3.1. Common Targets of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) and Antitumor Agents
As part of our investigation into the antitumor potential of
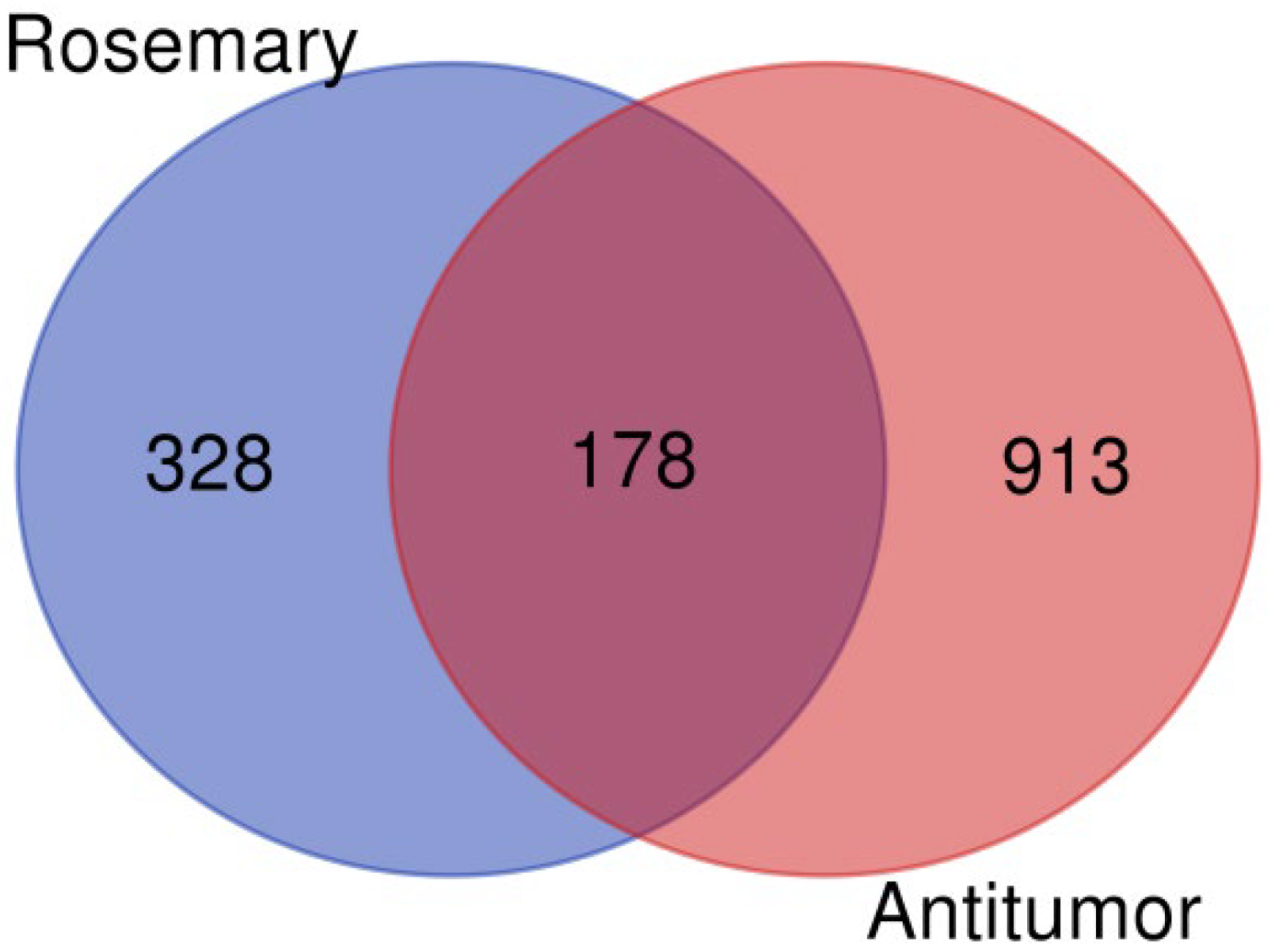
R. officinalis (rosemary) compounds, we first compiled a list of target proteins associated with the 12 bioactive compounds extracted from this plant. These proteins were then cross-referenced with known proteins involved in antitumor mechanisms, which were retrieved from the GeneCards database (
https://www.genecards.org/) using the keyword ‘tumor suppressor’ to identify relevant targets associated with cancer biology. This intersection yielded 178 proteins, as illustrated in
Figure 1, generated using the VennDiagram website (
https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/, accessed on 18 September 2025). The full list of identified proteins is provided in
Table S1.
