Abstract
In the process of diagenesis and burial of sedimentary basins, basin fluid activities participate in the process of hydrocarbon accumulation and metal mineralization. Understanding the evolution of basin fluid is of great significance in revealing the related hydrocarbon accumulation and mineralization. Paleo-reservoirs are closely associated with Carlin-type gold deposits in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin, South China. Calcite, the fluid activity product, is closely related to bitumen and gold-bearing pyrite. By integrating petrographic, cathode luminescence, and fluid inclusion analysis, as well as the relevant chronological results of predecessors, this paper attempts to establish the relationship between fluid evolution, hydrocarbon accumulation, and gold mineralization. Two types of calcite (black/gray and white) developed in the Banqi-Yata-Laizishan area, the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin. Black/gray calcite is symbiotic with bitumen and features dark red colors in cathode luminescence. Many hydrocarbon inclusions developed along with fluid inclusion analysis at low homogenization temperatures (65.7~173.1 °C). Combining the previously reported U-Pb ages (~250–230 Ma) of this kind of calcite with some geochemistry data on the associated reservoir and gold deposit, this calcite records the consecutive hydrocarbon accumulation and Carlin-type gold mineralization from the Late Permian to the Late Triassic periods controlled by Indosinian tectonic movement. The white calcite featuring bright red in cathodoluminescence is symbiotic with gold-bearing pyrite and realgar, and the associated fluid inclusions have high homogenization temperatures (128.2~299.9 °C). Combined with regional tectonic background and isotopic chronology (~140–106 Ma), it seems to record the early Cretaceous Carlin-type gold mineralization controlled by the subduction of the paleo-Pacific plate in the late Yanshanian period.
1. Introduction
During petroleum and mineral exploration, petroleum reservoirs and metal deposits are often closely associated in sedimentary basins. Liquid oil and lead–zinc deposits occur in the same stratum, and bitumen is widely present in the ores in the Saddle area of Cumberland, USA [1]. Stratified lead–zinc deposits, sandstone-type copper deposits, and hydrocarbon reservoirs coexist in the Chu-Sarysu Basin of Kazakhstan [2]. As a typical low-temperature hydrothermal deposit district, various types of hydrothermal deposits (mercury, lead-zinc, tungsten tin) are closely symbiotic with paleo-reservoirs in the Yangtze Block [3,4,5]. However, the relationship between the spatially associated hydrocarbon reservoirs and metal deposits is still under debate. As for the formation sequence, hydrocarbons could form both before and after mineralization [2]. In terms of genetic relationship, organic matter, especially the source rock, which is rich in metal elements, can be a common source for both hydrocarbons and metals [6]. Meanwhile, organic matter (oil and bitumen) can also help the metal enrichment by reacting with ore-forming elements and finally forming soluble metal-organic complexes [7]. In addition, organic matter which acts as a reducing agent could also help metal precipitation by directly reducing sulfur or through sulfate reduction [8,9].
Basin fluids which include formation water and hydrocarbons inside the basin and atmospheric water and metamorphic fluids outside the basin, occupy and flow in sediment pores within the basin [10]. Basin fluid evolution plays an important role in controlling hydrocarbon reservoirs and metal deposits in the basin [2]. In terms of hydrocarbon accumulation, basin fluids could promote the maturity of source rocks, improve physical reservoir conditions, and help hydrocarbon accumulation [11]. In terms of metal mineralization, basin fluids are closely related to the activation, migration, enrichment, and precipitation of metal [12]. As a link between metal deposits and hydrocarbon reservoirs [13], understanding the evolution of basin fluids is of great significance in revealing hydrocarbon accumulation and metal mineralization. Calcite, as a direct product of fluid activities in sedimentary basins, records a lot of information about the fluid evolution of the basin. Carrying out petrography and fluid inclusion analysis on calcite related to hydrocarbon reservoirs and metal deposits could help understand hydrocarbon accumulation and metal mineralization as well as the relationship between them.
Paleo-reservoirs and Carlin-type gold deposits are widely developed in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin, Yangtze Block [2]. Hydrocarbons are widely enriched in Devonian and Permian limestone [14], Carlin-type gold deposits are abundant in Permian-Triassic carbonate rocks and terrigenous clastic rocks, and the proven Au resources exceed 1000 t [15,16]. There is a close spatial correlation between paleo-reservoirs and the gold deposits in the basin [17]. The Yata gold deposit and Yata paleo-reservoir, the Lannigou gold deposit, and the Laizishan paleo-reservoir overlap [2]. Solid bitumen can be observed within the gold-bearing strata [13]. As an important gangue mineral, the calcite in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin is closely associated with bitumen, gold-bearing pyrite, and other ore minerals, which is key to understanding the hydrocarbon accumulation and Carlin-type gold mineralization. Here we focus on the Laizishan, Yata, and Banqi districts that include paleo-reservoirs and gold deposits as the research area (Figure 1). Integrating petrographic, cathode luminescence, and fluid inclusion analysis on the calcite in this work and some chronological data (calcite U-Pb date, bitumen Re-Os date) related to petroleum evolution and mineralization from published works, this study aims at establishing the relationship between fluid evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation and Carlin-type gold mineralization in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin against the geological background.
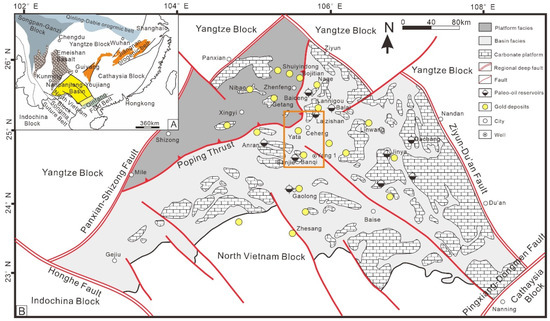
Figure 1.
(A) Tectonic location map of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin [18]). (B) Simplified geological and structural map of the Nanpanjiang Basin, showing locations of both hydrocarbon reservoir and gold deposits [17].
2. Geological Setting
The Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin, located at the junction of the Guizhou, Yunnan, and Guangxi provinces, is a Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic sedimentary basin developed on the lower early Paleozoic level in the southern margin of the Yangtze Plate [13] (Figure 1A). The basin is surrounded by deep fault zones, including the Honghe shear zone in the southwest, the Mile-Shizong-Panxian fault zone in the northwest, the Ziyun-Luodian-Nandan fault in the northeast, and the Pingxiang-Dongmen fault in the southeast [18] (Figure 1B). Controlled by the Paleotethys tectonic domain and the Pacific tectonic domain successively, the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin has experienced multiple periods of complex tectonic activities since the Early Paleozoic age [19]. From the Devonian to the Early Triassic, influenced by the Tethyan ocean extensional rift system, the Ailaoshan ocean basin opened and the South China continental block drifted from south to north [20]. The study area was in an extensional tectonic environment, forming multiple fault depression belts and thus forming the prototype of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin. With the closing of the Tethys ocean and the subduction of the Ailao orogenic belt, the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin collided with the YueBei block along the Heishui River in Vietnam during the Middle Triassic period (Indosinian orogeny) and entered the back-arc foreland basin stage [19]. After the late Indosinian, under the joint control of the Tethys, Pacific, and Indian plates, the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin entered the intracontinental orogenic stage and continuously superimposed and transformed to form its present status [21].
