Abstract
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) are among the main disease-driving players in most cases of monoarthritis (MonoA), oligoarthritis, and polyarthritis. In this review, we look at the characteristics and therapeutic challenges at the onset of arthritis and during follow-up management. In some cases, these forms of arthritis develop into autoimmune polyarthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), whereas local eradication of the RA synovium could still be combined with systemic treatment using immunosuppressive agents. Currently, the outcomes of local synovectomies are well studied; however, there is still a lack of a comprehensive analysis of current local intra-articular treatments highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, the aim of this study is to review local intra-articular therapy strategies. According to publications from the last decade on clinical studies focused on intra-articular treatment with anti-inflammatory molecules, a range of novel slow-acting forms of steroidal drugs for the local treatment of synovitis have been investigated. As pain is an essential symptom, caused by both inflammation and cartilage damage, various molecules acting on pain receptors are being investigated in clinical trials as potential targets for local intra-articular treatment. We also overview the new targets for local treatment, including surface markers and intracellular proteins, non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs), etc.
1. Introduction
The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) has launched a Europe-wide campaign, “Don’t delay, connect today”, to raise awareness of the major public health concerns of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs). Guidelines from the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as well as recommendations from the EULAR, emphasize the importance of early anti-inflammatory therapy (EIT) and the treat-to-target strategy (T2T) [1,2,3]. According to EULAR recommendations, a rheumatologist should see the patient within 6 weeks of the onset of arthritis and decide on a treatment strategy. The “window of opportunity” is usually up to three months, which is a crucial timeframe to choose an effective treatment strategy to stop the progression of the disease in its early stages [4,5].
Therefore, the management of inflammatory arthritis, especially monoarthritis (MonoA), before it develops into oligoarthritis and polyarthritis remains a challenge. The duration of acute MonoA is two to four weeks. Making an accurate diagnosis in such a short period is only sometimes possible. In most cases, acute MonoA is caused by a variety of causes ranging from benign to life-threatening. Thus, the onset of inflammatory arthritis (IA) may be MonoA, which needs to be carefully differentiated from diseases with different pathogenesis, such as gout (urine-type crystals), traumatic arthritis (trauma), infectious arthritis (virus or bacteria), paraneoplastic arthritis (cancer), and others [6,7,8]. It should be noted that several cases of MonoA have also been described since the beginning of 2021 after COVID-19 [9].
The PubMed scientific literature data on this topic could be more coherent, so we decided to review these issues. Thus, it remains to resolve and understand the main problem of MonoA as a choice of intervention strategy for synovial local inflammation. According to the literature, about 50% of MonoA cases resolve spontaneously; the rest develop into oligo- or polyarticular disease, but a significant proportion remains as persistent inflammatory MonoA. We attempt to analyze the data based on a basic pathogenetic message that FLSs are the key players in the majority of MonoA cases. As FLSs are key targets for local therapy, we focused on new targets related to surface markers and intracellular proteins, non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs), signaling, etc. Therefore, there is an urgent need to suppress or eradicate local inflammation, from which aggressive fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) are activated to induce cartilage degradation and may trigger a systemic autoimmune response [10,11], including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Synovial inflammation has recently been suggested as a target for the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) as well [12,13]. Thus, the synovitis-related phenotype or endotype of OA is an important factor in designing more effective disease-modifying interventions in these cases [14]. There is very little knowledge on the incidence and prevalence of early IA in primary care settings. Therefore, in most studies, the prevalence of early undifferentiated arthritis is around 30% [15,16,17].
Today, the scientific data on local synovectomy are well studied, one by one, but it is necessary to summarize the comparative data on this treatment modality. These challenges concern the scientific, medical, and pharmaceutical communities as they seek to establish a strong link between new intra-articular (i.a.) treatments. Thus, we analyzed local treatments from the US National Library of Medicine (clinicaltrials.gov, accessed on 1 January 2023) database with the following criteria: 2013–2023 years completed trials with results publications, adult population, and intra-articular arthritis treatment (in particular anti-inflammatory effects on synovium).
Therefore, in this paper, we will analyze the long-term monitoring results of MonoA and explore the local treatment strategies available today.
2. Materials and Methods
We tried to analyze the data based on the pathogenesis basic knowledge that FLSs are key players in most cases of arthritis (see graphical abstract). In the 1st step, the PubMed database was searched for the keyword ‘monoarthritis’ only. Monoarthritis was represented by 353 case reports, but these cases were not included in the pooled data.
Therefore, in the 2nd step, we had to solve and understand the main problem of the choice of the intervention strategy for local inflammation of the synovium, so we used different combinations of terms for local treatment approaches in the PubMed database search: ‘monoarthritis’, ‘local treatment’, ‘intra-articular treatment’, ‘synovectomy’, and ‘synovitis treatment’. On the basis of our analysis of these clinically evaluated synovectomies, we concluded that there is still a lack of data on selective local treatment.
In the 3rd step, we analyzed 53 contemporary local treatments from the US National Library of Medicine (clinicaltrials.gov) database according to the following criteria: completed trials with results, 10-year follow-up period, adult population, and intra-articular arthritis treatment. In the clinical studies, we searched for new intra-articular approaches, especially for OA patients with inflammatory phenotype where FLSs are less aggressive.
In the 4th step, we asked about new advances in the inhibition of aggressive FLS suppression, using an RA example. As FLSs are key targets for local therapy, we focused on new targets related to surface markers and intracellular proteins, non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs), signaling, etc.
3. Local Treatment of Arthritis
3.1. Monoarthritis: Treatment Challenges
The experience with MonoA shows that local treatment of joint synovitis is feasible, especially when large joints are affected (Figure 1).
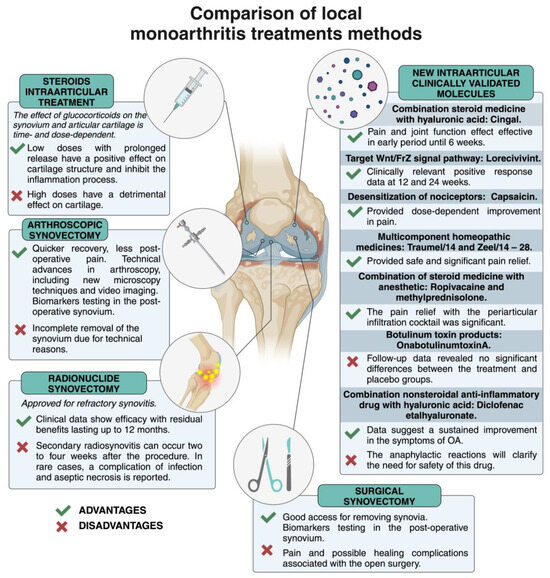
Figure 1.
Advantages and disadvantages of local monoarthritis treatments. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 4 July 2024).
In general, each of the local procedures used in clinical practice has its own advantages and disadvantages, and open and arthroscopic surgical interventions remove inflamed tissue while providing the opportunity to study biomarkers [18,19,20]. Currently, needle ultrasound and arthroscopy biopsy are used to assess synovitis [21,22], but new contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques are better able as a reference method to characterize the synovium and cartilage [23]. A decrease in orthopedic joints is linked to the development of more conventional new systemic biologics, medications, etc. [24,25].
