Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Acute Exacerbations of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective, Real-World Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
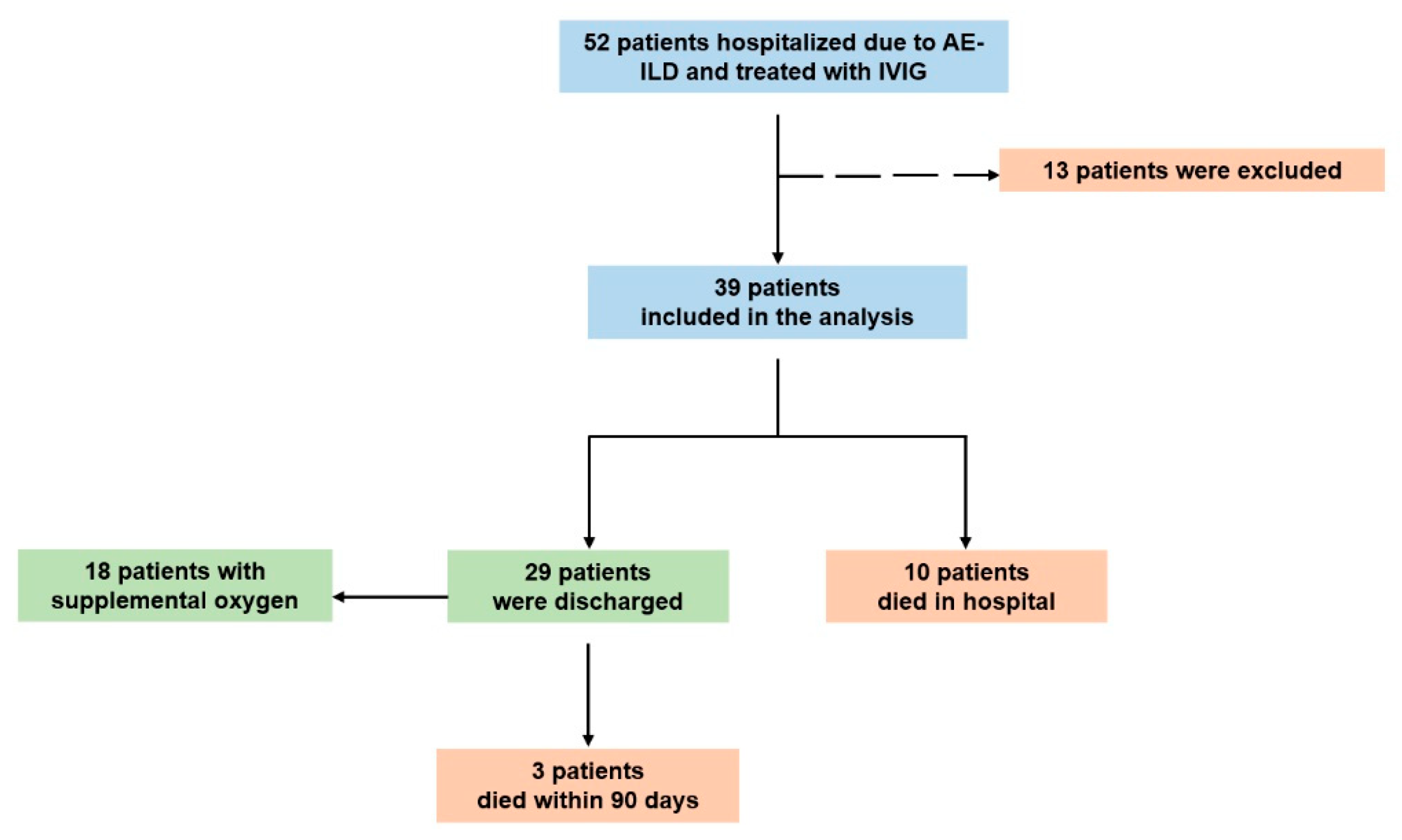
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. IVIG Exerts an Acceptable Safety Profile in Patients with AE-fILDs
3.3. IVIG Was Associated with Favorable Clinical Outcomes in Patients with AE-fILDs
3.4. Subgroup Analysis in Rituximab and Non-Rituximab Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE-fILDs | acute exacerbation of fibrotic interstitial lung diseases |
| AE-IPF | acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| BAL | bronchoalveolar lavage |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CT | computed tomography |
| CTD-ILDs | connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung diseases |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| fILDs | fibrotic interstitial lung diseases |
| ILDs | interstitial lung diseases |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| IVIG | intravenous immunoglobulin |
| LTOT | long-term oxygen therapy |
| MPA | microscopic polyangiitis |
| NSIP | non-specific interstitial pneumonia |
| PCT | procalcitonin |
| P/F ratio | PaO2/FiO2 ratio |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| UIP | usual interstitial pneumonia |
References
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An International Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Bondue, B.; Pesci, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Song, J.W.; Bhatt, N.Y.; Huggins, J.T.; Oldham, J.M.; Padilla, M.L.; Roman, J.; et al. Acute exacerbations of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Belloli, E.A.; Bendstrup, E.; Cerri, S.; Flaherty, K.R.; Shapera, S.; Song, J.W.; Mueller, H.; Rohr, K.B.; Kondoh, Y.; et al. Acute exacerbations in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00403-2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.W.; Hong, S.B.; Lim, C.M.; Koh, Y.; Kim, D.S. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Incidence, risk factors and outcome. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolo, P.; Wuyts, W. Acute exacerbations of interstitial lung disease: Lessons from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2017, 23, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakugawa, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Sato, S.; Yura, H.; Harada, T.; Nakashima, S.; Hara, A.; Oda, K.; Ishimoto, H.; Yatera, K.; et al. Risk factors for an acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, I.; Usuda, H. Acute exacerbation of IPF has systemic consequences with multiple organ injury, with SRA(+) and TNF-alpha(+) cells in the systemic circulation playing central roles in multiple organ injury. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, M.; Carter, H.; Espindola, M.S.; Doyle, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; Merriam, L.T.; Zhang, F.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Sparks, J.A.; Hogaboam, C.M.; et al. Immune mechanisms in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Cell 2024, 187, 3506–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, H.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wu, S.; Jiang, C.; Ye, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. Animal models of acute exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Markart, P.; Steiropoulos, P. Acute Exacerbations of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Focus on Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.F.; Raghu, G. Treatment of acute exacerbations of interstitial lung diseases with corticosteroids: Evidence? Respirology 2024, 29, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Sun, W.; Xu, Z.J. The immune mechanisms of acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1450688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, J.; Purokivi, M.; Bloigu, R.; Kaarteenaho, R. Prognosis and causes of death of patients with acute exacerbation of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2020, 7, e000563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, M.; Polke, M.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Krisam, J.; Collard, H.R.; Chaudhuri, N.; Avdeev, S.; Behr, J.; Calligaro, G.; Corte, T.; et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: International survey and call for harmonisation. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, F.; Manfredi, A.; Faverio, P.; Franco, G.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Sebastiani, M. Treatment of acute exacerbation in interstitial lung disease secondary to autoimmune rheumatic diseases: More questions than answers. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccache, J.M.; Jouneau, S.; Didier, M.; Borie, R.; Cachanado, M.; Bourdin, A.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Bonniaud, P.; Israel-Biet, D.; Prevot, G.; et al. Cyclophosphamide added to glucocorticoids in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (EXAFIP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papiris, S.A.; Manali, E.D.; Kolilekas, L.; Triantafillidou, C.; Tsangaris, I.; Kagouridis, K. Steroids in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis acute exacerbation: Defenders or killers? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Swigris, J.; Day, B.M.; Stauffer, J.L.; Raimundo, K.; Chou, W.; Collard, H.R. Pirfenidone Reduces Respiratory-related Hospitalizations in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misirci, S.; Ekin, A.; Yagiz, B.; Coskun, B.N.; Basibuyuk, F.; Birlik, A.M.; Sari, I.; Karaca, A.D.; Koca, S.S.; Yildirim Cetin, G.; et al. Treatment with nintedanib is as effective and safe in patients with other connective tissue diseases (CTDs)-interstitial lung disease (ILD) as in patients with systemic sclerosis-ILD: A multicenter retrospective study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 44, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campochiaro, C.; De Luca, G.; Lazzaroni, M.G.; Armentaro, G.; Spinella, A.; Vigone, B.; Ruaro, B.; Stanziola, A.; Benfaremo, D.; De Lorenzis, E.; et al. Real-life efficacy and safety of nintedanib in systemic sclerosis-interstitial lung disease: Data from an Italian multicentre study. RMD Open 2023, 9, e002850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, E.E.; Orange, J.S.; Bonilla, F.; Chinen, J.; Chinn, I.K.; Dorsey, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Harville, T.O.; Hossny, E.; Mazer, B.; et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: A review of evidence. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S1–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Bernstein, E.J.; Bolster, M.B.; Chung, J.H.; Danoff, S.K.; George, M.D.; Khanna, D.; Guyatt, G.; Mirza, R.D.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. 2023 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) Guideline for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in People with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1182–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Z. Adverse Effects of Immunoglobulin Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kareva, L.; Mironska, K.; Stavric, K.; Hasani, A. Adverse Reactions to Intravenous Immunoglobulins—Our Experience. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 2359–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, Y.; Cottin, V.; Brown, K.K. Recent lessons learned in the management of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Sun, J.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Li, Q.; Villalba, J.A.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Lynn, H.; Juan-Guardela, B.M.; Risquez, C.; Osorio, J.C.; et al. Validation of a 52-gene risk profile for outcome prediction in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An international, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Ryerson, C.J.; Putman, R.; Oldham, J.; Salisbury, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Valenzuela, C.; Guler, S.; Jones, S.; Wijsenbeek, M.; et al. Early diagnosis of fibrotic interstitial lung disease: Challenges and opportunities. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higo, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Nakamura, N.; Fujii, M.; Matsuoka, K.; Seki, S.; Wada, T.; Suzaki, N.; Nagata, T.; Arakawa, Y.; et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin for acute exacerbation of fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2022, 39, e2022038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, T.; Criner, G.J.; Kass, D.J.; Rosas, I.O.; Scholand, M.B.; Dilling, D.F.; Summer, R.; Duncan, S.R. Design of the STRIVE-IPF trial- study of therapeutic plasma exchange, rituximab, and intravenous immunoglobulin for acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, K.; Kono, M.; Saito, G.; Koyanagi, Y.; Tsutsumi, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Miki, Y.; Hashimoto, D.; Nakamura, Y.; Suda, T.; et al. Prognosis after acute exacerbation in patients with interstitial lung disease other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 15, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Isshiki, T.; Shimizu, H.; Kurosaki, A.; Homma, S. The Activities of Daily Living after an Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, Y.; Azuma, A.; Inoue, Y.; Ogura, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Tsushima, K.; Johkoh, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Ichikado, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; et al. Thrombomodulin Alfa for Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Baseline Characteristics | (N, %) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) (Mean ± SD) | 70 ± 12 |
| Male/Female | 19 (49%)/20 (51%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Dyslipidemia | 26 (67%) |
| Arterial hypertension | 22 (56%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 14 (36%) |
| Coronary artery disease | 11 (28%) |
| Depression | 11 (28%) |
| Thyroid disorder | 6 (15%) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 5 (13%) |
| Underlying ILD diagnosis | |
| Idiopathic pulmonary disease | 12 (31%) |
| Connective tissues disease associated ILDs | 11 (28%) |
| [RA/Myositis/MPA/SLE] | [5 (45%)/3 (28%)/2 (18%)/1 (9%)] |
| Idiopathic fibrotic NSIP | 5 (13%) |
| Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis | 3 (8%) |
| Newly diagnosed ILD | 8 (21%) |
| Underlying CT patterns (28 available) | |
| Definite/Probable/Indeterminate UIP | 6 (21%)/5 (18%)/5 (18%) |
| Fibrotic NSIP | 10 (36%) |
| Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis | 2 (7%) |
| Prior treatment | |
| Antifibrotics: nintedanib/pirfenidone | 9 (23%)/7 (18%) |
| Corticosteroids (≤4 mg methylprednisolone/day) | 7 (18%) |
| Investigation and Treatment | (N, %) |
|---|---|
| Laboratory exams | |
| IVIG on admission (mg/dL) (Mean ± SD) | 998 ± 447 |
| CRP on admission (mg/dL) (Mean ± SD) | 11.57 ± 8.3 |
| PCT on admission (μg/L) (Median, 95%CI) | 0.07 (0.05 to 0.13) |
| Bronchoscopy | 12 (31%) |
| Pharmacological treatment | |
| IVIG | 39 (100%) |
| Methylprednisolone pulse therapy | 39 (100%) |
| Empiric antibiotics | 39 (100%) |
| Anticoagulation | 39 (100%) |
| Rixutimab/Cyclophosphamide | 23 (59%)/2 (5%) |
| Supportive oxygen therapy | |
| High flow nasal cannula | 25 (64%) |
| Continuous positive airway pressure | 6 (15%) |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 8 (21%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotiropoulou, V.; Theochari, E.; Katsaras, M.; Tsiri, P.; Komninos, D.; Christopoulos, I.; Tsirikos, G.; Kalogeropoulou, C.; Daoussis, D.; Karkoulias, K.; et al. Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Acute Exacerbations of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective, Real-World Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091594
Sotiropoulou V, Theochari E, Katsaras M, Tsiri P, Komninos D, Christopoulos I, Tsirikos G, Kalogeropoulou C, Daoussis D, Karkoulias K, et al. Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Acute Exacerbations of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective, Real-World Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091594
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotiropoulou, Vasilina, Eva Theochari, Matthaios Katsaras, Panagiota Tsiri, Dimitrios Komninos, Ioannis Christopoulos, Georgios Tsirikos, Christina Kalogeropoulou, Dimitrios Daoussis, Kyriakos Karkoulias, and et al. 2025. "Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Acute Exacerbations of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective, Real-World Study" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091594
APA StyleSotiropoulou, V., Theochari, E., Katsaras, M., Tsiri, P., Komninos, D., Christopoulos, I., Tsirikos, G., Kalogeropoulou, C., Daoussis, D., Karkoulias, K., Sampsonas, F., & Tzouvelekis, A. (2025). Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Acute Exacerbations of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective, Real-World Study. Medicina, 61(9), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091594





