Abstract
A chemical-epigenetic method was used to enhance the chemodiversity of a marine algicolous fungus. Apart from thirteen known compounds, (+)-brevianamide R ((+)-3), (‒)-brevianamide R ((‒)-3), (+)-brevianamide Q ((+)-4), (‒)-brevianamide Q ((‒)-4), brevianamide V ((+)-5), brevianamide W ((‒)-5), brevianamide K (6), diorcinol B (7), diorcinol C (8), diorcinol E (9), diorcinol J (10), diorcinol (11), 4-methoxycarbonyldiorcinol (12), two new compounds, (+)- and (‒)-brevianamide X ((+)- and (‒)- 2)), as well as a new naturally occurring one, 3-[6-(2-methylpropyl)-2-oxo-1H-pyrazin-3-yl]propanamide (1), were isolated from chemical-epigenetic cultures of Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 with 10 µM vorinostat (SAHA). Compared to cultures in the same medium without SAHA, compounds 1–4, 8, 9, 11, and 12 were solely observed under SAHA condition. The structures of these compounds were elucidated based on spectroscopic analysis, specific rotation analysis, ECD, and X-ray crystallographic analysis. (±)-3, (±)-4, and (±)-5 were further resolved into the corresponding optically pure enantiomers and their absolute configurations were determined for the first time. Compounds 11 and 12 showed selective antibacterial against Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 17.4 and 13.9 μM, respectively. Compound 10 exhibited better α-glucosidase inhibitory activity than the assay control acarbose with IC50 values of 117.3 and 255.3 μM, respectively.
1. Introduction
Marine natural products (NPs) are an important source for developing new drugs, especially those from marine-derived fungi which possess novel structures and significant biological activities [1,2]. Aspergillus is a kind of productive fungal genus and has been reported to produce many new NPs [3], such as alkaloids [4,5,6], diketopiperazines [7,8], xanthones [8], and diphenyl ethers [9]. However, the whole genome sequencing studies of fungi have indicated that most genes of fungi were silent and not expressed in the conventional experimental conditions. Fungi treated with DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors enhanced NPs’ chemical diversity, demonstrating that small molecule epigenetic modifiers are effective tools for rationally generating new and bioactive NPs [10]. Both molecular-based and chemical approaches targeting histone and DNA posttranslational processes have the great potential for rationally activating or suppressing NP-encoding gene clusters [11,12,13]. Epigenetic modification has become a widely applied strategy to find new and bioactive NPs today [14,15,16].
In our continuous study on the discovery of new and bioactive NPs from algicolous microorganisms isolated from Enteromorpha prolifera by epigenetic modification [12,13] and other strategies [17,18,19], we found that the algicolous Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 could produce different NPs after chemical-epigenetic modification by 10 µM SAHA. From the epigenetically modified fermentation of A. versicolor OUCMDZ-2738, we isolated and identified a new naturally occurring compound 1, two new enantiomers ((+)-2 and (‒)-2), and thirteen known compounds (3–12). Their structures were determined as 3-[6-(2-methylpropyl)-2-oxo-1H-pyrazin-3-yl] propanamide (1), (+)-brevianamide X ((+)-2) and (‒)-brevianamide X ((‒)-2), (±)-brevianamide R (3) [20], (±)-brevianamide Q (4) [20], brevianamide V ((+)-5) [21], brevianamide W ((‒)-5) [22], brevianamide K (6) [23], diorcinol B (7) [24], diorcinol C (8) [24], diorcinol E (9) [24], diorcinol J (10) [24], diorcinol (11) [25], and methyl diorcinol-4-carboxylate (12) [26,27], respectively (Figure 1). (±)-Brevianamide R (3) and (±)-brevianamide Q (4) were further resolved as (+)- and (‒)- brevianamide R ((+)- and (‒)- 3) and (+)- and (‒)- brevianamide Q ((+)- and (‒)- 4), respectively.
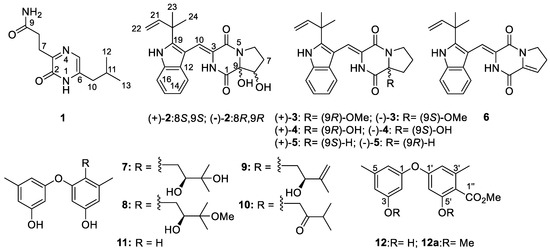
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1−12.
