Abstract
The increasing demand for sustainable building solutions has directed attention toward bio-based materials, among which mycelium bio-composites (MBCs) have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional insulation materials. Grown from fungal mycelium and lignocellulosic waste, MBCs offer low embodied energy, biodegradability, and effective hygrothermal performance. This review assesses the current state of the art in MBC fabrication and hygrothermal properties, encompassing both laboratory-scale and industrial methods. MBCs demonstrate thermal conductivity values in the range of 0.036–0.06 W·m−1·K−1, moisture buffering capacity comparable to plant-fiber composites, and up to 70% lower embodied carbon than conventional materials. Key challenges are identified, including process standardization, scalability, and durability under real-world conditions. These composites also offer moisture buffering, compostability, and design flexibility. Moreover, recent advancements in additive manufacturing and microstructural optimization suggest a path toward broader adoption of MBCs in construction. By highlighting critical technical and scientific developments, this review identifies targeted research priorities, including the development of standardized fabrication protocols, quantitative lifecycle assessment of MBCs across varying climates, and strategies to scale up production while maintaining mechanical and hygrothermal consistency.
1. Introduction
Improving energy efficiency, lowering embodied energy, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions is nowadays becoming the key issue in all sectors. In particular, the construction sector is one of the most energy-consuming industries [1] and, therefore, one of the biggest contributors to GHG emissions [2]. Today, there is a strong effort to meet increasingly stringent energy efficiency criteria, which is essential for the environment and global sustainability [3,4]. The building sector contributes significantly to mankind’s environmental footprint [5]. Buildings are responsible for 40% of energy consumption and 36% of carbon emissions in the EU [6]. In 2020, residential buildings accounted for 14% of Canada’s total energy consumption, while commercial and institutional buildings accounted for 13% [7].
A key feature of sustainable buildings is energy efficiency, both during operation and throughout the lifecycle of each component. Historically, sustainability measures have focused on operational energy, but a full life cycle analysis provides a more comprehensive view of a building’s total energy use and GHG emissions. Embodied energy, often overlooked, can account for 10–30% of a building’s total carbon emissions [8,9,10]. Thus, it requires an exhaustive approach when it comes to the study of the life cycle of materials and their embodied energy, as well as their corresponding associated GHG emissions.
There is a growing shift in the construction sector toward bio-based, low-embodied-energy, and locally sourced materials. Compared to conventional materials like concrete, steel, and plastics, these alternatives offer lower toxicity, high durability, low emissions, strong recyclability, and minimal processing requirements [11]. In other words, moving from zero energy buildings (ZEB) to life-cycle ZEBs (LCZEB) is seen as a key strategy to address sustainability issues [12]. Therefore, selecting building materials should involve evaluating their entire lifecycle and prioritizing those with minimal environmental impact [11].
Materials such as hempcrete and flax-lime composites have already entered niche markets; however, challenges remain regarding scalability, mechanical strength, and moisture durability. A major barrier to adoption is balancing environmental benefits with performance metrics, including thermal resistance and structural viability at scale. Additionally, many rely on energy-intensive binders like lime, which undermine their sustainability. A recent review of crop-based materials reported favorable thermal conductivity (0.04–0.12 W·m−1·K−1) and moisture buffering capacity for options like hempcrete and straw, while identifying mycelium-based composites as promising but underdeveloped. This highlights the need for further research on fabrication consistency, long-term performance, and structural applicability [13].
Mycelium bio-composites (MBCs) are an emerging class of crop-based materials that use fungal mycelium as a natural binder. Cultivated from lignocellulosic waste and fungal strains, these composites exhibit low environmental impact and favorable thermal properties. Beyond their environmental benefits, mycelium bio-composites also contribute to energy performance goals in the building sector. Due to their inherently low embodied energy and strong thermal insulation capabilities, MBCs can support both passive heating and cooling strategies. This dual benefit—lowering both operational and material production energy—positions MBCs as strong candidates for energy-efficient and net-zero buildings. Recent studies have further demonstrated the effectiveness of bio-based insulation materials—such as MBCs—in climate-responsive net-zero building design, particularly when combined with shading and roof vegetation strategies [14].
The specific interest in these materials is rooted in their three-dimensional structure, which grows on a base substrate typically composed of residues of other agricultural and forestry materials [15,16]. Despite growing interest, MBCs face significant technical challenges. These include variability in mechanical and hygrothermal properties, absence of standardized fabrication protocols, and sensitivity to moisture, which can compromise durability. Additionally, most experimental studies are conducted on a laboratory scale, and methods for reliable industrial-scale production are still under development. In the literature, research on bio-based materials typically falls into four categories: environmental impacts, thermo-hygro-mechanical characteristics, social aspects and economic feasibility, and affordability [17].
While recent studies have explored various aspects of MBC fabrication and performance, there is limited synthesis connecting fabrication methods and microstructural development to hygrothermal and mechanical behavior, particularly in the context of real-world building applications aimed at evaluating their suitability as net-zero carbon insulation materials. Furthermore, existing literature often treats lab-scale and industrial practices separately, without bridging them to material performance outcomes or assessing their potential for real-world implementation. This review fills that gap by articulating a clear framework that links fabrication parameters to thermal and moisture performance and evaluating key barriers to scalability and long-term durability.
This paper presents a two-fold review: first, it surveys recent advances in MBC fabrication—including traditional molding and emerging 3D printing techniques, highlighting the influence of fungal species, substrates, and processing conditions. Second, it examines hygrothermal performance data, such as thermal conductivity, water absorption, and vapor permeability, in relation to microstructural characteristics. By linking fabrication parameters with material properties, the review aims to identify key enablers and barriers to the effective deployment of MBCs as building insulation.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 details the review methodology. Section 3 reviews lab-scale and industrial-scale fabrication techniques. Section 4 addresses issues related to scalability and durability. Section 5 focuses on the mechanical and hygrothermal characterization of MBCs, including recent insights into microstructural effects. The review concludes with a synthesis of findings and recommendations for future research.
2. Review Methodology
This review focuses on two primary aspects: the fabrication techniques reported in the existing literature and the comprehensive thermo-hygro-mechanical characterization. Its main objective is to assess the technical feasibility of mycelium-based building materials for use in modern construction. This evaluation focuses on their physical properties and potential to replace energy-intensive conventional materials. The study spans a wide range of MBCs, from basic formulations to advanced agglomerates and fabrication methods, demonstrating their suitability for use in construction.
The search strategy incorporated thematic keywords across three categories:
- (i)
- Material and fabrication technologies: mycelium-based building materials, extrusion, 3D printing, robotic manufacturing, modular growth;
- (ii)
- Performance and characterization: thermal conductivity, thermal resistance, thermal effusivity, moisture buffering, vapor permeability, mechanical strength, fire resistance, durability;
- (iii)
- Sustainability and application context: embodied energy, low-carbon materials, energy efficiency, regenerative design, life cycle assessment (LCA), scalability, and standardization.
Geographical limitations are not imposed, although the primary focus pertains to Europe and North America, both for technical advancements and industry standards. Within the category of physical characteristics, studies with similar properties are filtered based on material proximity and specific experimental methods.
The review was carried out in a three-step process:
- Titles and abstracts of the retrieved studies are screened, focusing on embedded concepts, keywords, and specific terms. The 80 reviewed references were retrieved primarily from peer-reviewed databases, with the majority published by MDPI (25%) and Elsevier (16.25%). Additional sources include ACS, Springer, Nature Publishing Group, IEEE, Wiley, and Taylor & Francis, with 37.5% of sources categorized as grey literature or unclassified.
- Then, the full texts of the selected studies from Step 1 were reviewed to extract detailed data, considering parameters including physical characteristics, replacement of traditional energy-intensive building materials, and their contribution to regenerative design and waste valorization. A short and relevant description and a reference for each contribution were written at that stage. Numerous mycological and biological references pertain to mycelium, yet they fall outside the purview of this review, and, as such, are omitted from the study’s scope.
- At the final step, a qualitative assessment of the data extracted from stage 2 was conducted to identify common themes, trends, and knowledge gaps. The reviewed literature was synthesized under two main topics: Fabrication of Mycelium Bio-Composites, which includes lab-scale processes, industrial production methods, additive manufacturing, and scalability; and Performance Characterization of MBCs, covering mechanical properties, hygrothermal behavior, durability, fire resistance, and environmental impact.
3. Fabrication of Mycelium Bio-Composites: From Lab to Industry
3.1. Laboratory Methods
MBC development is based on a controlled laboratory process that allows researchers to tailor material performance through substrate selection, fungal growth, and process optimization. In laboratory settings, MBCs are generally produced by cultivating filamentous fungi that grow dense mycelial networks over lignocellulosic substrates [16]. The core fabrication stages, sterilization, inoculation, and incubation, are broadly standardized across studies, although variations are employed to fine-tune material properties. As shown in Figure 1, these stages are often supplemented by molding, pre-compression, and post-incubation drying, each step contributing to specific mechanical or hygrothermal characteristics [18]. The images in section (c) of the figure are from the authors’ own fabrication campaign for MBCs, which were subsequently characterized and presented in [19].
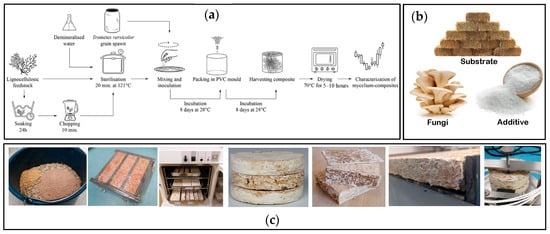
Figure 1.
(a) Step-by-step fabrication process of mycelium bio-composites [18]; (b) primary constituents; (c) representative images showing the process from raw materials to fully grown samples.
Figure 1a illustrates the fabrication process of MBCs, which begins with soaking, chopping, and sterilizing lignocellulosic feedstock prior to inoculation with grain spawn. The inoculated substrate is packed into PVC molds and incubated at 28 °C for two 8-day cycles to ensure full colonization. After harvesting, the samples are dried at 70 °C for 5–10 h. The accompanying photos depict: (b) the constituent materials; and (c) the progression from raw materials to finished samples.
A detailed three-stage cultivation strategy was described by Stelzer et al. [16] and Meyer et al. [20]. The process begins with agar-based fungal inoculation in a pre-culture medium, followed by a secondary inoculation on a sterilized intermediate substrate (e.g., rye), and culminates in the colonization of a final substrate, such as hemp shiv. This muti-stage approach enhances fungal distribution and composite uniformity. Escobar and Laibach [21] emphasized that substrate selection, fungal species, and processing technique play a critical role in determining the mechanical and hygric behavior of the final material.