In the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin, the middle Proterozoic to very Early Devonian strata are absent, and the late Early Devonian to Middle Triassic strata are well developed [18] (Figure 2). The Devonian strata have a total thickness of about 400 m and are well developed except for the absence of strata in the early Devonian. The early and middle Devonian strata are sandstone, siltstone, mud shale, and marl. In the late Early Devonian, the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin began to stretch. Both the carbonate platform and deep water basin depositional systems formed along the slope-flat fault zone. The depositional pattern lasted until the Permian period. The total thickness of carboniferous to Permian strata is about 3000 m. The sedimentary lithology of the northwest carbonate platform is mainly carbonate rocks, such as reef limestone, micritic limestone, oolitic limestone, and breccia. The sedimentary system of the southeast deep water basin is dominated by argillaceous, siliceous, and black mudstone [17]. The lower and middle Triassic strata are a set of clastic turbidite with thicknesses of up to 6000 m [18]. The Upper Triassic strata are mainly terrigenous clastic sediments, which are not developed with Jurassic to Quaternary strata in the region [18].
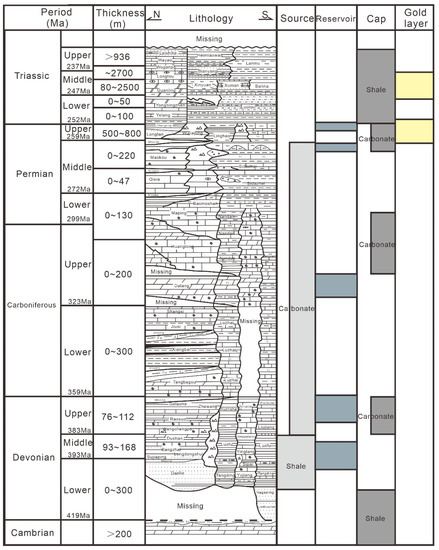
Figure 2.
Comprehensive stratigraphic column of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin [13]).
The Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin contains many paleo reservoirs and multiple sets of source-reservoir-cap assemblages developed in Devonian to Middle Triassic marine strata [22] (Figure 2). Regional geological survey and geochemical analysis results indicate the middle Devonian black argillaceous rocks distributed in the Wangmo-Nandan area with a thickness of about 1000 m and TOC (Total Organic Carbon) greater than 1.5% are the main source rocks in the basin. Carboniferous to Triassic carbonate rocks and mudstone featured with low TOC (<0.5%) are secondary source rocks [23]. Solid bitumen is mainly stored in Permian and Devonian reef limestone [13]. Monolayer shale with a thickness of hundreds of meters in the Lower and Middle Triassic are good regional cap rocks, while argillaceous rocks, siliceous rocks, and tight limestone in Devonian to Permian basin facies acted as local cap rocks [21].
The Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin is the main producing area of Carlin-type gold deposits in China. More than 20 similar gold deposits with a prospective resource of over 1000 t have been discovered [24] (Figure 2). The gold-bearing layers are mainly stored in Permian to Middle Triassic impure carbonate rocks and terrigenous clastic rocks. Three types of gold deposits can be identified according to their occurrence [25]. Stratified controlled type controlled by the horizon, paleokarst, or unconformity plane (Shuiyindong, Nibao, Getang deposits), faulted controlled type controlled by fault fracture zone (Lannigou, Banqi, Yata deposits), and compound controlled by strata and faults (Zimudang, Bojitian deposits). The metallogenic period can be divided into the hydrothermal metallogenic period and the supergene period [13,26]. The former period can be divided into the quartz–dolomite–pyrite stage, quartz–pyrite–arsenopyrite stage, and quartz–calcite–realgar stage. The main ore minerals are pyrite and arsenopyrite, followed by cinnabar, realgar, stibnite, etc. Previous works have confirmed that the gold for the Carlin-type gold deposit is mainly ionically bound in the pyrite lattice either as micrometer-scale (<10 μm) grains or within rims of gold-poor pyrite [27,28,29,30,31]. Gangue minerals are mostly calcite and quartz, followed by clay minerals and dolomite.
3. Samples and Methods
A total of 16 calcite samples were collected from the Banqi, Yata, and Laizishan areas of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin (Table 1). Two samples from the Yata area were taken from the Triassic Xinyuan Formation (T2x), and the remaining fourteen samples, from the Laizishan and Banzishan areas, were taken from the Permian Wujiaping Formation (P2w) (Figure 3A). Six samples were collected from the northern flank of the anticline, among which one black calcite sample (BQ-1) (Figure 3D) was developed in the 10 cm long fracture, and the other five calcite samples (BQ-2, BQ-3, BQ-4, BQ-5, BQ-6) were collected in the pores and fractures near the black calcite. BQ-2, BQ-3, and BQ-4 were white, and BQ-5 and BQ-6 were gray. White calcite is widely developed in the Yata area (Figure 3C). A total of two calcite samples (YT-1, YT-2) were collected at the entrance of mine cave No. 940. Similar to the Banqi area, two different colors (white and gray) of calcite can be found in the Laizishan area (Figure 3B). Eight typical samples (LZS-1–LZS-8) were collected in the southeastern part of the Laizishan dome (Figure 4). Three samples (LZS-1, LZS-2, and LZS-4), which contain both gray and milky white calcite, were further divided into two subsamples; for example, LZS-1 was separated into LZS-1A (white) and LZS-1B (gray).

Table 1.
Basic information for the calcite samples from the Banqi-Yata-Laizishan area.
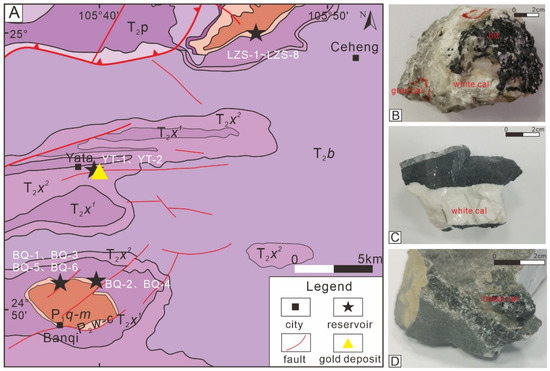
Figure 3.
(A) Geological map of the Banqi-Yata-Laizishan area showing sample locations. (B) gray and white calcite, Laizishan. (C) white calcite, Yata. (D) black calcite, Banqi.
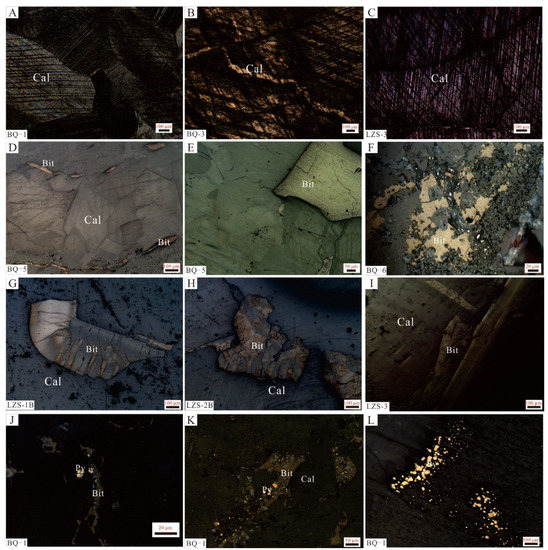

Figure 4.
