to conventional reactors), modular production and compactness—which make such reactors particularly suitable for use in hard-to-reach regions, military facilities, in space and as part of hybrid power systems. Special attention is paid to the prospects of advanced fuel cycles, including the conversion of thorium to uranium-233 and the reuse of actinides, which contributes to waste reduction and supports the realisation of a closed nuclear cycle. The current status of SMR projects around the world is also analysed, highlighting the most promising solutions and discussing regulatory, infrastructure readiness and geopolitical factors.
1. Introduction
SMRs are relatively compact nuclear plants with a capacity of up to 30 MW(e), whereas microreactors are even smaller systems typically producing up to 50 MW(e) or less. Compared to conventional nuclear power plant(s) (NPPs) they take up less space, are easier to assemble and require less investment [1]. Due to their modular design, many SMRs are designed with factory fabrication capabilities, which allows faster delivery and installation even in remote or low-energy-access areas where the construction of large power units would be too expensive or complex [2].
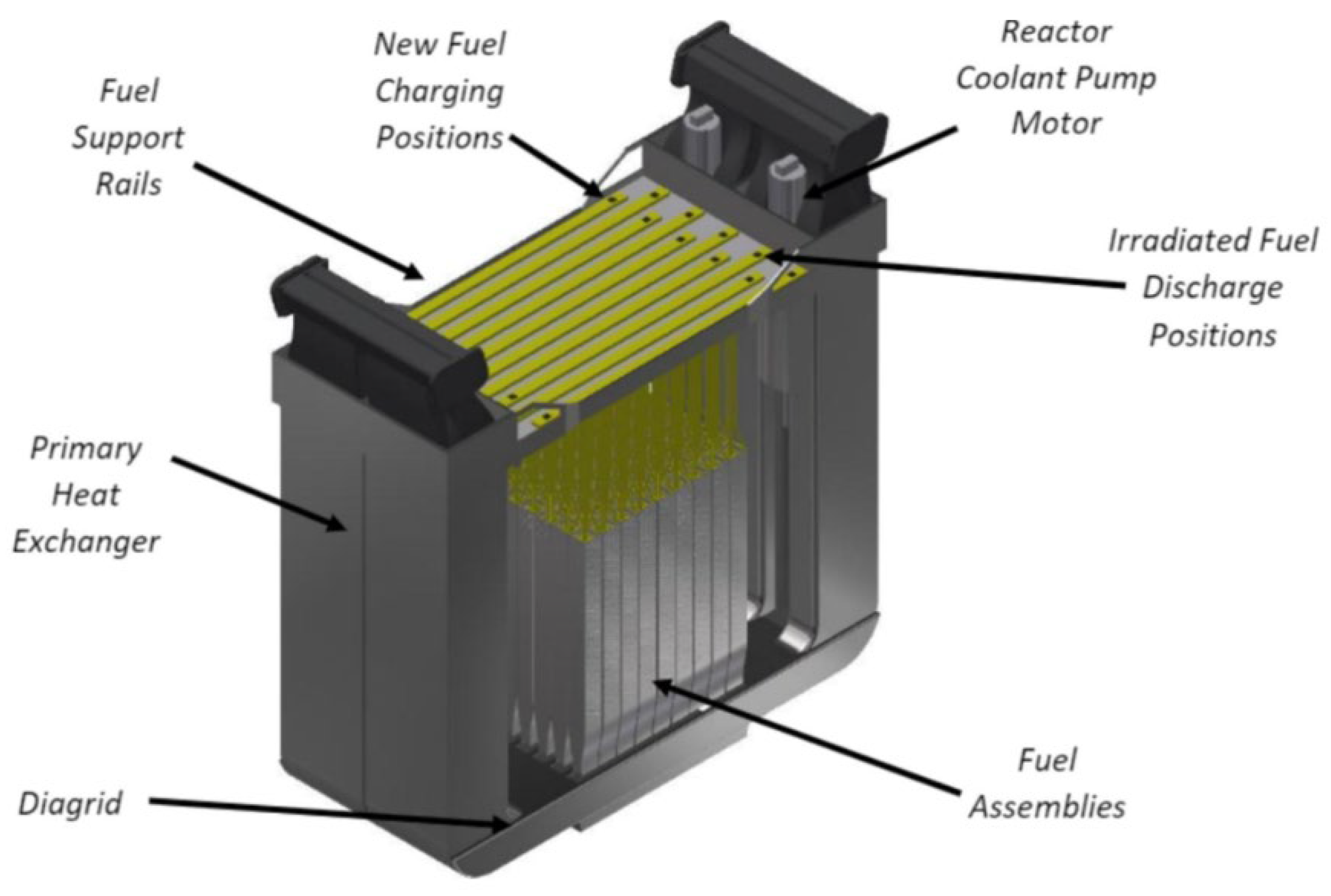
In addition to their relatively simple design, SMRs are characterised by high levels of safety, primarily based on passive safety systems, ensuring reliable operation under various conditions. Due to their relatively low power output and reduced operating parameters—such as lower core pressure, coolant temperature, and thermal power compared to conventional large-scale reactors—they can automatically shut down in the event of an abnormal situation without operator intervention or external power supply [3]. This is possible thanks to passive safety systems that operate through processes such as natural convection, gravity and pressure rise. These systems typically include passive residual heat removal units, gravity-fed emergency core cooling tanks, and containment cooling pools. By relying on inherent physical laws rather than active equipment or external power, they provide an additional layer of protection even in the case of total loss of power supply [4]. As a result, the risk of radioactive emissions into the environment is significant [5,6,7]. The main design and safety features of SMRs are illustrated in Figure 1.
Moreover, fuel replacement is much less frequent in SMRs—approximately every 3–7 years, whereas in conventional NPPs it is carried out every 1–2 years. Today, most SMRs are designed to use LEU (uranium enriched to less than 20% U-235), which is a safe and proven fuel [8,9]. In particular, the U.S. NuScale and Republic of Korea’s SMART operate on such uranium [4]. Argentina’s CAREM and China’s ACP100 use conventional uranium dioxide (UO2) fuel enriched to less than 5% U-235, and this is being developed with potential deployment in both national and international markets [10]. The ACP100, also known as Linglong One, is the first land-based small modular pressurised water reactor in China to enter commercial-scale construction, with its first unit under construction at the Changjiang site in Hainan Province since 2021. In addition to ACP100, China has pursued other innovative concepts such as the high-temperature gas-cooled reactor HTR-PM, which achieved grid connection in 2021, marking a milestone in Generation IV reactor development. Together, ACP100 and HTR-PM highlight China’s dual-track approach—developing both mature PWR-based SMRs and next-generation designs [11].
On the other hand, Russia’s RITM-200 reactors, which are already on icebreakers and are planned for the Arctic, use uranium with higher enrichment, ensuring autonomous operation in harsh conditions [12,13]. In addition, new-generation Micro Modular Reactors (MMRs), such as Moltex and TerraPower, are being actively developed. They use reprocessed nuclear fuel or innovative liquid-salt technologies based on thorium and uranium [14]. This makes nuclear power more sustainable and contributes to the reduction in nuclear waste generation and greenhouse gas emissions.
This article primarily focuses on Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and their technological development, while also providing an overview of Micro Modular Reactors (MMRs) as a subset of SMRs, categorised by fuel type and application. Both reactor plants fuelled by LEU and reactors fuelled by rarer and more promising fuels, such as thorium, and reprocessed nuclear fuel and uranium in various forms including HALEU and highly enriched uranium (HEU), including metallic compositions, are considered. Special attention is paid to new fuel cycles that can improve the efficiency and environmental friendliness of nuclear power. These include the transmutation of thorium into fissile uranium and the reuse of actinides, which can significantly reduce the amount of radioactive waste and move closer to a closed fuel cycle. Moreover, the article examines the current development of SMR technologies in the world: it highlights the most promising projects and analyses the regulatory and infrastructure challenges that may impact their licencing, construction, and operation.
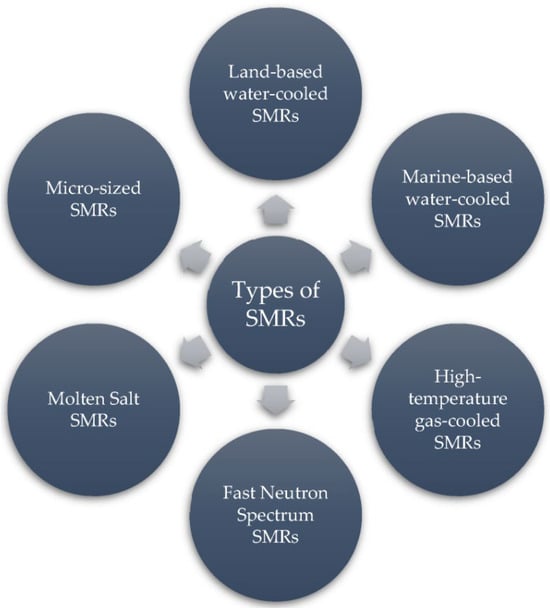
Figure 1.
SMR classification scheme from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) [15,16].
Figure 1.
SMR classification scheme from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) [15,16].
