A 62-year-old woman, without previous history of cardiovascular diseases, was admitted to our institution due to episodes of monomorphic non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) associated with dizziness. She had undergone radiotherapy and chemotherapy after a left mastectomy for breast cancer 20 years ago.
Resting ECG revealed right bundle branch block with left anterior hemiblock with wide QRS and short episodes of non-sustained VT of left ventricular (LV) origin.
Echocardiography showed the presence of a large LV antero-lateral wall aneurysm (maximal dimensions of 57 × 41 mm) with the wall thinning resulting in the moderately depressed LV ejection fraction of 35% with preserved contractility of the remaining LV segments (Figure 1A,B, arrows). Coronary artery disease with previous silent myocardial infarction was suspected. Subsequently performed coronary angiography demonstrated normal coronary arteries.
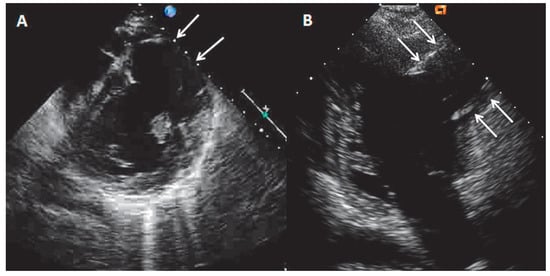
Figure 1.
Echocardiography parasternal short-axis (A) and apical two-chamber view (B) showing the presence of large left ventricular antero-lateral wall aneurysm (arrows).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed to search for the possible explanations of the nature of the aneurysm. It showed transmural late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) of the entire akynetic aneurysmal wall, consistent with transmural scar (Figure 2A,B, arrows).
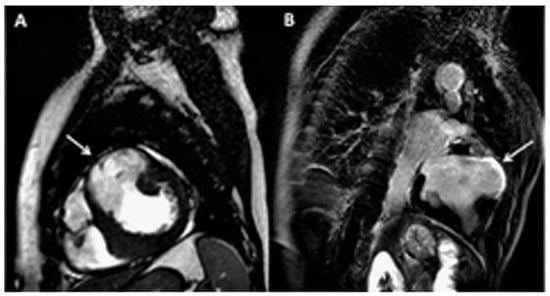
Figure 2.
Cardiac MRI sagittal view showing the thinning of the wall of the aneurysm (A, arrow) and the presence of transmural late gadolinium enhancement (B, arrow).
For better understanding of the anatomical relationship of the aneurysm with the coronary tree (planning a surgical resection of the aneurysm), the patient underwent CT angiography. It showed intact left anterior descending artery and diagonal branches without any wall lesions (Figure 3B). The arteries were spreading out extensively over the aneurysm wall. 3D CT volume rendering modality (Figure 3A), however, showed that the aneurysm involved not only the left, but also the right ventricle in its antero-apical region (Figure 3A, arrows). Unfortunately, the previously performed MRI study protocol was dedicated to the LV study so that the involvement of the right ventricle could be neither confirmed nor excluded. We could not repeat the MRI study later on as the patient underwent ICD implantation.
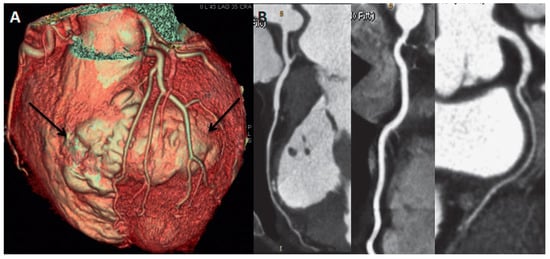
Figure 3.
CT angiography shows intact coronary arteries without any wall lesions (B). 3D CT volume rendering modality demonstrates an involvement not only of the left ventricle but also of the right ventricle in its antero-apical region (A, arrows).
Several speculations concerning the aetiology were discussed. A silent myocardial infarction was a diagnostic option, however, the aneurysm did not match with a specific coronary territory and the coronary walls of the entire tree were free of any intramural atherosclerotic plaque.
Radiotherapy induced myocardial damage was the most probable diagnosis considering the past history of radiotherapy in the early years of this type of treatment using old, sub-optimal radiation techniques [1].
However, the patient’s recordings revealed that radiotherapy was performed in supraclavicular and axillary regions, without irradiation of mediastinum (Figure 4). According to the recordings the cumulative radiation dose was 47.5 Gy divided into 23 sessions. Another possible cause of LV bulging could be a diverticulum. However, its wall should contain endocardium, myocardium and pericardium and display normal contraction [2]. On the contrary in our case, MRI showed akynetic region with transmural LGE, which excludes the presence of normal myocardium and consistent with transmural scar. Cardiac sarcoidosis is another rare cause of aneurysm formation in the heart [3]. However, the previous serial PET investigations performed in the follow-up setting of the breast cancer never showed any pathological uptake either in the lungs or in the heart. From the old patient recordings we were able to recover the ECG of 2005 which showed the similar findings as the ECG on the index event.
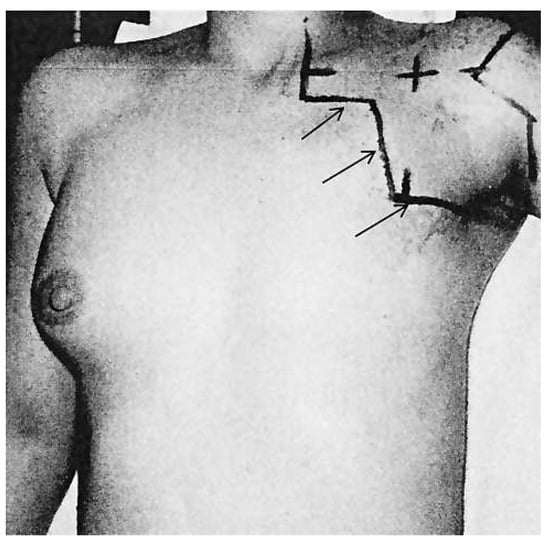
Figure 4.
The picture from the patient’s recordings from 1985 showing the region of radiotherapy application (arrows).
Thus, the origin of the aneurysm remained unknown despite the different tools of cardiovascular imaging that were employed in the diagnostic work-up. The probability of post-traumatic lesion during childhood or of congenital disease remained speculative. We restrained from surgical resection due to involvement of both ventricles. On the follow-up examination the patient remained asymptomatic without any episodes of VT on the interrogation of defibrillator.
Conflicts of Interest
No financial support and no other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article were reported.
References
- Hudecová, K.; Urbanová, D.; Petrásová, H. The risk of cardiovascular diseases induced by radiotherapy. Vnitr Lek. 2008, 54, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- SatMakkuni, P.; Kotler, M.N.; Figueredo, V.M. Diverticular and aneurysmal structures of the left ventricle in adults: report of a case within the context of a literature review. Tex Heart Inst J. 2010, 37, 699–705. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Ishida, Y.; Amaki, M.; Ohara, T.; Hasegawa, T. , et al. Second left ventricular aneurysm newly developed in a patient with untreated cardiac sarcoidosis. Circ J. 2010, 74, 2477–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
© 2012 by the author. Attribution-Non-Commercial-NoDerivatives 4.0.