Photographs showing the characteristic of black/gray calcite of the Banqi-Yata-Laizishan area. (A–C) Fine-grained calcite with clear and continuous cleavage lines. (D) Bitumen banded along the edge of calcite veins. (E,F) Bitumen with the pore of the calcite in the Banqi area. (G–I) Solid bitumen within the calcite pores from the Laizishan area. (J–L) Reflected light image showing pyrite within the black calcite.
Petrographic observation, cathode luminescence analysis, and the fluid inclusion test were carried out on the calcite collected in the field. The features of the calcite, bitumen, and pyrite grains, as well as their relationship, were observed under Zeiss optical microscopy at the China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). The calcite cathode luminescence test was carried out in the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). After the sample surface was polished, a CL8200 MK5 cathodoluminescence instrument (CITL, UK) was used for cathode luminescence analysis using a voltage of 10.8 kV, a current of 280 μA, and a vacuum of 0.03 Mbar.
To obtain a concentration of the Fe and Mn, both dark color and white calcite were chosen to conduct the trace element analysis. The analysis was performed at Guizhou Tongwei Analytical Technology Co., Ltd., on a Thermal Fisher iCAP RQ ICP-MS equipped with a Cetac ASX-560 AutoSampler. Approximately 50 to 100 mg of calcite powder was dissolved in a Teflon bomb with a double-distilled concentrated HNO3-HF (1:4) mixture. The dissolution was maintained in an oven at 185 °C for 3 days. The solutions were then evaporated to dryness. The sample residues were re-dissolved with double-distilled concentrated HNO3 and evaporated to dryness again. The samples were then dissolved in 3 mL of 2N HNO3. Finally, the sample solutions were diluted to 4000 times with 2 percent HNO3, with 9 ppb 61Ni, 6 ppb Rh, and In and Re internal tracer solutions were added. USGS standard W-2a was used as the reference standard and cross-checked with BHVO-2 and other reference materials. Instrument drift mass bias was corrected with internal spikes.
Fluid inclusion analysis was carried out in the Key Laboratory of Structure and Petroleum Resources of the Ministry of Education, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). The calcite samples were made into ~100 μm thick double-side polished slices. The petrography of the samples was observed using a NIKON microscope with a UV excitation light source. A THMS-600G cold and heat platform produced by Linkam, UK, was used to measure the temperature. The temperature range of the Linkam THMS600G cold and hot bench was from 190 °C to 600 °C. The homogenization temperature and freezing point temperature were measured by the cyclic testing method, and the measurement errors were controlled within ±1 °C and ±0.1 °C, respectively.
4. Results
4.1. Petrographic Characteristics
Black/gray calcite is mostly granular, with particle sizes ranging from tens to hundreds of micronmeters. Under the microscope, two groups of clear cleavage lines with good continuity and straight lines could be found (Figure 4A–C). In addition, a large number of cracks and intragranular/intercrystalline dissolved pores filled with bitumen had developed in the calcite. The occurrence of bitumen is strictly controlled by the pore morphology, and banded (Figure 4D), lumpy, and disseminated (Figure 4F) shapes were discovered. For example, bitumen directionally fills in the cracks at the edge of the calcite veins in sample BQ-5 (Figure 4D). According to the optical characteristics, two types of bitumen could be identified. The first type was mainly found in the black/gray calcite from the Banqi area. They were homogeneous and showed yellow under reflected light (Figure 4D–F). The other type of bitumen was mainly found in gray calcite samples from the Laizishan area. Compared with the first type, they were colored dark grey and possessed strong anisotropy. They featured a flat boundary, wavy extinction, and flowing structure (Figure 4G–I). In addition to bitumen, a small amount of fine-grained pyrite with a particle size <30 μm was developed in the black calcite sample BQ-1 (Figure 4L). Similar to previous studies [13], the pyrite and bitumen grains were closely associated, and some pyrite was wrapped by bitumen (Figure 4J,K).
The cleavage lines of white calcite were sparse, with unclear lines and poor continuity (Figure 5A–C). Though many dissolution pores had developed, only a few were filled with bitumen (Figure 5D–F). Under reflected light, the bitumen showed strong anisotropy and featured a flat boundary, wavy extinction, and mosaic structure (Figure 5D–F). Different from black/gray calcite, a wide range of fine-grained, banded pyrite was discovered within the dissolution pores of the white calcite. Fine-grained pyrite featured a small size (~10 μm) and a high degree of automorphism (Figure 5G–I). The large-sized banded pyrite (>50 μm) featured a core-rim structure (Figure 5J–L). Previous Backscattered electron (BSE) images and Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) (Figure 5M,N) indicated that the fine-pyrite and the rim of the banded pyrite were the major locations of the gold [16,31,32].
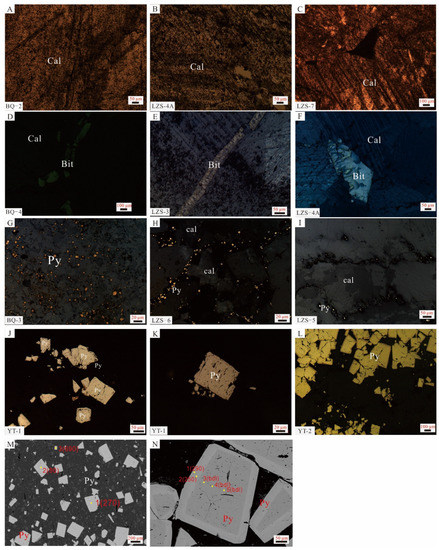
Figure 5.
Photographs showing the characteristic of white calcite of the Banqi-Yata-Laizishan area. (A–C) buck calcite, with fuzzy cleavage texture and poor continuity. (D–F) Mosaic bitumen within the white calcite. (G–I) Fine-grained pyrite distributed within calcite pores and fissures from the Banqi-Laizishan area. (J–L) Banded pyrite with core-rim structure from the Yata area. (M,N) Backscattered electron imaging and Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) of pyrite from No. 940 mine in the Yata gold deposit [32]).
4.2. Cathode Luminescence
The cathode luminescence of carbonate minerals is affected by many factors, such as Fe, Mn content, total rare earth element content, and crystal structure [33,34]. Respectively acting as activators and quenchers, Mn and Fe can activate and reduce cathode luminescence. Thus, the content and ratio of the Fe and Mn of the calcite have an important impact on the characteristics of cathode luminescence [33]. Under the conditions of Mn > 40 μg/g and Fe < 5 × 103 μg/g, the cathode luminescence of the carbonate is controlled by the ratio of the contents of Fe and Mn. With a decrease in the Fe/Mn ratio, the cathode luminescence intensity increases [33,35]. The Fe and Mn contents and Fe/Mn ratio of calcite samples in the Banqi, Yata, and Laizishan areas are shown in Table 2. The Fe content of black/gray calcite and white calcite is nearly in the same range (396–704 ppm vs. 395–619 ppm) (Table 2, Figure 6A). However, the Mn content of white calcite is significantly higher (273–409 ppm) and leads to a lower Fe/Mn ratio (1.0–2.3) than that of black/gray calcite (2.3–5.5) (Figure 6A,B). The cathode luminescence of black/gray calcite and white calcite are respectively dark red (Figure 7A,B) and bright red (Figure 7C,D).

Table 2.
Fe and Mn content of calcite in the Banqi-Yata-Laiizishan area.
