Factors Contributing to Haze Pollution: Evidence from Macao, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Macao’s Social and Economic Development
2. Method
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Stationarity of Time-Series
- Test for a unit root:where ∆ is the delta operator defined by and β is (ρ − 1).
- Test for a unit root with a drift:where is the drift.
- Test for a unit root with a drift and a deterministic time trend:where is coefficient of the time trend.
2.3. Association between Variables
2.4. Regression Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
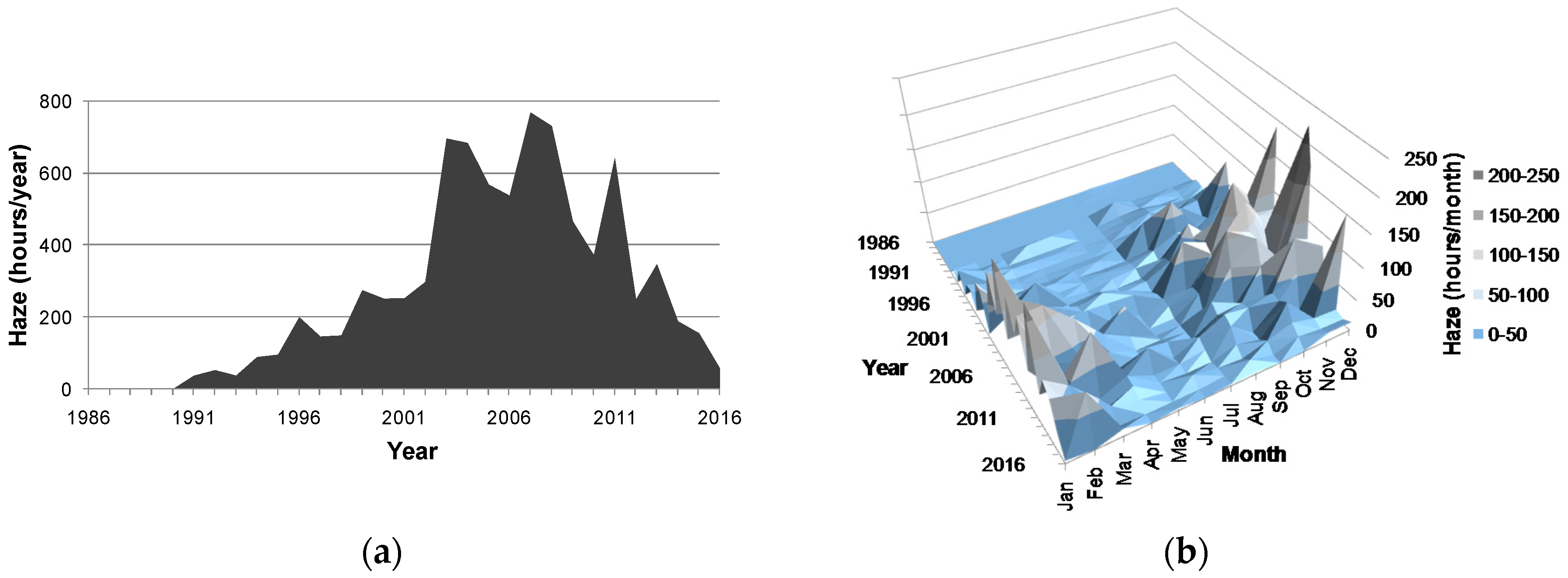
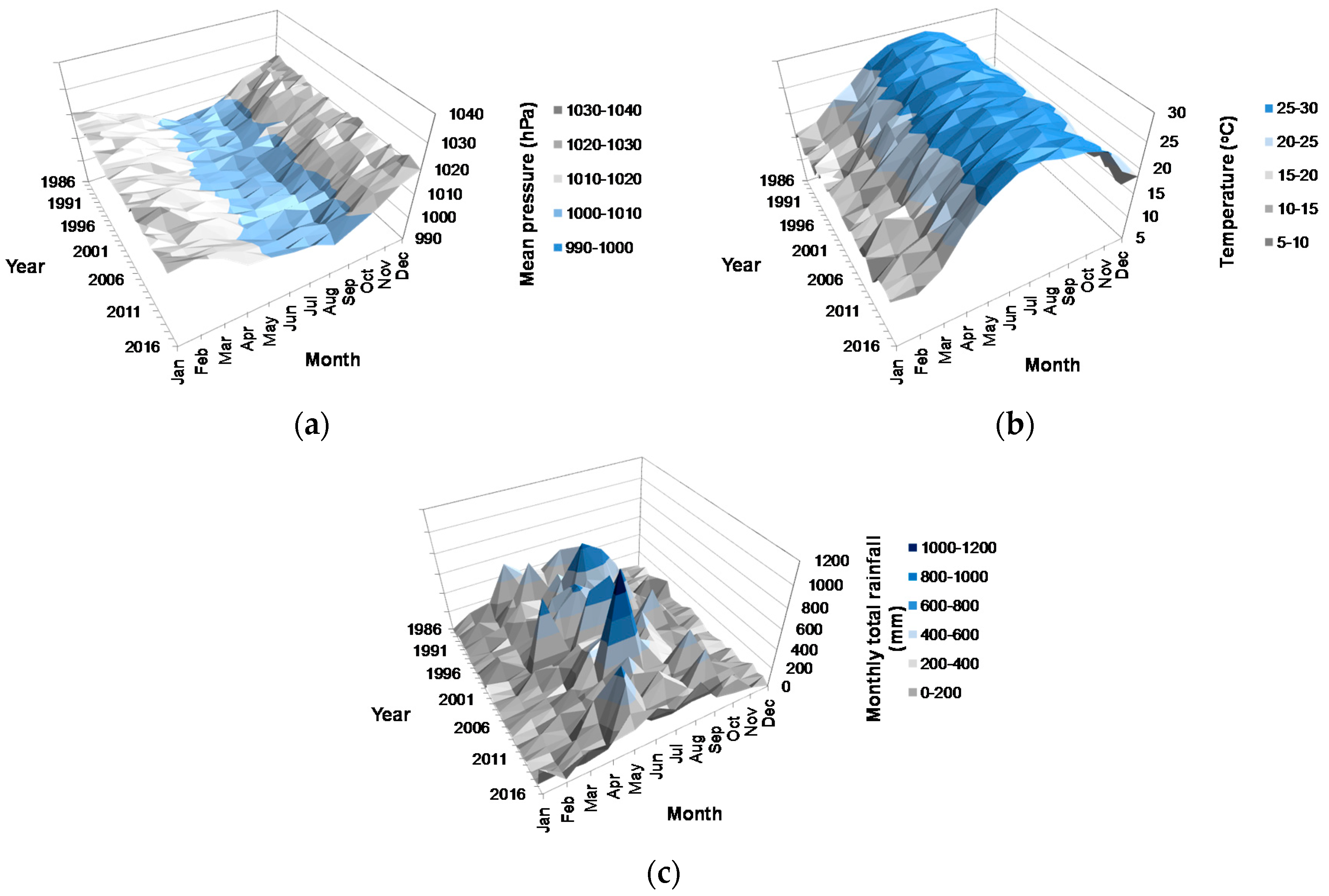
3.1. Haze and Meteorological Conditions
3.2. Energy Use in Macao
3.3. Stationarity of the Annual Haze Time-Series Data and the Annaul Energy Consumption Data
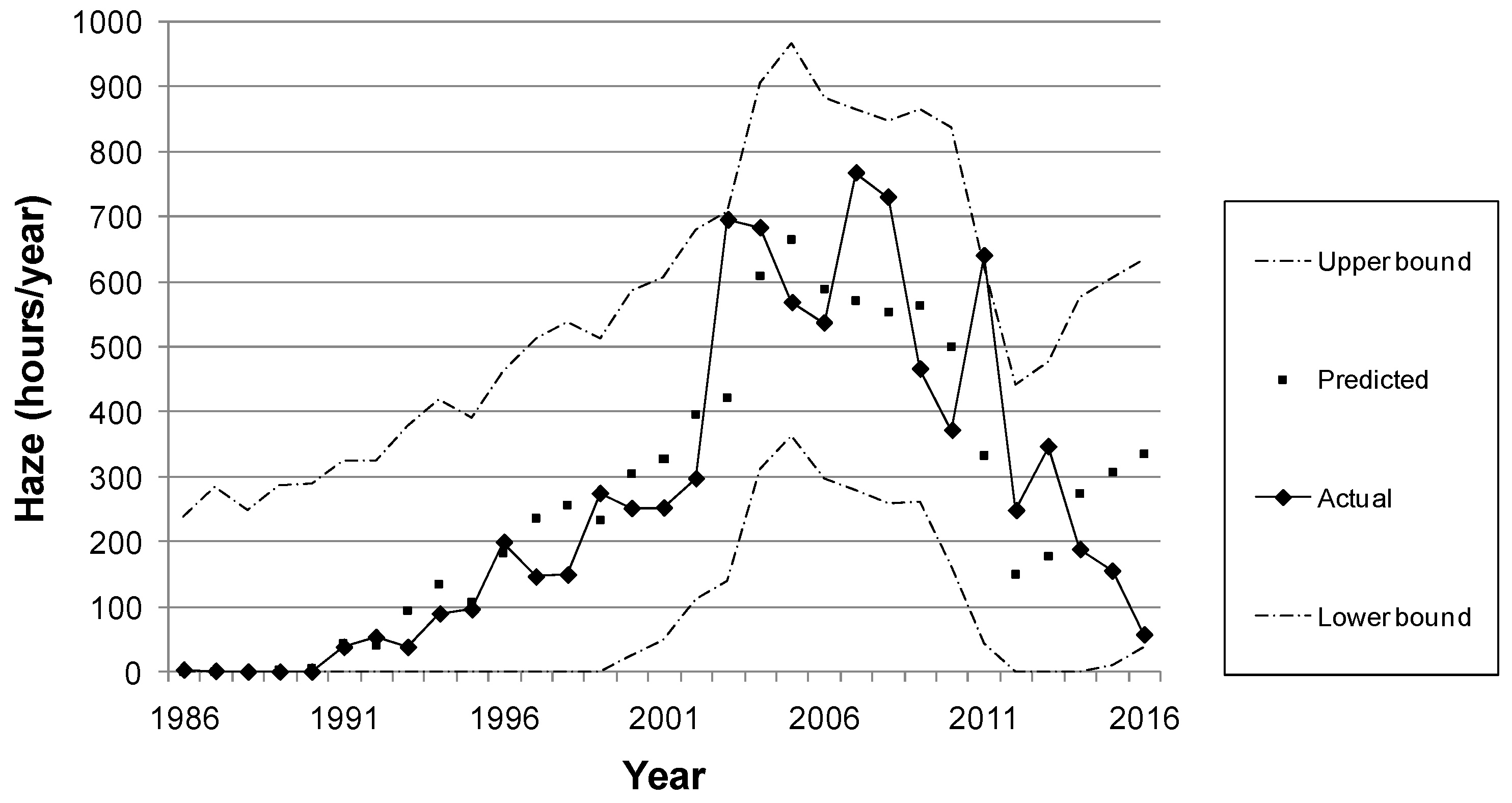
3.4. Correlation and Multiple Regression Analysis
3.5. Associations between Haze and Meteorological Variables on a Monthly Basis
3.6. Association between Haze in Macao and Haze Days in Guangzhou
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fajardo, O.A.; Jiang, J.; Hao, J. Assessing young people’s preferences in urban visibility in Beijing. Aerosol Air Q. Res. 2013, 13, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Xia, W.; Chen, J. Air pollution and chronic cough in China. CHEST J. 2013, 144, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, G.; Zhong, N.; Kan, H. Impact of haze and air pollution-related hazards on hospital admissions in Guangzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4236–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Cheng, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, X. A system dynamics analysis of investment, technology and policy that affect natural gas exploration and exploitation in China. Energies 2017, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thach, T.Q.; Wong, C.M.; Chan, K.P.; Chau, Y.K.; Chung, Y.N.; Ou, C.Q.; Yang, L.; Hedley, A.J. Daily visibility and mortality: Assessment of health benefits from improved visibility in Hong Kong. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, B.L.; Bell, P.A.; Loomis, R.J. Visibility and natural quiet in national parks and wilderness areas: Psychological considerations. Environ. Behav. 2004, 36, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, J.; Sahani, M.; Mahmud, M.; Ahmad, M.K.S. Transboundary smoke haze pollution in Malaysia: Inpatient health impacts and economic valuation. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, C.; Hong, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. Using hourly measurements to explore the role of secondary inorganic aerosol in PM2.5 during haze and fog in Hangzhou, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L. Haze in China: Current and future challenges. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.G.; Shao, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Qian, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Li, F. Fractionation of airborne particulate-bound elements in haze-fog episode and associated health risks in a megacity of southeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Tan, J.; Duan, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, F.; He, K.; Hao, J. Characteristics of atmospheric non-methane hydrocarbons during haze episode in Beijing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7235–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloway, B.J.; Ayres, D.C. Chemical Principles of Environmental Pollution; Blackie Academic & Professional: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Haus, N.; Zimmermann, S.; Wiegand, J.; Sures, B. Occurrence of platinum and additional traffic related heavy metals in sediments and biota. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyslop, N.P. Impaired visibility: The air pollution people see. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.C.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, C.S.; Pan, F.; Lu, Y.; Sharma, V.K. Impact of 2013 south Asian haze crisis: Study of physical and psychological symptoms and perceived dangerousness of pollution level. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The American Meteorological Organization. Haze. The American Meteorological Organization, 2017. Available online: http://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Haze (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- To, W.M.; Lai, T.M.; Chung, W.L. Fuel life cycle emissions for electricity consumption in the world’s gaming center—Macao SAR, China. Energy 2011, 36, 5162–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macao Statistics and Census Service. The Yearbook of Statistics (From 1986 to 2016); Macao Statistics and Census Service: Macao, China, 2016.
- Macao Statistics and Census Service. Energy Statistics (From 2000 to 2016); Macao Statistics and Census Service: Macao, China, 2017.
- Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau. The Meteorological Instruments Used by the Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau; Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau: Macao, China, 2017.
- Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau. The Yearbook of Meteorological Observations (From 1986 to 2016); Macao Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau: Macao, China, 2017.
