Abstract
Background and Objectives: In coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) on pump, achieving optimal visualization is critical for surgical precision and safety. The use of blowers to clear the CABG anastomosis poses risks, including the formation of micro-embolic gas bubbles, which can be insidious and increase the risk of cerebral or myocardial complications. This retrospective study compares the effectiveness of the use of irrigation mist and CO2 versus a direct CO2 blower without irrigation in terms of visualization, postoperative fibrillation, and micro-embolic gas activity. Materials and Methods: The study involved 40 patients who underwent on-pump CABG, with 20 patients assigned to the irrigation mist and CO2 group (ClearView™) and 20 to the direct CO2 blower group. Primary outcomes included the quality of intraoperative visualization, the incidence of fibrillation at aortic de-clamping, and the presence of micro-embolic gas activity detected via transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) in the cardiac chambers. Results: Patients in the irrigation mist and CO2 group experienced superior visualization and reduced tissue desiccation. Fibrillation at the time of aortic de-clamping occurred in two patients (10%) using the irrigation mist and CO2, compared to eight patients (40%) using the direct CO2 blower. Additionally, TEE monitoring revealed lower levels of micro-embolic gas activity in the irrigation mist and CO2 group, indicating a potential reduction in gas embolization risk. Conclusions: The irrigation mist and CO2 system not only provides enhanced visualization during CABG but also significantly reduces the incidence of fibrillation during aortic de-clamping and micro-embolic gas activity. These findings suggest improved patient safety and outcomes, highlighting the irrigation mist and CO2 system as a potentially safer alternative to direct CO2 blowing in the context of myocardial revascularization.
1. Introduction
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) remains a cornerstone in the surgical treatment of advanced coronary artery disease, offering long-term survival benefits and symptom relief for patients with multivessel coronary artery blockages. In on-pump CABG, where cardiopulmonary bypass is employed, ensuring a clear and unobstructed view of the surgical site is critical for precise anastomosis and optimal graft placement [1,2]. However, achieving and maintaining adequate visualization can be challenging due to continuous bleeding and the potential desiccation of tissues caused by commonly used CO2 blowers. Traditionally, CO2 blowers have been utilized to clear blood from the surgical field, but direct CO2 blowing can lead to tissue dehydration, fragility, and impaired healing. Moreover, this technique has been associated with the formation of micro-embolic gas bubbles, which pose significant risks of neurological and myocardial complications [3]. These micro-emboli, although not always immediately detectable, may cause cerebral or coronary ischemia and contribute to post-surgical morbidity. The irrigation mist and CO2 system was originally designed for off-pump coronary artery surgery, providing a dual-action approach that combines CO2 blowing with a gentle irrigation mist. This system aims to enhance intraoperative visualization while preserving tissue hydration and integrity [4]. The irrigation mist helps maintain moisture on the delicate myocardial and vascular tissues, reducing the risk of desiccation and minimizing potential tissue damage. However, its use in on-pump CABG has not been widely studied, raising questions about its effectiveness and safety in this particular surgical context. In this retrospective comparative analysis, we sought to evaluate the efficacy of irrigation mist and CO2 in on-pump CABG, comparing it with the traditional direct CO2 blower [5]. We focused on key clinical outcomes, such as intraoperative visualization, the incidence of fibrillation during aortic de-clamping, and the presence of micro-embolic gas activity detected via transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) within the cardiac chambers. The goal of this study is to determine whether the irrigation mist and CO2 system, initially developed for off-pump procedures, offers distinct advantages when applied to on-pump CABG, potentially improving surgical performance and patient safety.
2. Materials and Methods
This retrospective study compares two historical periods of on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) at our institution, focusing on the use of the irrigation mist and CO2 (ClearView™ Blower/Mister by Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) (Figure 1 and Figure 2) versus the traditional direct CO2 blower (Figure 3). The aim was to assess the impact of these two methods on intraoperative visualization, the incidence of fibrillation during aortic de-clamping, and the presence of micro-embolic gas activity detected via transesophageal echocardiography (TEE).