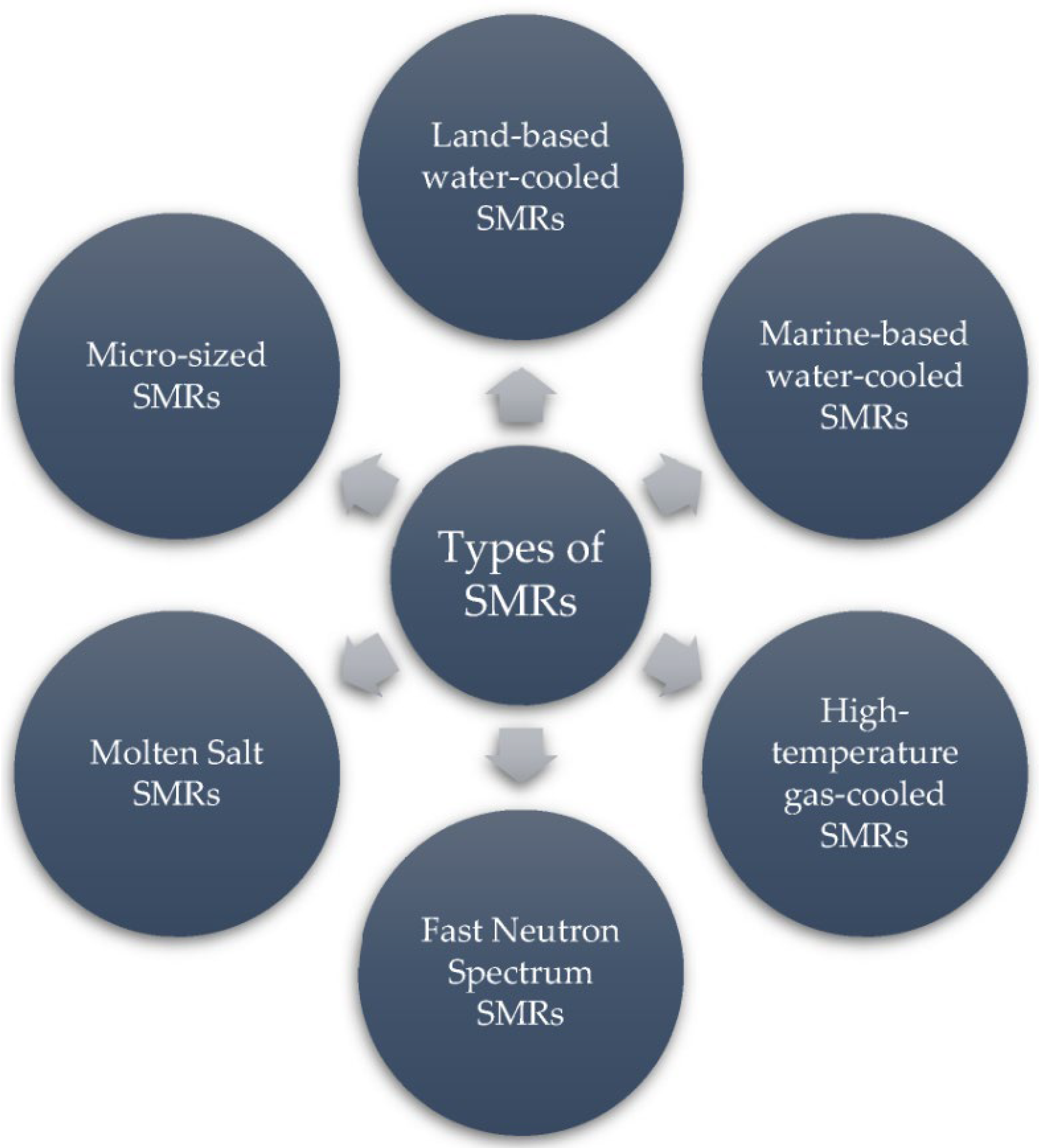
2. Advantages of Modular Nuclear Reactors
SMRs have a number of important advantages: advanced safety features, simple and reliable design, and the ability to be installed in remote or inaccessible areas where energy consumption is low [17]. In such regions, there is often no need for large-scale power generation facilities, and it is the SMRs that can effectively cover localised power needs [18]. The modular approach makes these reactors easier to standardise and suitable for mass production, which reduces construction costs and simplifies operation. Universal design elements and proven technical solutions make maintenance more predictable and economical. It is important to note, however, that small modular reactors are not a uniform technology. While all SMRs share certain design goals—such as compactness, modularity, and improved safety—their specific characteristics vary considerably depending on the reactor type. For example, water-cooled SMRs (such as NuScale or ACP100) rely on mature pressurised water reactor principles and emphasise proven safety systems, but offer only moderate thermal efficiency [19]. In contrast, high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) provide higher outlet temperatures that enable cogeneration and hydrogen production, though they face challenges with advanced fuel fabrication [20]. Liquid-metal fast reactors (LMFRs) promise closed-fuel-cycle potential and high power density, but require careful management of coolant reactivity and corrosion [21]. Finally, molten salt reactors (MSRs) introduce innovative liquid-fuel concepts with passive safety features, but still face materials and chemistry issues [22]. These differences demonstrate that generalisations should be made with caution, and each SMR concept should be evaluated in the context of its design features and intended applications.
Conventionally, SMR are divided by power level into two main categories [2]:
- Ultra-small modular reactors uSMRs, up to 50 MWe), used mainly in isolated areas, remote industrial sites, military bases and other areas with limited access to centralised power.
- SMR (50 to 300 MWe)—a balanced solution combining sufficient power with mobility, suitable for a wider range of applications, including power supply to small towns, industrial facilities and infrastructure.
One of the key advantages of SMRs is their high autonomy—they can operate for long periods of time without the constant presence of maintenance personnel [9,23]. And because these reactors are delivered as prefabricated modules, they can be quickly transported and started up in the most remote or inaccessible areas. This makes SMRs particularly useful not only for stable power supply in remote locations, but also for rapid responses in emergency situations. In addition, such plants are not only used in the power sector: they are also suitable for district heating, seawater desalination and even hydrogen production—a key element of future green energy [13,24].
Although today microreactors represent a real technological breakthrough in nuclear power, their history dates back to space exploration. Back in 1965, the United States launched the SNAP-10A nuclear reactor with a power of only 0.5 kW, which provided satellite operation for 43 days—until the electrical equipment failed. In 1964, the Soviet Union created the Romashka reactor, which operated on the principle of direct thermoelectric conversion of nuclear fission heat into electricity. It produced 6.1 MWh and operated for more than 15,000 h. Later, the USSR developed a 3 kW BUK unit, which was used in 32 space missions from 1970 to 1988. And in the 1980s, the US launched the SP-100 project, a concept of a lithium-cooled reactor for spacecraft using heat pipes and thermoelectric converters. Thus, microreactors have been serving for decades as a reliable source of energy in the most extreme conditions—from orbit to outer space [25,26,27].
It is important to realise that the so-called nuclear batteries used in some space missions are not full nuclear reactors. They are not based on a fission chain reaction, but on the natural radioactive decay of isotopes such as tritium (3H), strontium-90 (90Sr), plutonium-238 (238Pu) and curium-244 (244Cm). The heat produced is converted into electricity using the Seebeck thermoelectric effect. Usually, such sources produce only a few kilowatts and their efficiency is quite low. For example, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator, which is used in long-range spacecraft, can produce about 2 kW of electricity with a thermal output of 125 MW, giving an efficiency of only about 6.25 per cent [28,29]. Nevertheless, reliability and durability make these systems indispensable for environments where other power sources simply will not work. It is important to note, however, that small modular reactors are not a uniform technology. While all SMRs share certain design goals—such as compactness, modularity, and improved safety—their specific characteristics vary considerably depending on the reactor type. For example, water-cooled SMRs (such as NuScale or ACP100) rely on mature pressurised water reactor principles and emphasise proven safety systems, but offer only moderate thermal efficiency [19]. In contrast, HTGRs provide higher outlet temperatures that enable cogeneration and hydrogen production, though they face challenges with advanced fuel fabrication [20]. LMFRs promise closed-fuel-cycle potential and high power density, but require careful management of coolant reactivity and corrosion [21]. Finally, MSRs introduce innovative liquid-fuel concepts with passive safety features, but still face materials and chemistry issues [22]. These differences demonstrate that generalisations should be made with caution, and each SMR concept should be evaluated in the context of its design features and intended applications.
The low SMR is usually combined with compact dimensions, making it possible to install even where conventional reactors would not fit. Due to their compactness, such plants can easily fit into limited spaces—where the construction of a large nuclear plant would be impossible. They can be integrated into the infrastructure of cities, small towns, industrial plants, ports, ships and even remote sites with limited access [30]. In particular, Sweden’s 3 MW SEALER microreactor has a vessel weighing less than 30 tonnes, with a diameter of just 2.75 metres and a height of 6 metres—all of which fits into an area of about 600 m2 [31]. The more powerful US mPower (190 MW) weighs around 500 tonnes, but its design (4.15 m in diameter and 27.4 m high) allows it to be transported by rail. The ultra-compact ELENA (68 kW) can be disassembled into two modules, which is convenient for transporting it to hard-to-reach places. And the Danish Compact Molten Salt Reactor (CMSR) (100–115 MW) is only 2.5 m high, making it one of the lowest-profile plants. Other current examples include eVinci (0.2 to 15 MW), a compact waste-to-energy plant from Copenhagen Atomics (20 MW), as well as more powerful reactors such as SUPERSTAR (120 MW), UK SMR and Westinghouse SMR (up to 225 MW) [32]. All are being developed with a focus on mass production, mobility and versatility of application.
