Abstract
In order to determine the matching relationship of polymer molecular weight and reservoir permeability in ASP (alkaline/surfactant/polymer) flooding, a number of core flooding experiments with different polymer molecular weights are performed. Two types of curves for the relationship between the pressure difference and the injection pore volume multiples are obtained. One describes the characteristics of the core plugging; the other describes the characteristics of the injection well. The relationship between the polymer molecular cyclotron radius and the pore throat radius used to describe the relationship between the polymer molecular weight and the core permeability. The results indicate that when the ratio of the pore throat radius (rh) to the polymer molecular cyclotron radius (rp) is greater than 7, the injection of ASP system with a variety of molecular weights will not be blocked; on contrary, when the ratio is less than 7, the core will be blocked. The range of water permeability of the core is determined by the value of the polymer molecular weight. The ratio between the pore throat radius (rh) to the polymer molecular cyclotron radius (rp) for the ASP system is greater than that of polymer system (rh/rp = 5). A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is used to compare the morphology of polymer molecules in polymer solution and ASP solution, and shows that the dimension of polymer molecular coils in ASP solution is smaller than that in polymer solution, which is caused by the double effect of alkali and surfactant.
1. Introduction
About 7000 billion barrels of oil still remain in reservoirs after conventional recovery methods [1].This value is the target of enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques. Compared to brine flooding and polymer flooding, ASP (alkali/surfactant/polymer) flooding is the most promising chemical EOR process in Daqing oilfields due to their specific reservoir conditions. The main mechanism of ASP flooding is by adding oil displacement agent (alkali/surfactant/polymer) to produce synergistic enhancement effect to reduce the interfacial tension and improve the mobility ratio [2,3]. Polymers can increase the viscosity of injection fluid and reduces the water permeability thus improve the oil recovery [4,5,6]. As we know, polymer molecular weight plays an important role in ASP flooding for improving oil recovery. When the molecular weight of the polymer is too low, the need for the amount of polymer increases to satisfy the requirement for viscosity. This may impair the economy of ASP technology. However, if the molecular weight is too high it may block the oil-producing layer [7]. Therefore, before conducting ASP technology in the field it is a vital task to study the relationship between the molecular weight and the polymer concentration and the permeability of reservoir [8]. Cao et al., conducted experimental research on permeability limits of polymer flooding in low permeability oil layers. He used the relationship between molecular radius of gyration and pore radius to represent the relationship of the polymer molecular weight and the core permeability. He found when the ratio of the radius between the hole and the polymer molecule was greater than 5, the injection of the polymer was not blocked; when the ratio of the radius is less than 5, the injection of the polymer was blocked [9]. Han et al., used mathematical methods with membrane microfiltration and dynamic light scattering to study the relationship between polymer size and pore-throat size and suggested a relationship between them [10]. Cheng et al., studied the optimization of the polymer molecular weight in polymer flooding. They found when the ratio of the pore radius to the mean square radius of the polymer molecule was greater than 5 the pores of the rock were blocked due to the large size of the polymer molecules [7]. Zhang et al., reported a novel method of optimizing the molecular weight of polymer flooding and a matching chart on the relationship between molecular weight and layers [11]. Luo et al., studied the relationship between polymer molecular size and pore size for conglomerate reservoirs and found the conglomerate reservoir with water permeability more than 55 × 10−3 μm2 could not be blocked by polymers with molecular weight less than 3.57 × 107 [12]. All these studies just investigated the relationship between the polymer molecular weight and reservoir permeability for polymer flooding. However, no literature reported such a relationship for ASP flooding.
In this paper, core flooding experiments with different ASP systems were conducted. The dynamic characteristics in the process of injection were recorded. The resistance factors of different ASP systems in cores with different permeability were calculated to evaluate the injectivity of ASP system. The matching relationship was established between the molecular weight of polymer in the ASP system and the permeability of the core. This relationship can provide a technical basis for the design of polymer molecular weight in the ASP system.
