Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most common cancer worldwide with high recurrence, metastasis, and poor treatment outcome. Prognostic survival biomarkers can be a valid tool for assessing a patient’s life expectancy and directing therapy toward specific targets. Recent studies have reported microRNA (miR) might play a critical role in regulating different types of cancer. The main miR used as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and reported in the scientific literature for HNSCC is miR-21. Other miRs have been investigated to a lesser extent (miR-99a, miR-99b, miR-100, miR-143, miR-155, miR-7, miR-424, miR-183), but among these, the one that has attracted major interest is the miR-31. Methods: The systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines using electronic databases, such as PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, with the use of combinations of keywords, such as miR-31 AND HNSCC, microRNA AND HNSCC, and miR-31. The meta-analysis was performed using the RevMan 5.41 software (Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark). Results: This search produced 721 records, which, after the elimination of duplicates and the application of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, led to 4 articles. The meta-analysis was conducted by applying fixed-effects models, given the low rate of heterogeneity (I2 = 40%). The results of the meta-analysis report an aggregate hazard ratio (HR) for the overall survival (OS), between the highest and lowest miR-31 expression, of 1.59, with the relative intervals of confidence (1.22 2.07). Heterogeneity was evaluated through Chi2 = 5.04 df = 3 (p = 0.17) and the Higgins index I2 = 40; testing for the overall effect was Z = 3.44 (p = 0.00006). The forest plot shows us a worsening HR value of OS, in relation to the elevated expression of miR-31. Conclusions: In conclusion, the data resulting from the current meta-analysis suggest that miR-31 is associated with the prognosis of patients with HNSCC and that elevated miR-31 expression could predict a poor prognosis in patients with this type of neoplasm.
1. Introduction
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is an aggressive life-threatening disease associated with high mortality rates [1]. The 5-year survival, despite the chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery for stages 3 and 4 of the disease, is low (only 30% of the patients survive) [2].
The risk factors related to the onset are mainly tobacco and alcohol, but there is also a possible correlation with papilloma virus (HPV 16, HPV 18) [3]. Usually, HNSCC-HPV+ has a better prognosis compared to non-positive subjects, partly due to increased susceptibility to radiotherapy [4]. Therapy of patients with HNSCC, therefore, consists of radiotherapy (indicated in HPV+) in combination with chemotherapy and surgery, but potentially it involves an overall risk of disease recurrence of around 50% [5].
HNSCC are neoplasms, which, depending on the epithelium of origin, are recognized as laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC), hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC), and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). This last one is the carcinoma with the highest incidence in the head and neck region, corresponding to around 60% of HNSCC [6]. The main cancer of the head and neck region is, however, represented by OSCC, which accounts for about 60% of all HNSCCs [6].
At the base of the etiopathogenetic processes of cancerization, we found genetic alterations that involve mutations of the main oncogenes (APC, p53, NF1, VHL, Rb BCL2, BRCA2, PTCH CD95, ST5, SWI/SNF, p16, YPEL3, ST7, and ST14) and oncogenes (Ras, raf, gsp, jun, fas, erbA, abl, sis erbB fms). In addition, events affecting cell cycle progression and proliferation, such as DNA methylation [7], histone modifications, and non-coding alterations of RNA [8] (such as microRNAs), can influence, cancer progression, stemness and resistance of cancer cells to therapeutics [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
The microRNAs (miRs) are a large group of small single-stranded non-coding endogenous RNAs, approximately 18–25 nucleotides in length, which play a significant role in the post-transcriptional regulation of genes through the interaction with 3′UTR of target mRNA. The degradation or inhibition of their translation also plays an important role for cell development in differentiation, metabolism, proliferation, migration, induction of angiogenesis, and apoptosis, and they are stable molecules that can be found not only in tissues but also in body fluids, such as blood, saliva, and urine [19].