The EULAR recommendations on intra-articular therapy for different inflammatory arthritis should be considered [26]. The effect of corticosteroids on articular cartilage is time- and dose-dependent: a low dose has a beneficial effect, whereas a high dose has a detrimental effect on cartilage degradation [27]. There is a diverse scientific debate on the predictive factors of response to intra-articular steroid injections in knee osteoarthritis: degree of synovitis, site of discharge, and cartilage protection [28]. Intra-articular injections of glucocorticoids are probably the most common and widely used for local inhibition of synovial inflammation. This EULAR Guideline describes the basic principles for the use of i.a. steroid injections for knee pain relief in combination with release or for RA in cases where there is a need to adjust the disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs DMARDs therapy in one or more remaining active joints [26]. As previously described, in the MonoA, steroid therapy is the first choice for suppressing local inflammation; this treatment modality is good at suppressing synovitis and symptoms. In cases where steroids are injected close to the synovium (e.g., into the fat pad of the knee joint), the anti-inflammatory efficacy may be very similar to the same precise needle placement into the synovial cavity due to the distribution of the steroid through the tissues surrounding the joint [29]. Synovial inflammation has recently been proposed as an essential target for the treatment of OA [12]. Today, the FDA has approved low-dose, slow-release drugs for the treatment of OA local synovitis [30].
3.2. Recent Developments of Intra-Articular Medication
We analyzed and summarized 10 years of clinical studies in Table 1. Thus, novel molecules have been described as clinically validated i.a. therapies for synovitis treatment strategies. Joint damage due to synovial inflammation and cartilage breakdown are two of the factors that cause pain. Therefore, analgetic treatment is also very essential for local treatment. Brief comments on the solutions to these problems are given below.

Table 1.
New clinically tested treatment options for local synovial inflammation.
Summary: Thus, today, new steroid formats are approved for the local treatment of OA knees, hips, and shoulder joints with a slow-acting drug that has no detrimental effect on the cartilage or other aspects of the joint structure; the pain relief is dose-dependent. The 3b clinical study with a flexible dosing schedule repeated twice according to patient response was well tolerated and effective until 52 weeks [33]. Other studies in which steroids were administered slowly showed encouraging results in terms of pain relief and improvement in physical function at around 24 weeks [30,31,32,34,35,36,37]. Another important aspect is the combination of steroids with HA, which has been evaluated and found to have a beneficial anti-inflammatory effect in combination with viscosupplementation [38]; this combination is effective against pain in the early phase of the disease for up to 6 weeks. WNT inhibitors are being investigated and this drug has a positive effect on cartilage degeneration by affecting chondrocyte differentiation and inhibition of osteoblasts and synovial cells [39,40]. Meanwhile, molecules, involved in the long-term desensitization of nociceptors associated with calcium influx into nociceptive nerve endings show a beneficial pain inhibitory effect [42]. The regulation of the nociceptive response with botulinum toxin has not shown a beneficial effect on synovium pain [45]. Various combinations (steroids with anesthetics or NSAIDs with HA) are currently being clinically validated, and these agents have shown pain suppression [44,46,47]. Attention must be paid to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in combination with HA regarding anaphylactic reactions [47]. Consequently, multicomponent homeopathic medicines are also used in the clinical practice for pain relief [43]. The effects of all of these drugs are dose-dependent, with duration ranging from 12 weeks to 52 weeks. The summarized data are represented in Figure S1. Local treatment of early synovitis with targeted intra-articular suppression is essential, but at the same time, the per os treatment must be chosen to select an effective treatment strategy and to halt disease progression in the early stages [4,5]. MonoA data for local treatment, especially intra-articular treatment, have revealed that key target molecules are involved in OA. In the clinical studies described above, we analyzed novel molecules approved for intra-articular therapy, particularly targeting OA patients with an inflammatory phenotype where FLSs are less aggressive. Another approach is the investigation of new targets in inflammatory tissues after synovectomy in pre-clinical studies. As fibroblast-like synoviocytes are one of the targets of local treatment, we focused on these synovitis-promoting players. The behavior of FLS in RA is an excellent example for exploring new targets related to surface markers and intracellular proteins of these cells, non-coding RNAs, signal transduction, etc.
3.3. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes as Potential Targets for Early Local Therapy
In RA, fibroblast-like synoviocytes have intrinsic pathogenic properties and actively contribute to the disease process. They proliferate and promote joint destruction by stimulating inflammation. However, the reasons why they turn from beneficial to harmful in RA remain to be fully understood. Studies have shown that persistent inflammation can induce molecular changes in FLSs that transform them from passive responders to inflammation to active aggressors [48,49]. RA FLSs have specific characteristics that distinguish them from healthy FLSs. These characteristics remain unchanged even when RA FLSs are isolated from an environment rich in inflammatory cytokines [11,49]. Potential therapeutic strategies could target FLS surfaces and intracellular proteins, FLS metabolism, and signaling pathways that increase FLS invasive and migratory potential, non-coding ribonucleic acid, oxidative stress molecules, etc. Current therapeutic approaches focus on modifying the immune response, specifically by targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines, B cells, or T cells [50]. Some of these drugs may also influence the invasive behavior of FLSs, especially those that inhibit cytokines or signal transduction pathways [51,52]. Although these drugs can reduce the level of FLS activity in RA, they may not always be effective, which is why patients still suffer from this disease. In such cases, the use of a combination of alternative or complementary therapies may be useful to manage the disease effectively. Potential therapeutic targets related to FLS are described in Figure 2 and the following sections.
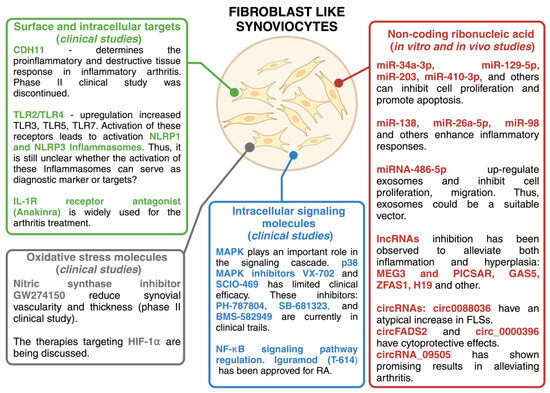
Figure 2.
Potential therapeutic targets related to FLSs. Created with BioRender.com.
3.3.1. Cell Surface Targets
The discovery of different FLS phenotypes that contribute to synovitis leads to the possibility of targeting cells based on their surface phenotype. This implies the identification of pathogenic cell-specific surface proteins and the development of innovative treatment strategies targeting specific RA FLS phenotypes. RA FLSs lineages are characterized by the expression of specific markers such as CD10, CD34, CD55, CD90, CD248, and podoplanin (PDPN) [53,54,55,56]. These surface markers characterize RA FLS subgroups with significant functional differences. For example, previous studies have shown that cadherin 11 (CDH11) significantly contributes to homotypic FLS aggregation in in vitro and in vivo models [57,58]. CDH11 has attracted considerable attention as a potential marker of RA and has been widely regarded as a promising target. Nevertheless, a clinical trial investigating the efficacy of a monoclonal antibody directed against CDH11 in a phase II study was discontinued due to low efficacy.
