Abstract
In this paper, the thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated binary blends composed of 30% microwave (MW) pre-treated biomass pellets (wheat straw, wood) and 70% of different origin raw biomass pellets (wheat straw, wood, or peat) was performed using originally developed experimental device with a heat output up to 20 kW. Biomass pellets were pre-treated at temperatures of 200 and 275 °C using a microwave laboratory scale torrefaction of the original construction. It was established that synergistic effects of interaction between the components of binary blends promote an increase in the efficiency of their thermochemical conversion by 5.8–9.4%. It was assumed that synergistic effects of thermochemical conversion can be related to an increase in surface area and porosity of pre-treated pellets. With a focus on different steps and rates of biomass degradation and heat amounts released for different types of blends, the thermal analysis (DTG/DSC) of ground blends in the temperature range of 25–650 °C was performed in air media with the heating rate of 10 °C/min. According to the thermal analysis data, the heat energy yield of ground blends meets the requirements of linear regression based on the additivity principle and the development of synergistic effects during thermochemical conversion of ground blends was not detected.
1. Introduction
To limit Earth climate changes caused by heavy use of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) for energy production, partial replacement of them by more intensive use of renewable fuels (forestry or agriculture residues) is gaining importance to reduce greenhouse gases and polluting emissions [1,2,3,4]. By studying the processes of co-combustion of different origin fuels, it has been found that the development of these processes is significantly influenced by the ratios of the components in fuel mixtures and by differences in their main characteristics (elemental and chemical composition) which enhance thermal and chemical interactions between the components [5,6,7,8]. The results of these studies suggest that additional measures are needed to improve the process development when co-combusting different origin pelletized fuels. With reference to the studies of the effect of MW pre-treatment on lignocellulosic biomass samples [9,10,11], it is suggested that an improvement of combustion characteristics when co-combusting different pelletized fuels can be achieved by selective microwave (2.45 GHz) pre-treatment of the mixture components. This leads to the activation of thermal decomposition of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin of the pre-treated components. Preliminary studies of the effect of MW pre-treatment of biomass pellets on combustion characteristics and energy production confirm that MW pre-treatment of biomass results in variations of the main characteristics of the components (elemental and chemical composition, heating values and energy density) promoting the enhanced formation of volatile compounds, their ignition and combustion, and suggests the enhanced thermal and chemical interaction between the components during the thermochemical conversion of selectively activated mixtures [12,13,14]. Furthermore, detailed research indicates that thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends is influenced by synergistic effects of interaction between the components [15,16,17]. In this paper, thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated binary blends composed of MW pre-treated and non-treated biomass pellets of different origins was studied using the originally-developed combustion device of technology readiness level TRL 5. The results of thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends were compared with the results of the comprehensive thermal analysis of ground blends containing the different proportions of non-treated and pre-treated biomass in oxidative media to evaluate the factors responsible for the synergistic effects developing during the thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Non-treated commercial softwood pellets with a diameter of 6.0 mm, wheat straw and peat pellets, both with a diameter of 8.0 mm and water contents of 7.0%, 10.2% and 8.9%, respectively, were used as an object of investigation.
2.2. MW Pre-Treatment of Biomass
Each batch of pellets with a weight of 300 g was pre-treated in the MW laboratory device of original construction (0.850 kW at 2.45 GHz) at a temperature of 200 °C and 275 °C correspondingly. The laboratory device was equipped with a magnetron, coaxial waveguide, Si glass rotating reactor (1300 cm3) placed in stainless steel tubular resonator (0.040 m3), condenser tool for the collection of liquid fraction and controller Pixsys ATR 142-ABC connected with K-type thermocouple IP-67 attached inside the reactor. For online monitoring of the pellet’s temperature, the thermocouple was connected with a USB thermometer (TEMPer14K USB industrial thermocouple). Two-step pretreatment includes dynamic dielectric heating up to a given temperature followed by 20 min of isothermal heating. Ten repeated experiments were conducted for each regime and biomass origin. The combined solid fractions of repeated tests were used for the preparation of binary blends used in thermal analysis and combustion tests. The construction of the device and regimes of processing were described in [12,18].
2.3. Elemental Analysis and Higher Heating Value (HHV)
Elemental analysis of non-treated and torrefied biomass was performed with Vario MACRO elemental analyzer (ELEMENTAR Analysensysteme). Average data of five repeated experiments were used for the calculation of HHV (MJ/kg) of each biomass sample [19]:
where, C, H, N is the carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen content in percent, of the dry matter (DM) of biomass.
HHV = (3.552 − 232C − 2230H + 51.2C × H + 131N + 20600)/1000
2.4. Ash Content
The ash content in non-treated and MW–pretreated biomass was determined as a residue after ignition at 550 ± 10 °C in accordance with LVS. EN 14775:2010 standard. For each biomass, a sample test was performed in triplicate.