Barta et al. [22] demonstrated that cellulose-rich feedstocks like straw promote rapid mycelial colonization and denser composite structures. The selection of fungal strain has also been shown to significantly influence growth consistency and final properties. Nussbaumer et al. [23] compared Trametes versicolor and T. pubescens, revealing that strain-specific growth patterns affect mechanical properties and that post-growth pressing improves uniformity only in some strains. Their findings underscore the importance of aligning strain morphology with fabrication and post-processing protocols.
Camilleri et al. [24] further emphasized the lack of standardization in lab-scale methods and its contribution to inconsistencies in structure and performance across studies. They advocate for tighter control of process parameters and the development of reproducible protocols during sterilization, inoculation, and incubation phases. Mohseni et al. [25] proposed a comparative framework outlining key fabrication steps, from autoclave sterilization to incubation in humid, sterile containers, highlighting the critical importance of contamination control during colonization.
3.2. Additive Manufacturing
Beyond traditional mold-based fabrication, additive manufacturing is reshaping how MBCs are scaled and formed. Scott et al. [26] proposed a hybrid method that combines knitted wool scaffolds with mycelium and bacterial cellulose, enabling precise growth through parametric modeling. This approach enhances structural strength and imparts water resistance, although substrate uniformity remains a challenge. To address such limitations, paste-like agglomerates have been suggested as alternatives to fibrous substrates, offering better consistency [27,28,29].
Meanwhile, extrusion-based 3D printing has emerged as a mold-free fabrication route for MBCs. Structure optimization through Direct Ink Writing (DIW) and material extrusion enables control over composition and porosity, allowing for the creation of functionally graded, multi-material mycelium structures. Teoh et al. [30] demonstrated that nutrient-modified inks can guide fungal growth spatially, resulting in tailored mycelial density and microstructures, which support localized property tuning and multi-scale reinforcement. Soh et al. [31] developed a waste-based agar ink suitable for non-sterile environments, using coffee grounds to increase compressive strength and reduce contamination risk. Luo et al. [32] developed a “Mycofluid” ink using coffee grounds and rice flour, enabling 3D-printed composites that fully colonize in non-sterile environments and exhibit strong mechanical performance and compostability after drying. Figure 2 depicts this 3D printing process and the composition of the fungal paste. Rahman et al. [33] optimized extrusion timing for improved print quality, while Soh et al. [34] enhanced mechanical properties by incorporating bamboo microfibers. Bhardwaj et al. [35] added psyllium husk to stabilize the ink and prevent nozzle clogging.
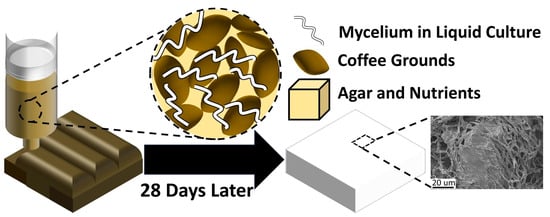
Figure 2.
Schematic of 3D printing process [31].
This figure illustrates the 3D printing process using the waste-based ink. The formulation composed of liquid-cultured mycelium, coffee grounds, agar, and nutrients. After 28 days, the printed structure becomes fully colonized, resulting in a cohesive composite. The SEM image confirms the formation of a dense mycelial network within the material.
To address the limitations of mold-based growth and enhance structural control, Soh et al. [31] optimized printing parameters for their mycelium-based ink to improve resolution, consistency, and mycelial colonization across complex geometries. Figure 3 depicts the impact of these optimizations on print quality and fungal development.
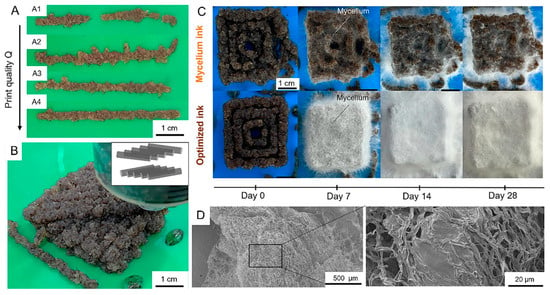
Figure 3.
Three-dimensional printing and mycelium growth: (A) Pictures of 3D printed filaments using the mycelium ink with varying printing parameters (A1–A4) showing improvement in the print quality; (B) Picture and schematics of a 3D printed multi-layered lay-up structure; (C) Optical images of square patterned block prints using mycelium and optimized inks over 28 days; (D) Electron micrographs of mycelium growth on printed optimized ink for 28 days [31].
Optimized printing parameters and ink formulations improve the definition, structural integrity, and mycelial colonization of 3D-printed composites. The improved ink enabled uniform fungal growth and denser mycelial networks, as confirmed by SEM imaging. Together, knitting-based and 3D-printed methods offer distinct advantages: the former offers design flexibility suited to architectural components, while the latter improves scalability and production efficiency. Both contribute to expanding the role of mycelium composites as practical, eco-friendly materials for diverse design and construction applications.
Regarding the effect of additive manufacturing on the properties of the material, Chen et al. [36] reinforced planar mycelium mats by 3D-printing thin layers of biopolymers (PHBH or PLA) onto them, resulting in significant improvements in tensile performance. The pure mycelium mat had an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of approximately ~0.65 MPa and a Young’s modulus of ~4.5 MPa, but printing a PLA lattice raised the UTS nearly fivefold (to ~3.1 MPa) and stiffness ~30-fold (to ~136 MPa). Even a biodegradable PHBH pattern produced a ~70% UTS increase (to ~1.1 MPa). The authors further highlight that altering line spacing or using auxetic infill patterns can redistribute stress and further improve both strength and toughness. Wang et al. [37] developed a lightweight entangled network composite where mycelial hyphae interweave with a PVA polymer phase, achieving a high specific strength of 8.15 MPa·cm3·g−1. Notably, the material exhibits 90% strength recovery after self-healing through mycelial regrowth across cracks.
3D-printed mycelium structures demonstrate improved hygric and thermal performance due to their tunable porosity and the intrinsic chemistry of fungal biomass. Their porous architecture enables effective thermal insulation, achieving densities as low as 0.12 g/cm3, comparable to conventional foams [36]. Moisture resistance is also enhanced; surface hydrophobins and post-print treatments contribute to water repellency [36]. For example, coffee-ground-based mycelium prints exhibit hydrophobic properties [32], and entangled mycelium–PVA composites absorb only ~33% of their weight in water after 15 days—a relatively low value for a bio-based material [37]. Post-processing methods such as calcium crosslinking further improve dimensional stability in wet conditions, enabling MBCs to buffer moisture effectively without structural degradation [36].
Collectively, the cross-study comparison reveals both consistencies and discrepancies in lab-scale experimental approaches. Most lab-scale protocols follow a three-stage inoculation–molding–drying sequence, yet the reported uniformity levels of the final samples vary widely. Barta et al. [22] and Nussbaumer et al. [23] both confirm that high-cellulose substrates (e.g., straw) accelerate colonization. However, Camilleri et al. [24] show that without strict sterilization and humidity control, substrate choice alone cannot guarantee uniform growth. Scott et al. [26] and Bhardwaj et al. [35] demonstrate that hybrid scaffolds (e.g., knitted textile or 3D-printed paste) can improve form factor and speed, but Mohseni et al. [25] caution that these novel methods can introduce new sources of contamination or heterogeneity. Overall, these findings suggest a trade-off: purely mold-based growth yields reproducible but geometrically limited samples, while additive manufacturing routes boost design freedom at the cost of process control.
3.3. Industrial-Scale Production
Over the past decade, industrial-scale MBC production has progressed through scalable fabrication methods, structural enhancements, and commercial initiatives. While the majority of research is still conducted on a laboratory scale, several manufacturing techniques demonstrated the potential for integrating MBCs into engineered materials for insulation, furniture, and structural applications.
Sun et al. [38] introduced two distinct methods for producing hybrid composites, composed of wood particles, mycelium, and cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs). In the first method (Group 1), wood particles are bound exclusively by mycelium growth, leading to high water permeability and dimensional instability. In the second method (Group 2), the addition of CNFs serves as a secondary binder, significantly improving moisture resistance and mechanical performance. As illustrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5, Group 2 composites demonstrate markedly reduced water adsorption and thickness swelling, offering better long-term dimensional stability. While reduced water uptake may limit performance in applications requiring high moisture buffering, the enhanced structural integrity presents clear advantages for insulation and paneling applications.
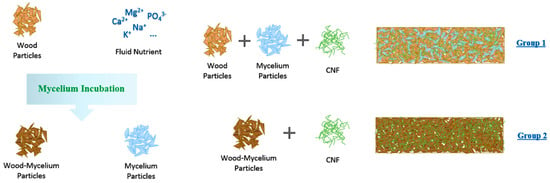
Figure 4.
Two production methods of mycelium bio-composites: Group 1 involves the direct integration of mycelium with woody particles; Group 2 incorporates cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) as a binder to improve structural stability and moisture resistance [38].
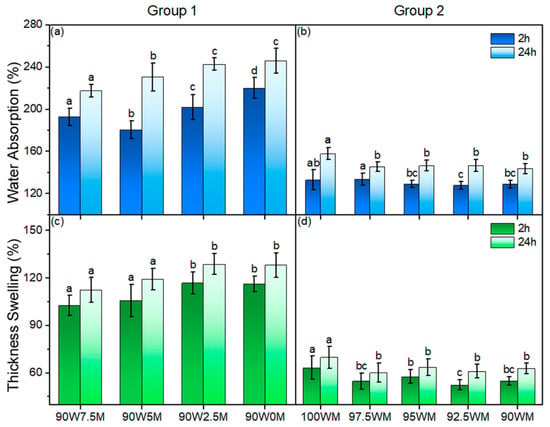
Figure 5.
Comparison of water adsorption and thickness swelling; (a) Water absorption (%) after 2 h and 24 h for Group 1 composites fabricated with wood particles bound solely by mycelium; (b) Water absorption (%) after 2 h and 24 h for Group 2 composites incorporating cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) as an additional binder; (c) Thickness swelling (%) after 2 h and 24 h for Group 1 composites; (d) Thickness swelling (%) after 2 h and 24 h for Group 2 composites. W and M on the horizontal axis represent the percentage of wood and mycelium in different fabricated samples. The letters “a”, “b”, “c”, “d”, “ab” and “bc” indicate statistically significant groupings based on ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05) [38].
Jiang et al. [39] developed sandwich-structured composites consisting of a mycelium core, textile skins (e.g., jute or hemp), and a bio-resin matrix. They observed that the stiffness of the resulting panels was primarily influenced by the colonization density of the mycelium, while the tensile strength was determined by the textile skin. Their manufacturing workflow (Figure 6) integrates conventional composite fabrication techniques with the biological growth phase characteristic of MBCs. The process includes gluing, mold filling with pre-colonized substrate, incubation for growth, drying, and resin infusion, as illustrated in Figure 6.