2. Results and Discussion
Compound 1 was isolated as a brown, amorphous powder. The molecular formula was determined as C11H17O2N3 by a HRESIMS peak at m/z 246.1205 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H17O2N3Na, 246.1213) (Supplementary Figure S1). 1D (Table 1 and Supplementary Figures S2 and S3) and HSQC (Supplementary Figure S5) NMR spectra displayed one sp2 methine (δC 120.8, δH 7.01), one sp3 methine (δC 27.5, δH 1.91), three sp3 methylenes (δC 27.6, δH 2.79; δC 31.1, δH 2.41; δC 38.4, δH 2.25), and two methyls (δC 21.9, δH 0.86; δC 21.9, δH 0.84) (Table 1). The HMBC (Supplementary Figure S7 and Figure 2) correlations from H-7 (δH 2.79), H-8 (δH 4.64), and NH2 (δH 7.30, δH 6.72) to carbonyl carbon (δC-9 173.7) along with the 1H–1H COSY (Supplementary Figure S6 and Figure 2) between H-7 and H-8 indicated a 3-substituted propionamide moiety. 1H–1H COSY correlations from H-10 (δH 2.25) to H-12 (δH 0.86), and H-13 (δH 0.84) through H-11 (δH 1.91), demonstrated an isobutyl fragment. The remaining fragment, C4H2ON2, could be a pyrazin-2(1H)-one nucleus from the HMBC correlations from H-4 (δH 7.01) to C-3 (δC 155.2) and C-6 (δC 138.0). Furthermore, the key HMBC correlations from H-10 to C-5 (δC 120.8) and C-6, and H-7 to C-2 (δC 156.2) and C-3, allowed for the linkage of the isobutyl to C-6 and the 3-substituted propionamide moiety to C-3, respectively. Thus, structure 1 was established as 3-[6-(2-methylpropyl)-2-oxo-1H-pyrazin-3-yl] propenamide, which was only recorded in the Aurora Fine Chemicals with ID number K13.052.726 without any physical and chemical properties reported. Consequently, 1 was identified as a new naturally occurring compound.

Table 1.
1H (400 MHz) and 13C (100 MHz) NMR data of 1 in DMSO-d6 and 2 in MeOH-d4.
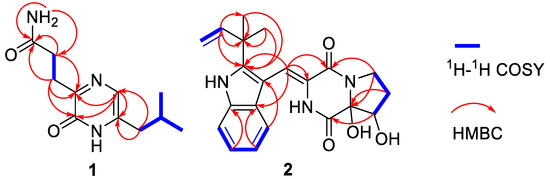
Figure 2.
Key HMBC and 1H–1H COSY correlations of 1 and 2.
The racemic 2 was isolated as light yellow crystal with the molecular formula of C21H23N3O4 from a HRESIMS peak at m/z 404.1570 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C21H23N3O4Na, 404.1581) (Supplementary Figure S8). Its 1D (Table 1 and Supplementary Figures S9 and S10) and HSQC (Supplementary Figure S12) NMR spectra displayed two methyls (δC 28.1, δH 1.57; δC 28.3, δH 1.54), two sp3 methylenes (δC 44.7, δH 3.96, δH 3.72; δC 29.0, δH 1.93, δH 2.41), one sp3 methine (δC 76.4, δH 4.41), five sp2 methines (δC 115.1, δH 7.29; δC 120.2, δH 7.37; δC 121.3, δH 7.07; δC 122.6, δH 7.12; δC 122.6, δH 7.43), and one sp2 methylene (δC 112.6, δH 5.10, 5.13), which demonstrated the presence of a monosubstituted double bond (Table 1). 1H–1H COSY (Supplementary Figure S13 and Figure 2) from H-21 (δH 6.11) to H-22 (δH 5.10; δH 5.13) and the HMBC (Supplementary Figure S14 and Figure 2) from H-21 (δH 6.11) to C-20 (δC 40.5), C-23 (δC 28.1), and C-24 (δC 28.3), along with H-23 (δH 1.57) to C-20 and C-24, which demonstrated the presence of a 2-methylbut-3-en-2-yl fragment. The 1H–1H COSY correlations from H-13 (δH 7.37) to H-16 (δH 7.43), along with the HMBC from H-13 (δH 7.37) to C-12 (δC 127.4), C-11 (δC 104.5), and C-17 (δC 127.4), and H-16 (δH 7.43) to C-12 and C-17, which demonstrated the presence of a 2,3-bisubstituted indole ring. Moreover, the key HMBC from H-21, H-23, and H-24 (δH 1.54) to C-19 (δC 146.2) connected the 