Abstract
In 2021, Mexico produced approximately 24.2 million tons of white corn, generating 3.6 million tons of corn cob residue. The final disposal of corn cob poses an environmental challenge in certain regions. This study examines the technical–economic feasibility and the greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation potential of integrating a small-scale cogenerating gasifier fueled by corn cob into a nixtamalized corn flour manufacturing small and medium-sized enterprise (SME). This integration enables the generation of heat and electricity from the produced synthesis gas. Moreover, the process yields residual carbon, which can be used as biochar for soil restoration and removing atmospheric CO2. This option holds significance for the corn flour agroindustry in Mexico, as, in 2021, it consumed approximately 601.9 GWh of electrical energy and 938,279 GJ of thermal energy from LP Gas in its manufacturing processes to produce 2.6 million tons of nixtamalized white corn flour. These processes contributed to a total emission of 410,232 tons of CO2 into the atmosphere. The findings of this study demonstrate a cumulative reduction of 51.7% in CO2 emissions, resulting in economic benefits of USD 85,401 in 2017 for a case study SME that annually produces 1039 tons of corn flour. This study reveals the integration of a gasifier–cogenerator system fueled by corn cob as an economically viable low-carbon technology in the corn flour manufacturing industry.
1. Introduction
Unlike first-generation bioenergy, agricultural and forestry residues constitute a renewable source of energy that has a greater capacity to reduce GHG emissions and replace fossil fuels [1]. Among the agricultural residues available in Mexico, corn cob constitutes the second most abundant residue after sugarcane bagasse [2,3]. Globally, in 2021, Mexico ranked ninth in corn production [4] and exported this food to 18 countries [5], ranking as the tenth most significant exporter of corn grains worldwide. In 2021, approximately 24.2 million tons of white corn were produced [6], generating 3.6 million tons of residual corn cobs (15% in weight [7]). In the period from October 2020 to September 2021, the destiny destination of 54.5% of white corn production was for human consumption, 18.2% for livestock consumption, 20.7% for self-consumption, 1.8% for exports, 0.7% for seed, and the remaining 4.1% were losses [8]. Currently, the consumption structure remains almost the same, with very slight variations. Corn cob is one of the primary residues of the maize harvest, along with stover and leaves [3]. While most residues remain in the field, most of the corn cob is generated in the agroindustrial process of corn grain production [9]. The composition of corn cob consists mainly of cellulose, 45%, lignin, 15.8%, and hemicelluloses, 33.6% [10,11]. It serves as a support to mitigate soil erosion [12], and researchers have explored its potential for obtaining organic compounds [13] and other industrial products [14,15,16]. However, its high content of lignocellulosic materials limits its use as an input for chemical product transformation [17,18]. Due to the high degree of lignification of corn cob, its low digestibility, and its low nutritional content [19], it is used as cattle feed only during the dry or drought seasons.
However, some regions in Mexico exhibit a much higher corn production compared to consumption, resulting in the final disposal of corn cob as an environmental problem [2]. Thus, there is a need for a more modern energy valuation of corn cob. Studies on the energy utilization of corn cob have been conducted since the beginning of the last century. A wide variety of thermochemical processes have been studied and applied [20,21], such as direct combustion, pyrolysis, gasification, and also biochemical processes: fermentation [22] and biodigestion [23].
Numerous studies agree that the thermochemical conversion of biomass by gasification is a technological alternative that is already commercially available for the transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into syngas, bio-oil, and waste coal [10,24,25,26]. The synthesis gas, or syngas for short, which is obtained by gasifying biomass above 700 °C typically contains approximately 18% ± 4% hydrogen (in mass units), 18% ± 3% carbon monoxide, less than 4% methane, and 13% ± 3% carbon dioxide [27]. The composition of syngas primarily depends mainly on the gasification temperature [9].
Syngas is usually used by direct combustion in boilers, burners, furnaces, and dryers [28]. When burned in an internal combustion engine, the mechanical energy produced can also produce electricity when coupled to a generator [29,30]; in addition, heat can be recovered from engine exhaust gases [31] or by direct combustion in burners [28].
Biomass gasifiers also have liquid by-products such as tar or bio-oil [32,33]. Second-generation liquid biofuels such as ethanol, methanol, and diesel can be produced from syngas refining [33].
In theory, an ideal gasifier regularly operating at temperatures above 700 °C [34,35] should not produce residual carbon; however, in practice, 5% to 10% by weight of the input biomass is converted to residual carbon or biochar [36,37]. This biochar has a high carbon content and has multiple applications, including its use in producing supercapacitor catalysts [38], filtering tar from combustion or gasification gases, acting as a catalyst in biodiesel production, and reducing nitrogen oxides [39]. The IPCC 1.5 °C special report recognizes biochar as a carbon removal technique due to its capability of sequestering carbon from the atmosphere, and when biochar is reintegrated into the soil, as a soil structure improver or fertilizer as it has the potential to remain in the soil for hundreds of years [40,41,42,43].
The total mitigation potential of residual biomass gasification is then the sum of the CO2 emissions removed from the atmosphere, as they are stored underground in biochar, and the avoided emissions are due to the substitution of fossil fuels used for the cogeneration of heat and power.
This article displays the corn flour manufacturing industry’s technical–economic feasibility and GHG mitigation potential by integrating a commercial small CHP gasifier fed by corn cob; it will co-generate heat and power from the synthesis gas obtained. This article quantifies the potential for mitigating GHG emissions in the corn flour industry. It considers substituting LP gas in conventional boilers by introducing corn cob as a fuel in a gasifier to produce synthesis gas and co-generate heat and electricity with it and biochar as a by-product. The mitigation potential also includes substituting electricity from the grid and carbon removal from the atmosphere due to using biochar for soil restoration, resulting in carbon storage.
