Abstract
Background and Objectives: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients experience sarcopenia and decreased muscle mass and handgrip strength, leading to decreased quality of life and disability. The prevalence of RA varies across regions. This study aimed to evaluate the factors associated with RA in Croatian regional centres and explore correlations between clinical parameters and muscle strength. Materials and Methods: Included in this study were 267 stable RA patients from four Croatian clinical centres. The patients’ mean age was 60.4 ± 12.0 years, with 12.7% of them being male. For each study participant, information was gathered on their anthropometric characteristics, clinical and laboratory indicators, quality of life, disease activity, and sociodemographics. Results: The main results showed that in the female RA participants, the significant positive predictors are weight, height, exercise, VAS, and haemoglobin level. The negative predictors are the use of conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, the use of biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, the number of tender joints, the number of swollen joints, the estimated sedimentation rate, the C-reactive protein, the disease activity score, the parameters of the EQ5D, and being prescribed with three or more medications. In the male RA participants, significant predictors of muscle strength are only weight, height, and anxiety/depression difficulties, according to the EQ5D. Conclusions: This study showed correlations between muscle strength and the parameters of disease activity, inflammation parameters, health-related quality of life, therapy, and exercise in the female RA participants in Croatia.
1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic, autoimmune disease of unknown aetiology characterised by articular and extra-articular manifestations leading to functional disabilities and a huge socioeconomic and medical burden on society. This is the most commonly diagnosed systemic inflammatory arthritis with typical inflammatory changes in the synovial membrane of the mainly small, but also other-sized, joints. RA patients have a higher cardiovascular risk and show higher rates of depression, osteoporosis, obesity, sarcopenia, and infections. Depending on the presence of autoantibodies (rheumatoid factor and antibodies against post-translational modified proteins like citrullination—ACPA—and carbamylation—antiCarP—antibodies) RA can be defined as seropositive or seronegative RA [1,2,3,4].
Although the exact aetiology is still unknown, it is believed that genetic and environmental causes play a key role in the development of the disease. Genetical susceptibility is described as an increased risk of developing RA if a person has inherited the specific HLA-DRB1 alleles (especially DR4 and DR1), which show the most association with seropositive cases. It is also known that a positive family history increases the risk for RA 3–5 times [1,3,5]. The most notable environmental factor is smoking, while alcohol and coffee consumption, obesity, and a lower socioeconomic status and educational level may play a role in the potential onset of the disease and, later, its activity [2,4,5,6,7]. Microbial infections have also been connected with the development and, later, the exacerbation of RA. Clinical and animal model studies have suggested that infections by some microorganisms contribute to the etiopathogenesis of RA, of which Porphyromonas gingivalis exhibited the strongest associations; however, larger studies are needed to confirm these ideas [8].
Studies on different populations have shown the constant prevalence of RA at 0.5–1.0%. In the U.S. population, the prevalence is approximately 1%, with some exceptions in the Native American populations (e.g., Prima and Pagago Indians show a prevalence of 5.3%, while Chippewa Indians show the highest prevalence of 6.8%). The prevalence is lowest in North Africa, the Middle East, and Asia (0.16%), while Western European countries and the Australian population have a slightly higher prevalence (0.44% and 0.46%, respectively) [9,10]. A systematic review of six WHO regions showed female predominance and that there was no difference between urban and rural settings, with the estimation of growth in prevalence in the future [11]. The sex ratio is from 2:1 to 3:1 for women in comparison to men, and some studies also show higher disease activity in women. Nulliparity is associated with an increased risk of disease development whereas pregnancy seems to decrease this, and in most patients, the clinical symptoms are less expressed during pregnancy. Relapses of the disease are frequent in the postpartum period [9,12,13].
Although there is not much prior research in this area, what we have located describes a comparable prevalence of 0.46%, with a female predominance. The prevalence of RA in Croatia was 0.38% in a multi-country survey study conducted in Central and Eastern Europe between March 2009 and March 2010, which is comparable to the other European nations. During the specified period, the prevalence was reported to be 0.37% in Hungary, 0.61% in the Czech Republic, and 0.46% in Estonia.
