Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic vLMW Fucoidan Formulas Decrease PD-L1 Surface Expression in EBV Latency III and DLBCL Tumoral B-Cells by Decreasing Actin Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
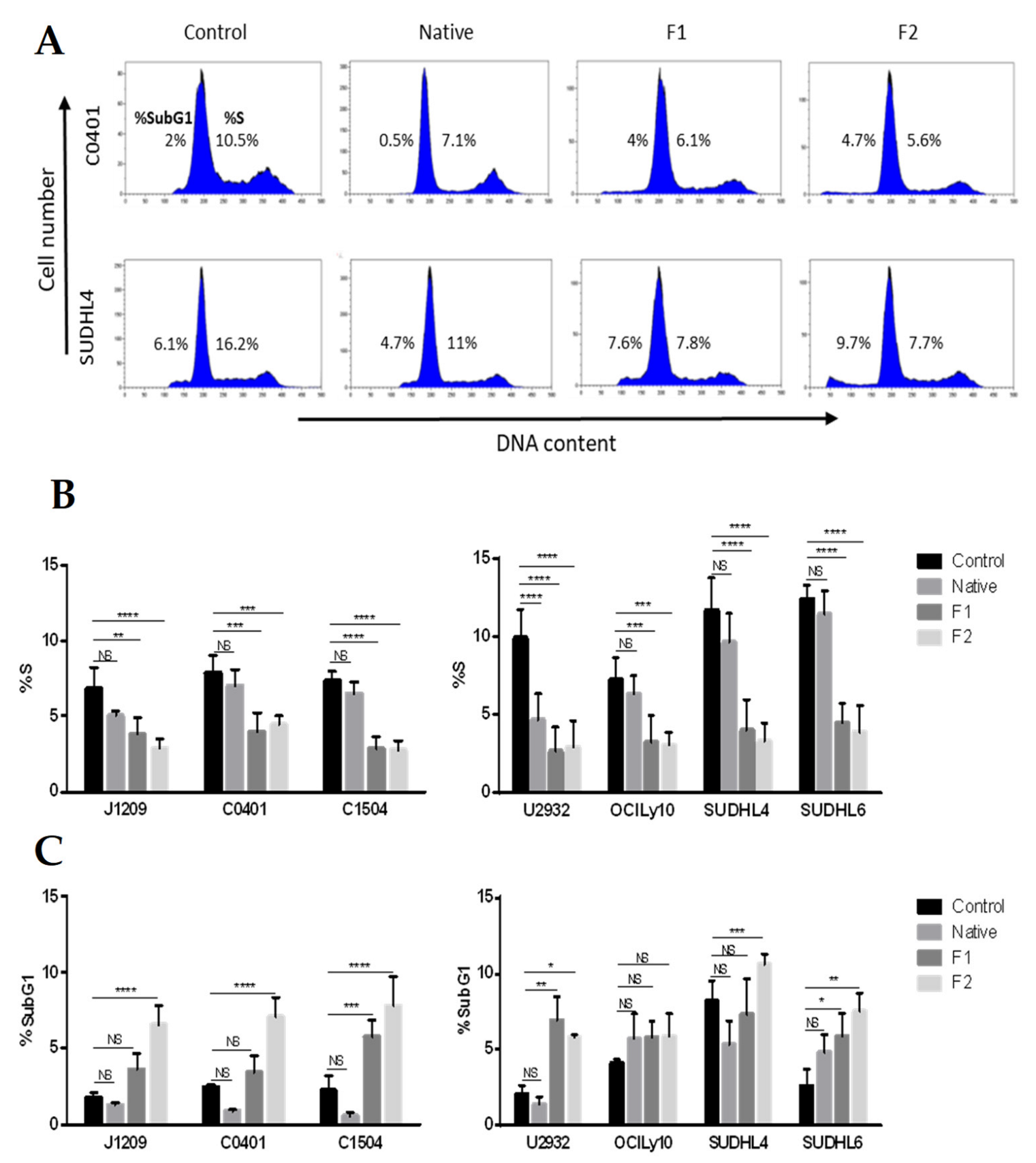
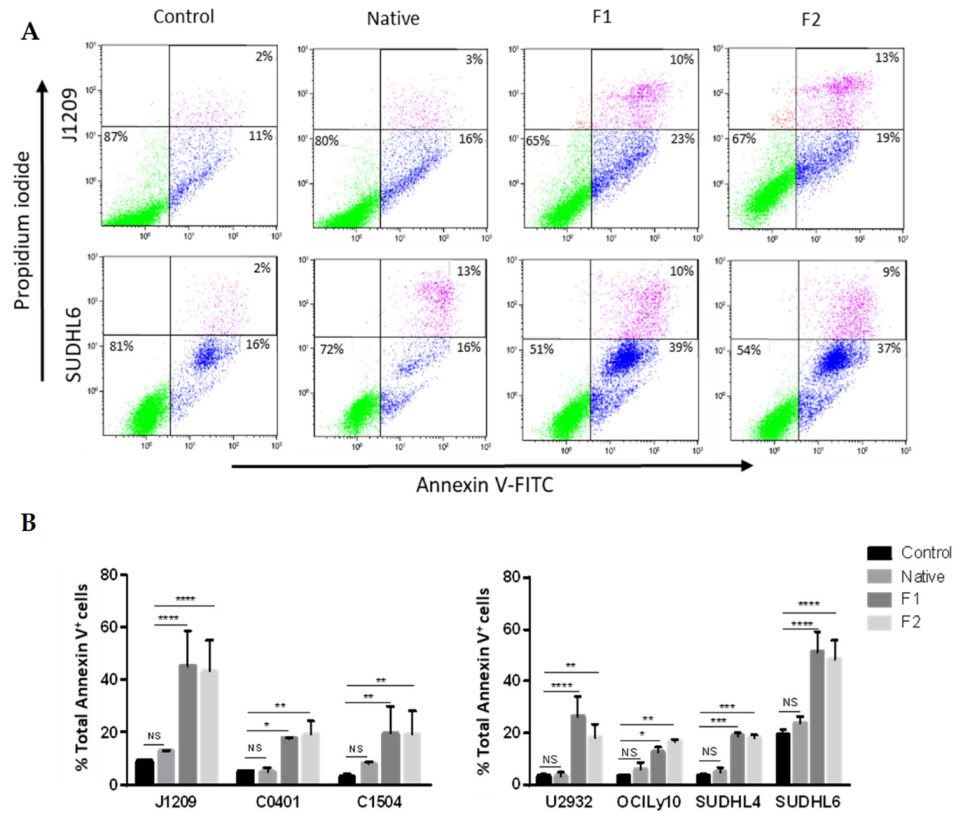
2.1. Proliferation Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction of Tumoral B-Cells
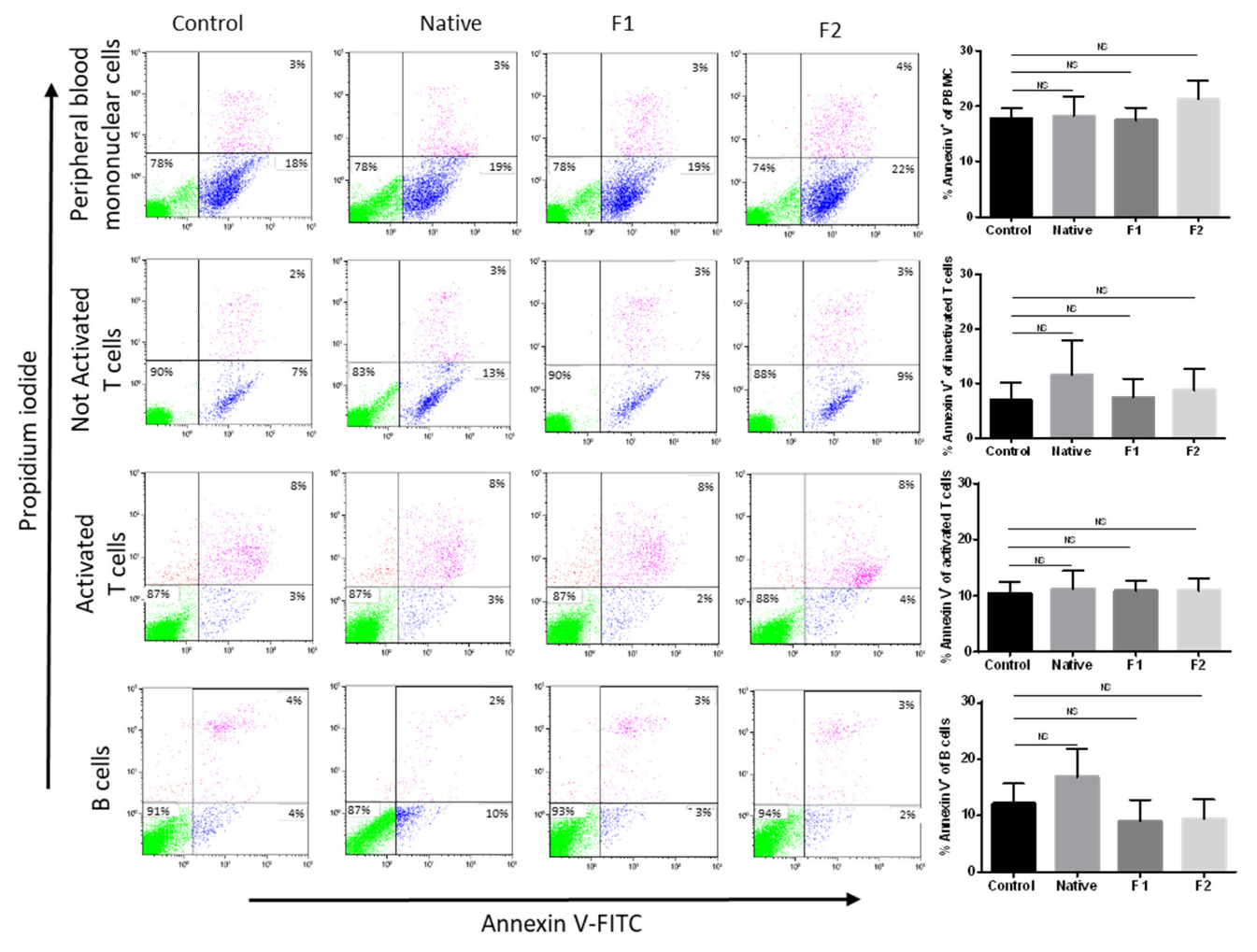
2.2. Absence of Toxicity for Normal B- and T-Cells
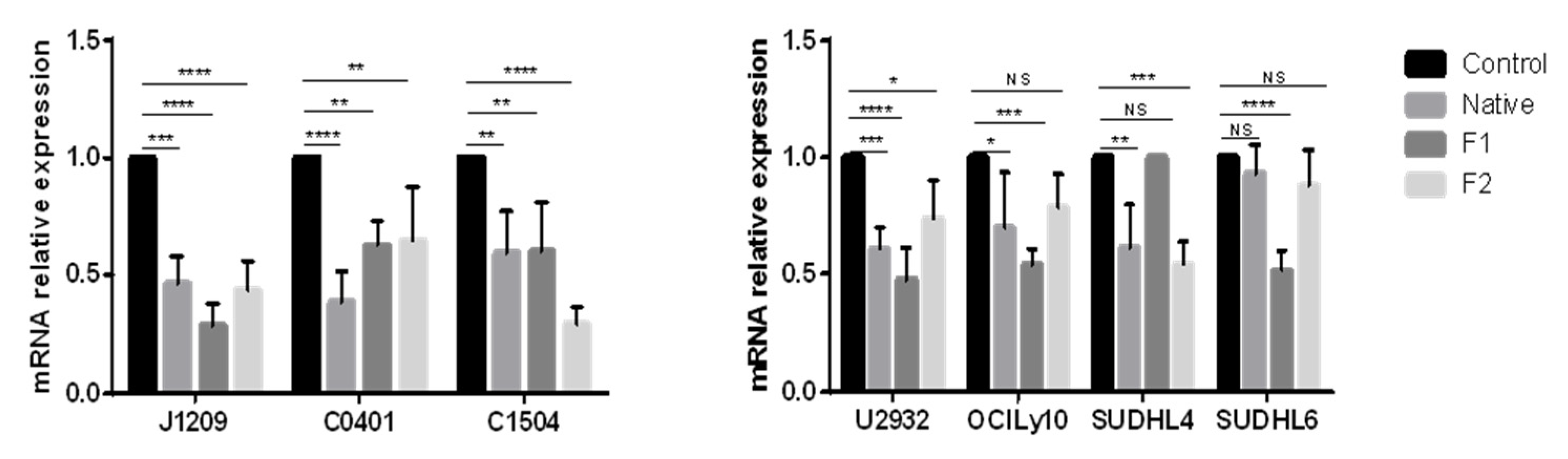
2.3. Decrease in PD-L1 Transcriptional Expression
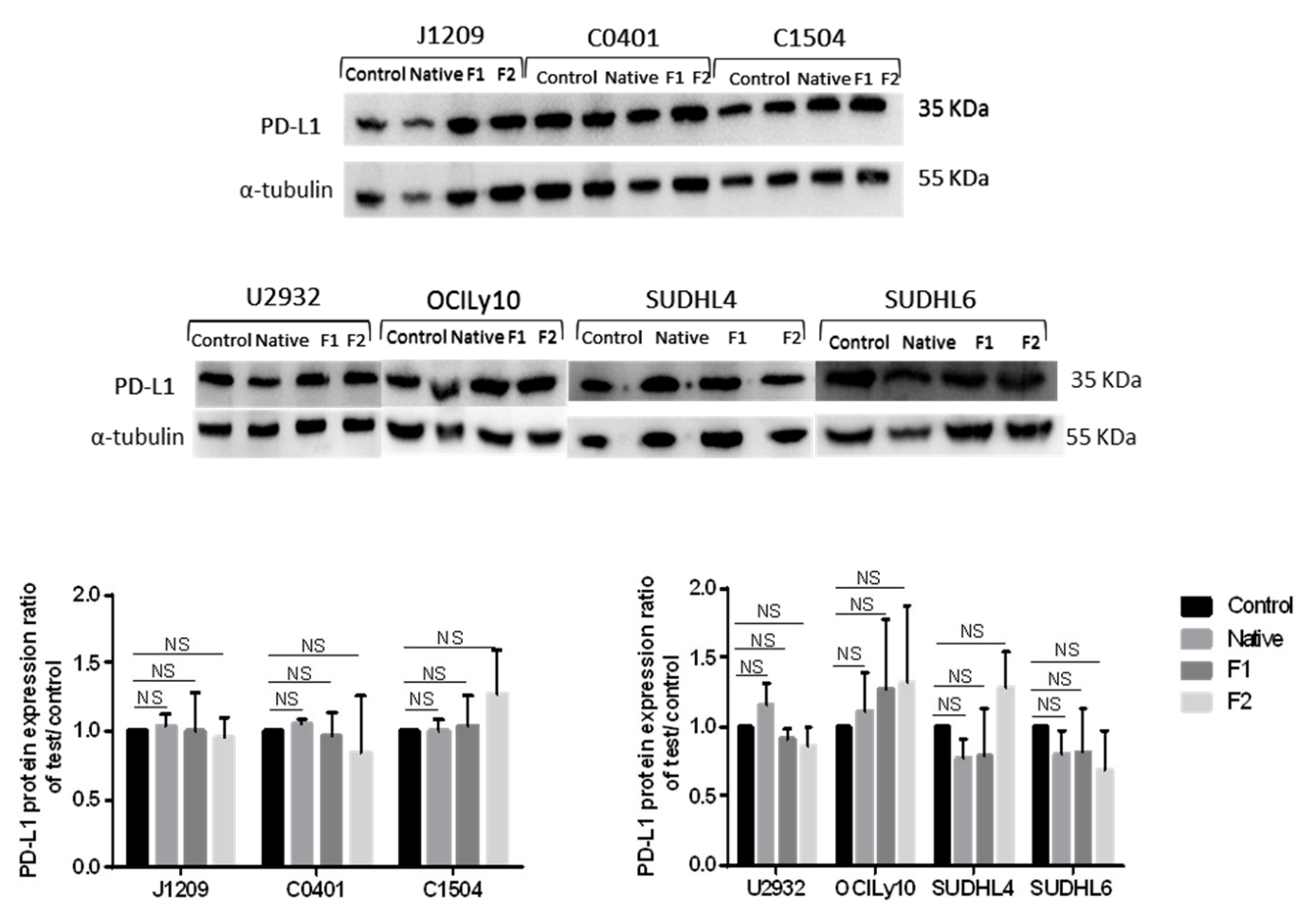
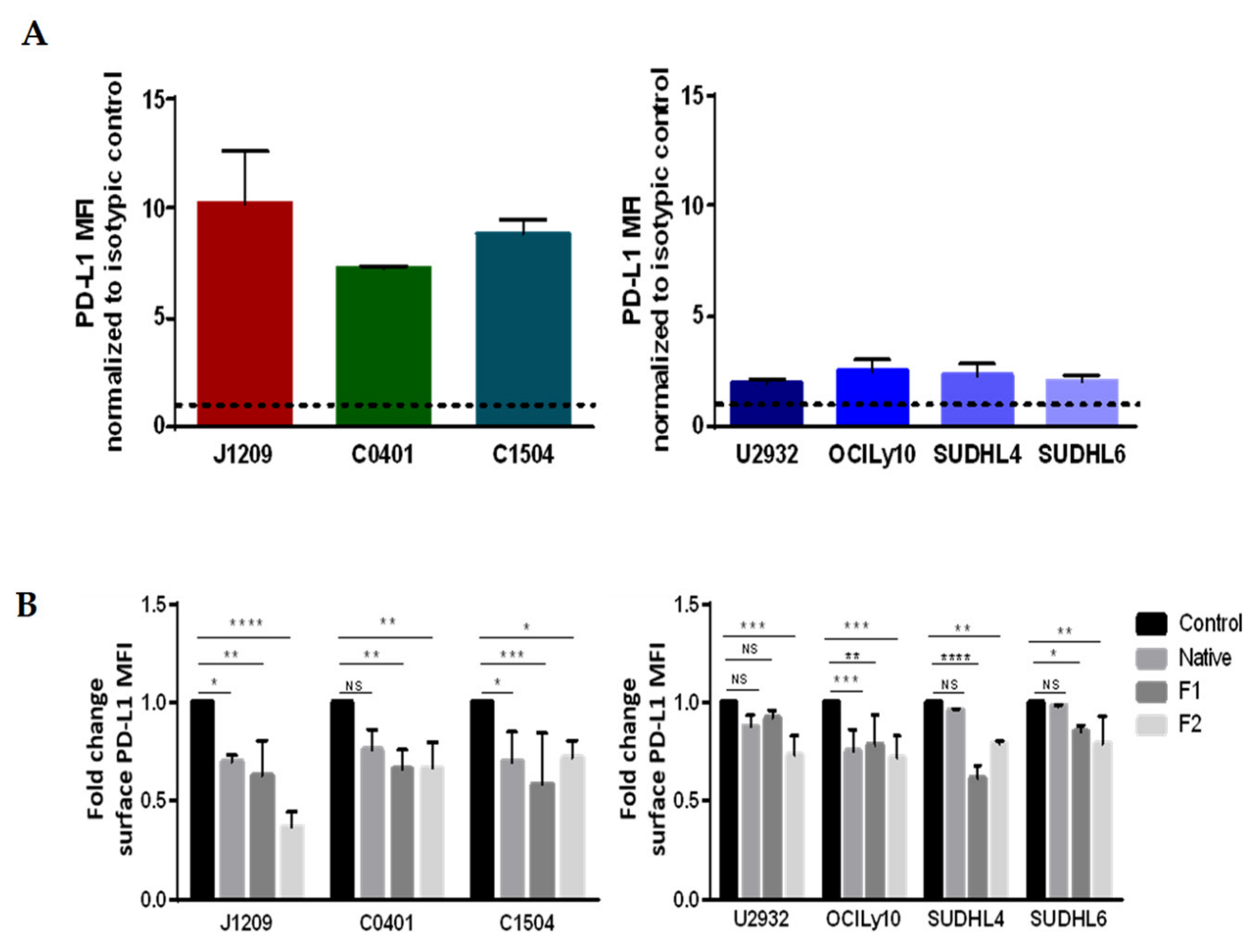
2.4. Decrease of membrane, but Not of total, PD-L1 protein expression
2.5. Disruption of Actin Network and Decrease in Secretory Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fucoidan Samples
4.2. Cell Culture Conditions
4.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.4. Apoptosis Analysis
4.5. Isolation of Healthy PBMC and Cell Subtypes (B- and T-Cells) for Apoptosis Assay
4.6. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcriptase and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. PD-L1 Expression Analysis: Immunofluorescent Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.9. F-Actin Cytoskeleton Immunofluorescence
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowe, M.; Raithatha, S.; Shannon-Lowe, C. Counteracting Effects of Cellular Notch and Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA2: Implications for Stromal Effects on Virus-Host Interactions. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12065–12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanibar-Adaniya, S.; Barta, S.K. 2021 Update on Diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A review of current data and potential applications on risk stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xu, C. Immune checkpoint signaling and cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.-H.; Chan, L.-C.; Li, C.-W.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.-C. Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, Z.P.; Gu, W. PD-L1 Distribution and Perspective for Cancer Immunotherapy—Blockade, Knockdown, or Inhibition. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, H.; Ouk-Martin, C.; Roland, L.; Santa, P.; Mohamad, H.A.; Faumont, N.; Feuillard, J.; Jayat-Vignoles, C. EBV Latency III–Transformed B Cells Are Inducers of Conventional and Unconventional Regulatory T Cells in a PD-L1–Dependent Manner. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussiotis, V.A. Cell-specific PD-L1 expression in DLBCL. Blood 2015, 126, 2171–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Nishikori, M.; Kitawaki, T.; Sakai, T.; Hishizawa, M.; Tashima, M.; Kondo, T.; Ohmori, K.; Kurata, M.; Hayashi, T.; et al. PD-1-PD-1 ligand interaction contributes to immunosuppressive microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3220–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Ao, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X. Soluble immune checkpoints in cancer: Production, function and biological significance. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Arooj, S.; Wang, H. Soluble B7-CD28 Family Inhibitory Immune Checkpoint Proteins and Anti-Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 651634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, M.; Naidoo, J. Immune-related adverse events and the balancing act of immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, J.M.; Bigenwald, C.; Champiat, S.; Collins, M.; Carbonnel, F.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Berdelou, A.; Varga, A.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 54, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, D.J.; Carlino, M.S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Huang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y. Improvement of the anticancer efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via combination therapy and PD-L1 regulation. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-O.; Chauhan, P.S.; Arukha, A.P.; Chavda, V.; Dubey, A.; Yadav, D. The Therapeutic Potential of the Anticancer Activity of Fucoidan: Current Advances and Hurdles. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citkowska, A.; Szekalska, M.; Winnicka, K. Possibilities of Fucoidan Utilization in the Development of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products. In Assessment Report on Fucus vesiculosus L., Thallus; European Medecine Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 55.