2.5. Preparation of Binary Biomass Blends
Ten types of binary blends composed of 30% (on DM) of wheat straw or softwood pellets, pretreated at temperatures of 200 °C or 275 °C and moisture content in pellets 1–2%, respectively, and non-treated wheat straw (WS n.t.), softwood (SWn.t.) or peat pellets with a mass fraction of 70% on DM and moisture content in pellets 7.0%, 10.2% and 8.9%, respectively, were used to produce selectively pre-treated blends. The blends with a total mass of pre-treated and raw pellets of 1800 g were prepared by careful hand mixing of components without crushing them. Five samples of blends were prepared for each of the pre-treated conditions. To provide thermal analysis of pre-treated blends, the content of pre-treated components in binary blends was varied in the range of 0–100% (0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%) on DM. Before the mixing of components, they were ground using a knife-type mill Retch 100 with a sieve size of 0.5 mm. After weighing two components by analytical balances, each binary blend was additionally ground by a Mixer Ball Mill MM 200 for 10 min and was oven dried. The wheat straw and softwood biomass MW pre-treated at 200 °C and 275 °C were abbreviated as WS200 °C, WS275 °C and SW200 °C, SW275 °C, respectively.
2.6. Thermal Analysis
Non-isothermal TG/DTG/DSC analysis of non-treated and pre-treated at 275 °C biomass constituents of binary blends was performed separately in air and argon media (flow rate 50 cm3/min) in the temperature range of 25–650 °C and at a heating rate of 10 °C/min using Setaram Setline device. All binary blends were tested in air media at the same temperature regime. The sample weight in all experiments was 10 mg. Exemplified in non-treated softwood, DTG/DSC curves used for the analysis of biomass thermal degradation are presented in Figure 1. The peak values of thermal degradation of softwood at different degradation steps, including volatilization (1) and char thermal oxidation (2), were evaluated.
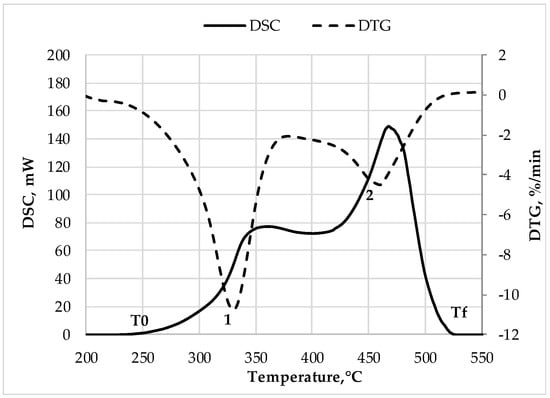
Figure 1.
DTG/DSC curves of non-isothermal thermal analysis of non-treated softwood in air atmosphere.
The released total heat amount during thermal degradation was calculated using DSC data (2):
where: Q-the total amount of heat energy, J;
T0-onset temperature of heat release, °C;
Tf-offset temperature of heat release, °C;
P-heat output, mW.
The released total heat amount was recalculated per unit weight of dry matter (DM) of the biomass sample. The Setline Software Calisto was used for the integration of heat output.
To estimate the synergetic effect of thermal conversion of biomass blends in terms of heat energy obtained the experimental data were compared with that calculated based on the additivity principle. In this case, the experimental data of single components and their portion in the blends were considered (3):
where:
qblend—released heat amount per unit weight of the blend, MJ/kg
q1—the value of experimentally determined heat amount released per unit weight of the first pre-treated component, MJ/kg;
q2—the value of experimentally determined heat amount released per unit weight of the second non-treated component, MJ/kg;
m1—weight of first pre-treated component in binary mix, g;
m2—weight of second non-treated component in binary mix, g.
Three repeated tests were performed for each of the binary blends. The mean values were applied and standard deviation was plotted on the graphs.
2.7. Combustion Tests of Binary Blends Containing MW Pre-Treated and Non-Treated Biomass Pellets Using 20 kW Device
Preliminary studies of the effects of MW pre-treatment of biomass pellets on thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends were provided using a batch-size pilot device by limiting produced heat power to 5 kW [15]. A recent study was provided using the originally developed experimental device with a heat output of up to 20 kW ensuring a highly efficient thermochemical conversion of biomass pellets and their selectively activated blends (92–94%) (Figure 2). The experimental device is designed for domestic heating when different origin biomass pellets as well as selectively MW pre-treated biomass blends can be used as fuels. The device consists of a combustion chamber (1), burner (4) and two heat exchanger units (2, 3). The device is equipped with special openings for the measurements of flue gas temperature, composition, and mass flow rate. Furthermore, the device is equipped with tools to provide calorimetric measurements of cooling water flow providing measurements of the cooling water mass flow rate and temperature at the inlet and outlet of each of the three sections. The bottom section of the device is water cooled combustor (1) using the pellets burner (4) to provide pellets feeding, air blow control, ignition, and combustion by using the algorithm of its in-built control system. At the bottom of the combustor, the ash collector (3) is mounted.
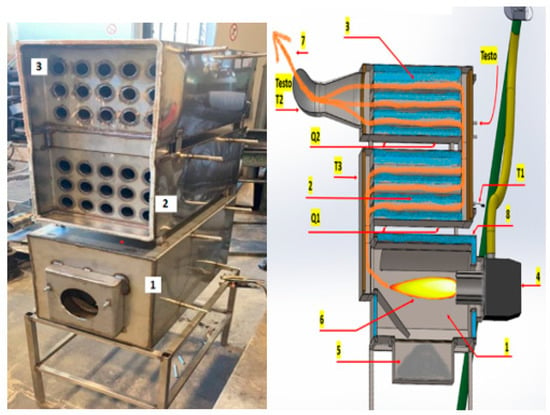
Figure 2.
