Abstract
The lipid A moiety of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide is a hexaacylated disaccharide of glucosamine phosphorylated at the 1- and 4′-positions. It can be recognized by the TLR4/MD-2 complex of mammalian immune cells, leading to release of proinflammatory cytokines. The toxicity of lipid A depends on its structure. In this study, two E. coli mutants, HW001 and HW002, were constructed by deleting or integrating key genes related to lipid A biosynthesis in the chromosome of E. coli W3110. HW001 was constructed by deleting lacI and replacing lacZ with the Francisella novicida lpxE gene in the chromosome and only synthesizes monophosphoryl lipid A. HW002 was constructed by deleting lpxM in HW001 and synthesizes only the pentaacylated monophosphoryl lipid A. The structures of lipid A made in HW001 and HW002 were confirmed by thin layer chromatography and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. HW001 and HW002 grew as well as the wild-type W3110. LPS purified from HW001 or HW002 was used to stimulate murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells, and less TNF-α were released. This study provides a feasible way to produce interesting lipid A species in E. coli.
Keywords:
lipopolysaccharide; lipid A; MPLA; endotoxin; vaccine adjuvant; Escherichia coli; murine macrophage 1. Introduction
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), known as endotoxin, is the prominent constituent in the outer leaflet of outer membranes in most Gram-negative bacteria [1,2,3] and plays an important role in membrane permeability, cell adhesion and stability [4]. It can be divided into three parts: lipid A, core-oligosaccharide [5] and O-antigen repeats. Lipid A, the hydrophobic anchor of LPS, is responsible for the bioactivity of LPS [6]. It can be recognized by the TLR4/MD-2 complex of mammalian immune cells, leading to release of cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), upregulation of MHC class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells [6,7] and generation of strong Th1 responses [8].
Kusumoto’s group has synthesized lipid A molecules with different structures and demonstrated that the toxicity of lipid A is closely related to its precise chemical structure [9]. Small amounts of lipid A with the right chemical structure is beneficial for the host to clear the invading microbe; high levels of lipid A, however, lead to the release of high levels of circulating cytokines, whose procoagulant activity could damage the microvasculature and facilitate the syndrome of septic shock [10]. Wild-type Escherichia coli lipid A (Figure 1) contains two phosphate groups and six acyl chains [1,2] and activates both TLR4–TRAM–TRIF and TLR4–Mal–MyD88 signaling pathways [11,12]. Lipid A containing only one phosphate group weakens the ligand affinity, induces structural rearrangement of the TLR4/MD-2 complex [11] and selectively activates the TLR4–TRAM–TRIF signaling pathway, leading to secretion of lower levels of cytokines [13]. This suggests that the monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA) is much less toxic than the wild-type lipid A, but still retains the immunomodulatory properties. In addition, Salmonella typhimurium lipid A lacking a secondary acyl chain at the 3′-position, that is, the pentaacylated lipid A, is also less toxic than the wild-type lipid A [14].
Since MPLA and pentaacylated lipid A are immunogenic, but less toxic [15], they could be used as vaccine adjuvant to enhance the strength and duration of the immune response to antigens [8,16]. However, most Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli, synthesize lipid A with two phosphate groups and six acyl chains. In recent years, the biosynthesis of lipid A in E. coli has been well characterized, and several enzymes that modify the structure of lipid A are reported. Therefore, now it is possible to construct E. coli strains to synthesize lipid A with the desired structures. For example, deleting the gene lpxM in E. coli can make it synthesize pentaacylated lipid A [17]. Expressing Francisella novicida lpxE in E. coli can remove the phosphate group from the 1-position of lipid A [18,19] (Figure 1).
In this study, E. coli mutants that synthesize hexaacylated MPLA or pentaacylated MPLA (P-MPLA) were constructed by integrating and/or deleting key genes related to lipid A biosynthesis and modification in the chromosome. The structures of lipid A in these mutants were confirmed by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI/MS). All mutants grew as well as the wild-type, and their LPS induces less TNF-α than the wild-type E. coli LPS when used to stimulate murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. This study provides a convenient method to produce novel lipid A vaccine adjuvant in E. coli.
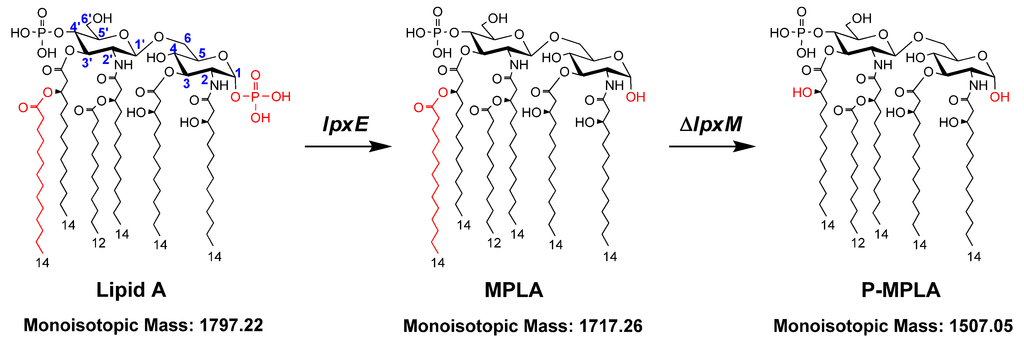
Figure 1.
The strategic diagram of structural modification of E. coli lipid A. The numbers that specify the glucosamine ring positions and the fatty acid chain length of lipid A are indicated. The gene lpxE encodes LpxE, which removes the phosphate group from the 1-position of lipid A. The gene lpxM encodes LpxM, which adds a secondary tetradecanoyl residue at 3′-position of lipid A. Therefore, expression of lpxE in E. coli changes the structure of lipid A to monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA); expression of lpxE and deletion of lpxM in E. coli changes the structure of lipid A to pentaacylated MPLA (P-MPLA).