To further analyze these proteins, we used the STRING database to study protein–protein interaction (PPIs) and construct an interaction network. This network was then exported to Cytoscape for visualization and in-depth analysis.
To refine our selection and identify the most biologically relevant proteins, we applied three key network analysis metrics: Mathew’s Correlation Coefficient (MCC)—Assesses the correlation strength between proteins, helping to identify those with robust and significant interactions in biological processes [
31]. Betweenness Centrality—Measures a protein’s role in the network based on its ability to connect different nodes. Proteins with high Betweenness Centrality often serve as critical regulators of biological pathways [
32]. Degree—Quantifies the number of direct interactions a protein has within the network. Proteins with high Degree values are frequently involved in essential cellular functions, making them promising therapeutic targets [
33].
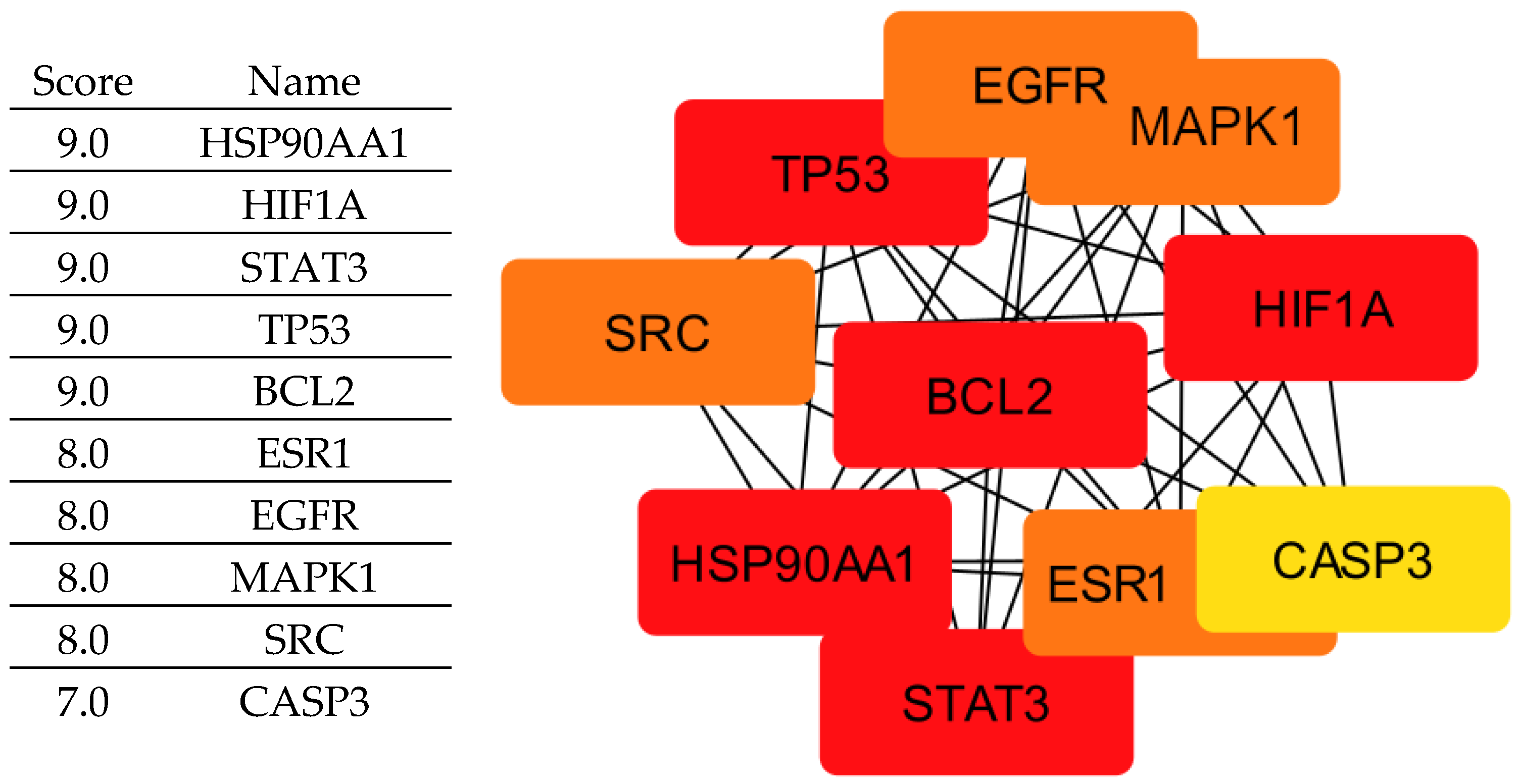
By integrating these criteria, we identified ten key proteins (
Figure 2) (EGFR, ESR1, HIF1A, HSP90AA1, MAPK1, BCL2, STAT3, TP53, CASP3, and SRC) that play central roles in tumor progression and are therefore considered crucial therapeutic targets for rosemary-derived compounds. It is important to clarify that not all of these proteins act exclusively as tumor suppressors; some, such as EGFR, STAT3, SRC, and HSP90AA1, are oncogenic drivers whose inhibition can suppress cancer growth. Others, like TP53 and CASP3, function as tumor suppressors but may be indirectly modulated or stabilized by the compounds rather than inhibited. Therefore, the compounds may exert their effects either by inhibiting oncogenic targets or by supporting and enhancing the activity of tumor-suppressive pathways.