The miRs can express themselves in an altered way (downregulated or upregulated) in the different tumor forms. For HNSCC tumors, and more specifically for OSCC, the downregulated miRs mainly involved are: let-7a, let-7b, let-7c, let-7d, let-7e, let-7f, let-7g, let-7i, miR-26a, miR-99a-5p, miR-137, miR-139-5p, miR-143-3p, miR-184, and miR-375; while the upregulated ones are miR-21, miR-27a (-3p), miR-31, miR-93, miR-134, miR-146, miR-155, miR-196a, miR-196b, miR-211, miR-218, miR-222, miR-372, and miR-373 [20].
The different expression of miRs can be used as a prognostic biomarker, and the main miR established as a bioindicator, as described in the current scientific literature for HNSCC, is miR-21. Other miRs have been investigated to a lesser extent (miR-99a, miR-99b, miR-100, miR-143, miR-155, miR-7, miR-424, miR-183), but among these, the one that attracted the most interest is miR-31 [21,22,23].
Through the effect of RNA polymerase 2 intermediate forms of miR-31, pri-miR-31 and pre-miR-31 are assembled in succession, obtaining a pre-miR-31 of 70 nucleotides, which is transported out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm through exportin 5 (XPO5) and then cleaved by Dicer endonuclease in combination with TRBP, generating the miR-31 duplex complex (miRNA-31-3p and miRNA-31-5p) in the cytoplasm. Argonaute proteins (AGOs) play crucial roles in RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) formation and activity. AGOs loaded with small RNA molecules (miRNA or siRNA) either catalyze the endoribonucleolytic cleavage of target RNAs or recruit factors responsible for translational silencing and target destabilization, forming a silencing complex while miR-31-5p degrades [24].
In the last 10 years, many studies have investigated the altered miR-31 expression, correlating it to the prognosis and progression of tumor growth [25,26,27,28]. A clinical study on 56 patients conducted by Qiang et al. (2019) [29] investigated the prognostic potential by identifying a longer survival period in patients presenting a lower expression of miR-31, indicating how this non-coding RNA sequence can be considered a crucial reference indicator for the prognosis of patients with HNSCC. These data are partially in agreement with the results of Tu et al. (2021) [30], which identify a worse overall survival in patients with a higher expression of miR-31. These two very recent studies highlight how miR-31, as well miR-21, could represent a prognostic biomarker of survival. Furthermore, no other systematic reviews have been conducted on the prognostic role of the altered expression of miR-31. Taking in account these premises, the aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to investigate the prognostic potential of miR-31 as a survival biomarker for HNSCC in the light of new miR-31 studies, providing a pooled hazard ratio (HR) value (high and low expression of miR-31) on the overall survival (OS) in patients presenting HNSCC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
The drafting of the review was carried out following the indications of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) [31]. The protocol with which the systematic review was performed was established before proceeding with the search and screening of records in data banks.
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
All prospective and retrospective studies and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated differences in the tissue expression of miR-31 in HNSCC in correlation with prognostic survival indices were considered, with the following PICO question: Participants (patients with HNSCC), Intervention (altered expression of miR-31 in HNSCC), Control (patients with HNSCC who have low expression of miR-31), Outcome (difference in prognosis of survival among patients with low and high miR-31 expression in HNSCC). The PICO question, therefore, was as follows: Is there a difference in OS between HNSCC patients with high miR-31 expression versus those with low expression?
The inclusion criteria were as follows: all study reports that indicated and reported data on prognostic survival indices (Kaplan–Meier curves, hazard ratio, Cox regression) between low and high miR-31 expression in tumor tissues (HNSCC) were included.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: studies published in a language other than English, those that did not present data on survival and the expression of miR-31, and those at high risk of bias.
2.3. Sources of Information, Research, and Selection
The studies were identified through a literature search in electronic databases by two researchers (M.D. and D.S.). Limits relating to the language of publication were applied, and articles in a language other than English were excluded. The literature search was conducted on the PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane databases. The last bibliographic search was conducted on 3 March 2022, for a further update of the Bibliography. In addition, a search of the gray literature on Google Scholar was also conducted, and the bibliographic sources of previous systematic reviews on the miR-31 in HNSCC were investigated.