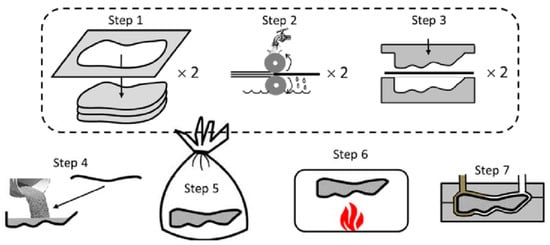
Figure 6.
The manufacturing process of mycelium fiber composites [39].
3.4. Scalability of Production
The scalability of MBCs depends on their ability to be adapted for both digital design and modular fabrication. Attias et al. [27] illustrated this potential of MBCs through two design-driven case studies, an insulating container shell and a modular architectural unit, fabricated using CAD-based mold design and local agricultural waste. Their study not only showcases the feasibility of reproducible, large-scale geometries but also underscores the role of MBCs in integrating sustainable materials into contemporary industrial design workflows (Figure 7). These examples highlight how mycelium composites can be designed and fabricated at multiple scales with reproducible geometry and minimal environmental impact.
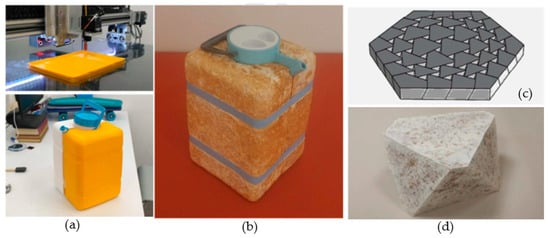
Figure 7.
(a) Scalable production practice of mycelium; (b) CAD-aided industrial design; (c) CAD-aided architectural design; (d) Unit element [27].
Scalability remains a significant barrier to widespread MBC commercialization. As emphasized by Alaneme et al. [40], the biological nature of MBC production, where materials are “grown” rather than assembled, makes the process inherently time-consuming and sensitive to environmental fluctuations. Their review identifies key limitations to scaling, including contamination risks, variability in fungal growth, and the lack of standardized protocols across fabrication methods such as molding, additive manufacturing, and hybrid composites. These factors lead to inconsistency in material performance, thereby undermining reproducibility on industrial scales. Additionally, restricted access to proprietary fabrication techniques, held by companies such as Ecovative, Green Island, NY, USA and MycoMaterials, Green Island, NY, USA, limits innovation and impedes the development of scalable, open-source solutions.
Bitting et al. [41] reviewed the limitations to MBC upscaling and noted that inconsistencies in density, strength, and surface quality often prevent these materials from meeting industry certification standards. They identified variability in environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and airflow as a key contributor to structural inconsistency in the structure of the material. Wattanavichean et al. [42] similarly noted that without standardized growth conditions, ensuring the mechanical reliability of MBCs at scale becomes difficult.
Efforts to address these challenges are being led by companies such as Ecovative and Biohm, which apply genetic engineering, strain refinement, and the incorporation of supplementary microorganisms into the production process. Moreover, Shin et al. [43] reported efforts to genetically optimize fungal strains to improve growth rate, colonization uniformity, and bonding strength. These advancements, combined with supplementary microbial consortia, have improved batch-to-batch consistency and predictability.
Elsacker et al. [28] proposed a modular and robotic hybrid approach to scalability, combining layered fabrication, robotic wire cutting, and the self-healing ability of fungal hyphae to produce larger components (Figure 8). Modular growth allows each unit to be optimized and later fused into a larger structure, while robotic cutting ensures design precision. The biological bonding ability of mycelium at seams enables structural continuity without adhesives, offering a scalable method without compromising material integrity.
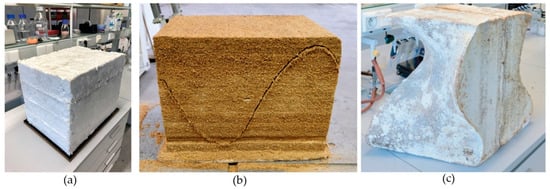
Figure 8.
Bio-hybrid practice: (a) modular layered fabrication; (b) wire-cutting; (c) self-healed composites [28].
As shown above, this figure illustrates the practical outcomes of this bio-hybrid fabrication strategy. Image (a) shows stacked modules grown separately. In (b), precision wire-cutting is used to shape complex geometries directly into the material. Image (c) demonstrates successful biological fusion across segments, highlighting the potential for seamless large-scale components without mechanical fasteners.
3.5. Durability
Long-term durability is critical for the integration of MBCs into building applications. A primary concern is their hygroscopic nature, which can lead to moisture absorption, swelling, fungal decay, or degradation of mechanical performance. Post-treatment strategies such as heat drying, surface coatings, and material densification are commonly employed to enhance durability, although these methods often introduce added cost and complexity [24].
Schultz et al. [44] further evaluated the performance of mycelium-based composites under accelerated weathering conditions. When subjected to wet–dry and freeze–thaw cycles, the materials maintained mechanical integrity, with only minor surface softening observed in surface layers. Crucially, thermal stability and impact strength remained largely unaffected, which confirms the resilience of MBCs under environmental stress. However, prolonged exposure to uncontrolled humidity can eventually degrade the material. Outdoor trials of mycelium structures showed that they remained intact for several weeks, but after four months they developed cracks, decay, pest infestation, and microbial contamination [45]. These findings indicate that long-term durability without protection is limited, as MBCs will gradually biodegrade under environmental conditions.
Biological degradation is a double-edged sword for MBCs: their compostability aligns with sustainability goals, but it means they are susceptible to breakdown when exposed to prolonged moisture. Soil burial experiments have quantified this susceptibility. For example, mycelium–hemp composite samples lost up to 43% of their mass after 16 weeks in moist soil, with the mycelial binder decomposing first [46]. These findings confirm that in a high-humidity or soil-contact environment, mycelium composites will biodegrade within months. Even in less extreme conditions, high relative humidity can encourage mold growth on the material’s surface. MBCs’ natural fungal origins are prone to “biological corrosion” (mold/mildew) when damp [24]. Ensuring long-term durability thus requires mitigating moisture ingress and biological attack.
Notably, coatings and treatments have proven effective in extending MBC lifespan. Gan et al. [45] found that applying sustainable protective coatings can slow down degradation. In one case, an uncoated mycelium panel had a useful life before biodegrading within 5 months, whereas a coated panel lasted significantly longer. The coated samples resisted moisture uptake and retained mechanical strength for a longer period. Gauvin and Vette [47] highlighted the low vapor permeability of MBC as a durability concern in insulation. Resin coatings have been widely adopted to mitigate moisture uptake; however, their weak adhesion to the mycelial surface often results in poor long-term performance. The study proposes an alternative strategy: cultivating engineered dense mycelium structures, either through extended growth cycles or genetic optimization, to inherently reduce porosity and improve hydrophobicity. In simulated climatic aging tests, involving extreme temperature and humidity cycling, the materials exhibited no notable decline in performance, confirming the feasibility of this approach. Applying water-repellent coatings is an effective way to protect MBCs from humidity. Recent studies favor bio-based coatings (to preserve sustainability) such as plant waxes and oils. Farrahnoor et al. [48] coated mycelium composites with a beeswax–coconut oil blend, drastically reducing water absorption and preventing mold growth. The best-performing coating (80% beeswax) cut water uptake to 26% and prevented fungal/mold growth for 36 days, whereas uncoated samples readily grew mold.
Another approach is to combine mycelium with other materials that impart strength or water resistance. Natural polymer additives have shown promise. For instance, researchers have reinforced mycelium composites with bacterial cellulose, a strong biopolymer produced by certain bacteria. Elsacker et al. [49], incorporating bacterial cellulose into a mycelium–hemp composite (followed by hot pressing) significantly strengthened the internal bonding of the material. The resulting hybrid had tunable mechanical properties and improved structural integrity. Complementary findings by Alemu et al. [50] demonstrate that mechanically pressed MBCs, primarily used in furniture applications, demonstrate enhanced durability due to reduced porosity. Nussbaumer et al. [23] quantified this effect, showing that hot-pressed MBCs derived from Trametes species had lower water absorption and higher structural integrity compared to unpressed samples. Additionally, pressing helps collapse pore structures, thus reducing moisture ingress and dimensional instability.
Recent studies have explored how fungal strain selection can improve MBC durability. Certain strains produce thicker, more hydrophobic hyphae, contributing to the development of naturally water-resistant surfaces [23]. For example, Trametes hirsuta fungus grows a dense, continuous mycelial network that creates a firm outer shell on the composite. This shell was shown to confer remarkable shape stability even when the composite is soaked—remaining flexible and intact in the wet state, unlike a composite made with a looser mycelium network (Pleurotus ostreatus) [51]. While promising, this strategy requires further optimization of growth conditions and strain-specific protocols.
Patent analysis by Cerimi et al. [15] confirms that industry stakeholders are actively pursuing scalable solutions to durability, as evidenced by a growing number of patents focused on densification methods, hybrid matrices, and surface treatments. Collectively, studies in the literature identify key fabrication parameters (Figure 9), such as fungal strain, substrate type, growth time, and pressing pressure, that directly influence durability.
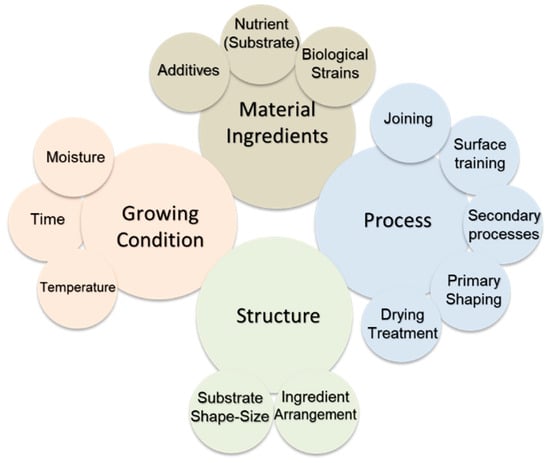
Figure 9.
Fabrication parameters of mycelium bio-composite [52].
3.6. Real-World Demonstrations
Several artistic and architectural projects have demonstrated the transition of MBCs from lab research to real-world applications. Recently, mycelium has been employed in full-scale installations by artists. This interdisciplinary convergence is an emerging trend in studies and related projects.
“Grown” architecture enables organic structures with complex geometries that are difficult to build using conventional materials. This approach supports interdisciplinary collaboration, where science informs growth protocols, engineering enables material functionality, and design drives cultural and aesthetic expression.