Other potential markers and targets of RA include Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and inflammasomes. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). If regulatory mechanisms fail, TLR activation can trigger local inflammation and contribute to inflammatory or autoimmune diseases. Necrotic cells in inflamed joints may be a source of endogenous ligands for these receptors. Heat shock proteins and low molecular weight hyaluronan were originally thought to activate TLR2/TLR4 heterodimers directly, but pure ligands do not effectively activate these receptors [59]. However, citrullination of endogenous ligands such as fibrinogen and histones can stimulate the TLR4-mediated pathway [60,61]. The involvement of the TLR4-mediated pathway in the development of RA is suggested by the significant inhibition of monocyte activation observed in these patients with ACPA when treated with anti-TLR4 antibodies [62]. TLR4 can increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-6 and IL-17, by binding to exogenous ligands, such as peptidoglycan, in the FLS of RA patients and in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), leading to inflammation and degeneration of cartilage [63]. In addition to the up-regulation of TLR2 and TLR4, an increased expression of TLR3, TLR5, and TLR7 has been observed in FLSs from RA patients compared to individuals with OA or without inflammatory diseases [64,65,66,67]. Activation of these receptors leads to enhanced local inflammatory responses, including the formation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor family pyrin domain-rich receptor 1 (NLRP1) and NLRP3 inflammasomes [68].
Inflammasomes are multicellular protein complexes that activate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in response to cellular stress or infection. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to the development of autoimmune diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis, systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and RA [69,70]. Two signals are required to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. The first signal is transduced via membrane receptors such as TLRs. Meanwhile, the second signal is linked to stimuli such as changes in ATP, K+ and Ca2+ levels, lysosomal destabilization, mitochondrial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species, and uric acid crystals [71,72,73]. Targeting TLRs and inflammasomes is promising for modulating the immune response and possibly treating inflammatory disorders. However, it is still unclear whether the activation of these inflammasomes can serve as diagnostic markers to differentiate undifferentiated early inflammatory arthritis into specific diseases such as RA.
The question is whether these different populations are definitive subsets with a consistent phenotype or whether the FLS phenotype is flexible and microenvironment-dependent, leading to differences in the relative prevalence of the various putative phenotypes.
3.3.2. Intracellular Signaling Molecules
Various cell signaling molecules have been investigated as potential biomarkers of RA, which can help diagnose, monitor, and predict the disease’s progression.
There are several strategies to combat FLSs, including inhibition of components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, inhibition of kinases that activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and blocking the nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) pathway [74].
MAPK regulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and plays an important role in the signaling cascade downstream of interleukin (IL)-1, IL-17, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α receptors [75,76]. Activation of MAPK family members occurs primarily in synovial tissues. Their activation is important for the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF, IL-6, and IL-1. p38 kinase is a potential target for the treatment of RA, but clinical trials have yet to identify effective inhibitors. The results show that the p38 MAPK inhibitor VX-702 has limited clinical efficacy and is accompanied by transient inhibition of inflammatory biomarkers [77]. However, it may not offer a significant and permanent inhibitory impact on the chronic inflammation observed in RA. For instance, the clinical trial, including SCIO-469, an orally administered inhibitor of p38-α MAPK, did not show greater efficacy than a placebo in individuals diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis [78]. PH-797804, SB-681323, and BMS-582949 are p38 inhibitors currently in clinical trials [74]. As an alternative approach, higher members of the MAPK cascade, such as MKK3, MKK6, and MAP3K5, have been investigated as potential targets in pre-clinical models [79].
Targeting JNK in this pathway has shown encouraging results in alleviating the clinical symptoms of RA. JNK1 plays a crucial role in maintaining and promoting inflammation in the synovium [80]. It is expressed in FLS and macrophage-like synoviocytes (MLS), and targeting JNK1 with blocking agents can reduce its endogenous expression in both synovial cell types [81,82]. For example, the use of the JNK inhibitor SP600125 has decreased c-Jun transcription and enhanced the accumulation of phospho-Jun, thereby attenuating the inflammatory response. In addition, the JNK inhibitor AS601245 can relieve symptoms of collagen-induced arthritis rat model (CIA) rats [83].
Current pharmacological drugs used for treatment therapy specifically target or interact with the NF-κB signaling pathway. The NF-κB signaling pathway regulates a variety of cellular processes, including inflammation, immune response, and cell survival [74,84]. These drugs act by modulating NF-κB activity, inhibiting its activation or blocking downstream signaling events. For example, methotrexate (MTX) is an effective drug for the treatment of RA and affects TNF-α levels in early RA patients via the NF-κB pathway [85]. Prednisolone, a synthetic glucocorticoid, inhibits the transcription of inflammatory genes via the NF-κB signaling pathway and is clinically used to reduce RA inflammation [86].
In addition, new drugs are currently being investigated and developed to reduce the activity of aggressive FLS by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Iguramod (T-614) is a new disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug that inhibits NF-κB activation and is approved for the treatment of RA in Japan and China [87]. Denosumab inhibits NF-κB ligand–receptor activator and can partially restore bone erosions in RA patients. The combination of Denosumab with DMARDs may be considered in RA patients with progressive bone erosions. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of an antagonist targeting cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (CysLT1) in inhibiting NF-kB pathway activation as well as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) secretion in FLS [88]. The results of this study suggest that modulation of CysLT1 and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptors may be an effective therapeutic strategy to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of RA patients [89]. However, further studies are needed to confirm their efficacy and to investigate their clinical application. The integration of multiple biomarkers and the use of advanced technologies may increase their diagnostic and prognostic value in the future [10,90,91].
3.3.3. Non-Coding Ribonucleic Acids
Non-coding ribonucleic acids (ncRNAs) have emerged as potential biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). ncRNAs are RNA molecules that do not encode proteins but play important regulatory roles in gene expression and cellular processes, including signaling pathways. ncRNAs comprise a diverse group of molecules, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs).
