Lower Circulating Cytotoxic T-Cell Frequency and Higher Intragraft Granzyme-B Expression Are Associated with Inflammatory Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Renal Allograft Recipients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Differential Diagnosis of Allograft Dysfunction
2.3. Definition of Differential Diagnosis
2.4. Ethical Clearance
2.5. Sample Collection
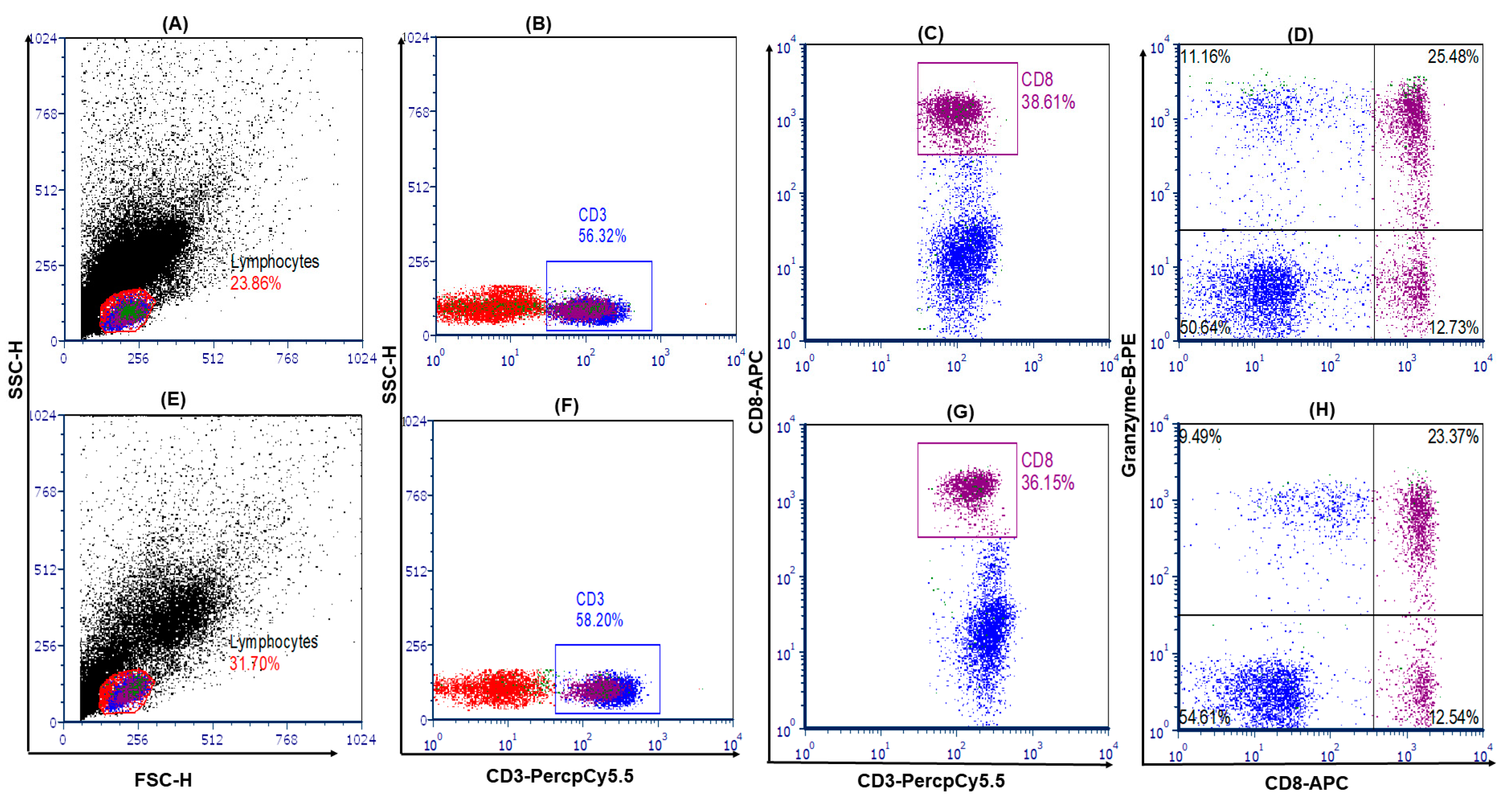
2.6. Cytotoxic T-Cell Staining and Frequency Analysis
2.6.1. Cell Stimulation
2.6.2. Cytotoxic T-Cell Staining
2.6.3. Cell Analysis and Gating Strategy
2.7. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Intact Granzyme-B Level Measurement
2.7.1. Serum Granzyme-B Level Analysis
2.7.2. Intragraft Granzyme-B Gene mRNA Transcript Expression Analysis
2.7.3. Granzyme-B Gene mRNA Transcript Expression Analysis
2.8. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Profiles of Patients
3.2. Circulating Cytotoxic T-Cell Frequency Was Lower in i-IFTA Patients
3.3. Serum Soluble and Cell Intact Granzyme-B Level
3.4. Intragraft Granzyme-B Gene mRNA Transcript Expression Analysis
3.5. Cytotoxic T-Cell Profiles Correlation with Kidney Function Markers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Loupy, A.; Haas, M.; Solez, K.; Racusen, L.; Glotz, D.; Seron, D.; Nankivell, B.J.; Colvin, R.B.; Afrouzian, M.; Akalin, E.; et al. The Banff 2015 Kidney Meeting Report: Current Challenges in Rejection Classification and Prospects for Adopting Molecular Pathology. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Yadav, B.; Agrawal, V.; Jain, M.; Agarwal, V. Role of pathogenic T-helper cells-17 in chronic antibody-mediated rejection in renal allograft recipients. Indian J. Transplant. 2022, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannon, R.B.; Matas, A.J.; Grande, J.; Leduc, R.; Connett, J.; Kasiske, B.; Cecka, J.M.; Gaston, R.S.; Cosio, F.; Gourishankar, S.; et al. Inflammation in areas of tubular atrophy in kidney allograft biopsies: A potent predictor of allograft failure. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Borrows, R.J.; Fung, C.L.S.; O’Connell, P.J.; Chapman, J.R.; Allen, R.D.M. Delta Analysis of Posttransplantation Tubulointerstitial Damage. Transplantation 2004, 78, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengel, M.; Reeve, J.; Bunnag, S.; Einecke, G.; Jhangri, G.S.; Sis, B.; Famulski, K.; Guembes-Hidalgo, L.; Halloran, P.F. Scoring Total Inflammation Is Superior to the Current Banff Inflammation Score in Predicting Outcome and the Degree of Molecular Disturbance in Renal Allografts. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Prasad, N.; Agrawal, V.; Jain, M.; Agarwal, V.; Jaiswal, A.; Bhadauria, D.; Sharma, R.K.; Gupta, A. T-bet-positive mononuclear cell infiltration is associated with transplant glomerulopathy and interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in renal allograft recipients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 13, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashton-Chess, J.; Dugast, E.; Colvin, R.B.; Giral, M.; Foucher, Y.; Moreau, A.; Renaudin, K.; Braud, C.; Devys, A.; Brouard, S.; et al. Regulatory, Effector, and Cytotoxic T Cell Profiles in Long-Term Kidney Transplant Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, H.; Prasad, N.; Jaiswal, A.; Yadav, B.; Kumar, S.; Bhadauria, D.; Kaul, A.; Gupta, A.; Srivartava, A.; Sharma, R.K. Outcomes of living donor renal transplant recipients with and without basiliximab induction: A long-term follow-up study. Indian J. Transplant. 