Linking Kawasaki Disease to Mental Health: A Nationwide Study on Long-Term Neurological Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
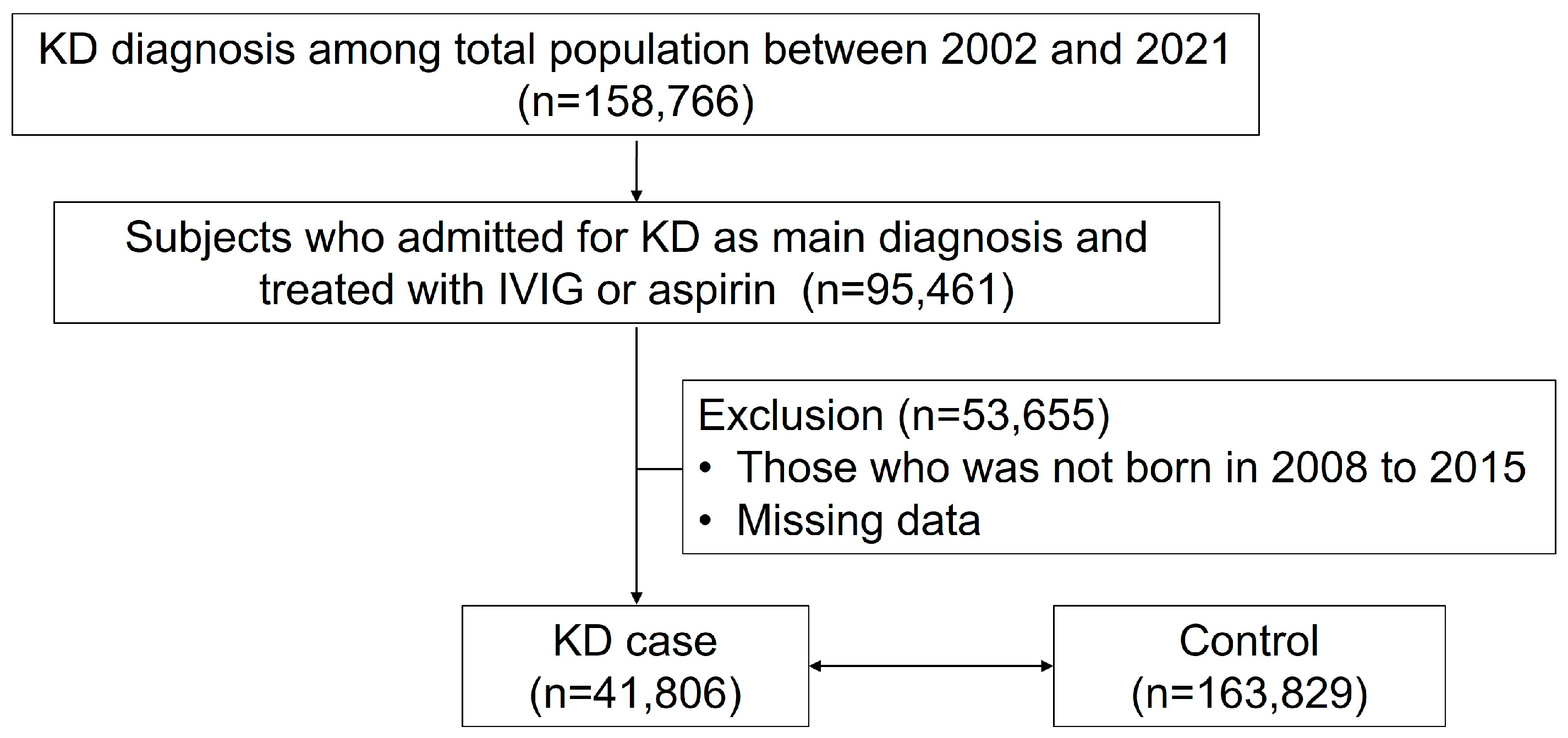
2.2. Study Design and Population
2.3. Study Outcomes
2.4. Ethics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of Study Participants
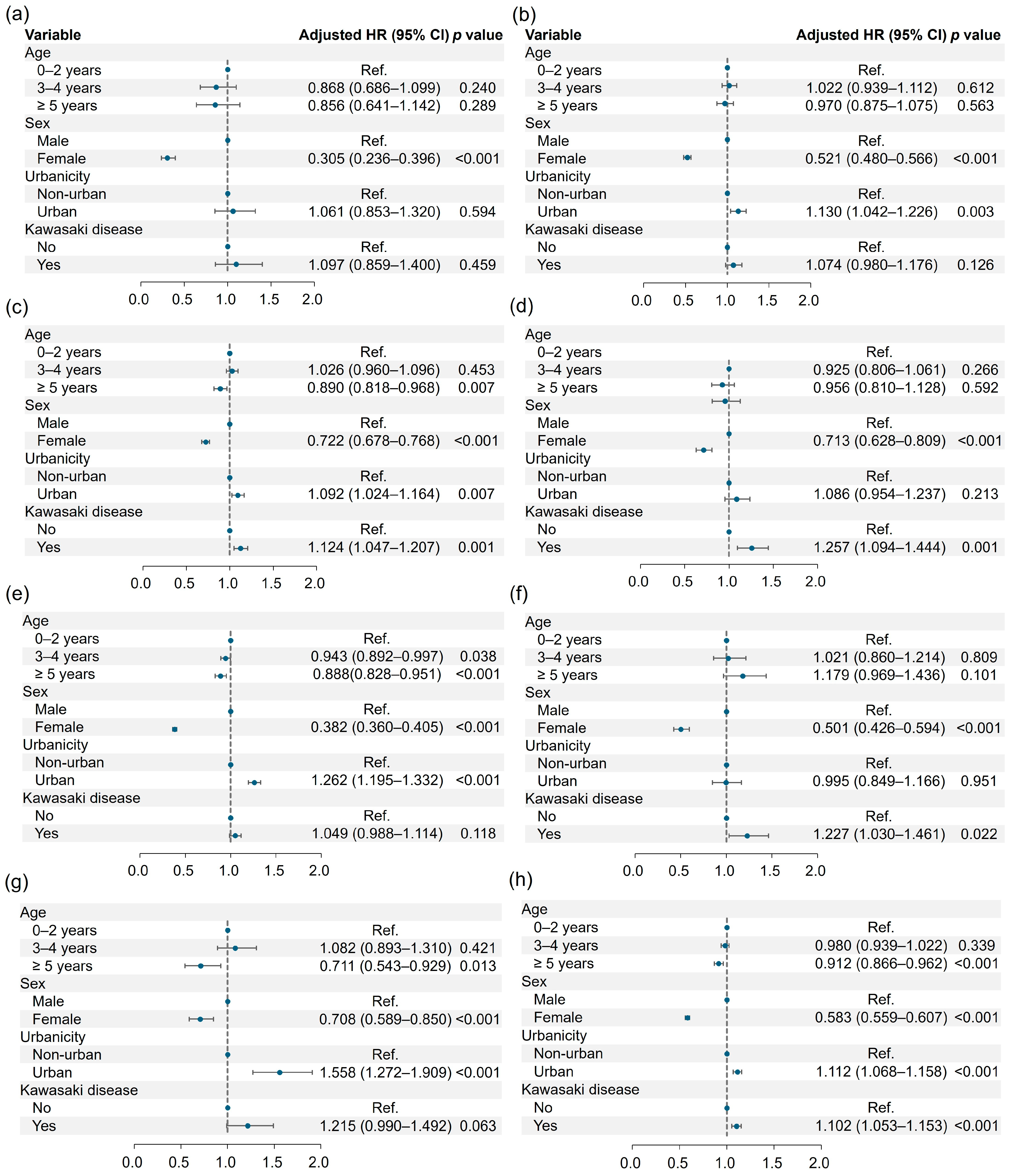
3.2. Risk of Neuropsychiatric Disorders
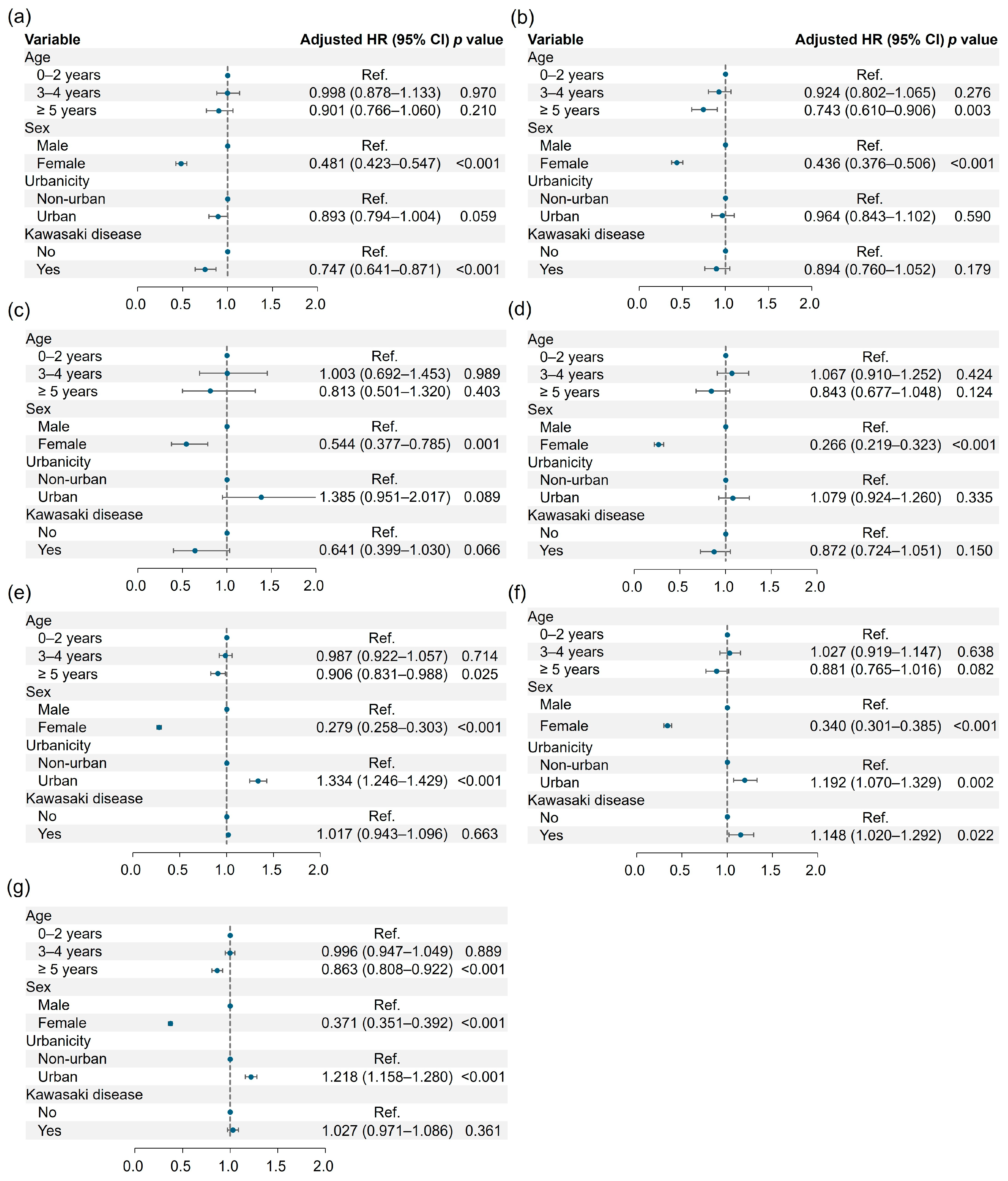
3.3. Risk of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KD | Kawasaki Disease |
| ADHD | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| SPECT | Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography |
| NHIS | National Health Insurance Service |
References
- Kawasaki, T.; Kosaki, F.; Okawa, S.; Shigematsu, I.; Yanagawa, H. A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics 1974, 54, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, T.; Evans, M. Intestinal obstruction as a complication of Kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1996, 31, 985–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.B.; Kahn, A.M.; Burns, J.C. When children with Kawasaki disease grow up: Myocardial and vascular complications in adulthood. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, A.; Di Mari, C.; Casini, F.; Giani, T.; Sandini, M.; Biondi, L.; Calcaterra, V.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Bernardo, L. Neurological manifestations of Kawasaki disease and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19: A comparison of two different clinical entities. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1088773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, C.S. Migraine and Raynaud phenomenon: Possible late complications of Kawasaki disease. Headache 2002, 42, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, Y.; Ogata, S.; Nomoto, K.; Ebato, T.; Sato, K.; Kokubo, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Ishii, M. Transcriptional regulation by infliximab therapy in Kawasaki disease patients with immunoglobulin resistance. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 76, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ichiyama, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Hayashi, T.; Koga, M.; Tashiro, N.; Furukawa, S. Cerebral hypoperfusion during acute Kawasaki disease. Stroke 1998, 29, 1320–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikita, T.; Kaminaga, T.; Wakita, S.; Ogita, K.; Ikemoto, H.; Fujii, Y.; Oba, H.; Yanagawa, Y. Regional cerebral blood flow abnormalities in patients with kawasaki disease. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2011, 36, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauteux, A.A.; Gutierrez Rojas, R.; Agbogba, K.; Benovoy, M.; Charlebois-Poirier, A.R.; Lalancette, E.; Lippe, S.; Dahdah, N. Electroencephalography signals and neurodevelopment after Kawasaki disease: A pilot study. Pediatr. Int. 2023, 65, e15482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crider, A.; Feng, T.; Pandya, C.D.; Davis, T.; Nair, A.; Ahmed, A.O.; Baban, B.; Turecki, G.; Pillai, A. Complement component 3a receptor deficiency attenuates chronic stress-induced monocyte infiltration and depressive-like behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbonaite, G.; Knyzeliene, A.; Bunn, F.S.; Smalskys, A.; Neniskyte, U. The impact of maternal high-fat diet on offspring neurodevelopment. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 909762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chourpiliadis, C.; Hammar, N.; Seitz, C.; Valdimarsdottir, U.A.; Fang, F.; Song, H.; Wei, D. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Risk of Psychiatric Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2024, 81, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundquist, K.; Li, X.; Hemminki, K.; Sundquist, J. Subsequent risk of hospitalization for neuropsychiatric disorders in patients with rheumatic diseases: A nationwide study from Sweden. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benros, M.E.; Eaton, W.W.; Mortensen, P.B. The epidemiologic evidence linking autoimmune diseases and psychosis. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, W.W.; Byrne, M.; Ewald, H.; Mors, O.; Chen, C.Y.; Agerbo, E.; Mortensen, P.B. Association of schizophrenia and autoimmune diseases: Linkage of Danish national registers. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, G.M.; Zammit, S.; Lewis, G.; Jones, P.B. A population-based study of atopic disorders and inflammatory markers in childhood before psychotic experiences in adolescence. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 152, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.T.; Chang, J.P.; Cheng, S.W.; Chang, H.C.; Hsu, J.H.; Chang, H.H.; Chiu, W.C.; Su, K.P. Kawasaki disease in childhood and psychiatric disorders: A population-based case-control prospective study in Taiwan. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 100, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Lao, F.; Chanchlani, R.; Gayowsky, A.; Darling, E.; Batthish, M. Long-term hearing and neurodevelopmental outcomes following Kawasaki disease: A population-based cohort study. Brain Dev. 2021, 43, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Wu, C.M.; Chang, W.P.; Kuo, C.N.; Yeter, D.; Lin, C.Y.; Pai, J.T.; Chi, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, L.J.; et al. Association between Kawasaki disease and autism: A population-based study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3705–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Lin, W.D.; Chou, I.C.; Lee, I.C.; Hong, S.Y. Heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorders in children with Kawasaki disease: What is new today? BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Chang, W.C.; Wang, L.J.; Li, S.C.; Chang, W.P. Association of Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and Kawasaki disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2016, 25, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Kuo, H.C. Cognitive Development After Kawasaki Disease—Clinical Study and Validation Using a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Tsai, Z.Y.; Chang, L.S.; Kuo, H.C. Cognitive development of children with Kawasaki disease and the parenting stress of their caregivers in Taiwan: A case-control study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e042996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Lin, Y.W.; Chen, Y.B.; Wang, L.J.; Kuo, H.C. Association of Kawasaki disease with intellectual disability, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2025, 51, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambeitz, J.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Modelling the impact of environmental and social determinants on mental health using generative agents. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.C.F.; Wirgenes, K.V.; Shadrin, A.; Lunding, S.H.; Rodevand, L.; Hjell, G.; Ormerod, M.; Haram, M.; Agartz, I.; Djurovic, S.; et al. Immune marker levels in severe mental disorders: Associations with polygenic risk scores of related mental phenotypes and psoriasis. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheol Seong, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Khang, Y.H.; Heon Park, J.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, H.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Hyon Bang, J.; Ha, S.; et al. Data resource profile: The national health information database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Yun, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Yu, J.; Yang, H.J.; Suh, D.I.; Korean Childhood Asthma, REsearch Team. Leukotriene receptor antagonists and risk of neuropsychiatric events in children, adolescents and young adults: A self-controlled case series. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, L.; Bateman, B.T.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; York, C.; Zhu, Y.; Suarez, E.A.; Lester, B.; Gonzalez, L.; Hanson, R.; Hildebrandt, C.; et al. Validity of claims-based algorithms to identify neurodevelopmental disorders in children. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2021, 30, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park-Min, K.H.; Serbina, N.V.; Yang, W.; Ma, X.; Krystal, G.; Neel, B.G.; Nutt, S.L.; Hu, X.; Ivashkiv, L.B. FcgammaRIII-dependent inhibition of interferon-gamma responses mediates suppressive effects of intravenous immune globulin. Immunity 2007, 26, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriou, D.; Levin, M.; Shingadia, D.; Tulloh, R.; Klein, N.J.; Brogan, P.A. Management of Kawasaki disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Tang, H.; Ding, Y. Kawasaki disease involving both the nervous system and cardiovascular system: A case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1459143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Lai, J.N.; Lee, I.C.; Chou, I.C.; Lin, W.D.; Lin, M.C.; Hong, S.Y. Kawasaki Disease May Increase the Risk of Subsequent Cerebrovascular Disease. Stroke 2022, 53, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jone, P.N.; Tremoulet, A.; Choueiter, N.; Dominguez, S.R.; Harahsheh, A.S.; Mitani, Y.; Zimmerman, M.; Lin, M.T.; Friedman, K.G. Update on Diagnosis and Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e481–e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lersch, R.; Mandilaras, G.; Schrader, M.; Anselmino, F.; Haas, N.A.; Jakob, A. Have we got the optimal treatment for refractory Kawasaki disease in very young infants? A case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1210940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takekoshi, N.; Kitano, N.; Takeuchi, T.; Suenaga, T.; Kakimoto, N.; Suzuki, T.; Kada, T.T.; Shibuta, S.; Tachibana, S.; Murayama, Y.; et al. Analysis of Age, Sex, Lack of Response to Intravenous Immunoglobulin, and Development of Coronary Artery Abnormalities in Children With Kawasaki Disease in Japan. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2216642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.J.; Butt, C.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, S.; Li, Y. Immune regulation based on sex differences in ischemic stroke pathology. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1087815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotomayor-Zarate, R.; Cruz, G.; Renard, G.M.; Espinosa, P.; Ramirez, V.D. Sex hormones and brain dopamine functions. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodes, G.E.; Bangasser, D.; Sotiropoulos, I.; Kokras, N.; Dalla, C. Sex Differences in Stress Response: Classical Mechanisms and Beyond. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, H.; Harley, V.; Lee, J. Biological factors underlying sex differences in neurological disorders. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 65, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engemann, K.; Pedersen, C.B.; Arge, L.; Tsirogiannis, C.; Mortensen, P.B.; Svenning, J.C. Residential green space in childhood is associated with lower risk of psychiatric disorders from adolescence into adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5188–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassos, E.; Agerbo, E.; Mors, O.; Pedersen, C.B. Urban-rural