The level of miRNAs can influence the secretion of inflammatory cytokines or metalloproteinases (MMPs), which in turn can impact the progression of RA [92]. Certain miRNAs have been found to inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis [93], while others have been shown to contribute to the inflammatory environment, possibly leading to tissue damage [94,95]. Animal and cell culture experiments have shown promising results when certain miRNAs alleviate or enhance RA symptoms. For example, when overexpressed, miR-34a-3p [96], miR-129-5p [97], miR-203 [98], miR-410-3p [99], and others can inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis by targeting different proteins. On the other hand, miR-138 [100], miR-26a-5p [94], miR-98 [101], and similar miRNAs enhance inflammatory responses. In addition, miRNA-486-5p up-regulation in exosomes has been found to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, suggesting that exosomes could be a suitable vector for the therapeutic delivery of miRNA-486-5p [102]. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) over 200 nucleotides in length are widely expressed in many human tissues and can be a diagnostic tool for RA [103]. However, like miRNAs, they may have dual effects. Some lncRNAs have anti-inflammatory properties, while others can enhance inflammatory reactions. For example, inhibition of specific long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) has been observed to alleviate both inflammation and hyperplasia. The involvement of non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) FER1L4 and MEG3 in RA has been demonstrated in [104,105]. MEG3 upregulation has an inflammation-suppressive effect by modulating the AKT/mTOR signaling cascade [106]. PICSAR, an additional (ncRNA), influences several cellular processes, including cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and the synthesis of IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-3. It exerts this influence by interacting with miR-4701-5p [107]. The role of the miR-222-3p/Sirt1 axis is central to the action of GAS5 in mitigating RA FSL proliferation, inflammation, and apoptosis [108]. Silencing of the lncRNA ZFAS1 may mitigate inflammation and hyperplasia by competitively binding to miR-296-5p and regulating MMP-15 expression in the context of an experimental arthritis model. Inhibition of ZFAS1 has been observed to alleviate both inflammation and hyperplasia. This effect is achieved by binding ZFAS1 to miR-296-5p, which subsequently regulates MMP-15 expression [109]. Furthermore, IncRNAs expressing lncRNA-H19 injected into the ankles of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice ameliorate the progression by competing with miR-124a, which directly acts on CDK2 and MCP-1 [110].
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a recently discovered class of endogenous ncRNA molecules whose importance in regulating gene expression is increasingly recognized. CircRNAs have been found to be abnormally elevated in RA and to contribute to disease progression. These circRNAs have been identified as abnormally increased in RA and contribute to the advancement of the disease. These ncRNAs have great potential and promising targets for the treatment of RA. They have several functional properties, including RNA polymerase II elongation, regulation of RNA maturation, and protein localization [111]. Several studies have started to investigate the involvement of circRNAs in the pathogenesis of RA. As an example, the molecule circ0088036 has been observed to have an atypical increase in FLSs. This abnormality contributes to the progression of RA by acting as a molecular sponge for miR-140-3p, thereby augmenting the production of SIRT 1 [112]. Other circRNAs, circFADS2 and circ_0000396, have been shown to have cytoprotective effects against apoptosis and suppress cell proliferation [113]. Furthermore, it has been observed that circRNA_09505 plays a significant role in promoting the expression of AKT1 by regulating the IkBa/NF-kB signaling pathway in macrophages. Notably, the knockdown of circRNA_09505 has shown promising results in alleviating arthritis and inflammation in mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) [114]. RNA plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and has great potential for diagnostic and therapeutic target treatment. Despite challenges related to identification and characterization, tissue specificity, standardization and reproducibility, functional characterization, validation, and clinical utility, ncRNA are promising potential biomarkers of RA due to their stability, detectability in various body fluids, and involvement in regulatory processes [115,116,117]. However, further studies are needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms underlying these different forms of RNA.
3.3.4. Oxidative Stress Molecules
Oxidative stress is defined as a harmful condition characterized by an imbalance of oxidative molecules, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to an excess of prooxidants [118]. This imbalance can lead to disruption of redox signaling and molecular damage. Under physiological conditions, ROS are required to maintain the cellular redox status and play an important role in cell signaling pathways, differentiation, proliferation, growth, apoptosis, regulation of the cytoskeleton, and phagocytosis. However, when ROS levels exceed physiological levels, they can have detrimental effects on many cellular components, such as cell membranes, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids [119,120]. In RA patients and animal models, there is a significant association between blood ROS levels and RA severity. Several studies have shown alteration in the expression of nitric oxide (NO) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), which lead to impaired infiltration of T- and B-cells into the joints by interfering with their chemotaxis and adhesion [121,122]. Furthermore, promising results have been observed with NOS and iNOS inhibitors L-NAME and iNOS inhibitor GW274150 in reducing the inflammatory response and synovial thickness, offering the potential for targeted treatments [123,124]. In addition, patients with active RA are characterized by increased ROS levels and reduced antioxidant capacity, leading to increased levels of lipid peroxidation, which can be observed in synovial fluid and blood samples [125,126,127,128]. Based on previous studies, a positive correlation between lipid peroxidation biomarker malondialdehyde (MDA) and proinflammatory cytokines has been observed in the serum of individuals with RA [129]. Furthermore, studies have shown that reactive oxygen metabolites (ROM) are increased in blood samples from RA patients and positively correlate with disease activity [130]. In line with these findings, it has been observed that RA patients have reduced levels of antioxidants in serum and synovial fluid [131,132].
A link between oxidative damage to synovial tissue, mitochondrial dysfunction, and hypoxic status in arthritic joints has also been demonstrated. For example, inflammatory mediators and hypoxic conditions can impair the mitochondrial state of synovial cells, leading to metabolic shifts and increased mutation rates. Furthermore, oxidative stress can alter energy metabolism, increase ROS production, and raise mitochondrial mutagenesis, thereby contributing to inflammatory processes and impaired angiogenesis in RA patients. The metabolic disparity between healthy synovial tissue and RA-affected synovial tissue particularly highlights the alterations in cellular metabolism known as the Warburg effect or aerobic glycolysis [133]. This phenomenon describes the overexpression of glycolytic enzymes in RA synovial tissue and its potential impact on inflammatory cytokines, cell proliferation, and disease activity [134,135]. In the context of RA, studies have shown that hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α is important in maintaining oxygen balance and regulating the expression of genes involved in angiogenesis and inflammation in the synovium. Various factors, including hypoxia, ROS, cytokines, hormones, and mechanical stress, influence HIF-1α activation. In terms of clinical relevance, the potential of therapies targeting HIF-1α or angiogenic factors as an alternative approach to the treatment of RA has been suggested [136,137]. Furthermore, studies on the Notch signaling pathway in the context of RA have revealed its role in regulating cellular processes and promoting inflammation. It has also been suggested that the Notch signaling pathway could be used as a pharmacological treatment for RA [138].