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Construction of E. coli Strains that Can Synthesize MPLA or P-MPLA by Chromosomal Gene Integration and/or Gene Deletion
Four plasmids, pBS-Ikan, pDTW202, pBS-Mkan and pKD-Cre, were constructed to facilitate the chromosomal gene integration and/or gene deletion in E. coli (Figure 2a). Plasmid pBS-Ikan contains the fragment lacIU-loxp-kan-loxp-lacID, which was designed to facilitate the deletion of the lacI gene and the subsequent removal of the inserted kan gene from the chromosome. Plasmid pDTW202 contains the fragment loxpLE-kan-loxpRE, which was designed for the easy removal of the kan gene by recombination of loxpLE and loxpRE. Plasmid pBS-Mkan contains the fragment lpxMU-loxpLE-kan-loxpRE-lpxMD, which was designed to facilitate the deletion of the lpxM gene and the subsequent removal of the kan gene from the chromosome. Plasmid pKD-Cre was designed to remove the inserted kan gene from the chromosome at the later stage of deletion.
Three E. coli mutants, HW000, HW001 and HW002, were constructed by using the above plasmids (Figure 2b). HW000 was constructed by deleting the lacI gene to avoid the lactose regulation. HW001 was constructed by integrating the F. novicida lpxE into the site of lacZ gene in the lac operon of E. coli HW000. HW002 was constructed by deleting the lpxM gene in the chromosome of HW001. The correct insertion or deletion of these genes and the removal of kan in these three E. coli mutants were confirmed by PCR analysis and DNA sequencing.
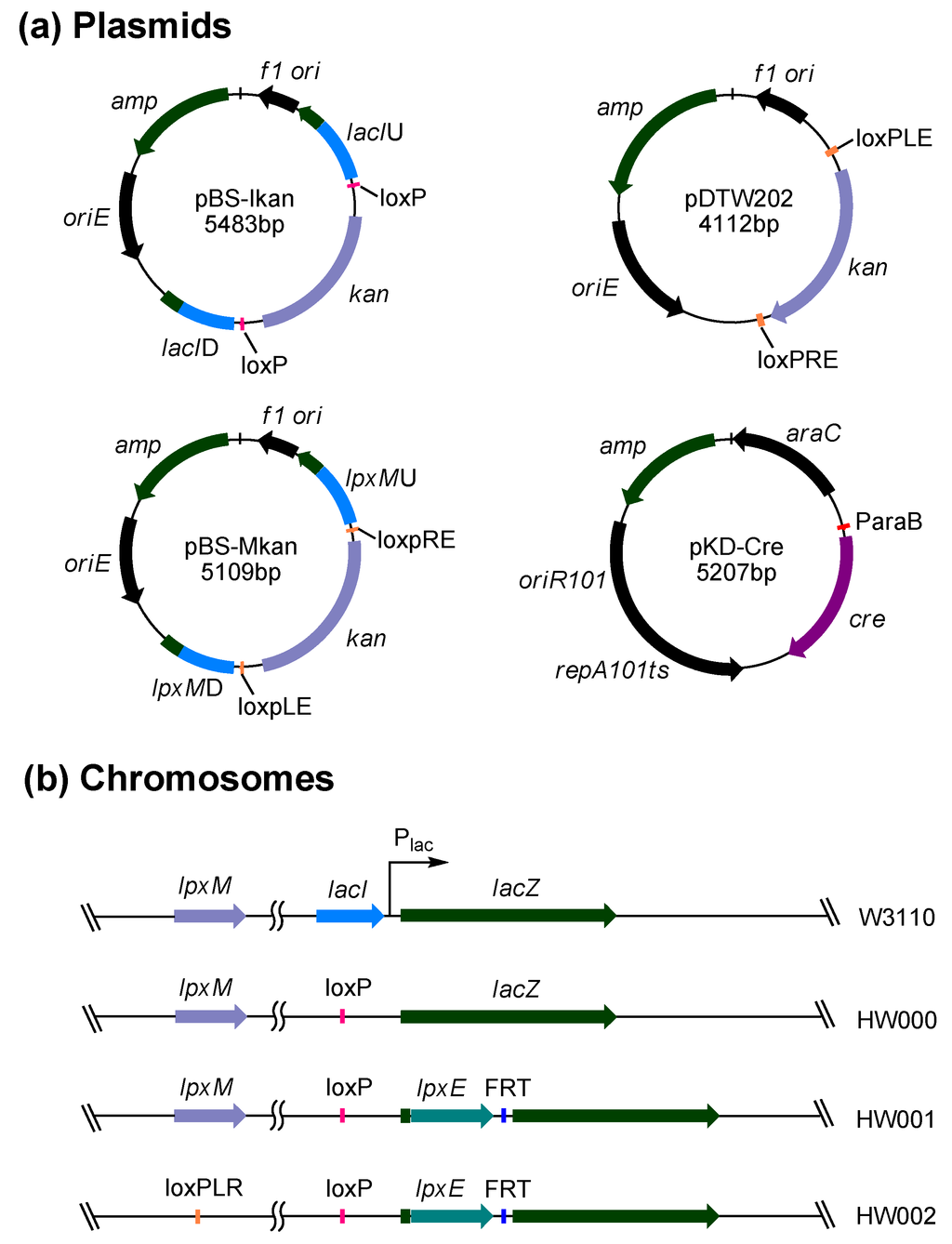
Figure 2.
Plasmids and E. coli mutant strains constructed in this study. (a) Maps of four plasmids pBS-Ikan, pDTW202, pBS-Mkan and pKD-Cre constructed in this study; (b) The comparison of chromosomes of E. coli strains W3110, HW000, HW001 and HW002.
The growth rates of all these E. coli mutants were similar to that of wild-type W3110 (Figure 3).