We are considering, on the one hand, the abundant amount of residual corn cob in some regions of Mexico and, on the other hand, the energy needs of the corn flour industry in Mexico. In this article, we propose, for the first time in the literature, the gasification of corn cob for heat and power generation in this industry. We also are accounting for the GHG mitigation benefit from the reutilization of residual carbon as biochar for soil restoration and CO2 sequestration. Furthermore, we present the technical–economic feasibility results and the potential of GHG mitigation in an SME of nixtamalized corn flour case study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Corn Characterization
We conducted a literature review on studies that performed proximate and elemental analyses of corn cob. The results of the proximate analyses are presented in Table 1. The corn cob is a residue from the corn grain agroindustry and it can be directly utilized as fuel due to its calorific value and high carbon content [44]. Table 1 provides typical values for the fixed carbon content in corn cob from various countries. The results obtained from proximate analysis range from 11.7% to 21.3% by weight [9,10,28,45,46,47,48]. Fixed carbon represents the mass of organic matter that remains after moisture and volatile material release due to increasing biomass temperature in this analysis. It plays a crucial role in energy applications, as almost all fixed carbon forms carbon dioxide during combustion reactions [49].

Table 1.
Values obtained from the proximate analysis of corn cob.
Elemental values of C, H, O, N, and S and the higher calorific value obtained through calorimetry are displayed in Table 2. The higher calorific value ranges from 14.37 to 19.34 MJ/kg. Based on the provided information, the elemental composition, calorific value, emission factors, and amount of ash per biomass unit were determined to characterize the corn cob.

Table 2.
Corn cob elemental analysis.
Carbon and oxygen are the main components of solid biofuels and are involved in an exothermic reaction during combustion, generating CO2 and H2O [52]. Table 2 exhibits that for all corn cob samples, carbon content ranged from 39.3% to 51.8%, oxygen content ranged from 41.6% to 48.3%, and hydrogen content ranged from 5.0% to 6.2%.
The literature normally recommends a biomass moisture content below 20% for optimal gasification. In this article, we assume a 10% average moisture content, an 80.42% volatile material content, and a 17.65 MJ/kg lower calorific value, which represents the average values obtained from [9,28]. Based on these assumptions, it can be asserted that the volatile content is relatively high compared to other biomass studies, which creates favorable conditions for the generation of synthesis gas. Furthermore, the calorific value and the percentage contents of fixed carbon and ash are considered average.
2.2. Gasification of Corn Cob for Cogeneration and Residual Biochar
There are many routes for treating biomass for bioenergy; among the most employed are the biological and thermochemical processes. Gasification, as one of the thermochemical options, has gained significant recognition [53]. Gasification involves the conversion of biomass via partial oxidation reactions into synthesis gas, also known as syngas or producer gas. Syngas primarily consists of hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapor (H2O), making it suitable for environmentally friendly cogeneration applications [53]. In addition to syngas, the gasification process allows for the production of valuable by-products, including bio-oil and biochar. Utilizing corn cobs through gasification presents a sustainable approach to valorizing this residue, a by-product of the grain corn agroindustry [14].
Some authors are still considering gasification technology as emerging [54]; nevertheless, a range of small-scale gasifier manufacturers are already available in the market, typically designed for capacities between 5 and 100 kWt. Most gasifiers require forest biomass with a maximum moisture content of 20% [55]. To accommodate a broader range of biomass inputs, including firewood, agricultural residues, and agro-industrial residues, we sought a versatile gasifier capable of accepting biomass with a moisture content of up to 30% (by weight). The Power Pallet [56] meets these criteria. According to the manufacturer’s specifications, this gasifier incorporates a multi-stage gasification system, which involves preheating the biomass input to reduce its moisture content to suitable levels for gasification. This flexibility enables the utilization of different forest or agricultural biomass sources with high efficiency, as shown in Figure 1 and Table 3. The PP30 gasifier integrates a 25 kWe electric generator and cogenerates up to 50 kWt of thermal energy through process heat recovery. It operates with a specific biofuel consumption of 1 kg Biomass/kWhe and produces up to 0.08 kg of biochar per kilogram of biomass input [57].
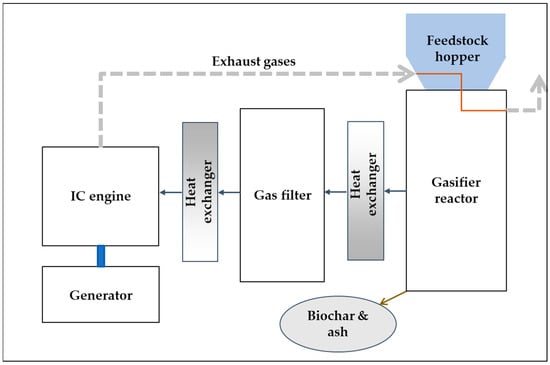
Figure 1.
Simplified arrangement of components of the PP30 gasifier. Source: [58].

Table 3.
All Power Labs PP30 operation specifications.
In this study, we utilized the available information of a small-scale cogenerating gasifier manufactured by All Power Labs, model PP30, which features a downflow reactor with fixed bed architecture and has a single throat and a patented Imbert-type design (refer to Figure 1) [58]. Once the user turns on the reactor, it reaches operating temperature in approximately 30 min, ranging from 860 to 950 °C. The heating rate varies depending on the balance between combustion and reduction reactions. At the bottom of the reactor is a stirring and moving grate, facilitating the discharge of biochar through an auger. Considering the grate basket’s consumption and geometrical data, the char’s residence time is estimated to be around 4 h. The plant design incorporates dry filtration for gas cleaning, wherein the gas is cooled and filtered using felt bags above the water dew point. This method enables gas filtration without condensing tarry compounds, as they are retained within the baghouse [58].