In one study conducted in south Croatia on 869 RA patients from June 2013 to August 2015, Split-Dalmatia County showed a prevalence of 0.24% in adult patients with the Sinj region having the highest one, which was explained by a higher incidence of HLA-DRB1*04 in those patients. In addition, the RA population is characterised by a lower socioeconomic status [14,15,16]. There is a need for future RA studies to define the characteristics of the RA population in Dalmatia and Croatia [15].
Over the years, there has been an increase in RA prevalence and incidence in women but only in its prevalence in men, which has been interpreted as being because of the increase in life expectancy, the environmental factor effects, and because of better diagnostic and therapeutic treatments developing through the years among patients with RA [17].
The disease activity score (DAS) index, of which DAS-28 is most frequently employed, is the most popular method used to monitor RA patients [18,19]. Many studies have shown that RA patients have a higher frequency of sarcopenia, lower muscle mass and handgrip strength, and changes in body composition in favour of fat tissue. There is a lower quality of life in those patients because of the acute and chronic changes to the joints that lead to deformities, disability, and lower physical activity [20,21,22]. Lower handgrip strength was associated with lower quality of life, leading to less everyday physical activity and higher levels of pain and discomfort [23]. These factors depend on disease activity since in the patients with higher disease activity scores (DAS-28 and HAQ-DI), they are more significant. Smoking was also one of the factors correlated with the worsening of skeletal muscle density in patients [24,25]. With today’s modern radiological methods (magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound) and functional tests, we can detect a positive correlation between joint inflammation and functional disability [26]. Although RA is a chronic condition, there are now efficient pharmaceutical therapy options that reduce inflammation, joint damage, and overall disease activity. Nevertheless, a patient’s physical function or strength is never fully restored [27].
The aim of this study was to assess the determinants of RA in the regional centres in Croatia and to investigate possible associations between muscle strength and clinical parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
This national study was carried out on the initiative of the Croatian Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. This nationwide study included 267 stable RA patients and was conducted at four centres in Croatia in 2017. In total, 134 participants were recruited from the Lipik centre, 72 participants were recruited from the Split centre, 35 participants were recruited from the Osijek centre, and 26 participants were recruited from the Rijeka centre.
RA diagnosis was made using the criteria of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification [28].
All measurements for a single participant were performed on the day he/she was screened. Participants were screened on different days during the recruitment period.
The geographical locations of centres are represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Geographical locations of clinical centres in Croatia which were included in this study.
We excluded patients who were minors, had active infection, had serious cognitive impairment, had overlap syndromes, or were unwilling to participate.
2.1. Clinical and Lab Specifications
Data on the length of RA illness, the existence of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, chronic renal disease, hyperlipidaemia, and stomach ulcers were gathered for each participant by carefully reviewing their medical history. The following groups of medications were identified based on data collected on medication usage: NSAIDs, paracetamol/tramadol, corticosteroids (CSs), conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (CSDMARDs), biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (BDMARDs), and the usage of three or more medications.
Data on haemoglobin, C-reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were gathered in relation to laboratory parameters.
2.2. Sociodemographic Information
Data on marital status were gathered using a sociodemographic questionnaire. Information about the kind, length, and frequency of exercise was also gathered for every research subject.
2.3. Disease Activity and Quality-of-Life Assessment
The disease activity score (DAS28) is a measurable disease activity indicator that is displayed as a total score. It is derived from the number of sensitive joints, the number of swollen joints, the ESR, and a general health assessment (VAS).
Each participant’s health-related quality of life (hrQoL) was measured using the EQ5D-3L questionnaire. The five dimensions that make up the EQ-5D-3L descriptive system are mobility, self-care, regular activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression. There are three levels for each dimension: minimal issues, moderate issues, and severe issues, depicted on a 1–3 scale. By checking the box next to the statement that best fits each of the five dimensions, the patient is asked to identify the state of his or her health. The level chosen for that dimension is expressed as a 1-digit number as a result of this decision.