In general, local treatment of early synovitis with conventional glucocorticoids and synovectomy involves targeted suppression or eradication of aggressive fibroblast-like synoviocytes. In advanced RA, combining immunosuppressants with local FLS-targeted therapy can more effectively control disease activity.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
In the course of MonoA, local synovitis treatment involves targeted inhibition or destruction of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Today, several new intra-articular therapies have been approved in clinical studies, especially for osteoarthritis patients with an inflammatory endotype where FLSs are less aggressive. Currently, various slow-acting steroidal drugs for the local treatment of synovitis, which do not have a detrimental effect on cartilage, are gradually being marketed in clinics. Various combination therapies (steroids with HA, steroids with anesthetic, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with HA, etc.) are currently approved in clinical practice and have proven to be effective in pain relief. Thus, personalized medicine initiatives involve the choice and decision of medicines based on the unique clinical characteristics or risk factors and biomarker expression of each patient [130]. A local approach to the elimination of synovial tissue inflammation will lead to the discovery of new local targets related to surface markers and intracellular proteins, non-coding RNAs, signaling molecules, and improvement in the treatment techniques and protocols.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/medicina60111819/s1, Table S1: Local treatments: advantages and disadvantages.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, G.K. and J.D.; writing—review and editing, G.K., J.D., D.M., J.P. and E.B.; conceptualization, G.K. and E.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We wish to acknowledge financial support from the European Research Executive Agency according to the project “Twinning for Promoting Excellence, Ability and Knowledge to develop novel approaches for targeting inflammatory and degenerative age-related joint diseases (TWINFLAG)”. GRANT_NUMBER: 101079489.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study and are referred to in the list of references.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lane, N.E.; Brandt, K.; Hawker, G.; Peeva, E.; Schreyer, E.; Tsuji, W.; Hochberg, M.C. OARSI-FDA Initiative: Defining the Disease State of Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Kvien, T.K.; Navarro-Compán, M.V.; Oliver, S.; Schoels, M.; et al. Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target: 2014 Update of the Recommendations of an International Task Force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffer, M.A.; Schoels, M.M.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.; Bykerk, V.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Haraoui, B.; et al. Evidence for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target: Results of a Systematic Literature Search Update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combe, B.; Landewe, R.; Lukas, C.; Bolosiu, H.D.; Breedveld, F.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Ferraccioli, G.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Klareskog, L.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Early Arthritis: Report of a Task Force of the European Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combe, B.; Landewe, R.; Daien, C.I.; Hua, C.; Aletaha, D.; Álvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Bakkers, M.; Brodin, N.; Burmester, G.R.; Codreanu, C.; et al. 2016 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Early Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.M. Acute Monoarthritis. JAAPA Off. J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2019, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, C.; Velazquez, C.; Mody, A.; Brasington, R. Diagnosing Acute Monoarthritis in Adults: A Practical Approach for the Family Physician. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 68, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.A.; Daily, J.P.; Pohlgeers, K.M. Acute Monoarthritis: Diagnosis in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 94, 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Cincinelli, G.; Di Taranto, R.; Orsini, F.; Rindone, A.; Murgo, A.; Caporali, R. A Case Report of Monoarthritis in a COVID-19 Patient and Literature Review: Simple Actions for Complex Times. Medicine 2021, 100, e26089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Rose, P.; Mao, J.; Zhu, Y.Z. Signaling Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications for Targeted Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, G.; Firestein, G.S. Restoring Synovial Homeostasis in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Targeting Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiessen, A.; Conaghan, P.G. Synovitis in Osteoarthritis: Current Understanding with Therapeutic Implications. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Fang, Y.; Tan, X.; Jiang, H.; Gong, X.; Wang, X.; Hong, W.; Tu, J.; Wei, W. The Emerging Role of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes-Mediated Synovitis in Osteoarthritis: An Update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9518–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Spil, W.E.; Kubassova, O.; Boesen, M.; Bay-Jensen, A.-C.; Mobasheri, A. Osteoarthritis Phenotypes and Novel Therapeutic Targets. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 165, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooy, D.P.C.; van der Linden, M.P.M.; Knevel, R.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M. Predicting Arthritis Outcomes—What Can Be Learned from the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic? Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2011, 50, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combe, B.; Benessiano, J.; Berenbaum, F.; Cantagrel, A.; Daurès, J.-P.; Dougados, M.; Fardellone, P.; Fautrel, B.; Flipo, R.-M.; Goupille, P.; et al. The ESPOIR Cohort: A Ten-Year Follow-up of Early Arthritis in France: Methodology and Baseline Characteristics of the 813 Included Patients. Joint Bone Spine 2007, 74, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.A.; Green, M.J.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Proudman, S.; Karim, Z.; Wakefield, R.J.; Conaghan, P.G.; Emery, P. Prognostic Factors in a Large Cohort of Patients with Early Undifferentiated Inflammatory Arthritis after Application of a Structured Management Protocol. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3039–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, C.; Vieira-Sousa, E.; Boyle, D.L.; Buch, M.H.; Buckley, C.D.; Cañete, J.D.; Catrina, A.I.; Choy, E.H.S.; Emery, P.; Fearon, U.; et al. Synovial Tissue Research: A State-of-the-Art Review. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hair, M.J.H.; Harty, L.C.; Gerlag, D.M.; Pitzalis, C.; Veale, D.J.; Tak, P.P. Synovial Tissue Analysis for the Discovery of Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Patients with Early Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroosh, S.G.; Ghatfan, A.; Farbod, A.; Meftah, E. Synovial Biopsy for Establishing a Definite Diagnosis in Undifferentiated Chronic Knee Monoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ike, R.W.; Kalunian, K.C. Will Rheumatologists Ever Pick up the Arthroscope Again? Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, V.; Monaco, E.; Garufi, C.; Spinelli, F.R.; Rossi, G.; Dagget, M.; Conti, F.; Ferretti, A. In-Office Needle Arthroscopic Synovial Biopsy Is an Effective Diagnostic Tool in Patients With Inflammatory Arthritis. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2022, 4, e2099–e2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernotiene, E.; Bagdonas, E.; Kirdaite, G.; Bernotas, P.; Kalvaityte, U.; Uzieliene, I.; Thudium, C.S.; Hannula, H.; Lorite, G.S.; Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; et al. Emerging Technologies and Platforms for the Immunodetection of Multiple Biochemical Markers in Osteoarthritis Research and Therapy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 572977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momohara, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, H.; Mibe, J.; Iwamoto, T.; Ikari, K.; Nishino, J.; Kadono, Y.; Yasui, T.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Recent Trends in Orthopedic Surgery Performed in Japan for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 21, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jämsen, E.; Virta, L.J.; Hakala, M.; Kauppi, M.J.; Malmivaara, A.; Lehto, M.U.K. The Decline in Joint Replacement Surgery in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Associated with a Concomitant Increase in the Intensity of Anti-Rheumatic Therapy: A Nationwide Register-Based Study from 1995 through 2010. Acta Orthop. 2013, 84, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uson, J.; Rodriguez-García, S.C.; Castellanos-Moreira, R.; O’Neill, T.W.; Doherty, M.; Boesen, M.; Pandit, H.; Möller Parera, I.; Vardanyan, V.; Terslev, L.