Abstract
Mycalamide A, a marine natural compound previously isolated from sponges, is known as a protein synthesis inhibitor with potent antitumor activity. However, the ability of this compound to prevent malignant transformation of cells has never been examined before. Here, for the first time, we report the isolation of mycalamide A from ascidian Polysincraton sp. as well as investigation of its cancer preventive properties. In murine JB6 Cl41 P+ cells, mycalamide A inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced neoplastic transformation, and induced apoptosis at subnanomolar or nanomolar concentrations. The compound inhibited transcriptional activity of the oncogenic nuclear factors AP-1 and NF-κB, a potential mechanism of its cancer preventive properties. Induction of phosphorylation of the kinases MAPK p38, JNK, and ERK was also observed at high concentrations of mycalamide A. The drug shows promising potential for both cancer-prevention and cytotoxic therapy and should be further developed.
Abbreviations
| AP-1 | activator protein-1 |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| IC50 | inhibition concentration 50% |
| INCC50 | inhibition of number of colonies formed in soft agar concentration 50% |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinases |
| MTS | 5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl)-3-(4-sulfophenyl) tetrazolium, inner salt |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| PI | propidium iodide |
1. Introduction
Marine flora and fauna is a rich source of natural compounds that possess potent cancer preventive as well as cytotoxic activities [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. We studied an ethanol extract of the ascidian Polysincraton sp. that was selected in a screening process due to its cytotoxic activity against the human cancer cell line HeLa. Cytotoxicity-guided fractionation of the extract resulted, among other findings, in the isolation of the previously described substance mycalamide A [9].
Mycalamides and related compounds are inhibitors of protein synthesis and show apoptosis-inducing activity [10,11]. Initially, they were isolated from the marine sponges Mycale sp. (mycalamide A, B and D) [12,13], Stylinos sp. (mycalamide C) [14], Theonella sp. (onnamides) and Discodermia sp. (theopederins), for review see [15]. Previously, mycalamide A was shown to be rather toxic, putting into question its potential as a cancer therapeutic [11,12,16,17]. However, cancer preventive activity of this compound at lower concentrations has so far not been examined. In the work presented here, we investigated the cancer preventive and pro-apoptotic properties of mycalamide A.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structural Identification of Mycalamide A from Ascidian Polysincraton sp.
The crude ethanolic extract of Polysincraton sp. possessed cytotoxic activity against the human cancer cell line HeLa, with an inhibitory concentration (IC50) < 62.5 μg/mL, determined by the MTS test [18]. Bioassay guided fractionation of the Polysincraton sp. extract led us to the isolation of the previously described mycalamide A. The substance was structurally identified by determination and comparison of its NMR and MS data, as well as physical constants with values published before [9,12].
Interestingly, we report isolation of mycalamide A from a representative of the subphylum Tunicata (family Didemnidae) for the first time. This finding strongly supports the hypothesis that symbiotic bacteria are the most likely origin of mycalamides and related compounds in marine invertebrates [19,20]. Surprisingly, extract of Mycale sp. has been reported to have an inhibitory effect on larvae settling of another ascidian, Podoclavella moluccensis [21]. The fact that we have isolated mycalamide A from the ascidian Polysincraton sp. suggests a species-specific character of this inhibition.
2.2. Mycalamide A Prevents EGF-Induced Transformation of JB6 Cl41 P+ Cells and Colony Growth of HeLa Cancer Cells
To assess whether mycalamide A exerts cancer preventive properties, we used EGF (10 ng/mL) as a promoter of neoplastic transformation of JB6 Cl41 P+ cells, a well established model of anchorage-independent growth in soft agar [22,23,24,25]. The JB6 cell system comprising clonal variants, including promotion sensitive (P+) and promotion resistant (P−) cells, or cells showing malignant transformation, is a valuable tool to identify compounds showing cancer preventive properties, and furthermore can be used to determine their action at the molecular level [26,27]. The JB6 P+, P−, and transformed variants are a series of cell lines representing early to late stages of neoplastic progression [22,23,28]. JB6 Cl41 P+ cells undergo neoplastic transformation upon stimulation with tumor promoters such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) or 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), resulting in anchorage-independent growth of colonies in soft agar. The transformation involves the activation of the nuclear factor AP-1, which regulates the transcription of various genes related to inflammation, proliferation, and metastasis [22,29,30]. Blocking AP-1- and NF-κB-transcriptional activity leads to inhibition of promoter-induced neoplastic transformation of these cells [22,31,32].
As shown in Figure 1a, mycalamide A is able to inhibit EGF-induced neoplastic transformation of JB6 Cl41 P+ cells at very low, non-cytotoxic concentrations. The so called INCC50, the concentration leading to a 50% inhibition of colonies formed in soft agar, was 0.137 ± 0.035 nM after one week. This cancer preventive effect was observed at concentrations almost 50 times lower than the concentration causing 50% reduction (IC50) in the number of viable cells after 24 h treatment, which was determined at 6.32 ± 1.31 nM with the trypan blue exclusion method (Figure 1c).