2-methylbut-3-en-2-yl group to C-19 of the indole ring. Chemical shifts of C-1 (δC 165.7) and C-4 (δC 161.3) indicated two amide carbonyl carbons. In addition, 1H–1H COSY correlations from H-6 (δH 3.72; δH 3.96) to H-8 (δH 4.41) through H-7 (δH 1.93; δH 2.41) and HMBC correlations from H-6 to C-4 and C-9 (δC 91.0), H-7 to C-9, H-8 (δH 4.41) to C-1 and C-9 and, H-10 (δH 7.29) to C-3 (δC 125.1) and C-4 were observed. This data indicated a 2-methylene-(2,3-dihydroxytetrahydro) pyrrolo[1,2-a] diketopiperazine nucleus. The key HMBC correlations from H-10 to C-11, C-12, and C-19 (Figure 2) allowed for the linkage of the isopentenylindole and tetrahydropyrrolo[1,2-a] diketopiperazine moieties by a C-11–C-10 sigma bond. Thus, the planar structure of 2 was determined as 9-hydroxybrevianamide Q. A literature survey showed that 2 has the same planar structure as brevianamide U without resolution of the configuration ( +20 (c 0.17, MeOH)) [21]. Although their 1H and 13C NMR data were similar, they displayed obvious different chemical shifts of C-1 and C-9 in 13C NMR, indicating the different configurations. The configuration of 2 was confirmed by X-ray single crystallographic diffraction that clearly indicated trans-configuration between 8-OH and 9-OH and the Z-geometry of the ∆3(10)-double bond (Figure 3). However, the X-ray crystallographic results were space group P-1 and the planus line of the electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectrum indicated 2 might be a pair of enantiomers. Thus, two enantiomers with 1.1:1 ratio of HPLC peaks area were separated by a chiral column (Supplementary Figure S15A), whose specific rotations were +44 and –40 (c 0.05, MeOH), respectively. The absolute configurations of (+)-2 and (–)-2 were respectively assigned as (8S, 9S) and (8R, 9R) by comparing the experimental and calculated ECD values obtained using TD-DFT at the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level [19,28,29] (Figure 4). Therefore, we named (+)-2 and (–)-2 as (+)-brevianamide X and (–)-brevianamide X, respectively.
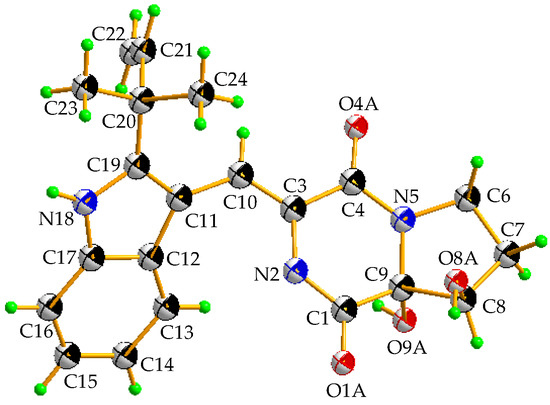
Figure 3.
X-ray crystallographic structure of 2.
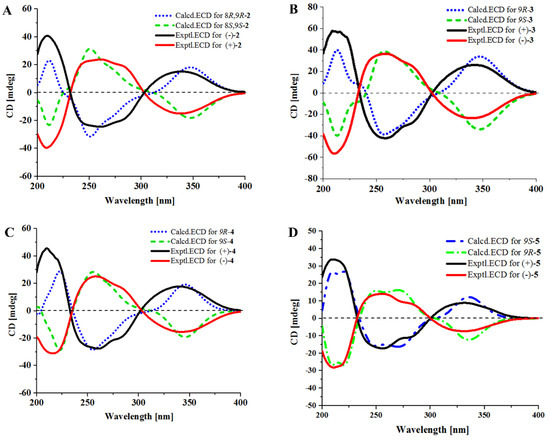
Figure 4.
Experimental and calculated ECD spectra of 2 (A), 3 (B), 4 (C) and 5 (D).
The planar structures of compounds 3–5 were reported previously without assignment of the absolute configurations [20,22]. Their small specific rotations, +10 (c 0.82, MeOH) for 3, –7 (c 1.75, MeOH) for 4, and +19 (c 0.33, MeOH) for 5, indicated that compounds 3–5 might be enantiomeric mixtures, perhaps having an excess of one of the enantiomers. They were analyzed and resolved by chiral HPLC. As we expected, (±)-3, (±)-4, and (±)-5 were further separated into their optically pure enantiomers (Supplementary Figure S15B–D). The absolute configurations were determined by comparing the experimental ECD with those calculated using TD-DFT at the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level (Figure 4). As a result, compounds (+)-3 and 4 were assigned to have a 9R-configuration, while the (–)-3 and 4 were assigned a 9S-configuration. This is the first time that racemic brevianamides R (3), Q (4), and V (5) have been resolved into their chiral enantiomers and their absolute configurations have been determined.