2.3. Scenario Building Methodology
The methodology employed in this study involves comparing technological scenarios to assess the feasibility of integrating corn cob gasification into the corn flour manufacturing process. The reference year chosen is 2022, as it provides the necessary technical and economic information for scenario construction. The analysis period is 20 years, which aligns with the typical equipment lifetime.
The first scenario, known as the Base Scenario (BS), uses steam boilers fueled by LP gas to provide process heat to corn flour production in small and medium enterprises in Mexico. The required electricity is purchased from the CFE distribution network. This scenario presents the calculations of thermal and electrical energy consumption and GHG emissions.
In the Alternative Scenario (AS), a significant portion of the heat required for corn flour manufacturing is provided by cooling both the syngas from corn cob gasification and the exhaust gases resulting from the combustion of the syngas in an internal combustion engine that drives an electric generator. We assume that all the electricity generated in this scenario is consumed in the corn flour production process, with any remaining demand being met by electricity from the grid. Unlike the Base Scenario, a smaller LPG-fired steam boiler is utilized to cover the thermal demand not met by the cogenerating gasifier. The scenario calculates thermal and electrical energy consumption and the associated GHG emissions.
Furthermore, we conduct a cost–benefit analysis to determine the economic feasibility of both scenarios, making the following assumptions. We assume a zero cost for the corn cob because, as already mentioned, some Mexican regions have high corn productivity, such as the one assumed in this case study, where the corn cob is a residual product that involves transportation costs to its final disposal site; in contrast, in this study, we assume that the corn cob is in situ at the flour plant and therefore its cost is zero. Also, to determine the cost of LPG and electricity over the 20-year analysis period starting in 2022, we use official forecasts, see Figure 2.
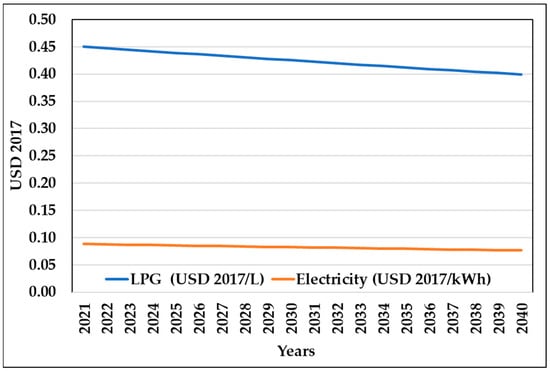
Figure 2.
Electricity and LPG future price scenarios. Source: Own elaboration based on data from [59,60,61].
2.4. Cost Analysis Methodology
The following cost model was developed following [62], and was applied to estimate the costs of the options analyzed in the comparison between feedstock LPG and electricity in the Base Scenario and corn cob feedstock for heat and power generation in the Alternative Scenario, where:
with:
where:
with:
where:
with:
where:
To obtain the net present value (NPV) of the incurred costs, we considered a discount rate (TD) of 12% and an analysis period of 20 years because it is equal to the useful life of the gasifier reactor.
3. Case Study: Corn Flour Production
3.1. Description of the Production Process
Healthy and clean corn grains are subjected to alkaline cooking and grinding to obtain nixtamalized corn flour [63]. This process, known as traditional nixtamalization, involves cooking the corn grains in a solution of calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 at a 1% concentration per kilogram of grain (w/w) dissolved in water at 90 °C for 40 min. The ratio is 2 L of water to each kilogram of grain [64]. This cooking softens and breaks the pericarp of the grain, increases its moisture content, and makes it easier to grind into a dough known as “nixtamal”. The term “nixtamalization” comes from the Nahuatl words “nextli” (ash lime) and “tamalli” (cooked corn dough) and refers to the process of alkaline cooking of corn grains.
After washing, the grain is crushed in a stone mill to obtain fresh dough with a moisture content ranging from 45% to 55%. It is then passed through a flash dryer at 260 °C for 4 s to obtain dehydrated dough as lumps with a 10% maximum moisture content [64]. The lumps are subsequently pulverized in a hammer mill, and the resulting flour is sieved through a 0.5 mm mesh. Once sieved, the flour is ready to be packaged and stored (see Figure 3).
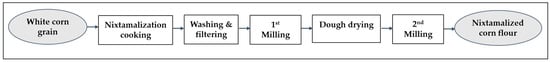
Figure 3.
Stages in the manufacturing process of nixtamalized corn flour.
Electrical energy is required to provide mechanical energy through electric motors for pumping water, transporting cooked grain, washing and rinsing cooked grain, wet grinding of nixtamal, dry grinding of flour, sifting/sifting, and packaging flour. The thermal energy requirements are for the alkaline grain cooking and wet dough drying stages. Table 4 shows the average energy consumption per kilo of white corn grain.

Table 4.
Average unit consumption of thermal and electric energy for the corn flour manufacturing process; CO2 Emission Factors due to LPG combustion in boilers and electricity consumption from the grid of the Mexican Electric System (MES).
3.2. Base Scenario
The Base Scenario considers a small and medium-sized industry (SME) with the capacity to produce 1039 tons of nixtamalized white corn flour annually. This study assumes that this production is achieved by operating two shifts of eight hours per day, five days a week throughout the year (3840 h). According to [65], for every kilogram of white corn grain, 0.93 kg of flour is obtained. Using the unit values from Table 4, we determined the daily energy demand for this production, resulting in 3145 kWht/day of thermal energy and 540 kWhe/day of electrical energy.