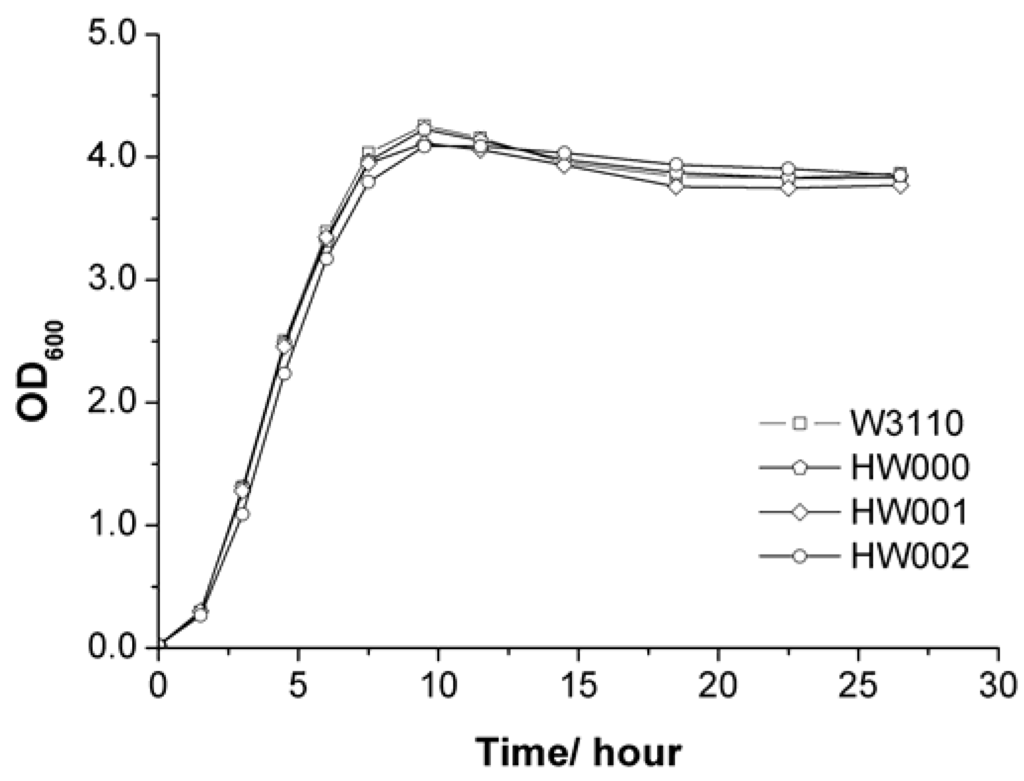
Figure 3.
Comparison of growth of E. coli strains W3110, HW000, HW001 and HW002.
2.2. Structure Analysis of Lipid A Extracted from Three E. coli Mutants
Lipid A was isolated from strains of W3110, HW000, HW001 and HW002 and analyzed by TLC (Figure 4). The typical lipid A band was shown on the TLC for samples isolated from W3110 and HW000. Considering the hydrophilic property of phosphate and hydrophobic property of fatty acid chain, lipid A containing less phosphate groups and more and longer fatty acid chains should migrate faster on TLC. A more rapidly migrating substance was observed on the TLC in the sample from HW001; likely MPLA. For the sample from HW002, a substance migrating faster than lipid A, but slower than MPLA, was observed; likely P-MPLA.
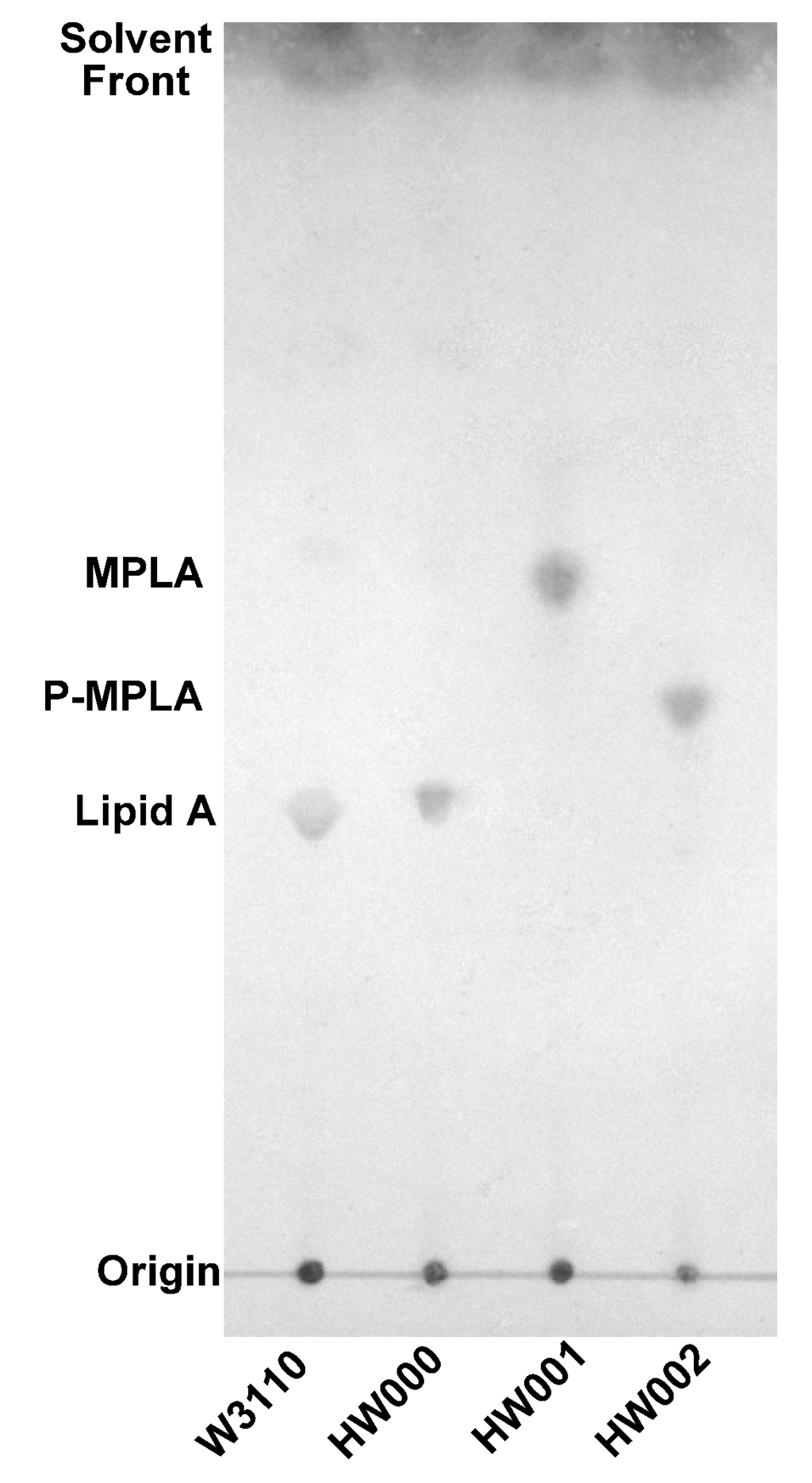
Figure 4.
TLC analysis of lipid A isolated from E. coli strains W3110, HW000, HW001 and HW002. The lipid A samples were dissolved in chloroform/methanol (4:1, v/v), spotted onto a silica gel 60 TLC plate and developed in a solvent containing chloroform, methanol, water and ammonia (40:25:4:2, v/v/v/v). The plate was dried and sprayed with 10% sulfuric acid in ethanol and the positions of lipid A on the plate were visualized by charring at 175°C.
