Contributions of Retinoid Signaling to Autism-like Behaviors Induced by Early Postnatal Lead Exposure in the Mouse Cerebellum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Establishment of Animal Models and Grouping
2.2. ASD-like Behavior Tests
2.2.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.2.2. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
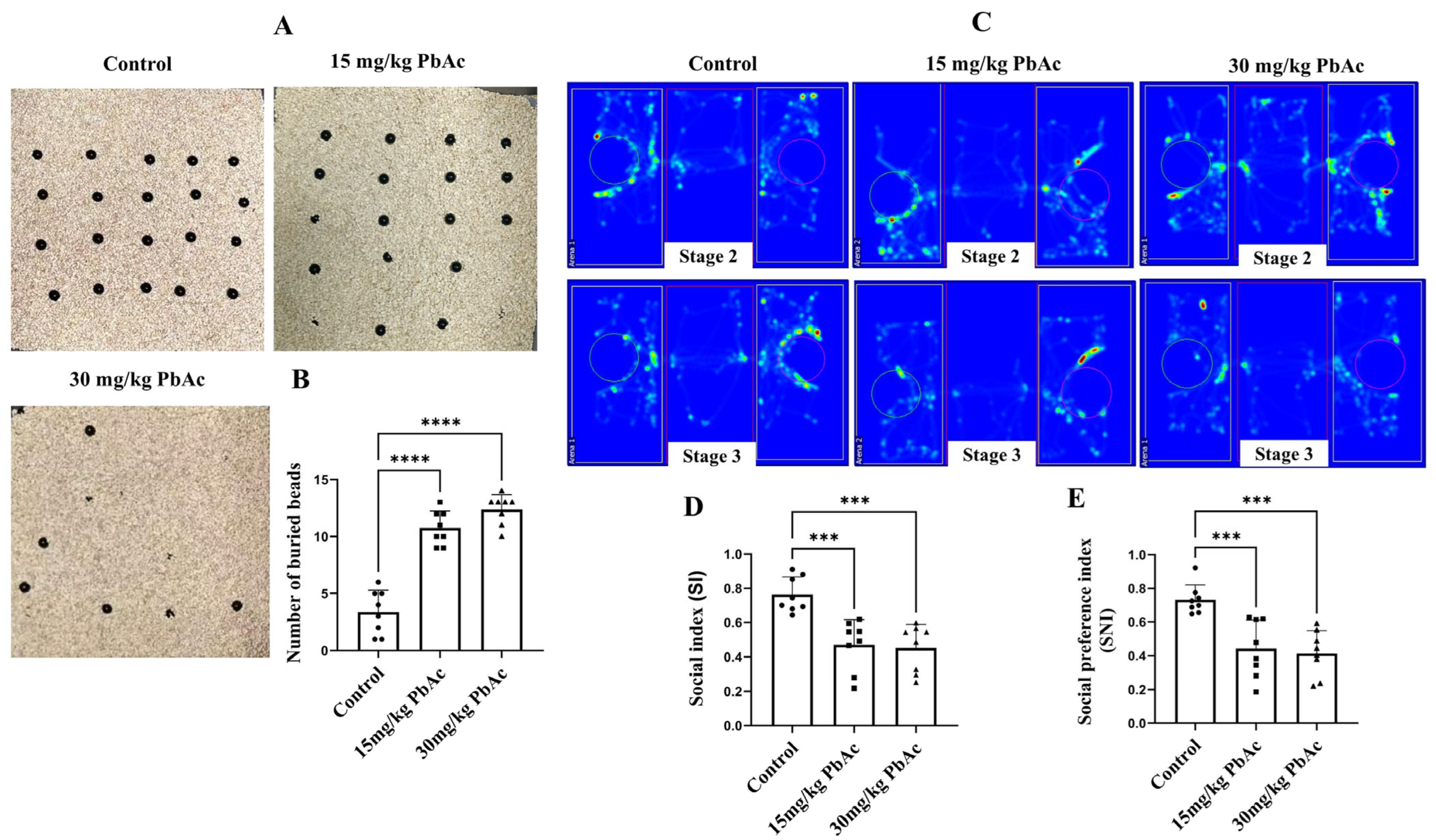
2.2.3. Marble Burying Test
2.2.4. Three-Chamber Social Test
2.3. Pb Level Determination in Cerebellum
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
2.5.1. Protein Extraction and Trypsin Digestion
2.5.2. TMT Labeling
2.5.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5.4. Cluster Analysis and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Early Postnatal Pb Exposure Induced Significant Autism-like Behaviors in Offspring
3.2. Early Postnatal Pb Exposure Induced Cerebellar Impairment
3.3. Pb Levels in Cerebellum
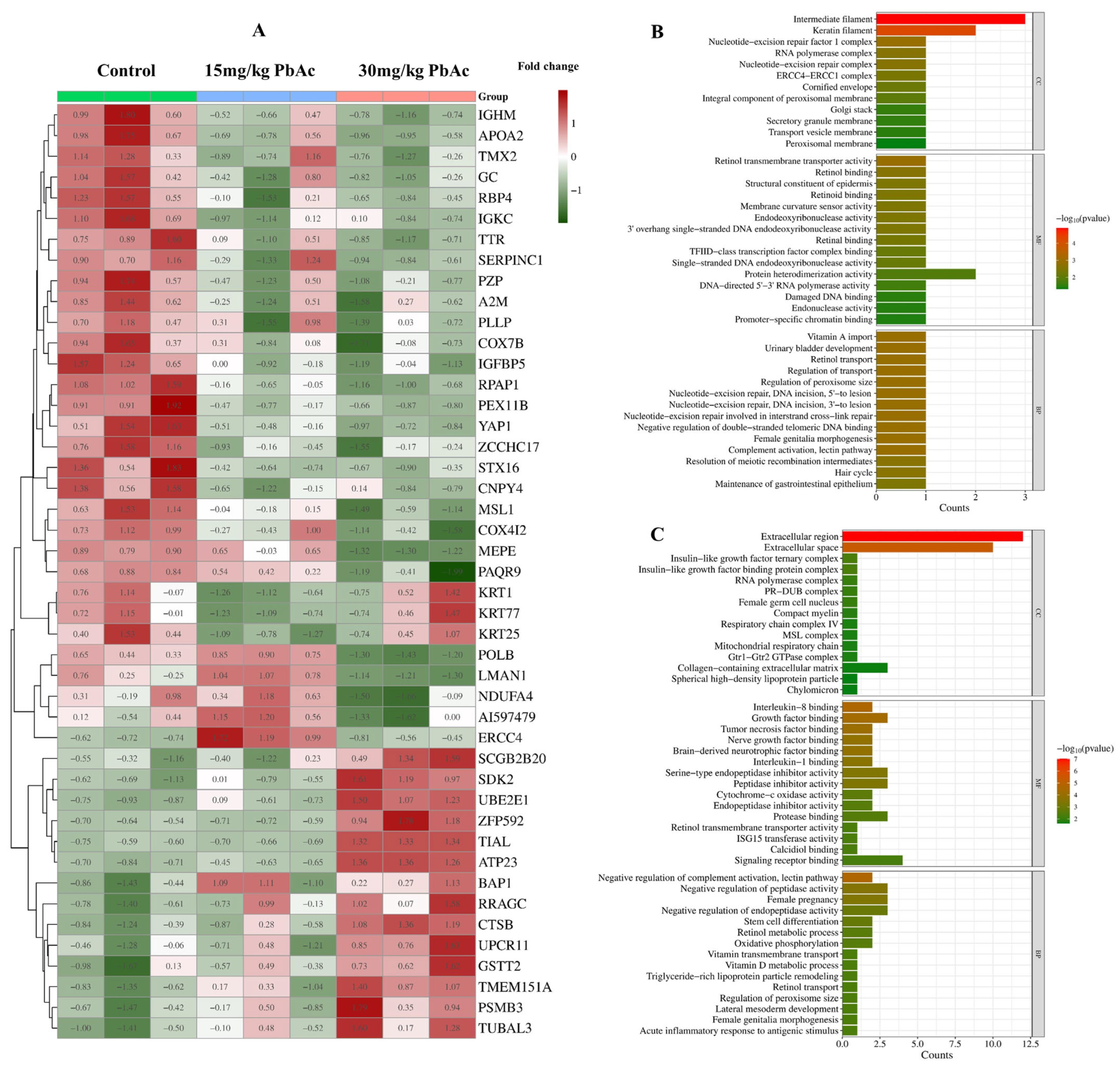
3.4. Protein Identification and Quantitative Analysis
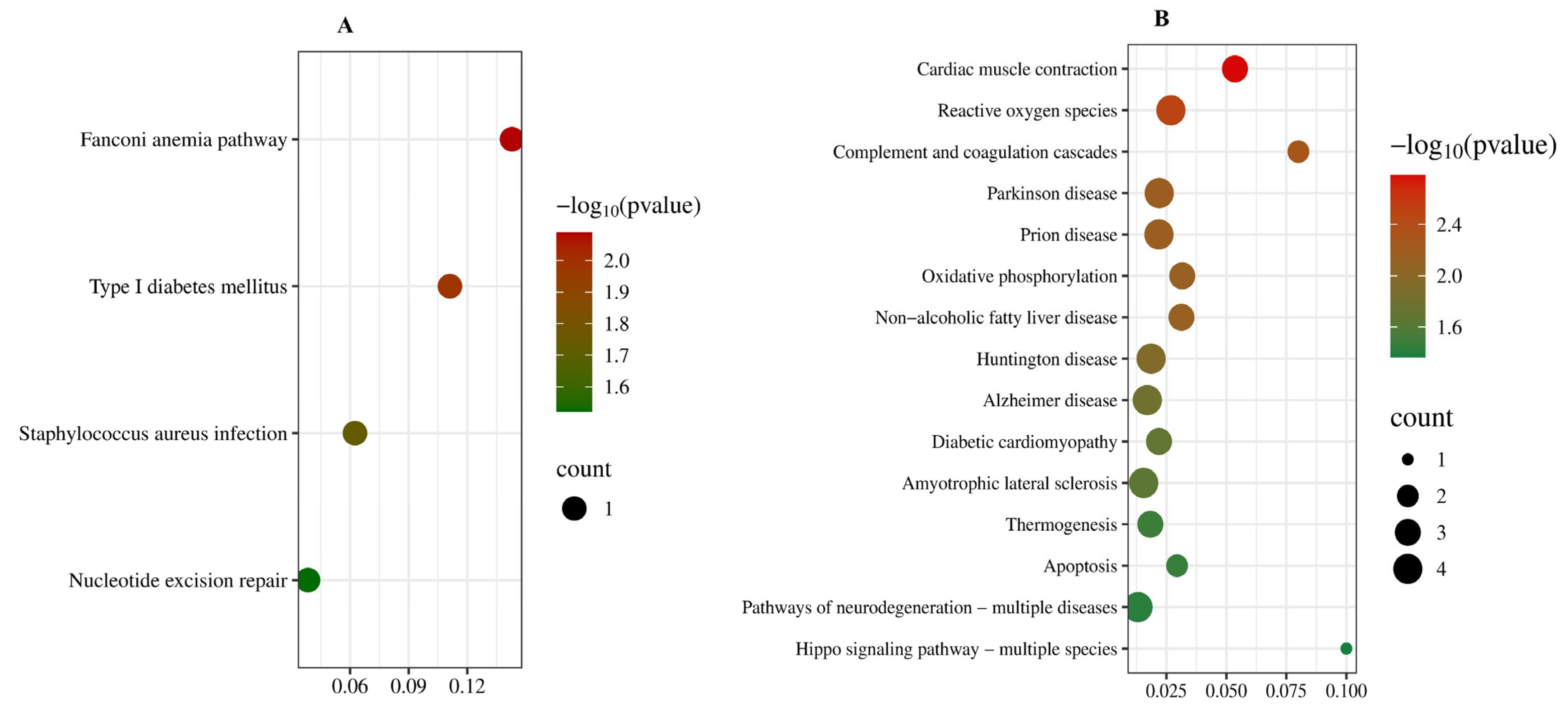
3.5. Go Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Analysis
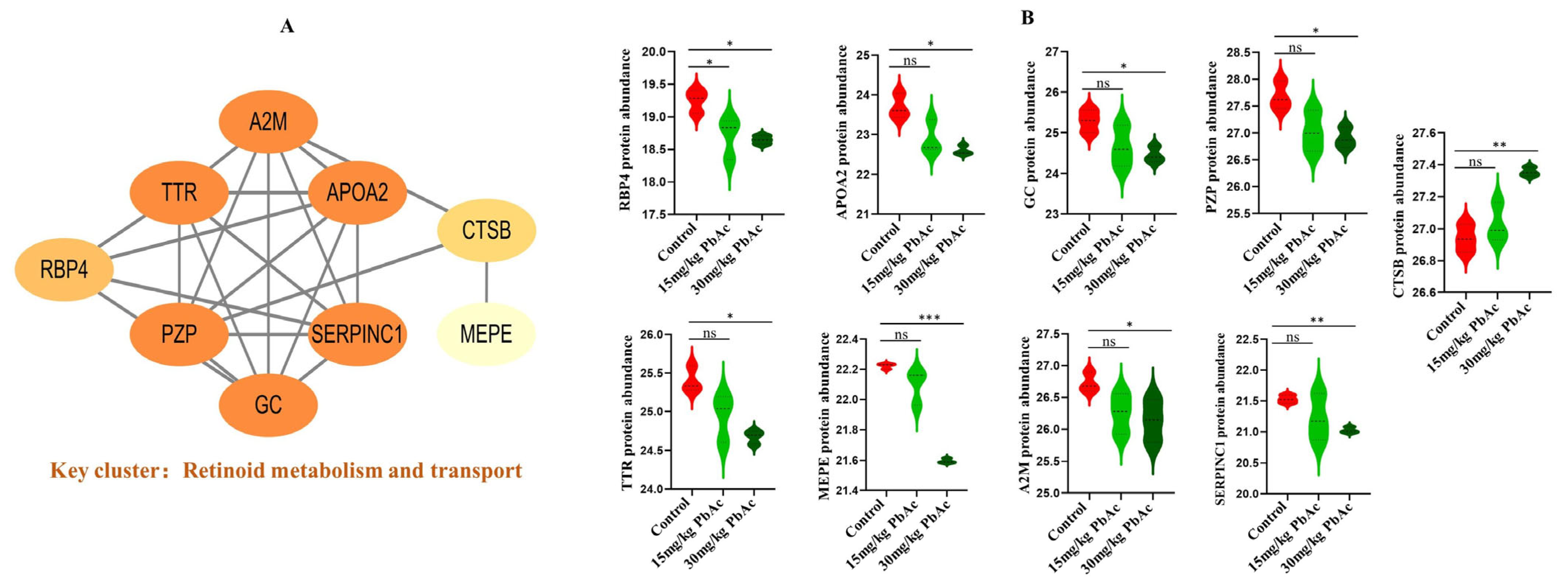
3.6. PPI Network Construction and Hub Protein Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.; Gulzar, M.; Sattar, B.; Sehar, S.; Abbas, Q.; Adnan, M.; Sun, J.; Luo, Z.; Hu, G.; Yu, R.; et al. Silent threats of lead-based paints in toys and households to children’s health and development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 136984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojsavljevic, A.; Lakicevic, N.; Pavlovic, S. Does Lead Have a Connection to Autism? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxics 2023, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.L.I.; Covington, M.; Visintainer, P.F.; Branch, H.J. Association of autism with lead poisoning in an environmental health clinic. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhaee, S.; Amirabadizadeh, A.; Farnia, V.; Azadi, N.A.; Mansouri, B.; Radmehr, F. Association Between Biological Lead Con centrations and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 1567–1581, Correction in Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Dietrich, K.; Ware, J.; Radcliffe, J.; Rogan, W. IQ and blood lead from 2 to 7 years of age: Are the effects in older children the residual of high blood lead concentrations in 2-year-olds? Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, B.; He, Y.H.; Dong, D.; Quan, L.; Feng, T.Y.; Li, M. Developmental Trajectory of Autistic-Like Behaviors in a Prenatal Valproic Acid Rat Model of Autism. Dev. Psychobiol. 2025, 67, e70008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Barone, R.