Hormonal Alterations in Individuals with Obesity After Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: From Weight Loss to Metabolic Transformation
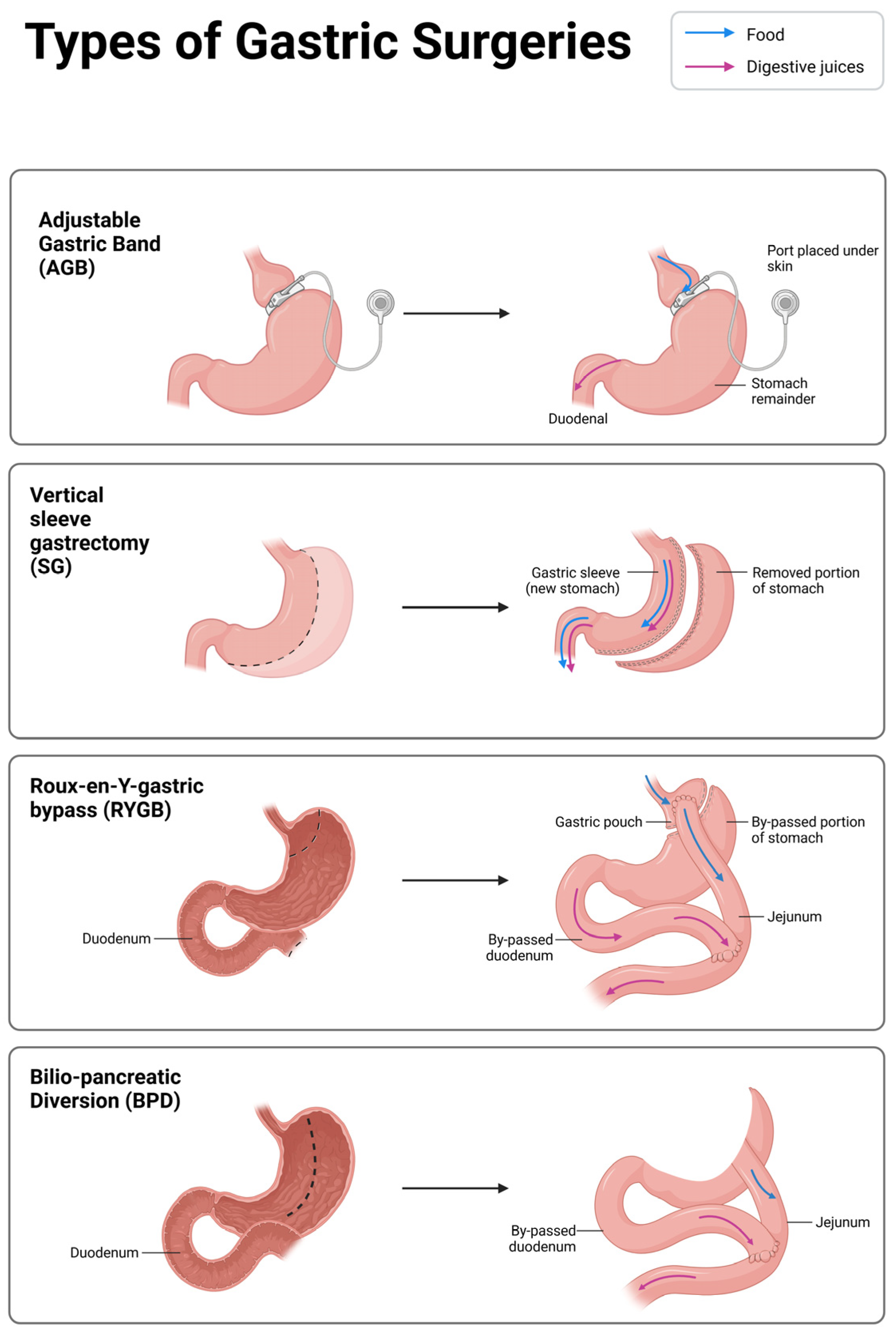
4. Principal Techniques of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery
4.1. Adjustable Gastric Band (AGB)
4.2. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Bilio-Pancreatic Diversion (BPD)
4.3. Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG)
4.4. One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB)
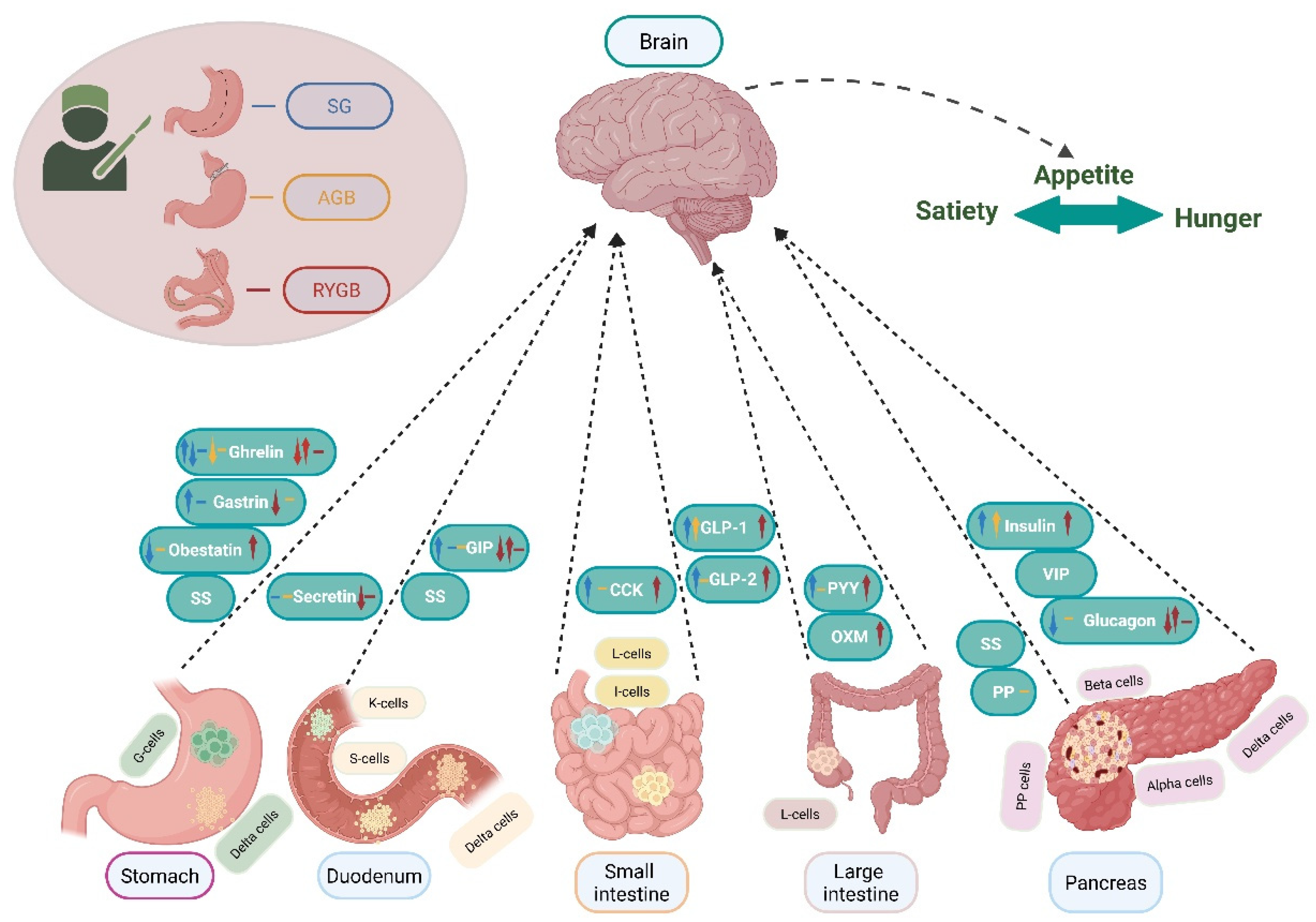
5. Gastrointestinal Hormones and Metabolic Bariatric Surgery
5.1. Stomach Hormones
5.1.1. Gastrin
5.1.2. Ghrelin
5.1.3. Obestatin
5.2. Pancreatic Hormones
5.2.1. Insulin
5.2.2. Glucagon
5.2.3. Somatostatin (SS)
5.2.4. Pancreatic Polypeptide (PP)
5.2.5. Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide (VIP)
5.3. Small and Large Intestine Hormones
5.3.1. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (GLP-1)
5.3.2. Glucagon-like Peptide 2 (GLP-2)
5.3.3. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
5.3.4. Pancreatic Peptide YY
5.3.5. Oxyntomodulin (OXM)
5.4. Duodenum Hormones
5.4.1. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP)
5.4.2. Secretin
6. Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF-19, FGF-21)
7. Endocrine and Reproductive Outcomes of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery
8. Current Evidence and Challenges in Comparing Surgical Techniques for Obesity and Metabolic Outcomes
9. Limitations, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
10. Clinical and Translational Relevance
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; Report of a WHO Consultation; World Health Organization Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; Volume 894, pp. i–xii+1–253.
- Safaei, M.; Sundararajan, E.A.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W.; Shapi’i, A. A systematic literature review on obesity: Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounatidis, D.; Vallianou, N.G.; Stratigou, T.; Voukali, M.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. The Kidney in Obesity: Current Evidence, Perspectives and Controversies. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 680–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Haboubi, H.; Haboubi, N. Adult obesity complications: Challenges and clinical impact. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 2042018820934955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, S.; Sockalingam, S.; Dash, S. Obesity as a multisystem disease: Trends in obesity rates and obesity-related complications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23 (Suppl. S1), 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztanek, F.; Tóth, L.I.; Pető, A.; Hernyák, M.; Diószegi, Á.; Harangi, M. New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes-Beyond and within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Svane, M.S.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Dirksen, C.; Martinussen, C. Mechanisms in bariatric surgery: Gut hormones, diabetes resolution, and weight loss. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, D.E.; Telem, D.A.; Kushner, R.F.; Courcoulas, A.P. Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinto, N.; Olatunji, G.; Kokori, E.; Olaniyi, P.; Isarinade, T.; Yusuf, I.A. Recent advances in bariatric surgery: A narrative review of weight loss procedures. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 6091–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Gill, R.S.; de Gara, C.J.; Karmali, S.; Gagner, M. Biliopancreatic diversion: The effectiveness of duodenal switch and its limitations. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 974762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, K.; Huang, C.-K.; Patel, A.; Wong, L.-F.; Lu, Y.-C.; Hsin, M.-C. Conversion of One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is Effective in Dealing with Late Complications of OAGB: Experience from a Tertiary Bariatric Center and Literature Review. J. Metab. Bariatr. Surg. 2021, 10, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, M.K. The Incretins and Pancreatic β-Cells: Use of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide to Cure Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2010, 34, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yu, B.; Chen, D. The effects of gut microbiota on appetite regulation and the underlying mechanisms. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2414796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, C.; Abi Mosleh, K.; Aeschbacher, P.; Halfdanarson, T.R.; McKenzie, T.J.; Rosenthal, R.J.; Ghanem, O.M. The feasibility and outcomes of metabolic and bariatric surgery prior to neoplastic therapy. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2024, 20, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.A. Comment on: The feasibility and outcomes of metabolic and bariatric surgery prior to neoplastic therapy. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2024, 20, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, R. The history and role of gastric banding. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2008, 4, S7–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kassab, G.S. Efficacy and Mechanisms of Gastric Volume-Restriction Bariatric Devices. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 761481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclellan, W.C.; Johnson, J.M. Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass: Still the Gold Standard? Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 101, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopinaro, N.; Adami, G.F.; Marinari, G.M.; Gianetta, E.; Traverso, E.; Friedman, D.; Camerini, G.; Baschieri, G.; Simonelli, A. Biliopancreatic diversion. World J. Surg. 1998, 22, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Johari, Y.; Ooi, G.; Playfair, J.; Laurie, C.; Hebbard, G.; Brown, W.; Burton, P. Diagnostic Criteria for Gastro-esophageal Reflux Following Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataya, K.; Al Jaafreh, A.M.; El Bourji, H.; Bsat, A.; Nassar, H.; Al Ayoubi, A.; Abi Saad, G. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Versus One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass as Revisional Surgery After Failed Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Metab. Bariatr. Surg. 2023, 12, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, M.; Pereira, S.S.; Monteiro, M.P. Metabolomic signatures after bariatric surgery—A systematic review. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Rehfeld, J.F. On premises and principles for measurement of gastrointestinal peptide hormones. Peptides 2021, 141, 170545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaoli, L.; Wu, C.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Tian, W.; Chiang, F.Y.; Liu, R.; Anuwong, A.; Randolph, G.W.; Dionigi, G.; Lavazza, M. Gastric acid secretion and gastrin release during continuous vagal neuromonitoring in thyroid surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.L. Gastric acid secretion. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 32, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.H.; Olesen, S.C.; Dirksen, C.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Kielgast, U.; Worm, D.; Almdal, T.; Naver, L.S.; Hvolris, L.E.; et al. Changes in gastrointestinal hormone responses, insulin sensitivity, and β-cell function within 2 weeks after gastric bypass in non-diabetic subjects. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundbom, M.; Holdstock, C.; Engström, B.E.; Karlsson, F.A. Early changes in ghrelin following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: Influence of vagal nerve functionality? Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedberg, J.; Hedenström, H.; Nilsson, S.; Sundbom, M.; Gustavsson, S. Role of gastric acid in stomal ulcer after gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2005, 15, 1375–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shak, J.R.; Roper, J.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Tseng, C.H.; Francois, F.; Gamagaris, Z.; Patterson, C.; Weinshel, E.; Fielding, G.A.; Ren, C.; et al. The effect of laparoscopic gastric banding surgery on plasma levels of appetite-control, insulinotropic, and digestive hormones. Obes. Surg. 2008, 18, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grong, E.; Græslie, H.; Munkvold, B.; Arbo, I.B.; Kulseng, B.E.; Waldum, H.L.; Mårvik, R. Gastrin Secretion After Bariatric Surgery—Response to a Protein-Rich Mixed Meal Following Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Pilot Study in Normoglycemic Women. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safatle-Ribeiro, A.V.; Petersen, P.A.; Pereira Filho, D.S.; Corbett, C.E.; Faintuch, J.; Ishida, R.; Sakai, P.; Cecconello, I.; Ribeiro, U., Jr. Epithelial cell turnover is increased in the excluded stomach mucosa after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes. Surg. 2013, 23, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillakivi, T.; Suumann, J.; Kirsimägi, U.; Peetsalu, A. Plasma levels of gastric biomarkers in patients after bariatric surgery: Biomarkers after bariatric surgery. Hepatogastroenterology 2013, 60, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, S.L.; Egecioglu, E.; Landgren, S.; Skibicka, K.P.; Engel, J.A.; Jerlhag, E. The role of the central ghrelin system in reward from food and chemical drugs. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Abdalla, M.M. Ghrelin–Physiological Functions and Regulation. Eur. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egecioglu, E.; Jerlhag, E.; Salomé, N.; Skibicka, K.P.; Haage, D.; Bohlooly, Y.M.; Andersson, D.; Bjursell, M.; Perrissoud, D.; Engel, J.A.; et al. Ghrelin increases intake of rewarding food in rodents. Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.E.; Weigle, D.S.; Frayo, R.S.; Breen, P.A.; Ma, M.K.; Dellinger, E.P.; Purnell, J.Q. Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Rotellar, F.; Hernández-Lizoain, J.L.; Gil, M.J.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Salvador, J.; Cienfuegos, J.A. Fasting plasma ghrelin concentrations 6 months after gastric bypass are not determined by weight loss or changes in insulinemia. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Diez-Caballero, A.; Gil, M.J.; Montero, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Salvador, J.; Cienfuegos, J.A. The decrease in plasma ghrelin concentrations following bariatric surgery depends on the functional integrity of the fundus. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.; Switzer, N.J.; Almamar, A.; Shi, X.; Birch, D.W.; Karmali, S. The impact of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy on plasma ghrelin levels: A systematic review. Obes. Surg. 2013, 23, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, C.; Mulita, F.; Alexandrides, T.; Kehagias, D.; Kalavrizioti, D.; Albanopoulos, K.; Georgopoulos, N.; Papachristou, E.; Kehagias, I. Ghrelin, glucagon-like peptide-1, and peptide YY secretion in patients with and without weight regain during long-term follow-up after bariatric surgery: A cross-sectional study. Menopause Rev. 2022, 21, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehagias, D.; Georgopoulos, N.; Habeos, I.; Lampropoulos, C.; Mulita, F.; Kehagias, I. The role of the gastric fundus in glycemic control. Hormones 2023, 22, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, I.; Amorim, L.; Walpole, C.; Carter, S.; Chopin, L.K.; Herington, A.C. Ghrelin gene-related peptides: Multifunctional endocrine/autocrine modulators in health and disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, E.; Burch, K.J.; Green, B.D.; Grieve, D.J. Obestatin as a key regulator of metabolism and cardiovascular function with emerging therapeutic potential for diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2165–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Xu, X.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, W.H. The role of obestatin in roux-en-Y gastric bypass-induced remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.S.; Durham, B.H.; Wong, S.P.; Deepak, D.; Kerrigan, D.; McCulloch, P.; Ranganath, L.; Pinkney, J.; Wilding, J.P. Plasma obestatin levels are lower in obese and post-gastrectomy subjects, but do not change in response to a meal. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Kjelstrup, L.; Mostad, I.L.; Kulseng, B. Impact of sustained weight loss achieved through Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or a lifestyle intervention on ghrelin, obestatin, and ghrelin/obestatin ratio in morbidly obese patients. Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bradley, D.; Conte, C.; Mittendorfer, B.; Eagon, J.C.; Varela, J.E.; Fabbrini, E.; Gastaldelli, A.; Chambers, K.T.; Su, X.; Okunade, A.; et al. Gastric bypass and banding equally improve insulin sensitivity and β cell function. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4667–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannipieri, M.; Baldi, S.; Mari, A.; Colligiani, D.; Guarino, D.; Camastra, S.; Barsotti, E.; Berta, R.; Moriconi, D.; Bellini, R.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: Mechanisms of diabetes remission and role of gut hormones. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4391–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camastra, S.; Muscelli, E.; Gastaldelli, A.; Holst, J.J.; Astiarraga, B.; Baldi, S.; Nannipieri, M.; Ciociaro, D.; Anselmino, M.; Mari, A.; et al. Long-term effects of bariatric surgery on meal disposal and β-cell function in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Dirksen, C.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Serup, A.K.; Albers, P.H.; Hansen, D.L.; Worm, D.; Naver, L.; Kristiansen, V.B.; et al. Early enhancements of hepatic and later of peripheral insulin sensitivity combined with increased postprandial insulin secretion contribute to improved glycemic control after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cătoi, A.F.; Pârvu, A.; Mironiuc, A.; Galea, R.F.; Mureşan, A.; Bidian, C.; Pop, I. Effects of sleeve gastrectomy on insulin resistance. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, M.M.; Isaacs, M.; Bliuc, D.; Baldock, P.A.; Eisman, J.A.; White, C.P.; Greenfield, J.R.; Center, J.R. Effects of bariatric surgery and dietary intervention on insulin resistance and appetite hormones over a 3 year period. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J.; Lefèbvre, P.J. Glucagon, from past to present: A century of intensive research and controversies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Sun, S.; Sun, G. Role of Glucagon and Its Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 928016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, L.M.; Silva, E.A.; Carneiro, G.; Arasaki, C.H.; Geloneze, B.; Zanella, M.T. Early improvement in glycemic control after bariatric surgery and its relationships with insulin, GLP-1, and glucagon secretion in type 2 diabetic patients. Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farey, J.E.; Preda, T.C.; Fisher, O.M.; Levert-Mignon, A.J.; Stewart, R.L.; Karsten, E.; Herbert, B.R.; Swarbrick, M.M.; Lord, R.V. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy on Fasting Gastrointestinal, Pancreatic, and Adipose-Derived Hormones and on Non-Esterified Fatty Acids. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, D.; Moriconi, D.; Mari, A.; Rebelos, E.; Colligiani, D.; Baldi, S.; Anselmino, M.; Ferrannini, E.; Nannipieri, M. Postprandial hypoglycaemia after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelos, E.; Moriconi, D.; Scalese, M.; Denoth, F.; Molinaro, S.; Siciliano, V.; Anselmino, M.; Taddei, S.; Ferrannini, E.; Nannipieri, M. Impact of Postprandial Hypoglycemia on Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricò, D.; Sacchetta, L.; Rebelos, E.; Cimbalo, N.; Chiriacò, M.; Moriconi, D.; Nesti, L.; Nesti, G.; Frascerra, S.; Scozzaro, M.T.; et al. Postprandial hypoglycaemia after gastric bypass in type 2 diabetes: Pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wei, N.; Guo, W.; Qiang, O.; Li, X.; Ou, Y.; Huang, W.; Tang, C.W. Octreotide alleviates obesity by reducing intestinal glucose absorption and inhibiting low-grade inflammation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xue, L.; Wu, Z.B. Structure and Function of Somatostatin and Its Receptors in Endocrinology. Endocr. Rev. 2024, 46, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, D.; Arad, Y.; Azulai, S.; Baker, A.; Bergel, M.; Elad, A.; Haran, A.; Hefetz, L.; Israeli, H.; Littor, M.; et al. Inhibition of somatostatin enhances the long-term metabolic outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy in mice. Mol. Metab. 2024, 86, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.L.; Le Roux, C.W.; Cohen, M.A.; Park, A.J.; Ellis, S.M.; Patterson, M.; Frost, G.S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Pancreatic polypeptide reduces appetite and food intake in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3989–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.F.; le Roux, C.W.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; McGee, T.L.; Dixon, J.B. Pancreatic polypeptide meal response may predict gastric band-induced weight loss. Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Ganea, D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: A neuropeptide with pleiotropic immune functions. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirinek, K.R.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Howe, B.; McFee, A.S. Neurotensin, Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide, and Roux-en-Y Gastrojejunostomy: Their Role in the Dumping Syndrome. Arch. Surg. 1985, 120, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutch, C.R.; Sandoval, D. Correction to: “The Role of GLP-1 in the Metabolic Success of Bariatric Surgery”. Endocrinology 2024, 165, bqae042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.; Pamuklar, Z.; Rosko, J.; Mahaney, P.; Jiang, N.; Park, C.; Torquati, A. Gastric bypass surgery restores meal stimulation of the anorexigenic gut hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 and peptide YY independently of caloric restriction. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Mixson, L.A.; Chakravarthy, M.; Chisholm, R.; Acton, A.J.; Jones, R.; Mattar, S.G.; Miller, D.L.; Petry, L.; Beals, C.R.; et al. Metabolic improvements following Roux-en-Y surgery assessed by solid meal test in subjects with short duration type 2 diabetes. BMC Obes. 2017, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoli, M.; Chronaiou, A.; Kehagias, I.; Kalfarentzos, F.; Alexandrides, T.K. Hormone changes and diabetes resolution after biliopancreatic diversion and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A comparative prospective study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.B.; Dirksen, C.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Worm, D.; Hansen, D.L.; Kristiansen, V.B.; Naver, L.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J. Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide 1 response is important for improved β-cell function and glucose tolerance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3044–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korner, J.; Bessler, M.; Inabnet, W.; Taveras, C.; Holst, J.J. Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide-1 and blunted glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide secretion are associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not adjustable gastric banding. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2007, 3, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, C.