Inhibition of colony growth by mycalamide A at non-cytotoxic concentrations was also observed in HeLa cells that show anchorage-independent growth in soft agar. The inhibition of colony formation of HeLa cells in soft agar was determined at an INCC50 = 0.67 nM (Figure 1b). This concentration was 8 fold lower than the IC50 of 5.5 ± 0.8 nM, determined in HeLa cells by the MTS test [18].
2.3. Mycalamide A Induces Apoptosis of JB6 Cl41 P+ Cells
Effects of mycalamide A on induction of apoptosis were determined by flow cytometry using double staining with annexin-V-FLUOS for binding of phosphatidylserine, and propidium iodide (PI) [33]. Although the number of viable JB6 Cl41 P+ cells decreased during the first 48 h of treatment with different concentrations of mycalamide A starting from 1.25 nM (Figure 1c), induction of apoptosis was not observed at concentrations below 6.25 nM (Figure 1d). This indicates that the decrease in cell numbers at low concentrations is caused by an inhibitory effect on cell growth rather than by induction of programmed cell death. Nonetheless, apoptosis was induced by mycalamide A in JB6 Cl41 P+ cells at concentrations of 12.5–50 nM (Figure 1d,e). We confirmed that mycalamide A induces apoptosis at higher concentrations by Western blotting. Exposing JB6 Cl41 P+ cells to mycalamide A concentrations of 12.5 nM and more for 24 h induced cleavage of caspase-3, a hallmark of apoptosis (Figure 1e).
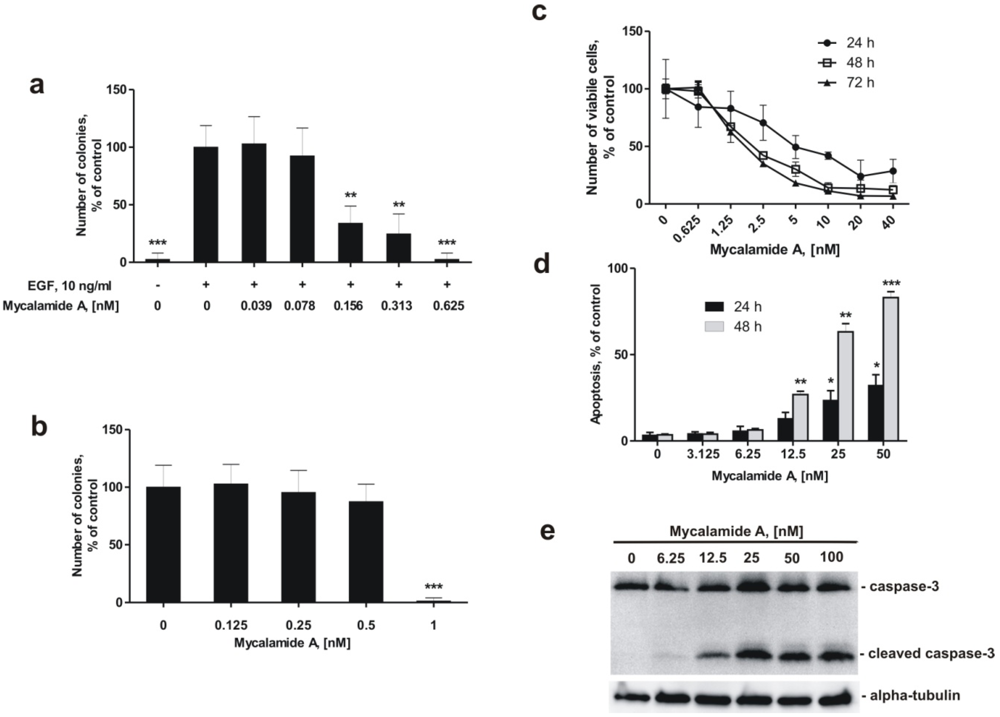
Figure 1.
Effects of mycalamide A on cell viability, induction of apoptosis, neoplastic transformation, and colony formation. (a) Inhibition of EGF-induced neoplastic transformation of JB6 Cl41 P+ cells by mycalamide A; (b) Inhibition of colony formation of the human cancer cell line HeLa by mycalamide A; (c) Effect of mycalamide A on the proliferation of murine epidermal JB6 Cl41 P+ cells, analyzed by a cell proliferation assay; (d) Induction of apoptosis by mycalamide A in JB6 Cl41 P+ cells; (e) Caspase-3 cleavage in JB6 Cl41 P+cells treated with mycalamide A. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Statistically significant differences between treated and control cells are indicated as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 (Student’s t-test).