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.N.; Karpiniec, S.S. Therapies from Fucoidan: An Update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5920–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological Activities of Fucoidan and the Factors Mediating Its Therapeutic Effects: A Review of Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Liang, H.; Tang, Q.; Xue, C.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Bian, K.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Protective and Immunomodulatory Effects of Fucoidan Against 7,12-Dimethyl benz[a]anthracene-Induced Experimental Mammary Carcinogenesis Through the PD1/PDL1 Signaling Pathway in Rats. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruya, K.; Kusumoto, Y.; Eto, H.; Nakamichi, N.; Shirahata, S. Selective Suppression of Cell Growth and Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Expression in HT1080 Fibrosarcoma Cells by Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan Extract. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-O.; Song, M.-G.; Kim, Y.-N.; Park, J.-I.; Kwak, J.-Y. The mechanism of fucoidan-induced apoptosis in leukemic cells: Involvement of ERK1/2, JNK, glutathione, and nitric oxide. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 49, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, E. Fucoidan from Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Lung Cancer Cell via PI3K-Akt-mTOR Pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, H.-J.; Hong, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-C.; Kang, J.-I.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, E.-J.; Hyun, J.-W.; Koh, Y.-S.; Yoo, E.-S.; Kwon, J.-M.; et al. The Anticancer Effect of Fucoidan in PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2982–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, C. The Natural Product Fucoidan Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Ovarian Cancer Cells: Focus on the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6195–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Antitumor Effects of Fucoidan on Human Colon Cancer Cells via Activation of Akt Signaling. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, C.C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.D. Regulation of PD-L1: A novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashrazm, F.