The structures of 6–11 were determined by comparing their NMR data and specific rotations those reported [23,24,25]. Although the structure of 12 has been previously reported in the references, there were no 13C NMR data [26] and nor NMR solvent reported [27], and chemical shifts of 12 (Table 2) were obviously different to those in ref. [27]. The difficulty was in the assignment of the position of the methoxycarbonyl group at C-2′ or C-4′. Thus, its dimethyl ether (12a) was prepared from 12 by reaction with MeI/K2CO3 and the 2D NMR of both 12 (Supplementary Figures S21–S23) and 12a (Supplementary Figures S27–S29) were recorded. The ROESY correlations of CH3O-5′ (δH 3.72) with H-6′(δH 6.61) and the protons (δH 3.78) of the methyl ester in 12a (Supplementary Figure S28 and Figure 5) located the methoxycarbonyl group at C-4′. Therefore, the structures of compounds 12 and 12a were determined as methyl diorcinol-4-carboxylate and methyl 3,3′-di(O-methyl) diorcinol-4-carboxylate, respectively.

Table 2.
1H (400 MHz) and 13C (100 MHz) NMR data of 12 and 12a in DMSO-d6.
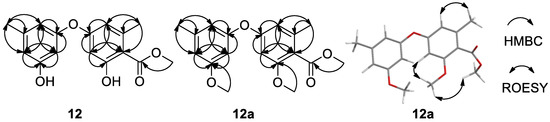
Figure 5.
HMBC correlations of 12 and 12a, and key ROESY correlations of 12a.
A plausible biosynthetic relationship linking 2–6 through a sequence of oxidative transformations and hydrolysis or methanolysis is illustrated in Figure 6. Positions 8 and 9 in 6 have no steric hindrance when performing electrophilic addition or oxidation. Therefore, it is easy to form enantiomeric mixtures or excess of 2–5.
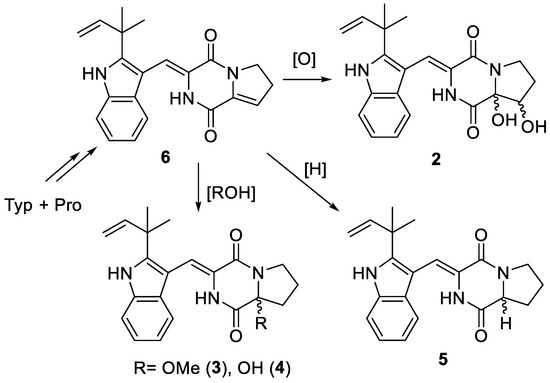
Figure 6.
Plausible biosynthetic relationship among 2–6.
HPLC-UV was used to identify which compounds are solely produced under SAHA. Both extracts, generated with and without addition of SAHA, were analyzed using the same elution gradient. Compared to those in the same medium without SAHA, epigenetic modification with SAHA enhanced the NP diversity of A. versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 and the compounds 1–4, 8, 9, 11, and 12 were solely observed under SAHA condition. This demonstrated SAHA as the actual inducer to produce compounds 1–4, 8, 9, 11, and 12 (Supplementary Figure S31 and Figure 7), further indicating that chemically epigenetic regulation is an effective method for expanding the chemical space of fungal natural products.
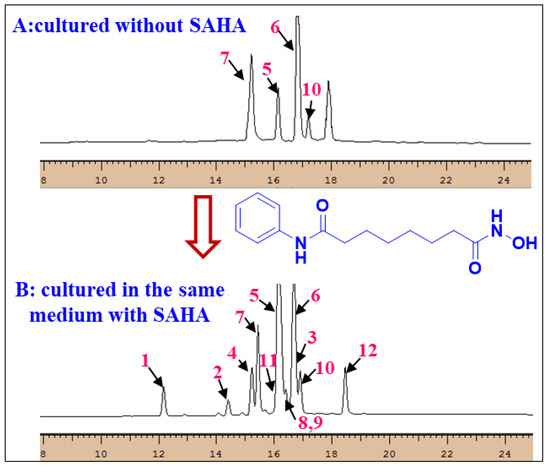
Figure 7.
HPLC-UV profiles of the fungal metabolites with and without SAHA.