One of the most notable architectural applications of mycelium is the growing pavilion project (Figure 10). It was constructed in Floriade Expo 2022 for the Dutch Design Week. The 10-ton CO2-equivalent-negative and 95% circular structure, composed of five bio-based materials (wood, mycelium, agricultural residuals, bulrush, and cotton) presents a visually distinctive form with organic textures and colors. Other full-scale demonstrations, such as MycoTree, developed for the 2017 Seoul Biennale, have explored the structural capabilities of MBCs in load-bearing applications. In that project, a network of bamboo struts and mycelium nodes formed a self-supporting spatial structure. While many current implementations focus on non-load-bearing elements, these examples show the expanding architectural potential of mycelium.
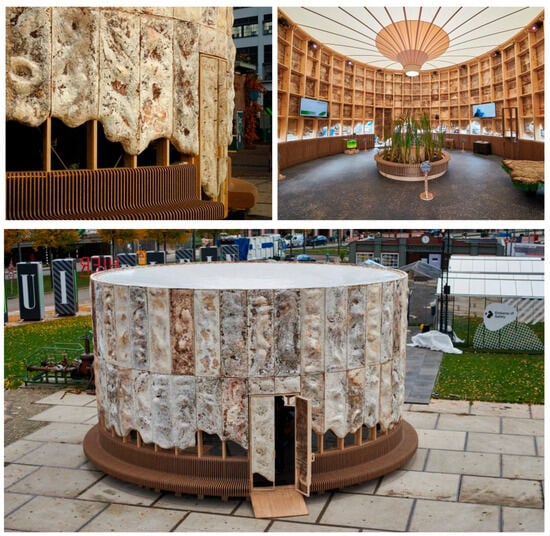

Figure 10.
Growing pavilion in Dutch design week.
Despite their promise, most MBC-based installations remain temporary and experimental. While the moisture buffering capacity and durability of MBCs are recognized, further investigation is needed on their long-term performance under UV radiation, biological decay, and fluctuating weather conditions. Drawing parallels from other bio-based materials, Es-sakali et al. [53] reported that hemp-clay bricks maintained significant moisture buffering value (2.25 g·m−2·%RH) and thermal insulation (0.31 W·m−1·K−1) even after four years of outdoor exposure without protective treatment. This suggests that with proper formulation and application strategies, bio-based composites like MBCs may also sustain hygrothermal functionality and structural performance over time.
Moreover, building regulations and certification requirements must adapt to accommodate this new class of materials. Nonetheless, these proof-of-concept projects are vital. They validate material behavior at scale, stimulate innovation, and shift public perception around regenerative architecture. As fabrication techniques mature and material consistency improves, MBCs are likely to move from conceptual showcases to integral components of mainstream sustainable construction.
To summarize, the reviewed fabrication techniques—from lab-scale protocols to industrial-scale methods—demonstrate the versatility of MBC production but also highlight significant variation in control, consistency, and scalability. The selection of substrates, fungal strains, and fabrication routes directly affects both structural and hygrothermal outcomes. The following key points synthesize the main insights from Section 3:
- MBCs can be fabricated through mold-based, additive manufacturing, and industrial hybrid methods, each with trade-offs between reproducibility and geometric complexity.
- Substrate type, fungal strain, and incubation protocols significantly affect mycelial growth and material performance.
- Additive manufacturing offers design flexibility but presents challenges in contamination control and material consistency.
- Industrial-scale production methods increasingly use composite layering, textile reinforcement, and CNFs to enhance structure and moisture resistance.
- Scalability remains constrained by biological variability, IP protection, and lack of standardized growth protocols.
These observations are further summarized in Table 1 below, which contrasts lab-scale and industrial-scale MBC fabrication methods across key technical metrics.

Table 1.
Comparison of lab-scale and industrial-scale MBC fabrication methods, thermal properties, and scalability limitations.
4. Performance Characterization of MBCs
Mechanical and hygrothermal performance are critical to the suitability of MBCs in building, yet they are rarely evaluated in conjunction. Variations in fungal species, substrate composition, and processing methods allow for the development of composites tailored to a wide range of architectural functions. This section reviews recent studies examining how these factors influence the structural and thermal behavior of MBCs.
4.1. Mechanical Response to Processing Methods
Appels et al. [54] investigated the effects of cold and hot pressing on thermo-physical properties. The results indicate that the tensile strength and elastic modulus of these materials increase significantly under hot pressing compared to cold pressing. The resulting densification shifted the stress–strain behavior from foam-like to cork- and wood-like profiles, underscoring its impact on mechanical performance (Figure 11). The study also suggested that enhancing colonization in the composite’s core, e.g., through air injection, could improve consistency and internal bonding.
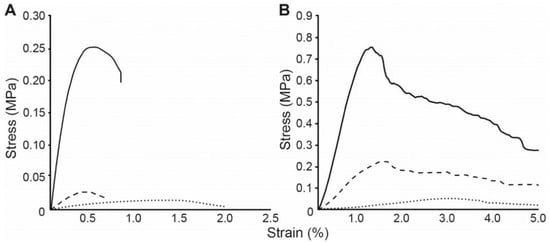
Figure 11.
Tensile (A) and bending (B) tests of P. ostreatus grown on rapeseed straw without pressing (dotted line), with cold pressing (striped line) or with hot pressing (solid line) [44].
Karana et al. [52] evaluated six mycelium-based composites fabricated under varying levels of compression and compared them to conventional materials such as MDF and cork. Heat-compressed samples exhibited the highest tensile strength, demonstrating that fabrication technique plays a critical role in mechanical optimization (Figure 12). Similarly, Lingam et al. [55] conducted a comprehensive analysis of engineered MBCs, reporting that hot-pressed composites displayed superior compressive and flexural strength, directly attributed to increased density and microstructural integrity.
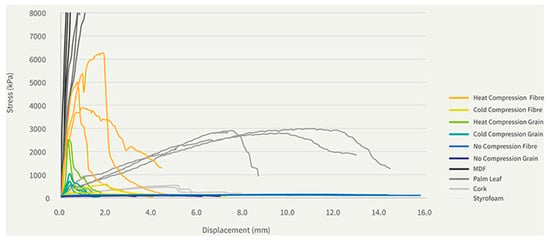
Figure 12.
Tensile test results of mycelium composites in comparison to the reference materials [52].
Islam et al. [56] characterized the mechanical response of MBCs under cyclic compressive loads. The study developed a multi-scale model, employing a random fiber network on the microscale, as well as a continuum model on the macroscale, to investigate density variation and capture its rate of change. The non-linear compressive behavior of the material was successfully characterized through the integration of the two modeling approaches. The results depicted in Figure 13 (right hand-side) show strong agreement with experimental measurements.
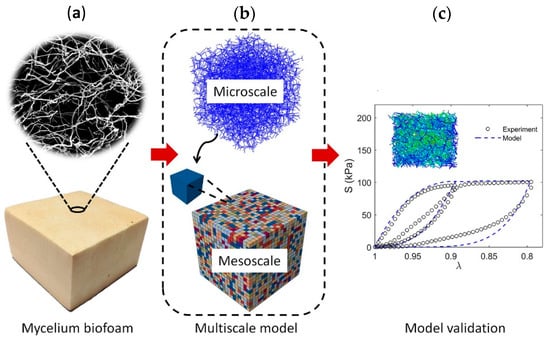
Figure 13.
(a) Scanning electron micrograph of mycelium biofoam showing its filamentous hyphal network; (b) Multiscale modeling framework linking a microscale fiber network to a mesoscale stochastic continuum representation; (c) Model validation: simulated stress–stretch response (dashed blue line) compared to experimental data (black circles), with inset showing a mesoscale simulation snapshot [56].
4.2. Hygrothermal Behavior
Water absorption and vapor permeability are critical factors influencing both the durability and insulation performance of MBCs. Attias et al. [57] measured water adsorption capacity (Figure 14) across three MBCs produced using different fungal species grown on vine and apple wood substrates. Their comparative analysis revealed that the pairing of fungal strain and substrate significantly impacts both density and water absorption behavior, emphasizing that tailored biological inputs can be used to optimize the hygrothermal performance of MBCs for specific building applications.
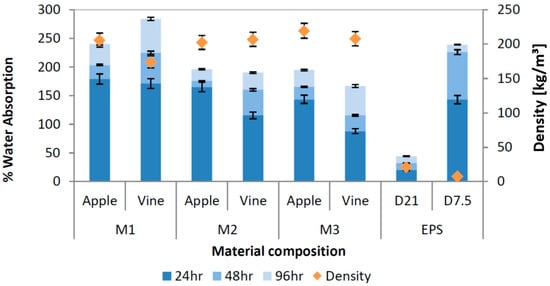
Figure 14.
Comparative analysis to evaluate the effect of material composition and incubation method on density and water absorbance performance [57].
This figure shows the variation in water absorption over time and corresponding density across different mycelium-based composites. In general, higher-density samples tend to demonstrate lower water absorption, indicating an inverse relationship between density and hygroscopic behavior. These results highlight how composition and growth conditions directly influence MBC hygrothermal performance.
Elsacker et al. [18] similarly demonstrated that densified, pre-compressed substrates reduce both water uptake and thermal conductivity (Figure 15, Table 2), reinforcing broader findings that mechanical densification generally enhances hygrothermal resilience. The results in Table 2 demonstrate that mycelium-based materials exhibit insulating properties comparable to those of traditional construction materials. Yang et al. [58] further emphasized the importance of fungal strain and pore architecture in enhancing both thermal and moisture performance. Nguyen et al. [59] provided benchmark hygrothermal data for bio-insulation materials made from bamboo fibers and natural binders, illustrating that mycelium-based materials perform comparably or better in terms of moisture buffering capacity and thermal conductivity, further supporting their viability for sustainable building envelopes.
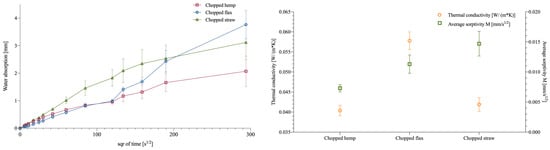
Figure 15.
Hygric and mechanical characterization of mycelium with different substrate processing [18].

Table 2.
Comparison of mycelium bio-composite’s conductivity with traditional insulation materials (letters indicate significant differences based on Tukey’s family error rate at p ≤ 0.05 for sample-specific ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)) [18].
Figure 15 shows that chopped straw yields the lowest thermal conductivity and water absorption among the tested substrates, whereas flax performs the worst. These trends reflect substrate-dependent differences in porosity and moisture affinity. Table 2 further highlights that mycelium–hemp and straw composites offer thermal conductivity comparable to conventional insulators like glass wool, despite their much lower density—underscoring their potential as efficient, lightweight, bio-based insulation materials.