Lipid A isolated from W3110, HW000, HW001 and HW002 were further analyzed by ESI/MS (Figure 5). The lipid A isolated from W3110 yielded a major peak at m/z 1796.2 in the spectrum, suggesting that the peak is created by the molecular ion [M − H]− of lipid A. The minor peak at m/z 1716.3 might arise by loss of a phosphate, indicating that the hydrolysis conditions for the cleavage of the lipid A from the core-oligosaccharide was too harsh and resulted in a partial loss of the α-anomeric C-1-phosphate at GlcN(I). Lipid A isolated from HW000 showed a similar pattern as that from W3110. In the spectrum of lipid A isolated from HW001, there is only one major peak at m/z 1716.3, suggesting that the lipid A in HW001 is completely dephosphorylated at the 1-position. In the spectrum of lipid A isolated from HW002, there is only one major peak at m/z 1506.1, suggesting that lipid A isolated from HW002 is P-MPLA. Both TLC and ESI/MS data indicate that HW001 can convert all lipid A into MPLA and HW002 can convert all lipid A into P-MPLA. This indicates that the gene lpxE inserted in the chromosome of HW001 and HW002 was well expressed and LpxE can modify the structure of lipid A in vivo and that lpxM encodes the only late acyltransferase in E. coli that adds a secondary acyl chain to the 3′-position of lipid A.
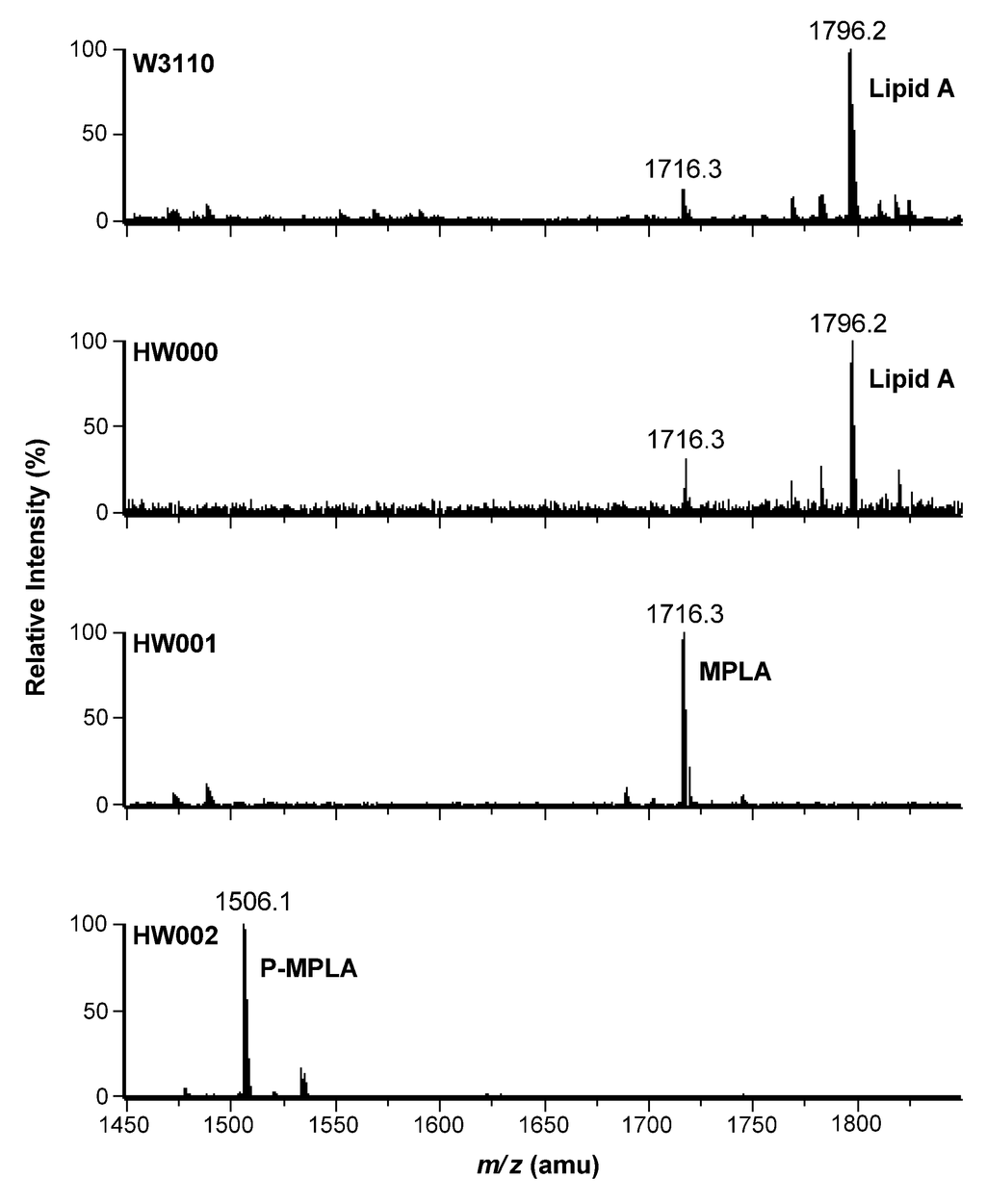
Figure 5.
ESI/MS analysis of lipid A isolated from E. coli W3110, HW000, HW001 and HW002. Lipid A samples were dissolved in chloroform/methanol (4:1, v/v) and subjected to ESI/MS in the negative ion mode.
2.3. Comparison of the Stimulation Activities of LPS Isolated from Different E. coli Mutants
LPS was purified from W3110, HW001 and HW002 and used to stimulate macrophage cell line RAW264.7. Levels of TNF-α released by the cells after stimulation were examined (Figure 6). E. coli O111:B4 LPS was used as a positive control, and PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) was used as a negative control.
The levels of TNF-α released by RAW264.7 cells were proportional to the concentration of LPS up to 100 ng/mL, but there was little difference between LPS concentrations of 100 ng/mL and 1000 ng/mL. At all concentrations, lower levels of TNF-α were released when RAW264.7 cells were stimulated by HW001 LPS and HW002 LPS than by the controls O111:B4 LPS or W3110 LPS (Figure 6). The lowest levels of TNF-α were induced by HW002 LPS from 17,472 pg/mL at 1 ng/mL to 37,578 pg/mL at 1000 ng/mL, which were 39% and 55% of the levels induced by W3110 LPS, respectively.
