Microbial Regulation in Gorgonian Corals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
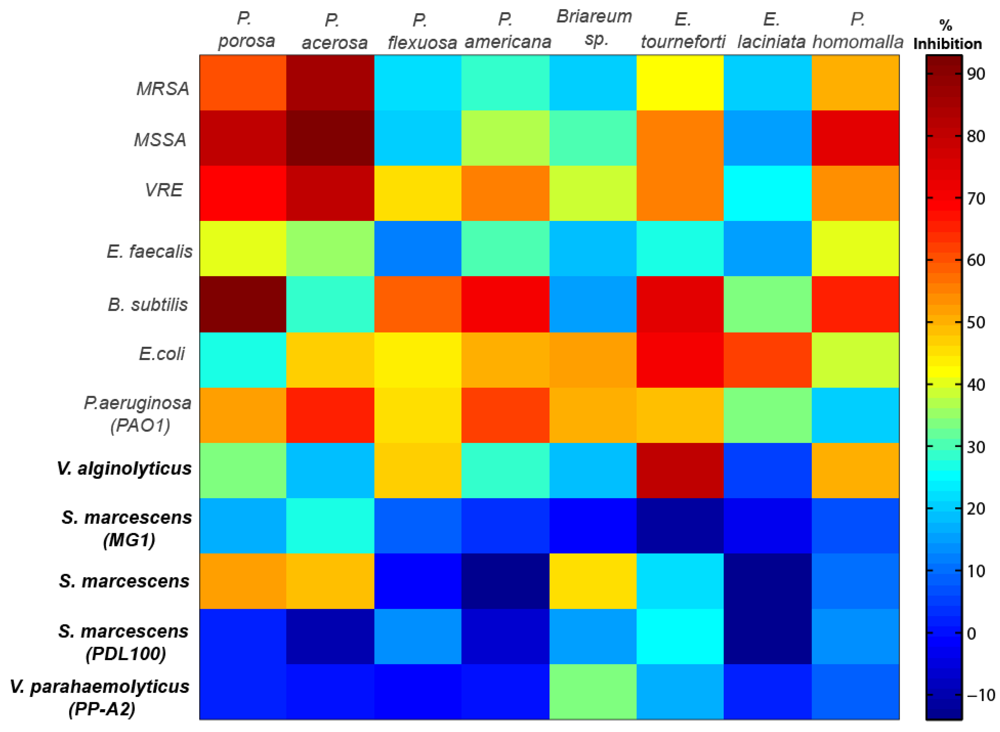
2.1. Antimicrobial Activity
| Bacteria species | Environment | Gram Stain | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | Non marine | + | ATCC # 29213 |
| Methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) | Non marine | + | ATCC # 43300 |
| Vancomycin resistant Enterococcus faecium (VRE) | Non marine | + | ATCC # 700221 |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Non marine | + | ATCC # 29212 |
| Bacillus subtilis | Non marine | + | ATCC # 6051 |
| Escherichia coli | Non marine | − | ATCC # 10536 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) | Non marine | − | ATCC # 39018 |
| Serratia marcescens (MG1) | Non marine | − | M. Teplitski |
| Serratia marcescens | Marine | − | ATCC # 39006 |
| Serratia marcescens (PDL100) | Marine | − | ATCC # BAA-632 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | Marine | − | GenBank # X744690 |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus (PP-A2) | Marine | − | Genbank # FJ892748 |
| Factor | ANOVA data | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| F | df | p | |
| Coral species | 63.50 | 7 | <0.0001 |
| Bacteria species | 153.65 | 11 | <0.0001 |
| Coral species × Bacteria species | 16.87 | 77 | <0.0001 |
| Gram stain (+) or (−) | 14.71 | 1 | 0.0002 |
| Coral species × Gram stain | 5.11 | 7 | <0.0001 |
| Environment (non-marine or marine) | 14.74 | 1 | 0.0002 |
| Coral species × Environment | 4.41 | 7 | <0.0001 |

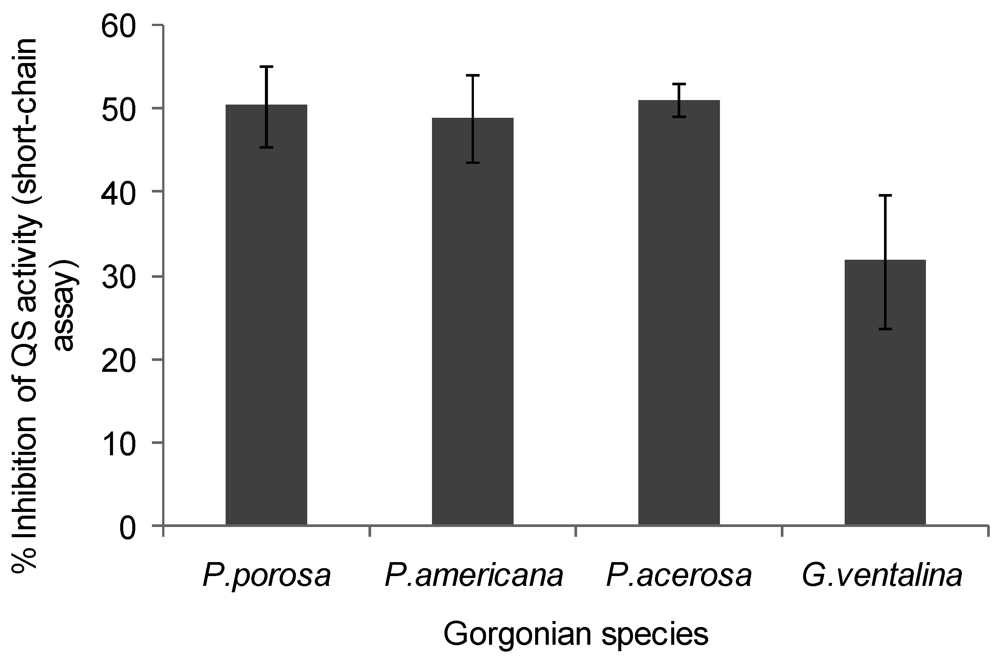
2.2. Quorum Sensing (QS) Inhibitory Activity in Gorgonian Extracts

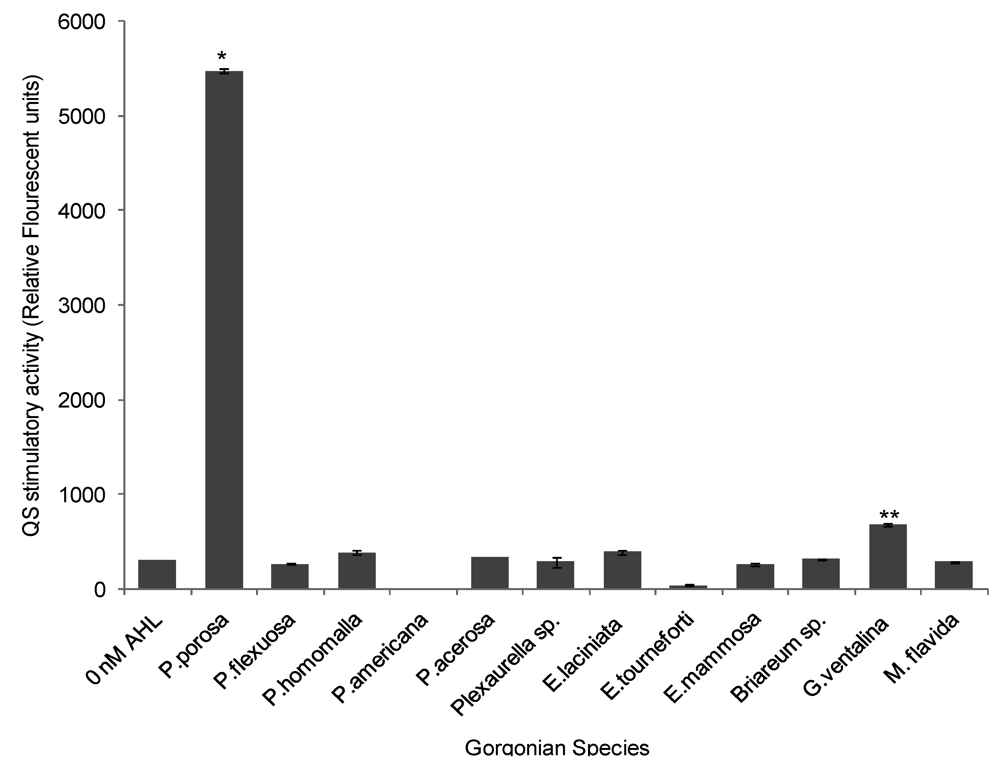
2.3. Quorum Sensing (QS) Stimulatory Activity in Gorgonian Extracts
3. Discussion
| Collection Location | Coral Species | Inhibitory QS Biossays | Inductive QS Biossays | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Long chain AHL | Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 Short chain AHL | Pseudomonas aeruginosa Long chain AHL | Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 Short chain AHL | ||
| Puerto Rico | Pseudoplexaura porosa | − | + | + | − |
| Puerto Rico | Plexaura flexuosa | + | − | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Plexaura homomalla | − | − | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Pseudopterogorgia americana | + | + | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Pseudopterogorgia acerosa | + | + | − | − |
| Florida Keys | Plexaurella sp. | − | − | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Eunicea laciniata | − | − | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Eunicea tourneforti | − | − | − | − |
| Florida Keys | Eunicea mammosa | − | − | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Briareum sp. | − | − | − | − |
| Puerto Rico | Gorgonia ventalina | + | + | + | − |
| Florida Keys | Muriceopsis flavida | − | − | − | − |
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Gorgonian Coral Collection
4.2. Extract Preparation
4.3. Antibacterial Assays
4.4. Isolation and Identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
4.5. Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3-oxo-C12-HSL Bioassay
4.6. Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 Bioassay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Bayer, F.M. The Shallow-Water Octocorallia of the West Indian Region: A Manual for Marine Biologists; Martinus Nijhoff: The Hague, The Netherland, 1961; Volume 55. [Google Scholar]