3.2. Enrichment Analysis of Key Proteins
To further investigate the 10 selected proteins (identified based on their high MCC, Betweenness Centrality, and Degree in the PPI network), we conducted functional annotation and enrichment analysis using the DAVID (Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery) platform (
https://davidbioinformatics.nih.gov/, accessed on 18 September 2025). This analysis allowed us to explore the biological functions, signaling pathways, and cellular processes associated with these proteins. The results, presented in
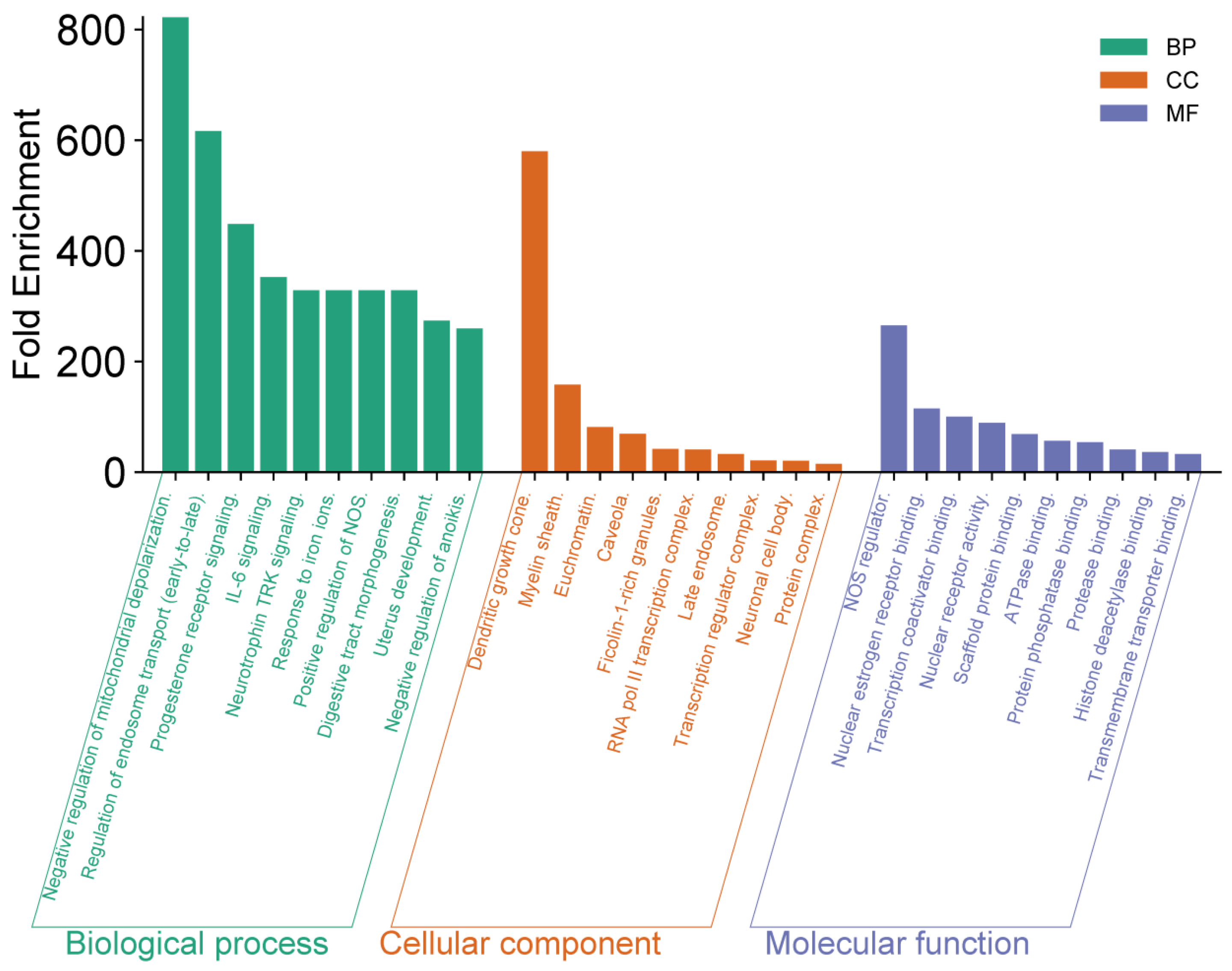
Figure 3, highlight key biological functions and interactions that may contribute to the antitumor efficacy of
R. officinalis compounds.
The functional enrichment analysis revealed several significant observations. At the biological process (BP) level, negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization exhibited the highest enrichment, exceeding 800-fold. Other highly enriched processes included regulation of endosome transport and progesterone receptor signaling, both surpassing 400-fold enrichment. Regarding cellular components (CC), dendritic growth cone and myelin sheath showed remarkable enrichments, reaching values close to 350-fold and 300-fold, respectively. In terms of molecular function (MF), NOS regulation and nuclear receptor binding displayed high enrichment values, approaching 