All the isolated compounds (1–12) were evaluated for antibacterial activity against a panel of pathogenic microorganisms, including four Gram-positive bacteria, (Bacillus subtilis ATCC6051, Clostridium perfringens ATCC13048, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538, and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923), two Gram-negative bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC10145 and Escherichia coli ATCC11775), and two pathogenic fungi (Candida albicans ATCC10231, Candida glabrata ATCC2001). The results showed that compound 11 selectively inhibited P. aeruginosa while 12 inhibited P. aeruginosa and C. glabrata with MIC values of 17.4, 13.9, and 27.8 μM, respectively (Table 3). The inhibitory activities of 1–12 against α-glucosidase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae were also evaluated using the pNPG method. Only compounds 9–11 displayed α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 117.3, 237.4 and 275.3 μM, respectively. Acarbose, used as the assay control, had an IC50 of 255.3 μM.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial bioassay results of active compounds.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured using an AUTOPOL1 polarimeter (Rudolph Research Analytical, Hackettstown, NJ, USA). UV spectra were measured on a Beckman DU 640 spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA, USA). ECD spectra were measured on JASCOJ-715 spectropolarimeter (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). IR spectra were taken on a Nicolet Nexus 470 spectrophotometer (Thermo Nicolet Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) as KBr disks. 1D (one-dimensional) and 2D (two-dimensional) NMR spectra were recorded on an INOVA-400MHz spectrometer with TMS (tetramethylsilane) as the internal standard. ESIMS and HRESIMS were carried out on a Waters 2695 LCQ-MS liquid chromatography mass spectrometer (Thermo Finnigan, San Francisco, CA, USA). Semi-preparative HPLC separations were performed using a Hitachi Primaide Organizer HPLC system (Hitachi High-Tech Science Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). YMC-Pack ODS-A column (S-5 μm, 12 nm, 250 × 4.6 mm and S-5 μm, 12 nm, 250 × 10 mm, Shenzhen Chemist Technology Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, China). Chiral column (Lux® 5 µm Cellulose-2 and Lux® 5 µm i-Cellulose-5, LC Column 250 × 4.6 mm., Phenomenex, CA, USA). Thin layer chromatography (TLC) and column chromatography (CC) were performed on plates precoated with silica gel GF 254 (10–40 µm) and over silica gel (200–300 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China), respectively. Chemical reagents for isolation were analytical grade (Tianjin Kaixin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China); chromatographic grade MeOH for HPLC was from Tianjin Siyou Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China.
3.2. Fungal Material
The fungus Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 was isolated from a piece of fresh tissue from the Enteromorpha prolifera, collected from the Shilaoren beach, Qingdao, China, in July 2012 [12,13]. The pure cultures were deposited in the Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, Shandong province, China, with the GenBank (NCBI) accession number MH150818.
3.3. Cultivation and Extraction of Strain OUCMDZ-2738
The cultivation and extraction process were the same described in previous papers [12,13], and the EtOAc solutions were concentrated under reduced pressure to give a crude extract (13.1 g).
3.4. Purification
The crude extract was applied to a silica gel (200–300 mesh) column and was separated into twelve fractions (Fr.1 to Fr.12) using a step-gradient elution of petroleum ether/EtOAc (0–100%) and CHCl3/MeOH.
Fr.1 (0.2 g) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (50:50 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give 1 (11.6 mg, tR 9.6 min). Fr.12 (0.24 g) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (70:30 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give the racemic-2 (8.0 mg, tR 6.5 min). Fr.7 (0.85 g) was separated on a preparative TLC eluted with CH2Cl2/CH3OH (v/v, 30:1), then subfraction Fr.7-1 (142.0 mg) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (70:30 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give compound 6 (78.6 mg, tR 6.4 min). Subfraction Fr.7-3 (101 mg) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (50:50 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give racemic-4 (9.3 mg, tR 8.3 min). Subfraction Fr.7-4 (75 mg) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (60:40 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give 9 (10.5 mg, tR 7.0 min) and 8 (5.3 mg, tR 8.1 min). Fr.8 (0.42 g) was separated on a preparative TLC eluted with CH2Cl2/MeOH (v/v, 50:1), then subfraction Fr.8-1 (178.3 mg) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (65:35 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give racemic-3 (7.3 mg, tR 8.0 min) and racemic-5 (90.0 mg, tR 8.5 min). Fr.5 (0.21 g) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (70:30 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give 7 (40.8 mg, tR 9.7 min) and 10 (9.8 mg, tR 8.7 min). Fr.4 (0.12 g) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (65:35 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give 11 (14.6 mg, tR 6.7 min). Fr.2 (0.18 g) was purified by semipreparative HPLC (70:30 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give 12 (48.6 mg, tR 7.3 min). The racemic-2 was resolved as the optically pure (+)-2 (1.0 mg, tR 13.7 min) and (–)-2 (1.1 mg, tR 10.5 min) by semi-preparative HPLC (25:75 MeCN/H2O, 0.9 mL/min) equipped with a chiral column (Lux® 5 µm Cellulose-2, LC Column 250 × 4.6 mm, Phenomenex). Using the same procedure, the racemic 3 and 4 were chirally separated as the optically pure (-)-3 (1.3 mg, tR 6.5 min), (+)-3 (1.5 mg, tR 5.7 min), (+)-4 (2.1 mg, tR 4.3 min) and (–)-4 (2.2 mg, tR 4.8 min) by a chiral HPLC column (80:20 MeOH/H2O, 0.9 mL/min) (+)-5 (35.6 mg, tR 7.1 min) and (-)-5 (20.9 mg, tR 9.8 min) were chirally separated by semi-preparative HPLC (80:20 MeOH/H2O, 0.9 mL/min) equipped with a chiral column (Lux® 5 µm i-Cellulose-5, LC Column 250 × 4.6 mm, Phenomenex).