The EQ VAS, named for the Visual Analogue Scale it includes, is the second section of the questionnaire. This represents the respondent’s overall evaluation of their health on a range of 0 (the poorest possible health) to 100 (the finest possible health) [29].
2.4. Muscle Strength Assessment
Handgrip strength was assessed using a hand-held dynamometer (Saehan, Masanhoewon-gu, Changwon-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea) for every study participant. Three measurements were taken, and average values were calculated.
2.5. Statistics
The Shapiro–Wilk test was performed to assess the normality of the continuous data. If the continuous data followed a normal distribution, they were presented with means and standard deviations (SDs); otherwise, medians and interquartile ranges (IQRs) were used. Categorical data were presented as numbers with percentages. To examine the difference among the three groups (remission + low disease activity vs. moderate disease activity vs. high disease activity), a chi-square test was used for the categorical data, whereas a one-way ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis test was used for continuous data depending on the normality distribution. Due to the large variation in the number of male and female participants, a complete statistical analysis was conducted separately for each gender.
To identify independent predictors of muscle mass in RA patients, a generalised linear model was used, adjusted for age, BMI, and the location of the clinical centre. Results of the generalised linear models were presented with beta coefficients and standard errors. Statistically significant results were those with a p-value < 0.05. The entire statistical analysis was performed using the free software environment for statistical computing, R version 4.0.0.
3. Results
In this cross-sectional study, 267 RA patients were included; the mean age was 60.4 ± 12.0 years and 12.7% of the patients were male. The average time that the RA illness persisted was 15.1 ± 11.3 years.
Based on their DAS-28 scores, participants were split into three groups: remission combined with low disease activity (DAS-28 score < 3.3), moderate disease activity (DAS-28 score from 3.3 to 5.1), and high disease activity (DAS-28 score > 5.1).
Table 1 presents the differences in the measured parameters related to the disease activity for the female and male participants, respectively.

Table 1.
Differences in the measured parameters related to the disease activity.
Table 2 and Table 3 display the beta coefficients for the effect of several independent predictors on muscle strength in the RA participants, adjusted for age, BMI, and the location of the clinical centre (only statistically significant values are shown) for female and male participants, respectively.

Table 2.
Predictors of muscle strength in female rheumatoid arthritis participants.

Table 3.
Predictors of muscle strength in male rheumatoid arthritis participants.
In the female RA participants, the significant positive predictors are weight, height, exercise, VAS, and Hb. The negative predictors are the use of BDMARDs, the use of CSDMARDs, the number of tender joints, the number of swollen joints, the ESR, CRP, the DAS, the parameters of the EQ5D, and being prescribed with three or more medications. In the male RA participants, the significant predictors of muscle strength are only weight, height, and anxiety/depression difficulties according to the EQ5D.
Figure 2 presents differences in muscle strength regarding the different medication prescriptions.
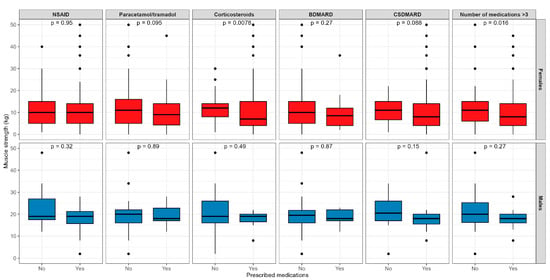
Figure 2.
Differences in muscle strength regarding the different medication prescriptions in Croatian rheumatoid arthritis participants. Abbreviations: NSAID—non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug, BDMARD—biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug, CSDMARD—conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug.
The only significant difference found was that the female RA participants prescribed with CS therapy and those prescribed with more than three medications had a lower level of muscle strength.
To determine the differences in disease activity regarding the RA therapy, we divided participants into the three mentioned stages of disease activity regarding the DAS-28 score and compared the differences regarding the prescription of different medication groups, which is shown in Figure 3.