The electricity supply in this scenario is from the Federal Electricity Commission (CFE, by its acronym in Spanish) distribution network, demanding a total necessary for an installed capacity of 33.7 kWe, and all the required heat is supplied by the combustion of LPG to produce steam in a pyrotubular boiler with a capacity of 196.5 kWt (equivalent to 20 BHP (Boiler Horsepower)) [70] and an efficiency of 82%. To perform the cost analysis of this BS scenario, we will use the information given in Table 5.

Table 5.
Unit investment cost and investment cost of a 20 BHP boiler.
3.3. Alternative Scenario
This scenario considers the reuse of corn cob for the partial substitution of fossil fuels involved in the annual manufacturing of 1039 tons of nixtamalized corn flour. Corn cob is a residue of the corn agroindustry; for each ton of corn grain, 150 kg of corn cob is obtained [65]. See Figure 4, a scheme showing the integration of a biomass CHP gasifier to the nixtamalized white corn flour manufacturing process.
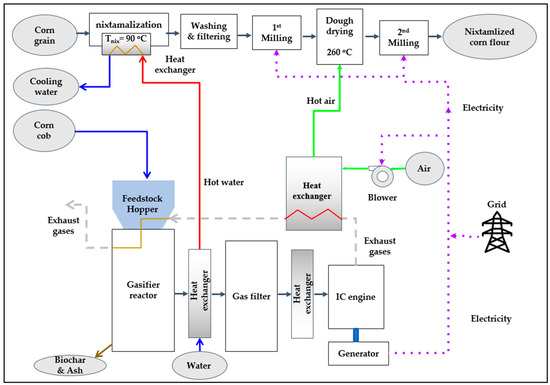
Figure 4.
Scheme of the integration of a CHP gasifier, with its components disaggregated.
The corn cob will be the input for a cogenerating biomass gasifier. Using corn cob with the characteristics presented by [9] is considered (see Table 1 and Table 2). Also, the gasifier–cogenerator equipment considered is that described in Section 2.2, which generates 25 kWe of electrical energy and 50 kWt of thermal energy with an input of 27.5 kg of biomass fuel per hour. However, the above annual production requires more than this cogeneration capacity. An extra heat generator, an LPG boiler of the same type as the one in BS, must be included to satisfy the thermal demand. Nevertheless, with a smaller capacity, 147.7 kWt (15 BHP) [70], and to satisfy the electrical demand, the purchase of electricity from the grid is needed. To perform the cost analysis of this AS scenario, we will use the information given in Table 6.

Table 6.
Unit investment cost and investment cost of a 15 BHP boiler and a CHP gasifier.
4. Results
4.1. Reduction of GHG Emissions
Based on the average unit consumptions provided in Table 4, the production of 270.8 kg of flour per hour, operating in two shifts per day, five days per week throughout the year to achieve a total production of 1039 tons per year of nixtamalized white corn flour, requires an installed thermal capacity of 196.5 kWt and an electrical equipment capacity of 33.7 kWe. We obtained the following emission scenarios by applying the CO2 emission factors associated with the National Electric System and LPG, as summarized in Table 7 and Figure 5.

Table 7.
Annual, cumulative, and avoided CO2 emissions (tCO2) in the Base Scenario (BS) and in the Alternative Scenario (AS), and the total emissions reduction.
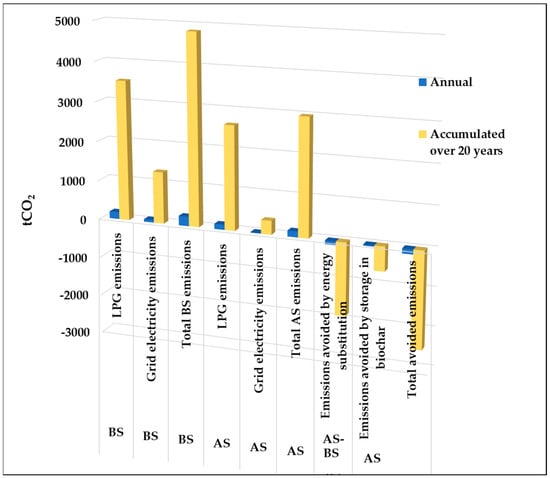
Figure 5.
Cumulative CO2 emissions in tons. In the traditional BS, and avoided emissions in the AS due to the use of a smaller size LPG boiler and integration of a corn cob gasifier that produces heat, electricity, and biochar.
In the Base Scenario, we observe that all thermal energy is supplied by a 196.5 kWt boiler fueled by LPG, while all the electricity consumed is sourced from the CFE network. The annual emissions in this scenario amount to 241.9 tons of CO2, with 73% attributed to thermal demand and 27% to electricity demand.
In the Alternative Scenario, we introduce a gasifier that utilizes corn cob as fuel, providing 27.5 kg/h. This gasifier generates 50 kWt of thermal energy and cogenerates 25 kWe of electricity. Additionally, heat generation is complemented by a 146.5 kWt boiler, and an additional electricity requirement of 8.7 kW is purchased from the CFE network to meet the same energy demand as in the Base Scenario. The Alternative Scenario results in annual emissions of 149.1 tons of CO2, with 88% corresponding to the thermal demand of the boiler and 12% to the electrical demand.
Thanks to the integration of corn cob gasification, which accounts for 25.4% of heat generation and 74.2% of electricity generation, a reduction of 92.9 tCO2 per year is achieved compared to the Base Scenario. This reduction corresponds to a decrease of 38.4% relative to the Base Scenario. Furthermore, as mentioned in Section 2.2, corn cob gasification also generates biochar as a by-product, with an average production of 80 g per kilo of corn cob, equivalent to 2.2 kg of carbon per hour, which further translates to 8.1 kg of CO2/h. Over a year, this amounts to 31.1 tons of avoided CO2 emissions, assuming the biochar is a soil improver and restorer. Importantly, the biochar remains stored in solid form for extended periods, effectively removing CO2 from the atmosphere. This additional atmospheric removal represents a further reduction of 12.9% compared to the Base Scenario. When combined with the reduction mentioned above, the total avoided emissions reach 124.0 tons per year, summing up to 2479.4 tCO2 in all the analyzed period, corresponding to a total reduction percentage of 51.2% compared to the Base Scenario. The contribution to emission reduction from corn cob gasification, which partially substitutes LPG and electricity, accounts for 18.6% of thermal and 19.8% of electrical energy.