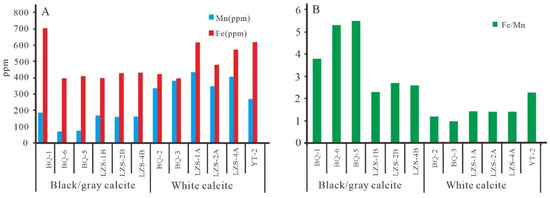
Figure 6.
Histogram of Fe and Mn content of calcite in the Banqi-Yata-Laiizishan area. (A) the abundance of the Fe and Mn in the calcite samples. (B) The ratio of Fe/Mn for the calcite samples.
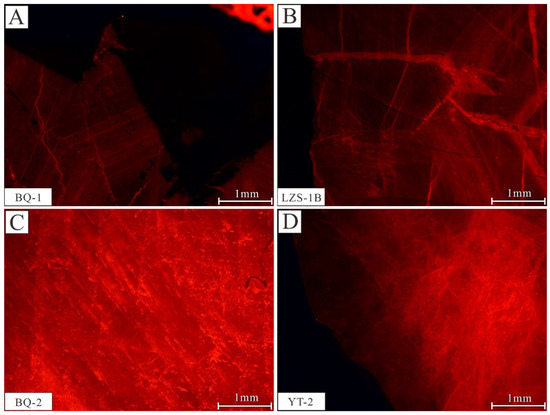
Figure 7.
Cathode luminescence characteristics of calcite in the Laizishan-Banqi-Yata area, Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin. (A) Dark red cathodoluminescence of black calcite. (B) Dark red cathodoluminescence of gray calcite. (C,D) Bright red cathodoluminescence of white calcite.
4.3. Fluid Inclusion Characteristics
Three dark color and white color calcites possessing abundant fluid inclusions were selected for the Fluid inclusion analysis (Table 3). Hydrocarbon inclusions (from 5 to 10 μm) were found in black/gray calcite and showed a blue–white color under fluorescence (Figure 8A–D). The aqueous fluid inclusions (from 5 to 10 μm) associated with hydrocarbon inclusions were typical gas-liquid two-phase fluids and featured elliptic, needle-like, or short column shapes (Figure 8E). The homogenization temperature and salinity results are shown in Table 3. The homogenization temperature of aqueous fluid inclusions in black/gray calcite varied from 65.7 °C to 173.1 °C. Based on the frequency homogenization temperature, two groups, <150 °C (65.7–146.2 °C, mean ~110 °C) and >150 °C (155.4–173.1 °C, mean ~160 °C), were divided (Figure 9). According to the ice melting temperature (Tice), the calculated salinity of the fluid inclusion obtained using the formula [36] (Salinity = 1.78 Tice − 0.0442 Tice2 + 0.000557 Tice3) varied from 7.45 to 22.27 wt.% NaCl eq (average 17.01 wt.% NaCl eq) (Table 3). No hydrocarbon inclusions were found in white calcite. However, two-phase gas-liquid aqueous fluid inclusions were widely developed. The diameter of fluid inclusions was about 10 μm to 15 μm long and had oval, needle-like, and rectangular shapes (Figure 8G,H). The homogenization temperature (Th) of the inclusions varied from 128.2 °C to 299.9 °C. Three groups, >230 °C, 190–230 °C (mean ~205 °C), and <190 °C (mean ~160 °C), were divided according to the homogenization temperature frequency, and more than half (~57.8%) of the homogenization temperatures were lower than 190 °C (Figure 9). The measured salinity of fluid inclusions ranged from 0.88 to 13.51% (average 5.29 wt.% NaCl eq) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Summary of fluid inclusion data of the various calcite types from the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin.
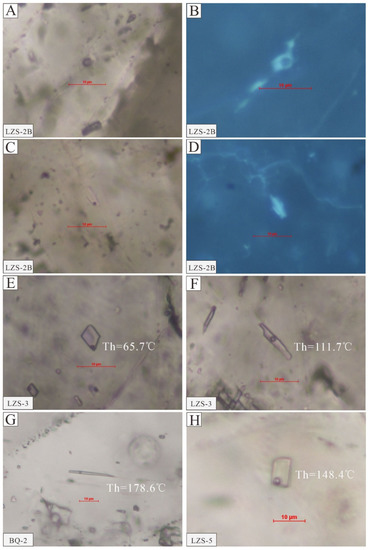
Figure 8.
Typical characteristics of fluid inclusions in calcite in the Banqi-Yata-Laizishan area, Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin. (A–D) Irregular hydrocarbon inclusions, blue–white under fluorescence. (E) aqueous fluid inclusions, negative crystal, Th = 65.7 °C. (F) short columnar-shaped aqueous fluid inclusions, Th = 111.7 °C. (G) needle-like shape aqueous fluid inclusions, Th = 178.6 °C. (H) rectangle-shaped aqueous fluid inclusions, Th = 148.4 °C.
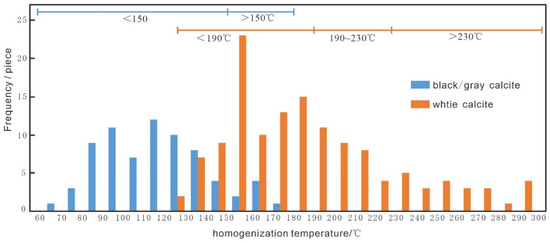
Figure 9.
Histogram of homogenization temperatures of the aqueous inclusion from different type calcite.
5. Discussion
5.1. Characteristics of the Basin Fluid Activity
The black/gray and white calcite in the Banqi, Yata, and Laizishan areas of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin showed different characteristics in petrographic, cathode luminescence, and fluid inclusion results. The pores and fractures of the black/gray calcite were widely filled with bitumen. In addition, these calcites featured a high Fe/Mn ratio (~2.9), dark grey cathode luminescence, and rich hydrocarbon fluid inclusion. The relatively low homogenization temperature of aqueous fluid inclusions associated with hydrocarbon fluid inclusion in black/gray calcite (65.7~173.1 °C, majority < 150 °C) indicated that the fluid was formed in low-temperature conditions (oil–gas window condition). Compared with the dark-colored calcite, the pores of white calcite were rich in gold-bearing pyrite. Furthermore, the white calcites featured a low Fe/Mn ratio (~1.5), bright red cathode luminescence, and nearly no hydrocarbon-bearing fluid inclusion. The much higher homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions in milky calcite (128.2~299.9 °C, majority > 160 °C) indicated that the fluid formed at a relatively high temperature (ore-forming fluid). Regarding the formation sequence of the two types of calcite, the gradually brightening cathode luminescence from black/gray calcite to white calcite and the gray calcite U-Pb age (~250 Ma), older than the white calcite (~120 Ma) [37], indicated the black/gray calcite formed earlier than the white calcite.