We used the following terms to search the databases: miR-31 AND HNSCC, Microrna AND HNSCC AND prognosis, miR-31 AND OSCC, miR-31 AND laryngeal cancer. Duplicates were removed using EndNote and manually. The articles identified were independently evaluated and scrutinized by two reviewers (M.D. and D.S.) for title and abstract analysis and for potentially eligible studies and text analyses for inclusion in the systematic review. Furthermore, the k agreement between the three reviewers was assessed. A third reviewer (A.B.) had the task of resolving the situations of disagreement.
2.4. Data Collection Process, Data Characteristics
The data to be extracted were previously established by the two reviewers (M.D. and D.S.) responsible for screening the studies and were reported in two tables independently to be subsequently compared to reduce the risk of errors. The data that were extracted from the articles concerned the type of study, the year of publication, the first author, the country that conducted the study, the number of patients, the type of HNSCC, the type of miR investigated, the cut-off between low and high expression, hazard ratio (HR), and the presence of a Kaplan–Meier curve. Specifically, all the HR data between high expression vs. low expression of miR-31 in tumor tissues (HNSCC) concerning the OS were searched and extracted, and secondly, data concerning disease-free survival (DFS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and cancer-specific survival (CSS) were searched and extracted if the data were in the form of Kaplan–Meier curves. The HR data were obtained through the method of Tierney et al., using a point and curve acquisition software (Engauge digitizer) and subsequently using an Excel spreadsheet, dedicated and available as additional material in the publication by Tierney et al. [32].
2.5. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies, Summary Measures, Summary of Results, Risk of Bias between Studies, Additional Measures
The risk of bias in the individual studies was assessed by an author (M.D.), with a second author tasked with verifying the correct assessment (D.S.). Parameters derived from the Reporting Recommendations for prognostic studies of markers (REMARK) were used for the assessment, and studies with a high risk of bias were excluded from the meta-analysis. The results were represented by forest plots, and inconsistency indices, such as the Higgins index I2, were evaluated.
The risk of bias between the studies was assessed graphically through the analysis of the overlaps of the confidence intervals, through the I2 inconsistency index (an I2 value greater than 75% was considered high, and a random effects analysis was applied in specific cases), and through a funnel plot. In the presence of a meta-analysis with high heterogeneity indices, a sensitivity analysis could be performed, excluding only the studies that presented a low overlap of the confidence intervals or that emerged graphically from the funnel plot. For the meta-analysis, and in particular for the calculation of the pooled HR, the software Reviewer Manager 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark) was used. We used the GRADE pro-Guideline Development Tool online software (GRADEpro GDT, Evidence Prime, Hamilton, ON, Canada) to assess the quality of the evidence.
The trial sequential analysis (TSA) was performed using Stata 13 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA), with the implementation of the R 4.2 software (Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) and by installing the idbounds and metacumbounds commands.
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Studies
The search in the Scopus, PubMed, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trial databases provided 716 bibliographic citations. Following the removal of overlaps, 512 registrations were obtained, of which 459 were excluded because it was found that they did not meet the eligibility criteria upon reading the abstracts, and 15 articles were potentially admissible but only 4 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. Furthermore, the analysis of the gray literature (Google Scholar, Open gray) and previous systematic reviews did not allow the identification of further studies to be included in the meta-analysis (Figure 1). Finally, an update of the research on the sources was carried out on 3 March 2022, with the addition of records from Web of Science and with the updating of keywords and results on Scopus and PubMed. All keywords and records search details are also represented in Table 1.
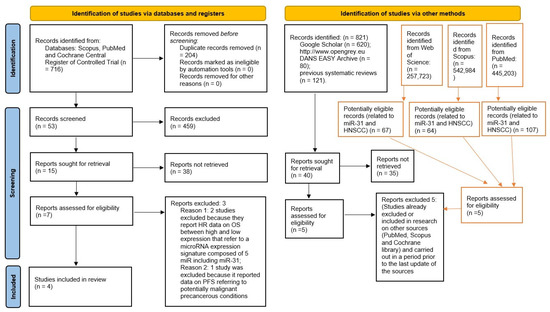
Figure 1.