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for Intra-Articular Therapies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernecke, C.; Braun, H.J.; Dragoo, J.L. The Effect of Intra-Articular Corticosteroids on Articular Cartilage: A Systematic Review. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2015, 3, 2325967115581163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricar, N.; Callaghan, M.J.; Felson, D.T.; O’Neill, T.W. Predictors of Response to Intra-Articular Steroid Injections in Knee Osteoarthritis—A Systematic Review. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2013, 52, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, G.; O’Neill, T.W.; Kitas, G.; Sinha, A.; Klocke, R. Accuracy of Injection and Short-Term Pain Relief Following Intra-Articular Corticosteroid Injection in Knee Osteoarthritis - an Observational Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.; Duggan, S.T.; Keam, S.J. Triamcinolone Acetonide Extended-Release: A Review in Osteoarthritis Pain of the Knee. Drugs 2019, 79, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodick, N.; Lufkin, J.; Willwerth, C.; Kumar, A.; Bolognese, J.; Schoonmaker, C.; Ballal, R.; Hunter, D.; Clayman, M. An Intra-Articular, Extended-Release Formulation of Triamcinolone Acetonide Prolongs and Amplifies Analgesic Effect in Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2015, 97, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conaghan, P.G.; Cohen, S.B.; Berenbaum, F.; Lufkin, J.; Johnson, J.R.; Bodick, N. Brief Report: A Phase IIb Trial of a Novel Extended-Release Microsphere Formulation of Triamcinolone Acetonide for Intraarticular Injection in Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, A.I.; Richmond, J.C.; Kraus, V.B.; Gomoll, A.; Jones, D.G.; Huffman, K.M.; Peterfy, C.; Cinar, A.; Lufkin, J.; Kelley, S.D. Safety and Efficacy of Repeat Administration of Triamcinolone Acetonide Extended-Release in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Phase 3b, Open-Label Study. Rheumatol. Ther. 2019, 6, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivitz, A.; Mehra, P.; Hanson, P.; Kwong, L.; Cinar, A.; Lufkin, J.; Kelley, S. A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Dose Study to Assess Safety and Systemic Exposure of Triamcinolone Acetonide Extended-Release in Patients With Hip Osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, P.; Kivitz, A.; Mehra, P.; Kwong, L.; Cinar, A.; Lufkin, J.; Kelley, S.D. Safety and Systemic Exposure of Triamcinolone Acetonide Following Ultrasound-Guided Intra-Articular Injection of Triamcinolone Extended-Release or Standard Triamcinolone Acetonide in Patients with Shoulder Osteoarthritis: An Open-Label, Randomized Study. Drugs RD 2021, 21, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, V.B.; Conaghan, P.G.; Aazami, H.A.; Mehra, P.; Kivitz, A.J.; Lufkin, J.; Hauben, J.; Johnson, J.R.; Bodick, N. Synovial and Systemic Pharmacokinetics (PK) of Triamcinolone Acetonide (TA) Following Intra-Articular (IA) Injection of an Extended-Release Microsphere-Based Formulation (FX006) or Standard Crystalline Suspension in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Chang, C.-C.; Wei, J.C.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Brown, C.; Tai, T.-T.; Wu, C.-F.; Chuang, W.C.-M.; Shih, S.-F. TLC599 in Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Phase IIa, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Finding Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangody, L.; Szody, R.; Lukasik, P.; Zgadzaj, W.; Lénárt, E.; Dokoupilova, E.; Bichovsk, D.; Berta, A.; Vasarhelyi, G.; Ficzere, A.; et al. Intraarticular Injection of a Cross-Linked Sodium Hyaluronate Combined with Triamcinolone Hexacetonide (Cingal) to Provide Symptomatic Relief of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial. Cartilage 2018, 9, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, Y.; McAlindon, T.E.; Gibofsky, A.; Lane, N.E.; Lattermann, C.; Skrepnik, N.; Swearingen, C.J.; Simsek, I.; Ghandehari, H.; DiFrancesco, A.; et al. A Phase 2b Randomized Trial of Lorecivivint, a Novel Intra-Articular CLK2/DYRK1A Inhibitor and Wnt Pathway Modulator for Knee Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambiah, J.R.S.; Kennedy, S.; Swearingen, C.J.; Simsek, I.; Yazici, Y.; Farr, J.; Conaghan, P.G. Individual Participant Symptom Responses to Intra-Articular Lorecivivint in Knee Osteoarthritis: Post Hoc Analysis of a Phase 2B Trial. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambiah, J.R.S.; Simsek, I.; Swearingen, C.J.; Kennedy, S.; Cole, B.J.; McAlindon, T.E.; Yazici, Y. Comparing Patient-Reported Outcomes From Sham and Saline-Based Placebo Injections for Knee Osteoarthritis: Data From a Randomized Clinical Trial of Lorecivivint. Am. J. Sports Med. 2022, 50, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, R.M.; Ervin, J.; Nezzer, J.; Nieves, Y.; Guedes, K.; Burges, R.; Hanson, P.D.; Campbell, J.N. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Intraarticular Trans-Capsaicin for Pain Associated With Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozada, C.J.; Del Rio, E.; Reitberg, D.P.; Smith, R.A.; Kahn, C.B.; Moskowitz, R.W. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Saline-Controlled Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Co-Administered Intra-Articular Injections of Tr14 and Ze14 for Treatment of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee: The MOZArT Trial. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 13, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.; Mallesh, M.; Wakankar, H.; Prajapati, R.; Pandit, H. Effect of Methylprednisolone in Periarticular Infiltration for Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty on Pain and Rehabilitation. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 1646–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlindon, T.E.; Schmidt, U.; Bugarin, D.; Abrams, S.; Geib, T.; DeGryse, R.E.; Kim, K.; Schnitzer, T.J. Efficacy and Safety of Single-Dose onabotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Symptoms of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Results of a Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018, 26, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Kano, K.; Osato, T.; Seo, T. Open-Label Phase 3 Study of Diclofenac Conjugated to Hyaluronate (Diclofenac Etalhyaluronate: ONO-5704/SI-613) for Treatment of Osteoarthritis: 1-Year Follow-Up. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Kano, K.; Nobuoka, Y.; Seo, T. Efficacy and Safety of Diclofenac-Hyaluronate Conjugate (Diclofenac Etalhyaluronate) for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Phase III Trial in Japan. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Kriegsmann, J.; Franklin, B.N.; Matsumoto, S.; Geiler, T.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S. Synovial Fibroblasts of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Attach to and Invade Normal Human Cartilage When Engrafted into SCID Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in RA: Passive Responders and Imprinted Aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.H.; Kavanaugh, A.F.; Jones, S.A. The Problem of Choice: Current Biologic Agents and Future Prospects in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, T.; Orr, C.; Wade, S.; Biniecka, M.; Wade, S.; Gallagher, L.; Low, C.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. JAK/STAT Blockade Alters Synovial Bioenergetics, Mitochondrial Function, and Proinflammatory Mediators in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Cheng, A.; Guma, M. Can Metabolic Pathways Be Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, A.P.; Naylor, A.J.; Marshall, J.L.; Hardie, D.L.; Zimmermann, B.; Turner, J.; Desanti, G.; Adams, H.; Yemm, A.I.; Müller-Ladner, U.; et al. Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts Differentiate into Distinct Subsets in the Presence of Cytokines and Cartilage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkovskij, J.; Rudys, R.; Bernotiene, E.; Minderis, M.; Bagdonas, S.; Kirdaite, G. Cell Surface Markers and Exogenously Induced PpIX in Synovial Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cytom. Part J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2015, 87, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, F.; Slowikowski, K.; Wei, K.; Marshall, J.L.; Rao, D.A.; Chang, S.K.; Nguyen, H.N.; Noss, E.H.; Turner, J.D.; Earp, B.E.; et al. Functionally Distinct Disease-Associated Fibroblast Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, W.; Donlin, L.T.; Butler, A.; Rozo, C.; Bracken, B.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Goodman, S.M.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Bykerk, V.P.; Orange, D.E.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Tissue Using Low-Cost Microfluidic Instrumentation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.K.; Gu, Z.; Brenner, M.B. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Inflammatory Arthritis Pathology: The Emerging Role of Cadherin-11. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.M.; Kiener, H.P.; Agarwal, S.K.; Noss, E.H.; Watts, G.F.M.; Chisaka, O.; Takeichi, M.; Brenner, M.B. Cadherin-11 in Synovial Lining Formation and Pathology in Arthritis. Science 2007, 315, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebid, R.; Lichtnekert, J.; Anders, H.