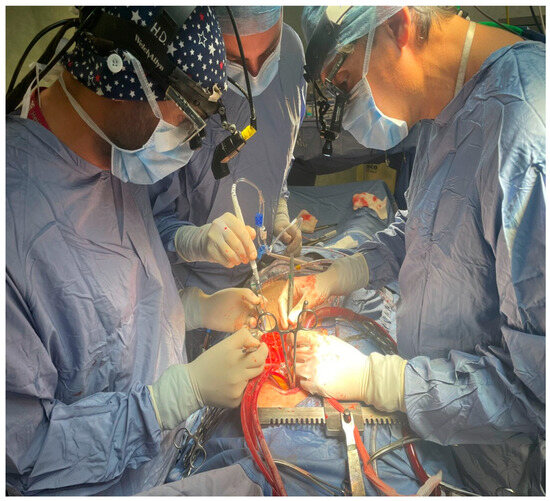
Figure 1.
Perioperative use of the irrigation mist and CO2 during CABG.
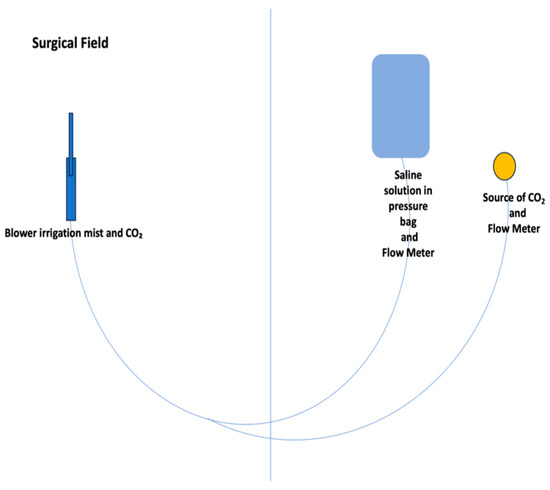
Figure 2.
Irrigation mist and CO2 sketch.
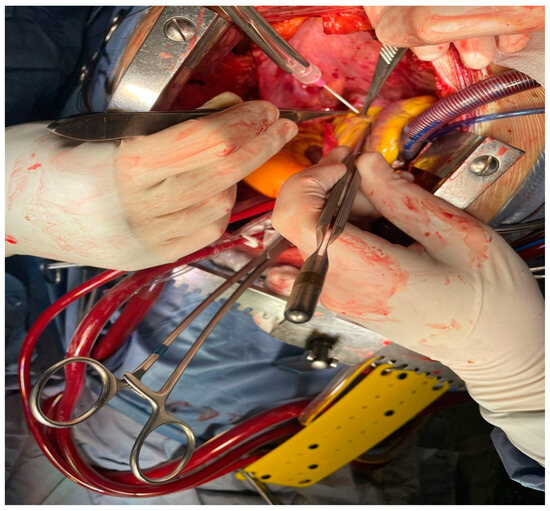
Figure 3.
Perioperative use of the traditional direct CO2 blower.
Study Design and Population
The study included 40 patients who underwent elective on-pump CABG, divided into the following two groups:
- Group 1 (n = 20): patients operated on during a period before the introduction of the irrigation mist and CO2, where direct CO2 blowers were used;
- Group 2 (n = 20): patients operated on after the ClearView™ Blower/Mister system became available and was routinely used during surgery.
Intervention
- Group 1 (Direct CO2 Blower): Patients in this group underwent CABG using a traditional direct CO2 blower to clear blood from the surgical field. No irrigation mist was applied, and the CO2 blower was operated continuously during critical stages of the procedure, including the anastomosis phase;
- Group 2 (Irrigation Mist and CO2): patients in this group received CABG using the irrigation mist and CO2, which combines a CO2 blower with a fine irrigation mist to improve visualization and maintain tissue hydration during surgery.
Outcomes Assessed
- Visualization Quality: assessed subjectively by the operating surgeon, rated on a scale from 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent), and recorded in operative notes;
- Incidence of Fibrillation During Aortic Declamping: the number of patients experiencing fibrillation immediately after aortic cross-clamp removal was documented;
- Microembolic Gas Activity: transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) was used intraoperatively to detect the presence of microembolic gas bubbles in the cardiac chambers during and after aortic declamping.