Entire selection and screening procedures are described in the PRISMA flowchart; tables with the red lines are the searches performed subsequently (on 3 March 2022), with the addition of Web of Science and with an update of the keywords and results on PubMed and Scopus.

Table 1.
Complete overview of the search methodology. In total, 716 records were identified by the databases (512 records after removal of duplicates); Records identified by other research sources: 721 records.
3.2. Data Characteristics
Articles included in the meta-analysis are as follows: Jakob et al. (2019) [33], Wang et al. (2018) [34], Tu et al. (2021) [30], and Qiang et al. (2019) [29]. In total, three studies were excluded, despite presenting HR values for OS and PFS, because they did not fully meet the eligibility criteria. In the studies of Gao et al. (2013) [35] and Chen et al. (2018) [36], the HR values referred to a microRNA expression signature composed of five miR, including miR-31; while for the study of Hung et al. (2016) [36], the data on PFS referred to potentially malignant disorders.
The characteristics of the extracted data are described in the Materials and Methods section for the survival data expressed in the form of a Kaplan–Meier curve and HR and extracted according to the Tierney method [32]. All extracted data are reported in Table 2.

Table 2.
The data extracted from the four articles included in the meta-analysis and from the three articles excluded are reported in the present table. R (radiotherapy), OPMD (oral potentially malignant disorder).
Only four articles were included in the meta-analysis. All four studies included are retrospective clinical studies whose results were published between 2018 and 2021 and included a follow-up period of 5 to 13 years (Tu et al. [30]). The total number of HNSCC patients recruited is 240.
Studies by Tu et al. (2021) [30] and Jakob et al. (2019) [33] investigated patients with OSCC; Qiang et al. (2019) [29] considered HSCC and LSCC, while Wang et al. (2018) [34] considered more generally the HNSCC without specifying the site of the neoplasm.
All four studies considered OS as a prognostic parameter; Jakob (2019) [33] also used DFS and RFS, while Wang et al. used only DFS [34]. All the data concerning the prognostic survival indices were extracted and reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Assessment of risk of bias within the studies, with scores 8 to 10 = low quality, 11 to 14 = intermediate quality, and 15 to 18 = high quality.
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
The risk of bias was assessed through parameters derived from the REMARK. Based on the REMARK guidelines, a score from 0 to 3 was considered for each factor.
3.4. Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis was conducted by applying fixed-effects models, given the low rate of heterogeneity (I2 = 38%). The results of the meta-analysis report aggregate HR for OS. Between high and low miR-31 expression of 1.58, with the relative intervals of confidence [1.21, 2.06], heterogeneity was evaluated through Chi2 = 4.80 df = 3 (p = 0.19) and the Higgins index I2 = 38. Testing for the overall effect was Z = 3.39 (p = 0.0007). The forest plot presents the black diamond in a position of worsening of OS, in relation to the high miR-31 expression (Figure 2).
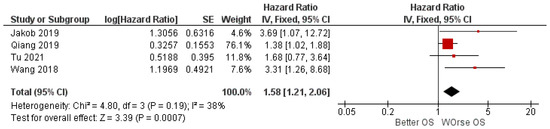
Figure 2.
Forest plot of the fixed-effects model of the meta-analysis; HR = 1.58, 95% CI: [1.21, 2.06]; df = degrees of freedom; I2 = Higgins heterogeneity index, I2 < 50%, heterogeneity irrelevant; I2 > 75%, significant heterogeneity; C.I. = confidence intervals; P = p value; SE = standard error. The graph for each study shows the first author and the date of publication, hazard ratio with confidence intervals, log HR standard error, and weight of each study expressed as a percentage. The final value is expressed in bold with the relative confidence intervals. The black line shows the position of the average value, and the rhombus in light black shows the measure of the average effect.