5.2. First Basin Fluid Activity, Related Hydrocarbon Migration, and Gold Mineralization
5.2.1. Timing of Hydrocarbon Migration/Accumulation
Fluid inclusion analysis combined with basin burial history simulation is widely used in qualitative constraining of the hydrocarbon evolution history [38]. The burial history of the Yang 1 Well in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin shows that the Middle–Lower Devonian source rocks received continuous burial from the Carboniferous to Permian periods [39]. As mentioned above, the homogenization temperatures of aqueous fluid inclusions associated with hydrocarbon inclusions from the Banqi and Laizishan reservoirs could be generally divided into two groups: 65.7~146.2 °C (mean ~110 °C) and 155.4~173.1 °C (mean ~160 °C), corresponding to the oil and gas windows, respectively. Under the formula [40] of H = 100 × (Th − T0)/G (H: depth of inclusion formation (m); Th: the homogenization temperature of aqueous fluid inclusions (°C); T0: the paleo-surface temperature (°C) 20 °C; G: the paleo-geothermal gradient in the late Paleozoic to Mesozoic study area: 4 °C/100 m), the calculated burial depths were 1142.5–3155 m and 3385–3827.5 m. Plotting the depth of the burial history of the Yang 1 well, a continuous liquid oil and gas migration/accumulation event was considered to have occurred from the Early to Late Triassic, respectively (Figure 10). During the Late Permian to Middle Triassic periods, the collision between Indosinian and the South China block (Indosinian event) caused hydrocarbon migration in the reservoir [41]. The number of hydrocarbon inclusions within black/gray calcite (Figure 8B,D) and widely found solid bitumen-filled dissolution pores and fractures (Figure 4) are direct evidence of petroleum migration. Furthermore, the bitumen in sample BQ-5, directionally distributed along the edge of calcite veins (Figure 4D), indicates a temporal and migration relationship between hydrocarbons and basin fluids.
Corresponding to the fluid inclusion data, the in situ U-Pb dating of calcite closely associated with bitumen in paleo-oil reservoirs in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin (253 ± 27 Ma~229.1 ± 6.7 Ma, mean 241.4 Ma) showed that liquid hydrocarbon migration occurred before the middle Triassic period [37]. As shown in the basin modeling result, the Permian carbonate reservoirs were buried to a depth of more than 5 km during the late Triassic with a reservoir temperature exceeding 150 °C, which led to the thermal cracking of the previously formed oil [39,42]. The solid bitumen within the paleo-oil reservoirs of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin possessed high bitumen reflectance (Rb: 2.16–4.26%, mean 3.55%), low H/C ratio (<0.4), and did not dissolve in organic solvents [43,44]. In addition, the solid bitumen in this study also possessed flowing and mosaic structures under a microscope (Figure 5). All of the above features indicate the solid bitumen within the Nanpanjiang Basin is high-maturity pyrobitumen formed by the thermal cracking of liquid oil [45,46]. Previous studies found the Re-Os dating of pyrobitumen that formed contemporaneously with methane in the Majiang-Wanshan reservoir, Xuefeng uplift, and the Micang Shan reservoir, northern Sichuan Basin, South China block, recorded the timing of gas generation [47,48]. The Re-Os age of 228 ± 16 Ma for pyrobitumen from the Laizishan and the Banqi reservoirs [32], younger than that inferred for liquid oil migration [37,39] but in agreement with the estimated timing of the thermal cracking of liquid oil, further suggests the late Triassic was a key period for gas formation in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin.
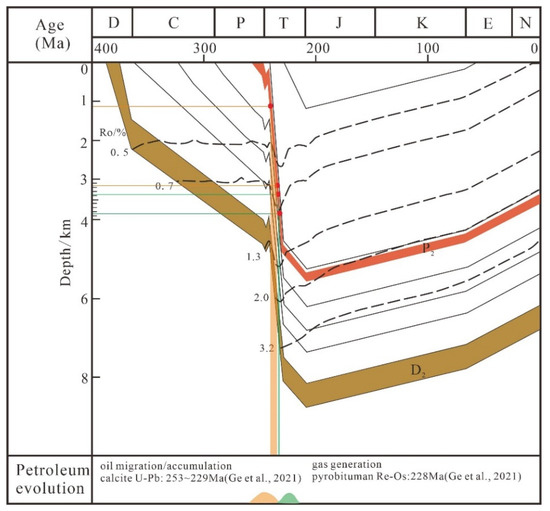
Figure 10.
Burial history map of Yangba Depression (Yang 1 well), the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin [32,43]).
In summary, hydrocarbon reservoirs in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin underwent a continuous process of oil migration/accumulation to form oil reservoirs and oil thermal cracking to form natural gas reservoirs during the Late Permian to Late Triassic. The black/gray calcite closely associated with bitumen, as the product of basin fluid activity coexisting with hydrocarbon, records the complete process of petroleum evolution.
5.2.2. The Relationship between Hydrocarbon Migration/Accumulation and Gold Mineralization
Though there is still controversy regarding the timing of Carlin-type gold mineralization in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin [49], the arsenopyrite Re-Os ages (235 ± 33~204 ± 19 Ma) of the Lannigou-Jinya-Shuiyindong deposit [24], fine-grained (5–10 μm) illite Rb-Sr isochron age (218 ± 4.6 Ma) from the Yata gold deposit [50], hydrothermal rutile in situ SIMS U–Pb age (213.6 ± 5.4 Ma) from the Zhesang deposit [51], as well as gold-bearing pyrite associated calcite in situ U-Pb ages (204.3 ± 2.0~202.9 ± 4.2 Ma) from the Shuiyudong gold deposit [52] indicate a gold mineralization event during the Late Triassic period in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin (Figure 11). Interestingly, this metallogenic event agrees with previously mentioned key timings for hydrocarbon evolution and especially coincides with timing related to gas generation. In addition to the consistency in time, the phenomenon that gold-bearing pyrite encased by solid bitumen in black calcite (Figure 4J,K) and the characteristics of solid pyrobitumen cross-cut by pyrite in the Shuiyindong gold deposit [13] also indicate that the formation of bitumen and pyrite precipitation occurred almost simultaneously with the gas generation, which may be a little earlier than pyrite precipitation. All these close relationships between bitumen and ore-related minerals in formation time and space indicate a close relationship between hydrocarbon evolution and mineralization.
The LA-ICP-MS analyses of the bitumen in the Carlin trend, Nevada, show the abundance of Au in bitumen reached 4.6 ppm [53]. Similarly, atomic absorption spectrometer tests and Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) of the bitumen from Yanzidong and Shitouzhai paleo-oil reservoirs in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin found Au content in bituminous could reach tens of ppm [18]. Besides, in a water–oil–rock system, gold has been experimentally shown to predominantly enter in the oil phase [9]. Recent experiments of metal solubility in crude oils at different temperatures showed that metal (Zn, Au, U) abundances in crude oil are related to temperature, and that the abundance increases from 100 to 200 °C and begins to decrease when the oil changes into gas [54]. The fluid inclusion analysis of the reservoirs in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin showed that the homogenization temperature of the gas-bearing fluid inclusion was higher than 160–180 °C, consistent with the temperature conditions when Au abundance decreased because of oil cracking. Combining the high gold abundance in bitumen in the Carlin-type gold deposit and metal solubility in the crude oils experiment, it seemed the crude oil could enrich and migrate Au and began to release it into the basin fluid during cracking under high-temperature conditions.