- Guangzhou Meteorological Bureau. Guangzhou Climate Bulletin (From 1986 to 2016, in Chinese); Guangzhou Meteorological Bureau: Guangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Likelihood ratio statistics for autoregressive time series with a unit root. Econometrica 1981, 49, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W.M. Association between energy use and poor visibility in Hong Kong SAR, China. Energy 2014, 68, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, B.; Tesche, M.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, A.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Fan, Q.; Li, M.; Ta, N.; et al. Meteorological conditions and structures of atmospheric boundary layer in October 2004 over Pearl River Delta area. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6174–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, J. Revisiting CO2 mitigation potential and coasts in China’s electricity sector. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4209–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, G.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Czechowski, P.O.; Badyda, A.; Brandyk, A. The impact of selected parameters on visibility: First results from a long-term campaign in Warsaw, Poland. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1154–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, R.K.; Lee, B.K.; Karki, R.; Gurung, A.; Kandasamy, J.; Pathak, B.K.; Sharma, S.; Giri, N. Seasonal PM 10 dynamics in Kathmandu Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8623–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, R.K.; Lee, B.K.; Karki, R.; Gurung, A.; Baral, B.; Byeon, S.H. Dynamics of PM2.5 concentrations in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, S. Pollution Clouds Hong Kong’s Future. BBC News. 2007. Available online: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/6768977.stm (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- Carslaw, D.C.; Beevers, S.D.; Ropkins, K.; Bell, M.C. Detecting and quantifying aircraft and other on-airport contributions to ambient nitrogen oxides in the vicinity of a large international airport. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5424–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
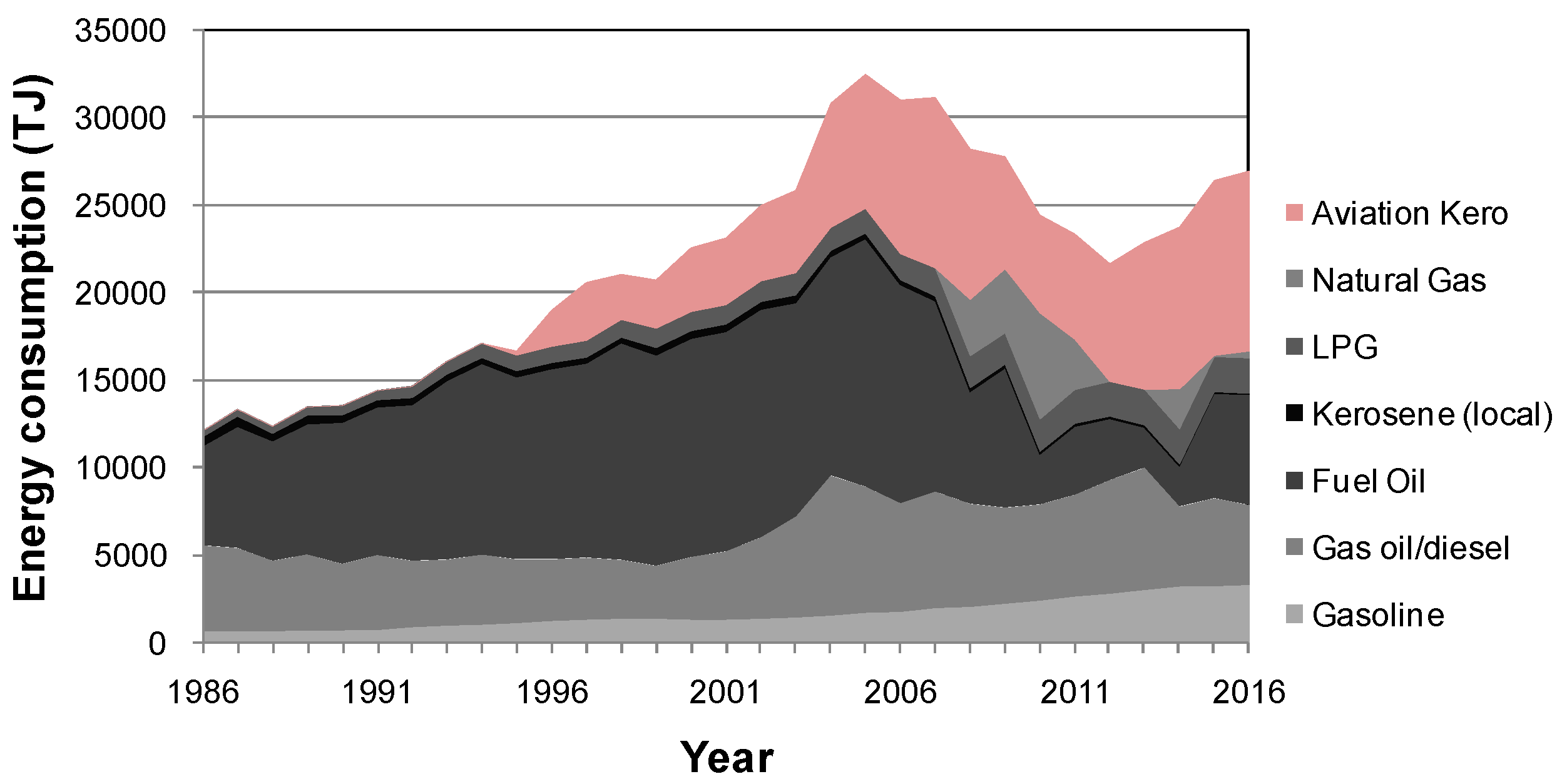

| Year | Primary Energy in TJ | ||||||
| Motor Gasoline | Gas oil & Diesel | Fueloil | Kerosene | Liquefied Petroleum Gas | Natural Gas | Aviation Kerosene 1 | |
| 1986 | 666 | 4878 | 5660 | 533 | 358 | 0 | 0 |
| 1991 | 748 | 4240 | 8438 | 417 | 561 | 0 | 0 |
| 1996 | 1263 | 3498 | 10,842 | 363 | 952 | 0 | 2057 |
| 2001 | 1340 | 3869 | 12,509 | 447 | 1117 | 0 | 3803 |
| 2006 | 1777 | 6195 | 12,427 | 295 | 1488 | 0 | 8769 |
| 2011 | 2659 | 5787 | 3864 | 190 | 1954 | 2873 | 6003 |
| 2016 | 3329 | 4526 | 6270 | 95 | 2032 | 393 | 10,258 |
| Year | Secondary Energy (i.e., Electricity in GWh) | ||||||
| Net Imported Electricity 2 | Net Electricity Produced Locally 3 | Electricity Consumed | |||||
| 1986 | 42 | 489 | 531 | ||||
| 1991 | 95 | 756 | 860 | ||||
| 1996 | 222 | 1126 | 1348 | ||||
| 2001 | 249 | 1353 | 1602 | ||||
| 2006 | 946 | 1459 | 2424 | ||||
| 2011 | 3165 | 691 | 3856 | ||||
| 2016 | 4306 | 988 | 5294 | ||||
| Critical/Tau Values | Annual Haze Time-Series | Annual Total Primary Energy Consumption Time-Series | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant, No Trend | Constant, with Trend | Constant, No Trend | Constant, with Trend | |||
| Calculated tau value | −1.693 | −1.256 | −1.351 | −1.081 | ||
| Critical value [24]: | For a sample size of 25 | Significant at 0.01 level | −3.75 | −4.38 | −3.75 | −4.38 |
| Significant at 0.05 level | −3.00 | −3.60 | −3.00 | −3.60 | ||
| For a sample size of 50 | Significant at 0.01 level | −3.58 | −4.15 | −3.58 | −4.15 | |