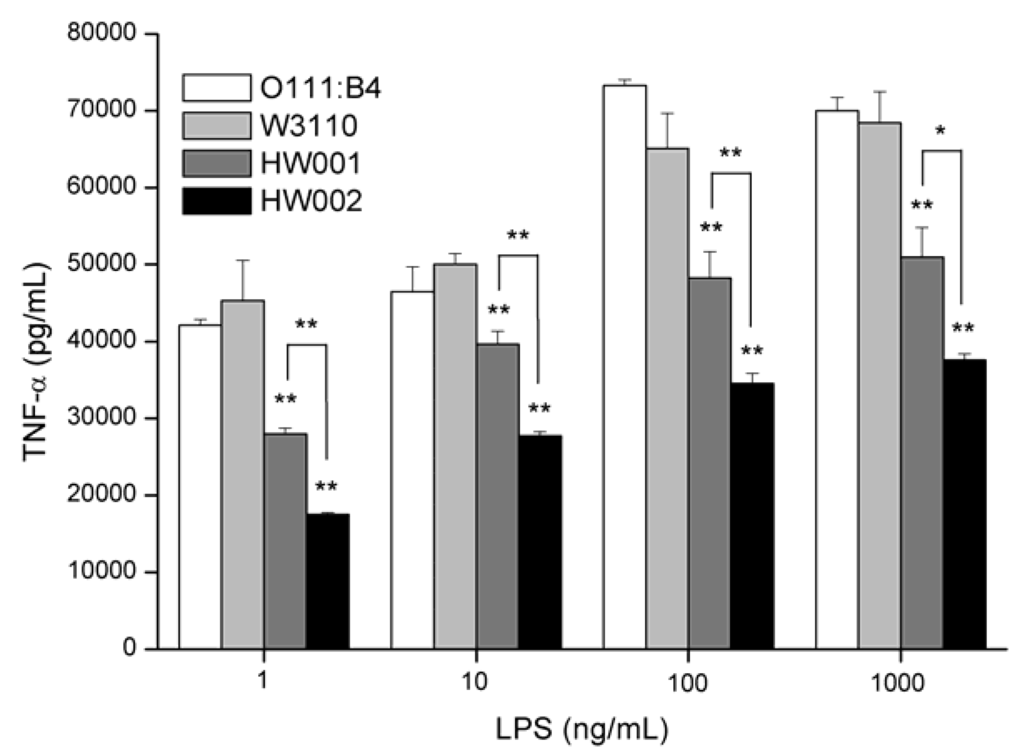
Figure 6.
Cytokine concentrations in tissue-culture supernatants of RAW264.7 cells stimulated by increasing concentrations of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) sample. Supernatants from RAW264.7 murine macrophages were collected after 24 h stimulation with LPS and tested for the presence of TNF-α. One-way analysis of variance was used to evaluate differences in cytokine concentrations. Significant differences between stimulations by LPS from different sources were shown. * p <0.05, ** p < 0.01. The experiments were performed in triplicate, and data were shown as means ± standard deviation.
These results demonstrated that LPS from HW001 and HW002 induced lower secretion of TNF-α than that of wild-type E. coli LPS, suggesting they are good candidates for vaccine adjuvant development. The changes in the number of the acyl chains and the phosphate groups of lipid A might decrease the binding ability by TLR4/MD-2 and lead to the lower release of TNF-α.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. DNA Preparation and PCR Techniques
Restriction enzymes, shrimp alkaline phosphatase, T4 DNA ligase and DNA ladder were purchased from Sangon (Shanghai, China). Plasmid DNA was prepared by using the EZ-10 spin column plasmid mini-preps kit from Bio Basic Inc. (Markham, Canada). PCR reaction mixtures (50 μL) used in this study contain 5 μL 10× Ex Taq buffer, 4 μL dNTP mixture (2.5 mM each), 1 μL plasmid template (100 ng/μL), 1 μL forward primer (20 μM), 1 μL reverse primer (20 μM) and 0.5 μL TaKaRa Ex Taq DNA polymerase. The PCR reaction was first heated to 94 °C and maintained for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation (94 °C for 30 s), annealing (30 s at 55 °C or 58 °C) and extension (72 °C for 3 min). At the end, an additional 10 min incubation at 72 °C was used. PCR products were purified by using the TIANgel midi purification kit from Tiangen (Beijing, China). Primer synthesis and DNA sequencing were performed by Sangon. The sequences of primers used in this study are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Primers used in this study. The recognition sites for restriction enzymes are underlined.
| Primers | Sequences (5′→3′) | Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| lacIU-F | CCGCTCGAGACAGTATCGGCCTCAGGAAGAT | XhoI |
| lacIU-R | CGGAATTCTTAATGCAGCTGGCACGACAGG | EcoRI |
| lacID-F | GAAGATCTGCGACATCGTATAACGTTACTG | BglII |
| lacID-R | AACTGCAGCAAGACCGCAAGGAATTAATCG | PstI |
| lpxMU-F | CCCAAGCTTGCGTTACGGCGATCATCACCAT | HindIII |
| lpxMU-R | CCCGGCTAGCAAAGATCTTTATCCCATCAAAT | NheI |
| lpxMD-F | GTGGATCCATCAAACTCAGGAATGTATTCGC | BamHI |
| lpxMD-R | ATGAGCTCATGGTCGCAGCTACACCACGCG | SacI |
| kan-loxP-F | ATGAATTCGCGGCCGCATAACTTCGTATAA | EcoRI |
| kan-loxP-R | AGAGATCTGCGGCCGCATAACTTCGTATAA | BglII |
| loxpLE-F | TTACCGTTCGTATAATGTATGCTATACGAAGTTATA | / |
| loxpLE-R | TCGATATAACTTCGTATAGCATACATTATACGAACGGTAAGGCC | / |
| loxpRE-F | CTAGTATAACTTCGTATAATGTATGCTATACGAACGGTATAGC | / |
| loxpRE-R | TATACCGTTCGTATAGCATACATTATACGAAGTTATA | / |
| kan-F | TAACTCGAGATTCACGCTGCCGCAAGCACTCAGG | XhoI |
| kan-R | AAGTCTAGACGAACCCCAGAGTCCCGCTCAGA | XbaI |
| kan-loxpLE-F | ATGGATCCAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCG | BamHI |
| kan-loxpRE-R | ACCTCTAGAGCGCAATTAACCCTCACTAAAG | XbaI |
| cre-F | CGAGCTCAGGAGGTTATAAAGGATGTCCAATTTACTG | SacI |
| ACCGTACACCA | ||
| cre-R | TACCATGGTCTAATCGCCATCTTCCAGCAG | NcoI |
| lacZ-F | CCATTCAGGCTGCGCAACTGTT | / |
| lacZ-R | TTAATGCAGCTGGCACGACAGG | / |
3.2. Construction of Plasmids and Bacterial Strains
All bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 2. Bacteria were usually grown at 37 °C in LB media (10 g/L trypton, 5 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L NaCl). When necessary, antibiotics were added with a final concentration of 100 μg/mL for ampicillin, 30 μg/mL for kanamycin and 30 μg/mL for chloramphenicol.