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Cristaldi, A.; Rizzo, R.; Ferrante, M. Metal and essential element levels in hair and association with autism severity. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 57, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.B.; Audhya, T.; McDonough-Means, S.; Rubin, R.A.; Quig, D.; Geis, E.; Gehn, E.; Loresto, M.; Mitchell, J.; Atwood, S.; et al. Toxicological Status of Children with Autism vs. Neurotypical Children and the Association with Autism Severity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 151, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Xia, X.C.; Li, L.M.; Ye, Y.H.; Chen, Q.H.; Ke, M.Y.; Cui, Q.; He, Y.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Lin, S.Q.; et al. Evaluation of Heavy Metals and Essential Minerals in the Hair of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Their Association with Symptom Severity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M.; Nadeem, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Attia, S.M.; Albekairi, T.H.; Alhosaini, K.; Algahtani, M.; Alsaad, A.M.S.; Al-Mazroua, H.A.; et al. Lead (Pb) exposure exacerbates behavioral and immune abnormalities by upregulating Th17 and NF-kB-related signaling in BTBR T+Itpr 3tf/J autistic mouse model. Neurotoxicology 2022, 91, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assiri, M.; Albekairi, T.; Ansari, M.; Nadeem, A.; Attia, S.; Bakheet, S.; Shahid, M.; Aldossari, A.; Almutairi, M.; Almanaa, T.; et al. The Exposure to Lead (Pb) Exacerbates Immunological Abnormalities in BTBR T+ Itpr3tf/J Mice through the Regulation of Signaling Pathways Relevant to T Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhao, B.; He, Z.; Gu, S. Emerging roles of epigenetics in lead-induced neurotoxicity. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Balawi, H.; Al-Akel, A.; Al-Misned, F.; Suliman, E.; Al-Ghanim, K.; Mahboob, S.; Ahmad, Z. Effects of Sub-lethal Exposure of Lead Acetate on Histopathology of Gills, Liver, Kidney and Muscle and its Accumulation in these Organs of Clarias gariepinus. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Han, Q.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Teng, X. Dietary selenium supplementation alleviates immune toxicity in the hearts of chickens with lead-added drinking water. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, K.; Sanders, C. Lung clearance, translocation, ans acute toxicity of arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, cobalt, lead, selenium, vanadium, and ytterbium oxides following deposition in rat lung. Environ. Res. 1985, 36, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, G.; Tippairote, T.; Hangan, T.; Chirumbolo, S.; Peana, M. Early-life Lead Exposure: Risks and Neurotoxic Consequences. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.Y.; Lu, L.L.; Liang, Y.; Peng, D.J.; Aschner, M.; Jiang, Y.M. Signal transduction associated with lead-induced neurological disorders: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrazza, M.; Magro, D.; Salamaia, E.; Guareschi, T.; Erzinger, L.; Maia, T.; Siebert, C.; dos Santos, T.; Wyse, A.; Borgmann, G.; et al. Sub-chronic administration of lead alters markers of oxidative stress, acetylcholinesterase and Na+K+-ATPase activities in rat brain. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2024, 83, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Khanna, V.; Khan, M.; Srimal, R. Protective effect of curcumin against lead neurotoxicity in rat. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, C.; Ai, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, K.; Nie, M.; Gu, X.; Xu, Y.; et al. Epigenetic reprogramming of HDAC2 in CA1 excitatory neurons determines Pb-induced non-spatial memory deficits. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pei, X.; Jing, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H. Lead induced cerebellar toxicology of developmental Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) via oxidative stress-based Nrf2/Keap1 pathway inhibition and glutathione-mediated apoptosis signaling activation. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, J.; Pontes-Silva, A.; Gianlorenço, A. The cerebellum and its connections to other brain structures involved in motor and non-motor functions: A comprehensive review. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 465, 114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivalingam, A.M.; Pandian, A. Cerebellar Roles in Motor and Social Functions and Implications for ASD. Cerebellum 2024, 23, 2564–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kloth, A.; Badura, A. The Cerebellum, Sensitive Periods, and Autism. Neuron 2014, 83, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, S.; Sherrard, R. Cerebellum and neurodevelopmental disorders: RORα is a unifying force. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1108339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, S.; Bardawil, T.; Stephan, C.; Darwiche, N.; Abbas, O.; Kibbi, A.; Nemer, G.; Kurban, M. Retinoids: A journey from the molecular structures and mechanisms of action to clinical uses in dermatology and adverse effects. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2017, 28, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomhoff, R.; Blomhoff, H. Overview of retinoid metabolism and function. J. Neurobiol. 