Hemi-Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Using Transphyseal Screws at Lateral Proximal Tibias After Epiphyseal Fusion of Distal Phalanges in the Hand Results in Undercorrection of Genu Varum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
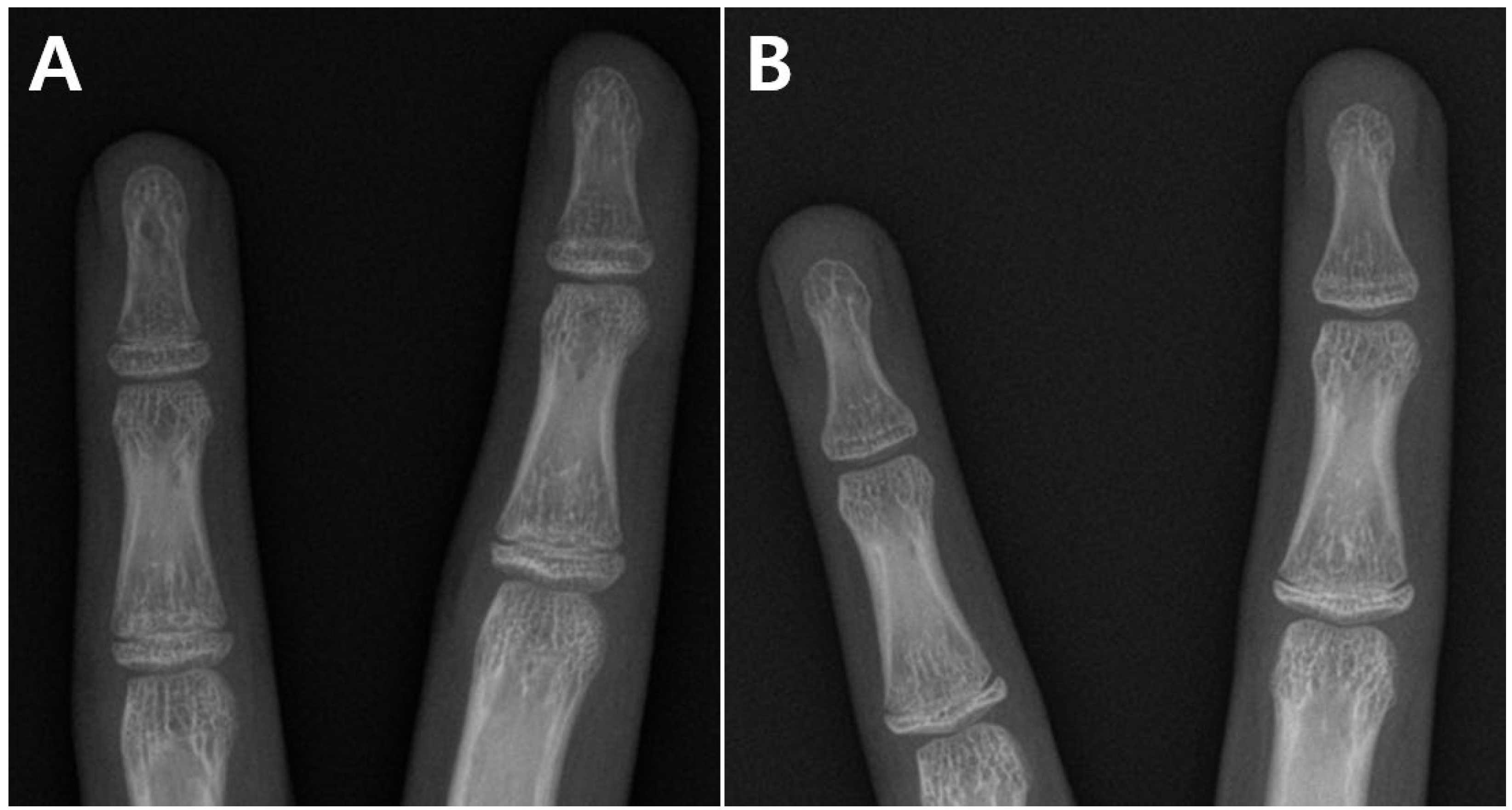
2.1. Selection of the Study Subjects
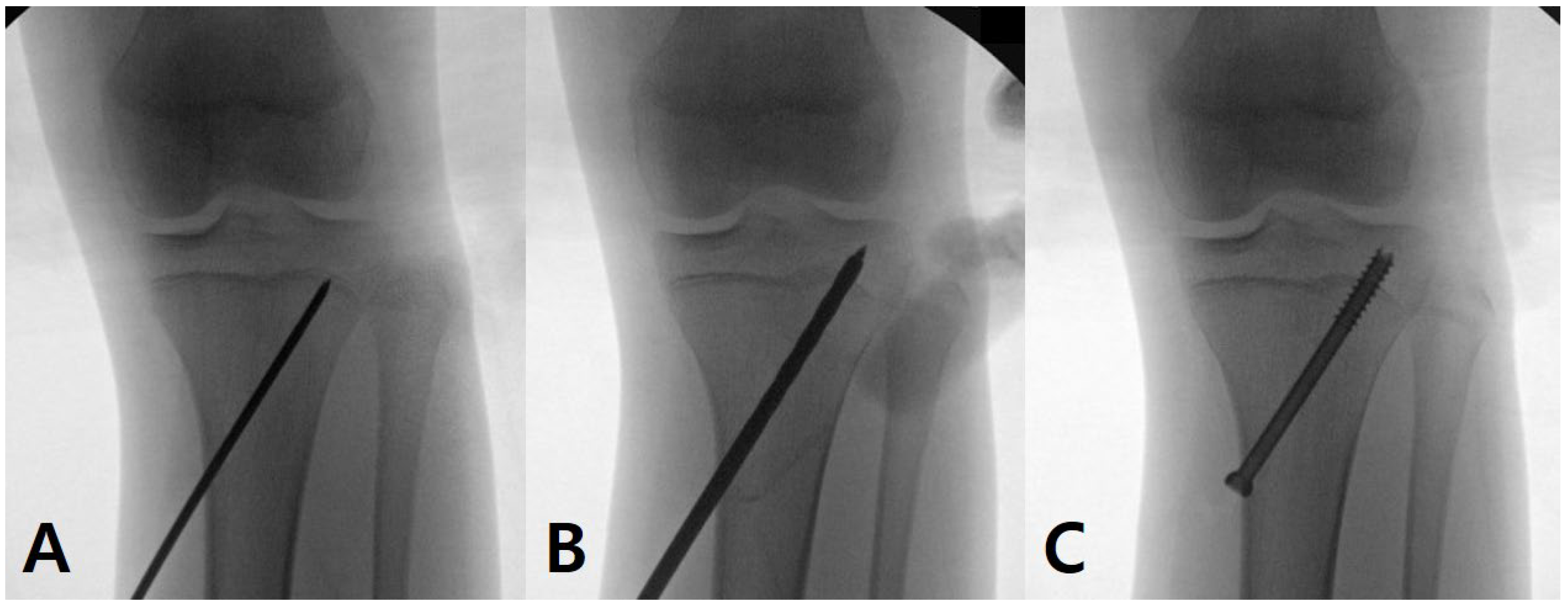
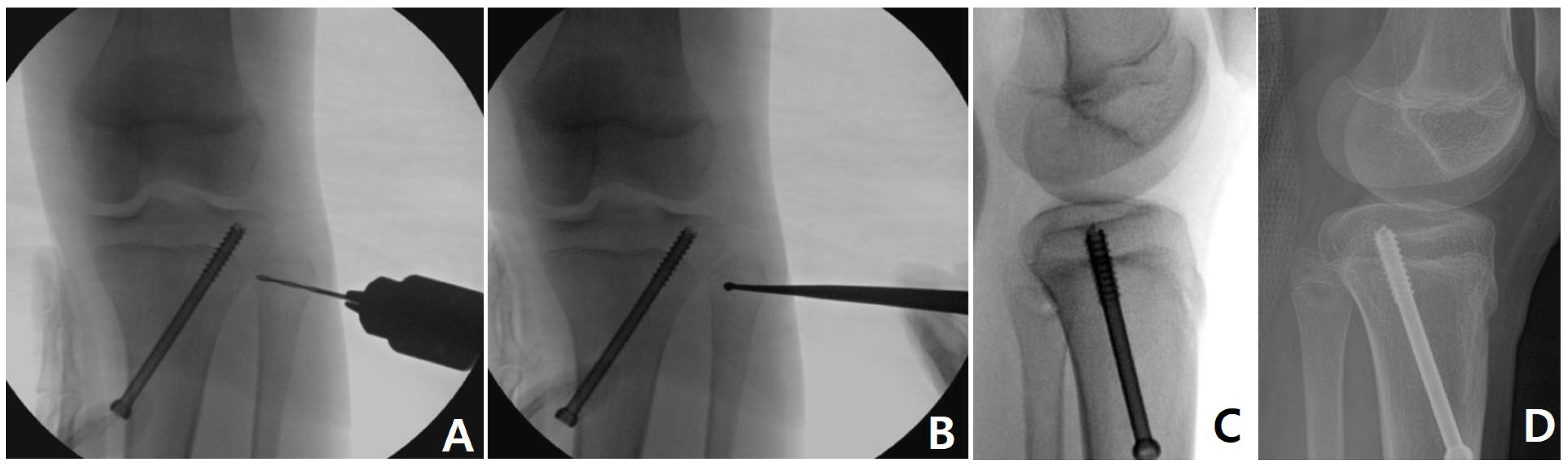
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Radiographic Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparisons Between the Open and Fusion Groups
3.2. Details of the Fusion Group
3.3. Linear Regression Analyses to Describe the f-CA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shohat, N.; Machluf, Y.; Farkash, R.; Finestone, A.S.; Chaiter, Y. Clinical Knee Alignment among Adolescents and Association with Body Mass Index: A Large Prevalence Study. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2018, 20, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Cock, L.; Dauwe, J.; Holzer, L.A.; Bellemans, J. Knee alignment in adolescents is correlated with participation in weight-bearing sports. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isın, A.; Melekoğlu, T. Genu varum and football participation: Does football participation affect lower extremity alignment in adolescents? Knee 2020, 27, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memmel, C.; Sporrer, D.; Szymski, D.; Weber, J.; Hanke, A.; Denzinger, M.; Kerschbaum, M.; Alt, V.; Krutsch, W.; Koch, M. High Prevalence of Varus Knee Malalignment in Adolescent Football Players-Clinical Lower Leg Axis Measurements of Male Junior Football Players Aged 7 to 18 Years. Children 2024, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanamas, S.; Hanna, F.S.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Wluka, A.E.; Berry, P.; Urquhart, D.M. Does knee malalignment increase the risk of development and progression of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.J.; Lee, S.; Park, M.S.; Sung, K.H. Rebound phenomenon and its risk factors after hemiepiphysiodesis using tension band plate in children with coronal angular deformity. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-Z.; Liang, Z.-P.; Li, H.; Ding, J.; Wu, Z.-K.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Li, H. Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis using an eight-plate implant for coronal angular deformity around the knee in children aged less than 10 years: Efficacy, complications, occurrence of rebound and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.R.; Shim, J.S.; Shin, T.S.; Jang, M.C. Factors Affecting Rebound Phenomenon After Temporary Hemiepiphysiodesis and Implant Removal for Idiopathic Genu Valgum in Adolescent Patients. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2022, 42, e336–e342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, K.J.; Cho, C.H.; Ye, H.U.; Yon, C.J.; Choi, H.U.; Kim, Y.H.; Song, K.S. Affecting Factors and Correction Ratio in Genu Valgum or Varum Treated with Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Using Transphyseal Screws. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, H.W.; Park, H.; Lee, S.K.; Park, K.B. Natural behaviours after guided growth for idiopathic genu valgum correction: Comparison between percutaneous transphyseal screw and tension-band plate. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Ko, K.R.; Lim, K.S.; Na, S. Factors Affecting Postoperative Courses After Removal of Transphyseal Screws Inserted for Correction of Genu Valgum. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2024, 44, e411–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Cho, T.J.; Park, M.S.; Bae, J.Y.; Yoo, W.J.; Chung, C.Y.; Choi, I.H. Angular deformity correction by asymmetrical physeal suppression in growing children: Stapling versus percutaneous transphyseal screw. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2010, 30, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilharreborde, B.; Gaumetou, E.; Souchet, P.; Fitoussi, F.; Presedo, A.; Penneçot, G.F.; Mazda, K. Efficacy and late complications of percutaneous epiphysiodesis with transphyseal screws. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2012, 94, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métaizeau, J.P.; Wong-Chung, J.; Bertrand, H.; Pasquier, P. Percutaneous epiphysiodesis using transphyseal screws (PETS). J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1998, 18, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.H.; Choi, E.S.; Park, M.S.; Yoo, W.J.; Chung, C.Y.; Choi, I.H.; Cho, T.J. Percutaneous epiphysiodesis using transphyseal screws in the management of leg length discrepancy: Optimal operation timing and techniques to avoid complications. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2015, 35, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, J.; Worrall, H.; Althoff, C.; Clark, C.; Jo, C.H.; Birch, J.G.; Wilson, P.L.; Ellis, H.B. Faster Rate of Correction with Distal Femoral Transphyseal Screws Versus Plates in Hemiepiphysiodesis for Coronal-Plane Knee Deformity: Age- and Sex-Matched Cohorts of Skeletally Immature Patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2023, 105, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, M.