250-fold, indicating a crucial role in intracellular signal regulation. These findings highlight the potential role of rosemary-derived bioactive compounds in modulating key cellular processes associated with tumor development, and opening promising avenues for novel anticancer therapeutic strategies.
To gain deeper insights, we further analyzed the ten selected proteins using the SHINY GO platform (
https://bioinformatics.sdstate.edu/go/, accessed on 18 September 2025). The results, presented in
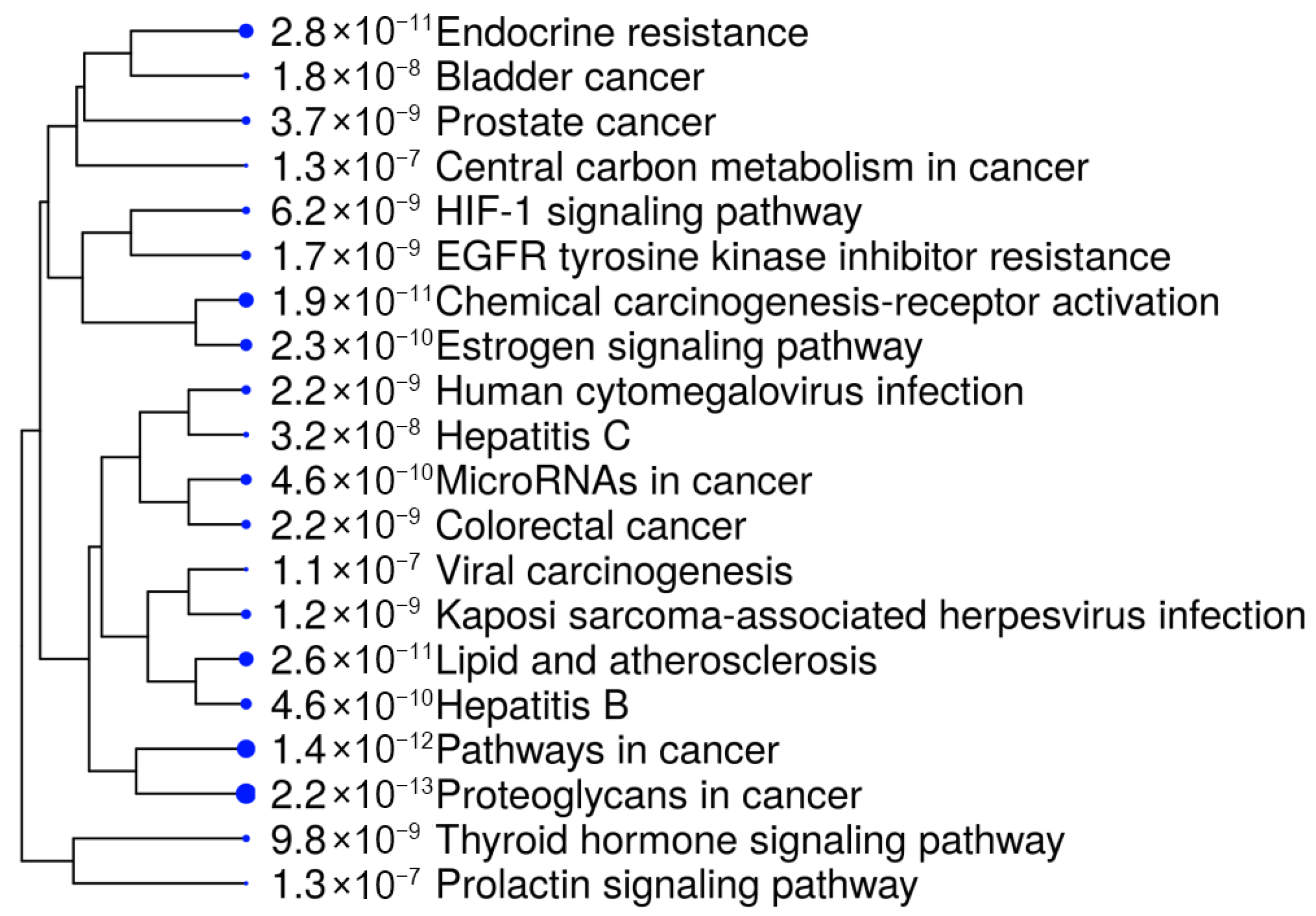
Figure 4 and
Table 3, demonstrated a significant involvement of these genes in several cancer-related biological and pathological pathways. Notably, the most enriched pathways included bladder cancer, resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and endocrine resistance, suggesting a strong association with tumor progression and drug resistance mechanisms [
34,
35].
Other relevant pathways included central metabolic pathways, prolactin signaling, and microRNAs involved in cancer, underscoring the regulatory role of the selected targets in tumorigenesis and cancer cell survival. Additionally, chemical carcinogenesis pathways and their involvement in Hepatitis B/C-related cancer development indicate the broader therapeutic potential of R. officinalis compounds in various oncogenic and pathological contexts. The high enrichment values observed in proteoglycans in cancer and estrogen signaling pathways further reinforce their potential as targeted cancer therapeutics.
Based on the enrichment analysis and pathway data presented in