A digital image (left) and schematic sketch (right) of experimental device: a, b: 1—combustion chamber block (furnace), 2, 3—heat exchangers; 4.—burner, 5.—ash collector, 6.—flame, 7.—flue gases pathway, 8.—water supply to combustion chamber, T1, T2, T3—flue gas temperature measurements, Q1, Q2—calorimetric measurements of the cooling water flow.
Pt/Pt/Rh thermocouples were used for local online measurements of the flue gas temperature at different stages of thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends with an accuracy of ±5% providing data online data registration being performed by a Pico logger.
Measurements to characterize the effect of selective MW pre-treatment of biomass blends on flue gas composition and combustion efficiency were performed at the outlet of the device. These consist of simultaneous measurements of the mass fraction of volatiles (CO, H2), the volume fraction of the main product (CO2), the mass fraction of NOx and the combustion efficiency using a gas sampling probe and a gas analyzer Testo 350 XL. In accordance with the apparatus specification, the CO2 volume fraction was measured with an accuracy of ±1%, and with an accuracy of about ±0.5% for the mass fraction of CO, H2 and NOx.
The calorimetric measurements of the cooling water flow were provided to estimate heat output from the device and produced heat energy per mass of burned blends. They involve the joint measurements of the cooling water mass flow, which was measured with an accuracy of ±2.5%, and the water flow temperature at the inlet and outlet of each section of the pilot device, which was measured with an accuracy of ±1%, using thermo sensors AD 590, providing online data registration by the Data Translation DT9805 data acquisition module and Quick DAQ program.
3. Results
3.1. Fuel and Combustion Characteristics of Non-Treated and MW Pre-Treated Biomass of Different Origination
The fuel characteristics of single biomass used for the preparation of binary blends are presented in Table 1. As was shown the MW-pre-treatment leads to the increase in fixed carbon content in both softwood and wheat straw biomass in comparison with non-treated biomass indicating that carbonization of the lignocarbohydrate complex takes place at low MW pre-treatment temperatures (200 °C).

Table 1.
The fuel characteristics on DM of non-treated and MW pre-treated biomass used as components of binary blends.
With an increase in pre-treatment temperature up to 275 °C, the content of fixed carbon in pre-treated softwood and wheat straw biomass was increased more significantly and exceeds the fixed carbon content of non-treated peat biomass. Such non-treated peat in major consists of plant biomass partly coalifield/carbonized as the results of long-term natural geological processes [20] (Table 1). Correspondingly, the calorific values of 275 °C pre-treated wheat straw and softwood were higher vs. that of non-treated peat. The previous results of non-isothermal thermal analysis of lignocellulosic biomass allow us to conclude that MW pre-treatment of wheat straw and softwood pellets also significantly influences activation energies related to the thermochemical conversion of volatiles and char, which influences the rate of gas-phase reactions and char conversion with changes in the main flame characteristics, produced heat energy and composition of the products [21]. The average values of activation energy for non-treated biomass varied in the range of 75–118 kJ/mol vs. 132–211 kJ/mol for MW pre-treated biomass in the temperature range of 200–300 °C. This indicates that a higher energy input is needed for thermal conversion of MW pre-treated biomass vs. that of non-treated. Nevertheless, the balance between output and input energy is more beneficial for MW pre-treated biomass. In comparison with MW pre-treated biomass, during thermal oxidative conversion due to the presence of non-combustible volatiles including H2O, CO2, acetic acid, etc., increases a part of the weight loss of non-treated biomass, which is produced during the initial stage of thermal degradation without increase in produced heat. According to differential thermal analysis (DTA) data of MW pre-treated biomass in the air, the onset temperature and weight losses at which the exothermic effect occurred were lower than that of non-treated biomass (Figure 3).
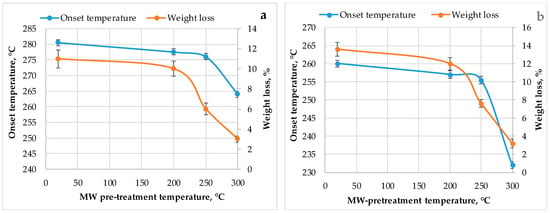
Figure 3.
The effect of MW pre-treatment temperature on the weight loss and onset temperatures values at which exothermic effect occurred for pretreated and non-treated (20 °C) biomass according to DTA analysis: (a) softwood; (b) wheat straw [21].