3-[6-(2-Methylpropyl)-2-oxo-1H-pyrazin-3-yl]propanamide (1): a brown amorphous powder, mp 141–143 °C; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 217 (3.75), 230 (3.79), 262 (3.15), 325 (3.66) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3400, 3198, 2959, 2929, 2861, 1655, 1614, 1529, 1408, 1168, 575 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1); HRESIMS m/z 246.1205 [M + Na]+ (calculated for C11H17O2N3Na, 246.1213).
(±)-Brevianamide X (2): light yellow crystal; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 233 (4.34), 245 (4.33), 287 (4.18), 329 (4.19), 357 (4.20) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3351, 2968, 1684, 1620, 1427, 1326, 1244, 1107, 1062, 1022, 979, 960, 921, 749, 655, 584, 518 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1); ESI-MS m/z 404 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 404.1570 [M + Na]+ (calculated for C11H17O2N3Na, 404.1581). (+)-2: mp 241–243 °C; + 44 (c 0.05, MeOH); ECD (0.0014 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 208.5 (–6.5), 261 (+3.9), 337 (–2.5) nm. (–)-2: mp 220–222 °C; –40 (c 0.05, MeOH); ECD (0.001 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 208.5 (+6.4), 261 (–3.8), 337 (+2.4) nm.
(±)-Brevianamide R (3): a colorless powder; ESI-MS m/z 402.2 [M + Na]+; 1H and 13C NMR (see supporting information). (+)-3: mp 121–123 °C; +208 (c 0.15, MeOH); ECD (0.007 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 212 (+26.2), 258 (–19.1), 342 (+11.8) nm. (–)-3: mp 140–142 °C; –213 (c 0.13, MeOH); ECD (0.007 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 212 (–25.9), 258 (+16.7), 340.5 (–10.8) nm.
(±)-Brevianamide Q (4): a colorless powder; ESI-MS m/z 388.2 [M + Na]+; 1H and 13C NMR (see supporting information). (+)-4: mp 141–143 °C; +105 (c 0.2, MeOH); ECD (0.003 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 212 (+21.8), 258 (–14.3), 340 (+9.3) nm. (–)-4: mp 160–163 °C; –109 (c 0.2, MeOH); ECD (0.003 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 213 (–19.3), 258 (+15.8), 340 (–9.7) nm.
(±)-Brevianamide V (5): a light yellow powder; ESI-MS m/z 372.3 [M + Na]+; 1H and 13C NMR (see supporting information). (+)-5: mp 128–130 °C; +40 (c 2.0, MeOH); ECD (0.0014 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 212 (+24.3), 258 (–12.2), 330 (+6.3) nm. (–)-5: mp 131–132 °C; –38 (c 2.0, MeOH); ECD (0.001 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 213 (–22.2), 258 (+11.0), 330 (–5.7) nm.
Methyl diorcinol-4-carboxylate (12): a white solid; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 224 (3.42), 262 (2.95), 200 (1.36), 301 (1.23) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3401, 2954, 1656, 1598, 1454, 1322, 1262, 1207, 1161, 1104, 1031, 998, 952, 843, 677 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR (see Table 2); ESI-MS m/z 311.1 [M +Na]+.
Methyl 3,3-di(O-methyl) diorcinol-4-carboxylate (12a): a white solid; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 222 (3.34), 228 (3.32), 279 (1.49) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3440, 2950, 1731, 1587, 1463, 1324, 1268, 1193, 1158, 1093, 1064, 1028, 996, 935, 836 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR (see Table 2); HRESIMS m/z 317.1392 [M + H]+ (calculated for C18H21O5, 317.1384) (Supplementary Figure S24).
3.5. Crystallographic Data for Racemic 2
Racemic 2 was obtained as a light-yellow monoclinic crystal with molecular formula C11H17O2N3 from CH3CH2OH and CH2Cl2. Space group P-1, a = 9.8007 (9) Å, b = 10.4560(12) Å, c = 12.9125(14) Å, α = 122.466(3)°, β = 97.4200(10)°, γ = 106.988(2)°, V = 1125.2(2) Å3, Z = 2, Dcalcd = 1.259 mg/m3, μ = 0.089 mm-1, F(000) = 454, crystal size 0.34 × 0.21 × 0.13 mm, T = 298(2) K, 2.27° ≤ 2θ ≤ 25.02°, 5737 reflections collected, 3915 unique (R(int) = 0.0364). Final R indices R1 = 0.0310, wR2 = 0.0748 based on 3915 reflections with I > 2 sigma(I) (refinement on F2), 316 parameters, 0 restraint. Crystallographic data (excluding structure factors) for structure (±)-2 in this dissertation have been deposited in the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre as supplementary publication number CCDC 1837585 (fax, +44-(0)-1223-336033; e-mail, deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk).