2.4. Mycalamide A Inhibits AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53-Dependent Transcriptional Activity in JB6 Cells
It has previously been shown that inhibition of the transcriptional activity of the oncogenic nuclear factors AP-1 and NF-κB can result in cancer prevention [3,6,22]. We therefore examined the effects of mycalamide A on AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53-dependent transcriptional activity using the JB6 Cl41 cell line stably expressing a luciferase reporter gene controlled by AP-1, NF-κB, or p53 DNA binding sequences, respectively. After 6 h of incubation with the indicated concentrations of mycalamide A, transcriptional activities of AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53 were inhibited, while cell viability (determined with the MTS test) decreased only moderately, even at high concentrations (Figure 2a–c). The substance inhibited transcriptional activity of AP-1 or NF-κB after 6 h of treatment starting from concentrations of 7.8–15.6 nM (Figure 2a,b). Interestingly, in contrast to many pro-apoptotic drugs, mycalamide A did not increase p53-dependent transcriptional activity, although apoptosis was induced by the substance at that concentration (Figure 1d,e), suggesting that apoptosis induced by mycalamide A occurs via a p53-independent pathway. Similar findings have previously been reported for other cancer preventive agents, e.g., induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by indole-3-carbinol or flavones from fruit and vegetable diet, without affecting p53 activity [34,35]. However, p53 is also known to induce apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner [36,37]. Therefore, further experiments are needed to clarify the role of p53 in mycalamide A-induced apoptosis.
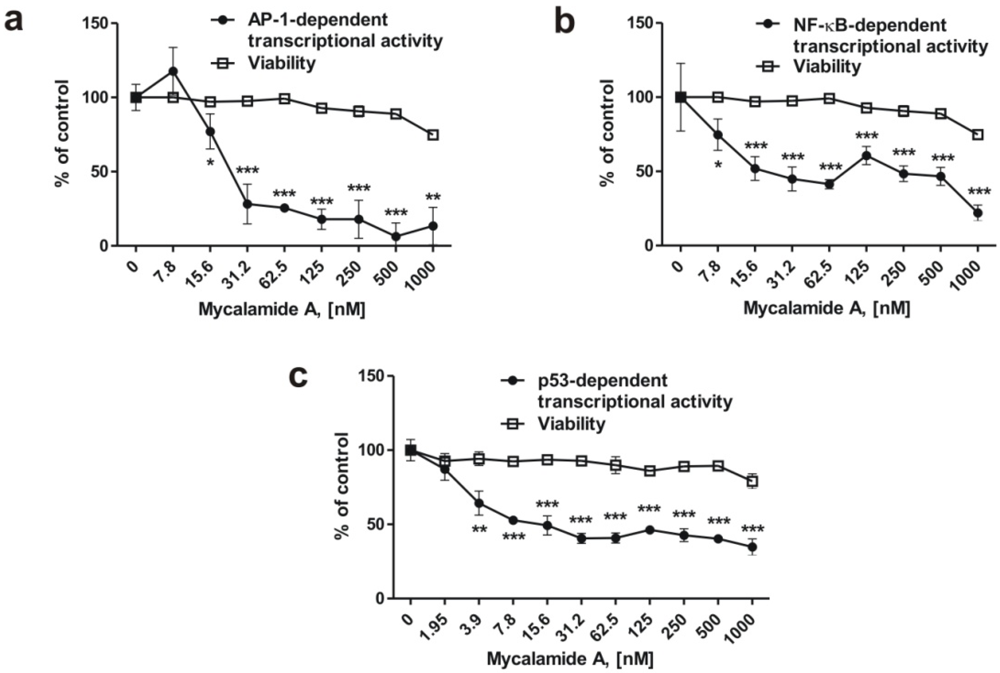
Figure 2.
Inhibition of basal AP-1- (a), NF-κB- (b) or p53- (c) dependent transcriptional activity in JB6 Cl41 cells stably expressing a luciferase reporter gene controlled by AP-1, NF-κB, or p53 DNA binding sequences. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Statistically significant differences between treated and control cells are indicated as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 (Student’s t-test).
2.5. Analysis of Phosphorylation of MAPK p38, JNK, and ERK under Mycalamide A Treatment
Furthermore, we investigated the role of several signaling pathways in the cellular response to mycalamide A. Western blotting analysis of JB6 Cl41 P+ cells treated with increasing concentrations of the substance for 1 h revealed a concentration-dependent induction of phosphorylation of p38, JNK and ERK (Figure 3a–c). Similar to mycalamide A, other marine alkaloids like polycarpine and its synthetic derivative dimethylpolycarpine, as well as marine sesquiterpenoid dactylone, have been reported to simultaneously activate p38, JNK and ERK kinases [38,39]. The ability to activate p38 kinase and JNK has previously been described for the structurally related compounds onnamide A and theopederin B, and it has been suggested that this activation is important for the antitumor activity of these compounds [40]. Our findings suggest that similar biological effects are induced by mycalamide A. For example, the activation of p38 and JNK could be involved in mycalamide A-induced apoptosis [41,42]. Therefore, we postulate that MAPK p38, JNK and ERK signaling pathways are involved in the cellular response to mycalamide A at least at high concentrations of the drug.