The results presented in Table 1 and in Figure 3 clearly indicate that both factors, increasing the calorific values of the formed volatiles and increasing the fixed carbon content, are responsible for higher heat output at combustion of MW pre-treated biomass. For softwood and wheat straw biomass MW pre-treated at 300 °C the heat released in the results of volatiles and char combustion during their thermal conversion exceeded that of non-treated biomass by 1.43–1.45 and 1.63–1.83 times correspondingly [21]. The results of the thermal analysis were confirmed by combustion experiments performed by the authors in a number of works [13,22,23]. It has been shown that MW pre-treatment of softwood and wheat straw pellets has a positive effect on the combustion process of pre-treated biomass creating the increased reactivity of pre-treated pellets, which causes faster and more complete combustion of volatiles. As a result, the CO content in products decreases as does the air excess, while combustion efficiency and the yield of heat obtained per unit weight of fuel increases in comparison with non-treated biomass pellets. This effect was explained by different factors: the thermal transformation of the chemical structure of the lignocellulose matrix due to the carbonization processes and the increasing porosity of pre-treated biomass. Based on the results presented above, in this work, the approach of co-combustion of MW pre-treated and non-treated biomass in the form of pellet blends was developed. The hypothesis proposed was as follows: the co-combustion of MW-pre-treated biomass with higher calorific values and non-treated biomass with comparatively low calorific values will result in more beneficial temperature conditions of thermal oxidation of raw biomass due to faster and higher heat output during the primary stage of thermochemical conversion of the blends and higher temperature in the combustion zone. Therefore, more complete combustion of non-treated biomass will be achieved in comparison with the process of non-treated biomass combustion. Correspondingly, the higher heat output in comparison with the results of additive principle-based calculations could be achieved. As was shown, the wheat straw and softwood biomass MW pre-treated at 275 °C has significantly higher calorific values vs. that of non-treated biomass including peat, suggesting a more significant synergistic effect in comparison to that of blends containing non-treated and 200 °C MW pre-treated biomass.
3.2. Thermochemical Conversion of Selectively MW Pre-Treated Biomass Blends of Different Origin in Pilot Scale Combustion Device
The results of the experimental study of the effects of MW pre-treatment on the thermochemical conversion of selectively MW pre-treated blends using a batch-size experimental device with limited heat power (5 kW) [15] suggest that MW pre-treatment of biomass pellets (wheat straw and wood) enhances the thermochemical conversion of pre-treated pellets, which depends on the temperature of MW pre-treatment and the mass fraction of pre-treated pellets in the blend. It was shown that MW pre-treatment of softwood and wheat straw pellets has a positive effect on the combustion process of pre-treated biomass creating the increased reactivity of pre-treated pellets which causes faster and more complete combustion of volatiles, decreasing CO content in products, the air excess in products, while increasing combustion efficiency and the yield of heat obtained per unit weight of fuel in comparison with parent biomass pellets. This effect was explained by both factors: the thermal transformation of the chemical structure of the lignocellulosic matrix due to the carbonization processes and structural changes of pre-treated pellets, increasing the porosity of pre-treated biomass [13]. Providing the measurements of the weight loss rates of the blends during thermal decomposition of MW pre-treated blends indicate the presence of synergistic effects of interaction between pre-treated and raw pellets [16,17,24], confirming that increased reactivity and volatilization of pre-treated pellets enhance thermal decomposition of raw pellets by varying the yields of combustible volatiles, their ignition, combustion, heat energy production and composition of emissions thus confirming the hypothesis described in 3.1 chapter.
In the present paper, the effects of biomass pellets MW pre-treatment on thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated biomass blends were studied using an upscaled pilot device designed for domestic heating with heat power up to 20 kW (Figure 2). The test experiments of the device were provided for heat power of pilot device 14 kW using binary component blends of fixed mass fractions (30%) of wheat straw and wood pellets previously selectively MW pre-treated at 200 °C and 275 °C with 70% mass fraction of non-treated (raw) wheat straw, softwood, and peat pellets in the blends.
The experimental studies include the time-dependent measurements of the flue gas temperature at the outlet of the furnace, heat power of the device and composition of products during thermochemical conversion of pre-treated blends with estimation of the influence of selective MW pre-treatment on the average values of the main characteristics of the device. A kinetic study of temperature at the outlet of the device suggests that the configuration of the device stabilizes kinetics of thermochemical conversion of biomass blends by minimizing the influence of selective pre-treatment of additives on the rise of flue gas temperature and heat power during the primary stage of thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends. A more pronounced effect of MW pre-treatment on the thermochemical conversion of blends is observed by evaluating the changes in the average heat outlet from the furnace, temperature at the outlet of the device and produced heat energy per mass of selectively pre-treated blends (Figure 4a–c). It was found that for the fixed mass fraction of pre-treated pellets in the blends (30%) increasing MW pre-treatment temperature of additives up to 275 °C results in changes in the heat output from the device, the temperature at the outlet of the furnace and composition of products (Figure 4a–c).
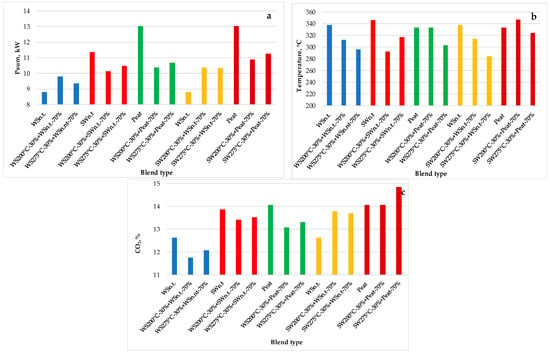
Figure 4.
Tests of the influence of composition and temperature of MW pre-treated wheat straw and softwood binary blends with raw biomass pellets on the heat power of the device (a), temperature at the outlet of the furnace (b) and the volume fraction of CO2 in the products (c). Binary blends consisting of non-treated and pre-treated wheat straw, non-treated softwood and pre-treated wheat straw, non-treated peat and pre-treated wheat straw, non-treated wheat straw and pre-treated softwood, non-treated peat and pre-treated softwood are in blue, rich red, green, yellow, red-brown colors correspondingly.