3.6. ECD Calculation Assays
The calculations were performed by using the density functional theory (DFT) using Gaussian 03. The preliminary conformational distributions search was performed by HyperChem 7.5 software. All ground-state geometries were optimized at the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level. Conformers within a 2 kcal/mol energy threshold from the global minimum were selected to calculate the electronic transitions. The overall theoretical ECD spectra were obtained according to the Boltzmann weighting of each conformers. Solvent effects of methanol solution were evaluated at the same DFT level by using the SCRF/PCM method.
3.7. Methylation of 12
To a solution of 12 (10 mg) in DMF (1 mL) were added K2CO3 (20 mg) and MeI (0.03 mL), and the mixture was then stirred for 2 h [30]. The reaction was stopped by the addition of water (10 mL) and extracted three times with EtOAc (3 × 20 mL), then EtOAc solutions were concentrated under reduced pressure. The mixture was purified by semi-HPLC (80:20 MeOH/H2O, 4 mL/min) to give dimethylether derivative 12a (7.4 mg, tR 7.8 min).
3.8. Antimicrobial Assays
The MICs of the compounds were tested using the broth microdilution method [31,32]. The pathogenic bacteria included B. subtilis ATCC6051, S. aureus ATCC6538, S. aureus ATCC25923, P. aeruginosa ATCC10145, E. aerogenes, and E. coli ATCC11775 and the pathogenic fungi were C. albicans ATCC10231, and C. glabrata ATCC2001. Ciprofloxacin and ketoconazole were used as positive controls against bacteria and fungi, respectively. All of the microbial strains used in the bioassays are preserved at the Key Laboratory of Chemistry for Natural Products of Guizhou Province, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
3.9. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effect Assays
The inhibitory effects were assayed as described previously [12,13,33]. Absorbance of 96-well plates at 405 nm was recorded by an Epoch microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA). Acarbose was used as a positive control with an IC50 value of 255.3 μM.
4. Conclusions
We identified sixteen compounds from the fermentation of Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 under chemical-epigenetic modification, including a new naturally occurring diketopiperazine derivative (1) and two new compounds, (+)-brevianamide X ((+)-2) and (–)-brevianamide X ((–)-2). We also chirally separated the racemic brevianamides R (3), Q (4), and V (5) into the corresponding optically pure compounds and resolved their absolute configurations for the first time. We clearly determined the structure of the methyl diorcinol-4-carboxylate (12) by preparing 3,3′-dimethylether derivative (12a). Compounds 11 and 12 showed selective antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa both with the MIC value of 17.4 and 13.9 μM, respectively.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/17/1/6/s1, Figure S1. HRESIMS spectrum of compound 1; Figure S2–S7. NMR spectrum of compound 1; Figure S8. HRESIMS spectrum of compound 2; Figure S9–S14. NMR spectrum of compound 2; Figure S15. The chiral HPLC analysis of compounds 2–5; Figure S16. The chiral HPLC analysis of compounds 7–9; Figure S17. DFT-optimized structures for low-energy conformers of compounds 2–5; Figure S18. Phylogenetic tree mapping for the Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738; Figure S19–S23. NMR spectrum of compound 12; Figure S24. HRESIMS spectrum of compound 12a; Figure S25–S29. NMR spectrum of compound 12a; Figure S30. The UPLC-MS Analysis of Fermented Extracts. Figure S31. Retention times of compounds 1–12 in the same elution gradient with original extract fingerprint. The physical properties of the known compounds 3–11.