Farrera-Vázquez et al. [60] studied MBCs made from Trametes elegans and measured hygrothermal parameters including moisture sorption and buffering capacity. Their findings confirm that MBCs contribute to regulating indoor humidity while maintaining thermal insulation, supporting passive building strategies. Pittau et al. [61] and Babenko et al. [62] also conducted comparative assessments of MBCs with plant-fiber composites. Both studies found that MBCs exhibit competitive or superior performance in thermal conductivity, moisture buffering, and biodegradability, positioning them as effective alternatives for environmentally responsive building envelopes.
Thermal insulation performance is a key property in evaluating mycelium-based composites in building applications, and recent studies have shown that fabrication parameters directly influence their effectiveness. A detailed exploration of thermal insulation performance was provided by Sağlam and Özgünler [63], who evaluated mycelium composites fabricated from Ganoderma lucidum. The study found that both incubation time and substrate choice significantly influenced thermal conductivity, which ranged from 0.036 to 0.048 W·m−1·K−1, comparable to those of commercial insulation products. Jin et al. [64] examined Pleurotus ostreatus grown on straw, showing that thermal performance improved with increased incubation time and optimized fiber packing density. These findings suggest that fine-tuning growth parameters can significantly enhance insulation performance.
However, comprehensive hygrothermal characterization of MBCs remains limited. Koh et al. [65] explicitly measured both moisture sorption isotherms and coupled heat-moisture behavior in MBCs. In this work, equilibrium moisture sorption isotherms were obtained for mycelium-based composites alongside other plant-based insulations (Figure 16), and the dependence of thermal conductivity on relative humidity was quantified (Figure 17). This study provided one of the first quantitative links between hygric and thermal properties in mycelium materials.
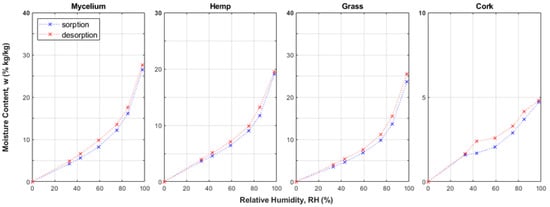
Figure 16.
Sorption isotherms for mycelium, hemp, grass and cork composites [65].
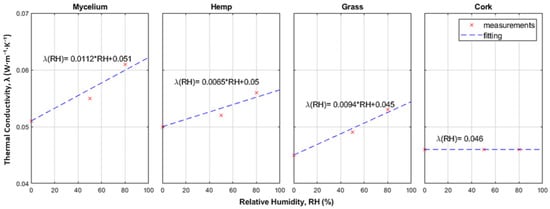
Figure 17.
Thermal conductivity against RH for mycelium, hemp, grass and cork composites [65].
Hemp, grass, and mycelium exhibit comparable thermo-hygric performance in the presented data. However, cork (on the right-hand side) shows the lowest thermal conductivity and sorption capacity among the tested materials.
Subsequent studies have built upon these findings by examining the direct correlation between thermal and hygric properties and the role of microstructure in MBC performance. Wildman et al. [66] reaffirmed that moisture content is a critical extrinsic factor influencing the effective thermal conductivity of mycelium composites. In practical terms, absorbed moisture within the pore network increases thermal conductivity because water conducts heat more readily than air. Song et al. [67] addressed this issue by applying a hydrophobic alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) treatment to mycelium-based insulation materials. The AKD treatment significantly reduced the water absorption of the composites and improved their mold resistance, thereby preserving low thermal conductivity under humid conditions. This modification underscores that limiting moisture ingress (for instance, via surface hydrophobization) can substantially enhance the hygrothermal stability and durability of MBCs.
These findings collectively underscore that both formulation and microstructure critically influence MBC hygrothermal performance.
4.3. Environmental Impact of MBCs
Owing to their favorable hygrothermal performance—characterized by low thermal conductivity, high vapor permeability, and effective moisture buffering—mycelium-based composites (MBCs) can significantly reduce operational energy demand for heating and cooling in buildings. Beyond these operational benefits, recent life cycle assessment (LCA) studies also highlight their low embodied carbon, positioning MBCs as promising materials for environmentally sustainable and low-impact construction.
Recent studies assessing the environmental impact of mycelium-based composites (MBCs) consistently demonstrate their potential as low-carbon or even carbon-negative building materials, especially when produced under optimized conditions. Stelzer et al. [16] conducted a cradle-to-gate life cycle assessment (LCA) of fungal composite bricks and reported emissions of approximately 0.49 kg CO2-eq per brick on a laboratory scale, which could be reduced by up to 68% in an industrialized scenario. The study highlighted electricity consumption during sterilization, incubation, and drying as the dominant contributor to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Compared to conventional bricks, MBCs showed 2.5 to 6 times lower emissions, though they performed worse in categories such as eutrophication and land use due to the agricultural origin of the substrates. Similarly, Volk et al. [68] evaluated mycelium insulation produced in Germany and found its embodied carbon to be around 0.37 kg·CO2-eq·kg−1 lower than many synthetic insulations like XPS and PIR. However, they noted that bio-based insulations such as strawboard and wood fiber still outperform MBCs in terms of overall climate impact when end-of-life phases are considered.
Other LCA studies reinforce these findings, while also pointing to key trade-offs. Alaux et al. [69] found that mycelium insulation blocks could achieve lower emissions than petroleum-based foam insulation, but did not outperform mineral wool in most impact categories. They emphasized that electricity use during manufacturing remains the most significant environmental hotspot. In a carbon sequestration-focused study, Livne et al. [70] demonstrated that MBCs could act as carbon sinks, reporting a net negative embodied carbon of −39.5 kg·CO2-eq·m−3 due to biogenic carbon storage in the fungal matrix. Akromah et al. [71] showed that in African contexts, mycelium bricks produced with renewable energy could emit five times less GHG than concrete bricks, but with fossil-fuel-based electricity, their impact could exceed that of concrete. These studies collectively indicate that while MBCs are promising environmentally, their actual carbon performance is highly sensitive to energy sourcing, processing methods, and regional context.
4.4. Fire Resistance and Safety of MBCs
Fire performance testing over the past decade indicates that MBCs can exhibit favorable fire behavior compared to conventional synthetic and wood-based materials. Cone calorimetry studies report that MBCs have competitive or lower flammability metrics, including delayed ignition and reduced heat release. For example, Irbe et al. [72] found peak heat release rates (pHRRs) of roughly 134–243 kW·m−2 for various mycelium-based insulation boards—values significantly below those of expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam or plywood (which typically reach 240–280 kW·m−2) [72]. Correspondingly, total heat release (THR) from mycelium composites (often <~30 kW·m−2) was much lower than that of wood-based panels (98–127 kW·m−2) [72]. Such improvements are largely attributed to the mycelium’s propensity to char. Under fire, the fungal biomass forms an insulating char layer that slows thermal decomposition and inhibits volatile fuel release. Jones et al. [73] demonstrated via thermogravimetry and pyrolysis combustion flow calorimetry that pure mycelium has a significantly lower combustion propensity than common polymers (PMMA or PLA), making it noticeably less prone to ignition and flaming. In cone calorimetry, even a modest mycelial content in composites was shown to reduce the heat release rate by promoting char formation, which acts as a thermal barrier [73]. Notably, the charring tendency of mycelium-rich composites does not substantially benefit from extended growth time (beyond a certain point), meaning even relatively short-grown mycelium can impart inherent fire-resistance to the material [73]. Decomposition of mycelium generally starts around 250 °C—overlapping with hemicellulose and lignin breakdown—but yields a high char residue (aided by the fungi’s natural chitin/protein content) [72]. This robust char network in turn delays combustion and reduces peak temperatures, explaining why MBCs often outperform high-density foams and wood in fire tests [72].
Other fire-relevant behaviors of MBCs have also been documented through standardized lab-scale tests. In cone calorimeter experiments (ISO 5660), mycelium composites consistently showed lower smoke production than petrochemical foams: Irbe et al. [72] observed total smoke release values of 7–281 m2·m−2 for MBC specimens, compared to hundreds for polyurethane or polyisocyanurate insulations. The lowest-smoke MBC formulations (e.g., dense waste-fiber/mycelium boards) yielded an order-of-magnitude less smoke than typical rigid foam, suggesting a potential safety advantage in reducing toxic fire effluents. Flame-spread performance has been evaluated with small-scale flame tests as well. Chulikavit et al. [74] incorporated mycelium into an epoxy polymer and found that UL-94 vertical burn tests exhibited slower flame spread and shorter burn lengths in the mycelium-infused samples relative to neat epoxy [74]. In practice, many mycelium composites tend to self-extinguish once the ignition source is removed, due to the protective char layer starving the flame of fuel and oxygen [73]. Even at sustained heat flux (e.g., 35 kW·m−2 in cone tests), mycelium-based panels often burn out with smaller THR and leave substantial char residue [72]. Overall, recent validated fire tests—including cone calorimetry, thermogravimetric analysis, and UL 94 classifications—concur that mycelium bio-composites exhibit reduced flammability, slower flame spread, high char yield, and lower smoke generation compared to many conventional building materials [75]. These properties underscore the promise of MBCs as an inherently fire-resilient, sustainable material class for applications like insulation and cladding in buildings.
4.5. Influence of Microstructure on the Hygrothermal Performance of MBCs
As MBC research progresses, increasing attention is placed on how microstructural features affect thermal insulation and moisture control. New research has shown that the microstructure of MBCs plays a pivotal role in governing their thermal–hygrothermal performance. Zhang et al. [76] fabricated an ultra-light mycelium composite (approximately 94% porosity) with a hierarchical pore architecture, achieving a thermal conductivity as low as 0.044 W·m−1·K−1. This performance, comparable to conventional foam insulations, highlights that tailoring the pore size distribution (e.g., combining micro- and macro-pores in an optimal ratio) can markedly improve insulation effectiveness.
Verhelst et al. [77] further demonstrated that the intrinsic mycelial network structure, shaped by fungal strain and growth conditions, directly influences both thermal and hygric outcomes. In their study, composites produced by fungi that developed denser, more homogenously colonized mycelium networks showed lower bulk density and enhanced thermal insulation capacity. This seemingly counterintuitive result, where denser fungal growth leads to reduced thermal conductivity, is attributed to microstructural transformation: the fungal colonization partially consumes and binds the lignocellulosic substrate, reducing solid mass while maintaining volume. This process generates more small, air-filled pores and reduces the size and connectivity of larger voids. As a result, the material contains a higher fraction of insulating micropores and fewer interconnected macro-pores, thus impeding convective heat transfer and lowering the effective thermal conductivity.