Table 1 summarises the current status of the SMR. It should be noted that there are around 90 SMR concepts under development worldwide. For clarity and conciseness, Table 1 includes only the most representative reactor designs that are either already in operation, under construction, or at an advanced stage of licencing. The selection also prioritises projects that have attracted significant international attention due to their technological maturity, unique design features, or relevance to current energy strategies. As such, the table highlights reactors that best illustrate the diversity of SMR technologies while maintaining focus on the most practically advanced concepts. So far, only one of them—RITM-200 reactor operating on Russian nuclear icebreakers—has been commissioned worldwide; the rest are still under development or under construction. Although some of the plants are slightly above the 300 MW threshold, they are still categorised as SMRs due to their modular architecture and compactness. Today, reactors fuelled by LEU (less than 20 per cent U-235) are the most widespread. This fuel meets international safety standards and is easier to handle. Such solutions include NuScale VOYGR Power Module (USA) [33], SMART (Republic of Korea) [34], CAREM (Argentina), ACP100 (China) [35] and the BWRX-300 boiling reactor from GE Hitachi (USA/Japan) [13,36,37]. All of them use proven uranium oxide (UO2) fuel similar to that used in conventional nuclear power plants. Russia’s RITM-200 reactor, which is already operating on nuclear icebreakers and is planned for use in land-based power plants, also uses uranium fuel, but with a higher level of enrichment. This makes it possible to extend the duration of the fuel campaign and increase the plant’s efficiency. Russia has also achieved commercial deployment of the KLT-40S, a small modular pressurised water reactor (SMR) with a thermal power of 150 MW. Two such reactors are installed on the floating nuclear power plant Akademik Lomonosov, which entered operation in 2019 and has been supplying power since 2020. The KLT-40S employs dispersed uranium dioxide fuel enriched up to 18.6%, embedded in an aluminium alloy matrix, and is designed for long autonomous operation in remote Arctic regions [38,39]. In addition to conventional solutions, reactors using alternative fuel types are being actively developed. For example, liquid salt reactors such as Seaborg CMSR (Denmark) and TAP (USA) use fuel in dissolved form, which makes it possible to reprocess it directly during operation. Fast sodium reactors such as the ARC-100 (Canada/USA), as well as metallic compact reactors such as Oklo Aurora, which, after its initial licence denial in 2022, is currently in the pre-application phase with the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)—focus on the use of reprocessed or highly enriched fuel. Thus, next-generation technologies open up new opportunities for a closed nuclear fuel cycle, reducing radioactive waste and increasing the sustainability of nuclear power in the long term [40,41,42,43].
In addition to differences in power level and fuel types, various SMR concepts also differ in their inherent safety features and potential accident scenarios (Table 2). Water-cooled SMRs (PWR, BWR, iPWR) rely on well-established Generation III+ safety measures, including passive residual heat removal systems and robust containment, but they remain vulnerable to loss-of-coolant accidents and require reliable emergency core cooling [44]. HTGRs feature coated particle (TRISO) fuel, which provides high resistance to fuel failure and enables passive decay heat removal, reducing the likelihood of core melt [45]. Liquid-metal-cooled fast reactors (sodium or lead-bismuth) achieve high thermal conductivity and natural circulation, which enhances passive safety; however, sodium is chemically reactive with water and air, and lead-bismuth systems face corrosion and polonium-210 generation issues [46]. Molten salt reactors use liquid fuel that operates at low pressure and can be drained into passive cooling tanks in emergency scenarios, minimising the risk of high-pressure accidents, but they face challenges related to long-term material corrosion and fuel salt chemistry control. The freeze plug is actively cooled to stay solid; loss of power leads to melting and passive fuel-salt draining, after which decay heat still requires passive removal in the drain tanks [22].
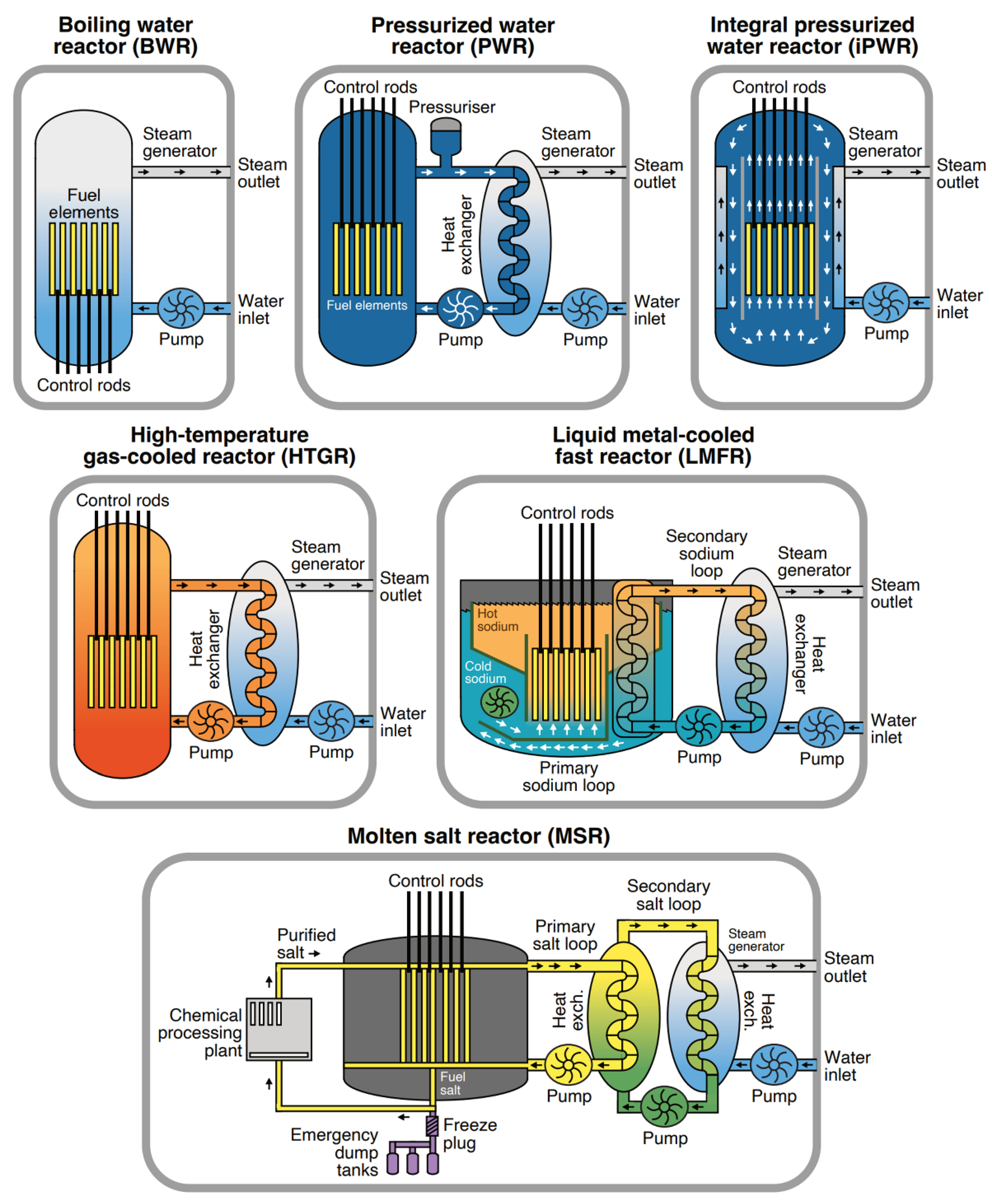
Figure 2 illustrates the main technological solutions underlying modern SMRs and highlights four principal reactor categories. These include (1) water-cooled SMRs (e.g., pressurised water and boiling water designs), which rely on conventional Rankine steam cycles; (2) HTGRs, which can also incorporate Brayton cycles using helium or air as the working fluid; (3) LMFRs, where sodium or lead coolants transfer heat to steam or hybrid cycles; and (4) MSRs, which use liquid fuel in fluoride or chloride salts and can be coupled to steam turbines or advanced conversion systems. Despite their structural and thermal design differences, all of these reactor types ultimately serve the same function: driving a turbogenerator that converts thermal energy into electricity. This classification underscores the versatility of SMR technology and demonstrates how diverse engineering pathways converge toward the common goal of reliable, scalable, and safe power generation.

Table 1.
Designs of modular reactors of different capacities [36,47,48,49].
Table 1.
Designs of modular reactors of different capacities [36,47,48,49].
| Reactor Name | Country | Power | Type | State |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seaborg CMSR | Denmark | <50 MWe | Liquid salt | Under development |
| USNC MMR | USA/Canada | 15 MWe | Gas-cooled, VTGR | Demonstration project |
| Oklo Aurora | USA | 1.5 MWe | Fast on metal | Development is suspended |
| TAP | USA | <50 MWe | Liquid salt | Cancelled project |
| Megapower | USA | 5 MWe | Metal-cooled | Development completed (military use) |
| NuScale VOYGR Power Module | USA | 77 MWe | Water–water | Licenced, in progress |
| SMART | Republic of Korea | 100 MWe | Water–water | Ready for construction |
| CAREM | Argentina | 32–125 MWe | Water–water | Construction of the first block |
| ACP100 | China | 125 MWe | Water–water | Construction |
| RITM-200 | Russia | 55 MWe | Water–water | In operation (on ships) |
| BANDI-60S | Republic of Korea | 60 MWe | Water–water | Development |
| Flexblue | France | ~160 MWe | Underwater, water–water | Concept |
| Holtec SMR-160 | USA | 160 MWe | Water–water | At the licencing stage |
| ARC-100 | Canada/USA | 100 MWe | Fast, sodium | Development |
| GE Hitachi BWRX-300 | USA/Japan | 300 MWe | Boiling water–water | Licencing |
| X-energy Xe-100 | USA | 80 × 4 = 320 MWe | Gas-cooled, VTGR | Development |
| SVBR-100 | Russia | 100 MWe | Fast, lead-bismuth | The project is suspended |

Table 2.
Safety characteristics and potential risks of SMR concepts [22,46,50].