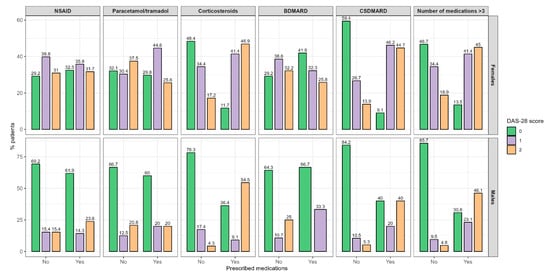
Figure 3.
Disease activity differences regarding the prescription of different medication groups. Abbreviations: DAS 28—disease activity score 28, NSAID—non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug, BDMARD—biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug, CSDMARD—conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug. 0—remission + low disease activity, 1—moderate disease activity, 2—high disease activity.
A significant difference was found for the CS and CSDMARD therapies in males and females. The CS were more frequently prescribed in higher stages of disease activity in both males and females (p = 0.003 and p < 0.001, respectively). On the other hand, CSDMARDs in females were prescribed in higher disease activity stages (p < 0.001); meanwhile, in the male participants, they were equally prescribed in the lowest and highest disease activity groups (p = 0.018).
Also, the prescription of more than three drugs was significantly more common in the higher disease stages (p = 0.003 and p < 0.001 in males and females, respectively).
4. Discussion
This study showed correlations between muscle strength and the parameters of disease activity, inflammation parameters, health-related quality of life, therapy, and exercise in female RA participants in Croatia. The age difference may account for the differences in the different stages of disease activity identified in our study, including a higher BMI, more prescribed drugs, and a higher frequency of comorbidities. A regression analysis reduced this confounding effect.
The DAS-28 scores and the CRP and ESR values were found to be negative predictors of muscle strength in female RA participants. The number of swollen and tender joints was also associated with lower muscle strength. These results suggest an association between inflammation, muscle strength, and disease activity, but unfortunately, we were unable to establish causal relationships due to the study design. These findings are consistent with the results of a study of 199 Finnish RA patients, which found that the decrease in the patients’ composite score for muscle performance was linearly related to the increase in the DAS28 activity level [30]. This was also the case in a study of 50 RA patients from Egypt, which found that the DAS28-ESR score was significantly correlated with muscle performance tests, physical activity level, and fatigue score [31]. A prospective study on 107 RA participants showed that factors affecting muscle density decline include female sex, disease activity, smoking, and lower insulin-like growth factor 1 levels. Greater muscle density reduces annual worsening and clinically important worsening in HAQ scores and walking speeds [25].
Regarding inflammatory markers, the results of a review by Tuttle et al. show a strong correlation between higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers and lower skeletal muscle strength and muscle mass [32]. Another meta-analysis also confirmed a significant inverse correlation between the CRP and hs-CRP concentrations and muscle strength [33].
For all the parameters of the EQ5D—mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression—difficulty was found to be a negative predictor of muscle strength in the female RA participants along with VAS, as patients’ self-rated health.
The data on associations between quality of life and muscle strength in RA patients are rather scarce.
A study on 2365 arthritis patients from Korea found significantly higher odds ratios for the impairment of the mobility, usual activity, self-care, and pain/discomfort dimensions in RA patients with weak handgrip strength than those with normal handgrip strength [23]. In a study with 289 RA participants, Wiegmann et al. discovered that HAQ was an associated risk factor for falling [22]. When it comes to muscle strength and therapy associations, negative predictors of muscle strength in the women were the prescription of biological therapy and CSDMARDs as well as being prescribed three or more medications. This finding is probably related to the higher disease activity and a greater number of comorbidities in the patients treated with more drugs, which is supported by the results of our study depicted in Figure 2.
The use of CS therapy was not significant in our regression model, but we did find significant differences in females prescribed with CS therapy who showed lower levels of muscle strength than those not prescribed CSs. It is important to mention that our results also showed that CSs were more frequently prescribed in higher stages of disease activity in both females and males.