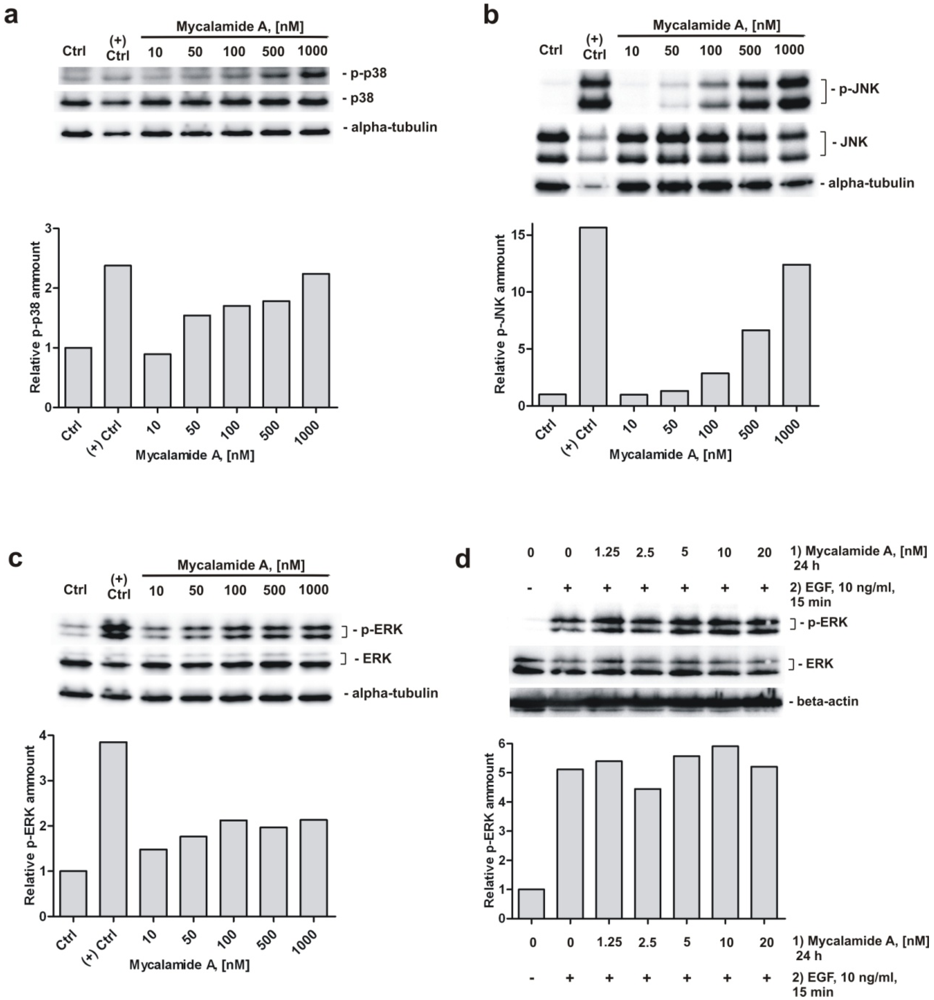
Figure 3.
Analysis of MAPK p38, JNK, and ERK changes under mycalamide A treatment. Activation of p38 (a); JNK (b); and ERK (c) in JB6 Cl41 P+ cells treated with mycalamide A for 1 h. Anisomycin treated cells (50 μM for 1 h) were used as a positive control for detection of p38 and JNK phosphorylation, EGF-treated cells (10 ng/mL for 15 min) were used as positive control for detection of ERK phosphorylation; (d) Mycalamide A pretreatment does not inhibit EGF-induced ERK phosphorylation in JB6 Cl41 P+ cells. The relative amount of phosphorylated MAPK was quantified based on optical density of the signal intensity of the correspondent bands. The signal was normalized using beta-actin or alpha-tubulin. Primary and secondary antibodies used are listed in the supplementary data.
An important finding is our observation that pretreating JB6 Cl41 P+ cells with different concentrations of mycalamide A for 24 h in serum-free medium before EGF treatment (10 ng/mL) could not prevent EGF-induced phosphorylation of ERK (Figure 3d). It is conceivable that the cancer preventive effect might be associated with altered EGFR phosphorylation, leading to inhibition of the downstream signal transduction pathway. However, our result that mycalamide A is not able to prevent phosphorylation of ERK induced by EGF strongly suggests that the cancer preventive effect of mycalamide A is not mediated through direct or indirect inhibition of this pathway. However, this assumption awaits further experimental confirmation.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents and Antibodies
Mycalamide A was isolated and purified from the sea ascidian Polysincraton sp. as described below and was pure in accordance with NMR, MS, and TLC data. Anisomycin was purchased from Merk Chemicals (Nottingham, UK), epidermal growth factor (EGF) was purchased from Collaborative Research (Bedford, MA, USA), trypsin-EDTA solution and FBS were purchased from Invitrogen (Paisley, UK). The Cell Titer 96 Aqueous One Solution Reagent [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt (MTS)] Kit was purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). A list of the antibodies used is given in supplementary data.