These complex changes in the temperature, the heat output from the furnace and produced heat energy during thermochemical conversion of selectively MW pre-treated biomass blends can be related to MW-induced changes in the main characteristics of pre-treated pellets. In accordance with data presented in [21], microwave pre-treatment of wheat straw and wood pellets promote structural changes of pellets with changes in their elemental composition and heating values of pre-treated pellets, increasing reactivity and higher heating value (HHV) of pre-treated pellets and by varying produced heat energy per mass of burned biomass blends (Figure 5a,b).
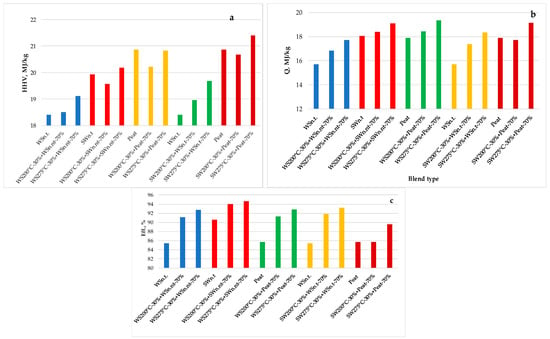
Figure 5.
Influence of temperature values at MW pre-treatment of wheat straw and softwood pellets presented in binary blends on their heating values (a) the yield of heat energy at furnace combustion (b) and process efficiency (c). Binary blends consisting of non-treated and pre-treated wheat straw, non-treated softwood and pre-treated wheat straw, non-treated peat and pre-treated wheat straw, non-treated wheat straw and pre-treated softwood, non-treated peat and pre-treated softwood are in blue, rich red, green, yellow, red-brown colors correspondingly.
HHV is an important characteristic of any fuel which indicates the upper limit of the available thermal energy produced by the complete combustion of fuel including the heat released in the results of water steam condensation [25]. Incomplete combustion of fuels is one of the major reasons for decreased efficiency of real combustion processes, heat energy losses and environmental pollution. Therefore, it can be assumed that at the equal extent of the biomass thermal oxidative conversion and equal heat exchanging conditions the amount of heat obtained by its combustion in the boiler will directly correlate with HHV of fuels resulting in similar changes in process efficiency, which is defined as the ratio of heat produced per unit weight of fuel to its calorific value. The experiments have shown that the addition of MW-pretreated biomass in amounts of 30% has increased the efficiency of the combustion process up to 91–95% vs. 85–86% for non-treated biomass (Figure 5c). Moreover, the highest values of efficiency were calculated for blends containing biomass MW pre-treated at higher temperatures. This indicates that the co-combustion of MW pre-treated biomass with raw biomass pellets leads to more effective combustion of non-treated biomass in comparison with its alone combustion in terms of released heat amount as well as the composition of emission products which is more environmentally friendly. It is also an important result from an economical point of view because higher efficiency of raw pellets combustion is achieved without any additional energy and labor-expensive pre-treatment of them. The presented results confirm the preliminary research on the effects of MW pre-treatment on thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated biomass blends using the batch-size device suggesting [15] that the main characteristics of the blends are influenced by the synergistic interaction between pre-treated and raw pellets in the blend. As a result of synergistic effects increasing the mass fraction of pre-treated pellets in the blend shows deviation from linearity of the main flame characteristics and produced heat energy, which depends on the temperature of MW pre-treatment and blend composition. Similar deviation from linear dependence is observed also providing test experiments using 20 kW (TRL-5) combustion device for the fixed mass fraction of pre-treated pellets (30%) in the blend (Figure 6a–e).
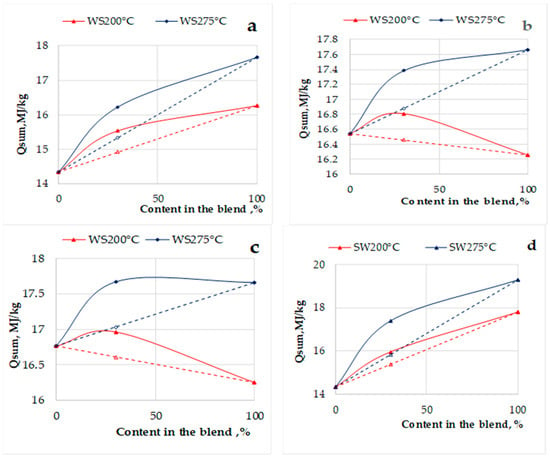
Figure 6.
The heat output from the pilot device (TRL 5) in the result of combustion of binary blends containing 30% of biomass pellets previously pretreated at 200 and 275 °C and 70% of non-treated pellets: MW pre-treated WS +WS n.t. (a); MW pre-treated WS +SW n.t. (b), MW pre-treated WS +Peat (c); MW pre-treated SW+WS n.t.(d). The linear dependence is marked by dashed lines.
As follows from Figure 6a–d, the most pronounced synergistic interaction between MW pre-treated and raw pellets can be observed at pre-treatment temperature (T = 275 °C) of selectively pre-treated blends. For the blend of pre-treated wood with non-treated straw pellets (30%), the synergistic effect of produced heat energy reaches 9.8%, while for the blend of pre-treated and raw wheat straw pellets-5.8%.