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Woods, G.M.; Holloway, A.F.; Dickinson, J.L. Fucoidan and Cancer: A Multifunctional Molecule with Anti-Tumor Potential. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2327–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, L.; Burney, M.; Gaikwad, A.; Nyshadham, P.; Nugent, E.K.; Gonzalez, A.; Smith, J.A. Preclinical Evaluation of Safety of Fucoidan Extracts from Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus for Use in Cancer Treatment. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, H.; Xue, K.; Xu, S.; Tian, Z. The anti-cancer effects of fucoidan: A review of both in vivo and in vitro investigations. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, M.E.; Riquelme, I.; Salvo, T.; Zanella, L.; Letelier, P.; Brebi, P. Brown Seaweed Fucoidan in Cancer: Implications in Metastasis and Drug Resistance. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent-Fabert, C.; Roland, L.; Zimber-Strobl, U.; Feuillard, J.; Faumont, N. Pre-clinical blocking of PD-L1 molecule, which expression is down regulated by NF-κB, JAK1/JAK2 and BTK inhibitors, induces regression of activated B-cell lymphoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Pan, W.; Wang, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ji, Y.; Bei, J.-X.; et al. Fucoidan-Supplemented Diet Potentiates Immune Checkpoint Blockage by Enhancing Antitumor Immunity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 733246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Chen, D.; Ye, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lui, E.M.K.; Xue, C.; Xiao, M. Fucoidan Isolated from Saccharina japonica Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation in Macrophages via Blocking NF-κB, MAPK and JAK-STAT Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand-Panteix, S.; Farhat, M.; Youlyouz-Marfak, I.; Rouaud, P.; Ouk-Martin, C.; David, A.; Faumont, N.; Feuillard, J.; Jayat-Vignoles, C. B7-H1, which represses EBV-immortalized B cell killing by autologous T and NK cells, is oppositely regulated by c-Myc and EBV latency III program at both mRNA and secretory lysosome levels. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-L.; Tai, C.-J.; Huang, C.-W.; Chang, F.-R.; Wang, J.-Y. Efficacy of Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan as a Supplemental Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, G.