3.2. Animal Material
The sea ascidian Polysincraton sp. was collected by scuba divers during the 36th scientific cruise of the research vessel “Akademik Oparin”, in August 2008, at 46°18′30′′N, 150°15′30′′E in the Natalyi Bay, off the Urup Island (Kuril Islands), Sea of Okhotsk, Russian Federation, at depths of 166–200 m. A voucher specimen is kept in the collection of the Pacific Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Vladivostok, Russia. Taxonomic identification was provided by Boris B. Grebnev.
3.3. Isolation of Mycalamide A
Animal material (sea ascidian Polysincraton sp., 1000 g, wet weight) was frozen immediately after collection and later extracted with 2 L of EtOH. The ethanol extract, after evaporation in vacuo, was extracted with CHCl3 (2 × 200 mL). The chloroform extract was evaporated in vacuo (5 g) and subjected to separation on a silica gel column (150 × 40 mm). Fractions were subsequently eluted with 2000 mL of EtOAc/n-hexane (1:1) and 500 mL of CHCl3/MeOH (9:4). The CHCl3/MeOH fraction was evaporated in vacuo (260 mg) and subjected to separation on a YMC*GEL ODS-A column (90 × 25 mm) system using the solvent EtOH/H2O (7:3) as eluent. Fractions containing mycalamide A (TLC was used as control) were collected, evaporated in vacuo (47.2 mg) and separated with semi-preparative HPLC using Diasfer-110-C18 column and EtOH/H2O (1:1) as eluent. Mycalamide A was collected as a major peak of the chromatogram (5.2 mg, 0.00052% of animal wet weight).
3.4. Cell Culture
The JB6 Cl 41 P+ mouse epidermal cell line and it’s stable transfectants JB6-Luc AP-1, JB6-Luc NF-κB, and JB6-Luc p53 (PG-13) were cultured in monolayers at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in MEM, containing 5% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK). The human cancer cell line HeLa (originally cultured from a patient with a cervical carcinoma) was cultured at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in RPMI medium containing 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. JB6 cell lines were generously provided by Zigang Dong, Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, MN, USA. The HeLa cell line was purchased from the ATCC collection. Information regarding the genetic background of these cell lines is available at the ATCC website.
3.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
Inhibition of cell growth of JB6 Cl41 P+ cells by mycalamide A was determined by the trypan blue exclusion method using the cell counter Vi-CELL Beckman Coulter (Krefeld, Germany). In brief, 8 × 104 cells/well were seeded in 12-well plates and incubated overnight. The medium was replaced with fresh medium containing the indicated concentrations of mycalamide A in a total volume of 2 mL/well, and cells were incubated for 24, 48, and 72 h. Drug-containing medium was removed and cells were washed with 0.5 mL of PBS and trypsinized with 0.5 mL of trypsin-EDTA solution. The number of viable (trypan blue excluding) cells in both the medium and after trypsination was evaluated with the cell counter Vi-CELL according to the manufacture’s protocol. Assays were performed in triplicate.
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay (MTS Test)
The effect of mycalamide A on HeLa cell viability was evaluated using the MTS test, using reduction of MTS into its formazan product [18]. The cells were pre-incubated overnight in 96-well plates (6 × 103 cells/well) in medium, 100 μL/well. The medium was then replaced by fresh medium containing different concentrations of mycalamide A, and the cells were incubated for 22 h. Subsequently 20 μL of Cell Titer 96 Aqueous One Solution Reagent was added into each well, and MTS reduction was measured 2 h later spectrophotometrically at 492 and 690 nm as background using µQuant equipment (Bio-Tek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
3.7. Detection of Apoptosis
Detection of induction of apoptosis by mycalamide A was performed by FACS-based analysis with Annexin-V-FLUOS (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) and propidium iodide (PI) (Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany) double staining as previously described [33]. In brief, JB6 Cl41 P+ cells were pre-incubated overnight in 6-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well). The medium was changed with fresh medium containing different concentrations of mycalamide A. After 48 h of treatment, cells were harvested with trypsin-EDTA solution, washed with PBS and incubated with 0.1 mL of Annexin-V-FLUOS and PI containing labelling buffer for 30 min in the dark at RT. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using a FACS Calibur apparatus (BD Bioscience, Bedford, MA, USA). The results were analyzed with the Cell Quest Pro software (BD Bioscience, Bedford, MA, USA).