3.3. The Non-Isothermal Thermal Oxidative Analysis of Binary Blends Containing MW Pre-Treated and Non-Treated Biomass
In addition to studying the effects of selective MW pre-treatment of biomass pellets on combustion characteristics, produced heat energy and combustion efficiency, the effects of selective MW pre-treatment of carefully ground components on thermochemical conversion of the blends were studied using analytical methods of thermal analysis including thermal gravimetric (TG/DTG) analysis and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).
From the results of thermal analysis of selectively pre-treated biomass blends, it follows that in all cases the blends of MW pre-treated and non-treated biomass are characterized by combustion profiles DTG) and heat output profiles (DSC) (Figure 7 and Figure 8) with strong differences from those of separate constituents. Additives of pre-treated WS in the blends with non-treated biomass led to an increase in starting degradation temperature (Figure 7b) of blends in comparison with non-treated WS. Besides that, the peak area attributed to volatilization of biomass in the range of 200–350 °C is decreased increasing the portion of biomass degraded in the results of heterogenic char oxidation performed in the range of 350–550 °C. Additionally, the temperature at which the active heat output occurred was lower and the higher calorific values of volatiles were obtained at the initial degradation step of pre-treated biomass (Figure 7a). The strong decrease in both start degradation and onset temperatures promoting an increase in heat flow (heat output) decreases the total duration of thermal conversion of selectively pre-treated wheat straw blends in comparison with that of non-treated softwood biomass (Figure 7c,d). Moreover, the significantly lower temperature at which starts active heat release was observed for WS 275 °C-peat blends vs. non-treated peat (Figure 7e). The addition of pre-treated wheat straw strongly increases both volatile degradation and char oxidation rates decreasing the total time of thermal conversion of peat-containing blends (Figure 7f).
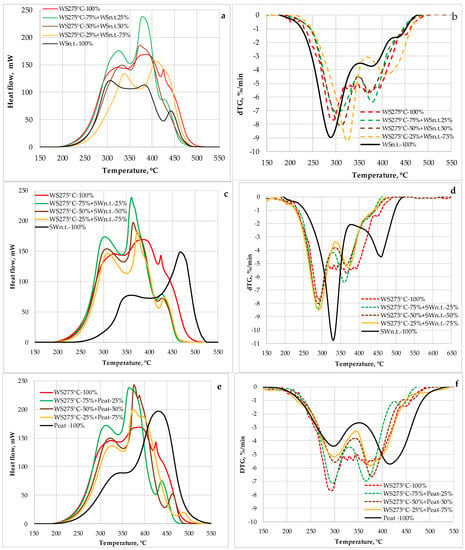
Figure 7.
The DSC (a,c,e) and DTG (b,d,f) curves of binary blends containing MW pre-treated wheat straw and non-treated biomass of different origination.
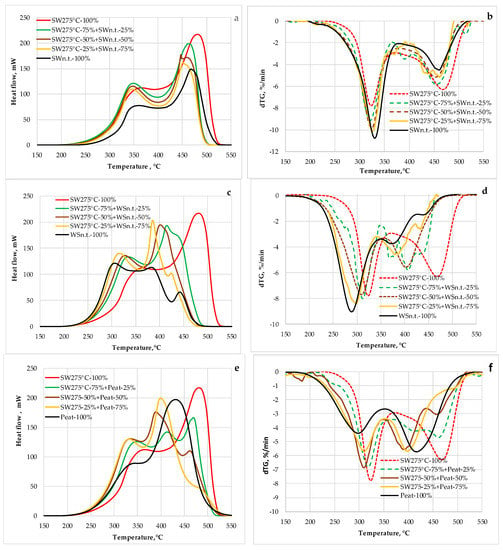
Figure 8.
The DSC (a,c,e) and DTG (b,d,f) curves of binary blends containing MW pre-treated softwood and non-treated biomass of different origination.
The blending of MW pre-treated softwood with that of non-treated leads to the insignificant shifting of starting degradation temperature of blends into the higher temperature zone vs. pure non-treated softwood (Figure 8b), which can be explained by the increase in activation energy of thermal degradation of MW pre-treated softwood biomass [21]. In contrast, the starting temperature of active heat release for blends is lower indicating the higher calorific values of volatiles formed from MW-activated biomass (Figure 8a). A more complicated effect of MW pre-treated softwood biomass on the thermal conversion of its blends with non-treated wheat straw and peat was observed. Again, additives of pre-treated softwood biomass significantly increase the temperature of starting the degradation of both biomass blends (Figure 8e,f). However, in this case, the temperature at which the active heat flow starts was higher for pre-treated biomass. This can be explained by the significantly lower activation energy of thermal conversion of both peat and wheat straw biomass in comparison with MW pre-treated softwood. According to [21], the activation energy of volatilization of wheat straw and peat consisted of 38 kJ/mol and 109 kJ/mol correspondingly in comparison with 168 kJ/mol and 208 kJ/mol for softwood MW pre-treated at 250 °C and 300 °C, respectively. As a result, the wheat straw and peat-derived volatiles with quite higher calorific values were obtained at comparatively low temperatures of thermal degradation. The results obtained substantially confirmed the results of real combustion tests including faster ignition and higher combustion rates of MW pre-treated biomass and their blends with raw biomass pellets vs. that of non-treated biomass [11,15,23]
To estimate the synergetic effect at the thermal conversion of blends containing MW pre-treated and non-treated biomass in terms of heat release, the total amounts of heat output, determined experimentally by DSC were compared with the data calculated considering the additivity principle described in chapter 2.5 (Figure 9).