3.5. Risk of Bias across Study
The risk of bias between the studies is low (I2 = 38%), as evidenced by the overlapping of the confidence intervals, and further confirmation comes from the funnel plot, which does not identify sources of heterogeneity (Figure 3).
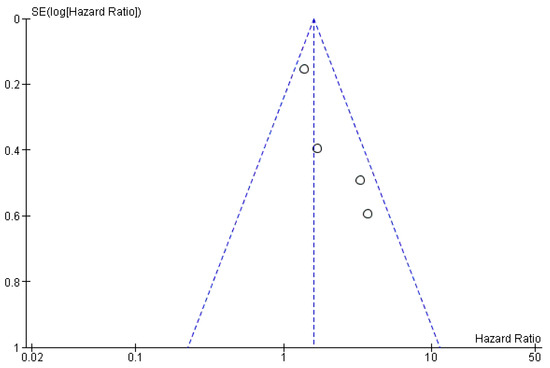
Figure 3.
Funnel plot. The absence of heterogeneity is evident graphically. I2 = 38%, SE: standard error.
To reduce the weight of the study by Qiang et al. of 76.1% in the meta-analysis, it was decided to also apply a random-effects model. In fact, the weight of the study on the meta-analysis drops to 50% with an HR value of 1.86 [1.18, 2.93], always in favor of the worsening of OS (Figure 4).
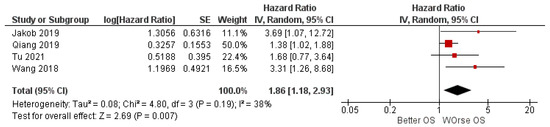
Figure 4.
Forest plot of the random-effects model of the meta-analysis.
3.6. Trial Sequential Analysis, Grade
Trial sequential analysis (TSA) was performed to evaluate the power of the meta-analysis, adjusting the results to avoid type I and II errors. The program used was Stata 13 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA), with the integration of the R 4.2 software (Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) through the Metacumbounds commands, as described by Miladinovic et al. [38]. The O’Brien—Fleming spending function was used by applying random effects. The accrued information size (AIS) and, subsequently, a priori information size (APIS) commands were used by the Dialog BOX to determine the optimal sample size and assuming a reduction risk relative (RRR) of 38%, an Alpha value equal to 5% (type 1 error), and beta at 20% (type 2 error) (Figure 5) for the power of the results.
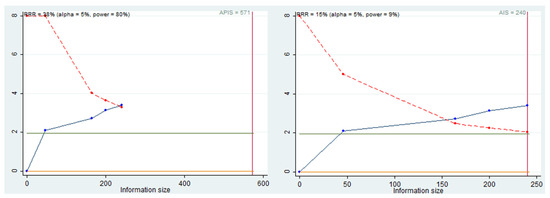
Figure 5.
AIS, APIS, light green line (Z = 1.98), dashed red line (monitoring boundary), blue line (cumulative z curve), red line (sample size).
The TSA curve crosses the line Z = 1.98, and crossing of the monitoring boundary before reaching the information size provides for firm evidence of effect. The APIS graph shows that, for an RRR of 38%, alpha 5%, and for a power of 80%, the number of optimal patients is 571.
The authors also used GRADE pro-GDT to assess the quality of the primary outcome (Table 4). The results suggested that the quality of evidence is low for outcome as the primary result.

Table 4.
Evaluation of GRADE pro-GDT.
4. Discussion
We conducted a systematic review through a meta-analysis of the data published in the literature on HNSCC to establish and expose a complete picture of the role of miR-31 as a prognostic biomarker of the altered expression of tissue miR-31 in HNSCC. To our knowledge, this is the very first meta-analysis review describing the role of miR-31 in HNSCC prognosis, in which four studies were analyzed with a total of 240 patients.
Many studies confirm that miR-31 is found to be upregulated under HNSCC, including a recent systematic review conducted by Al Rawi et al. 2021 [39] on the salivary expression of non-coding RNA.