Moreover, a well-developed mycelial “skin” and network tend to increase the surface hydrophobicity of the composite. In dense mycelium composites, this inherent hydrophobic character helps resist moisture uptake, allowing air pockets to remain dry and effective for insulation even under high humidity. Verhelst et al. observed that all their mycelium samples exhibited considerable hydrophobicity, with water contact angles ranging from approximately 105° to 122°. As a result, only subtle inter-strain differences in moisture sorption could be detected. Consequently, no strong statistical correlation between contact angle and thermal conductivity emerged among those samples; nevertheless, the concept that moisture incurs a thermal penalty was evident.
Motamedi et al. [19] systematically evaluated the coupled heat and moisture behavior of MBCs fabricated from hemp and straw substrates colonized by Ganoderma lucidum and Trametes versicolor, using a multi-scale experimental protocol. Notably, their study includes one of the rare experimental characterizations of sorption isotherms for MBCs, showing moisture contents reaching up to 30% at 90% RH and confirming the influence of additives, substrate type, and fungal species on hygroscopic behavior. Additive-enriched composites exhibited up to 21.8% higher moisture uptake at 90% RH, while straw-based composites reached free water saturation values up to 704 kg·m−3, indicating greater moisture sensitivity. In contrast, hemp–Ganoderma composites exhibited lower vapor permeability and a moisture sensitivity coefficient thirty times lower than Trametes-based samples in thermal conductivity response. Thermal conductivity ranged from 0.045 to 0.08 W·m−1·K−1, increasing nonlinearly with relative humidity and temperature. These findings confirm that dense, interconnected hyphal networks suppress capillary condensation and vapor transport, enhancing moisture buffering and thermal stability. A comparison of the average thermal conductivities obtained in this study with various EPS grades is presented in Figure 18.
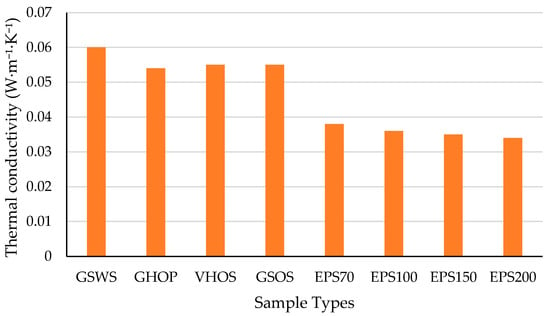
Figure 18.
Comparison of average thermal conductivity values of selected mycelium-based composites with conventional expanded polystyrene (EPS) insulation materials (EPS70–EPS200).
The sample codes in the figure above represent specific combinations of fungal species, substrates, additives, and treatment methods, following a standardized naming convention. Full definitions of these abbreviations are provided in the Nomenclature section. The results highlight the competitive insulation performance of MBCs, with thermal conductivity values ranging from 0.054 to 0.06 W·m−1·K−1, approaching those of conventional EPS products, particularly in denser, well-structured formulations like GHOP.
Recent studies confirm that optimizing pore architecture and controlling moisture interaction are vital for maximizing MBC insulation performance. Overall, the integration of mechanical, thermal, and hygric characterization, alongside microstructural analysis, provides a more holistic understanding of MBC performance. By leveraging these insights, researchers and practitioners can better design mycelium-based composites with balanced mechanical strength, enhanced insulation value, and robust moisture resistance for sustainable building applications.
In conclusion, the performance of MBCs is closely tied to the interplay between fabrication parameters and microstructural development. Mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and moisture buffering can be improved through densification, fungal selection, and surface treatments. Environmental and safety evaluations further reinforce the suitability of MBCs as sustainable alternatives to conventional insulation materials. The main findings are summarized below:
- Mechanical performance improves significantly with densification techniques such as hot pressing, which reduce porosity and enhance strength.
- Hygrothermal performance is strongly influenced by fungal strain, substrate, and microstructure; denser mycelial networks yield better insulation and lower water uptake.
- MBCs exhibit thermal conductivities (0.036–0.048 W·m−1·K−1) comparable to commercial insulation while offering biodegradability and carbon negativity.
- Life cycle assessments confirm MBCs’ low embodied carbon, though results vary based on region, energy sourcing, and end-of-life treatment.
- MBCs demonstrate promising fire resistance and self-extinguishing behavior due to char formation and low combustion rates, enhancing safety for building applications.
5. Discussion
This review aimed to move beyond cataloging the properties of mycelium bio-composites (MBCs) by synthesizing observed relationships between fabrication methods, microstructural development, and performance characteristics, particularly in relation to real-world feasibility. Its central contribution lies in structuring a fragmented body of experimental data into a cohesive framework that explains how MBCs can transition from lab-scale innovations to scalable, application-ready materials. To that end, we categorized the literature into eight thematic domains and evaluated each with respect to fabrication techniques, resulting properties, and performance outcomes.
5.1. Fabrication Methods
MBCs are produced using mold-based growth, additive manufacturing techniques such as direct ink writing (DIW) and paste extrusion, and hybrid methods combining biological growth with textiles or cellulose nanofibrils. Mold-based techniques offer reproducibility (Elsacker et al. [18]; Stelzer et al. [16]), while additive manufacturing enables complex geometries and tailored microstructures (Teoh et al. [30]; Soh et al. [31]; Luo et al. [32]). However, these approaches face challenges with contamination, growth variability, and process standardization (Camilleri et al. [24]; Mohseni et al. [25]). Emerging robotic fabrication and modular strategies (Attias et al. [27]; Elsacker et al. [28]) show promise for scalable production. Despite innovation in additive manufacturing and robotic methods, fabrication processes remain highly variable due to inconsistent sterilization, contamination risks, and lack of standardized protocols, which limits reproducibility and comparability across studies (Camilleri et al. [24]; Mohseni et al. [25]; Jones et al. [29]).
5.2. Mechanical and Hygrothermal Properties
MBCs exhibit thermal conductivity values between 0.036 and 0.06 W·m−1·K−1, comparable to materials like mineral wool, hempcrete, and cork (Koh et al. [65]; Motamedi et al. [19]; Babenko et al. [62]). Mechanical strength, particularly tensile and compressive properties, is significantly improved through densification processes such as hot pressing (Appels et al. [54]; Karana et al. [52]; Lingam et al. [55]). Performance varies with fungal strain, substrate, and processing: dense mycelial networks reduce water uptake and enhance insulation, while loosely structured composites offer better moisture buffering (Verhelst et al. [77]; Yang et al. [58]; Attias et al. [57]; Farrera-Vázquez et al. [60]).
Recent studies have characterized sorption isotherms and demonstrated the impact of relative humidity on thermal conductivity (Koh et al. [65]; Motamedi et al. [19]). Moisture uptake increases effective conductivity, emphasizing the importance of microstructural control. Motamedi et al. also quantified vapor permeability and moisture sensitivity across fungal–substrate combinations, highlighting hyphal density as a key determinant. Additionally, multi-scale models have been used to describe compressive behavior in relation to density and pore architecture, bridging microstructure with mechanical response (Islam et al. [56]). These findings underscore the potential to tailor MBCs for both structural and hygrothermal applications through process and material optimization. However, maintaining consistent performance remains challenging due to sensitivity to ambient humidity and the variability introduced by fungal strain and substrate heterogeneity.
5.3. Environmental Impact and Life Cycle Performance
Several LCA studies demonstrate the environmental benefits of MBCs, including low embodied energy and carbon-negative performance under optimal conditions (Stelzer et al. [16]; Livne et al. [70]). Carbon footprints range from 0.37 kg CO2-eq·kg−1 to −39.5 kg CO2-eq·m−3 depending on the production method and energy source (Volk et al. [68]; Akromah et al. [71]). However, high electricity demand for sterilization and drying remains a key impact driver (Alaux et al. [69]). Compared to petroleum-based materials like XPS and PIR, MBCs offer a favorable emissions profile, but trade-offs exist in categories such as eutrophication and land use. While MBCs have low embodied carbon, their environmental footprint is highly dependent on energy-intensive steps such as sterilization and drying. Regional variation in electricity sourcing significantly affects LCA outcomes.
5.4. Fire Resistance and Safety
MBCs demonstrate intrinsic fire resistance via formation of a char layer that slows flame spread and reduces heat release and smoke generation (Irbe et al. [72]; Jones et al. [73]). Cone calorimetry and UL-94 vertical burn tests confirm that certain formulations not only resist ignition but also self-extinguish once the heat source is removed (Chulikavit et al. [74]). These properties make MBCs promising candidates for safe insulation applications, although further validation under standardized conditions is needed. Fire performance testing of MBCs remains limited to lab-scale studies; standardized certification procedures for fire safety are still lacking, which hinders integration into building codes.
5.5. Durability and Long-Term Performance
As bio-derived materials, MBCs are inherently biodegradable, making moisture exposure a critical concern. Without treatment, samples may lose up to 43% of their mass after 16 weeks in soil (Van Wylick et al. [46]). However, post-treatments such as beeswax–coconut oil coatings (Farrahnoor et al. [48]) and hot pressing (Nussbaumer et al. [23]; Alemu et al. [50]) significantly enhance moisture resistance and delay microbial decay. Strain selection for dense, hydrophobic hyphae (e.g., Trametes hirsuta) has also been shown to improve performance under wet conditions (Kuribayashi et al. [51]; Gauvin and Vette [47]). Despite these advances, long-term exposure to UV, freeze–thaw cycles, and microbial attack still warrants further study (Schultz et al. [44]; Gan et al. [45]). Another challenge is that uncoated MBCs degrade rapidly under outdoor or high-humidity conditions, while protective treatments that enhance durability may compromise their inherent compostability (Van Wylick et al. [46]; Gan et al. [45]; Gauvin and Vette [47]).
5.6. Scalability and Real-World Implementation
Pilot-scale installations such as the Growing Pavilion and MycoTree highlight the architectural potential of MBCs (Es-sakali et al. [53]), but full-scale commercialization remains limited. Scaling is challenged by batch variability, growth inconsistency, and the absence of standardized, reproducible fabrication protocols (Alaneme et al. [40]; Bitting et al. [41]; Shin et al. [43]). Many fabrication techniques remain proprietary, limiting transparency and broader adoption. A synthesis of the literature also points to systemic barriers: the lack of open-source methods hinders collaborative development, and the absence of certification pathways restricts integration into regulatory frameworks. Despite these constraints, advances in genetic engineering, robotic automation, and modular bio-hybrid strategies offer promising routes toward scalable and consistent production (Attias et al. [27]; Elsacker et al. [28]; Wattanavichean et al. [42]).