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Kristiansen, V.B.; Naver, L.S.; Hansen, D.L.; Worm, D.; Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S. Exaggerated release and preserved insulinotropic action of glucagon-like peptide-1 underlie insulin hypersecretion in glucose-tolerant individuals after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2679–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estall, J.L.; Drucker, D.J. Dual Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Survival via Activation of Glucagon-Like Peptide-2 Receptor Signaling. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3708–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martin, G.R.; Wallace, L.E.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Demchyshyn, L.; Toney, K.; Sigalet, D.L. Nutrient-stimulated GLP-2 release and crypt cell proliferation in experimental short bowel syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G431–G438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzo, E.; Pareja, J.C.; Chaim, E.A.; Geloneze, B.; Barreto, M.R.; Magro, D.O. GLP-1 and GLP-2 Levels are Correlated with Satiety Regulation After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: Results of an Exploratory Prospective Study. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.J.; Harikumar, K.G.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P.M. Roles of Cholecystokinin in the Nutritional Continuum. Physiology and Potential Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 684656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterli, R.; Steinert, R.E.; Woelnerhanssen, B.; Peters, T.; Christoffel-Courtin, C.; Gass, M.; Kern, B.; von Fluee, M.; Beglinger, C. Metabolic and hormonal changes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: A randomized, prospective trial. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, C.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Kielgast, U.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Clausen, T.R.; Worm, D.; Hartmann, B.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Damgaard, M.; et al. Gut hormones, early dumping and resting energy expenditure in patients with good and poor weight loss response after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Palomera, E.; Suñol, X.; Clavé, P. Sleeve gastrectomy effects on hunger, satiation, and gastrointestinal hormone and motility responses after a liquid meal test. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, G.H. Peptide YY(1-36) and peptide YY(3-36): Part I. Distribution, release and actions. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.L.; Cowley, M.A.; Small, C.J.; Herzog, H.; Cohen, M.A.; Dakin, C.L.; Wren, A.M.; Brynes, A.E.; Low, M.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Gut hormone PYY(3-36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature 2002, 418, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, A.B.; Grybäck, P.; Holst, J.J.; Hilsted, L.; Hellström, P.M.; Jacobsson, H.; Schmidt, P.T. Differential effect of PYY1-36 and PYY3-36 on gastric emptying in man. Regul. Pept. 2009, 158, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roux, C.W.; Batterham, R.L.; Aylwin, S.J.; Patterson, M.; Borg, C.M.; Wynne, K.J.; Kent, A.; Vincent, R.P.; Gardiner, J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, G.K.; Randeva, M.S.; Miras, A.D. Potential Hormone Mechanisms of Bariatric Surgery. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueh, M.T.W.; Chong, M.C.; Miras, A.D.; le Roux, C.W. Oxyntomodulin physiology and its therapeutic development in obesity and associated complications. J. Physiol. 2024; ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Laferrère, B.; Swerdlow, N.; Bawa, B.; Arias, S.; Bose, M.; Oliván, B.; Teixeira, J.; McGinty, J.; Rother, K.I. Rise of oxyntomodulin in response to oral glucose after gastric bypass surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4072–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkén, Y.; Hellström, P.M.; Holst, J.J.; Näslund, E. Changes in glucose homeostasis after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for obesity at day three, two months, and one year after surgery: Role of gut peptides. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, A.; Tsilingiris, D.; Simati, S.; Stefanakis, K.; Angelidi, A.M.; Tentolouris, N.; Anastasiou, I.A.; Connelly, M.A.; Alexandrou, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Bariatric surgery, through beneficial effects on underlying mechanisms, improves cardiorenal and liver metabolic risk over an average of ten years of observation: A longitudinal and a case-control study. Metabolism 2024, 152, 155773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guccio, N.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide—A Postprandial Hormone with Unharnessed Metabolic Potential. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, C.H.; Widenmaier, S.; Kim, S.J. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide; GIP). Vitam. Horm. 2009, 80, 409–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salinari, S.; Bertuzzi, A.; Asnaghi, S.; Guidone, C.; Manco, M.; Mingrone, G. First-phase insulin secretion restoration and differential response to glucose load depending on the route of administration in type 2 diabetic subjects after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.C.; Blackstone, R.; Thearle, M.S.; Vinales, K.L.; Votruba, S.; Krakoff, J. Changes in glycemia, insulin and gut hormone responses to a slowly ingested solid low-carbohydrate mixed meal after laparoscopic gastric bypass or band surgery. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroze, S.; Meng, F.; Jensen, K.; McDaniel, K.; Rahal, K.; Onori, P.; Gaudio, E.; Alpini, G.; Glaser, S.S. The physiological roles of secretin and its receptor. Ann. Transl. Med. 2013, 1, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, T.E.; Holloway, J.L.; Lofton-Day, C.E.; Maurer, M.F.; Chen, L.; Quinton, T.J.; Vincent, J.B.; Scherer, S.W.; Lok, S. Human secretin (SCT): Gene structure, chromosome location, and distribution of mRNA. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2000, 90, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modvig, I.M.; Andersen, D.B.; Grunddal, K.V.; Kuhre, R.E.; Martinussen, C.; Christiansen, C.B.; Ørskov, C.; Larraufie, P.; Kay, R.G.; Reimann, F.; et al. Secretin release after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass reveals a population of glucose-sensitive S cells in distal small intestine. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, N.A.; Wahlgren, C.D.; Pedersen, J.; Mortensen, B.; Langholz, E.; Wandall, E.P.; Friis, S.U.; Vilmann, P.; Paulsen, S.J.; Kristiansen, V.B.; et al. Effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on the distribution and hormone expression of small-intestinal enteroendocrine cells in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2254–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nergård, B.J.; Lindqvist, A.; Gislason, H.G.; Groop, L.; Ekelund, M.; Wierup, N.; Hedenbro, J.L. Mucosal glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide cell numbers in the super-obese human foregut after gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Laurila, S.; Lahesmaa, M.; Rebelos, E.; Virtanen, K.A.; Schnabl, K.; Klingenspor, M.; Nummenmaa, L.; Nuutila, P. Secretin modulates appetite via brown adipose tissue-brain axis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurila, S.; Rebelos, E.; Lahesmaa, M.; Sun, L.; Schnabl, K.; Peltomaa, T.M.; Klén, R.; U-Din, M.; Honka, M.J.; Eskola, O.; et al. Novel effects of the gastrointestinal hormone secretin on cardiac metabolism and renal function. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 322, E54–E62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Schnabl, K.; Gabler, S.M.; Willershäuser, M.; Reber, J.; Karlas, A.; Laurila, S.; Lahesmaa, M.; U-Din, M.; Bast-Habersbrunner, A.; et al. Secretin-Activated Brown Fat Mediates Prandial Thermogenesis to Induce Satiation. Cell 2018, 175, 1561–1574.e1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, L.; Lin, X.; Cheng, P.; He, L.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, H.; Cai, L.; et al. Minireview: Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21 in Metabolic Regulation and Chronic Diseases. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolegowska, K.; Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Nowosiad-Magda, M.; Slawinski, M.; Dolegowska, B. FGF19 subfamily members: FGF19 and FGF21. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Domingo, P.; Moncada, R.; Valentí, V.; Salvador, J.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F.; et al. FGF19 and FGF21 serum concentrations in human obesity and type 2 diabetes behave differently after diet- or surgically-induced weight loss. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez de la Escalera, L.; Kyrou, I.; Vrbikova, J.; Hainer, V.; Sramkova, P.; Fried, M.; Piya, M.K.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, G.; McTernan, P.G. Impact of gut hormone FGF-19 on type-2 diabetes and mitochondrial recovery in a prospective study of obese diabetic women undergoing bariatric surgery. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, S.D.; Chen, C.Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Regulation in Obese Diabetics, and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease After Gastric Bypass. Nutrients 2022, 14, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid Tanweer, A.; Shaheen, M.H.; Alshamsi, B.A.; Almazrouei, M.A.; Almasri, R.M.; Shahid Tanveer, A.; Rajeh, J.M. Endocrine Dysfunction Following Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review of Postoperative Changes in Major Endocrine Hormones. Cureus 2025, 17, e77756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, S.; Wan, K.; Yang, W.; Global Obesity Collaborative. Effects of bariatric surgery on sexual function and fertility: A narrative review. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelgreed, T.A.; Elatreisy, A.; El-Sherbeiny, A.F.; Abdelaal, M.A.; Saafan, T.; Shalkamy, O.; Farag, H.; Ghoneimy, O.M.; El-Dydamony, E.M.; Ibrahim, E.H.; et al. Long-term effect of sleeve gastrectomy surgery on Hormonal Profile, Semen Parameters and sexual functions of obese infertile men; a prospective observational study. Basic. Clin. Androl. 