2014, 8, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Tyznik, A.J.; Bevan, M.J. Interleukin-2 signals during priming are required for secondary expansion of CD8+ memory T cells. Nature 2006, 441, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Prasad, N.; Agarwal, V.; Agrawal, V.; Jain, M. Immunophenotyping of Granzyme-B Expressing Lymphocyte Subset in Renal Allograft Recipients with Chronic Allograft Dysfunction. Int. J. Org. Transplant. Med. 2023, 13, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Afonina, I.S.; Cullen, S.P.; Martin, S.J. Cytotoxic and non-cytotoxic roles of the CTL/NK protease granzyme B. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 235, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boivin, W.A.; Shackleford, M.; Vanden Hoek, A.; Zhao, H.; Hackett, T.L.; Knight, D.A.; Granville, D.J. Granzyme B cleaves decorin, biglycan and soluble betaglycan, releasing active transforming growth factor-β1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Bologa, R.M.; Li, B.; Xu, G.P.; Lagman, M.; Hiscock, W.; Mouradian, J.; Wang, J.; Serur, D.; Rao, V.K.; et al. Molecular executors of cell death--differential intrarenal expression of Fas ligand, Fas, granzyme B, and perforin during acute and/or chronic rejection of human renal allografts. Transplantation 1996, 62, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strehlau, J.; Pavlakis, M.; Lipman, M.; Shapiro, M.; Vasconcellos, L.; Harmon, W.; Strom, T.B. Quantitative detection of immune activation transcripts as a diagnostic tool in kidney transplantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B.; Prasad, N.; Agarwal, V.; Agarwal, V.; Jain, M. Hidden Granzyme B-Mediated Injury in Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2020, 18, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hartono, C.; Ding, R.; Sharma, V.K.; Ramaswamy, R.; Qian, B.; Serur, D.; Mouradian, J.; Schwartz, J.E.; Suthanthiran, M. Noninvasive diagnosis of renal-allograft rejection by measurement of messenger RNA for perforin and granzyme B in urine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Iking-Konert, C.; Denefleh, B.; Stegmaier, S.; Hug, F.; Hänsch, G.M. Granzyme B and perforin: Constitutive expression in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Blood 2004, 103, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-J.; Kim, H.; Suk, K.; Lee, W.-H. Macrophages express granzyme B in the lesion areas of atherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Lett. 2007, 111, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagn, M.; Jahrsdörfer, B. Why do human B cells secrete granzyme B? Insights into a novel B-cell differentiation pathway. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.I.; Sarwar, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Hunger, E.; Sattler, A.; Aigner, F.; Regele, H.; Sauter, M.; Klingel, K.; Schneeberger, S.; et al. Natural Killer Cells Promote Kidney Graft Rejection Independently of Cyclosporine A Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boivin, W.A.; Cooper, D.M.; Hiebert, P.R.; Granville, D.J. Intracellular versus extracellular granzyme B in immunity and disease: Challenging the dogma. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 1195–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, F.; Sharma, M.; Merkulova, Y.; Raithatha, S.A.; Parkinson, L.G.; Zhao, H.; Westendorf, K.; Bohunek, L.; Bozin, T.; et al. Granzyme B Deficiency Protects against Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.M.-K.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Mak, T.S.-K.; Tang, P.C.-T.; Huang, X.-R.; Lan, H.-Y. Transforming growth factor-β signalling in renal fibrosis: From Smads to non-coding RNAs. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.-H.; Li, Y.-J.; Wu, H.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Hsu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-W.; Chu, P.-H.; Tian, Y.-C. Interleukin-17A induces renal fibrosis through the ERK and Smad signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AkimoAkimova, T.; Kamath, B.M.; Goebel, J.W.; Meyers, K.E.C.; Rand, E.B.; Hawkins, A.; Levine, M.H.; Bucuvalas, J.C.; Hancock, W.W. Differing Effects of Rapamycin or Calcineurin Inhibitor on T-Regulatory Cells in Pediatric Liver and Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Tang, P.M.K.; Li, J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonina, I.S.; Tynan, G.A.; Logue, S.E.; Cullen, S.P.; Bots, M.; Lüthi, A.U.; Reeves, E.P.; McElvaney, N.G.; Medema, J.P.; Lavelle, E.C.; et al. Granzyme B-Dependent Proteolysis Acts as a Switch to Enhance the Proinflammatory Activity of IL-1α. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, L.A. The IL-1 cytokine family and its role in inflammation and fibrosis in the lung. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnemann, G.; Shapiro, L.; Engler-Blum, G.; Müller, G.A.; Koch, K.M.; Dinarello, C.A. Cytokines in human renal interstitial fibrosis. I. Interleukin-1 is a paracrine growth factor for cultured fibrosis-derived kidney fibroblasts. Kidney Int. 1995, 47, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzynski, L.C.; Humphry, M.; Bennett, M.R.; Clarke, M.C.H. Interleukin-1α Activity in Necrotic Endothelial Cells Is Controlled by Caspase-1 Cleavage of Interleukin-1 Receptor-2: Implications for Allograft Rejection. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25188–25196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, J.; Subrt, P.; Paré, M.; Hartell, D.; Sénécal, L.; Blydt-Hansen, T.; Cardinal, H. Practice Patterns in the Treatment and Monitoring of Acute T Cell–Mediated Kidney Graft Rejection in Canada. Can. J. Kidney Heal. Dis. 2018, 5, 2054358117753616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Broxmeyer, H.E. Chemokines: Signal lamps for trafficking of T and B cells for development and effector function. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, L.J.C.; Kirby, J.A.; Cunningham, A.C. Role of the mucosal integrin alpha(E)(CD103) beta (7) in tissue-restricted cytotoxicity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 149, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowshani, A.T.; Florquin, S.; Bemelman, F.; Kummer, J.A.; Hack, C.E.; Berge, I.J.T. Hyperexpression of the granzyme B inhibitor PI-9 in human renal allografts: A potential mechanism for stable renal function in patients with subclinical rejection. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heutinck, K.M.; Kassies, J.; Florquin, S.; Berge, I.J.T.; Hamann, J.; Rowshani, A.T. SerpinB9 expression in human renal tubular epithelial cells is induced by triggering of the viral dsRNA sensors TLR3, MDA5 and RIG-I. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.; Khan, K.; Pavlosky, A.; Yin, Z.; Huang, X.; Haig, A.; Liu, W.; Singh, B.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Jevnikar, A.M. Serine Protease Inhibitor-6 Inhibits Granzyme B–Mediated Injury of Renal Tubular Cells and Promotes Renal Allograft Survival. Transplantation 2014, 98, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, B.; Ding, H.; Ren, H.; Shi, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Lai, C.; Yu, G.; Xu, Y.; Su, Z. Diagnostic Performance of Fas Ligand mRNA Expression for Acute Rejection after Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Peritubular Capillaritis | |||
| Scores | SGF (n = 10) | i-IFTA (n = 30) | p |
| p0 | 9 (90%) | 25 (83.3%) | 0.52 |
| p1 | 1 (10%) | 5 (16.6%) | |
| p2 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| p3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Glomerulitis | |||
| g0 | 9 (90%) | 23 (76.6%) | 0.62 |
| g1 | 1 (10%) | 6 (20%) | |
| g2 | 0 (0%) | 1 (3.3%) | |
| g3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Tubulitis | |||
| t0 | 9 (90%) | 29 (96.6%) | 0.44 |
| t1 | 1 (10%) | 1 (3.33%) | |
| t2 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| t3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Interstitial fibrosis | |||
| i0 | 10 (14.2%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 |
| i1 | 0 (0%) | 6 (20%) | |
| i2 | 0 (0%) | 18 (60%) | |
| i3 | 0 (0%) | 6 (20%) | |
| Tubular atrophy | |||
| t0 | 6 (60%) | 2 (6.6%) | <0.001 |
| t1 | 4 (40%) | 7 (23.3%) | |
| t2 | 0 (0%) | 15 (50%) | |
| t3 | 0 (0%) | 6 (20%) | |
| Interstitial inflammation | |||
| i0 | 8 (80%) | 0 (0%) | 0.002 |
| i1 | 2 (20%) | 18 (60%) | |
| i2 | 0 (0%) | 9 (30%) | |
| i3 | 0 (0%) | 3 (10%) | |
| Intimal arteritis | |||
| v0 | 9 (90%) | 11 (36.66%) | 0.014 |
| v1 | 1 (10%) | 16 (53.3%) | |
| v2 | 0 (0%) | 3 (10%) | |
| v3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) | |||
| IFTA0 | 9 (90%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 |
| IFTA1 | 1 (10%) | 10 (33.3%) | |
| IFTA2 | 0 (0%) | 15 (50%) | |
| IFTA3 | 0 (0%) | 5 (16.7%) | |
| Characteristics | SGF (Mean ± sd) | i-IFTA (Mean ± sd) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. Gender (M:F) | 10:0 | 22:8 | 0.068 |
| Do. Gender (M:F) | 2:8 | 8:22 | 0.673 |