Table 2.
Safety characteristics and potential risks of SMR concepts [22,46,50].
| Reactor Type | Key Safety Features | Potential Accident Scenarios/Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Water-cooled SMRs (PWR, BWR, iPWR) | Proven technology, passive cooling systems, robust containment, low-enriched UO2 fuel | Loss-of-coolant accidents (LOCA), need for reliable emergency core cooling, residual heat removal in station blackout |
| HTGRs | TRISO fuel with high fission-product retention, low power density, strong passive decay heat removal | Graphite oxidation in air ingress, helium leakage, structural integrity at very high temperatures |
| LMFRs, sodium, lead-bismuth | Excellent heat transfer, natural circulation, potential for inherent shutdown response | Sodium fires and sodium-water reactions, lead-bismuth corrosion, polonium-210 radio-toxicity |
| MSRs | Low-pressure operation, negative temperature coefficients, drain tanks for passive shutdown | Corrosion of structural materials, complex salt chemistry, potential release of volatile fission products |
Overall, small and micro reactors offer a flexible and scalable solution for localised energy supply. Thanks to their compact design, autonomy and broad functionality, they are suitable for a wide range of applications, from power and heat generation to water desalination and hydrogen production. Their reliability has already been proven in practice, including operation in the harshest environments, even in space. Today’s development of SMRs is aimed at making them even more affordable and efficient: mass production is simplified, costs are reduced, and applications are expanded. All of this makes small modular reactors a promising basis for future low-carbon energy. A comparative evaluation of the available data shows that power density among water-cooled SMRs typically ranges from 50 to 100 MWth m−3, while advanced gas-cooled and fast-spectrum systems may exceed 200 MWth m−3. Fuel reloading intervals vary significantly—from 3 to 4 years for LEU-based designs to over 10 years for HALEU or metallic–fuel configurations. Economic assessments indicate that modular factory production can potentially reduce capital costs by 15–30% compared with conventional LWR units [51].
In addition to these advantages, SMRs also face specific safety and regulatory challenges. Potential accident scenarios depend on reactor type and coolant properties—for instance, sodium- and lead-cooled systems may involve chemical interactions with air or water, while high-temperature gas reactors require reliable depressurisation control. Furthermore, SMR licencing remains a complex process, as existing regulatory frameworks were primarily developed for large-scale LWRs. International efforts, including those led by the IAEA, are currently focused on harmonising safety assessment approaches and establishing flexible licencing pathways for modular and distributed reactor systems [51].
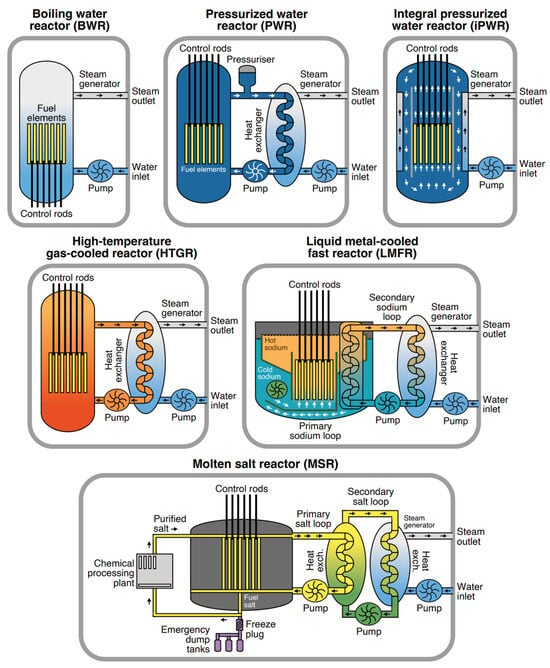
Figure 2.
Steam generation schemes in various reactor types, from conventional to advanced SMR technologies [52]. Used under CC BY 4.0.
Figure 2.
Steam generation schemes in various reactor types, from conventional to advanced SMR technologies [52]. Used under CC BY 4.0.
3. Small Modular Reactors on Low-Enriched Fuel
To date, LEU-fuelled reactors (with U-235 content less than 20%) are the most mature and widely used category among SMRs [53,54,55]. Due to their proven technology, high level of safety and compliance with international requirements, such plants are considered to be one of the main contenders for mass introduction into the civilian energy sector.
LEU fuel is recognised as safe from a nuclear non-proliferation point of view—this has been confirmed by organisations such as the IAEA and the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). Its use reduces the risks of military use and makes it easier to obtain export licences. In addition, LEU has long been used in large commercial nuclear power plants, which has provided a wealth of practical experience, from reliable operation and maintenance to the development of clear regulatory standards [56].
One of the most famous and advanced projects in the field of small modular reactors based on low-enriched uranium is the NuScale VOYGR [57]. Each module of this plant generates 50 MW of electricity and is built according to the classical water–water reactor (PWR) scheme. NuScale’s special feature is its high autonomy: one module can operate for up to 12 years without fuel reloading. In addition, the system is scalable—up to 12 modules in one complex—which allows it to be adapted to the needs of different regions and energy consumption scenarios.
Another striking example is Republic of Korea’s SMART (System-integrated Modular Advanced Reactor). The original SMART design is an integral pressurised water reactor (iPWR) developed for electricity production and seawater desalination, with a thermal output of about 330 MW and an electrical capacity of approximately 100 MWe [22]. In addition to this baseline design, a smaller variant, SMART-100, has been proposed to provide greater flexibility for localised power generation and water desalination in regions with more limited demand. This multifunctionality makes both SMART and SMART-100 particularly attractive for coastal or arid areas where the combined need for electricity and fresh water is critical [58].
China’s ACP100 project, based on PWR technology, is in the final stages of construction. It is designed to power remote areas, industrial zones and infrastructure facilities [59]. The design emphasises automation and advanced safety systems, both active and passive, in line with the latest global trends in nuclear power.
Advantages of LEU-based small modular reactors [60,61,62]:
- Reliability and technological maturity. LEU fuel has been widely used in the power industry for decades. This experience reduces risks when introducing new reactors and speeds up the licencing and operation process.
- Ready infrastructure. LEU-fuel production and supply rely on existing and certified chains, from uranium enrichment plants to fuel assembly fabrication factories.
- Serialisation and standardisation. Thanks to standardised designs, LEU reactors can be mass-produced, which significantly reduces their cost and facilitates logistics for deployment in different countries and regions.
- Export control compliance. Unlike HEU or reprocessed fuel reactors, LEU plants are easier to align with international non-proliferation regulations, including nuclear material control treaties.
- Application flexibility. Due to their compactness, high safety and autonomy, these reactors are suitable for remote communities, small towns, and industrial sites and can complement renewable sources in hybrid energy systems.
- Multifunctionality. LEU reactors can provide not only electricity but also heat, making them effective for district heating, seawater desalination and industrial applications—especially in environments where reliable and sustainable energy is needed.
LEU reactors are finding their place in the energy industry of the future, especially in the next generation of smart grids and energy infrastructure. They provide a stable and predictable energy supply, compensating for the instability of solar and wind sources. Recent studies emphasise that coupling nuclear power with renewables in integrated energy systems offers a practical solution to grid flexibility challenges, energy security concerns, and climate change mitigation [63]. Such hybrid systems not only ensure reliable electricity but can also support cogeneration applications, including hydrogen production, seawater desalination, and process heat for industry. This combination is becoming a key element in achieving emission reduction targets and the transition to clean energy [64].
Owing to international support, a well-established production base, a high degree of standardisation and a positive reputation for nuclear safety, LEU small modular reactors are now considered one of the most reliable and promising areas of civil nuclear power development. Their compactness, adaptability and ability to operate in decentralised environments make them an important part of the global transition to sustainable, low-carbon energy. Nevertheless, the large-scale deployment of LEU-based SMRs still faces challenges, particularly related to economic competitiveness with renewables and the regulatory adaptation needed for modular construction.
4. Small Modular Reactors Using Highly Enriched Fuel
Small modular reactors using HEU (above 20 percent U-235) or HALEU (between 5 and 20 percent) represent a promising technology for the development of compact and energy-efficient autonomous power systems [8]. One of the advantages of some SMR designs is the potential for extended fuel cycles—up to 10–20 years without the need for refuelling. This feature is particularly relevant for deployment in remote regions, military facilities, and space missions. However, the realisation of such long fuel cycles is not universal to all SMRs and depends on the specific reactor concept and fuel technology. Achieving this requires the use of advanced fuel elements with cladding resistant to high radiation damage and thermal loads, enabling high burnup and reducing risks associated with hydrogen formation [31].
The practical implementation of such technologies is already underway in a number of countries. One example is the Russian RITM-200 reactor, successfully used on nuclear icebreakers and considered as an option for land-based power plants in the Arctic [65]. The eVinci microreactor, developed by Westinghouse (USA), with a capacity from 200 kW to 5 MW, was designed to supply power to isolated and hard-to-reach areas [66]. Another promising project, Oklo Aurora, uses reprocessed highly enriched fuel and a passive cooling system, but it is currently facing obstacles at the licencing stage. Special attention should be paid to floating nuclear power plants, such as the Offshore Floating Nuclear Plant (OFNP), which have internal safety systems and passive residual heat removal. Russia is actively implementing and developing such plants, including ABV-6M, KLT-40S and RITM-200 reactors, based on the thermal spectrum and fuel element layout similar to VVER-1000. KLT-40S-type units are already operating at the Akademik Lomonosov floating NPP and are being considered for such purposes as seawater desalination, process support and shipboard applications [67,68].