Table 3, we selected HSP90 (Heat Shock Protein 90) as the primary target for molecular docking studies. HSP90 exhibited the highest Degree score and was the most frequently implicated protein in cancer-related pathways, reinforcing its role as a key therapeutic target. These findings support the hypothesis that bioactive compounds from
R. officinalis may exert anticancer effects by modulating HSP90 and other critical pathways, paving the way for future experimental validation and potential drug development.
3.3. Docking Study of Substances from R. Officinalis as Hsp90 Inhibitors
This study focused on the Hsp90 protein as the primary target for docking analysis with twelve bioactive compounds sourced from
R. officinalis (rosemary). The aim was to investigate the molecular interactions between Hsp90 and rosemary-derived substances, particularly their potential as inhibitors. The three-dimensional structure of Hsp90 (PDB ID: 3OWD) was obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) (
https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3OWD, accessed on 10 October 2024). The active site was identified based on the reference compound, Mey (N-{[1-(5-chloro-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl]methyl}naphthalene-1-sulfonamide), which had previously been docked into the crystalline structure. The principal amino acids forming the active site include a hydrophobic component, consisting of residues Ala55, Ile96, Met98, Leu107, Phe138, and Val150, and a hydrophilic component, comprising residues Asn51, Asp93, and Thr184. These findings are consistent with previous studies [
23,
36].