It has been shown that glucocorticoids induce oxidative stress in a variety of tissues, including muscle, nerve fibres, and bone. A common reaction to this type of stress is the up-regulation of the transcription factors classified as “anti-oxidants” in the forkhead box O family. This could be the reason for some of the hypodynamic/adynamic bone and muscle atrophy. It is more difficult to distinguish between physiological responses brought on by stress exposure and those brought on by inflammation as inflammatory reactions have access to the FOXO/anti-oxidant pathways [34]. It is important to highlight that when this study was conducted, JAK inhibitors were not approved for prescription for this indication in Croatia as per the National Health Insurance reimbursement criteria.
Interestingly, a positive predictor of muscle strength in female RA participants in Croatia was exercise, but no significant association was found between muscle strength and the type, frequency, or duration of exercise. The possible bias in our study could be that the data about exercise were collected by self-administered questionnaires.
It is important to remember that exercise in any form does not worsen the ESR or disease activity, suggesting that exercise is generally safe for people with RA. Further research is needed as the data on the type and duration of exercise that are useful for patients with RA are inconclusive [35].
The anthropometric parameters of height and weight were significant positive predictors of muscle strength in both male and female RA participants, which is self-explanatory.
Other than those mentioned, the only significant predictor of muscle strength in the male RA participants was anxiety/depression difficulties based on the EQ5D. The discrepancy of significant predictors of muscle strength regarding sex could be due to the small number of male participants in our study, and these results should be interpreted in such a way.
The cross-sectional design of this study limits our ability to determine causal relationships, which is the main source of this study’s limitations. Additionally, the self-reported questionnaire used to measure physical activity may introduce bias into the interpretation of the findings.
5. Conclusions
The findings of this nationally based study on RA in Croatia provide important new information about the clinical factors associated with RA in this context. Relationships have been found between muscle strength and physical functioning, therapy, inflammatory indicators, quality of life, and disease activity.
Author Contributions
M.R., I.V. and M.V. contributed equally to this paper. Conceptualisation, M.R. and T.V.; methodology, M.R., T.V. and J.R.; validation, M.R., M.V., A.B. and I.V.; formal analysis, A.G.; resources, M.R. and T.V.; data curation, M.R., M.V., I.V., S.R.S., M.K., D.S., D.B., T.V., A.G. and J.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R., M.V., A.B. and I.V.; writing—review and editing, T.V., J.R. and E.B.; supervision, M.R.; project administration, M.R. and T.V.; funding acquisition, M.R. and T.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially funded by Abbot Nutrition.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Clinical University Hospital Split 19 May 2016. (class: 520-01/16-01/73, ur.br.2181-147-01/06/J.B.-16-2).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the corresponding author upon e-mail request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Scherer, H.U.; Häupl, T.; Burmester, G.R. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radić, M.; Vlak, I.; Vučković, M.; Radić, J.; Bešić, E.; Vlak, T. Association between Nutritional Status, Lifestyle Habits, and Disease Activity in Dalmatian Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delft, M.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibofsky, A. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: A Synopsis. Am. J. Manag. Care 2014, 20 (Suppl. S7), S128–S135. [Google Scholar]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, M.; Morgan, C.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Bruce, I.N. Modifiable risk factors for RA: Prevention, better than cure? Rheumatology 2012, 51, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Han, K.H.; Park, S.J.; Shin, J., II. Smoking and rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22279–22295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Su, K. Microbial Infection and Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silman, A.J.; Pearson, J.E. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4 (Suppl. S3), S265–S272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, K.; Navarro-Millán, I. Racial, ethnic, and healthcare disparities in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudan, I.; Sidhu, S.; Papana, A.; Meng, S.