| Patient age (Years) | 44.36 ± 8.20 | 40.88 ± 8.37 | 0.257 |
| Post-transplant biopsy interval (Months) | 46.70 ± 17.30 | 56.90 ± 25.37 | 0.246 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 70.62 ± 22.14 | 44.13 ± 13.83 | <0.001 |
| Tac level (ng/mL) | 4.82 ± 0.98 | 5.02 ± 1.51 | 0.689 |
| Hemoglobin (gm/dL) | 12.94 ± 1.60 | 10.88 ± 1.61 | 0.001 |
| TLC | 8.39 ± 2.12 | 8.50 ± 5.02 | 0.94 |
| BUN | 25.79 ± 13.3 | 32.55 ± 8.84 | 0.074 |
| Baseline creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.81 ± 0.47 | 0.92 ± 0.41 | 0.500 |
| S. Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.21 ± 0.18 | 2.22 ± 0.53 | <0.001 |
| 24 h urine protein (gm) | 0.16 ± 0.085 | 0.90 ± 0.61 | <0.001 |
| HLA mismatch | 3.40 ± 0.69 | 3.10 ± 0.54 | 0.170 |
| Induction regimen (Basiliximab) | 10 | 30 | 1.00 |
| Baseline Immunosuppression Tacrolimus + MMF + Pred | 10 | 30 | 1.00 |
| ESRD cause MN/HTN/NOS | 6/3/1 | 20/9/1 | 0.69 |
| Characteristics | SGF | i-IF-TA | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD3+ T | 66.08 ± 6.8 | 65.18 ± 9.35 | 0.68 |
| CD3+CD8+ T | 37.29 ± 4.11 | 34.68 ± 5.43 | 0.28 |
| CD3+CD8+ granzyme-B T cell | 27.96 ± 4.86 | 23.19 ± 3.85 | 0.011 |
| Proteinuria | Serum Creatinine | eGFR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTLCs (%) | R = −0.51 p < 0.001 | r = −0.28 p = 0.007 | r = −0.28 p = 0.037 |
| Serum Granzyme B (pg/mL) | r = 0.343 p = 0.001 | r = 0.09 p = 0.3 | r = −0.18 p = 0.09 |
| Supernatants Granzyme B (pg/mL) | r = −0.37 p < 0.001 | r = −0.31 p = 0.002 | r = 0.27 p = 0.011 |
| Fold change in intragraft mRNA | r = 0.38 p < 0.001 | r = −0.12 p = 0.24 | r = −0.061 p = 0.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, B.; Prasad, N.; Agrawal, V.; Agarwal, V.; Jain, M. Lower Circulating Cytotoxic T-Cell Frequency and Higher Intragraft Granzyme-B Expression Are Associated with Inflammatory Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Renal Allograft Recipients. Medicina 2023, 59, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061175
Yadav B, Prasad N, Agrawal V, Agarwal V, Jain M. Lower Circulating Cytotoxic T-Cell Frequency and Higher Intragraft Granzyme-B Expression Are Associated with Inflammatory Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Renal Allograft Recipients. Medicina. 2023; 59(6):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061175
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Brijesh, Narayan Prasad, Vinita Agrawal, Vikas Agarwal, and Manoj Jain. 2023. "Lower Circulating Cytotoxic T-Cell Frequency and Higher Intragraft Granzyme-B Expression Are Associated with Inflammatory Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Renal Allograft Recipients" Medicina 59, no. 6: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061175
APA StyleYadav, B., Prasad, N., Agrawal, V., Agarwal, V., & Jain, M. (2023). Lower Circulating Cytotoxic T-Cell Frequency and Higher Intragraft Granzyme-B Expression Are Associated with Inflammatory Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Renal Allograft Recipients. Medicina, 59(6), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061175