Cardioplegia delivery
In both groups, a normothermic blood cardioplegia protocol was employed using a Saint Thomas solution, administered at regular intervals of every 20 min. This approach was chosen to provide consistent myocardial protection throughout the procedure, maintaining cardiac tissue viability during periods of ischemia. The cardioplegia solution was delivered at normothermic temperature to balance myocardial protection with metabolic demands, aiming to minimize ischemic damage during aortic cross-clamping.
Statistical Analysis
A comparative statistical analysis was conducted between the two groups. Continuous variables, such as the number of anastomoses and visualization quality, were compared using the Student’s t-test, while categorical variables like fibrillation incidence were analyzed using the chi-square test. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. This comparative analysis allowed for an evaluation of the irrigation mist and CO2 system’s effectiveness in on-pump CABG compared to traditional methods, focusing on key outcomes including tissue preservation, fibrillation risk, and micro-embolic gas activity.
3. Results
Patient and Surgical Characteristics
The demographic and baseline clinical characteristics of the two groups were comparable, with no significant differences in age, gender distribution, or preoperative risk factors, such as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia. Additionally, the surgical characteristics, including the number of proximal and distal anastomoses, and the use of specific grafting techniques, were similar between the two groups (Table 1).

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
- Proximal Anastomoses: the average number of proximal anastomoses was 2.3 ± 0.6 in Group 1 (direct CO2 blower) and 2.4 ± 0.5 in Group 2 (the irrigation mist and CO2);
- Distal Anastomoses: the average number of distal anastomoses was 3.1 ± 0.8 in Group 1 and 3.2 ± 0.7 in Group 2;
- Grafting Techniques: use of the Y-mammary graft was 40% in Group 1 and 50% in Group 2, while sequential grafting with the mammary artery and saphenous vein was performed in 60% of Group 1 and 50% of Group 2 patients.
Visualization Quality
The quality of visualization, as subjectively assessed by the three operating surgeon, was significantly better in Group 2, where the irrigation mist and CO2 was used. The average visualization score was 4.7 ± 0.5 in Group 2, compared to 3.8 ± 0.6 in Group 1 (p < 0.01). Surgeons in Group 2 consistently reported clearer visual fields with reduced blood obscuration and less tissue desiccation compared to Group 1 (Figure 4).
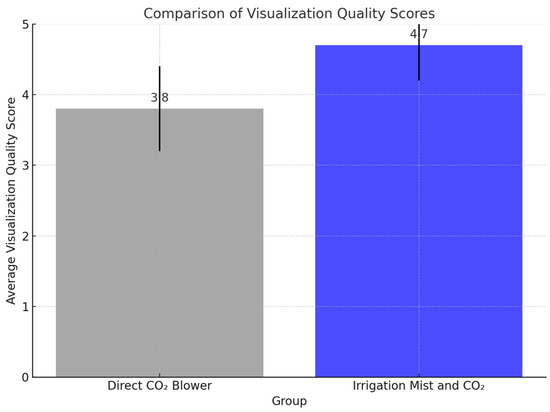
Figure 4.
Bar graph comparing the visualization quality scores between the two groups.
Incidence of Fibrillation During Aortic De-Clamping
A marked difference in the incidence of fibrillation during aortic de-clamping was observed between the two groups. In Group 1 (direct CO2 blower), eight patients (40%) experienced fibrillation at the time of de-clamping, whereas in Group 2 (irrigation mist and CO2), only two patients (10%) exhibited fibrillation (p = 0.03). This significant reduction suggests that the irrigation mist and CO2 system may help to stabilize the myocardium during this critical phase of surgery, potentially due to better tissue hydration, reduced stress on the cardiac tissues, and reduction of gaseous micro-emboli delivery.
Micro-Embolic Gas Activity
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) revealed a significantly lower incidence of micro-embolic gas activity in the cardiac chambers in Group 2 compared to Group 1. Micro-embolic bubbles were detected in 10 patients (50%) in Group 1, while only 3 patients (15%) in Group 2 showed evidence of micro-embolic gas activity (p = 0.02). The reduced micro-embolic gas activity in the irrigation mist and CO2 group suggests that the irrigation mist component may help mitigate gas embolization, potentially reducing the risk of neurological and myocardial complications postoperatively.