The design features and approach to fuel cycle management of SMRs significantly distinguish them from conventional reactors. Unlike standard large light water reactors (LWRs), where the fuel enrichment level is typically less than 5 percent, the modular reactors described above utilise a once-through fuel cycle with enrichments up to 20 percent. Due to the limited core volume and higher surface-to-volume ratio, such reactors are characterised by lower power density and relatively higher neutron leakage compared with large LWRs, an effect mitigated by design features such as neutron reflectors and optimised fuel management [69,70].
Similar technological approaches have been reflected in international analyses. According to the Evaluation and Screening (E&S) study conducted by the US Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy (DOE-NE), various nuclear fuel cycles were categorised into 40 evaluation groups, considering parameters such as neutron spectrum, fuel reprocessing and other features. The floating reactors mentioned above are categorised in the EG02 group, which is characterised by the single use of enriched uranium in thermal or fast spectrum reactors with high burnup. As a typical example for the EG02 group, a modular high temperature gas cooled reactor (mHTGR) operating with 15.5% enriched uranium and achieving a burn-up of about 120 GWpd/t, is considered [71,72]. The E&S study concluded that no single fuel cycle option is universally optimal across all evaluation criteria; however, closed or partially closed cycles provide long-term sustainability and waste reduction benefits compared with once-through cycles. At the same time, advanced fuel cycles involving fast reactors and recycling could significantly improve resource utilisation and reduce high-level waste inventories, though they face technical and economic challenges. In the near term, the study emphasised that deployment will continue to rely mainly on once-through cycles using LEU or HALEU, while research into advanced cycles remains critical for future energy security. In parallel, the transition away from HEU (>20% U-235) toward safer alternatives is coming into focus. Current international non-proliferation policy does not support the use of HEU in commercial power reactors, and all advanced SMR designs under development rely instead on LEU (<5% U-235) or HALEU (5–20% U-235). HALEU offers a balanced combination of higher energy density, improved thermal efficiency, and resilience to changing operating conditions. At present, active work is underway in the US and several European countries to establish infrastructure for HALEU production, which opens opportunities for the large-scale deployment of new SMR systems [73,74,75]. HALEU-based reactors are considered strategically important for cases where long core lifetimes, compactness, and high reliability are required, such as in remote regions, research stations, or specialised applications [63]. The adoption of HALEU ensures compliance with strict nuclear safety requirements while simultaneously enabling higher performance, thereby forming a sustainable basis for the next generation of small modular reactors. Despite their potential, HALEU and HEU reactors require significant infrastructure for fuel supply and highlight waste management and proliferation concerns that remain unresolved.
5. Small Modular Reactors Using Thorium Fuel
Thorium-232 is considered a promising material for use in nuclear power, as it transforms into a fissile isotope of uranium-233 upon capture of thermal neutrons. This property makes thorium fuel a potential alternative to conventional uranium fuel cycles. Among its key advantages are its high abundance in nature, reduced plutonium-239 generation, and lower production of long-lived transuranic waste. These characteristics make thorium a particularly attractive option for next-generation small modular reactors, especially in countries with significant reserves of the element [76,77].
Thorium’s potential becomes particularly apparent when considering its behaviour in a once-through fuel cycle. In this approach, thorium exhibits a high conversion efficiency and reduced formation of secondary actinides, making it promising in terms of improving fuel efficiency. Although natural thorium reserves are about 3–4 times higher than uranium reserves, special conditions are required to start a thorium fuel cycle. Since thorium itself is not a fissile isotope, it must be converted into uranium-233 by thermal neutron irradiation. To initiate the chain reaction, fissile material, typically U-235, U-233 or Pu-239, must be present in the core [78].
An additional advantage of thorium is its high breeding ratio in the thermal neutron spectrum, exceeding similar values for U-235 and Pu-239. This contributes to improved fuel cycle performance, especially in terms of conversion efficiency. From a non-proliferation perspective, the use of thorium in the cores of PWRs can significantly limit the generation of weapons-grade plutonium [79].
Nevertheless, despite these promising characteristics, thorium fuel has not yet been adopted in commercial light water reactors. The main reasons are economic and technological: uranium fuel is cheaper and benefits from a fully developed industrial supply chain, while thorium requires additional infrastructure, complex reprocessing technologies, and handling of U-233 contaminated with U-232, which complicates fuel fabrication and safety [80,81]. These factors make thorium less competitive than conventional uranium fuel in the current energy market. Moreover, there is limited operational experience with thorium fuel cycles compared with uranium, which increases regulatory and commercial risks [82]. Looking at specific reactor types, thorium-based fuel cycles in water-cooled (LWR) and heavy-water reactors (HWR) demonstrate attractive neutron-physical characteristics, such as higher conversion ratios and the potential for extended burnup. Studies confirm that thorium can be integrated into modern PWR fuel assemblies without major geometric modifications, which would simplify adoption [80]. Computer simulations also show that thorium fuel cycles can effectively complement or partially replace uranium–plutonium chains, improving fuel utilisation and reducing the burden on spent fuel management infrastructure [82]. However, the transition to a closed Th–U-233 cycle requires solving technical challenges, including the need for external fissile additives, the development of advanced reprocessing technologies, and the establishment of an industrial-scale regulatory framework [77,83,84].
Against this background, specific thorium-focused projects are being pursued, such as the ThorCon molten salt reactor (Indonesia) [83] and India’s large-scale IThER programme [85]. Earlier concepts, such as the Liquid Fluoride Thorium Reactor (LFTR) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, laid the foundation for these modern developments [83]. Despite challenges, thorium-based SMRs retain significant potential to enhance fuel efficiency, improve safety, and reduce long-lived waste, making them a promising option for sustainable nuclear energy in the future. For instance, the Oklo Aurora reactor, which aims to utilise advanced metallic fuel, is currently in the pre-application phase with the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission following its initial licence denial in 2022.
6. Small Modular Reactors on Metallic Fuel and Reprocessed Fuel
One of the most promising areas in the development of SMRs is considered to be the use of metallic nuclear fuel—in particular, uranium–zirconium (U-Zr) and molybdenum (U-Mo) alloys. Originally developed for fast reactors, these materials have a number of unique characteristics that make them particularly attractive for compact and highly efficient power systems. Metallic fuel provides significantly higher energy density than conventional oxide forms and is characterised by excellent thermal conductivity. This allows for efficient heat dissipation from the core and, consequently, a reduction in its geometric dimensions. The compact design opens up a wide range of possibilities for the use of such reactors in a wide variety of environments, from remote areas to space missions and military mobile power plants [86,87,88].
According to the IAEA’s 2023 status report on advanced reactor technologies, molten salt reactors are attracting renewed interest due to their inherent safety features, low-pressure operation, and potential compatibility with thorium-based fuel cycles [51]. At the same time, the report emphasises several challenges that remain unresolved, including material corrosion under high-temperature salt conditions, complex fuel salt chemistry control, and the need for a robust regulatory framework. Opportunities identified include the use of MSRs for load-following to complement renewable energy sources, as well as their application in cogeneration for hydrogen production and desalination. These findings highlight that while MSRs remain at the development stage, they represent one of the most innovative SMR concepts with significant long-term potential.
These features are embodied in a number of modern developments. Due to its high temperature resistance and ability to adapt quickly to changes in thermal load, metallic fuels are particularly well suited for microreactors designed for backup power supply, field conditions and operation in extreme environments [4]. One prominent example is the ARC 100 project being developed in Canada and the US [89]. It is a fast sodium reactor designed for long-term autonomous operation without fuel reloading and is designed based on passive safety principles, which reduces operational risks. Similar interest in metallic fuel is also manifested in space developments, for example in the framework of the American SP-100 programme, which created lithium-cooled reactors with metallic fuel capable of operating in weightlessness and increased radiation background [4]. Another example is the Oklo Aurora microreactor, which was originally envisaged as a reprocessed fuel plant but also included uranium metal variants combined with passive cooling and an ultra-compact design [90].
Despite the obvious advantages, metallic fuel technology is also accompanied by certain engineering limitations. Nevertheless, the use of metallic fuels comes with a number of technical challenges. Its safe operation requires reliable sealing and protection against oxidation—especially at high temperatures—as well as strict temperature control in the heat release zone. This places high demands on the design of cladding, the quality of fuel element sealing and the operation of diagnostic systems. Despite such difficulties, the combination of advantages, such as high energy density, excellent thermal conductivity, and resistance to sudden changes in heat load, makes metallic fuel one of the most promising options for next-generation compact nuclear plants [91].
Against the backdrop of the search for sustainable solutions, the use of reprocessed nuclear fuel is also actively developing. In parallel, the use of reprocessed nuclear fuel, including minor actinides such as neptunium, americium and curium, is being developed. Such approaches are aimed at a significant reduction in spent fuel volumes and more complete utilisation of the energy potential of previously recovered materials [92]. The inclusion of reprocessed isotopes in the fuel cycle makes it possible to form a virtually closed system in which waste is transformed into a resource for new reactor plants. This solution is becoming increasingly important against the backdrop of growing environmental requirements, the need to manage accumulated waste, and the desire to transition to sustainable nuclear technologies.
Molten salt reactors are among the most innovative reprocessing-compatible designs. These reactors are still under development, and their fuel concepts often involve liquid-salt mixtures such as LiF–ThF4–UF4, currently under study for both thorium-based and reprocessed actinide cycles [93]. One of the most ambitious projects in the field of new nuclear technologies is the CMSR being developed by the Danish company Seaborg Technologies [94]. In this concept, the fuel circulates as a melt directly in the primary circuit, eliminating the need for traditional fuel assemblies. This engineering solution improves safety, reduces sensitivity to emergencies and enables the realisation of fully passive residual heat removal. The modular nature of the CMSR makes it particularly suitable for mass production and rapid deployment in regions with limited infrastructure [95]. A similar idea is being developed by Copenhagen Atomics, which is developing small-sized reactors using recycled actinides. The focus here is on technology availability, lower costs and shorter deployment times, making these plants promising for commercial applications in decentralised power grids [96,97].