Author Contributions
W.L. performed the most experiments and prepared the draft of the manuscript. L.W. analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. G.Z. and M.L. performed the chemical calculations. B.W. and Y.X. checked the data. K.S. designed the research, checked the data and revised the manuscript. W.Z. designed the research and revised the final version.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the NSFC (Nos. 81803423 & 41376148), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang (No. LQ18D060005), the 100 Leading Talents of Guizhou Province (fund for W.Z.), the science and technology project of Guizhou (No. QKHT Z-2014-4007) and the academician workstation of Guizhou (No. QKH YSZ-2015-4009).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.H.; Ma, Y.N.; Wang, W.L.; Chen, Z.B.; Qin, S.D.; Du, Y.Q.; Wang, D.Y.; Zhu, W.M. New marine natural products from the marine-derived fungi other than Penicillium sp. and Aspergillus sp. (1951–2014). Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2015, 34, 56–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Teng, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, G.; Zhu, W. New quinazolinone alkaloids within rare amino acid residue from coral-associated fungus, Aspergillus versicolor LCJ-5-4. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Miao, F.P.; Qiao, M.F. Aspeverin, a new alkaloid from an algicolous strain of Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2327–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Lou, L.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; Proksch, P.; Yin, S.; Lin, W. Versiquinazolines A−K, fumiquinazoline-type alkaloids from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor LZD-14-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, W.G.; Wu, Z.Y.; Pang, W.W.; Ma, L.F.; Ying, Y.M.; Zhan, Z.J. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from the fungus Aspergillus versicolor 3.05358. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.P.; Li, X.D.; Liu, X.H.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Ji, N.Y. Secondary metabolites from an algicolous Aspergillus versicolor strain. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Qi, J.; Shao, C.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Hou, X.M.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive diphenyl ethers and isocoumarin derivatives from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.B.; Henrikson, J.C.; Hoover, A.R.; Lee, A.E.; Cichewicz, R.H. Epigenetic remodeling of the fungal secondary metabolome. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 1857–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichewicz, R.H. Epigenome manipulation as a pathway to new natural product scaffolds and their congeners. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Zhu, G.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. Chemical-epigenetic method to enhance the chemodiversity of the marine algicolous fungus, Aspergillus terreus OUCMDZ-2739. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhu, G.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. Corrigendum to “Chemical-epigenetic method to enhance the chemodiversity of the marine algicolous fungus, Aspergillus terreus OUCMDZ-2739” [Tetrahedron 74 (2018) 83–87]. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 6465–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrikson, J.C.; Hoover, A.R.; Joyner, P.M.; Cichewicz, R.H. A chemical epigenetics approach for engineering the in situ biosynthesis of a cryptic natural product from Aspergillus niger. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Kusari, S.; Golz, C.; Laatsch, H.; Strohmann, C.; Spiteller, M. Epigenetic modulation of endophytic Eupenicillium sp. LG41 by a histone deacetylase inhibitor for production of decalin-containing compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Sayed, A.M.; Mohammed, R.; Hassan, H.M.; Zaki, M.A.; Rateb, M.E.; Mohammed, T.A.; Amin, E.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Epigenetic modifiers induce bioactive phenolic metabolites in the marine-derived fungus Penicillium brevicompactum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, G.; Wang, L.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. Phenolic polyketides from the marine alga-derived Streptomyces sp. OUCMDZ-3434. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5451–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Gong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Zhu, W. New α-pyridones with quorum sensing inhibitory activity from diversity-enhanced extracts of a marine algae-derived Streptomyces sp. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Kong, F.; Zhu, W. New α-glucosidase inhibitors from marine algae-derived Streptomyces sp. OUCMDZ-3434. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Li, L.M.; Yang, T.; Chen, X.Z.; Fang, D.M.; Zhang, G.L. Four new alkaloids, brevianamides O–R, from the fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2010, 93, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Andrew, M.P.; Yu, K.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; et al. Brevianamides with antitubercular potential from a marine-derived isolate of Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4770–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Cai, S.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D.; Luan, Y. Secondary metabolites of a deep sea derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor CXCTD-06-6a and their bioactivity. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Yang, T.; Luo, Y.G.; Chen, X.Z.; Fang, D.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Brevianamide, J. A new indole alkaloid dimer from fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuravleva, O.I.; Kirichuk, N.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Minʹko, E.M.; Ivanets, E.V.; Afiyatullov, S.S. New diorcinol J produced by co-cultivation of marine fungi Aspergillus sulphureus and Isaria felina. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabashi, T.; Nozawa, K.; Nakajima, S.; Kawai, K. A new azaphilone, falconensin H., from Emericella falconensis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 2040–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nitta, K.; Oohata, Y.; Furukawa, T. Studies on the metabolic products of a strain of Aspergillus fumigatus DH 413. V. A new metabolite produced by ethionine inhibition. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1972, 20, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.L.; Wang, X.J.; Xiang, Z.D.; Wang, J.D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.X.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, W.S. Diphenyl etheric metabolites from Streptomyces sp. neau50. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.G.; Goodman, J.M. Assigning stereochemistry to single diastereoisomers by GIAO NMR calculation: The DP4 probability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12946–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berova, N.; Di Bari, L.; Pescitelli, G. Application of electronic circular dichroism in configurational and conformational analysis of organic compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomcheon, P.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Sriubolmas, N.; Ngamrojanavanich, N.; Kengtong, S.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Aromatase inhibitory, radical scavenging, and antioxidant activities of depsidones and diaryl ethers from the endophytic fungus Corynespora cassiicola L36. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Syu, W.J.; Li, S.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, G.H.; Sun, C.M. Antimicrobial activities of naphthazarins from Arnebia euchroma. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.D.; Li, X.M.; Xu, G.M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.G. Antimicrobial phenolic bisabolanes and related derivatives from Penicillium aculeatum SD-321, a deep sea sediment-derived fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Hao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, W. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus flavipes HN4-13. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).