| Significant at 0.05 level | −2.93 | −3.50 | −2.93 | −3.50 | ||
| Null hypothesis-stationary | rejected | rejected | rejected | rejected | ||
| Energy Use (in TJ) | |||||||
| Motor Gasoline | Gas Oil/Diesel | Fuel Oil | Kerosene | Liquefied Petroleum Gas | Natural Gas | Aviation Gasoline | |
| Haze | 0.38 * | 0.73 ** | 0.17 | −0.33 | 0.59 ** | 0.34 | 0.66 ** |
| Annual Meteorological Conditions | |||||||
| Annual Mean Atmospheric Pressure | Annual Mean Air Temperature | Annual Total Rainfall | |||||
| Haze | −0.10 | −0.35 | 0.08 | ||||
| Year | Correlation between Haze and Monthly Mean Atmospheric Pressure | Correlation between Haze and Monthly Mean Air Temperature | Correlation between Haze and Monthly Total Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 | −0.47 | −0.47 | −0.11 |
| 1991 | −0.24 | 0.22 | 0.24 |
| 1996 | 0.10 | −0.33 | −0.35 |
| 2001 | 0.31 | −0.15 | −0.31 |
| 2006 | 0.70 ** | −0.43 | −0.75 ** |
| 2011 | 0.79 ** | −0.82 ** | −0.63 * |
| 2016 | 0.51 * | −0.43 | −0.32 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
To, W.-M.; Lee, P.K.C.; Ng, C.T. Factors Contributing to Haze Pollution: Evidence from Macao, China. Energies 2017, 10, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091352
To W-M, Lee PKC, Ng CT. Factors Contributing to Haze Pollution: Evidence from Macao, China. Energies. 2017; 10(9):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091352
Chicago/Turabian StyleTo, Wai-Ming, Peter K. C. Lee, and Chi To Ng. 2017. "Factors Contributing to Haze Pollution: Evidence from Macao, China" Energies 10, no. 9: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091352
APA StyleTo, W.-M., Lee, P. K. C., & Ng, C. T. (2017). Factors Contributing to Haze Pollution: Evidence from Macao, China. Energies, 10(9), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091352