When comparing the two scenarios of corn flour production in relative terms, we verified that the total energy consumption per mass product unit is the same in both scenarios, as we initially assumed (0.791 kWh/kg corn flour). Nevertheless, introducing a corn cob gasifier into the manufacturing process significantly reduced CO2 emissions per product unit. Specifically, emissions decreased from 233 grCO2/kg corn flour in the BS to 114 grCO2/kg corn flour in the AS, representing a substantial overall reduction of 51.2% per product unit.
4.2. Cost Analysis
Data from Table 5 and Table 6, Figure 6, and Table 8 show the resulting costs in net present value, considering a discount rate of 12% and an analysis period of 20 years due to the useful life of the gasifier [56]. Although the investment and O&M costs are 33% and 54% higher in the AS, respectively, considerable savings are obtained in LPG and electricity, although its price reduction is expected, see Figure 2 A notable saving is in electricity, which, in the AS, costs approximately only a quarter of the BS. Furthermore, the NPV of the cash flow is negative, which indicates that this investment will not only be recovered but will also yield benefits.
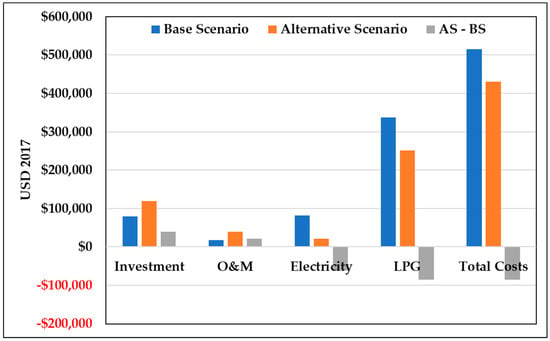
Figure 6.
Net present value of investment, O&M, and energy costs in the Base and Alternative Scenarios.

Table 8.
Net present value of investment, O&M, and energy costs and the total costs in the BS, the AS, and the difference between the two scenarios.
The levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for each scenario (BS and AS) was estimated by annualizing the total costs presented in Table 8 and considering the annual thermal and electrical energy requirements, using kWh units, thus obtaining that for the Base Scenario the LCOE is USD 7.80 cents/kWh while for the Alternative Scenario it is USD 6.51 cents/kWh, which indicates that the energy cost for the AS is 17% lower than that found for the BS, which reiterates that it is economically viable to use corn cob as an option to mitigate climate change.
The mitigation cost of the partial substitution of a conventional LPG boiler for a cogenerator gasifier with a smaller size boiler in the small and medium-sized nixtamalized corn flour industry in Mexico, resulting from the ratio of the NPV of the cash flow between the avoided emissions, was USD −85,688/2479 = USD −34.44/tCO2. Being negative, this value means that these expenses and investments result in a benefit in the long term. Another indicator of this investment’s convenience is the investment’s payback period; considering an additional investment cost of USD 39,764 divided by the annual equivalent value of the savings obtained, USD 16,757, the resulting payback period is 2.4 years. Table 8 presents the net present value of the investment, O&M, energy costs, and the resulting total cost. The calculations were performed considering the BS, the AS, and the difference between them.
5. Conclusions
This article analyzes the GHG mitigation potential and the technical–economic feasibility of a small-scale industry manufacturing 1039 tons of corn flour annually. The industry considers the integration of a gasifier with cogeneration capacity, which will be fueled by corn cobs, one of the major agricultural residues in Mexico. The gasification process produces synthesis gas, which can generate electricity when burned in an internal combustion engine coupled to a 25 kWe power generator. In addition, heat recovery from the engine’s exhaust gases can produce up to 50 kWt of thermal energy, used in the corn flour manufacturing process jointly with the electricity that is generated initially. Moreover, biochar is obtained as a by-product of corn cob gasification, which will be used for soil restoration, CO2 removal, and underground carbon sequestration. Due to this carbon removal plus the avoided emissions from heat and electricity generation from corn cob gasification, a low-carbon technology is harnessed in small-scale industries. This option represents an overall cumulative reduction related to the Base Scenario of 2479 tCO2, which represents a 51.2% reduction in GHG emissions compared to the conventional system. In relative terms, the emissions decreased from 233 grCO2/kg corn flour in the BS to 114 grCO2/kg corn flour in the AS, representing a substantial overall reduction of 51.2% per product unit.
Finally, the mitigation cost of the partial substitution of a conventional LPG boiler for a cogenerator gasifier with a smaller size boiler in the small and medium-sized nixtamalized corn flour industry in Mexico, resulting from the ratio of the NPV of the cash flow between the avoided emissions, was USD −34.44/tCO2, and since this value is negative, it means that these expenses and investments result in a benefit in the long term. Additionally, according to our results, the LCOE for the BS is USD 7.80 cents/kWh and the LCOE for the AS is USD 6.51 cents/kWh. This means that the energy cost for the Alternative Scenario is 17% lower than that found for the Base Scenario. Therefore, it is economically feasible to use corn cobs as an option to mitigate climate change.