2006, 66, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudas, L. Retinoid metabolism: New insights. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 69, T37–T49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, C.; DiPette, D.; Singh, U. Ethanol Impairs Activation of Retinoic Acid Receptors in Cerebellar Granule Cells in a Rodent Model of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, J.K.; Yang, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Mou, Q.H.; Xiang, X.L.; Long, D.; Wei, Q.H.; et al. Association of the retinol to all-trans retinoic acid pathway with autism spectrum disorder. World J. Pediatr. 2024, 20, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, S. Decreased levels of serum retinoic acid in chinese children with autism spectrum disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 269, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xia, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M.; Miao, P.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Z.; Hu, R. Retinoic Acid Supplementation Rescues the Social Deficits in Fmr1 Knockout Mice. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 928393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, C.F.; Liang, J.J.; Cheng, B.L.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cao, Q.J.; et al. Mechanistic insights into retinoic-acid treatment for autism in the improvement of social behavior: Evidence from a multi omics study in rats. Neuropharmacology 2025, 265, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Xin, B.; Wang, Q.; Fu, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, Y. Change of the retinoic acid pathway in hypothalamus and pituitary damage induced by combined exposure to low-level Pb~(2+) and 1-nitropyrene in mice. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 2023, 52, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Azu, B.; Adebayo, O.G.; Wopara, I.; Aduema, W.; Onyeleonu, I.; Umoren, E.B.; Kolawole, T.A.; Ebo, O.T.; Akpotu, A.E.; Ajibo, D.N.; et al. Lead acetate induces hippocampal pyramidal neuron degeneration in mice via up-regulation of executioner caspase-3, oxido-inflammatory stress expression and decreased BDNF and cholinergic activity: Reversal effects of Gingko biloba supplement. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 71, 126919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Sharifabad, A.; Naghibzadeh, S.; Hajhashemi, V. The effect of lead, restraint stress or their co-exposure on the move ment disorders incidence in male mice. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.L.; Ke, H.