Four plasmids pBS-Ikan, pDTW202, pBS-Mkan and pKD-Cre were constructed in this study (Figure 2a). Plasmid pBS-Ikan was constructed by inserting a DNA fragment, lacIU-loxp-kan-loxp-lacID, in the vector pBlueScript II SK+. Primers lacIU-F and lacIU-R were used to amplify the upstream fragment of lacI; primers lacID-F and lacID-R were used to amplify the downstream fragment of lacI; primers kan-loxP-F and kan-loxP-R were used to amplify the fragment loxp-kan-loxp from pMG2-kanr [20]. Plasmid pDTW202 was constructed by inserting a fragment, loxpLE-kan-loxpRE, in the vector pBlueScript II SK+. Fragments loxpLE and loxpRE were obtained by the annealing of the primers loxpLE-F, loxpLE-R and loxpRE-F, loxpRE-R, respectively, according to the method of Arakawa [21], and the kanamycin resistance gene kan was PCR amplified from pK18mobsacB [22] with primers kan-F and kan-R. Plasmid pBS-Mkan was constructed by inserting a fragment, lpxMU-loxpLE-kan-loxpRE-lpxMD, in the vector pBlueScript II SK+. Primers lpxMU-F and lpxMU-R were used to amplify the upstream fragment of lpxM; primers lpxMD-F and lpxMD-R were used to amplify the downstream fragment of lpxM, and primers kan-loxpLE-F and kan-loxpRE-R were used to amplify the fragment loxpLE-kan-loxpRE from pDTW202. Plasmid pKD-Cre was constructed by replacing the λ Red genes with the gene cre in the vector pKD46 [23]. The gene cre was amplified from the vector pSH47 [24], using primers cre-F and cre-R, digested with SacI and NcoI and ligated with the vector pKD46, which is similarly digested. The gene cre was put under the arabinose-inducible ParaB promoter. The plasmid pKD-Cre has a temperature sensitive replicon.

Table 2.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study.
| Strains or Plasmids | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| W3110 | Wild-type E. coli, F−, λ− | Laboratory strain |
| W3110/pKD46 | W3110 transformed by pKD46 | This work |
| HW000 | W3110 ΔlacI | This work |
| HW001 | W3110 ΔlacIlacZ::lpxE | This work |
| HW002 | W3110 ΔlacIΔlpxMlacZ::lpxE | This work |
| Plasmids | ||
| pKD46 | ParaBγβ exo, Repts,AmpR | [23] |
| pMG2-kanr | loxP-kan-loxP, AmpR, KanR | [20] |
| pK18mobsacB | Mob+, sacB, KanR | [22] |
| pDTW202 | loxPLE-kan-loxPRE, AmpR, KanR | This work |
| pCP20 | FLP+, λ cI857+, λpRRepts, CamR, AmpR | [23] |
| pSH47 | GAL1p-Cre-CYC1T, AmpR | [24] |
| pKD-Cre | ParaB cre, Repts, AmpR | This work |
| pBlueScript II SK+ | Cloning vector, ColE1, lacZ, AmpR | Stratagene |
| pBS-Ikan | Plasmid for deleting lacI in E. coli | This work |
| pBS-Mkan | Plasmid for deleting lpxM in E. coli | This work |
| pWSK29-FnlpxE-Fkan | Plasmid for containing lpxE | [19] |
Three E. coli mutants, HW000, HW001 and HW002, were constructed by deleting and/or integrating genes in the chromosome of E. coli (Figure 2b). Firstly, the DNA fragment lacIU-loxp-kan-loxp-lacID was amplified from pBS-Ikan using primers lacIU-F and lacID-R and transformed into E. coli W3110/pKD46. Under the help of Red enzymes expressed by pKD46, the lacI gene in the chromosome should be replaced by DNA fragment loxp-kan-loxp; the transformants were selected on LB agar plates containing kanamycin. The kan gene inserted in the chromosome was further eliminated by transforming pKD-Cre. Plasmid pKD-Cre expresses the Cre recombinase, which directly acts on the repeated loxp (Cre recognition target) sites flanking the kan gene and excises the kan gene, resulting in the lacI mutant HW000. Secondly, the DNA fragment lacZU-lpxE-FRT-kan-FRT-lacZD was amplified from pWSK29-FnlpxE-Fkan [19] using primers lacZ-F and lacZ-R and transformed into HW000/pKD46. Under the help of Red enzymes expressed by pKD46, the lacZ gene was broken by the inserted DNA fragment lpxE-FRT-kan-FRT. The kan gene was then eliminated by transforming pCP20. Plasmid pCP20 expresses the FLP recombinase, which acts on the directly repeated FRT (FLP recognition target) sites flanking the kan gene and excises the kan gene [23], resulting in the double mutant HW001. Thirdly, the DNA fragment lpxMU-loxpLE-kan-loxpRE-lpxMD was amplified from pBS-Mkan using primers lpxMU-F and lpxMD-R and transformed into HW001. Under the help of Red enzymes expressed by pKD46, the lpxM gene in the chromosome was replaced by the DNA fragment loxpLE-kan-loxpRE. The kan gene was then eliminated by transforming pKD-Cre, resulting in the triple mutant HW002. Since the short sequences loxp left by deleting lacI, loxpLR left by deleting lpxM and FRT left by inserting lpxE are different, they could not recombine with each other in the double or triple mutants.