Surgical Efficiency
Although both groups underwent similar surgical procedures, a trend toward shorter total operative times was observed in Group 2. The improved visualization afforded by the ClearView™ system contributed to more efficient anastomosis construction, with Group 2 surgeries being approximately 10–15 min shorter on average compared to Group 1. However, this difference did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.07).
Postoperative Outcomes
No significant differences were observed in major postoperative complications, such as graft failure, infection, or prolonged ICU stays, between the two groups. Both groups had similar rates of recovery and postoperative hospital stay duration, indicating that while intraoperative conditions improved with the irrigation mist and CO2 system, the overall patient recovery was comparable between the groups (Table 2) (Figure 5).

Table 2.
Perioperative results.
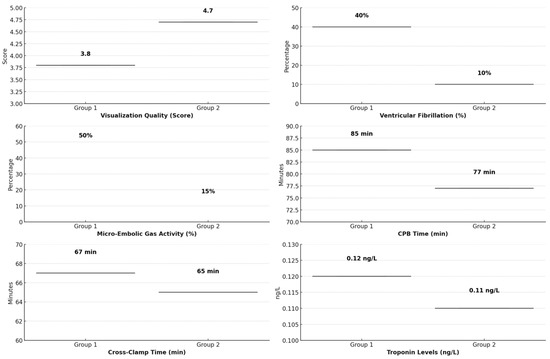
Figure 5.
Comparative analysis of key perioperative outcomes in Group 1 (direct CO2 blower) vs. Group 2 (irrigation mist and CO2).
4. Discussion
This retrospective comparative study evaluated the use of an irrigation mist and CO2 system versus the traditional direct CO2 blower in on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). By focusing on key outcomes such as intraoperative visualization, ventricular fibrillation during aortic de-clamping, and micro-embolic gas activity, the study highlights the potential value of this novel approach in enhancing surgical outcomes and improving patient safety. The findings demonstrate that the irrigation mist and CO2 system provides significantly superior intraoperative visualization, as reported by surgeons. The combination of CO2 and a fine irrigation mist helps maintain a clear surgical field and preserve tissue hydration, in contrast to the direct CO2 blower, which is associated with tissue desiccation and fragility. This improved visualization may also contribute to enhanced procedural efficiency, as indicated by the trend toward shorter operative times in the irrigation mist group. Although the difference in surgical times was not statistically significant, this may reflect the limited sample size rather than a lack of clinical impact. Improved visualization reduces the need for repeated field clearing, thus facilitating smoother anastomosis construction and procedural flow [6,7,8].
A significant finding of the study is the reduced incidence of ventricular fibrillation during aortic de-clamping in the irrigation mist group (10% vs. 40%). This benefit is likely due to the better preservation of myocardial stability and reduced stress on cardiac tissues, which can otherwise be exacerbated by desiccation and irritation caused by traditional CO2 blowers. Furthermore, the reduction in fibrillation may be linked to the system’s ability to lower micro-embolic gas activity, a known risk factor for myocardial and neurological complications [6,7]. Another notable result is the significant reduction in micro-embolic gas activity in the irrigation mist and CO2 group, as detected by transesophageal echocardiography (TEE). By minimizing gas bubble formation, the system addresses one of the most insidious risks of cardiac surgery—the potential migration of gaseous emboli to the coronary or cerebral circulation. This finding underscores the potential for the irrigation mist system to reduce postoperative neurological deficits and myocardial injury, although the absence of long-term follow-up data in this study limits a full assessment of these benefits. Future studies should include extended follow-up to evaluate the impact on cognitive and neurological outcomes comprehensively [7,8].