2. Experiment
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Core
The cores used in this experiment are synthetic with an average porosity of 30%. The synthetic cores were purchased from the EOR Research Institute of Northeast Petroleum University (Daqing, China). The synthetic cores use quartz sand (Daqing Refining and Chemical Company, Daqing, China) as production material and epoxy resin (Daqing Refining and Chemical Company, Daqing, China) as cementing agent. The grain size of quartz sand controls permeability and pore-throat ratio. The cement controls the porosity. The addition of clay minerals and natural core debris makes the synthetic core similar to real reservoir cores. The diameter of the core is 2.5 cm and the length of the core is 10 cm. The structure and permeability of the synthetic cores are similar to those of the cores from Duanxi reservoir in Daqing oilfield.
2.1.2. Chemicals
The polymers used in this experiment are partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide. The average relative molecular weights are 4 million, 6 million, 9 million, 12 million, 15 million, 19 million, 25 million, 28 million, and 35 million, respectively. The concentration of polymer is 1000 mg/L. The polymers are manufactured by Daqing Refining and Chemical Company (Daqing, China). Analytical-grade Na2CO3 is used as the alkali, with the mass concentration of 1.2%. The surfactant is alkyl benzene sulfonate from Daqing Refining and Chemical Company in China with the solid content of 50% and mass concentration of 0.3%.
2.1.3. Brine
The brines used in the core flooding experiments are injection brine and formation brine. The injection brine is sampled from the injection allocation station II of No.1 Oil Production Company from Daqing Oilfield (Daqing, China) with the total salinity of 3927.8 mg/L. The formation brine with a salinity of 7270.6 mg/L is used to saturate the cores. The composition of the injection and the formation brines are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Composition of the injection and the formation brines.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Measurement of Intrinsic Viscosity (η)
The buffer solution is prepared by adding 1.335 g citric acid (Daqing Zhifei Bio-chemical Co. LTD, Daqing, China), 26.6 g disodium hydrogen phosphate (Weifang Huabo Chemical Co. LTD, Weifang, China), 116.9 g sodium chloride (Weifang Huabo Chemical Co. LTD, Weifang, China), and 1000 g distilled water. Then the stock solution of the injection fluid is prepared. The buffer solution and distilled water is used to dilute the stock solution to obtain four injection fluids with different concentrations. Then the injection fluid is filtered. The outflow time of the injected solution is measured when it is between the two scales on the viscometer at 30 °C. The temperature is controlled by a water bath. The average value is obtained after repeating three times. The average outflow time of the buffer solution is determined after three repetitions. The specific viscosity of the injected fluids calculated as:
where, is specific viscosity, dimensionless; t is the flow time of injected solution, in seconds; t0 is the flow time of buffer solution, in seconds. The values of /C for the four solutions are calculated. C is the concentration of the injected solution. /C is used as the ordinate. C is used as the abscissa in the coordinate. The intercept of the linear part of the curve is obtained by four-point extrapolation.
2.2.2. Core Flooding Experiment
First, the core is vacuumed to remove the air. The vacuum is done when the pressure decreases to 0.1 Mpa in about 2 h. Then, the formation brine is injected at 0.1 mL/min for more than four hours to saturate the cores. The injected volume, effluent volume, and the retained volume in the pipeline are recorded. The pore volume is calculated based on the above data. The pressure differences over the time are recorded during core flooding. Next, the ASP solution is injected into the cores at 0.1 mL/min. The pressure difference across the core is recorded. To prevent channeling, the pressure is kept higher than 2 MPa during the entire core flooding. Lastly, the injection brine is injected to replace ASP solution in the core. The resistance factor is calculated. The diagram of the experimental process is shown in Figure 1.
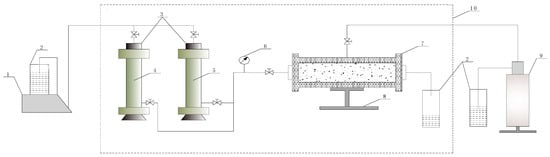
Figure 1.
Diagram of the experimental process. 1—plunger pump; 2—beaker; 3—container; 4—water; 5—ASP solution; 6—pump sensor; 7—core holder; 8—base; 9—manual pump; 10—oven [14].
The residual resistance can be calculated as [13]
where, Rf is residual resistance; Δpp is the stabilized pressure difference after ASP flooding; Δpwi is the stabilized pressure difference after brine flooding.