3.3. Isolation and Analysis of Lipid A from E. coli Strains
Typically, 200 mL cultures were inoculated from overnight cultures and grown to an OD600 of 1.0. The cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 20 min and washed with PBS. The final cell pellet was resuspended in a single phase Bligh-Dyer mixture [25] (76 mL) consisting of chloroform/methanol/water (1:2:0.8 v/v) and agitated by stirring for 1 h at room temperature. The cell debris was collected by centrifugation at 2000 rpm for 20 min, and the insoluble material was washed twice with the same solvent. The pellets were resuspended in 27 mL 12.5 mM sodium acetate (pH 4.5) by sonication and heated at 100 °C for 30 min to release lipid A from LPS. After cooling to room temperature, the suspensions were converted to two-phase Bligh-Dyer mixtures consisting of chloroform/methanol/water (2:2:1.8 v/v) by adding 30 mL chloroform and 30 mL methanol. The mixture was vigorously shaken to extract lipid A and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 20 min. The lower phase containing lipid A was dried with a rotary evaporator and stored at −20 °C.
The dried lipid A was dissolved in chloroform/methanol (4:1 v/v) and spotted onto a silica gel 60 TLC plate. The plate was developed in the solvent of chloroform/methanol/water/ammonia (40:25:4:2 v/v/v/v). After drying and spraying with 10% sulfuric acid in ethanol, the separation of lipid A on the plate could be visualized by charring at 175 °C.
For ESI/MS analysis, dried lipid A was dissolved in chloroform/methanol (4:1 v/v) and subjected to ESI/MS in the negative ion mode. The mass spectra were acquired on a Waters SYNAPT Q-TOF mass spectrometer equipped with an ESI source. Data acquisition and analysis were performed using MassLynx V4.1 software [26].
3.4. Extraction and Purification of LPS
LPS were isolated from E. coli strains using the phenol-water procedure [27]. Wet E. coli cells (3 g) were suspended in water (10 mL) at 68 °C, and 90% aqueous phenol (10 mL) was added. The mixture was stirred for 1 h at 68 °C, then cooled to 4 °C and centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 20 min to separate the water and phenol phases. The water phase was collected, dialyzed against water and lyophilized. The crude LPS (0.5 g) was resuspended in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5, 10 mL) and then by treating with DNase I, RNase A at the concentration of 100 and 50 μg/mL at 37 °C for 2 h, respectively. Then 100 μg/mL proteinase K at 37 °C for 2 h was performed. For further purification, 5 mL water-saturated phenol was added to the crude LPS sample. The mixture was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 20 min. The water phase was collected, dialyzed and lyophilized. Phospholipid contaminants in the sample were removed by extraction with chloroform/methanol (2:1 v/v) [28]. Purified LPS product was lyophilized and stored at 4 °C [29].
3.5. LPS Stimulation of the Murine Macrophage Cell Line RAW264.7
E. coli O111:B4 LPS was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The murine macrophage cell line RAW264.7 was obtained from the cell bank of the Chinese Academy of Science (Shanghai, China). It was maintained at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in DMEM (Gibco BRL, USA) containing 10% FBS (Hyclone Logan, UT, USA), supplemented with penicillin (100 U/mL) and streptomycin (100 μg/mL). Cells were cultured at 105/well in 96-well plates with 200 μL medium each well. After 18 h, the RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with increasing concentration of LPS (1, 10, 100 and 1000 ng/mL). 24 h later, culture supernatants were collected, centrifuged to remove the contaminates and stored at −80 °C for cytokine analysis. Concentrations TNF-α were determined using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (eBioscience), according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
One-way analysis of variance was performed to determine the statistical significance of the differences between mean values for various experimental and control groups. Data were expressed as means ± standard deviation, and the experiments were performed in triplicate. The means were compared using the least significant difference test. p < 0.05 was considered a significant difference and p < 0.01 was considered extremely significant difference. All data were analyzed with SPSS Statistics 17.0.
4. Conclusions
MPLA is safe and effective in eliciting Th1 response to heterologous proteins in animal and human vaccines [8]; therefore, it is becoming an important target molecule for developing novel vaccine adjuvant. MPLA can be chemically synthesized, but the chemically synthesized MPLA has a slightly different structure, which might affect its recognition by TLR4/MD-2 [30]. MPLA can also be prepared by extracting the lipid A from Salmonella Minnesota R595 and then removing the 1-phosphate group chemically. This MPLA product was 0.1% as toxic as wild-type LPS without affecting the immune-stimulating activity when tested in pre-clinical rabbit pyrogenicity assays [31,32]. However, this method has limitations on the efficiency and quality of MPLA production, because S. minnesota makes multiple lipid A species, which are difficult to separate from each other [33].
However, E. coli, the most common bacterium used for gene engineering, synthesizes only one type of lipid A. Therefore, we constructed two E. coli strains, HW001 and HW002, that could produce MPLA, by deleting or constitutively expressing genes related to lipid A biosynthesis in the chromosome. The gene lpxE encoding a phosphatase LpxE was integrated in the chromosome of HW001. LpxE can remove the phosphate at the 1-position of lipid A and has been used to develop Salmonella vaccines [34]. HW002 was constructed by deleting the gene lpxM in the chromosome of HW001. The lpxM gene product is an important virulence factor in a murine model of E. coli pathogenicity [35], and Salmonella lpxM mutants produce pentaacylated lipid A with reduced affinity to TLR4, resulting in virulence attenuation [36]. As expected, HW001 only synthesizes MPLA, and HW002 only synthesizes P-MPLA. Lower levels of cytokines TNF-α were released when RAW264.7 cells were stimulated by HW001 LPS and HW002 LPS than by the wild-type W3110 LPS (Figure 6), suggesting HW001 LPS and HW002 LPS are good candidates for developing lipid A vaccine adjuvant.
Heterologous genes are usually expressed in E. coli using plasmids as the vector, but plasmids are not stable in bacteria and usually need antibiotics as selection markers. The markerless chromosomal integration of lpxE in HW001 and HW002 make these strains ideal for industrial production of MPLA. Other than LpxE and LpxM, there are enzymes, such as PagL and PagP, which could also modify the structure of lipid A to change its interaction with TLR4/MD-2 [37].
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2012CB725202), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170069), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20100093110005) and the Program of SKLF (SKLF-ZZA-201205).