3.8. Anchorage-Independent Neoplastic Transformation or Colony Growth Assay
The cancer preventive effect of mycalamide A was evaluated using an anchorage-independent neoplastic transformation assay. Briefly, EGF (10 ng/mL) was used to induce neoplastic transformation of JB6 Cl41 P+ cells. The assay was carried out in 6-well tissue culture plates. Mouse JB6 Cl41 P+ cells (8 × 103 cells/mL) were treated with various concentrations of mycalamide A in 1 mL of 0.33% basal medium Eagle (BME)-agar containing 10% FBS over 3 mL of 0.5% BME-agar containing 10% FBS and various concentrations of mycalamide A. The cultures were maintained at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for a time period of 1 week, after which the number of cell colonies was scored using an Olympus CKX31 inverted research microscope (Olympus, Center Valley, PA, USA). The ability of mycalamide A to inhibit the growth of cell colonies of the human cancer cell line HeLa in soft agar was determined using the same protocol, however without EGF-stimulation.
3.9. Protein Preparation and Western Blotting
Preparation of protein extracts for Western blotting was performed as described previously [43,44,45]. In brief, 1 × 106 cells/well were seeded in Petri dishes and incubated overnight. The medium was replaced with fresh medium containing substance at the indicated concentrations in a total volume of 10 mL/dish, and cells were incubated for the indicated times. Cells were harvested by mechanical scratching, pelleted by centrifugation for 5 min at 453× g, and washed 3 times with PBS, followed by pelleting using the same conditions. Cells were lysed with 100 µL of lysis buffer (0.88% [w/v] NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), 1% NP-40 [v/v], 0.25% [w/v] NaClO2, 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM Na3VO4) on ice for 20 min. Lysates were frozen overnight at −20 °C and centrifuged 10 min at 11,170× g. Protein concentration in the supernatants was determined using the Bradford assay. Protein extracts were diluted with lysis buffer and loading dye up to a total protein concentration of 1 µg/µL, heated 5 min at 99 °C, and subjected to electrophoresis in 15% SDS-PAGE at 120 V. Proteins were transferred from gel to a 0.2 µm pore PVDF membrane (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA) at 20 V for 1 h. The membrane was blocked with 5% [w/v] non-fat dry milk in 0.05% Tween-20/TBS before treatment with the primary antibodies, according to the manufacturer’s protocol. After washing, the membrane was incubated with the appropriate secondary antibody during 1 h at RT. Signals were detected using the ECL chemiluminescence system (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Relative optical density of the signal intensity of the bends was quantified with Quantity One 4.6 software (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA).
3.10. Determination of the Effect of Mycalamide A on the Basal Transcriptional Activity of AP-1, NF-κB or p53
The effect of mycalamide A on the basal transcriptional activities of AP-1, NF-κB, or p53 was evaluated using JB6 Cl41 cell lines stably expressing a luciferase reporter gene controlled by an AP-1-, NF-κB-, or p53-DNA binding sequence, as described previously [6]. Briefly, cells were pre-incubated overnight in 96-well plates (6 × 103 cells/well) in culture medium (100 μL/well). Then the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing different concentrations of mycalamide A. After incubation for 6 h, cells were lysed for 1 h at RT with lysis buffer (0.1 M PBS (pH 7.8), 1% Triton X-100, 1 mM DTT, 2 mM EDTA). Then, 30 μL of lysate from each well was transferred into a plate for luminescent analysis, and luciferase activity was measured using luciferase assay buffer (100 μL/well) (0.47 mM D-luciferin, 20 mM Tricin, 1.07 mM (MgCO3)4 × Mg(OH)2 × 5H2O, 2.67 mM MgSO4 × 7H2O, 33.3 mM DTT, 0.53 mM ATP, 0.27 mM CoA, and 0.1 mM EDTA (pH 7.8)) and the Luminoscan Ascent Type 392 microplate reader (Labsystems, Helsinki, Finland).
4. Conclusions
Mycalamide A shows promising potential for both cancer prevention and cytotoxic therapy, warranting further exploration. Inhibition of EGF-induced neoplastic transformation by mycalamide A can be explained, at least in part, by downregulation of AP-1- and NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity. At higher concentrations, the substance induces apoptosis which is executed via caspase-3. Furthermore, the kinase signaling pathways MAPK p38, JNK, and ERK are involved in the cellular response to mycalamide A. These results help to better understand the antitumor activity of this interesting marine natural compound.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD) (S.A.D.), by a Grant 546.2012.4, supporting the leading Russian scientific schools, by the Program of Presidium of RAS “Molecular and Cell Biology” and by the Grant 12-04-00749a from RFBR (S.A.D., S.N.F., L.K.S., V.A.S.), by the Werner Otto Stiftung (F.H.) and by FEB RAS Grants 12-III-B-05-020 (S.D.). The authors are grateful to Boris B. Grebnev, Pacific Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, for the identification of the ascidian specimen; to Zigang Dong, Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, MN, USA, for providing the JB6 cell lines; and to Stefan Balabanov, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, for technical support and fruitful discussion of the results.