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, Z.T.; Li, S.T.; Lv, P.J.; Li, F.; Chen, Y. Metformin Alleviates Autistic-Like Behaviors Elicited by High-Fat Diet Consumption and Modulates the Crosstalk Between Serotonin and Gut Microbiota in Mice. Behav. Neurol. 2022, 2022, 6711160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.M.; Merced-Nieves, F.M.; Midya, V.; Liu, S.H.; Martinez-Medina, S.; Wright, R.J.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Wright, R.O. Prena tal exposure to metal mixtures and childhood temporal processing in the PROGRESS Birth Cohort Study: Modification by childhood obesity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, X.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Liu, R.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.W.; Xia, X.C.; Wang, J. Hippocampal Proteomics Reveals the Novel Molecular Profiling of Postnatal Lead (Pb) Exposure on Autism-like Behaviors. Toxics 2025, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, W.; Hao, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Role of NF-κB in lead exposure-in duced activation of astrocytes based on bioinformatics analysis of hippocampal proteomics. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 370, 110310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, M.Y.; He, J.; Bai, Y.A.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Q.Q.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, B.L.; Shen, L. Integration of Proteomic and Metabolomic Data Reveals the Lipid Metabolism Disorder in the Liver of Rats Exposed to Simulated Microgravity. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.D.; Chen, M.J.; Huang, X.H.; Zhang, G.C.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.S.; Wu, S.J.; Wang, Y.W. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baizer, J.S. Neuroanatomy of autism: What is the role of the cerebellum? Cereb. Cortex. 2024, 34, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.A.; Silva, J.D.; Kawamoto, E.M. Cerebellar Alterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Mini-Review. Cerebellum 2025, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenkoyan, K.; Grigoryan, A.; Kutna, V.; Shorter, S.; O’Leary, V.B.; Asadollahi, R.; Ovsepian, S.V. Cerebellar impairments in genetic models of autism spectrum disorders: A neurobiological perspective. Prog. Neurobiol. 2024, 242, 102685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kano, M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of developmental synapse elimination inthe cerebellum: Involve ment of autism spectrum disorder-related genes. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B-Phys. Biol. Sci. 2024, 100, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.B.E.; Stoodley, C.J. Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Cerebellum. In International Review of Neurobiology; Konopka, G., Ed.; Neurobiology of Autism; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 113, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, G. Serum retinol-binding protein: A link between obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankam, P.; Blüher, M. Retinol-binding protein 4 in obesity and metabolic dysfunctions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 531, 111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Yu, S.; Fu, Y.; Du, Y. Retinol-binding protein 4 in combination with lipids to predict the regression phenomenon of autism spectrum disorders. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, J.; Lass, A.; Schupp, M. Biological Functions of RBP4 and Its Relevance for Human Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 659977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.L.; Luo, L.J.; Hu, C.Q.; Lin, F.; Yang, T.; Chen, J.; Li, T.Y. Retinoic acid supplementation ameliorates motor incoordination via RARα-CBLN2 in the cerebellum of a prenatal valproic acid-exposed rat autism model. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 809, 137316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uçar, N.; Grant, W.; Peraita-Costa, I.; Suárez-Varela, M. How 25(OH)D Levels during Pregnancy Affect Prevalence of Autism in Children: Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengenç, E.; Kiykim, E.; Saltik, S. Vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with autism. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520934638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.W.; Siddiqui, T.W.; Siddiqui, S.W. Vitamin D and Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Intriguing Association. Ann. Child Neurol. 2024, 32, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Amer, A.; Sobh, A.; Zaki, M.; Abou-Elsaad, T. Vitamin D profile in autism spectrum disorder children and its relation to the disease severity. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 40, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, R.; Shieh, A.; Gottlieb, C.; Yacoubian, V.; Wang, J.; Hewison, M.; Adams, J. Vitamin D Binding Protein and the Biological Activity of Vitamin D. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, E.; Guerini, F.; Sotgiu, S.; Chiappedi, M.; Carta, A.; Mensi, M.; Agliardi, C.; Zanzottera, M.; Clerici, M. GC1f Vitamin D Binding Protein Isoform as a Marker of Severity in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Jiang, X.; Leak, R.; Shi, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J. Microglial Responses to Brain Injury and Disease: Functional Diversity and New Opportunities. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 474–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Huang, W.; Qiu, X.; Chen, J.; Luo, R.; Zeng, R.; Tong, S.; Lyu, Y.; Sun, P.; Lian, Q.; et al. Unveiling promising drug targets for autism spectrum disorder: Insights from genetics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ye, D.; Han, M.; Wang, H. Regulatory Roles of Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 in Pb-induced Neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinirad, H.; Shahrestanaki, J.; Moghaddam, M.; Mousazadeh, A.; Yadegari, P.; Afsharzadeh, N. Protective Effect of Vitamin D3 Against Pb-Induced Neurotoxicity by Regulating the Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lin, X.; Wu, D.; Yan, B.; Bao, M.; Zheng, P.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; et al. Poly(I:C)-exposed zebrafish shows autism-like behaviors which are ameliorated by fabp2 gene knockout. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1068019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Kim, W.; Missig, G.; Finger, B.C.; Landino, S.M.; Alexander, A.J.; Mokler, E.L.; Robbins, J.O.; Li, Y.; Bolshakov, V.Y.; et al. Maternal and early postnatal immune activation produce sex-specific effects on autism-like behaviors and neuroimmune function in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Contributions of Retinoid Signaling to Autism-like Behaviors Induced by Early Postnatal Lead Exposure in the Mouse Cerebellum. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100861
Xia X, Zhou X, Ma Z, Liu L, Wang Y, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wang J. Contributions of Retinoid Signaling to Autism-like Behaviors Induced by Early Postnatal Lead Exposure in the Mouse Cerebellum. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(10):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100861
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xiaochun, Xulan Zhou, Zihan Ma, Li Liu, Yaqi Wang, Yongli Wu, Ying Zhang, and Juan Wang. 2025. "Contributions of Retinoid Signaling to Autism-like Behaviors Induced by Early Postnatal Lead Exposure in the Mouse Cerebellum" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 10: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100861
APA StyleXia, X., Zhou, X., Ma, Z., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). Contributions of Retinoid Signaling to Autism-like Behaviors Induced by Early Postnatal Lead Exposure in the Mouse Cerebellum. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(10), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100861