References
- Wang, X.; Quinn, P.J. Lipopolysaccharide: Biosynthetic pathway and structure modification. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Quinn, P.J. Endotoxins: Lipopolysaccharides of Gram-Negative Bacteria. In Endotoxins: Structure, Function and Recognition; Wang, X., Quinn, P.J., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; Volume 53, pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar]
- Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A. The Diversity of the Core Oligosaccharide in Lipopolysaccharides. In Endotoxins: Structure, Function and Recognition; Wang, X., Quinn, P.J., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; Volume 53, pp. 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, P.J.; Hraba, T.; Taylor, C.E.; Myers, K.R.; Takayama, K.; Qureshi, N.; Stuetz, P.; Kusumoto, S.; Hasegawa, A. Structural features that influence the ability of lipid A and its analogs to abolish expression of suppressor T cell activity. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2694–2701. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Moingeon, P.; Haensler, J.; Lindberg, A. Towards the rational design of Th1 adjuvants. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4363–4372. [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki, S.; Kojima, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Homma, J.Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Kumazawa, Y.; Tanamoto, K.; Yasuda, T.; Tsumita, T.; Imoto, M.; et al. Biological activities of analogues of lipid A based chemically on the revised structural model. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984, 143, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M. Endotoxins and Other Sepsis Triggers. In Endotoxemia and Endotoxin Shock: Disease, Diagnosis and Therapy; Ronco, C., Piccinni, P., Rosner, M., Eds.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 167, pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.S.; Song, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, B.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature 2009, 458, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Gaekwad, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Reeves, J.; Wolfert, M.A.; Boons, G.J. Differential induction of innate immune responses by synthetic lipid A derivatives. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29375–29386. [Google Scholar]
- Mata-Haro, V.; Cekic, C.; Martin, M.; Chilton, P.M.; Casella, C.R.; Mitchell, T.C. The vaccine adjuvant monophosphoryl lipid A as a TRIF-biased agonist of TLR4. Science 2007, 316, 1628–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Everest, P.; Servos, S.; Foxwell, N.; Zähringer, U.; Brade, H.; Rietschel, E.T.; Dougan, G.; Charles, I.G.; Maskell, D.J. A lethal role for lipid A in Salmonella infections. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 29, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Persing, D.H.; Coler, R.N.; Lacy, M.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Baldridge, J.R.; Hershberg, R.M.; Reed, S.G. Taking toll: Lipid A mimetics as adjuvants and immunomodulators. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, S32–S37. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.T.; Cluff, C.W.; Johnson, D.A.; Lacy, M.J.; Persing, D.H.; Baldridge, J.R. Enhancement of antigen-specific immunity via the TLR4 ligands MPL adjuvant and Ribi. 529. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2003, 2, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Guan, Z.; Ingram, B.O.; Six, D.A.; Song, F.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Discovery of new biosynthetic pathways: The lipid A story. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S103–S108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Karbarz, M.J.; McGrath, S.C.; Cotter, R.J.; Raetz, C.R.H. MsbA transporter-dependent lipid A 1-dephosphorylation on the periplasmic surface of the inner membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49470–49478. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tao, G.; Wang, X. Construction of an Escherichia coli mutant producing monophosphoryl lipid A. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Shi, G.Y. Improving ethanol productivity by modification of glycolytic redox factor generation in glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants of an industrial ethanol yeast. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 935–943. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, H.; Lodygin, D.; Buerstedde, J.M. Mutant loxP vectors for selectable marker recycle and conditional knock-outs. BMC Biotechnol. 2001, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, A.; Tauch, A.; Jaeger, W.; Kalinowski, J.; Thierbach, G.; Puehler, A. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK 18 and pK 19: Selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 1994, 145, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueldener, U.; Heinisch, J.; Koehler, G.; Voss, D.; Hegemann, J. A second set of loxP marker cassettes for Cre-mediated multiple gene knockouts in budding yeast. Nucl. Acids Res. 2002, 30, e23–e23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, F.; Hu, X. Purification and Characterization of Lipopolysaccharides. In Endotoxins: Structure, Function and Recognition; Wang, X., Quinn, P.J., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; Volume 53, pp. 27–52. [Google Scholar]
- MassLynx Software, version 4.1, Waters Corporation: Milford, MA, USA, 2005.
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide-Extraction with Phenol Water and Further Application of Procedure. In Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry; Whistler, R.L., Wolfrom, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; Volume 9, pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tirsoaga, A.; Novikov, A.; Adib-Conquy, M.; Werts, C.; Fitting, C.; Cavaillon, J.M.; Caroff, M. Simple method for repurification of endotoxins for biological use. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.W.; Sanders, R.E.; Napoli, C.; Albersheim, P. Host-symbiont interactions III. Purification and partial characterization of Rhizobium lipopolysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1978, 62, 912–917. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, C.B.; Friede, M.; Reed, S.G.; Ireton, G.C. Synthetic and Natural TLR4 Agonists as Safe and Effective Vaccine Adjuvants. In Endotoxins: Structure, Function and Recognition; Wang, X., Quinn, P.J., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; Volume 53, pp. 303–321. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.G.; Bertholet, S.; Coler, R.N.; Friede, M. New horizons in adjuvants for vaccine development. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Casella, C.R.; Mitchell, T.C. Putting endotoxin to work for us: Monophosphoryl lipid A as a safe and effective vaccine adjuvant. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Lim, K.B.; Gunn, J.S.; Bainbridge, B.; Darveau, R.P.; Hackett, M.; Miller, S.I. Regulation of lipid A modifications by Salmonella typhimurium virulence genes phoP-phoQ. Science 1997, 276, 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Six, D.A.; Roland, K.L.; Liu, Q.; Gu, L.; Reynolds, C.M.; Wang, X.; Raetz, C.R.H.; Curtiss, R. Salmonella synthesizing 1-monophosphorylated lipopolysaccharide exhibits low endotoxic activity while retaining its immunogenicity. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 412–423. [Google Scholar]
- Somerville, J.E.; Cassiano, L.; Darveau, R.P. Escherichia coli msbB gene as a virulence factor and a therapeutic target. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 6583–6590. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, K.J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.W.; Chang, K.T. Multi-immunogenic outer membrane vesicles derived from an MsbB-deficient Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium mutant. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, K.; Ernst, R.K.; Miller, S.I. Deacylation and palmitoylation of lipid A by Salmonella outer membrane enzymes modulate host signaling through Toll-like receptor 4. J. Endotoxin Res. 2004, 10, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).