- Lasker, H.R. Prey preferences and browsing pressure of the butterflyfish Chaetodon capistratus on Caribbean gorgonians. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1985, 21, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Defensive properties of secondary metabolites from the Caribbean gorgonian coral Erythropodium caribaeorum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, W. The ecology of the coral-octocoral communities off the southeast Florida coast: Geomorphology, species composition and zonation. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1973, 23, 465–488. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, N.D.; Dardeau, M.R.; Schroeder, W.W.; Benke, A.C. Secondary production of gorgonian corals in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 87, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvell, C.D.; Fenical, W.; Greene, C.H. Chemical and structural defenses of Caribbean gorgonians (Pseudopterogorgia spp.). 1. Development of an in situ feeding assay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 49, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Alstyne, K.L.; Wylie, C.R.; Paul, V.J.; Meyer, K. Antipredator defenses in tropical Pacific soft corals (Coelenterata: Alcyonacea). I. Sclerites as defenses against generalist carnivorous fishes. Biol. Bull. 1992, 182, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.; Mcclintock, J.B.; Heine, J.N. Chemical defenses in Antarctic soft corals : Evidence for antifouling compounds. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 190, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.R.; Harvell, C.D.; Wirtz, K.; Fenical, W. Antimicrobial activity of extracts of Caribbean gorgonian corals. Mar. Biol. 1996, 125, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. Antimicrobial activity in gorgonian corals (Coelenterata, Octocorallia). Coral Reefs 1994, 13, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, K.B. Regulation of microbial populations by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 322, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, T.B.; Bruck, W.M.; Santiago-Vazquez, L.Z.; McCarthy, P.J.; Kerr, R.G. Diversity of the bacterial communities associated with the azooxanthellate deep water octocorals Leptogorgia minimata, Iciligorgia schrammi, and Swiftia exertia. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Agudelo, D.L.; Myers, C.; Smith, G.W.; Kim, K. Changes in the microbial communities associated with Gorgonia ventalina during aspergillosis infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, P.A.; Lasker, H.R.; Gottfried, M.; Roman, M.R. Production and bacterial colonization of mucus from the soft coral Briarium asbestinum. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1980, 30, 888–893. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Vazquez, L.Z.; Bruck, T.B.; Bruck, W.M.; Duque-Alarcon, A.P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Kerr, R.G. The diversity of the bacterial communities associated with the azooxanthellate hexacoral Cirrhipathes lutkeni. ISME J. 2007, 1, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, N.; Rohwer, F. Multispecies microbial mutualisms on coral reefs: The host as a habitat. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, S51–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, K.B.; Smith, G.W. Microbial Communities of Coral Surface Mucopolysaccharide Layers. In Coral Health and Disease; Rosenberg, E., Loya, Y., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rohwer, F.; Seguritan, V.; Azam, F.; Knowlton, N. Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microboil. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, G.M.; Biavasco, F.; Danovaro, R. Bacteria associated with the rapid tissue necrosis of stony corals. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantos, O.; Cooney, R.P.; Le Tissier, M.D.A.; Barer, M.R. The bacterial ecology of a plague-like disease affecting the Caribbean coral Montastrea annularis. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlarz, L.; Harvell, C. Peroxidase activity and inducibility in the sea fan coral exposed to a fungal pathogen. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlarz, L.; Jacobs, R. An inducible release of reactive oxygen radicals in four species of gorgonian corals. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2006, 39, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.E.; Bythell, J.C. Perspectives on mucus secretion in reef corals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 296, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.J.; Wagner, P.; Maki, J.S.; Walch, M.; Mitchell, R. Factors influencing the adhesion of microorganisms to surfaces. J. Adhes. 1986, 20, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, C.; Greenberg, E.P. Listening in on bacteria: Acyl-homoserine lactone signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S.A.B. N-Acylhomoserine Lactones and Quorum Sensing in Proteobacteria. In Cell-Cell Signaling in Bacteria; Dunny, G.M., Winans, S.C., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 291–312. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, N.A.; Barnard, A.M.L.; Slater, H.; Simpson, N.J.L.; Salmond, G.P.C. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 365–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glessner, A.; Smith, R.S.; Iglewski, B.H.; Robinson, J.B. Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of twitching motility. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Sasaki, S. Control of the bioluminescence starting time by inoculated cell density. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.A.; Koh, K.S.; Queck, S.Y.; Labbate, M.; Lam, K.W.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Miller, M.B.; Vance, R.E.; Dziejman, M.; Bassler, B.L.; Mekalanos, J.J. Quorum-sensing regulators control virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3129–3134. [Google Scholar]
- Lupp, C.; Ruby, E.G. Vibrio fischeri uses two quorum-sensing systems for the regulation of early and late colonization factors. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3620–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visick, K.L.; Ruby, E.G. Vibrio fischeri and its host: It takes two to tango. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 632–638. [Google Scholar]
- Skindersoe, M.E.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; de Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Schupp, P.J.; Baillie, H.J.; Charlton, T.S.; de Nys, R.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P.D. Evidence for acyl homoserine lactone signal production in bacteria associated with marine sponges. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4387–4389. [Google Scholar]
- Tait, K.; Hutchison, Z.; Thompson, F.L.; Munn, C.B. Quorum sensing signal production and inhibition by coral-associated vibrios. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, K.; Eltzov, E.; Shnit-Orland, M.; Marks, R.; Kushmaro, A. Characterization of quorum sensing signals in coral-associated bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagely, A.; Krediet, C.J.; Ritchie, K.B.; Teplitski, M. Signaling-mediated cross-talk modulates swarming and biofilm formation in a coral pathogen Serratia marcescens. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplitski, M.; Ritchie, K. How feasible is the biological control of coral diseases? Trends Ecol. Volution 2009, 24, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, D.; Kashman, Y.; Rosenberg, E.; Kushmaro, A.; Loya, Y. Antimicrobial activity of Red Sea corals. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlarz, L.; Holthouse, S.; Peters, E.; Harvell, C.; May, R. Cellular responses in Sea Fan Corals: Granular amoebocytes react to Pathogen and climate stressors. PLoS One 2008, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Alker, A.P.; Kim, K.; Dube, D.H.; Harvell, C.D. Localized induction of a generalized response against multiple biotic agents in Caribbean sea fans. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, K.A.; Wang, E.; Shen, S.; Rao, S.; Smith, S.M.; Hunt, L.; Mydlarz, L.D. Direct affinity screening chromatography-mass spectrometry assay for identification of antibacterial agents from natural product sources. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 713, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.E.; Caiazza, N.C.; O’Toole, G.A. Rhamnolipid surfactant production affects biofilm architecture in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Dobretsov, S.; Ki, J.S.; Yang, L.H.; Qian, P.Y. Presence of acyl-homoserine lactone in subtidal biofilm and the implication in larval behavioral response in the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntharalingam, P.; Cvitkovitch, D.G. Quorum sensing in streptococcal biofilm formation. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P.; Baumann, L.; Mandel, M. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: The genus Beneckea. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 107, 268–294. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.M.; Katarski, M.E.; Weisrock, W.P. Correlation of taxonomic criteria for a collection of marine bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 708–713. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, S.; Silipo, A.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Molinaro, A. Molecular structure of endotoxins from gram-negative marine bacteria: An update. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gram, L.; Grossart, H.P.; Schlingloff, A.; Kiorboe, T. Possible quorum sensing in marine snow bacteria: Production of acylated homoserine lactones by Roseobacter strains isolated from marine snow. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4111–4116. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, N.M.; Cicirelli, E.M.; Kan, J.J.; Chen, F.; Fuqua, C.; Hill, R.T. Diversity and quorum-sensing signal production of Proteobacteria associated with marine sponges. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Jacobson, P.B.; Fenical, W.; Jacobs, R.S.; Glaser, K.B. Pharmacological characterization of the pseudopterosins: Novel anti-inflammatory natural products isolated from the caribbean soft coral, Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Life Sci. 1998, 62, PL401–PL407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epifanio, R.D.A.; Maia, L.F.; Pawlik, J.R.; Fenical, W. Antipredatory secosterols from the octocoral Pseudopterogorgia americana. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 329, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Dudler, R.; Eberl, L. Interactions between bacteria and eukaryotes via small molecules. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.T.; Sperandio, V. Inter-kingdom signalling: Communication between bacteria and their hosts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint, I.; Tait, K.; Callow, M.E.; Callow, J.A.; Milton, D.; Williams, P.; Camara, M. Cell-to-cell communication across the prokaryote-eukaryote boundary. Science 2002, 298, 1207–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P.; Givskov, M.; Gram, L.; Manefield, M.; de Nys, R. Do marine natural products interfere with prokaryotic AHL regulatory systems? Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 13, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manefield, M.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Henzter, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Givskov, M. Halogenated furanones inhibit quorum sensing through accelerated LuxR turnover. Microbiololy 2002, 148, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Harvell, C.D. The rise and fall of a six-year coral-fungal epizootic. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, S52–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.S.; Mydlarz, L.D.; Harvell, C.D.; Douglas, N.L. Variation in measures of immunocompetence of sea fan coral, Gorgonia ventalina, in the Florida Keys. Mar. Biol. 2008, 155, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.R.; Kim, K.; Harvell, C.D. Temperature affects coral disease resistance and pathogen growth. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, D.; Grossmann, G.; Sequin, U.; Brandl, H.; Bachofen, R. Effects of natural and chemically synthesized furanones on quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4. [Google Scholar]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar]
- Krick, A.; Kehraus, S.; Eberl, L.; Riedel, K.; Anke, H.; Kaesler, I.; Graeber, I.; Szewzyk, U.; Konig, G.M. A marine Mesorhizobium sp produces structurally novel long-chain N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3587–3594. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, K.L.; Porter, J.W.; Ritchie, K.B.; Polson, S.W. From the Cover: The etiology of white pox, a lethal disease of the Caribbean elkhorn coral, Acropora palmata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8725–8730. [Google Scholar]
- Mydlarz, L.D.; Couch, C.S.; Weil, E.; Smith, G.; Harvell, C.D. Immune defenses of healthy, bleached and diseased Montastraea faveolata during a natural bleaching event. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 87, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochfeld, D.J.; Aeby, G.S. Antibacterial chemical defenses in Hawaiian corals provide possible protection from disease. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 362, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, S.; Arnold, W.; Puhler, A. Diversity of uncultured microorganisms associated with the seagrass Halophila stipulacea estimated by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 766–771. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, J.P.; Feldman, M.; Iglewski, B.H.; Prince, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-to-cell signaling is required for virulence in a model of acute pulmonary infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4331–4334. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, L.; Konig, G.; Wright, A.; Pukall, R.; Stackebrandt, E.; Eberl, L.; Riedel, K. Secondary metabolites of Flustra foliacea and their influence on bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3469–3475. [Google Scholar]
- Riedel, K.; Hentzer, M.; Geisenberger, O.; Huber, B. N-Acylhomoserine-lactone-mediated communication between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia in mixed biofilms. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.; Sternberg, C.; Poulsen, L.; Bjorn, S.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S. New unstable variants of green fluorescent protein for studies of transient gene expression in bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2240–2246. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hunt, L.R.; Smith, S.M.; Downum, K.R.; Mydlarz, L.D. Microbial Regulation in Gorgonian Corals. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1225-1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061225
Hunt LR, Smith SM, Downum KR, Mydlarz LD. Microbial Regulation in Gorgonian Corals. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(6):1225-1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061225
Chicago/Turabian StyleHunt, Laura R., Stephanie M. Smith, Kelsey R. Downum, and Laura D. Mydlarz. 2012. "Microbial Regulation in Gorgonian Corals" Marine Drugs 10, no. 6: 1225-1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061225
APA StyleHunt, L. R., Smith, S. M., Downum, K. R., & Mydlarz, L. D. (2012). Microbial Regulation in Gorgonian Corals. Marine Drugs, 10(6), 1225-1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061225