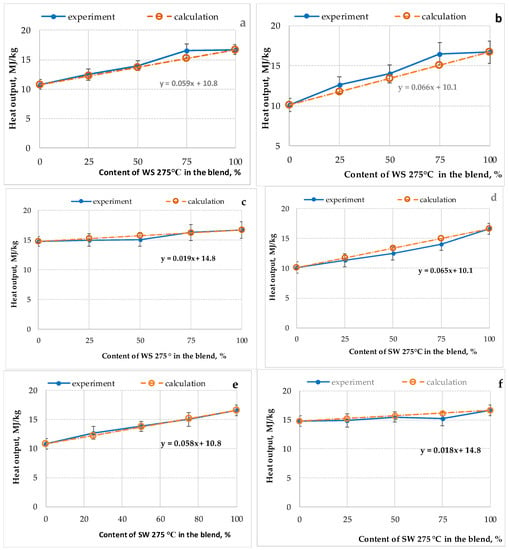
Figure 9.
The experimental and calculated values of heat output of biomass blends of different origination and composition according to DSC tests: WS 275 °C-WS n.t. (a); WS 275 °C-SW n.t. (b); WS 275 °C-Peat (c); SW 275 °C-SW n.t. (d); SW 275 °C-WS n.t. (e); SW 275 °C-Peat (f).
In all cases, the heat output can be expressed with a linear dependence on the mass fraction of MW pre-treated biomass in the blend (Figure 9). The lowest slopes were observed for blends containing peat biomass as one of the components because of its higher HHV (20.9 MJ/kg) in comparison with non-treated WS (18.4 MJ/kg) and SW (19.9 MJ/kg) (Table 1). Considering standard deviation values, it can be concluded that experimentally determined values of heat output meet the requirements of linear regression based on the additivity principle. Therefore, in the difference in the thermal decomposition of selectively pre-treated biomass pellets, synergistic effects in terms of heat release at the thermal conversion of selectively pre-treated and grounded biomass blends using the DSC method were not detected. Obviously, this can be explained by the fact that in the difference between combustion experiments, thermal conversion of carefully ground biomass in this study was not influenced by the morphological structure of pellets. In previous research, it was shown that, as the result of removing low calorific oxygen enriched volatiles, the MW pre-treatment of biomass leads to an increase not only in the carbon content in pre-treated biomass pellets but also in an increase in their porosity and specific surface area (Table 2).

Table 2.
Characteristics of porous structure of MW pre-treated and non-treated biomass determined Brunauer--Emmett--Teller (BET) method [13].
From the results presented above, it can be concluded that an increase in porosity and surface area of pre-treated biomass pellets promotes the chemical interaction of pre-treated biomass with oxygen during thermal conversion allowing more effective utilization of the fuel potential of MW pre-treated biomass and more complete combustion of non-treated biomass portion in the co-combustion regime.
4. Summary
From the test results on a TRL-5 device of the effects of selective MW pre-treatment of different origin biomass pellets on thermochemical conversion of biomass blends, the following conclusion can be made:
The MW-induced structural variations of pellets and changes in the main characteristics of pre-treated pellets promote changes in the thermochemical conversion of selectively pre-treated blends. These changes consist of a variation in the temperature of flue gases, heat power of the device and composition of the products. This indicates the presence of synergistic interaction between the components with a local increase in produced heat energy per mass of burned blends. The results of test experiments confirm the applicability of MW pre-treatment for control of the main flame characteristic.
The results of thermal analysis (TG/DTG/DSC) of the blends containing different proportions of MW pre-treated and non-treated biomass indicate faster thermal decomposition of selectively pre-treated blends by minimizing the synergistic effect on total heat output. It was proposed that this can be explained by the destruction of the morphological structure of MW pre-treated pellets during their grounding which was provided to perform the thermal analysis of selectively pre-treated blends. Therefore, it can be concluded that improvements in fuel characteristics of MW pre-treated biomass with a simultaneous increase in its porosity are important for the application of MW pre-treatment for a more effective valorization of plant biomass pellets as a solid biofuel in the single and co-combustion regimes.