differences in incidence rates of psychiatric disorders in Denmark. Br. J. Psychiatry 2016, 208, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukka, D.; Parkkola, R.; Hirvonen, J.; Ylikotila, P.; Vahlberg, T.; Salo, E.; Kivelev, J.; Rinne, J.; Rahi, M. Brain white matter hyperintensities in Kawasaki disease: A case-control study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 995480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Principe, D.; Pietraforte, D.; Gambardella, L.; Marchesi, A.; Tarissi de Jacobis, I.; Villani, A.; Malorni, W.; Straface, E. Pathogenetic determinants in Kawasaki disease: The haematological point of view. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.M.; Cowan, M.; Moonah, S.N.; Petri, W.A., Jr. The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Neurodevelopment. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, B.C.; Beltrao-Braga, P.C.B.; Marchetto, M.C. Modeling Inflammation on Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using Pluripotent Stem Cells. Adv. Neurobiol. 2020, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, A.L. Inflammation in psychiatric disorders: What comes first? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1437, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korematsu, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Miyahara, H.; Nagakura, T.; Okazaki, N.; Kawano, T.; Kojo, M.; Izumi, T. The characterization of cerebrospinal fluid and serum cytokines in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2007, 26, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, Z.; Tan, C.; Cao, Y. Altered gut microbiota correlated with systemic inflammation in children with Kawasaki disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Zeng, M.Y.; Nunez, G. The interplay between host immune cells and gut microbiota in chronic inflammatory diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouabbou, S.; He, Y.; Butler, K.; Tsuang, M. Inflammation in Mental Disorders: Is the Microbiota the Missing Link? Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroun, A.; Mitra, S.; Michaluk, P.; Pijet, B.; Stefaniuk, M.; Kaczmarek, L. MMPs in learning and memory and neuropsychiatric disorders. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3207–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizzo, A.; Lenzi, P.; Procaccini, C.; Damato, A.; Biagioni, F.; Ambrosio, M.; Amodio, G.; Remondelli, P.; Del Giudice, C.; Izzo, R.; et al. Pentraxin 3 induces vascular endothelial dysfunction through a P-selectin/matrix metalloproteinase-1 pathway. Circulation 2015, 131, 1495–1505, discussion 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.A.; Shin, K.S.; Kim, Y.W. Polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase-3 promoter gene as a risk factor for coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2005, 20, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Small, C.D.; Crawford, B.D. Matrix metalloproteinases in neural development: A phylogenetically diverse perspective. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, N.; Jelen, A.; Rush, J.; Manlhiot, C.; Boydell, K.M.; Sananes, R.; McCrindle, B.W. Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms: Psychosocial Impact on Parents and Children. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2017, 31, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | KD Cases (n = 41,806) | Controls (n = 163,829) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Mean (years) | 2.63 ± 1.84 | 2.64 ± 1.85 | 0.119 |
| ≤2 years | 22,038 (52.71) | 85,992 (52.49) | 0.225 |
| 3–4 years | 13,376 (32.00) | 52,226 (31.88) | |
| ≥5 years | 6392 (15.29) | 25,611 (15.63) | |
| Sex (female) | 17,643 (42.20) | 69,709 (42.55) | 0.199 |
| Urbanicity | 0.025 | ||
| Urban | 28,054 (67.11) | 108,991 (66.53) | |
| Non-urban | 13,752 (32.89) | 54,838 (33.47) |
| Kawasaki Disease | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case (n, %) | No | Yes | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Psychotic disorder (−) | 163,536 (95.82) | 41,722 (99.80) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Psychotic disorder (+) | 293 (0.18) | 84 (0.20) | 1.096 (0.859–1.400) | 0.459 | 1.097 (0.859–1.400) | 0.459 |
| Mood disorder (−) | 161,639 (98.66) | 41,218 (98.59) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Mood disorder (+) | 2190 (1.34) | 588 (1.41) | 1.068 (0.975–1.170) | 0.156 | 1.074 (0.980–1.176) | 0.126 |
| Anxiety disorder (−) | 160,403 (97.91) | 40,835 (97.68) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Anxiety disorder (+) | 3426 (2.09) | 971 (2.32) | 1.124 (1.046–1.207) | 0.001 | 1.124 (1.047–1.207) | 0.001 |
| Sleep-related disorder (−) | 163,027 (99.51) | 41,539 (99.36) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Sleep-related disorder (+) | 802 (0.49) | 267 (0.64) | 1.254 (1.091–1.441) | 0.001 | 1.257 (1.094–1.444) | 0.001 |
| Cognitive disorder (−) | 158,718 (96.88) | 40,446 (96.75) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Cognitive disorder (+) | 5111 (3.12) | 1360 (3.25) | 1.046 (0.985–1.111) | 0.140 | 1.049 (0.988–1.114) | 0.118 |
| Movement disorder (−) | 163,309 (99.68) | 41,636 (99.59) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Movement disorder (+) | 520 (0.32) | 170 (0.41) | 1.222 (1.026–1.454) | 0.025 | 1.227 (1.030–1.461) | 0.022 |
| Personality disorder (−) | 163,439 (96.76) | 41,686 (99.71) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Personality disorder (+) | 390 (0.24) | 120 (0.29) | 1.219 (0.993–1.496) | 0.058 | 1.215 (0.990–1.492) | 0.063 |