The sulfidation between Fe-bearing host rock and ore-forming fluids rich in Au and H2S is an important mechanism of gold-bearing pyrites precipitation in Carlin-type gold deposits [55]. Lithogeochemical data of the Shuiyindong gold deposits [16,56] show the gold was also transported in H2S-rich fluids for the Carlin-type gold deposits in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin. Meanwhile, the high content of iron from the Fe dolomite (11~17 wt.%) from the Lannigou deposit [57] and the phenomenon that arsenian pyrite replaces ferroan calcite and dolomite [16] supports that the gold-bearing pyrite was also formed by the sulfidation of Fe-bearing minerals and H2S rich ore-forming fluid. As to the source of the sulfur, the overall broad sulfur isotopic composition (δ34S) of hydrothermal pyrite in the Banqi, Yata, and Lannigou gold deposits (mean 9.92‰, −2.3~8.0‰, 7.3~13.6‰) [16,58] indicates that reduced sulfur leading to the precipitation of gold-bearing pyrite may mainly derive from sedimentary rocks. Recently, near-zero Δ33S values of the gold bearing pyrites in the Linwang deposits further indicates that S within the deposit was most likely sourced from the Triassic sedimentary rocks [59]. Therefore, the thermochemical sulfate reduction (TSR), with the reaction between organic matter (oil and gas) and sulfate at elevated temperatures (>100–140 °C), could be a significant process for the generation of reduced sulfur [34,60,61]. As the bond energy of 32S-O is weaker than that of 34S-O, more 34SO42− is involved in the TSR process than 32SO42−, resulting in lighter sulfur isotope composition in sulfide than coeval sulfate [62]. The slightly lighter δ34S values for the gold-bearing pyrite (−2.3~13.6‰) in the Banqi, Yata, and Lannigou gold deposits of the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin than Triassic seawater (δ34S 10~15‰) [63] supports that the TSR process occurred during the formation of gold-bearing pyrite. Regarding the reactant for the TSR process, the rapid subsidence during the Triassic with the reservoir temperature exceeding 200 °C and liquid oil cracked into gas and pyrobitumen show that the gas could play an important role [14]. Laser Raman analysis of the fluid inclusions in calcite from the reservoir, showing that CH4 was a dominant organic component [22] and a significant negative correlation between CO2 and CH4 content in the hydrocarbon inclusions [3], indicates that CH4 could have been involved in the TSR process.

Figure 11.
Compiled chronology and mineral formation sequence in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin [24,32,37,50,51,52,56].
Integrating the basin fluid evolution and context of regional tectonic history, the genetic relationship between petroleum evolution and the Late Triassic Carlin-type gold mineralization in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin could be generally established. From the Late Carboniferous to the Permian, Devonian source rock was continuously buried and went into the oil window (Figure 12A). After this, the Indosinian tectonic event triggered the hydrocarbon migration, and Au was enriched from sedimentary rocks during the process (Figure 12B). In the Late Triassic, the rapid burial of the Permian reservoir caused the reservoir temperature to exceed 200 °C, which led to the crude oil being cracked into gas and pyrobitumen (Figure 12C). The oil cracking released the Au into the basin fluid and led to the gas-dominated TSR process. Finally, when Au and H2S-rich ore-forming fluid migrated into the Fe-rich calcareous and dolomitic siltstone formation, the gold-bearing pyrite was precipitated (Figure 12C).
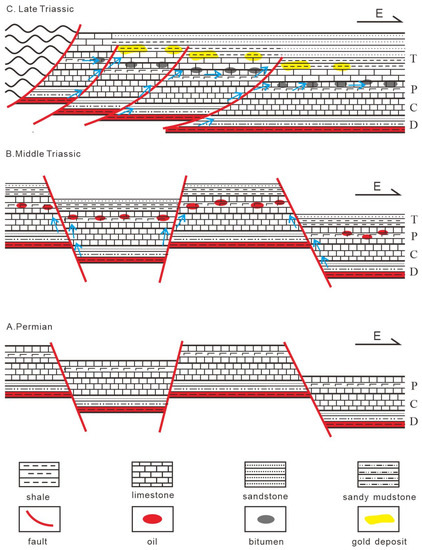
Figure 12.
Simplified model for the petroleum evolution and gold mineralization in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin.
5.3. Second Basin Fluid Activity and Related Gold Mineralization
Similar to a previous study [52], the white calcite associated with gold-bearing pyrite by petrographic analysis and featuring bright red cathode luminescence in this study revealed it belongs to the gangue minerals closely related to gold mineralization. The homogenization temperatures (Th) of fluid inclusions in gangue minerals at different mineralization stages showed a declining trend from 230–270 °C in the early stage, 200–230 °C in the intermediate stage, and 120~160 °C in the late stage [16,26,64]. Paragenetic sequences for the Carlin-type gold deposits also showed the calcite veins mainly formed in the late ore formation stage [26] (Figure 11). Corresponding to this understanding, the higher homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions in white calcite (128.2~299.9 °C), with a majority temperature lower than 190 °C (mean ~160 °C) (Figure 9), further supports this calcite was the product of high-temperature ore-forming fluids. Recent isotope dating on this kind of calcite, including Sm-Nd age (136 ± 3–134 ± 3 Ma) and the in situ U-Pb age (139.3 ± 5.7–137.1 ± 9.7 Ma) of calcite associated with realgar from the Shuiyindong deposit [16,52], as well as the in situ U-Pb age (121.0 ± 1.0–106 ± 17 Ma) of calcite associated with gold-bearing pyrite from the Laizishan deposit [37], shows the early Cretaceous could be a key interval for gold mineralization. In addition, some late ore-stage mineral dates, for example the Sm-Nd age (122 ± 15–126 ± 12 Ma) of fluorite coexisting with calcite from the Nibao deposit [50] and the Rb-Sr age (148 ± 4.1 Ma) of quartz coexisting with realgar from the Yata deposit [50], also indicate a secondary Carlin-type gold mineralization in the Early Cretaceous (Figure 11).
During the Early Cretaceous (~135 Ma), the subduction between the Paleo-Pacific and Eurasian plates (the Yanshanian tectonic event) formed an extensional environment resulting in lithospheric thinning and magmatic activity in the South China Block [65,66]. Corresponding to this tectonic event, a diversity of ore deposits such as low-temperature hydrothermal Cu-Ag deposits [67,68,69,70,71], antimony deposits [72], porphyry molybdenum deposits [73], and skarn tungsten deposits [74] developed in the whole of eastern China from the southeast coast to the inland area (Figure 13). Similar to the western edge of the South China Block, the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin possessed a tectonic background during the Early Cretaceous, and the secondary Carlin-type gold mineralization recorded by the white calcite may be a remote response to the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate [52,65].
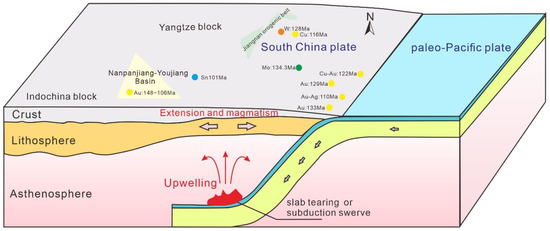
Figure 13.
Simplified diagram of the metallogenic tectonic setting of the Early Cretaceous Carlin-type gold deposit in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin.