Supplementary Files
References
- Kuzmich, A.S.; Fedorov, S.N.; Shastina, V.V.; Shubina, L.K.; Radchenko, O.S.; Balaneva, N.N.; Zhidkov, M.E.; Park, J.I.; Kwak, J.Y.; Stonik, V.A. The anticancer activity of 3- and 10-bromofascaplysins is mediated by caspase-8, -9, -3-dependent apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Dyshlovoy, S.; Fedorov, S.; Shubina, L.; Honecker, F.; Stonik, V. Anticancer activity of aaptamine and its derivatives isolated from marine Vietnamese sponge Aaptos sp. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 33–33. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fedorov, S.; Dyshlovoy, S.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Shubina, L.; Leychenko, E.; Kozlovskaya, E.; Jin, J.O.; Kwak, J.Y.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.G.; et al. The anticancer effects of actinoporin RTX-Afrom the sea anemone Heteractis crispa (=Radianthus macrodactylus). Toxicon 2010, 55, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Fedorov, S.N.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. Three new aaptamines from the marine sponge Aaptos sp. and their proapoptotic properties. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1881–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Shubina, L.K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Stonik, V.A. Marine two-headed sphingolipid-like compound rhizochalin inhibits EGF-induced transformation of JB6 P+ Cl41 cells. Lipids 2009, 44, 777–785. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Shubina, L.K.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kwak, J.Y.; Jin, J.O.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.G.; Stonik, V.A. Proapoptotic and anticarcinogenic activities of leviusculoside G from the starfish Henricia leviuscula and probable molecular mechanism. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.Y.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Kang, K.W.; Dong, Z.; Choi, H.S. Inhibitory effects of fucoidan on activation of epidermal growth factor receptor and cell transformation in JB6 Cl41 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.K. Marine antitumor drugs: Status, shortfalls and strategies. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2702–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Pannell, L.K. Mycalamide A, an antiviral compound from a New Zealand sponge of the genus Mycale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 4850–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, K.A.; West, L.M.; Northcote, P.T.; Berridge, M.V.; Miller, J.H. Induction of apoptosis by the marine sponge (Mycale) metabolites, mycalamide A and pateamine. Apoptosis 2001, 6, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burres, N.S.; Clement, J.J. Antitumor activity and mechanism of action of the novel marine natural products mycalamide-A and -B and onnamide. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 2935–2940. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Thompson, A.M. Antiviral and antitumor agents from a New Zealand sponge, Mycale sp. 2. Structures and solution conformations of mycalamides A and B. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- West, L.M.; Northcote, P.T.; Hood, K.A.; Miller, J.H.; Page, M.J. Mycalamide D, a new cytotoxic amide from the New Zealand marine sponge Mycale species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.S.; Garson, M.J.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Hooper, J.N.A. Mycalamides C and D, cytotoxic compounds from the marine sponge Stylinos n. species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H.; Singh, A.J.; Northcote, P.T. Microtubule-stabilizing drugs from marine sponges: Focus on peloruside A and zampanolide. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawara, H.; Higashi, K.; Uchino, K.; Perry, N.B. Change of ras-transformed NRK-cells back to normal morphology by mycalamides A and B, antitumor agents from a marine sponge. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1991, 39, 2152–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, F.; Freeman, G.J.; Raziwolf, Z.; Benacerraf, B.; Nadler, L.; Reiser, H. Effects of cyclosporin A, FK 506, and mycalamide A on the activation of murine CD4+ T cells by the murine B7 antigen. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barltrop, J.A.; Owen, T.C.; Cory, A.H.; Cory, J.G. 5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl)-3-(4-sulfophenyl)tetrazolium, inner salt (MTS) and related analogs of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reducing to purple water-soluble formazans as cell-viability indicators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1991, 1, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, R.L.L. Suppression of pederin biosynthesis through antibiotic elimination of endosymbionts in Paederus sabaeus. J. Insect Physiol. 2001, 47, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, J. A polyketide synthase-peptide synthetase gene cluster from an uncultured bacterial symbiont of Paederus beetles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14002–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.R.; Butler, A.J.; Vanaltena, I. Settlement behaviour of ascidian larvae: Preliminary evidence for inhibition by sponge allelochemicals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 72, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.G.; Birrer, M.J.; Watts, R.G.; Matrisian, L.M.; Colburn, N.H. Blocking of tumor promoter-induced AP-1 activity inhibits induced transformation in JB6 mouse epidermal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 609–613. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.G.; Watts, R.G.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, S.N.; Colburn, N.H. Progressive elevation of AP-1 activity during preneoplastic-to neoplastic progression as modeled in mouse JB6 cell variants. Int. J. Oncol. 