While the results underscore the promise of the irrigation mist and CO2 system, the study has limitations. As a retrospective analysis, it is prone to selection bias, which may have influenced the findings. Variations in patient characteristics or surgical technique, even if not statistically significant, could play a role. Additionally, the small sample size of 40 patients limits the statistical power, reducing the ability to generalize the results or detect subtler differences between groups. The subjective assessment of visualization quality by surgeons introduces potential observer bias, and future research should incorporate objective, quantitative metrics, such as automated imaging analysis, to validate this outcome [9,10]. The single-center nature of the study further limits the generalizability of its findings, as surgical outcomes may vary based on institutional protocols and surgeon experience. To address these issues, we plan to conduct a larger, multicenter, and prospective randomized controlled trial with a focus on eliminating selection bias, increasing sample size, and incorporating long-term follow-up data to better understand the clinical relevance of reduced micro-embolic activity [9]. Despite these limitations, the study provides compelling preliminary evidence supporting the use of the irrigation mist and CO2 system. Beyond its application in on-pump CABG, the system may offer benefits in other cardiac procedures, such as off-pump surgeries, where visualization and tissue preservation are critical. Expanding research to these areas could further validate the versatility and utility of this approach [10]. Finally, it is important to note that while this study evaluates a device (ClearView™ Blower/Mister), there are no conflicts of interest. The research was conducted without external funding, and no affiliations or financial relationships with the device manufacturer exist, ensuring the integrity and impartiality of the findings.
5. Conclusions
This retrospective study highlights the irrigation mist and CO2 system’s advantages over the traditional direct CO2 blower in on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). In our experience, this brief report shows that the system significantly improved intraoperative visualization, reduced tissue desiccation, and was associated with a lower incidence of fibrillation during aortic de-clamping. Additionally, the irrigation mist and CO2 system demonstrated a notable reduction in micro-embolic gas activity, as detected by transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), suggesting that it may reduce the risk of neurological and myocardial complications related to gas embolization. These findings suggest that the irrigation mist and CO2, initially designed for off-pump coronary surgery, is also highly beneficial in on-pump settings, future research should focus on conducting a prospective, multicenter, and randomized controlled trial with a larger sample size and long-term follow-up to validate the findings of this preliminary analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, I.C. and G.N.; original draft revision, F.F. and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Internal Ethical Institutional Board of Anthea Hospital GVM Care & Research (protocol code: TB0033; date of approval: 10 October 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, C.S.; Yoon, Y.S.; Shim, J.K.; Lim, H.K. Successful resuscitation of cardiac arrest caused by CO2 embolism with intra-aortic injection of epinephrine during off-pump coronary bypass surgery—A case report. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2013, 65, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Angelini, G.D.; Reeves, B.C.; Culliford, L.A.; Maishman, R.; Rogers, C.A.; Anastasiadis, K.; Antonitsis, P.; Argiriadou, H.; Carrel, T.; Keller, D.; et al. Conventional versus minimally invasive extracorporeal circulation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: A randomized controlled trial (COMICS). Perfusion 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plass, C.A.; Podesser, B.K.; Prusa, A.M. Effect of blower-mister devices on vasoreactivity of coronary artery bypass grafts. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 140, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wippermann, J.; Albes, J.M.; Liebing, K.; Breuer, M.; Kaluza, M.; Strauch, J.; Wahlers, T. Simple on-site assembled blower-mister device provides sufficient humidification and visualization in off-pump surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoo, K.J.; Kwak, Y.L. Carbon dioxide embolism induced right coronary artery ischemia during off-pump obtuse marginalis artery grafting. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2009, 36, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Badreldin, A.M.; Albert, A.A.; Ismail, M.M.; Heldwein, M.; Doerr, F.; Bossert, T.; Lichtenberg, A.; Hekmat, K. Gaseous emboli during off-pump surgery with T-graft technique, two different mechanisms. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 10, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jin, R.; Hiratzka, L.F.; Grunkemeier, G.L.; Krause, A.; Page, U.S., III. Aborted off-pump coronary artery bypass patients have much worse outcomes than on-pump or successful off-pump patients. Circulation 2005, 112 (Suppl. 9), I337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Jin, K.; Chen, L.; Bao, M.; Jiang, G. Carbon Dioxide Blower Facilitates Visceral Pleurectomy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 114, e71–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suma, H.; Isomura, T.; Horii, T.; SatWo, T. Intraoperative coronary artery imaging with infrared camera in off-pump CABG. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 70, 1741–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repossini, A.; Baudo, M.; D’Alonzo, M.; Petruccelli, R.; Rosati, F. MIDCAB Tips and tricks for a successful procedure. Multimed. Man. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).