In fact, Al-Rawi reports miR-31 among the 12 upregulated microRNAs during HNSCC and among the 4 non-coding RNAs investigated in relation to squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck region [39]. On the one hand, the prognostic power of miR-31 tissue expression has been investigated; on the other hand, only few recent studies and literature data are in partial agreement with different degrees of significance [28,29,32,33].
Wang et al. (2018) [34] demonstrated that miR-31 tissue levels were increased in HNSCC patients and closely associated with aggressive clinical variables. Furthermore, the elevated expression of miR-31 in tissues was positively correlated with shorter OS (HR 3.31 p = 0.015) and DFS, demonstrating that miR-31 tissue expression is an independent predictor for both OS and DFS of HNSCC and indicating how miR-31 could serve as a prognostic marker for HNSCC.
Jakob et al. (2019) [33] observed an over-regulated expression level of hsa-mir-31-5p in OSCC but without finding a correlation with clinical–pathological characteristics but associating it with a poorer OS (HR 3.69 p 0.028), as well as for the PFS.
Jakob et al. and Wang et al. report similar HR values (3.69 and 3.31), as also shown by the forest plot (Figure 2) and Table 2 [33,34].
Qiang et al. (2019) indicates, in agreement with Jakob and Wang [30,31], that the expression of miR-31 can be considered a crucial prognostic biomarker for the prognosis of patients with HNSCC, correlating it also with the clinical–pathological characteristics of the patient [29].
Analyzing and extrapolating the HR data from the Kaplan–Meier curve from the study by Tu et al. (2021) [30] (HR 1.68, C.I. = 0.77–3.64 p = 0.189) reveals a trend in which patients with higher miR-31 expression had worse OS but with differences that were not statistically significant.
Studies conducted on the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database report data that are not statistically significant; in fact, Jakob et al. identify an OS HR of 0.64 p = 0.19 for the TCGA cohort [33]. Furthermore, miR-31 has been included in prognostic predictor models with other miRs (miR-99a, miR-31, miR-410, miR-424, and miR-495) to evaluate the survival response to radiotherapy [36].
Our meta-analysis reports data that are statistically significant. In fact, aggregate HR for OS is 1.58 C.I. [1.21 2.06], Chi2 = 4.80, df = 3 (p = 0.19), giving useful information on how the altered expression of tissue miR-31 may be a valid prognostic biomarker. The data of our meta-analysis are in line with the four included studies, of which only three report statistically significant data. Indeed, by analyzing the confidence interval of HR in the forest plot (Figure 2), we can see how Tu et al. (2021) [30] intersect the center line to no effect, while Qiang (2019) comes very close to it [29]. The risk of bias within the studies is acceptable for all four studies, excluding only Tu et al. (2021) [30]. This last study has a slightly lower score, determined by the fact that the data (HR) for the outcome investigated in this meta-analysis were extrapolated by the authors of this review, starting from the Kaplan–Meier curve not being represented in a numerical value, and not being provided in the form of supplementary material. The risk of bias between the studies was low, as evidenced by the funnel plot and the heterogeneity indices (I2 = 38%).
Our systematic review through the meta-analysis shows some limitations. The first limitation is represented by a limited number of data and studies on the prognostic role of miR-31 expression in HNSCC, with only 240 patients included. In fact, further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the association between impaired expression of miR-31 and OS. The second limit is represented by the fact that the data reported by Tu et al. [30] on the HR were in the form of a Kaplan–Meier curve, and the data were extrapolated from the curve using the Tierney method [32]. This method, although widely validated, is not free from errors and could provide a slightly different HR value from the real one. This limit also affects the quality of evidence provided by the GRADE (Table 3).
Another limitation comes from the weight of Qiang et al. study [29], which presents an overweight of 76.1% in the meta-analysis, applying fixed effects—a limit that can be partially overcome by applying random effects. Certainly, the weight of the study on the meta-analysis drops to 50%, and in any case, the pooled HR is 1.86 [1.18, 2.93], always in favor of the worsening of OS.