-J.; Xin-Wei, Y.; Wang, W.; Campbell-Page, R.M.; Demaio, A.R.; Nair, H.; Sridhar, D.; et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review and analysis. J. Glob. Health 2015, 5, 010409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortona, E.; Pierdominici, M.; Maselli, A.; Veroni, C.; Aloisi, F.; Shoenfeld, Y. Sex-based differences in autoimmune diseases. Ann. Dell’Istituto Super. Sanita 2016, 52, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F. Sex differences in rheumatoid arthritis: More than meets the eye. BMC Med. 2009, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlewska, E.; Ancuta, I.; Anic, B.; Codrenau, C.; Damjanov, N.; Djukic, P.; Ionescu, R.; Marinchev, L.; Nasonov, E.L.; Peets, T.; et al. Access to biologic treatment for rheumatoid arthritis in Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2011, 17, SR1–SR13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Damjanović, V.; Vasilj, I.; Vlak, T.; Zelenika, D. Prevalence and Risk Factors of the Rheumatoid Arthritis in Herzegovina Region in 2003–2005. Coll. Antropol. 2009, 33 (Suppl. S2), 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Marinović, I. Populacijsko Istraživanje Sustava HLA kod Oboljelih od RA s Područja Sinjske Krajine. Ph.D. Thesis, Split: Medicinski fakultet Sveučilišta u Splitu, Split, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Is the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis rising?: Results from Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1955–2007. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Renskers, L. The Disease Activity Score (DAS) and the Disease Activity Score using 28 joint counts (DAS28) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34 (Suppl. S101), S40–S44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Riel, P.L.C.M. The development of the disease activity score (DAS) and the disease activity score using 28 joint counts (DAS28). Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. S85), S-65-74. [Google Scholar]
- Akar, B.; Calik, B.B.; Kabul, E.G.; Akbaş, A.N.B.; Cobankara, V. Examining the presence of sarcopenia in women with rheumatoid arthritis: Case-control study. Rom. J. Intern. Med. Rev. Roum. Med. Interne 2023, 62, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.F.; Von Feldt, J.; Mostoufi-Moab, S.; Noaiseh, G.; Taratuta, E.; Kim, W.; Leonard, M.B. Deficits in muscle mass, muscle density, and modified associations with fat in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegmann, S.; Armbrecht, G.; Borucki, D.; Buehring, B.; Buttgereit, F.; Detzer, C.; Schaumburg, D.; Zeiner, K.N.; Dietzel, R. Association between sarcopenia, physical performance and falls in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A 1-year prospective study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Han, B.D.; Han, K.D.; Park, H.J.; Kang, S. Relation between Handgrip Strength and Quality of Life in Patients with Arthritis in Korea: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2015–2018. Medicina 2022, 58, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, R.C.D.E.; Baker, J.F.; Dos Santos, L.P.; Silva, J.M.S.; Filippin, L.I.; Portes, J.K.S.; Brenol, C.V.; Chakr, R.M.D.S.; Xavier, R.M. Changes in physical function over time in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.F.; Mostoufi-Moab, S.; Long, J.; Taratuta, E.; Leonard, M.B.; Zemel, B. Association of Low Muscle Density With Deteriorations in Muscle Strength and Physical Functioning in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Ceccarelli, L.; Farah, S.; Giovagnoni, A. The value of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging scoring systems in explaining handgrip strength and functional impairment in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A pilot study. La Radiol. Medica 2022, 127, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Steinz, M.M.; Kenne, E.; Lanner, J.T. Muscle Weakness in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Ca2+ and Free Radical Signaling. EBioMedicine 2017, 23, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://euroqol.org/information-and-support/euroqol-instruments/eq-5d-3l/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Uutela, T.I.; Kautiainen, H.J.; Häkkinen, A.H. Decreasing muscle performance associated with increasing disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahran, S.; Fathi, N.; Seddek, M.; Goma, S.H. Physical Ability and Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Brief Comparison. Aktuelle Rheumatol. 2021, 46, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, C.S.L.; Thang, L.A.N.; Maier, A.B. Markers of inflammation and their association with muscle strength and mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri-Mashhadi, N.; Moradi, S.; Heidari, Z.; Saadat, S. Association of circulating C-reactive protein and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein with components of sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.L. The effect of glucocorticoids on bone and muscle. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia 2015, 1, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xu, A.; Gao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X. The effect of physical exercise on rheumatoid arthritis: An overviewof systematic reviews and meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2021, 77, 506–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).