6. Conclusions
Petrography, cathode luminescence, and fluid inclusion analysis of black/gray and white calcite indicated two basin fluid activity events in the Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin. The black/gray calcite, which featured dark red cathode luminescence, is closely associated with bitumen, and possesses lots of hydrocarbon inclusions and a small amount of pyrite recorded in the first basin fluid activity. Integrating the homogenization temperature of the aqueous inclusions (65.7–173.1 °C), basin burial history, and related isotope dates, the black/gray calcite recorded a consecutive hydrocarbon evolution and the first Carlin-type gold mineralization event from the Late Permian to Late Triassic periods under the control of the Indosinian tectonic movement. The liquid oil and gas, which acted as gold carriers and reactants, could involve gold mineralization. The white calcite, featuring the bright red cathode luminescence associated with gold-bearing pyrite and high homogenization temperature of the aqueous fluid inclusion, recorded the secondary fluid activity within the basin. Combined with the previous isotope dates of the late mineralization stage (~140–106 Ma) and the metallogenic age of typical deposits in South China, the white calcite seems to reflect that the secondary Carlin-type gold mineralization events during the Early Cretaceous were caused by subduction between the Paleo-Pacific plate and the Eurasian plate in the Yanshanian tectonic period.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.H. and X.G.; methodology, P.H.; software, P.H. and X.G.; validation, C.S. and S.L.; formal analysis, Y.C.; investigation, C.S.; resources, Y.C.; data curation, P.H. and X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, P.H. and X.G..; writing—review and editing, C.S.; visualization, S.L.; supervision, C.S.; project administration, X.G.; funding acquisition, C.S., X.G. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.42272168, 41802168, 41672140), the Innovation Team project of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2021CFA031), and the Open Topic Fund from Key Laboratory of Tectonics and Petroleum Resources of Ministry of Education (TPR-2021-03).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.42272168, 41802168, 41672140), the Innovation Team project of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2021CFA031), and the Open Topic Fund from the Key Laboratory of Tectonics and Petroleum Resources of Ministry of Education (TPR-2021-03). We also thank the three anonymous reviewers for their comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kesler, S.; Jones, H.; Furman, F.; Sassen, R.; Anderson, W.; Kyle, J. Role of crude oil in the genesis of Mississippi Valley-type deposits: Evidence from the Cincinnati arch. Geology 1994, 22, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Xue, C.; Dong, S.; Fu, S.; Cheng, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, C. The coupling relationship between metallization and hydrocarbon accumulation in sedimentaty basins. Earth Sci. Front. 2010, 17, 83–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, S.; Xu, S.; Dong, S. Physicochemical properities of hydrocarbon-bearing fluids in the Youjiang Basin, South China. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2007, 26, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Li, W.; Gu, X.; Xiao, D.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Chen, C.; Dong, S. A Study of Methane Inclusions of the Danzhai Mercury Ore Field in Guizhou Province and Its Geological Signific ance. Earth Sci. Front. 2013, 20, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Ren, T. Metal deposits, oil and gas reservoirs: Two brothers in sedimentary basin. Chin. J. Nat. 2019, 41, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Peng, P.; Lin, Q.; Liu, D.; Jia, R.; Shi, J.; Lu, J. Some Problems on Organic Geochemistry of Stratabound Deposits. Adv. Earth Sci. 1990, 5, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fu, J.; Lu, J. Experimental Study on Interaction between Organic Matters and Gold. Chin. J. Geol. 1993, 28, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins, L.; Rayner, M.; Groves, D.; Roche, M. Evaporites; in situ sulfur source for rhythmically banded ore in the Cadjebut mississippi valley-type Zn-Pb deposit, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Lu, J.; Fu, J.; Ren, Z.; Zou, D. Crude oil as a carrier of gold migration: Petrology and geochemical evidence. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1998, 28, 552–558. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Hu, R.; Su, W.; Zhu, L. Fluid flow and mineralization in the Youjiang Basin, Dianqiangui district. Sci. China (Ser. D) 2002, 32, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.; Zhao, J.; Pan, S.; Yan, D.; Lu, J.; Hao, S.; Gong, Y. A New Technology of Basin Fluid Geochronology: In Situ U-Pb Dating of Calcite. Earth Sci. Front. 2019, 44, 698–712. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Dynamics of Sedimentary Basins and Basin-Fluid Related Ore-Forming. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2000, 19, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. Organic Matter in Carlin-Type Gold Deposits and Paleo-Oil Reservoirs in Southwest Guizhou—Source, Maturity and Association; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Da, J. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the bitumen and gas in the Palaeo-reservoirs, Nanpanjiang Basin. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 37, 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Muntean, J. The Carlin gold system: Applications to exploration in Nevada and beyond. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2018, 20, 39–88. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Dong, W.; Zhang, X.; Shen, N.; Hu, R.; Hofstra, A.H.; Cheng, L.; Xia, Y.; Yang, K. Carlin-type gold deposits in the Dian-Qian-Gui “Golden Triangle” of southwest China. Rev. Econ. Geol. 2018, 20, 157–185. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Li, J.; Hofstra, A.; Marsh, E.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Relationship between Carlin-type gold deposits and paleopetroleum reservoirs in SW Guizhou, China: Evidence from gas compositions of fluid inclusions and Raman spectroscopic characteristics of bitumen. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 3295–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, K.; Han, S.; Sun, Z. The characteristics of organic matter and its relationship with the formation of Carlin-type gold deposits in southwest Guizhou Province. Geochimica. 2016, 45, 281–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, W.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, T. Evolution of Sedimentation and Tectonics of the Youjiang Composite Basin, South China. Acta Geol. Sin. 1995, 8, 358–371. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Wu, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, Z. Hercynian-Indosinian sedimentary-tectonic evolution of the Nanpanjiang Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 1996, 70, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M. A study on the pereoleum system of Nanpanjiang Sag. Yunnan Geol. 1999, 18, 248–265. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Fu, S.; Dong, S. Characteristics of hydrocarbon-bearing ore-forming fluids in the Youjiang Basin, South China: Implications for hydrocarbon accumulation and ore mineralization. Earth Sci. Front. 2007, 14, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, P. Geochemical characteristics of main source rocks in the Nanpanjiang Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2006, 28, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Dang, Y. Re–Os isochron ages for arsenopyrite from Carlin-like gold deposits in the Yunnan–Guizhou–Guangxi “golden triangle”, southwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Peng, Y.; Li, B. The Genetic Relationship between Carlin-type Gold Deposits and Paleo-Petroleum Reservoirs in SW Guizhou, China: Evidence from Organic Petrography. Earth Sci. Front. 2013, 20, 92–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Su, W.; Bi, X.; Tu, G.; Hofstra, A. Geology and geochemistry of Carlin-type gold deposits in China. Miner. Depos. 2002, 37, 378–392. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Zhang, H.; Hu, R.; Ge, X.; Xia, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C. Mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite from the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China: Implications for gold depositional processes. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J. Nevada’s Carlin-type gold deposits: What we’ve learned during the past 10 to 15 years. In Diversity in Carlin-Style Gold Deposits; Muntean, J.L., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists Special Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 2018; Volume 20, pp. 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liang, L.; Long, X.; Li, J.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hao, J. Genesis and evolution of framboidal pyrite and its implications for the ore-forming process of Carlin-style gold deposits, southwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 102, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.; Hofstra, A.; Muntean, J.; Tosdal, R.; Hickey, K. Carlin-type gold deposits in Nevada: Critical geologic characteristics and viable models. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 451–484. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Xia, Y.; Cline, J.; Koenig, A.; Wei, D.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Z. Are there Carlin-type gold deposits in China? A comparison of the Guizhou, China, deposits with Nevada, USA, deposits. In Diversity in Carlin-Style Gold Deposits; Muntean, J.L., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists Special Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 2008; Volume 20, pp. 187–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Selby, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, G.; Shen, C. Genetic relationship between hydrocarbon system evolution and Carlin-type gold mineralization: Insights from ReOs pyrobitumen and pyrite geochronology in the Nanpanjiang Basin, South China. Chem. Geol. 2021, 559, 119953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. Relationship between Cathodoluminescence and Concentration of Iron and Manganese in Carbonate Minerals. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 12, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Machel, H. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings—old and new insights. Sediment. Geol. 2001, 140, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, F. Cathodoluminescence Characteristics and Diagenetic Fluids of Dolomites in Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation of Central Sichuan Basin. Pet. Geol. Eng. 2016, 30, 28–31+148. [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar, R. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1993, 57, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shen, C.; Zhou, R.; He, P.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y. Tracing fluid evolution in sedimentary basins with calcite geochemical, isotopic and U-Pb geochronological data: Implications for petroleum and mineral resource accumulation in the Nanpanjiang Basin, South China. GSA Bull. 2022, 134, 2097–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Fu, S.; Dong, S. Analysis of The Charge History of The Shitouzhai Permian Paleo-Oil Reservoir, Guizhou, SW-China: Fluid Inclusion and Sm-Nd Isotope Constraints. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P. The thermal evolution history and oil and gas generation history of main source rocks in the Nanpanjiang Basin. Petroeum Geol. Exp. 2006, 28, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, R.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J. Timing and Phases of Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation of the Formation of Oil and Gas Pools in Lunnan Low Uplift of Tarim Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2002, 20, 320–325+332. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Liu, L. Relationship between tectonic movement and destruction of oil and gas reservoirs in the Dananpanjiang Area. Geotecton. Metallog. 2010, 34, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.; Xie, B.; Liu, K. Giant gas discovery in the Precambrian deeply buried reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin, China: Implications for gas exploration in old cratonic basins. Precambrian Res. 2015, 262, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P. Geochemistry and Genesis of Bitumen in Paleo-Oil Reservoir in the Nanpanjiang Basin, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2006, 28, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, K. Organic Petrology Characteristics of Nature Solid Bitumens. Coal Geol. &Explor. 1995, 23, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, H. Classification, structure, genesis and practical importance of natural solid oil bitumen (“migrabitumen”). Int. J. Coal Geol. 1989, 11, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, N.; Ma, Z.; Ning, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, G.; Rui, X.; Rao, D. Evalution of equivalent relationship between vitrinite reflectance and solid bitumen reference. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2020, 49, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Shen, C.; Selby, D.; Deng, D.; Mei, L. Apatite fission-track and Re-Os geochronology of the Xuefeng uplift, China: Temporal implications for dry gas associated hydrocarbon systems. Geology. 2016, 44, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shen, C.; Selby, D.; Wang, G.; Yang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Xiong, S. Neoproterozoic-Cambrian petroleum system evolution of the Micang Shan uplift, northern Sichuan Basin, China: Insights from pyrobitumen Re-Os geochronology and apatite fission track analysis. AAPG Bull. 2018, 102, 1429–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fu, S.; Xiao, J. Major scientific problems on low-temperature metallogenesis in South China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 32, 3239–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X. Geology, Mineralization and Genesis of the Nibao, Shuiyindong and Yata Gold Deposits in SW Guizhou Province, China; China University of Geoscience: Wuhan, China, 2017; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, Q.; Hu, R.; Xiong, B.; Li, Q.; Zhong, R. In situ SIMS U-Pb dating of hydrothermal rutile: Reliable age for the Zhesang Carlin-type gold deposit in the golden triangle region, SW China. Miner. Depos. 2017, 8, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Hofstra, A.; Deng, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Calcite U-Pb dating unravels the age and hydrothermal history of the giant Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit In the golden triangle, South China. Econ. Geol. 2021, 116, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, R.; Bull, S.; Maslennikov, V. A carbonaceous sedimentary source-rock model for Carlin-type and orogenic gold deposits. Econ. Geol. 2011, 106, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.; Guo, X.; Xu, H.; Williams-Jones, A.; Sun, C.; Vasyukova, O.; Sugiyama, I.; Fuch, S.; Pearce, K.; Roback, R. Hydrocarbons as ore fluids. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2017, 5, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsbo, P.; Hofstra, A. Origin and Significance of Postore Dissolution Collapse Breccias Cemented with Calcite and Barite at the Meikle Gold Deposit, Northern Carlin Trend, Nevada. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Hu, R.; Xia, B.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y. Calcite Sm-Nd isochron age of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Chem. Geol. 2009, 258, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Xia, Y.; Cline, J.; Pribil, M.; Koenig, A.; Tan, Q.; Wei, D.; Wang, Z.; Yan, J. Magmatic origin for sediment-hosted Au deposits, Guizhou Province, China: In situ chemistry and sulfur isotope composition of pyrites, Shuiyindong and Jinfeng deposits. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 1627–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. The Geology and Hydrothermal Evolution of Sediment-Hosted Gold Deposits in Southwestern Guzhou Province, PRC. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College of London, London, UK, 1997; p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Su, W.; Shen, N.; Xia, X.; Wang, F. In situ multiple sulfur isotopes and chemistry of pyrite support a sedimentary source-rock model for the Linwang Carlin-type gold deposit in the Youjiang basin, southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, T.; Zou, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Z. The fate of CO2 derived from thermochemical sulfate reduction (TSR) and effect of TSR on carbonate porosity and permeability, Sichuan Basin, China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Xie, Z.; Worden, R.; Hu, G.; Wang, L.; He, H. Methane-dominated thermochemical sulphate reduction in the Triassic Feixianguan Formation East Sichuan Basin, China: Towards prediction of fatal H2S concentrations. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, T.; Zou, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Z. Isotopic evidence of TSR origin for natural gas bearing high H2S contents within the Feixianguan Formation of the northeastern Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Sci. China 2005, 48, 1960–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Claypool, G.; Holser, W.; Kaplan, I.; Sakai, H.; Zak, I. The age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem. Geol. 1980, 28, 199–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Dong, S.; Xue, C.; Fu, S. Hydrocarbon- and ore-bearing basinal fluids: A possible link between gold mineralization and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Youjiang Basin, South China. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, M.; Franco, P. Major types and time–space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, J.; Cui, J.; Shi, W.; Su, J.; Li, Y. The New Progress in the Study of Mesozoic Tectonics of South China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2012, 33, 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.; Li, B.; Zhou, C.; Sun, J.; Wei, F. Gold mineralization events of the Jiangnan Orogen in Hunan and their tectonic settings. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2021, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Li, H.; Mei, Y. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Chronology of Diagenetic Mineralization of the Longtoushan Porphyry Gold Orefield‚Gui County‚Guangxi. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, H. Fluid Inclusion Rb-Sr Isochron Dating of Gold Deposits in Yunkai Uplifted Area. Miner. Depos. 1991, 10, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, G.; Gao, Y.; Wu, F. SIMS U-Pb zircon geochronology of porphyry Cu-Au-(Mo) deposits in the Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, eastern China: Magmatic response to early Cretaceous lithospheric extension. Lithos 2010, 119, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Xue, T. Isochronous ~(40)Ar/~(39)Ar Dating of Laser Microzone in Fine Disseminated Gold Deposit: A Case Study of Changkeng Large Gold Deposit. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Xie, G.; Guo, C.; Yuan, S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y. Spatial-Temporal Distribution of Mesozoic Ore Deposits in South China and Their Metallogenic Settings. Geol. J. China Univ. 2008, 14, 510–526. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z. Geological Characteristics and Mineralization Age of the Tongkengzhang Molybdenum Deposit in Xunwu County‚South Jiangxi Province‚ China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 924–928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Mei, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, H. Isochronology Study on the Xianglushan Scheelite Deposit in North Jiangxi Province and Its Geological Significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 927–931. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).