2023, 33, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soykan, Y.; Bayhan, H.; Akogul, S.; Bedirli, A. The Influence of Bariatric Surgery on Reproductive Hormones and Ovarian Morphology and Clinical Findings in Women: A Prospective Study. Obes. Surg. 2025, 35, 3149–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voros, C.; Varthaliti, A.; Bananis, K.; Mavrogianni, D.; Athanasiou, D.; Athanasiou, A.; Athanasiou, A.; Papahliou, A.-M.; Zografos, C.G.; Kondili, P.; et al. The Relationship Between Obesity, Bariatric Surgery, and Infertility: A Systematic Review. Life 2025, 15, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, P.; Helmiö, M.; Ovaska, J.; Juuti, A.; Leivonen, M.; Peromaa-Haavisto, P.; Hurme, S.; Soinio, M.; Nuutila, P.; Victorzon, M. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss at 5 Years Among Patients with Morbid Obesity: The SLEEVEPASS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Peterli, R.; Hurme, S.; Bueter, M.; Helmiö, M.; Juuti, A.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Slawik, M.; Peromaa-Haavisto, P.; Nuutila, P.; et al. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: 5-year outcomes of merged data from two randomized clinical trials (SLEEVEPASS and SM-BOSS). Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, K.A.; Cousins, S.E.; Blazeby, J.M. Randomized controlled trials comparing gastric bypass, gastric band, and sleeve gastrectomy: A systematic review examining validity and applicability to wider clinical practice. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.A.; Liem, R.; Al-Sabah, S.; Anvari, M.; Boza, C.; Cohen, R.V.; Ghaferi, A.; Våge, V.; Himpens, J.; Kow, L.; et al. Metabolic Bariatric Surgery Across the IFSO Chapters: Key Insights on the Baseline Patient Demographics, Procedure Types, and Mortality from the Eighth IFSO Global Registry Report. Obes. Surg. 2024, 34, 1764–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Surgery Procedure | Participants | Methodology | Follow-up Duration | Hormones Assessed | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roux-en-Y gastric bypass | ||||||
| Cummings et al., 2002 [36] | RYGB | 13 pre-/post-diet, 5 post-RYGB, 10 controls | Plasma hormones | Not specified | Ghrelin | Ghrelin increases with diet-induced weight loss |
| Hedberg et al., 2005 [28] | RYGB | 6 individuals with endoscopically confirmed stomal ulcer (2–6 yrs post), 6 controls | Endoscopy and clinical | 2–6 years | Gastric acid markers | Gastric acid involved in stomal ulcers |
| Laferrère et al., 2010 [89] | RYGB | 20 women with T2D | Glucose and hormone profiling | Not specified | GLP-1, PYY, OXM | Hormone peaks correlated with diabetes remission |
| Falkén et al., 2011 [90] | RYGB | 12 individuals with obesity | Postprandial hormones | 3 days, 2 months, and 1 year | GLP-1, OXM | Postprandial increases promote weight loss and insulin sensitivity |
| Umeda et al., 2011 [55] | RYGB | 10 individuals with T2D | Hormonal profiling | 7, 30, and 90 days | Ghrelin, GLP-1, PYY | Early hormonal changes support glycemic control |
| Dirksen et al., 2013 [81] | RYGB | 16 good responders, 17 poor responders, 8 controls | Meal-induced hormones | 1 week and 3 months | Various gut hormones | Favorable hormonal responses support weight loss in good responders |
| Safatle-Ribeiro et al., 2013 [31] | RYGB | 35 long-term (>36 months), 32 controls | Histological analysis | >36 months | Gastric mucosal markers | Down-regulated apoptosis and increased proliferation post-RYGB |
| Jørgensen et al., 2013 [73] | RYGB | 9 individuals with T2D | β-cell and glucose response tests | 1 week and 3 months | GLP-1, Glucagon | GLP-1 enhances β-cell function and gluc |
| Dirksen et al., 2013 [75] | RYGB | 11 severely glucose-tolerant obese | OGTT with hormonal analysis | 1 week and 3 months | Glucagon, Plasma glucose | Hypersecretion of glucagon; reduction in 2-h plasma glucose during OGTT |
| Camastra et al., 2013 [49] | RYGB | 12 individuals with T2D, 15 non-diabetic | Postprandial tests, insulin sensitivity | 1 year | Insulin, glucose, gut hormones | Improved insulin sensitivity; altered endogenous glucose output |
| Bojsen-Møller et al., 2014 [50] | RYGB | 10 individuals with T2D, 10 non-T2D | Oral glucose tests | 1 week, 3 months, and 1 year | Insulin, gut hormones | Increased insulin secretion in T2D after RYGB emphasizing gut’s role |
| Rhee et al., 2015 [99] | RYGB | 12 individuals with T2D, 11 controls | Enteroendocrine cell profiling | ~10 months | Various gut hormones | Altered enteroendocrine cell distribution and hormone gene expression |
| Nergård et al., 2015 [100] | RYGB | 18 individuals with obesity without DM | Jejunum cell density analysis | 12 months | Incretin hormones | Increased density of incretin-producing cells in jejunum |
| Guo et al., 2022 [108] | RYGB | 35 individuals with T2D/obesity | Post-surgery FGF analysis | 3 and 12 months | FGF-19, FGF-21 | Changes in FGF-19/FGF-21 explain remission of DM and MASLD; shift in serum levels indicates metabolic improvements |