This work shows, for the first time in the literature on gasification, the environmental and economic advantages of including a gasifier–cogenerator that takes advantage of a residue from the corn grain industry in the manufacturing industry of nixtamalized white corn flour in Mexico.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M. and J.M.I.-S.; methodology, F.M., J.M.I.-S. and G.K.G.-A.; validation, F.M., J.M.I.-S. and G.K.G.-A.; formal analysis, F.M. and G.K.G.-A.; investigation, F.M. and J.M.I.-S.; resources, F.M. and J.M.I.-S.; data curation, F.M. and G.K.G.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M.; writing—review and editing, F.M., J.M.I.-S. and G.K.G.-A.; visualization, F.M.; supervision, F.M., J.M.I.-S. and G.K.G.-A.; project administration, F.M.; funding acquisition, F.M. and J.M.I.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank María de Jesús Pérez Orozco for her technical support in the search and data collection, Tadzio Manzini for the graphic summary in this paper, Daniel Camarena for inspiring the use of corn cob gasification, and Santiago Camargo for starting to explore the integration of the produced syngas into the corn flour industry. Also, the authors wish to thank project UNAM-PAPIIT-IG101422 “Integration of a solar reactor for producing synthesis gas and biochar to a point focus solar concentration system at the LACYQS Central Tower Experimental Field”, project SENER-CONACYT 2014-05-246911 and project CONAHCYT-PRONACES No. 319333 “Development and implementation of sustainable energy alternatives in rural communities of the Purepecha plateau, Michoacán”. And finally, to the Arizona Institute for Resilience at the University of Arizona in Tucson, USA, for hosting Fabio Manzini as a visiting researcher.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| °C | Degrees Celsius |
| AS | Alternative Scenario |
| BHP | Boiler Horsepower |
| BS | Base Scenario |
| C | Carbon |
| Ca(OH)2 | Calcium Hydroxide |
| CFE | Federal Electricity Commission (CFE, by its acronym in Spanish) |
| CH4 | Methane |
| CHP | Combined Heat and Power |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| GJ | Gigajoule |
| GWh | Giga watt hour |
| H | Hydrogen |
| H2O | Water |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| kg | Kilogram |
| kW | Kilowatts |
| kWe | Kilowatt electric |
| kWh | Kilowatt hour |
| kWhe | Kilowatt hour electric |
| kWht | Kilowatt hour thermal |
| kWt | Kilowatt thermal |
| LCOE | Levelized cost of energy |
| LPG | Liquefied Petroleum Gas |
| MES | Mexican Electric System |
| MJ/kg | Megajoule/Kilogram |
| mm | Millimeters |
| N | Nitrogen |
| NPV | Net present value |
| O | Oxygen |
| O&M | Operation and Maintenance |
| S | Sulfur |
| SME | Small and medium-sized enterprise |
| tCO2 | Tons of Carbon Dioxide |
| USD | US Dollar |
| w/w | % Weight concentration |
References
- Global Bioenergy Partnership (GBEP). The Global Bioenergy Partnership Sustainability Indicators for Bioenergy, 1st ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011; ISBN 978-92-5-107249-3. [Google Scholar]
- Valdez-Vazquez, I.; Acevedo-Benítez, J.A.; Hernández-Santiago, C. Distribution and Potential of Bioenergy Resources from Agricultural Activities in Mexico. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorato-Salazar, J.A.; Sadhukhan, J. Annual Biomass Variation of Agriculture Crops and Forestry Residues, and Seasonality of Crop Residues for Energy Production in Mexico. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 119, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). FAOSTAT. Maize (Corn) Production by Country. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Secretaría de Economía. Sistema de Información Arancelaria vía Internet (SIAVI). Exportaciones de Maíz Blanco (Harinero). Available online: http://www.economia-snci.gob.mx/ (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera (SIAP) Statistical Yearbook of Agricultural Production. Agricultural Production of White Grain Corn. Available online: https://nube.siap.gob.mx/cierreagricola (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- González Huerta, A.; Vázquez García, L.M.; Sahagún Castellanos, J.; Rodríguez Pérez, J.E. Phenotypic Diversity of Maize Varieties and Hybrids in the Toluca-Atlacomulco Valley, Mexico. Rev. Fitotec. Mex 2008, 31, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera (SIAP). Balanza Disponibilidad-Consumo. Maíz Blanco. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/813719/Balanzas_disponibilidad_consumo_Marzo.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Aseffe, J.A.M.; González, A.M.; Jaén, R.L.; Lora, E.E.S. The Corn Cob Gasification-Based Renewable Energy Recovery in the Life Cycle Environmental Performance of Seed-Corn Supply Chain: An Ecuadorian Case Study. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 1523–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Wang, L.; Dzenis, Y.A.; Jones, D.D.; Hanna, M.A. Thermogravimetric Characterization of Corn Stover as Gasification and Pyrolysis Feedstock. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, J.A.; Salcedo, E.; Rodríguez, R.; Zamora, J.F.; Manríquez, R.; Contreras, H.; Delgado, E. Characterization and Chemical Titration of Olote: Hydrothermal Degradation under Subcritical Conditions. Rev. Latinoam. Quim. 2013, 41, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Knob, A.; Carmona, E.C. Purification and Characterization of Two Extracellular Xylanases from Penicillium Sclerotiorum: A Novel Acidophilic Xylanase. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, P.; Qin, P.; Wang, Z.; Tan, T. Biorefinery of Corn Cob for Microbial Lipid and Bio-Ethanol Production: An Environmental Friendly Process. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virmond, E.; Rocha, J.D.; Moreira, P.M.; José, H.J. Valorization of Agroindustrial Solid Residues and Residues from Biofuel Production Chains by Thermochemical Conversion: A Review, Citing Brazil as a Case Study. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 197–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Gautam, A.; Dutt, D. Biotechnological Transformation of Lignocellulosic Biomass in to Industrial Products: An Overview. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, T.Y.; Law, M.C.; Chan, Y.S. The Potentials of Corn Waste Lignocellulosic Fibre as an Improved Reinforced Bioplastic Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghlami, A.; Paës, G. Lignocellulosic Biomass: Understanding Recalcitrance and Predicting Hydrolysis. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.M.; Mota, T.R.; Grandis, A.; de Morais, G.R.; de Lucas, R.C.; Polizeli, M.L.; Marchiosi, R.; Buckeridge, M.S.; Ferrarese-Filho, O.; dos Santos, W.D. Lignin Plays a Key Role in Determining Biomass Recalcitrance in Forage Grasses. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Agricultura, Ganadería, Desarrollo Rural, Pesca y Alimentación (SAGARPA). Aprovechamiento de Esquilmos y Subproductos en la Alimentación del Ganado 2013; SAGARPA: Mexico City, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- DeBaufre, W.L. The Heating Value of Corn. Agron. J. 1923, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsfield, B.; Doster, H.; Peart, R. Drying Energy from Corn Cobs: A Total System. In Agriculture and Energy; Lockeretz, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977; pp. 47–63. ISBN 978-0-12-454250-1. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Li, Y.; Zong, H.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, W.; Jiang, Y. Production of Bioethanol and Xylitol from Non-Detoxified Corn Cob via a Two-Stage Fermentation Strategy. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.D.; Imrana, G. Biogas Production from Lignocellulosic Materials: Co-Digestion of Corn Cobs, Groundnut Shell and Sheep Dung. Imp. J. Interdiscip. Res. 2016, 2, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Manahan, E.; Enríquez-Poy, M.; Molina, L.T.; Durán-de-Bazúa, C. Energy and Activated Carbon Production from Crop Biomass by Products. In Towards a Cleaner Planet: Energy for the Future; Klapp, J., Cervantes-Cota, J.L., Chávez Alcalá, J.F., Eds.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 365–387. ISBN 978-3-540-71345-6. [Google Scholar]
- Low, Y.W.; Yee, K.F. A Review on Lignocellulosic Biomass Waste into Biochar-Derived Catalyst: Current Conversion Techniques, Sustainable Applications and Challenges. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 154, 106245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.D. Biomass Gasification Systems for Electric Power, Cogeneration, Liquid Fuels, and Hydrogen; Biomass Energy Workshop Stanford: Stanford, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ankur Scientific Charcoal Generator. Available online: https://www.ankurscientific.com/ankur-gasifiers-charcoal-generator.html (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Biagini, E.; Barontini, F.; Tognotti, L. Gasification of Agricultural Residues in a Demonstrative Plant: Corn Cobs. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 173, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suberu, M.Y.; Mokhtar, A.S.; Bashir, N. Potential Capability of Corn Cob Residue for Small Power Generation in Rural Nigeria. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 7, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Anshar, M.; Ani, F.N.; Kader, A.S. Makhrani Electrical Energy Potential of Corn Cob as Alternative Energy Source for Power Plant in Indonesia. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 4184–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allesina, G.; Pedrazzi, S.; Allegretti, F.; Morselli, N.; Puglia, M.; Santunione, G.; Tartarini, P. Gasification of Cotton Crop Residues for Combined Power and Biochar Production in Mozambique. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 139, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jones, D.D.; Hanna, M.A. Thermochemical Biomass Gasification: A Review of the Current Status of the Technology. Energies 2009, 2, 556–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Larocca, V.; Chianese, S.; Musmarra, D. Biofuels Production by Biomass Gasification: A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Shen, B.; Wu, C. Preparation, Modification and Development of Ni-Based Catalysts for Catalytic Reforming of Tar Produced from Biomass Gasification. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 1086–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Bioenergy Country Report Austria. 2021. Available online: http://task33.ieabioenergy.com/download.php?file=files/file/country_reports/2021/CR%20Austria%202022.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Brewer, C.E.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Satrio, J.A.; Brown, R.C. Characterization of Biochar from Fast Pyrolysis and Gasification Systems. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2009, 28, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackley, S.; Carter, S.; Knowles, T.; Middelink, E.; Haefele, S.; Sohi, S.; Cross, A.; Haszeldine, S. Sustainable Gasification–Biochar Systems? A Case-Study of Rice-Husk Gasification in Cambodia, Part I: Context, Chemical Properties, Environmental and Health and Safety Issues. Energy Policy 2012, 42, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casillas, D.C.; Mascorro-Gutiérrez, I.; Betancourt-Mendiola, M.L.; Palestino, G.; Quiroga-González, E.; Pascoe-Sussoni, J.E.; Guillén-López, A.; Muñiz, J.; Cuentas-Gallegos, A.K. Residue of Corncob Gasification as Electrode of Supercapacitors: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4123–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, R.; Leifeld, J.; Horák, J.; Neftel, A. Nitrous Oxide Emission Reduction with Greenwaste Biochar: Comparison of Laboratory and Field Experiments. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, A. The Biochar Solution: Carbon Farming and Climate Change; New Society Publisher: Gabriola Island, BC, Canada, 2010; ISBN 0-86571-677-3. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, M.; Pant, G.; Mansotra, D.K.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, P.C. Chapter 11 Biochar: A Carbon Negative Technology for Combating Climate Change. In Advances in Carbon Capture and Utilization; Pant, D., Kumar Nadda, A., Pant, K.K., Agarwal, A.K., Eds.; Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 251–272. ISBN 9789811606380. [Google Scholar]