5.7. Innovation Landscape
Beyond academic exploration, the development of MBCs is increasingly influenced by industrial innovation and intellectual property strategies. Cerimi et al. [15] identified a growing number of patents related to mycelium applications, including structural panels, fire-resistant boards, and packaging systems. These findings confirm that fungal composites are attracting commercial interest, particularly for low-carbon material applications. However, much of the innovation remains proprietary, and access to these fabrication technologies is limited—posing a challenge for standardization, open-source collaboration, and certification alignment.
5.8. Comparative Bio-Based Materials
Several studies have benchmarked MBCs against other bio-based insulators such as hempcrete, cork, straw, and bamboo fiber composites. While MBCs offer comparable or superior thermal conductivity and biodegradability (Koh et al. [65]; Nguyen et al. [59]; Verhelst et al. [77]), they often underperform in mechanical durability and moisture resistance unless treated (Song et al. [67]; Yang et al. [58]). In general, MBCs benefit from tunable composition and locally sourced lignocellulosic feedstocks, supporting material circularity and regional adaptability. However, further optimization is needed to match the long-term performance of more established bio-based materials in demanding building environments.
To complement this thematic synthesis, Table 3 presents an overview of the main constituents and technological approaches reported across the reviewed studies. This classification reflects the diversity of substrates, fungal strains, and fabrication strategies employed, along with the specific innovations or performance goals pursued in each case. These distinctions help situate the thematic insights within the broader context of material configurations and research directions observed in the field.

Table 3.
Overview of constituent materials and technological approaches used across the reviewed MBC studies.
Building on the diverse approaches and material strategies observed across the literature, future research should prioritize the development of standardized, reproducible fabrication protocols, particularly for additive and hybrid manufacturing, to improve consistency and enable certification. Further investigation is needed to optimize mechanical and hygrothermal performance under variable environmental conditions, with emphasis on coupled heat and moisture behavior, sorption isotherms, and long-term exposure. Expanding life cycle assessments to include diverse climatic regions and energy contexts will improve the comparability and robustness of environmental impact evaluations. Fire safety research should advance beyond laboratory-scale testing toward standardized assessments aligned with building codes. Addressing the durability and compostability trade-off remains essential, especially through bio-based treatments that preserve circularity. For real-world adoption, efforts must also target scalable, modular production systems and open-access knowledge sharing. Lastly, benchmarking MBCs against other bio-based materials under unified criteria will help position them more clearly within the broader landscape of sustainable construction options.
6. Conclusions
This review synthesizes a decade of experimental and applied research on mycelium bio-composites (MBCs), highlighting how fabrication methods directly influence mechanical and hygrothermal performance. Key findings include:
Fabrication methods such as mold-based, 3D printing, and hybrid techniques significantly impact consistency, scalability, and microstructure.
Mechanical and hygrothermal properties are strongly dependent on fungal strain, substrate, and densification techniques, with densified MBCs showing better insulation and moisture resistance.
- Environmental performance is promising, with several LCA studies confirming low or even negative embodied carbon under optimized conditions.
- Durability remains a critical limitation, especially under prolonged humidity; however, post-treatment and material hybridization strategies show potential.
- Fire resistance is generally favorable due to high char formation and low smoke release, making MBCs safer than many synthetic insulations.
Based on this synthesis, we recommend the following future research directions:
- Standardizing fabrication protocols to enable reproducibility and certification, especially for 3D printing and modular assembly.
- Advancing bio-hybrid strategies, including robotic manufacturing and self-healing systems, to improve scalability and reliability.
- Extending durability studies across diverse climates and building types, focusing on long-term moisture, UV, and biodegradation performance.
- Quantitative coupling of microstructure with thermal and moisture behavior, to enable predictive material design.
- Comprehensive LCA and end-of-life studies in various regional contexts to inform policy and market adoption.
Collectively, these findings provide a technical foundation for scaling MBCs as viable components in high-performance, low-carbon buildings.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Nomenclature
| Units: | |
| % | Percent (relative humidity, energy savings) |
| °C | Degrees Celsius (temperature) |
| W/m·K | Watts per meter-Kelvin (thermal conductivity) |
| MPa | Mega Pascal |
| Abbreviations: | |
| AKD | Alkyl Ketene Dimer |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| CNF | Cellulose Nanofibrils |
| CO2-eq | Carbon Dioxide Equivalent |
| DIW | Direct Ink Writing |
| EU | European Union |
| EPS | Expanded Polystyrene |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| GHOP | Ganoderma lucidum + Hemp + Without Additive + Pasteurized Substrate |
| GSOS | Ganoderma lucidum + Straw + Without Additive + Sterilized Substrate |
| GSWS | Ganoderma lucidum + Straw + With Additive + Sterilized Substrate |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LCZEB | Life-Cycle Zero Energy Building |
| MBC | Mycelium Bio-Composite |
| MDF | Medium Density Fiberboard |
| PHBH | Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) |
| PIR | Polyisocyanurate |
| PLA | Polylactic Acid |
| PVA | Polyvinyl Alcohol |
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| UTS | Ultimate Tensile Strength |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VHOS | Trametes versicolor + Hemp + Without Additive + Sterilized Substrate |
| XPS | Extruded Polystyrene |
| ZEB | Zero Energy Building |
References
- Moussa, T.; Maalouf, C.; Ingrao, C.; Scrucca, F.; Costantine, G.; Asdrubali, F. Bio-based and recycled-waste materials in buildings: A study of energy performance of hemp-lime concrete and recycled-polyethylene terephthalate façades for office facilities in France and Italy. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 2018, 24, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasreen, M.M.; Banfill, P.F.; Menzies, G.F. Life-cycle assessment and the environmental impact of buildings: A review. Sustainability 2009, 1, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, G.; Schade, J.; Olofsson, T. Requirements management for the design of energy efficient buildings. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2013, 18, 321–337. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Jain, R.; Paul, S.; Vu, T.; Saifullah, A.; Sha, M. An internet of things framework for smart energy in buildings: Designs, prototype, and experiments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2015, 2, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, A.; Hughes, M.; Winter, S.A. multidisciplinary approach to sustainable building material selection: A case study in a Finnish context. Build. Environ. 2014, 82, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Brischke, C. Performance of Bio-Based Building Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Canada Energy Regulator. Canada’s Energy Future 2023: Energy Supply and Demand Projections to 2050; Canada Energy Regulator: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2023; Available online: https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/canada-energy-future/2023/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Beccali, M.; Cellura, M.; Fontana, M.; Longo, S.; Mistretta, M. Energy retrofit of a single-family house: Life cycle net energy saving and environmental benefits. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M. Reducing the environmental impact of construction by using renewable materials. J. Renew. Mater. 2015, 3, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuéllar-Franca, R.M.; Azapagic, A. Environmental impacts of the UK residential sector: Life cycle assessment of houses. Build. Environ. 2012, 54, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.; Tretsiakova-McNally, S. Sustainable non-metallic building materials. Sustainability 2010, 2, 400–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutil, Y.; Rousse, D.; Quesada, G. Sustainable buildings: An ever evolving target. Sustainability 2011, 3, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, S.; Rousse, D.R.; Promis, G. The evolution of crop-based materials in the built environment: A review of the applications, performance, and challenges. Energies 2023, 16, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-sakali, N.; Pfafferott, J.; Mghazli, M.O.; Cherkaoui, M. Towards climate-responsive net zero energy rural schools: A multi-objective passive design optimization with bio-based insulations, shading, and roof vegetation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 120, 106142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerimi, K.; Akkaya, K.C.; Pohl, C.; Schmidt, B.; Neubauer, P. Fungi as source for new bio-based materials: A patent review. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, L.; Hoberg, F.; Bach, V.; Schmidt, B.; Pfeiffer, S.; Meyer, V.; Finkbeiner, M. Life cycle assessment of fungal-based composite bricks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorse, C.; Thomas, F.; Glew, D.; Shenton, D.M. Achieving sustainability in new build and retrofit: Building performance and life cycle analysis. In Building Sustainable Futures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 183–207. [Google Scholar]
- Elsacker, E.; Vandelook, S.; Brancart, J.; Peeters, E.; De Laet, L. Mechanical, physical and chemical characterisation of mycelium-based composites with different types of lignocellulosic substrates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedi, S.; Rousse, D.R.; Promis, G. Microstructure-Driven Hygrothermal Behavior of Mycelium-Based Composites for Bio-Based Insulation. Energies 2025, 18, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, V.; Schmidt, B.; Pohl, C.; Cerimi, K.; Schubert, B.; Weber, B.; Volpato, A. Mind the Fungi; Universitätsverlag der Technischen Universität Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar, N.; Laibach, N. Sustainability check for bio-based technologies: A review of process-based and life cycle approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, D.G.; Simion, I.; Tiuc, A.E.; Vasile, O. Mycelium-based composites as a sustainable solution for waste management and circular economy. Materials 2024, 17, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumer, M.; Van Opdenbosch, D.; Engelhardt, M.; Briesen, H.; Benz, J.P.; Karl, T. Material characterization of pressed and unpressed wood–mycelium composites derived from two Trametes species. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, E.; Narayan, S.; Lingam, D.; Blundell, R. Mycelium-based composites: An updated comprehensive overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2025, 79, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, A.; Vieira, F.R.; Pecchia, J.A.; Gürsoy, B. Three-dimensional printing of living mycelium-based composites: Material compositions, workflows, and ways to mitigate contamination. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Kaiser, R.; Ozkan, D.; Hoenerloh, A.; Agraviador, A.; Elsacker, E.; Bridgens, B. Knitted Cultivation: Textiling a Multi-Kingdom Bio Architecture, in Structures and Architecture a Viable Urban Perspective? CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Attias, N.; Danai, O.; Abitbol, T.; Tarazi, E.; Ezov, N.; Pereman, I.; Grobman, Y.J. Mycelium bio-composites in industrial design and architecture: Comparative review and experimental analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsacker, E.; Søndergaard, A.; Van Wylick, A.; Peeters, E.; De Laet, L. Growing living and multifunctional mycelium composites for large-scale formwork applications using robotic abrasive wire-cutting. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Huynh, T.; Dekiwadia, C.; Daver, F.; John, S. Mycelium composites: A review of engineering characteristics and growth kinetics. J. Bionanosci. 