| Any disorder (−) | 155,234 (94.75) | 39,400 (94.24) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Any disorder (+) | 8595 (5.25) | 2406 (5.76) | 1.101 (1.053–1.152) | <0.001 | 1.102 (1.053–1.153) | <0.001 |
| Kawasaki Disease | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case (n, %) | No | Yes | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Intellectual disorder (−) | 162,817 (99.38) | 41,612 (99.54) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Intellectual disorder (+) | 1012 (0.62) | 194 (0.46) | 0.747 (0.640–0.871) | <0.001 | 0.747 (0.641–0.871) | <0.001 |
| Communication disorder (−) | 163,051 (99.53) | 41,628 (99.57) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Communication disorder (+) | 778 (0.47) | 178 (0.43) | 0.897 (0.762–1.056) | 0.192 | 0.894 (0.760–1.052) | 0.179 |
| Specific learning disorder (−) | 163,708 (99.93) | 41,785 (99.95) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Specific learning disorder (+) | 121 (0.07) | 21 (0.05) | 0.643 (0.400–1.033) | 0.068 | 0.641 (0.399–1.030) | 0.066 |
| Autism spectrum disorder (−) | 163,226 (99.63) | 41,670 (99.67) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Autism spectrum disorder (+) | 603 (0.37) | 136 (0.33) | 0.876 (0.727–1.056) | 0.165 | 0.872 (0.724–1.051) | 0.150 |
| ADHD (−) | 160,512 (97.98) | 40,951 (97.95) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| ADHD (+) | 3317 (2.02) | 855 (2.05) | 1.021 (0.947–1.101) | 0.580 | 1.017 (0.943–1.096) | 0.663 |
| Tic disorder (−) | 162,608 (99.25) | 41,451 (99.15) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Tic disorder (+) | 1221 (0.75) | 355 (0.85) | 1.154 (1.025–1.298) | 0.018 | 1.148 (1.020–1.292) | 0.022 |
| Any disorder (−) | 157,926 (96.40) | 40,262 (96.31) | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Any disorder (+) | 5903 (3.60) | 1544 (3.69) | 1.029 (0.973–1.088) | 0.322 | 1.027 (0.971–1.086) | 0.361 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Shin, T.; Park, J.-M.; Seol, J.-H. Linking Kawasaki Disease to Mental Health: A Nationwide Study on Long-Term Neurological Risks. Medicina 2025, 61, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040604
Lee J-H, Shin T, Park J-M, Seol J-H. Linking Kawasaki Disease to Mental Health: A Nationwide Study on Long-Term Neurological Risks. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040604
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji-Ho, Taewoo Shin, Jung-Min Park, and Jae-Hee Seol. 2025. "Linking Kawasaki Disease to Mental Health: A Nationwide Study on Long-Term Neurological Risks" Medicina 61, no. 4: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040604
APA StyleLee, J.-H., Shin, T., Park, J.-M., & Seol, J.-H. (2025). Linking Kawasaki Disease to Mental Health: A Nationwide Study on Long-Term Neurological Risks. Medicina, 61(4), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040604