Rf = Δpp/Δpwi
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pore Size Characterization
The structure of the pore is very complex with a wide range of pore size. There are many parameters that describe the pore geometry. The most commonly used are median pore radius () and pore throat radius ().
represents corresponding pore radius when the cumulative mercury saturation reaches 50% on the curve of cumulative mercury saturation vs. pore radius. This parameter is usually obtained by measuring the capillary pressure with mercury. The measurement is complicated and the core after mercury injection cannot be reused. Therefore, the scope of application is limited [15].
of synthetic core is usually calculated by Kozeny Carmen formula [16]:
where, is the radius of pore throat, μm; c is Kozeny constant, c = 0.2; is the porosity of the pore, %; is the water permeability, 10−3 μm2. In this paper, we used to describe the synthetic pore geometry.
3.2. Polymer Molecular Size Characterization
There are two methods to measure the polymer’s molecular size: microporous membrane filtration and calculating the relative molecular mass of a polymer and the intrinsic viscosity of a polymer solution. One method is measuring the molecular size of a polymer by injecting the polymer solution through a membrane medium with a known pore size. The other method is to measure the polymer molecular size is by calculating the relative molecular mass of a polymer and the intrinsic viscosity of a polymer solution. For polymer with irregular coils the molecular conformation changes with time due to Brownian motion. The “size” can only be described by the average values. Polymer coils entangle each other along the shear direction while rotating and flowing in the process of polymer flowing through the membrane. When rotating, the coils may sweep a certain spherical space. In theoretical research, it is processed as hydrodynamically equivalent sphere. The coil radius req is related to the gyration radius rp (i.e., the gyration radius of the coil rotates around the center of mass) as Req = ξ rp. ξ is a constant relating to polymer, solvent, temperature, etc. RG can be easily obtained, such as measuring by ultracentrifugation and light scattering method. The molecular weight of polymer is calculated as follows [17]. RG is always chosen to represent the molecular size of a polymer.
where, rp is the molecular cyclotron radius, μm; η is the intrinsic viscosity of polymer solution, mg/L. η is measured following the national standard GB12005.1-1989 [18]. M is the molecular weight of the polymer.
3.3. Two Types of Experimental Curves
Through a large number of core flooding experiments, two different curves describing the relationships between the pressure difference and the injection volume are obtained. These two different curves represent different relationships between the polymer molecular weight and the core permeability.
One relationship shows a smooth flow without plugging in the core. The water permeability is determined after the pressure stabilizes during brine injection. In the following ASP flooding, the pressure increases rapidly at first, then slows down, and finally reaches stability. In the last step when the brine is injected to replace ASP in the core, the pressure decreases rapidly at first and stabilizes eventually. The curve is shown in Figure 2.The reason for this phenomenon is that, in the early stage of ASP injection, there is a significant difference in the concentration of the ASP component and the formation water. This concentration difference causes the components to diffuse quickly. When the polymer molecules are large in accessible pore volume exists. The migration rate of the polymer is the fastest which causes severe chromatographic separation among the components. With the migration of the ASP system and the increase of injected pore volume, the adsorption and detention of each component in the core gradually increases, resulting a pressure increase. After injecting several pore volumes of ASP solution, as the components reach the saturation dynamic adsorption, the pressure gradually stabilizes. The following brine injection is to wash out some of the components adsorbed in the core. This will cause the pressure to decrease. When the concentration of each component in the effluent approaches zero, the pressure seems to reach a constant value again. The retention of the polymers is much larger than those of the surfactant and alkali in the ASP system. Therefore, the stabilized pressure is mainly affected by the properties of the polymers. It is also an index of evaluating the ability of polymer solution to improve the mobility ratio and decrease the reservoir permeability.
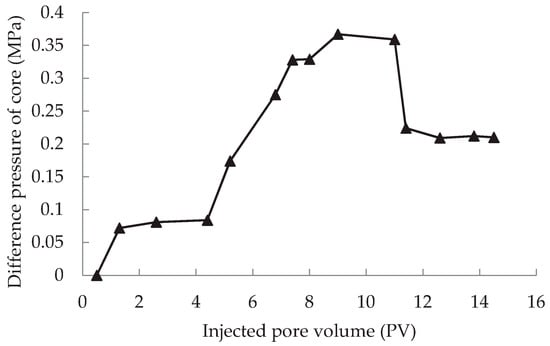
Figure 2.