-Y.; Cha, H.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, N.D.; Yoo, Y.H.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis by fucoidan in human leukemia U937 cells through activation of p38 MAPK and modulation of Bcl-2 family. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2347–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Xie, B.; Gao, M.; Tao, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhan, F.; Dai, B.; Shi, J.; et al. Antitumor activity of fucoidan against diffuse large B cell lymphoma in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2015, 47, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.-A.; Yan, M.-D.; Lin, H.-T.V.; Li, K.-L.; Lin, Y.-C. Toxicological Evaluation of Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Nikolova, M.; Iliev, I.; Peychev, L.; Trica, B.; Oancea, F.; Delattre, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Yadav, D.; Lee, P.C.; Jin, J.-O. Immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from marine algae for treating cancer, infectious disease, and inflammation. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.S.; Passos, C.P.; Madureira, P.; Vilanova, M.; Coimbra, M.A. Structure-function relationships of immunostimulatory polysaccharides: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-O.; Zhang, W.; Du, J.-Y.; Wong, K.-W.; Oda, T.; Yu, Q. Fucoidan can function as an adjuvant in vivo to enhance dendritic cell maturation and function and promote antigen-specific T cell immune responses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Oda, T.; Yu, Q.; Jin, J.-O. Fucoidan from Macrocystis pyrifera has powerful immune-modulatory effects compared to three other fucoidans. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Okimura, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. The potent activity of sulfated polysaccharide, ascophyllan, isolated from Ascophyllum nodosum to induce nitric oxide and cytokine production from mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells: Comparison between ascophyllan and fucoidan. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2011, 25, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidan from Sargassum sp. and Fucus vesiculosus reduces cell viability of lung carcinoma and melanoma cells in vitro and activates natural killer cells in mice in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Mao, R.; Fan, Y. The generation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in cancer cells: From nuclear chromatin reorganization to extracellular presentation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, W.; Young, K.H.; Li, Y. Posttranslational Modifications in PD-L1 Turnover and Function: From Cradle to Grave. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Bademosi, A.T.; Luo, J.; Meunier, F.A. Actin Remodeling in Regulated Exocytosis: Toward a Mesoscopic View. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat-Shliom, N.; Milberg, O.; Masedunskas, A.; Weigert, R. Multiple roles for the actin cytoskeleton during regulated exocytosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2099–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aseervatham, J. Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Cancer. Biology 2020, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, R.; Diaz, R.J. The remodelling of actin composition as a hallmark of cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Deng, S.; Gopal, V.; Yap, K.C.-H.; Halim, C.E.; Lye, M.L.; Ong, M.S.; Tan, T.Z.; Sethi, G.; Hooi, S.C.; et al. Cytoskeletal Dynamics in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Insights into Therapeutic Targets for Cancer Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, M.S.; Deng, S.; Halim, C.E.; Cai, W.; Tan, T.Z.; Huang, R.Y.-J.; Sethi, G.; Hooi, S.C.; Kumar, A.P.; Yap, C.T. Cytoskeletal Proteins in Cancer and Intracellular Stress: A Therapeutic Perspective. Cancers 2020, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwack, K.H.; Ji, J.Y.; Park, B.; Heo, J.S. Fucoidan (Undaria pinnatifida)/Polydopamine Composite-Modified Surface Promotes Osteogenic Potential of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Tsai, G.-Y.; Hsu, F.-Y.; Hwang, P.-A. Protective Effect of Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan on Radiation-Induced Fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smad Pathway-Mediated Inhibition of Collagen I Accumulation. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Pawar, J.S.; Ghosh, I. Fucoidan induces ROS-dependent epigenetic modulation in cervical cancer HeLa cell. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, X.; Xu, J. Lysosome as the Black Hole for Checkpoint Molecules. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1248, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, G. Exosome and Secretion: Action On? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1248, 455–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Li, H.; Li, R.-J.; Yin, L.; Zhang, H.-F.; Huang, Z.-N.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.-H.; Peng, H.-L. The roles of exosomal immune checkpoint proteins in tumors. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.M.; Câmara, R.B.G.; Monte, J.F.S.; Viana, R.L.S.; Melo, K.R.T.; Queiroz, M.F.; Filgueira, L.G.A.; Oyama, L.M.; Rocha, H.A.O. Commercial Fucoidans from Fucus vesiculosus Can Be Grouped into Antiadipogenic and Adipogenic Agents. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, J. Oligosaccharides from land plants and algae: Production and applications in therapeutics and biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Silva, M.; Radziun, K.; Martinez, D.C.; Hill, C.J.; Marshall, J.; Hearnden, V.; Puertas-Mejia, M.A.; Reilly, G.C. Fucoidan Inhibition of Osteosarcoma Cells is Species and Molecular Weight Dependent. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Hwang, P.-A. Clinical applications of fucoidan in translational medicine for adjuvant cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.-Y. Fucoidan as a marine anticancer agent in preclinical development. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.Y.; Nafia, I.; Stringer, D.N.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Fitton, J.H. Fucoidan Independently Enhances Activity in Human Immune Cells and Has a Cytostatic Effect on Prostate Cancer Cells in the Presence of Nivolumab. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hwang, J.; Yadav, D.; An, E.-K.; Kwak, M.; Lee, P.C.-W.; Jin, J.-O. Enhancement of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Mediated Anti-Cancer Immunity by Intranasal Treatment of Ecklonia cava Fucoidan against Metastatic Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, E.-K.; Hwang, J.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, H.-B.; Zhang, W.; Ryu, J.-H.; You, S.; Jin, J.-O. Comparison of the immune activation capacities of fucoidan and laminarin extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groult, H.; Cousin, R.; Chot-Plassot, C.; Maura, M.; Bridiau, N.; Piot, J.