Other engineering developments continue in this direction. Complementing this direction, the Canadian company Moltex is developing the SSR-W reactor, which implements the concept of sustainable incineration of radioactive waste. The facility combines the use of reprocessed fuel with passive safety systems and is designed for long-term operation near existing SNF storage facilities, which allows for a significant reduction in logistical and environmental costs.
Thus, whether through the high performance of metallic fuels, the sustainability of reprocessed fuels, or the novel safety features of molten-salt fuel cycles, these fuel innovations represent crucial pathways for advancing SMRs toward next-generation applications in both terrestrial and space environments.
Figure 3 shows the geometry of the SSR W reactor module and fuel assembly containing fuel tubes. This design ensures efficient placement of reprocessed fuel and contributes to the thermal efficiency of the system [14,98]. However, the implementation of such technologies requires appropriate infrastructure, from reprocessing and isotopic separation plants to systems for the safe handling of high-level radioactive substances, as well as international regulations and legal support. Nevertheless, the long-term benefits, including reduced dependence on natural uranium, reduced disposal volumes, and increased energy independence, make such developments extremely promising in the context of sustainable nuclear energy [99].
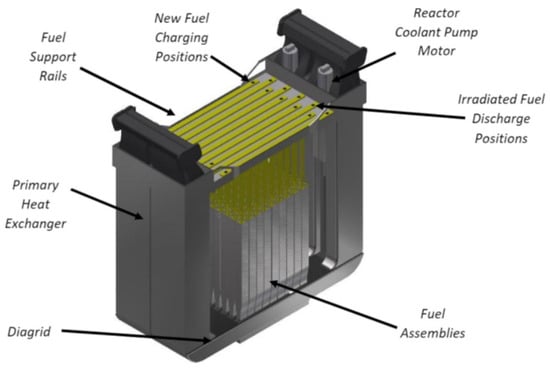
Figure 3.
Overview of the SSR module [14].
Such solutions become especially relevant for countries with significant stockpiles of spent nuclear fuel. Small modular reactors running on reprocessed fuel are especially important for countries with significant accumulations of spent nuclear fuel, such as the United States, France, Russia and Japan. However, the decision to reprocess spent nuclear fuel is influenced not only by technological capability but also by economic and policy considerations. For instance, the United States does not conduct commercial reprocessing, whereas France, Russia, and Japan maintain active programmes as part of their national closed fuel cycle strategies. These countries are interested in developing closed nuclear fuel cycles that allow them to utilise long-lived isotopes, extend the lifetime of storage facilities, and increase the efficiency of the use of already-recovered resources. In this context, SMRs using reprocessed actinides become not only a source of energy, but also a key tool in addressing environmental and resource challenges, contributing to sustainable development and the achievement of international climate and energy goals [36,100,101].
Thus, the areas under consideration create the potential for a new stage in the development of nuclear energy. The development of metallic and reprocessed fuel technologies marks an important direction in advancing nuclear power towards greater efficiency, environmental responsibility, and adaptability. These approaches form the foundation for the creation of a new generation of nuclear systems capable of operating in different environments, meeting the challenges of the times and ensuring a reliable and sustainable energy supply in the long term.
7. Comparative Characteristics of Small-Scale Reactor Technologies and Future Integration with Artificial Intelligence
Mainstream SMR technologies can be broadly divided into several categories, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Water-cooled SMRs (e.g., NuScale, SMART, ACP100) rely on proven pressurised water technology, offering mature safety standards, relatively low technical risk, and near-term deployability [4]. Their limitations include relatively modest efficiency (typically < 34%) and dependence on conventional uranium oxide fuel. In contrast, HTGRs, such as China’s HTR-PM, achieve outlet temperatures of 700–950 °C, enabling higher thermal efficiency and cogeneration applications (hydrogen, process heat), but face challenges in fuel manufacturing and helium leak management. Liquid-metal-cooled fast reactors, including sodium- and lead-bismuth-cooled concepts (e.g., ARC-100, SVBR-100), offer superior neutron economy, potential for closed fuel cycles, and high power density, though they are constrained by material compatibility issues and sodium or lead-bismuth coolant safety concerns. Finally, molten salt reactors, such as the Seaborg CMSR, stand out for low-pressure operation, online refuelling, and compatibility with thorium or actinide-recycling fuel cycles, but still face technical barriers related to salt chemistry, corrosion resistance, and regulatory readiness.
Looking ahead, the innovative potential of SMRs lies not only in their reactor physics and engineering, but also in integration with digital and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. Although AI technologies can also be integrated into the current LWR fleet, their application in SMRs is particularly promising due to their modularity, high degree of digitalisation, and potential for autonomous operation. Advanced reactor monitoring systems powered by machine learning can enhance anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, and optimised core performance under varying operational conditions [102]. AI-driven control algorithms may reduce operator workload, improve fault diagnosis, and increase overall plant resilience. Furthermore, digital twins of SMRs—real-time virtual models that mirror reactor operation—can enable scenario simulations, rapid safety assessments, and accelerated licencing processes [103]. Integrating SMRs with AI-based energy management platforms may also optimise hybrid energy systems where SMRs work alongside renewables, hydrogen production, or district heating networks [104]. Recent advances also highlight the use of AI-driven digital twins. For instance, a 2024 study introduced a novel graph neural network approach for developing whole-system digital twins, validated on the EBR-II and fluoride-salt-cooled high-temperature reactor (FHR) systems, demonstrating high accuracy in transient prediction and anomaly detection [103]. In the nuclear context, a digital twin is a high-fidelity virtual model that mirrors the physical reactor system in real time through continuous data exchange. It allows for the simulation of operational scenarios, prediction of transient events, and optimisation of safety and maintenance strategies, thereby enhancing reliability and reducing operational risks. Such methods enhance intelligent simulation, autonomous control, and safety management, paving the way for their integration into future SMR applications.
Thus, while mainstream SMR designs differ in technological maturity and application niches, their innovative trajectory increasingly depends on coupling proven nuclear safety concepts with emerging digital intelligence. This convergence could play a key role in enhancing both safety and economic competitiveness, ensuring that SMRs contribute effectively to future low-carbon energy systems. Nevertheless, beyond non-proliferation, the broader deployment of SMRs also faces challenges related to supply chain robustness, regulatory harmonisation, manufacturing scale-up, site selection, and licencing. Overcoming these barriers will require coordinated international frameworks, technological standardisation, and investment mechanisms to ensure safe, efficient, and economically viable commercialisation.
8. Conclusions
In summary, the main conclusions of this review are as follows. The current development of SMRs demonstrates a wide range of fuel solutions that open different pathways toward sustainable, safe and efficient nuclear energy. LEU-based reactors already provide a mature and reliable platform supported by standardisation, an established production base and existing regulatory frameworks, making them the most realistic option for near-term deployment. In parallel, HEU and HALEU concepts, although constrained by non-proliferation issues, remain highly attractive for applications where compactness and long operational autonomy are essential, such as in Arctic regions, defence facilities and space systems. Promising directions also include reprocessed fuel and actinide-based SMRs, reflecting the strategic shift toward a closed nuclear fuel cycle and the reduction in long-lived waste. Thorium-based systems stand out due to resource abundance and long-term sustainability, while metallic fuels, with their high energy density and excellent thermal conductivity, create opportunities for compact and mobile nuclear power solutions.
Looking ahead, the further development of SMRs can potentially focus on advancing innovative fuel cycles, achieving waste minimisation and moving closer to closed nuclear fuel systems. At the same time, challenges related to licencing, cost reduction, infrastructure readiness and international regulatory harmonisation remain critical to large-scale commercialisation. Addressing these issues through scientific diversification, international collaboration and adaptation to national contexts will determine the success of SMRs. Taken together, these features position small modular reactors as one of the most promising foundations for a decentralised, reliable and environmentally sustainable energy system for the 21st century.
Looking ahead, the development of SMRs will increasingly depend on the integration of advanced digital technologies, the adoption of sustainable fuel cycles, and the establishment of harmonised international licencing frameworks. In the author’s view, coordinated global efforts in standardisation, supply chain localisation, and public acceptance will be critical to realising the full potential of SMR deployment. Policymakers should prioritise collaborative R&D programmes and flexible regulatory pathways that can accelerate commercialisation while maintaining the highest safety standards.