Finally, the data from the current meta-analysis suggest that miR-31 is associated with the prognosis of patients with HNSCC and that high miR-31 expression could predict a poor prognosis in patients with this type of malignancy. From the HR, sample number, and standard error data extracted from the meta-analysis, the TSA was also conducted. The data results indicate that there is statistical power in the data, although from the APIS graphs (Figure 5) with a RRR of 38%, the ideal total number of people to have a power of both 80% is 571 patients. In our meta-analysis, the total number of patients included was 240. So, even if in the presence of a valid statistical power, it is not wrong to say that further studies on the issue are needed.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the data from the meta-analysis suggest that elevated miR-31 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with HNSCC. Consequently, exhaustive investigations of miRNA, for instance regarding intercommunication among miRNAs and between miRNAs and other genes, altered protein expression induced by miRNAs, and site-specific miRNA expression profiling, are, therefore, prerequisites before future clinical trials of therapeutic applications can go ahead.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D., D.S., M.D.C., L.L., A.P.C. and G.T.; methodology, M.D., G.A.C. and M.A.; software, M.D.; data analysis, M.D. and D.S.; visualization, M.D., R.A. and D.G.; bibliographic research, F.S. and A.B.; supervision and project administration, L.L.M., V.C. and A.B.; writing—review and editing, M.D., A.B.; accuracy and integrity of all parts of the work appropriately investigated and resolved: all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farhat, M.C.; Dyalram, D.; Ord, R.A.; Lubek, J.E. Oral squamous cell carcinoma in patients aged 45 and younger: Prognosis, survival, and quality of life. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2021, 133, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, A.; Muenyi, C.; Siegel, E.M.; Ajidahun, A.; Eschrich, S.A.; Wong, D.; Hendrick, L.E.; Putney, R.M.; Kim, S.; Hayes, D.N.; et al. Characterization of epigenomic alterations in HPV16+ head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2022, 31, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, L.L.; Ballini, A.; Cantore, S.; Bottalico, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Ambrosino, M.; Nocini, R.; Malcangi, A.; Dioguardi, M.; Cazzolla, A.P.; et al. Overview of Candida albicans and Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection Agents and their Biomolecular Mechanisms in Promoting Oral Cancer in Pediatric Patients. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7312611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, H.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X.; Ferris, R.L. The prognosis of HPV-associated metastatic pharyngeal patients by primary and distant site. Oral Oncol. 2021, 125, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, R.M.; Koopman, T.; Lavini, C.; Brug, T.V.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; Marcus, J.T.; Vergeer, M.R.; Leemans, C.R.; Bree, R.; Graaf, P.; et al. Early Response Prediction of Multiparametric Functional MRI and (18) F-FDG-PET in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with (Chemo) Radiation. Cancers 2022, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, S.; Kikuchi, M.; Harada, H.; Hamaguchi, K.; Asato, R.; Tamaki, H.; Mizuta, M.; Hori, R.; Kojima, T.; Honda, K.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics and Survival Outcomes of Patients with Buccal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Results of a Multi-Institutional Study. Medicina 2021, 57, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Eliot, M.; McClean, M.D.; Waterboer, T.; Pawlita, M.; Butler, R.; Nelson, H.H.; Langevin, S.M.; Christensen, B.C.; Kelsey, K.T. DNA methylation-derived systemic inflammation indices and their association with oropharyngeal cancer risk and survival. Head Neck 2022, 44, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, G.; Calin, G.A.; Ozpolat, B. RNAi-based therapeutics and tumor targeted delivery in cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 182, 114113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajbouj, K.; Al-Ali, A.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Saber-Ayad, M.; Hamid, Q. Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbullah, H.H.; Musa, M. Gene Therapy Targeting p53 and KRAS for Colorectal Cancer Treatment: A Myth or the Way Forward? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Cao, J.; Topatana, W.; Juengpanich, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Shen, J.; Cai, L.; Cai, X.; Chen, M. Targeting mutant p53 for cancer therapy: Direct and indirect strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasikci, Y.; Gronemeyer, H. Complexity against current cancer research—Are we on the wrong track? Int. J. Cancer 2021, 150, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.K.; Sun, X.J.; Gao, X.D.; Qian, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.L. Methylation alterations and advance of treatment in lymphoma. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Lewalle, P. Tumor Suppressor miRNA in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanism of Deregulation and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 708765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, P.; Ponzoni, M.; Corrias, M.V.; Ceccherini, I.; Candiani, S.; Bachetti, T. A Focus on Regulatory Networks Linking MicroRNAs, Transcription Factors and Target Genes in Neuroblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, J.M.; Zvereva, S.; Dalina, A.; Blatov, I.; Zubarev, I.; Luppov, D.; Bessmertnyi, A.; Romanishin, A.; Alsoulaiman, L.; Kumeiko, V.; et al. The p53 family member p73 in the regulation of cell stress response. Biol. Direct 2021, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, I.; George, A.; Seyhan, A.A. Therapeutic Targeting of Alternative RNA Splicing in Gastrointestinal Malignancies and Other Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, F.; Yang, A.-G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R. The role of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 24, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiiba, M.; Uzawa, K.; Tanzawa, H. MicroRNAs in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC). Cancers 2010, 2, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sannigrahi, M.K.; Sharma, R.; Panda, N.K.; Khullar, M. Role of non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A narrative review. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.F.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. MicroRNA aberrances in head and neck cancer: Pathogenetic and clinical significance. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 21, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, W.; Kumar, A. microRNAs in oral cancer: Moving from bench to bed as next generation medicine. Oral Oncol. 2020, 111, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, L.-A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. miR-31: A crucial overseer of tumor metastasis and other emerging roles. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, D. Prognostic markers in esophageal cancer: From basic research to clinical use. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagy, Á.; Lánczky, A.; Menyhárt, O.; Győrffy, B. Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, A.A.; Larcher, L.M.; Chen, S.; Veedu, R.N. Therapeutically Significant MicroRNAs in Primary and Metastatic Brain Malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, H.; Zhan, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, S.; Jiang, C. A Study on the Correlations of the miR-31 Expression with the Pathogenesis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.-F.; Liu, C.-J.; Hung, W.-W.; Shieh, T.-M. Co-upregulation of miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA MIR31HG in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 17, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, J.F.; Stewart, L.A.; Ghersi, D.; Burdett, S.; Sydes, M.R. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 2007, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakob, M.; Mattes, L.M.; Küffer, S.; Unger, K.; Hess, J.; Bertlich, M.; Haubner, F.; Ihler, F.; Canis, M.; Weiss, B.G.; et al. MicroRNA expression patterns in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Hsa-mir-99b-3p and hsa-mir-100-5p as novel prognostic markers for oral cancer. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3499–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Li, H.-X.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Su, Y.-L.; Lian, J.-S.; Li, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.-N.; Jin, N.; Liu, X.-F. MiR-31 is a potential biomarker for diagnosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4339–4345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Gay, H.A.; Chernock, R.D.; Zhang, T.R.; Luo, J.; Thorstad, W.L.; Lewis Jr, J.S.; Wang, X. A microRNA expression signature for the prognosis of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, F.; Wen, W. Prediction of radiotherapy response with a 5-microRNA signature-based nomogram in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.F.; Liu, C.J.; Chiu, P.C.; Lin, J.S.; Chang, K.W.; Shih, W.Y.; Kao, S.Y.; Tu, H.F. MicroRNA-31 upregulation predicts increased risk of progression of oral potentially malignant disorder. Oral Oncol. 2016, 53, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miladinovic, B.; Hozo, I.; Djulbegovic, B. Trial Sequential Boundaries for Cumulative Meta-Analyses. Stata J. 2013, 13, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Rawi, N.; Elmabrouk, N.; Abu Kou, R.; Mkadmi, S.; Rizvi, Z.; Hamdoon, Z. The role of differentially expressed salivary microRNA in oral squamous cell carcinoma—A systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 125, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).