- Sri Shalini, S.; Palanivelu, K.; Ramachandran, A.; Raghavan, V. Biochar from Biomass Waste as a Renewable Carbon Material for Climate Change Mitigation in Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions—A Review. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2021, 11, 2247–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Global Warming of 1.5 °C; Special Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ghaly, A.E.; Li, B. Physical Properties of Corn Residues. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannapeera, J.; Worasuwannarak, N.; Pipatmanomai, S. Product Yields and Characteristics of Rice Husk, Rice Straw and Corncob during Fast Pyrolysis in a Drop-Tube/Fixed-Bed Reactor. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 30, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Danje, S. Fast Pyrolysis of Corn Residues for Energy Production. Master’s Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, Sudáfrica, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, L.M.; Gutiérrez, G.A. Reporte de Resultados Experimentales de Pruebas de Gasificación de Biomasa: Olote. G2E S.A.P.I. de C.V. Programa de Fomento a La Agricultura 2014, Componente Bioenergía Sustentabilidad, Convenio SAGARPA-COFUPRO; SAGARPA: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anukam, A.I.; Goso, B.P.; Okoh, O.O.; Mamphweli, S.N. Studies on Characterization of Corn Cob for Application in a Gasification Process for Energy Production. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 6478389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante García, V.; Carrillo Parra, A.; Prieto Ruíz, J.Á.; Corral-Rivas, J.J.; Hernández Díaz, J.C. Chemistry of Plant Biomass upon Yield during Torrefaction: A Review. Rev. Mex. Cienc. For. 2016, 7, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fandiño, J.M.M.; German, S.J.S.; García, D.E.L.; Guarín, A.M.; Julio, J.D.R. Energy Characterization of Corn Agroindustry Waste in a Multi-Zone Gasification Prototype. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2022, 14, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Naqvi, M.; Farooq, U.; Naqvi, S. Characterization of South Asian Agricultural Residues for Potential Utilization in Future ‘Energy Mix’. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 2974–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernberger, I.; Brunner, T.; Bärnthaler, G. Chemical Properties of Solid Biofuels—Significance and Impact. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Buono, A.; Caputo, C.; Carotenuto, A.; Cirillo, D.; Costagliola, M.A.; Di Blasio, G.; La Villetta, M.; Macaluso, A.; Martoriello, G.; et al. The “INNOVARE” Project: Innovative Plants for Distributed Poly-Generation by Residual Biomass. Energies 2020, 13, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Bioenergy Status Report on Thermal Gasification of Biomass and Waste. 2021. Available online: https://www.ieabioenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Status-Report2021_final.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Walter Power from Wood Volter 40 Indoor Gasifier. Available online: https://volter.fi/products/volter-40-indoor/ (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- All Power Labs PP30 Power Pallet. Available online: http://www.allpowerlabs.com/pp30-power-pallet (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Pedrazzi, S.; Santunione, G.; Mustone, M.; Cannazza, G.; Citti, C.; Francia, E.; Allesina, G. Techno-Economic Study of a Small Scale Gasifier Applied to an Indoor Hemp Farm: From Energy Savings to Biochar Effects on Productivity. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 228, 113645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- All Power Labs Power Pallet PP30. Available online: https://www.allpowerlabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/PP30OneSheet2_1_23-2.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- U.S. Energy Information Administration Annual Energy Outlook 2023. Table 3. Energy Prices by Sector and Source. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/data/browser/#/?id=3-AEO2023®ion=1-0&cases=ref2023&start=2021&end=2050&f=A&sourcekey=0 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Comisión Reguladora de Energía (CRE). Historial de Precios Promedio al Público de Gas LP Reportados Por Los Distribuidores. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cre/documentos/historial-de-precios-promedio-al-publico-de-gas-lp-reportados-por-los-distribuidores (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Comisión Reguladora de Energía (CRE). Memorias de Cálculo de Tarifas de Suministro Básico. Tarifa Media Nacional Por Categoría y División Tarifaria. Available online: https://datos.gob.mx/busca/dataset/memorias-de-calculo-de-tarifas-de-suministro-basico (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Grande-Acosta, G.K.; Islas-Samperio, J.M. Boosting Energy Efficiency and Solar Energy inside the Residential, Commercial, and Public Services Sectors in Mexico. Energies 2020, 13, 5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Comercio y fomento Industrial Norma Mexicana NMX-F-046-S-1980. Harina de Maíz Nixtamalizado. Available online: http://www.economia-nmx.gob.mx/normas/nmx/1980/nmx-f-046-s-1980.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Campechano Carrera, E.M.; de Dios Figueroa Cárdenas, J.; Arámbula Villa, G.; Martínez Flores, H.E.; Jiménez Sandoval, S.J.; Luna Bárcenas, J.G. New Ecological Nixtamalisation Process for Tortilla Production and Its Impact on the Chemical Properties of Whole Corn Flour and Wastewater Effluents. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.; Moreno, E.; Chong, I.; Quintanilla, J. La Industria de la Masa y la Tortilla. Desarrollo y Tecnología; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Dirección General de Publicaciones: Mexico City, Mexico, 1996; ISBN 978-968-36-4793-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mounir, S.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Bhandari, B.; Fang, Z. Handbook of Drying of Vegetables and Vegetable Products, 1st ed.; Routledge, Taylor and Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4987-5386-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pulvex Molino de Martillos. Available online: https://www.pulvex.mx/molinos/de-martillos/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Instituto Nacional de Ecología y Cambio Climático (INECC). Factores de Emisión Para Los Diferentes Tipos de Combustibles Fósiles y Alternativos Que Se Consumen En México. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/110131/CGCCDBC_2014_FE_tipos_combustibles_fosiles.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Comisión Reguladora de Energía (CRE). Factor de Emisión Del Sistema Eléctrico Nacional. 2019. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/537538/2019.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Fulton Classic TM Steam. Vertical Tubeless Steam Boiler. Available online: https://www.fulton.com/products/classic/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2021; IRENA: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022; ISBN 978-92-9260-452-3. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).