-J. Hyaluronan Is Not a Ligand but a Regulator of Toll-like Receptor Signaling in Mesangial Cells: Role of Extracellular Matrix in Innate Immunity. ISRN Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 714081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, D.H.; Rhodes, C.; Onuma, K.; Zhao, X.; Sharpe, O.; Gazitt, T.; Shiao, R.; Fert-Bober, J.; Cheng, D.; Lahey, L.J.; et al. Local Joint Inflammation and Histone Citrullination in a Murine Model of the Transition from Preclinical Autoimmunity to Inflammatory Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Pernaute, O.; Filkova, M.; Gabucio, A.; Klein, M.; Maciejewska-Rodrigues, H.; Ospelt, C.; Brentano, F.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, R.E.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; et al. Citrullination Enhances the Pro-Inflammatory Response to Fibrin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatterer, E.; Shang, L.; Simonet, P.; Herren, S.; Daubeuf, B.; Teixeira, S.; Reilly, J.; Elson, G.; Nelson, R.; Gabay, C.; et al. A Specific Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody Profile Identifies a Group of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with a Toll-like Receptor 4-Mediated Disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, M.; Baron, B. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases through Failure of the Self-Recognition Mechanism. Int. J. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 8391230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, N.D.; Vila, O.M.; Volin, M.V.; Volkov, S.; Pope, R.M.; Swedler, W.; Mandelin, A.M.; Shahrara, S. TLR5, a Novel and Unidentified Inflammatory Mediator in Rheumatoid Arthritis That Correlates with Disease Activity Score and Joint TNF-α Levels. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Adebayo, A.; Pope, R.M. Increased Macrophage Activation Mediated through Toll-like Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-W.; Cho, M.-L.; Lee, S.-H.; Oh, H.-J.; Kang, C.-M.; Ju, J.H.; Min, S.-Y.; Cho, Y.-G.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y. Human Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts Promote Osteoclastogenic Activity by Activating RANKL via TLR-2 and TLR-4 Activation. Immunol. Lett. 2007, 110, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brentano, F.; Schorr, O.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Kyburz, D. RNA Released from Necrotic Synovial Fluid Cells Activates Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts via Toll-like Receptor 3. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Hosojima, S.; Hara, H.; Kushiyama, H.; Mahib, M.R.; Kinoshita, T.; Suda, T. Gasdermin D Mediates the Maturation and Release of IL-1α Downstream of Inflammasomes. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Bi, L. Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Autoimmune Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalyte, R.; Denkovskij, J.; Bernotiene, E.; Stropuviene, S.; Mikulenaite, S.O.; Kvederas, G.; Porvaneckas, N.; Tutkus, V.; Venalis, A.; Butrimiene, I. The Expression of Inflammasomes NLRP1 and NLRP3, Toll-Like Receptors, and Vitamin D Receptor in Synovial Fibroblasts From Patients With Different Types of Knee Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazár, B.; Ea, H.-K.; Narayan, S.; Kolly, L.; Bagnoud, N.; Chobaz, V.; Roger, T.; Lioté, F.; So, A.; Busso, N. Basic Calcium Phosphate Crystals Induce Monocyte/Macrophage IL-1β Secretion through the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Vitro. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.-S. Role of Inflammasomes in Inflammatory Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Physiol. Soc. Korean Soc. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Frayssinet, P.; Pelker, R.; Cwirka, D.; Hu, B.; Vignery, A.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Flavell, R.A. NLRP3 Inflammasome Plays a Critical Role in the Pathogenesis of Hydroxyapatite-Associated Arthropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14867–14872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, C.; Xin, P. Recent Advances on Signaling Pathways and Their Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 230, 108793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Malemud, C.J. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: A Regulator of Cell Growth, Inflammation, Chondrocyte and Bone Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanov, N.; Kauffman, R.S.; Spencer-Green, G.T. Efficacy, Pharmacodynamics, and Safety of VX-702, a Novel P38 MAPK Inhibitor, in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results of Two Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, M.C.; Cohen, S.B.; Wofsy, D.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Firestein, G.S.; Brahn, E.; Strand, V.; Baker, D.G.; Tong, S.E. A 24-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group Study of the Efficacy of Oral SCIO-469, a P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Hammaker, D.; Boyle, D.L.; Corr, M.; Flavell, R.; Davis, R.; Schett, G.; Firestein, G.S. Role of MAPK Kinase 6 in Arthritis: Distinct Mechanism of Action in Inflammation and Cytokine Expression. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Chang, L.; Bennett, B.; Karin, M.; Yang, L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Is Required for Metalloproteinase Expression and Joint Destruction in Inflammatory Arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guma, M.; Ronacher, L.M.; Firestein, G.S.; Karin, M.; Corr, M. JNK-1 Deficiency Limits Macrophage-Mediated Antigen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal Communication: When I’m Calling You, Will You Answer Too? Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, P.; Jeanclaude-Etter, I.; Ardissone, V.; Arkinstall, S.; Cambet, Y.; Camps, M.; Chabert, C.; Church, D.; Cirillo, R.; Gretener, D.; et al. Design and Synthesis of the First Generation of Novel Potent, Selective, and in Vivo Active (Benzothiazol-2-Yl)Acetonitrile Inhibitors of the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4596–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C. The Non-Canonical NF-κB Pathway in Immunity and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, P. The Advances of Methotrexate Resistance in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.F.; Ahmed Mohamed, A.A.; Emery, P. Glucocorticoids and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 33–46, vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, S.; Tian, J.; Li, F. Iguratimod as a New Drug for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Landscape. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Liu, F.; Ma, F.; Xu, L.; Pang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, L. Montelukast Inhibits Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 61, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, N.; Acharya, P.; Zarei, M.; Talahalli, R.R. Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor Antagonism: A Promising Pharmacological Strategy for Lowering the Severity of Arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imas, J.J.; Ruiz Zamarreño, C.; Zubiate, P.; Sanchez-Martín, L.; Campión, J.; Matías, I.R. Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Biomarkers: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Moots, R.J. Biomarkers for Treatment Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Where Are They? Rheumatol. Immunol. Res. 2020, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, C. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Fang, L.; Liu, X.; Nie, T.; Li, R.; Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Ji, Y. miR-22 Inhibits Synovial Fibroblasts Proliferation and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in RASF via Targeting SIRT1. Gene 2020, 724, 144144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xing, S.; Liu, M.; Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Guo, X.; et al. MiR-26a-5p Enhances Cells Proliferation, Invasion, and Apoptosis Resistance of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, L.; Yuan, X.; Xu, N.; Zhao, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, N. miR-483-3p Promotes Cell Proliferation and Suppresses Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Targeting IGF-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L. MicroRNA-34a-3p Inhibits Proliferation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, N.; Wang, X.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Y. MiR-129-5p Regulates Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis via IGF-1R/Src/ERK/Egr-1 Pathway in RA-Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczyk, J.; Ospelt, C.; Karouzakis, E.