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, D.H. Hemiepiphysiodesis for Idiopathic Genu Valgum: Percutaneous Transphyseal Screw Versus Tension-band Plate. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2018, 38, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, W.W.; Pyle, S.I. Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1959; p. 0804703981. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lyu, X.; Yang, Z.; Cheung, J.P.Y. Relationship between hand and wrist bone age assessment methods. Med. Baltim. 2020, 99, e22392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, C.Y.; Choi, I.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.M. Statistical consideration for bilateral cases in orthopaedic research. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timperlake, R.W.; Bowen, J.R.; Guille, J.T.; Choi, I.H. Prospective evaluation of fifty-three consecutive percutaneous epiphysiodeses of the distal femur and proximal tibia and fibula. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1991, 11, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, J.G.; Makarov, M.A.; Jackson, T.J.; Jo, C.H. Comparison of Anderson-Green Growth-Remaining Graphs and White-Menelaus Predictions of Growth Remaining in the Distal Femoral and Proximal Tibial Physes. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2019, 101, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paley, D.; Tetsworth, K. Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 280, 48–64. [Google Scholar]
- Menelaus, M.B. Correction of leg length discrepancy by epiphysial arrest. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1966, 48, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullaji, A.; Shah, R.; Bhoskar, R.; Singh, A.; Haidermota, M.; Thakur, H. Seven phenotypes of varus osteoarthritic knees can be identified in the coronal plane. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 2793–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullaji, A.; Bhoskar, R.; Singh, A.; Haidermota, M. Valgus arthritic knees can be classified into nine phenotypes. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmann, M.T.; Moser, L.B.; Amsler, F.; Behrend, H.; Leclercq, V.; Hess, S. Phenotyping the knee in young non-osteoarthritic knees shows a wide distribution of femoral and tibial coronal alignment. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, A.B.; Steen, H.; Pripp, A.; Hvid, I.; Horn, J. Comparison of Different Bone Age Methods and Chronological Age in Prediction of Remaining Growth Around the Knee. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2023, 43, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Observer 1 * | Observer 2 * | Interobserver † | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HKA alignment (°) | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| MPTA (°) | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.81 |
| Bone age (years) | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.83 |
| Screw angle (°) | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.81 |
| Moment arm of the screw (%) | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.85 |
| Variables | Open Group (n = 19) | Fusion Group (n = 10) | p | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male–female) | 6 (31.6%):13 (68.4%) | 6 (60.0%):4 (40.0%) | 0.236 * | N/A |
| Bone age (years) a | 12.5 ± 0.9 | 14.1 ± 0.8 | 0.001 † | 1.879 |
| Remaining growth (years) a | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | <0.001 † | 2.828 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) a | 17.5 ± 1.7 | 18.9 ± 2.7 | 0.161 † | 0.621 |
| Side (right–left) | 10 (52.6%):9 (47.4%) | 4 (40.0%):6 (60.0%) | 0.700 * | N/A |
| HKA alignment (°) a | Varus 6.3 ± 1.2 | Varus 6.9 ± 1.4 | 0.232 † | 0.460 |
| MPTA (°) a | 83.3 ± 1.3 | 82.4 ± 1.7 | 0.301 † | 0.595 |
| Screw angle (°) a | 79.7 ± 5.4 | 81.0 ± 5.0 | 0.581 † | 0.250 |
| Moment arm of the screw (%) a | 76.9 ± 2.8 | 77.0 ± 2.9 | 0.945 † | 0.035 |
| Final correction angle (°) | 6.7 ± 1.3 | 4.0 ± 1.9 | 0.001 † | 1.659 |
| Rebound angle (°) | 0.3 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 0.909 † | 0.000 |
| Acceptable correction (%) | 19/19 (100%) | 2/10 (20.0%) | <0.001 * | N/A |
| No. | Sex | Remaining Growth a,b | Open c | Partial Fusion c | Complete Fusion c | HKA Alignment b | f-CA d | Acceptable Correction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 1+6 year | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5.5° | 4.3° (78.2%) | No |
| 2 | Male | 1+6 year | 2 | 3 | 0 | 6.3° | 3.9° (61.9%) | No |
| 3 | Male | 1+6 year | 2 | 3 | 0 | 9.3° | 4.9° (52.7%) | No |
| 4 | Male | 1+5 year | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5.6° | 3.3° (58.9%) | No |
| 5 | Male | 1+4 year | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5.4° | 5.3° (98.1%) | Yes |
| 6 | Male | 11 months | 0 | 2 | 3 | 7.6° | 0.7° (9.2%) | No |