Relationship between pressure difference across the core and injected pore volume without core plugging.
The other relationship describes the ASP solution plugging the core. During the initial brine injection, the water permeability is determined when the pressure stabilizes. However, in the following ASP flooding, the pressure does not stabilize after 4–5 pore volumes. The pressure keeps increasing even after injecting more than 10 pore volumes. In the post-brine injection, the pressure only slightly decreases. The curve of this case is shown in Figure 3.The reason for this phenomenon is that most of the core pores are inaccessible pore volume for polymer in the ASP system, only the surfactant and alkali can migrate into the core. Since it is difficult for the polymer molecules to enter the pores, the polymer molecules block most of the migration pathways. This causes the pressure to keep increasing even after the post-brine injection. The pressure does not decrease or only decreases slightly.
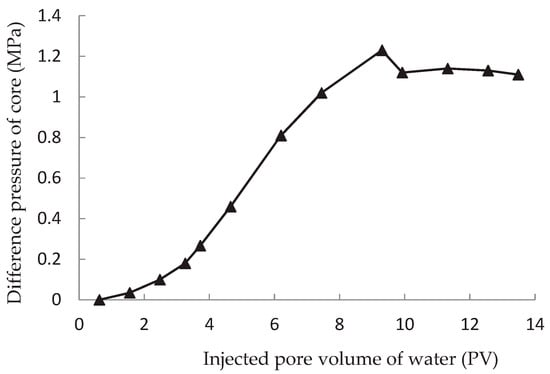
Figure 3.
The relationship between pressure difference and injected pore volume when the two ends of the core is blocked.
3.4. Relationship Between Polymer Molecular Weight in the ASP Systemand Core Permeability
In order to obtain the relationship between the permeability of cores from Duanxi reservoir and the molecular weight of polymer in the ASP system, a number of core flooding experiments are conducted using different molecular weight of polymers in the ASP system and cores with different permeability. The experimental data are shown in Table 2. From Table 2, we can find that the resistance factor decreases with the increase of brine permeability when the polymer molecular weight and concentration are the same. The reason is that greater brine permeability results in lower shear rate of ASP solution in the core. The ASP solution can easily flow through the core, resulting in the decrease of the resistance factor. According to the above analysis, we assume the relationship between the molecular cyclotron radiuses and the radius of the pore throat can be used to represent the relationship between the polymer molecular weight and the core permeability. The estimated results are listed in Table 2. The data in shown Table 2 concerns the Duanxi reservoir, when the radius ratio between the pore throat and the molecular cyclotron of the polymer is greater than 7 the injection of ASP solution with low molecular weight polymer will not be blocked; when the radius ratio is less than 7, the ASP solution will be blocked. The ratio of the pore throat to the polymer molecular cyclotron in the ASP system is greater than the ratio in the polymer system (rh/rp = 5) [7,9,15].

Table 2.
Core flooding experiments using different molecular weight of the polymers in ASP system.
The relationship between the polymer molecular weight in the ASP solution and the core permeability summarized from Table 2 and shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Matching relationship between polymer molecular weight of ASP solution and core permeability.
3.5. Injectivity Comparison Between ASP System and Polymer System
In order to explain the different injectivities of ASP and polymer solutions, the scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of these two systems are compared in this paper. The morphologies of the polymer molecular aggregate in the two systems are analyzed from the microscopic morphology.
Figure 4a shows that the polymer molecular forms a spatial network structure in the aqueous solution and has some fractal growth self-similarity [19]. This is mainly due to the electrostatic repulsion between neighboring carboxyl groups after partial hydrolysis of polyacrylamide causes increased stretching of the polymer molecular chain. The molecular chains of polymer can cross each other, or even winding, resulting in the formation of high-density multi-layer three-dimensional network structures with thick trunk and fine branches and holes of different sizes in the solution. This kind of network structure can not only brace, but also adsorb and wrap a large number of brine molecules to produce deformation resistance. Thus, the partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide solution has good adhesive ability. Further analysis has found that the polymer molecular weight has an influence on the structure of molecular aggregation as long as the other conditions are the same. The larger the molecular weight, the longer the molecular chain of the polymer; the smaller the molecular chain in the unit volume, the smaller the intermolecular force and the smaller the molecular space network structure [20].