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Kolling, C.; Gay, R.; Buckley, C.D.; Tak, P.P.; Gay, S.; et al. Altered Expression of microRNA-203 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Its Role in Fibroblast Activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, T.; Fu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, N. miR-410-3p Suppresses Cytokine Release from Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Regulating NF-κB Signaling in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 2019, 42, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Hou, C. miR-138 Activates NF-κB Signaling and PGRN to Promote Rheumatoid Arthritis via Regulating HDAC4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, S.; Huang, B.; Lou, S.; Zuo, J. Down-Regulation of microRNA-98 Promoted Apoptosis of TNF-α Stimulated Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes via up-Regulating IL-10. Gene 2019, 706, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Luo, X.; Peng, L.; Zhao, Z.; He, C.; He, Y. Exosomal miRNA-486-5p Derived from Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Induces Osteoblast Differentiation through the Tob1/BMP/Smad Pathway. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 3430–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Tu, J.; Liu, C.; Pan, A.; Xia, X.; Chen, X. Analysis of lncRNA Expression Profiles by Sequencing Reveals That Lnc-AL928768.3 and Lnc-AC091493.1 Are Novel Biomarkers for Disease Risk and Activity of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-R.; Yang, L.; Xu, Q.-Q.; Lu, X.-Y.; Ma, T.-T.; Huang, C.; Li, J. Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Targeting NLRC5. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14270–14284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ding, C.; Dai, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Long Noncoding RNA FER1L4 Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis via Targeting NLRC5. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Meng, F.; Xia, Z.; Wu, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D. LncRNA MEG3 Inhibits Rheumatoid Arthritis through miR-141 and Inactivation of AKT/mTOR Signalling Pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7116–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Guo, X.H.; Mo, B.Y.; Wang, M.L.; Luo, X.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, F.; Olsen, N.; Pan, Y.F.; Zheng, S.G. LncRNA PICSAR Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Sponging miRNA-4701-5p in Rheumatoid Arthritis. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, S.-D.; Zhan, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Y.-W. LncRNA GAS5 Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis through Regulating miR-222-3p/Sirt1 Signalling Axis. Autoimmunity 2021, 54, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zeng, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhu, W.; Jia, N.; Lin, L. Long Noncoding RNA ZFAS1 Silencing Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis via Blocking miR-296-5p-Mediated down-Regulation of MMP-15. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Song, G.; Ni, R.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; He, F.; Huang, G. LncRNA-H19 Silencing Suppresses Synoviocytes Proliferation and Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis Progression by Modulating miR-124a. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2021, 60, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, S. Roles of CircRNAs in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhu, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Fan, M.; Cai, Y.; Yang, M. Hsa_circ_0088036 Promotes the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Sponging miR-140-3p and Upregulating SIRT 1 Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 125, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Tan, W.; Fang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiu, G.; Liu, D. circFADS2 Protects LPS-Treated Chondrocytes from Apoptosis Acting as an Interceptor of miR-498/mTOR Cross-Talking. Aging 2019, 11, 3348–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, M.; Gu, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Xu, D. CircRNA_09505 Aggravates Inflammation and Joint Damage in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mice via miR-6089/AKT1/NF-κB Axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, M.; El-Daly, S.M.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNA Therapeutics - Challenges and Potential Solutions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, M.; Mallén, A.; Suñé-Pou, M.; Aran, J.M.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Navarro, E. ncRNAs in Therapeutics: Challenges and Limitations in Nucleic Acid-Based Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, R.; Grillone, K.; Citriniti, E.L.; Gualtieri, G.; Artese, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; Alcaro, S. Targeting Non-Coding RNAs: Perspectives and Challenges of in-Silico Approaches. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, M.J.; Nissim, A.; Knight, A.R.; Whiteman, M.; Haigh, R.; Winyard, P.G. Oxidative Stress in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippin, L.I.; Vercelino, R.; Marroni, N.P.; Xavier, R.M. Redox Signalling and the Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñonez-Flores, C.M.; González-Chávez, S.A.; Del Río Nájera, D.; Pacheco-Tena, C. Oxidative Stress Relevance in the Pathogenesis of the Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6097417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatani, Y.; Ono, K.; Suzuki, H.; Inaba, M.; Sawada, M.; Matsuda, N. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase during the Late Phase of Sepsis Is Associated with Hypothermia and Immune Cell Migration. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2018, 98, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Hong, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, J.; Zheng, F. Calreticulin Induced Endothelial ICAM-1 up-Regulation Associated with Tristetraprolin Expression Alteration through PI3K/Akt/eNOS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 107, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Bishayi, B. Effect of iNOS Inhibitor LNMMA along with Antibiotics Chloramphenicol or Ofloxacin in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages Regulates S.Aureus Infection as Well as Inflammation: An in Vitro Study. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, M.; Pétavy, F.; Chiesa, F.; Perry, H.; Lukey, P.T.; Binks, M.; Donatien, P.D.; Freidin, A.J.; Eckersley, R.J.; McClinton, C.; et al. Ultrasonographic Measures of Synovitis in an Early Phase Clinical Trial: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo and Comparator Controlled Phase IIa Trial of GW274150 (a Selective Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Attia, A.M.M.; Ibrahim, F.A.A.; Abd El-Latif, N.A.; Aziz, S.W.; Elwan, A.M.; Abdel Aziz, A.A.A.; Elgendy, A.; Elgengehy, F.T. Therapeutic Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Laser Acupuncture on Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lasers Surg. Med. 2016, 48, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, S.; Moin, S.; Khan, A.Q.; Zafar, A.; Fatima, N. Increased Reactive Oxygen Species Formation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PloS ONE 2016, 11, e0152925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, A.-R.; Nasir, B.; Haq, I.U.; Kim, S.J. Oxidative Stress, Consequences and ROS Mediated Cellular Signaling in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 281, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helli, B.; Mowla, K.; Mohammadshahi, M.; Jalali, M.T. Effect of Sesamin Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Alipour, B.; Sharif, S.-K.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, L.; Alipour-Ajiry, S. Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Oxidative Stress Indices in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Aoki, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Sonobe, M.; Terajima, F.; Takahashi, H.; Saito, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Yamada, M.; Nakagawa, K. Identification of Clinical Parameters Associated with Serum Oxidative Stress in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 24, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, L.J.S.; Nunes-Souza, V.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Rabelo, L.A. Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What the Future Might Hold Regarding Novel Biomarkers and Add-On Therapies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7536805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzad, H.; Aghdashi, M.A.; Asghari Jafarabadi, M.; Alipour, B. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Med. Res. 2015, 46, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. We Need to Talk about the Warburg Effect. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Armada, M.J.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.A.; Blanco, F.J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Tang, J.; Lu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, E.; Gao, B.; Liu, T.; Shao, P. Glycolysis Rate-Limiting Enzymes: Novel Potential Regulators of Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 779787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, J.; Molema, G.; Kallenberg, C.G.M. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 as Regulator of Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekanecz, Z.; Koch, A.E. Targeting Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2008, 4, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Su, A.; Gan, D.; Ke, L.; Liu, G.; et al. Notch-1 and Notch-3 Mediate Hypoxia-Induced Activation of Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).