| Sleeve gastrectomy | ||||||
| Cătoi et al., 2016 [51] | SG | 20 individuals with obesity | Blood tests | 7, 30 and 90 days | Insulin, HOMA-IR | Decreased insulin and HOMA-IR levels |
| Farey et al., 2017 [56] | SG | 11 individuals with obesity, SG, 22 controls | Hormonal and metabolic analyses | 3 months | Various gut hormones | Differences in weight loss mechanisms compared to other surgeries |
| Adjustable gastric banding | ||||||
| Shak et al., 2008 [29] | AGB | 24 | Hormonal response | 12 months | Ghrelin | AGB partially suppresses ghrelin spike during weight loss |
| Several techniques | ||||||
| Frühbeck et al., 2004 [37] | AGB, RYGB | 8 AGB, 8 RYGB, 8 controls | Hormonal profiling | 6 months | Ghrelin | RYGB reduces ghrelin via fundus bypass; not due to weight loss or insulin sensitivity |
| Frühbeck et al., 2004 [38] | AGB, RYGB, BPD | 7 AGB, 6 RYGB, 3 BPD | Cross-sectional analysis | Not specified | Ghrelin | Fundus dysfunction influences fasting ghrelin levels |
| Korner et al., 2007 [74] | RYGB, AGB | 13 RYGB, 10 AGB | Meal tests | Not specified | GLP-1, GIP | RYGB enhances postprandial GLP-1 and GIP, improving glucose regulation |
| Huda et al., 2008 [45] | Post-gastrectomy | 8 post-operation, 9 individuals with obesity, 9 controls | Gene and hormone expression | Not specified | Obestatin | Obestatin expression altered after gastrectomy |
| Salinari et al., 2009 [94] | Malabsorptive surgery | 9 individuals with T2D, 6 controls | Hormonal and metabolic assessments | Not specified | Insulin, gut hormones | Better insulin sensitivity associated with gut hormonal changes |
| Martins et al., 2011 [46] | RYGB, Lifestyle | 9 RYGB, 8 lifestyle, 9 controls | Hormonal measurements | 3 years | Ghrelin, Obestatin | Elevated fasting ghrelin/obestatin post-RYGB linked to weight maintenance |
| Peterli et al., 2012 [80] | RYGB, SG | 12 RYGB, 11 SG | Hormonal and clinical follow-up | 1 week, 3 and 12 months | Ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, PYY | Hormones influence weight loss mechanisms |
| Sillakivi et al., 2013 [32] | RYGB, SG | 20 RYGB, 20 SG | Gastric function tests | 22 months | Gastric hormones | Sleeve reduces corpus secretion, antral functions preserved |
| Grong et al., 2016 [30] | RYGB, SG | 20 RYGB/SG, 13 controls | Gastrin secretion assessment | Not specified | Gastrin | Gastrin secretion decreased after RYGB |
| Bunt et al., 2017 [95] | RYGB, AGB | 10 RYGB, 8 AGB | Glycemic response tests | 4–8 weeks | Glucose, insulin | Faster glycemic improvement after RYGB than AGB |
| Gómez-Ambrosi et al., 2017 [106] | SG, RYGB | 20 SG, 66 RYGB, 28 control | FGF-19 and FGF-21 levels | 1 year | FGF-19, FGF-21 | FGF-21 relates to glucose; FGF-19 associates with visceral fat reduction |
| Martinez de la Escalera et al., 2017 [107] | BPD, GCP, AGB | 39 women with T2D and obesity | Metabolic and FGF-19 analysis | 6 months | FGF-19, FGF-21 | BPD yields the best metabolic outcomes; FGF-19 may target mitochondria in adipose tissue during remission |
| Lampropoulos et al., 2022 [40] | SG and RYGB/BPD | 12 SG, 20 RYGB/BPD | Fasting/postprandial hormones | ≥7 years | Ghrelin, GLP-1, PYY | No significant differences between groups; hormonal responses reflect ongoing weight changes |
| Brzozowska et al., 2023 [52] | RYGB, SG, AGB | 7 RYGB, 21 SG, 11 AGB, 16 diet-controlled | Insulin resistance and HOMA-IR | 12–36 months | PYY, Adiponectin | Reduced insulin resistance, increased PYY and adiponectin during weight stability |
| Kokkinos et al., 2024 [91] | RYGB, SG | 11 RYGB, 17 SG | Hormonal secretion analysis | 3, 6 and 12 months and 10 years | Glicentin, OXM, TMAO | RYGB enhances proglucagon products and raises cardiovascular risk marker TMAO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anastasiou, I.A.; Kounatidis, D.; Rebelos, E.; Vallianou, N.G.; Tentolouris, A.; Tentolouris, N.; Dalamaga, M.; Karampela, I. Hormonal Alterations in Individuals with Obesity After Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101724
Anastasiou IA, Kounatidis D, Rebelos E, Vallianou NG, Tentolouris A, Tentolouris N, Dalamaga M, Karampela I. Hormonal Alterations in Individuals with Obesity After Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101724
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnastasiou, Ioanna A., Dimitris Kounatidis, Eleni Rebelos, Natalia G. Vallianou, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris, Maria Dalamaga, and Irene Karampela. 2025. "Hormonal Alterations in Individuals with Obesity After Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101724
APA StyleAnastasiou, I. A., Kounatidis, D., Rebelos, E., Vallianou, N. G., Tentolouris, A., Tentolouris, N., Dalamaga, M., & Karampela, I. (2025). Hormonal Alterations in Individuals with Obesity After Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review. Medicina, 61(10), 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101724