1995, 7, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Colburn, N.H.; Former, B.F.; Nelson, K.A.; Yuspa, S.H. Tumour promoter induces anchorage independence irreversibly. Nature 1979, 281, 589–591. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, J.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Z.G.; Colburn, N.H. Grafting assay distinguishes promotion sensitive from promotion resistant JB6 cells. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.W.; Tang, F.Q.; Ermakova, S.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Cho, Y.Y.; Ma, W.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Bode, A.M.; Yang, C.S.; et al. Fyn is a novel target of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate in the inhibition of JB6 Cl41 cell transformation. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S.; Ma, W.Y.; Goranson, A.; Dong, Z.G. Resveratrol suppresses cell transformation and induces apoptosis through a p53-dependent pathway. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.R.; Colburn, N.H. AP1/jun function is differentially induced in promotion-sensitive and resistant JB6 cells. Science 1989, 244, 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.S.; Ma, W.Y.; Young, M.R.; Colburn, N.; Dong, Z.G. Shortage of mitogen-activated protein kinase is responsible for resistance to AP-1 transactivation and transformation in mouse JB6 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.S.; Ma, W.Y.; Dawson, M.I.; Rincon, M.; Flavell, R.A.; Dong, Z.G. Blocking activator protein-1 activity, but not activating retinoic acid response element, is required for the antitumor promotion effect of retinoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5826–5830. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.C.; Nair, R.; Tulsian, P.; Camalier, C.E.; Hegamyer, G.A.; Young, M.R.; Colburn, N.H. Transformation nonresponsive cells owe their resistance to lack of p65/nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4160–4168. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Westergaard, C.; Ghosh, P.; Colburn, N.H. Inhibitors of both nuclear factor-kappa Beta and activator protein-1 activation block the neoplastic transformation response. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3569–3576. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Mayer, F.; Honecker, F.; Schittenhelm, M.; Bokemeyer, C. Efficacy of cytotoxic agents used in the treatment of testicular germ cell tumours under normoxic and hypoxic conditions in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinni, S.R.; Li, Y.W.; Upadhyay, S.; Koppolu, P.K.; Sarkar, F.H. Indole3-carbinol (I3C) induced cell growth inhibition, G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2927–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, N.; Toyofuku, A.; Emoto, Y.; Nagao, T.; Kuramoto, Y.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T. Induction of G(1) cell cycle arrest in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by flavone’s inhibition of the extracellular signal regulated kinase cascade. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regula, K.M.; Kirshenbaum, L.A. p53 activates the mitochondrial death pathway and apoptosis of ventricular myocytes independent of de novo gene transcription. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, N.D.; Moll, U.M. The role of ubiquitination in the direct mitochondrial death program of p53. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Shubina, L.K.; Bode, A.M.; Stonik, V.A.; Dong, Z.G. Dactylone inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced transformation and phenotype expression of human cancer cells and induces G(1)-S arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Bode, A.M.; Stonik, V.A.; Gorshkova, I.A.; Schmid, P.C.; Radchenko, O.S.; Berdyshev, E.V.; Dong, Z.G. Marine alkaloid polycarpine and its synthetic derivative dimethylpolyearpine induce apoptosis in JB6 cells through p53-and caspase 3-dependent pathways. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Nishimura, S.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Horinouchi, S.; Yoshida, M. Inhibition of protein synthesis and activation of stress-activated protein kinases by onnamide A and theopederin B, antitumor marine natural products. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.G.; Dickens, M.; Raingeaud, J.; Davis, R.J.; Greenberg, M.E. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 1995, 270, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, T.S.; Shapiro, P.S.; Ahn, N.G. Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv.Cancer Res. 1998, 74, 49–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaesener, S.; Honecker, F.; Veltman, I.M.; Gillis, A.J.M.; Rohlfing, T.; Streichert, T.; Otto, B.; Brummendorf, T.H.; Looijenga, L.H.J.; Bokemeyer, C.; et al. Comparative proteome, transcriptome, and genome analysis of a gonadal and an extragonadal germ cell tumor cell. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3890–3899. [Google Scholar]
- Ummanni, R.; Mundt, F.; Pospisil, H.; Venz, S.; Scharf, C.; Barett, C.; Falth, M.; Kollermann, J.; Walther, R.; Schlomm, T.; et al. Identification of clinically relevant protein targets in prostate cancer with 2D-DIGE coupled mass spectrometry and systems biology network platform. PLos One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Naeth, I.; Venz, S.; Preukschas, M.; Sievert, H.; Jacobsen, C.; Shubina, L.K.; Gesell Salazar, M.; Scharf, C.; Walther, R.; et al. Proteomic profiling of germ cell cancer cells treated with aaptamine, a marine alkaloid with antiproliferative activity. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2316–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).