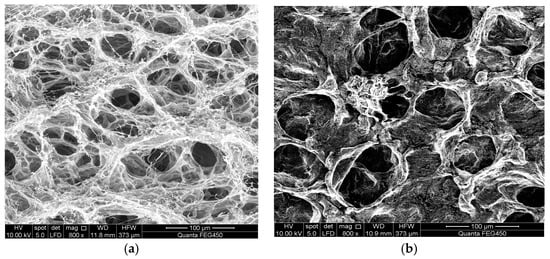
Figure 4.
(a) SEM image of polymer; (b) SEM image of ASP system.
Comparing Figure 4a with Figure 4b, we find the different morphologies of molecular aggregates of polymer and ASP systems. Unlike the three-dimensional network structure of the polymer system, the micro-molecules of the ASP system present spherical particles with a bead network and some self-similarity for fractal growth. However, the network is sparse and has no significant difference between the trunk and branch. This structure has a poor ability of wrapping brine molecules. Therefore, the adhesion ability is poor. This is mainly because when Na2CO3 is dissolved in brine, Na+ ions produce a shielding effect on the negatively charged polymer molecules. This results in the thinning of the electric double layer and hydration layer on the surface of the polymer (shown in Figure 5). The repulsion between the carboxyl groups in the molecular chain is weakened and the polymer chain undergoes crimp contraction, which results in the backbone of the network skeleton gradually retracting until the system is destroyed. On the other hand, when sulfonate is dissolved in brine, it produces Na+ and surface active sulfonate anions. The Van der Waals forces between the surfactant molecules, the micelles formed after aggregation, and the polymer molecules tend to overcome the electrostatic repulsion. Therefore, the effect of Van der Waals forces on the electrical double layer in the polymer molecules is adsorption. Under this condition, other ions in the solution can be regarded as "incoherent ions" [21,22]. However, the strong electrostatic repulsion weakens the adsorption of anionic surfactant molecules on the surface of polymer macromolecules. The effect of the sulfonate surfactant on the polymer molecule is similar to that of the organic salt, resulting in the contraction of the polymer molecular chain. The double compression effects from Na2CO3 and sulfonate on the polymer molecular chain make the morphology of the micro molecular aggregates in the ASP system very sparse. All of these cause the dimensions of polymer molecular coils in the ASP solutions to be smaller than those in the polymer solutions. Therefore, the radius ratio between the pore throats and the molecular cyclotron in the ASP solution is larger than that in the polymer solution.
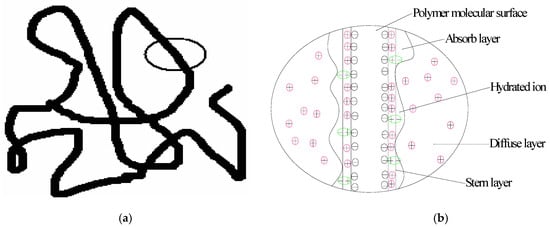
Figure 5.
(a) The sketch map of polymer molecule in ASP system; (b) Electrical double layer of polymer molecular surface [19].
4. Conclusions
- When the core is not plugged: during the initial brine injection, the pressure is gradually stabilized; during the following ASP flooding, the pressure increases rapidly at first, then slows down; during the post-brine injection for replacing the ASP solution in the core, the pressure is stabilized eventually. When the core is plugged: during the initial brine injection, the pressure is gradually stabilized; however, during the following ASP flooding, the pressure keeps increasing even after 4–5 pore volume injection, and continuously increases after 10 pore volumes.
- We apply the relationship between the polymer molecular cyclotron radius and the pore throat radius to represent the relationship between the polymer molecular weight and the core permeability. When the ratio of the pore throat radius to the molecular cyclotron radius is greater than 7, the ASP solution with a variety of molecular weight of polymer will not be blocked; when this ratio is less than 7, the ASP solution will be plug the pore throat. The ratio for the ASP system is bigger than that for polymer solution because the dimensions of polymer molecular coils in ASP solution are smaller than those in the polymer solution according to the SEM images of both systems.