In the framework of further development of advanced technology of co-combustion of MW pre-treated and raw biomass pellets, the investigation of continuous pellets supply into the boiler instead of the batch process is planned. For this purpose, the upscaling of the MW reactor up to 6 kW capacity is elaborated. The design of this device is patented.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and M.Z.; Data curation, M.P. and. A.A.; Formal analysis M.P. and A.A.; Funding acquisition, M.Z.; Investigation, L.J., M.P. and R.V.; Methodology, R.V., M.Z. and A.A.; Project administration, M.Z.; Resources, R.V. and M.Z.; Supervision, A.A. and M.Z.; Visualization, A.A. and L.J.; Writing—original draft, A.A.; Writing—review & editing, A.A., M.Z., M.P. and R.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Regional Development Fund and Grant Nr. 1.1.1.1/19/A/010.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McKendry, P. Energy Production from Biomass (Part 1): Overview of Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Potential Applications of Renewable Energy Sources, Biomass Combustion Problems in Boiler Power Systems and Combustion Related Environmental Issues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2005, 31, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glithero, N.J.; Wilson, P.; Ramsden, S.J. Straw Use and Availability for Second Generation Biofuels in England. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 55, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Bioenergy Networks. Biomass Co-Firing-An Efficient Way to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2; European Bioenergy Networks: Madrid, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Obernberger, I. Co-Firing Biomass with Fossil Fuels Firing Biomass with Fossil Fuels--Technological and Economic Evaluation Based on Austrian Experiences; Bios Bioenergiesysteme GmbH: Graz, Austria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hupa, M. Interaction of Fuels in Co-Firing in FBC. Fuel 2005, 84, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Frandsen, F.J.; Dam-Johansen, K. Solid Fuel Interactions in Co-Combustion: A Literature Survey; CHEC Research Centre: Lyngby, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nordgren, D.; Hedman, H.; Padban, N.; Boström, D.; Öhman, M. Ash Transformations in Pulverised Fuel Co-Combustion of Straw and Woody Biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 105, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S.; Omar, R.; Kamal, S.M.M.; Biak, D.R.A. Microwave-Assisted Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Review. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ingole, P.M.; Ranveer, A.C.; Deshmukh, S.M.; Deshmukh, S.K. MICROWAVE ASSISTED PYROLYSIS OF BIOMASS: A REVIEW. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Sci. 2016, 4, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Barmina, I.; Līckrastiņa, A.; Valdmanis, J.; Valdmanis, R.; Zaķe, M.; Arshanitsa, A.; Telysheva, G.; Solodovnik, V. Effect of Microwave Pre-Processing of Pelletized Biomass on Its Gasification and Combustion/Mikroviļnu Priekšapstrādes Ietekme Uz Granulētas Biomasas Gazifikācijas Un Degšanas Procesiem. Latv. J. Phys. Tech. Sci. 2013, 50, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshanitsa, A.; Akishin, Y.; Zile, E.; Dizhbite, T.; Solodovnik, V.; Telysheva, G. Microwave Treatment Combined with Conventional Heating of Plant Biomass Pellets in a Rotated Reactor as a High Rate Process for Solid Biofuel Manufacture. Renew Energy 2016, 91, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersone, A.; Arshanitsa, A.; Akishin, Y.; Semenischev, A.; Telysheva, G. Microwave Assisted Torrefaction of Plant Biomass of Different Origin with a Focus on Solid Products Valorisation for Energy and Beyond. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmina, I.; Goldsteins, L.; Valdmanis, R.; Zake, M. Improvement of Biomass Gasification/Combustion Characteristics by Microwave Pretreatment of Biomass Pellets. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2021, 44, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldšteins, L.; Dzenis, M.G.; Šints, V.; Valdmanis, R.; Zaķe, M.; Arshanitsa, A. Microwave Pre-Treatment and Blending of Biomass Pellets for Sustainable Use of Local Energy Resources in Energy Production. Energies 2022, 15, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ceylan, S.; Goldfarb, J.L. Synergism among Biomass Building Blocks? Evolved Gas and Kinetics Analysis of Starch and Cellulose Co-Pyrolysis. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 618, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Meng, H. Synergistic Effect on Thermal Behavior during Co-Pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass Model Components Blend with Bituminous Coal. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauberts, M.; Lauberte, L.; Arshanitsa, A.; Dizhbite, T.; Dobele, G.; Bikovens, O.; Telysheva, G. Structural Transformations of Wood and Cereal Biomass Components Induced by Microwave Assisted Torrefaction with Emphasis on Extractable Value Chemicals Obtaining. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 134, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, A.; Padouvas, E.; Rotter, H.; Varmuza, K. Prediction of Heating Values of Biomass Fuel from Elemental Composition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 544, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.; Sposito, G. Molecular Structure in Soil Humic Substances: The New View. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9009–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshanitsa, A.; Andersone, A.; Telysheva, G. Non-Isothermal Thermal Analysis of Different Originated Lignocellulosic Biomass, Non-Treated and Torrefied by Microwave Treatment. In Proceedings of the Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 26–28 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arshanitsa, A.; Jashina, L.; Pals, M.; Ponomarenko, J.; Akishin, Y.; Zake, M. Characteristics of the Main- and Side-Stream Products of Microwave Assisted Torrefaction of Lignocellulosic Biomass of Differents Origination. Energies 2022, 15, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldšteins, L.; Valdmanis, R.; Zaķe, M.; Arshanitsa, A.; Andersone, A. Thermal Decomposition and Combustion of Microwave Pre-Treated Biomass Pellets. Processes 2021, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Antunes, E.; Sanchez, P.B.; Duan, H.; Zhao, M. Influence of Microalgae on Synergism during Co-Pyrolysis with Organic Waste Biomass: A Thermogravimetric and Kinetic Analysis. Renew Energy 2021, 167, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A.; Demirbaş, A.H. Estimating the Calorific Values of Lignocellulosic Fuels. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2004, 22, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).