| 7 | Female | 1 year | 2 | 3 | 0 | 9.0° | 6.3° (70.0%) | No |
| 8 | Female | 11 months | 0 | 5 | 0 | 6.2° | 6.4° (100%) | Yes |
| 9 | Female | 10 months | 0 | 5 | 0 | 6.6° | 3.4° (51.5%) | No |
| 10 | Female | 3 months | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7.6° | 1.1° (14.5%) | No |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted Coefficient (95% CI) | p | Adjusted Coefficient (95% CI) | p | |
| HKA alignment (°) a | 0.44 (0.06, 0.82) | 0.033 | 0.53 (0.22, 0.85) | 0.003 |
| Screw angle (°) a | 0 (−0.1, 0.11) | 0.958 | 0 (−0.09, 0.08) | 0.97 |
| Moment arm of the screw (%) a | −0.1 (−0.29, 0.08) | 0.29 | −0.11 (−0.27, 0.04) | 0.169 |
| Sex b | 1.16 (0.16, 2.15) | 0.033 | N/A | |
| Remaining growth (years) a | 2.67 (1.79, 3.54) | <0.001 | N/A | |
| Partial fusion a,c | N/A | −2.15 (−3.03, −1.27) | <0.001 | |
| Complete fusion a,c,d | N/A | −4.55 (−6.33, −2.76) | <0.001 | |
| R2 = 0.670 | R2 = 0.777 | |||
| AIC value = 103.7 | AIC value = 92.2 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, K.R.; Shim, J.W.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S. Hemi-Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Using Transphyseal Screws at Lateral Proximal Tibias After Epiphyseal Fusion of Distal Phalanges in the Hand Results in Undercorrection of Genu Varum. Medicina 2024, 60, 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60111818
Ko KR, Shim JW, Shim JS, Kim DS, Lee S. Hemi-Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Using Transphyseal Screws at Lateral Proximal Tibias After Epiphyseal Fusion of Distal Phalanges in the Hand Results in Undercorrection of Genu Varum. Medicina. 2024; 60(11):1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60111818
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Kyung Rae, Jae Woo Shim, Jong Sup Shim, Dong Suk Kim, and Soonchul Lee. 2024. "Hemi-Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Using Transphyseal Screws at Lateral Proximal Tibias After Epiphyseal Fusion of Distal Phalanges in the Hand Results in Undercorrection of Genu Varum" Medicina 60, no. 11: 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60111818
APA StyleKo, K. R., Shim, J. W., Shim, J. S., Kim, D. S., & Lee, S. (2024). Hemi-Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Using Transphyseal Screws at Lateral Proximal Tibias After Epiphyseal Fusion of Distal Phalanges in the Hand Results in Undercorrection of Genu Varum. Medicina, 60(11), 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60111818