-M.; Maugard, T.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I. λ-Carrageenan Oligosaccharides of Distinct Anti-Heparanase and Anticoagulant Activities Inhibit MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Migration. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | H2O2 (w/w) | Time (h) | Mn (Da) | DP | I | DS (% SO3−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native fucoidan | 0 | 0 | 66744 * | 240.5 * | 1.4 * | 41.5 ± 0.7 |
| F1 fraction | 0.5 | 96 | 604 ** | 3.5 ** | 1.3 ** | 6.0 ± 1.0 |
| F2 fraction | 1.5 | 72 | 562 ** | 3.4 ** | 1.1 ** | 2.1 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saliba, J.; Manseur, C.; Groult, H.; Akil, H.; Tannoury, M.; Troutaud, D.; Maugard, T.; Feuillard, J.; Arnaudin, I.; Jayat-Vignoles, C. Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic vLMW Fucoidan Formulas Decrease PD-L1 Surface Expression in EBV Latency III and DLBCL Tumoral B-Cells by Decreasing Actin Network. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020132
Saliba J, Manseur C, Groult H, Akil H, Tannoury M, Troutaud D, Maugard T, Feuillard J, Arnaudin I, Jayat-Vignoles C. Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic vLMW Fucoidan Formulas Decrease PD-L1 Surface Expression in EBV Latency III and DLBCL Tumoral B-Cells by Decreasing Actin Network. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaliba, Jennifer, Chanez Manseur, Hugo Groult, Hussein Akil, Mona Tannoury, Danielle Troutaud, Thierry Maugard, Jean Feuillard, Ingrid Arnaudin, and Chantal Jayat-Vignoles. 2023. "Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic vLMW Fucoidan Formulas Decrease PD-L1 Surface Expression in EBV Latency III and DLBCL Tumoral B-Cells by Decreasing Actin Network" Marine Drugs 21, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020132
APA StyleSaliba, J., Manseur, C., Groult, H., Akil, H., Tannoury, M., Troutaud, D., Maugard, T., Feuillard, J., Arnaudin, I., & Jayat-Vignoles, C. (2023). Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic vLMW Fucoidan Formulas Decrease PD-L1 Surface Expression in EBV Latency III and DLBCL Tumoral B-Cells by Decreasing Actin Network. Marine Drugs, 21(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020132