- The matching relationship between the polymer molecular weight in the ASP solution and core permeability has been established. Based on this relationship, we conclude for the ASP system: the polymers with molecular weight of 4 million, 6 million, 9 million, 12 million, 15 million, 19 million, 25 million, 28 million, and 35 million are suitable for reservoirs with permeability greater than 40 × 10−3 μm2, 60 × 10−3 μm2, 90 × 10−3 μm2, 130 × 10−3 μm2, 160 × 10−3 μm2, 210 × 10−3 μm2, 310 × 10−3 μm2, 360 × 10−3 μm2 and 420 × 10−3 μm2, respectively.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51404070); Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (QC2015056); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M611350); Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (LBH-Z16002); Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Beijing; Important National Science & Technology Specific Projects (2016ZX05010-003).
Author Contributions
Bin Huang and Wei Zhang contributed to all parts of the process of this study: developing the methodology, designing the experiments, and writing the paper; Rui Xu and Zhenzhong Shi conducted the physical experiment; Cheng Fu and Kaoping Song analyzed the data. Ying Wang revised the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References and Notes
- Wu, Y.F.; Mahmoudkhani, A.; Watson, P. Development of new polymers with better performance under conditions oh high temperature and high salinity. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 16–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajire, A.A. Review of ASP EOR (alkaline surfactant polymer enhanced oil recovery) technology in the petroleum industry: Prospects and challenges. Energy 2014, 77, 963–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.J. A comprehensive review of alkaline-surfactant-polymer (ASP) flooding. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 9, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Hou, Q.F.; Liu, W.D. Recent progress and effects analysis of ASP flooding field tests. In Proceedings of the SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 14–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.; Wu, G.Z.; Hu, J.Q. The key theory and technology of ASP flooding in improving oil recovery. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 2, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Behruz, S.S.; Arne, S. Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) by combined low salinity water/polymer flooding. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.C.; Wang, D.M.; Wu, J.Z. Molecular weight optimization for polymer flooding. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2000, 21, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Pitts, M.J. Alkaline-surfactant-polymer flooding prepared for Daqing Petroleum Institute, June 1999, 45–51.
- Cao, R.B.; Ding, Z.H.; Liu, H.L. Experimental research on permeability limits and displacement characteristics of polymer flooding in low permeability oil layers. Petrol. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing. 2005, 24, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Tang, J.X.; Liu, Z.J. Experimental detection of polymer size with different molecular weight. J. Yangtze Univ. 2006, 3, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Pan, F.; Guan, W.T. A novel method of optimizing the molecular weight of polymer flooding. In Proceedings of the SPE Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference, Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 July 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.L.; Ma, D.S.; Nie, X.B. Study on matching relation between polymer molecular size and pore size for conglomerate reservoir. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.; Shi, M.; Gao, X.L. Effect on resistance factor and residual resistance factor for polymer solution flow through porous media. J. Daqing Petrol. Inst. 1992, 16, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H. A study on the optimization of surfactants in the main and vice slug in weak base ASP flooding. Energies 2017, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.G.; Gao, Z.H. Pore throat radius to coil gyration radius as characteristic of adaptively of polymer molecular mass to core permeability. Oilfield Chem. 1996, 13, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.P. The mechanism of reduction of water mobility by polymers in glass capillary arrays. SPE J. 1976, 16, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.G.; Wang, K.L.; Gao, S.S. Best selection of polymer molecular weight. J. Daqing Petrol. Inst. 1998, 22, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Determination for limiting viscosity number of polyacrylamide. GB 12005. 1-1989; Standards Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Lu, X.G.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Q. The polymer molecular configuration in the oil displacement agent with high temperature and salinity and its seepage property in the medium-low permeability layer. Acta Chim. Sin. 2010, 68, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Li, M.Y.; Lu, X.G. Influences of the strong base on the molecular clew-group dimension, aggregate states and seepage characteristics of the polymer. Petrol. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing. 2013, 32, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Lu, X.G.; Jiang, W.D. Influence of cations, anions and surfactants on molecular coil dimensions of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylaimde. Acta Polym. Sin. 2009, 12, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.G.; Jiang, W.D.; Wang, X.Y. Study on effects of Cr3+, alkali and surfactant on polymer molecular configuration and seepage flow characteristics. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 30, 749–753. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).