Funding
The research is funded by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan IRN BR24993225.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, L.; Pan, P. Performance Assessment of a Multiple Generation System Integrating Sludge Hydrothermal Treatment with a Small Modular Nuclear Reactor Power Plant. Energy 2025, 315, 134323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotný, V.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.-B.; Rigby, A.; Saeed, R.M. Nuclear-Based Combined Heat and Power Industrial Energy Parks—Application of High Temperature Small Modular Reactors. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2025, 26, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignacca, B.; Locatelli, G. Economics and Finance of Small Modular Reactors: A Systematic Review and Research Agenda. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 118, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I. Review of Small Modular Reactors: Challenges in Safety and Economy to Success. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 41, 2761–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, T.H.; Kim, Y.I. Microgrid Control Incorporated with Small Modular Reactor (SMR)-Based Power Productions in the University Campus. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2025, 183, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, G.; Bingham, C.; Mancini, M. Small Modular Reactors: A Comprehensive Overview of Their Economics and Strategic Aspects. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2014, 73, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, D.T. Deliberately Small Reactors and the Second Nuclear Era. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2009, 51, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, L.; Miller, J.; Wu, Z. Implications of HALEU Fuel on the Design of SMRs and Micro-Reactors. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2022, 389, 111648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, D.; Jiang, J. Review of Integration of Small Modular Reactors in Renewable Energy Microgrids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman Ishraq, M.A.; Shelley, A.; Sardar, M.R. Neutronic and Thermal Performance Analysis of Advanced Cladding Materials for ACP-100 SMR. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2025, 440, 114142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindra, V.O.; Rogalev, A.N.; Kovalev, D.S.; Ilin, I.V.; Levina, A.I. Research and Development of High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor Nuclear Power Plants for Combined Production of Electricity, Heat and Hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 148, 149968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, U.K.; Zhang, C. Phase-Based Safety Review of Micro and Small Modular Reactors from Design to Decommissioning. Saf. Sci. 2025, 188, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanatta, M.; Patel, D.; Allen, T.; Cooper, D.; Craig, M.T. Technoeconomic Analysis of Small Modular Reactors Decarbonizing Industrial Process Heat. Joule 2023, 7, 713–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, N.; Silva, C.A.M.; Lorduy-Alós, M.; Gallardo, S.; Pereira, C.; Verdú, G. Neutronic Assessment of Stable Salt Reactor with Reprocessed Fuels. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2025, 218, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoya, C.L.; Ubando, A.T.; Culaba, A.B.; Chen, W.-H. State-of-the-Art Review of Small Modular Reactors. Energies 2023, 16, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subki, H. Advances in Small Modular Reactor Technology Developments. In IAEA-NPTD Webinar on Advances in Small Modular Reactor (SMR) Design and Technology Developments. A Booklet Supplement to the IAEA Advanced Reactors Information System (ARIS); International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2020; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, O.; Finin, G.; Ivaschenko, T.; Iatsyshyn, A.; Hrushchynska, N. Current State and Prospects of Smallmodule Reactors Application in Different Countries of the World. In Systems, Decision and Control in Energy IV: Volume II. Nuclear and Environmental Safety; Zaporozhets, A., Popov, O., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 3–21. ISBN 978-3-031-22500-0. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.Y.Y.; Kuntjoro, Y.D.; Yusgiantoro, P. The Usage of Micro Modular Nuclear Reactors on Military Headquarters as a Prospective Solution to Achieve Energy Security and Improve National Defense. East Asian J. Multidiscip. Res. 2023, 2, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comparison of the Potential Risk Associated with Various SMR Designs. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/391260763_Comparison_of_the_potential_risk_associated_with_various_SMR_designs (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Shi, L.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, D. Testing the Feasibility of Multi-Modular Design in an HTR-PM Nuclear Plant. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C. Research Progress on Liquid Metal Corrosion Behavior of Structural Steels for Lead Fast Reactor. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2023, 43, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, B.M.; Krahn, S.L.; Sowder, A.G. A Unique Molten Salt Reactor Feature–The Freeze Valve System: Design, Operating Experience, and Reliability. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 368, 110803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, H.; Peng, M.; Wang, H.; Rasool, A. Autonomous Control Model for Emergency Operation of Small Modular Reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2023, 190, 109874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, G.; Boarin, S.; Pellegrino, F.; Ricotti, M.E. Load Following with Small Modular Reactors (SMR): A Real Options Analysis. Energy 2015, 80, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Usman, S. Advanced and Small Modular Reactors’ Supply Chain: Current Status and Potential for Global Cooperation. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2025, 184, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Arunachalam, M.; Elmakki, T.; Al-Ghamdi, A.S.; Bassi, H.M.; Mohammed, A.M.; Ryu, S.; Yong, S.; Shon, H.K.; Park, H.; et al. Evaluating the Economic and Environmental Viability of Small Modular Reactor (SMR)-Powered Desalination Technologies against Renewable Energy Systems. Desalination 2025, 602, 118624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Dincer, I. A Clean Hydrogen and Electricity Co-Production System Based on an Integrated Plant with Small Modular Nuclear Reactor. Energy 2024, 308, 132834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs): A Review of Current Challenges and Future Applications-Chemical Communications (RSC Publishing). Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2024/cc/d4cc03980g (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- A Comprehensive Review of Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator. A B S T R C T. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360719626_A_comprehensive_review_of_Radioisotope_Thermoelectric_Generator_A_B_S_T_R_C_T (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Hidayatullah, H.; Susyadi, S.; Subki, M.H. Design and Technology Development for Small Modular Reactors–Safety Expectations, Prospects and Impediments of Their Deployment. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2015, 79, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.M.A. Emerging Small Modular Nuclear Power Reactors: A Critical Review. Phys. Open 2020, 5, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.-D.; Khan, R. Techno-Economic Assessment of a Very Small Modular Reactor (vSMR): A Case Study for the LINE City in Saudi Arabia. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, G.T. 14-Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): The Case of the USA. In Handbook of Small Modular Nuclear Reactors; Carelli, M.D., Ingersoll, D.T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 353–377. ISBN 978-0-85709-851-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Lee, J. Social Acceptance of Small Modular Reactor (SMR): Evidence from a Contingent Valuation Study in South Korea. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2025, 57, 103128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, G.; He, F.; Tong, J.; Zhang, L. Study on the Costs and Benefits of Establishing a Unified Regulatory Guidance for Emergency Preparedness of Small Modular Reactors in China. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2023, 161, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, E.; Clarno, K.; Haas, D.; Webber, M.E. The Economics of Small Modular Reactors at Coal Sites: A Program-Level Analysis within the State of Texas. Energy Policy 2025, 202, 114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T. 17-Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): The Case of Japan. In Handbook of Small Modular Nuclear Reactors, 2nd ed.; Ingersoll, D.T., Carelli, M.D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 409–424. ISBN 978-0-12-823916-2. [Google Scholar]
- Beliavskii, S.; Alhassan, S.; Danilenko, V.; Karvan, R.; Nesterov, V. Effect of Changing the Outer Fuel Element Diameter on Thermophysical Parameters of KLT-40S Reactor Unit. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2023, 190, 109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliavskii, S.V.; Nesterov, V.N.; Laas, R.A.; Godovikh, A.V.; Bulakh, O.I. Effect of Fuel Nuclide Composition on the Fuel Lifetime of Reactor KLT-40S. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 360, 110524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz, E.; Yildirim, B.; Erdogan, M.; Aydin, N. Strategic Site Selection Methodology for Small Modular Reactors: A Case Study in Türkiye. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 215, 115545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, G.; Zhang, X.; Han, D. Small Modular Reactors Enable the Transition to a Low-Carbon Power System across Canada. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hee, N.; Peremans, H.; Nimmegeers, P. Economic Potential and Barriers of Small Modular Reactors in Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 203, 114743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmastro, D.F. 14-Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): The Case of Argentina. In Handbook of Small Modular Nuclear Reactors, 2nd ed.; Ingersoll, D.T., Carelli, M.D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 359–373. ISBN 978-0-12-823916-2. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, M.; Fan, J.; Shen, F.; Lu, D.; Li, L.; Yu, H.; Fan, J. Comparative Analysis on the Characteristics of Liquid Lead and Lead–Bismuth Eutectic as Coolants for Fast Reactors. Energies 2025, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarto; Santosa, S.; Khotimah, K.; Sriyana. Study on the Implementation of Quality Assurance Aspect on High-Temperature Gas Cooled Reactor (HTGR). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2048, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead-Cooled Fast Reactors (LFRs)-Book Chapter-IOPscience. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/book/mono/978-0-7503-6069-2/chapter/bk978-0-7503-6069-2ch12 (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Lim, S.G.; Nam, H.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, S.W. Design Characteristics of Nuclear Steam Supply System and Passive Safety System for Innovative Small Modular Reactor (i-SMR). Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2025, 57, 103697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirian, B.; Asad, A.; Krezan, L.; Yakout, M.; Hogan, J.D. A New Perspective on the Mechanical Behavior of Inconel 617 at Elevated Temperatures for Small Modular Reactors. Scr. Mater. 2025, 261, 116605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Liu, L.; Cao, J. Numerical Study of Forced Circulation and Natural Circulation Transition Characteristics of a Small Modular Reactor Equipped with Helical-Coiled Steam Generators. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2025, 183, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Safety Design Features of CAREM. In Design Features to Achieve Defence in Depth in Small and Medium Sized Reactors; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2009; pp. 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- 2023 IAEA Annual Report Presented to the UN General Assembly. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/newscenter/news/2023-iaea-annual-report-presented-to-the-un-general-assembly (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Nøland, J.K.; Hjelmeland, M.; Hartmann, C.; Tjernberg, L.B.; Korpå, M. Overview of Small Modular and Advanced Nuclear Reactors and Their Role in the Energy Transition. IEEE J. Mag. 2025, 40, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.R.; Worrall, A.; Todosow, M. Impact of Thermal Spectrum Small Modular Reactors on Performance of Once-through Nuclear Fuel Cycles with Low-Enriched Uranium. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2017, 101, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, N.A.Z.; Ismail, A.F.; Rabir, M.H.; Kok Siong, K. Neutronic Optimization of Thorium-Based Fuel Configurations for Minimizing Slightly Used Nuclear Fuel and Radiotoxicity in Small Modular Reactors. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2024, 56, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushamah, H.A.S.; Burian, O.; Ray, D.; Škoda, R. Integration of District Heating Systems with Small Modular Reactors and Organic Rankine Cycle Including Energy Storage: Design and Energy Management Optimization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 322, 119138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHart, M.D.; Karriem, Z.; Pope, M.A.; Johnson, M.P. Fuel Element Design and Analysis for Potential LEU Conversion of the Advanced Test Reactor. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2018, 104, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kwon, O.-S.; Bentz, E.; Tcherner, J. Evaluation of CANDU NPP Containment Structure Subjected to Aging and Internal Pressure Increase. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2017, 314, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Wisudhaputra, A.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, K.; Park, H.-S.; Jeong, J.J. Development of a Special Thermal-Hydraulic Component Model for the Core Makeup Tank. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2022, 54, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishraq, M.A.R.; Rohan, H.R.K.; Kruglikov, A.E. Neutronic Assessment and Optimization of ACP-100 Reactor Core Models to Achieve Unit Multiplication and Radial Power Peaking Factor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2024, 205, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.H.; Venneri, P.; Kim, Y.; Chang, S.H.; Jeong, Y.H. Preliminary Conceptual Design of a New Moderated Reactor Utilizing an LEU Fuel for Space Nuclear Thermal Propulsion. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2016, 91, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schickler, R.A.; Marcum, W.R.; Reese, S.R. Comparison of HEU and LEU Neutron Spectra in Irradiation Facilities at the Oregon State TRIGA® Reactor. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2013, 262, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposio, R.; Thorogood, G.; Czerwinski, K.; Rozenfeld, A. Development of LEU-Based Targets for Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturing: A Review. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 148, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Huning, A.J.; Burek, J.; Guo, F.; Kropaczek, D.J.; Pointer, W.D. The Pursuit of Net-Positive Sustainability for Industrial Decarbonization with Hybrid Energy Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, S.; Baumeister, B.; Wight, J. Qualification of Advanced LEU Fuels for High-Power Research Reactor Conversion Designs. EPJ Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2025, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Calculation of the Campaign of Reactor RITM-200-IOPscience. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/1019/1/012057 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Swartz, M.M.; Byers, W.A.; Lojek, J.; Blunt, R. Westinghouse eVinciTM Heat Pipe Micro Reactor Technology Development. In International Conference on Nuclear Engineering; ICONE28-67519; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York City, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 85246, p. V001T04A018. 12p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tian, Z.; Liu, J. Steady-State and Transient Analysis in Single-Phase Natural Circulation of ABV-6M. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering, Xi’an, China, 17–21 May 2010; ICONE18-30009. pp. 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xie, J.; Deng, N.; Chen, P.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T. Effect of KLT-40S Fuel Assembly Design on Burnup Characteristics. Energies 2023, 16, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, B.A.; Kotlyar, D.; Parks, G.T.; Lillington, J.N.; Petrovic, B. Reactor Physics Modelling of Accident Tolerant Fuel for LWRs Using ANSWERS Codes. EPJ Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarer, D.; Schulenberg, T.; Struwe, D.; Oka, Y.; Bittermann, D.; Aksan, N.; Maraczy, C.; Kyrki-Rajamäki, R.; Souyri, A.; Dumaz, P. High Performance Light Water Reactor. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2003, 221, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougar, H.D.; Petti, D.A.; Demkowicz, P.A.; Windes, W.E.; Strydom, G.; Kinsey, J.C.; Ortensi, J.; Plummer, M.; Skerjanc, W.; Williamson, R.L.; et al. The US Department of Energy’s High Temperature Reactor Research and Development Program–Progress as of 2019. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 358, 110397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wu, F.; Ai, C.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Zhong, P.; Yan, J. Modeling and Analysis of Control Rod Drop in a Floating Nuclear Power Plant under Ocean Conditions. Ocean Eng. 2025, 338, 121992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, P.; Read, N. On the Practicalities of Producing a Nuclear Weapon Using High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2025, 215, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.N.; Jo, C.K.; Kim, C.S. Conceptual Core Design and Neutronics Analysis for a Space Heat Pipe Reactor Using a Low Enriched Uranium Fuel. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2022, 387, 111603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, M.; Ansarifar, G.R.; Yeganeh, M.H.Z. Assessment and Predicting the Effect of Accident Tolerant Fuel Composition and Geometry on Neutronic and Safety Parameters in Small Modular Reactors via Artificial Neural Network and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2025, 433, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Jeyhouni, R.; Rezaei Ochbelagh, D.; Maiorino, J.R.; D’Auria, F.; de Stefani, G.L. The Utilization of Thorium in Small Modular Reactors—Part I: Neutronic Assessment. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2018, 120, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatullah, A.; Permana, S.; Irwanto, D.; Aimon, A.H. Comparative Analysis on Small Modular Reactor (SMR) with Uranium and Thorium Fuel Cycle. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2024, 418, 112934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Aghili Nasr, M.; D’Auria, F.; Cammi, A.; Maiorino, J.R.; de Stefani, G.L. Analysis of Thorium-Transuranic Fuel Deployment in a LW-SMR: A Solution toward Sustainable Fuel Supply for the Future Plants. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2024, 421, 113090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M. Small Modular Reactors and the Future of Nuclear Power in the United States. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2014, 3, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsige-Tamirat, H. Neutronics Assessment of the Use of Thorium Fuels in Current Pressurized Water Reactors. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2011, 53, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwijayanto, R.A.P.; Miftasani, F.; Harto, A.W. Assessing the Benefit of Thorium Fuel in a Once through Molten Salt Reactor. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 176, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ault, T.; Krahn, S.; Croff, A. Thorium Fuel Cycle Research and Literature: Trends and Insights from Eight Decades of Diverse Projects and Evolving Priorities. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2017, 110, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, T.; Feng, B.; Heidet, F. Molten Salt Reactor Core Simulation with PROTEUS. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 140, 107099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldova, D.; Fridman, E.; Shwageraus, E. High Conversion Th–U233 Fuel for Current Generation of PWRs: Part II—3D Full Core Analysis. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2014, 73, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, P.K.; Shivakumar, V.; Basu, S.; Sinha, R.K. Role of Thorium in the Indian Nuclear Power Programme. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2017, 101, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dawood, K.; Palmtag, S. METAL: Methodology for Liquid Metal Fast Reactor Core Economic Design and Fuel Loading Pattern Optimization. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 173, 105232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.C.; Porter, D.L. Applying U.S. Metal Fuel Experience to New Fuel Designs for Fast Reactors. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 171, 105135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Genk, M.S.; Schriener, T.M. Post-Operation Radiological Source Term and Dose Rate Estimates for the Scalable LIquid Metal-Cooled Small Modular Reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2018, 115, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Research and Community | Open Access Journals. Available online: https://www.onlinescientificresearch.com/journals/jmsmr/abstract/advanced-reactor-concept-arc-a-nuclear-energy-perspective-2040.html (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, Y.; Kim, N.; Jo, H. Design of Heat Pipe Cooled Microreactor Based on Cycle Analysis and Evaluation of Applicability for Remote Regions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 288, 117126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Dinavahi, V. Small Modular Reactors: An Overview of Modeling, Control, Simulation, and Applications. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 39628–39650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.H.; Hong, S.G. Neutronic Analysis on TRU Multi-Recycling in PWR-Based SMR Core Loaded with MOX (U-TRU) and FCM (TRU) Fueled Assemblies. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2022, 179, 109435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosolin, A.; Beneš, O.; Colle, J.-Y.; Souček, P.; Luzzi, L.; Konings, R.J.M. Vaporization Behaviour of the Molten Salt Fast Reactor Fuel: The LiF-ThF4-UF4 System. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 508, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schønfeldt, T.; Klinkby, E.; Schofield, A.V.; Pettersen, E.E.; Puente-Espel, F. Chapter 24-Seaborg Technologies ApS—Compact Molten Salt Reactor Power Barge. In Molten Salt Reactors and Thorium Energy, 2nd ed.; Dolan, T.J., Pázsit, I., Rykhlevskii, A., Yoshioka, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2024; pp. 907–918. ISBN 978-0-323-99355-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Branger, E.; Grape, S.; Elter, Z.; Mirmiran, S. Material Attractiveness of Irradiated Fuel Salts from the Seaborg Compact Molten Salt Reactor. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2024, 56, 3969–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuler, S.P.; Webler, T. The Challenge of Community Acceptance of Small Nuclear Reactors. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2024, 118, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M. Molten Salt Reactors: Current Technology Status and the Challenges for Maritime Applications. In Proceedings of the 17th International Naval Engineering Conference & Exhibition, Liverpool, UK, 5–7 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Stable Salt Reactor—A Radically Simpler Option for Use of Molten Salt Fuel | SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-13-2658-5_37 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Bushnag, M.; Oh, T.; Kim, Y. A Neutronic Study on Safety Characteristics of Fast Spectrum Stable Salt Reactor (SSR). In Proceedings of the Challenges and Recent Advancements in Nuclear Energy Systems; Shams, A., Al-Athel, K., Tiselj, I., Pautz, A., Kwiatkowski, T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 600–611. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, R.; Brown, N.R. Potential Fuel Cycle Performance of Floating Small Modular Light Water Reactors of Russian Origin. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 144, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, I.J.; Bang, I.C. The Time for Revolutionizing Small Modular Reactors: Cost Reduction Strategies from Innovations in Operation and Maintenance. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 174, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, B.; Su, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Pan, H. A Preliminary Study of Digital Twin for Nuclear Reactor Dynamics: A Synergy of Machine Learning and Model Predictive Control. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 153, 110940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Alsafadi, F.; Mui, T.; O’Grady, D.; Hu, R. Development of Whole System Digital Twins for Advanced Reactors: Leveraging Graph Neural Networks and SAM Simulations. Nucl. Technol. 2025, 211, 2206–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Peng, S.; Deng, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, P. A Review of the Application of Artificial Intelligence to Nuclear Reactors: Where We Are and What’s Next. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).