2017, 11, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, J.H.; Soh, E.; Le Ferrand, H. Manipulating fungal growth in engineered living materials through precise deposition of nutrients. Int. J. Bioprinting 2024, 10, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, E.; Teoh, J.H.; Leong, B.; Xing, T.; Le Ferrand, H. 3D printing of mycelium engineered living materials using a waste-based ink and non-sterile conditions. Mater. Des. 2023, 236, 112481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Yang, J.; Peek, N. 3D-Printed Mycelium Biocomposites: Method for 3D Printing and Growing Fungi-Based Composites. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 12, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.M.; Bhardwaj, A.; Pei, Z.; Ufodike, C.; Castell-Perez, E. The 3D printing of biomass–fungi composites: Effects of waiting time after mixture preparation on mechanical properties, rheological properties, minimum extrusion pressure, and print quality of the prepared mixture. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, E.; Chew, Z.Y.; Saeidi, N.; Javadian, A.; Hebel, D.; Le Ferrand, H. Development of an extrudable paste to build mycelium-bound composites. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Vasselli, J.; Lucht, M.; Pei, Z.; Shaw, B.; Grasley, Z.; Wei, X.; Zou, N. 3D printing of biomass-fungi composite material: A preliminary study. Manuf. Lett. 2020, 24, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Klemm, S.; Dönitz, A.G.; Ou, Y.; Schmidt, B.; Fleck, C.; Simon, U.; Völlmecke, C. Tailoring the Mechanical Properties of Fungal Mycelium Mats with Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing of PHBH and PLA Biopolymers. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 49609–49617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Wu, Z.; Weiland, K.; Wang, Z.; Masania, K.; Wang, B. Fabrication of living entangled network composites enabled by mycelium. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2309370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tajvidi, M.; Hunt, C.G.; McIntyre, G.; Gardner, D.J. Fully bio-based hybrid composites made of wood, fungal mycelium and cellulose nanofibrils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Walczyk, D.; McIntyre, G.; Bucinell, R.; Tudryn, G. Manufacturing of biocomposite sandwich structures using mycelium-bound cores and preforms. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Anaele, J.U.; Oke, T.M.; Kareem, S.A.; Adediran, M.; Ajibuwa, O.A.; Anabaranze, Y.O. Mycelium based composites: A review of their bio-fabrication procedures, material properties and potential for green building and construction applications. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 83, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitting, S.; Derme, T.; Lee, J.; Van Mele, T.; Dillenburger, B.; Block, P. Challenges and opportunities in scaling up architectural applications of mycelium-based materials with digital fabrication. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanavichean, N.; Phanthuwongpakdee, J.; Koedrith, P.; Laoratanakul, P.; Thaithatgoon, B.; Somrithipol, S.; Kwantong, P.; Nuankaew, S.; Pinruan, U.; Chuaseeharonnachai, C.; et al. Mycelium-Based Breakthroughs: Exploring Commercialization, Research, and Next-Gen Possibilities. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Ro, H.S.; Kawauchi, M.; Honda, Y. Review on mushroom mycelium-based products and their production process: From upstream to downstream. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2025, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, N.; Fazli, A.; Piros, S.; Barranco-Origel, Y.; DeLa Cruz, P.; Schneider, D.Y. Characterization of Mycelium Biocomposites under Simulated Weathering Conditions. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 8408–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.K.; Soh, E.; Saeidi, N.; Javadian, A.; Hebel, D.E.; Le Ferrand, H. Temporal characterization of biocycles of mycelium-bound composites made from bamboo and Pleurotus ostreatus for indoor usage. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wylick, A.; Elsacker, E.; Yap, L.L.; Peeters, E.; De Laet, L. Mycelium composites and their biodegradability: An exploration on the disintegration of mycelium-based materials in soil. Constr. Technol. Archit. 2022, 1, 652–659. [Google Scholar]
- Gauvin, F.; Vette, I.J. Characterization of Mycelium-Based Composites as Foam-Like Wall Insulation Material. Master’s Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Farrahnoor, A.; Sazali, N.A.A.; Yusoff, H.; Zhou, B.T. Effect of beeswax and coconut oil as natural coating agents on morphological, degradation behaviour, and water barrier properties of mycelium-based composite in modified controlled environment. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 196, 108763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsacker, E.; Vandelook, S.; Damsin, B.; Van Wylick, A.; Peeters, E.; De Laet, L. Mechanical characteristics of bacterial cellulose-reinforced mycelium composite materials. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemu, D.; Tafesse, M.; Mondal, A.K. Mycelium-based composite: The future sustainable biomaterial. Int. J. Biomater. 2022, 2022, 8401528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuribayashi, T.; Lankinen, P.; Hietala, S.; Mikkonen, K.S. Dense and continuous networks of aerial hyphae improve flexibility and shape retention of mycelium composite in the wet state. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 152, 106688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karana, E.; Blauwhoff, D.; Hultink, E.J.; Camere, S. When the material grows: A case study on designing (with) mycelium-based materials. Int. J. Des. 2018, 12, 119–136. Available online: https://research.tudelft.nl/en/publications/when-the-material-grows-a-case-study-on-designing-with-mycelium-b (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Es-sakali, N.; Charai, M.; Kaitouni, S.I.; Ait Laasri, I.; Mghazli, M.O.; Cherkaoui, M.; Pfafferott, J.; Ukjoo, S. Energy efficiency and hygrothermal performance of hemp clay walls for Moroccan residential buildings: An integrated lab-scale, in-situ and simulation-based assessment. Appl. Energy 2023, 352, 121967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, F.V.; Camere, S.; Montalti, M.; Karana, E.; Jansen, K.M.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Krijgsheld PWösten, H.A. Fabrication factors influencing mechanical, moisture-and water-related properties of mycelium-based composites. Mater. Des. 2019, 161, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, D.; Narayan, S.; Mamun, K.; Charan, D. Engineered mycelium-based composite materials: Comprehensive study of various properties and applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 391, 131841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Tudryn, G.; Bucinell, R.; Schadler, L.; Picu, R.C. Stochastic continuum model for mycelium-based bio-foam. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attias, N.; Danai, O.; Tarazi, E.; Pereman, I.; Grobman, Y.J. Implementing bio-design tools to develop mycelium-based products. Des. J. 2019, 22, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Park, D.; Qin, Z. Material function of mycelium-based bio-composite: A review. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 737377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.M.; Grillet, A.C.; Diep, T.M.H.; Thuc, C.N.H.; Woloszyn, M. Hygrothermal properties of bio-insulation building materials based on bamboo fibers and bio-glues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 852–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrera-Vázquez, N.; Aviles-Trujilo, L.; Moreira-Acosta, J.; García-Ramos, O.; Velazquez-Gurrola, A.; Aguilar-Castillejos, A.; Vargas-Estrada, L.; Sebastian, P.J. Development of an insulating material based on Trametes elegans mycelium and the study of its hygrothermal properties. Green Mater. 2022, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittau, F.; Carcassi, O.G.; Servalli, M.; Pellegrini, S.; Claude, S. Hygrothermal Characterization of Bio-Based Thermal Insulation Made of Fibres from Invasive Alien Lake Plants Bounded with Mycelium. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Beijing, China, 23–25 September 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK; Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 1078, p. 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, M.; Kononets, Y.; Bartos, P.; Pont, U.; Spalek, F.; Zoubek, T.; Kriz, P. Perspectives of Insulating Biodegradable Composites Derived from Agricultural Lignocellulosic Biomass and Fungal Mycelium: A Comprehensive Study of Thermal Conductivity and Density Characteristics. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sağlam, S.S.; Özgünler, S.A. Production of mycelium-based composite materials and evaluation of thermal insulation performance. J. Green Build. 2024, 19, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. A study on the thermal performance of Pleurotus Ostreatus/Straw mycelium composites and its application in building envelopes. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 92, 109646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.H.; Gauvin, F.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Investigation of material characteristics and hygrothermal performances of different bio-based insulation composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, A.; Wildman, J.; Walker, P.; Henk, D. Extrinsic and intrinsic determinants of thermal conductivity in mycelium composites. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2024, 46, 317–338. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Hon, K.C.; Gauvin, F.; Pantaleo, S.; Berger, F.; Chen, W.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Durability assessment of alkyl ketene dimer hydrophobic treatment of bio-based thermal insulation materials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Schröter, M.; Saeidi, N.; Steffl, S.; Javadian, A.; Hebel, D.E.; Schultmann, F. Life cycle assessment of mycelium-based composite materials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 205, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaux, N.; Vašatko, H.; Maierhofer, D.; Saade, M.R.M.; Stavric, M.; Passer, A. Environmental potential of fungal insulation: A prospective life cycle assessment of mycelium-based composites. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2024, 29, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livne, A.; Wösten, H.A.; Pearlmutter, D.; Gal, E. Fungal mycelium bio-composite acts as a CO2-sink building material with low embodied energy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12099–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akromah, S.; Chandarana, N.; Rowlandson, J.L.; Eichhorn, S.J. Potential environmental impact of mycelium composites on African communities. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irbe, I.; Kirpluks, M.; Kampuss, M.; Andze, L.; Milbreta, U.; Filipova, I. Assessing the Conformity of Mycelium Biocomposites for Ecological Insulation Solutions. Materials 2024, 17, 6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Bhat, T.; Kandare, E.; Thomas, A.; Joseph, P.; Dekiwadia, C.; Yuen, R.; John, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.-H.; et al. Thermal degradation and fire properties of fungal mycelium and mycelium-biomass composite materials. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chulikavit, N.; Wang, C.; Huynh, T.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Khatibi, A.; Kandare, E. Fireproofing flammable composites using mycelium: Investigating the effect of deacetylation on the thermal stability and fire reaction properties of mycelium. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 215, 110419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M. Waste-Derived Mycelium Materials for Non-Structural and Semi-Structural Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Y.; Wang, M.; Cao, J. Lightweight, thermal insulation, hydrophobic mycelium composites with hierarchical porous structure: Design, manufacture and applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 266, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, J.; Vandersanden, S.; Nouwen, O.; Rineau, F. Fungal Strain Influences Thermal Conductivity, Hydrophobicity, Color Homogeneity, and Mold Contamination of Mycelial Composites. Materials 2024, 17, 6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutimanukul, P.; Sukdee, S.; Prajuabjinda, O.; Thepsilvisut, O.; Panthong, S.; Athinuwat, D.; Poomipan, P.; Vachirayagorn, V. The Effects of Soybean Meal on Growth, Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Activity of Hericium erinaceus. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, G.A.; Mcintyre, G.; Flagg, D.; Bayer, E.; Wanjura, J.D.; Pelletier, M.G. Fungal mycelium and cotton plant materials in the manufacture of biodegradable molded packaging material: Evaluation study of select blends of cotton byproducts. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2012, 6, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisti, L.; Gioia, C.; Totaro, G.; Verstichel, S.; Cartabia, M.; Camere, S.; Celli, A. Valorization of wheat bran agro-industrial byproduct as an upgrading filler for mycelium-based composite materials. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).