To ensure the reliability of the docking method, we first validated its precision. During this validation phase, we used 35 active compounds known to inhibit Hsp90 and 1000 inactive compounds sourced from the PubChem database. Several statistical metrics were calculated to assess the docking procedure, including ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic curve), BEDROC (Boltzmann-enhanced discrimination of ROC), AUC (Area Under the Curve), and RIE (Robust Initial Enhancement), as detailed in
Tables S2–S5.
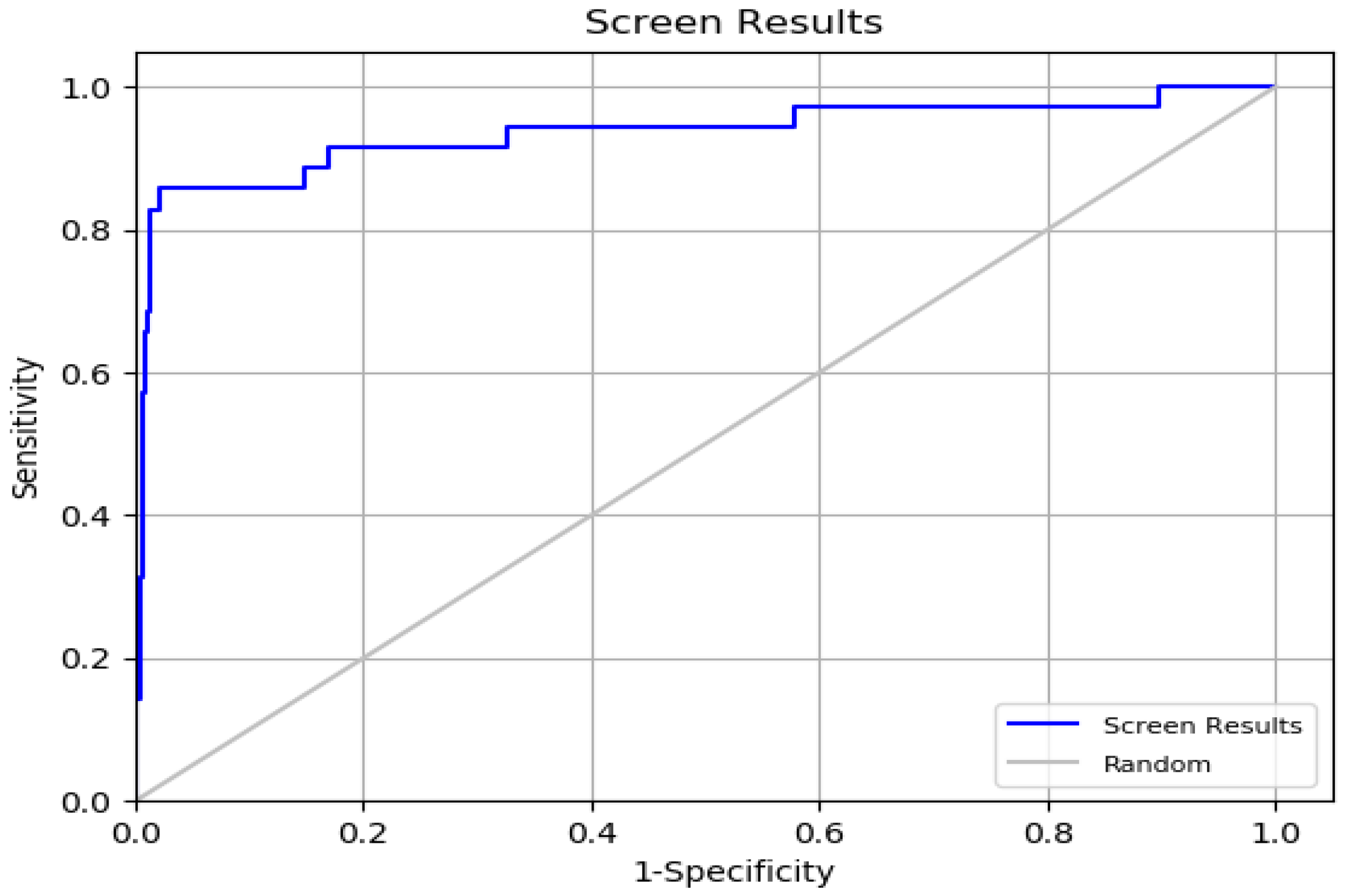
The ROC value, which ranges from 0 to 1, was found to be 0.93, indicating strong efficacy in ranking active compounds above inactive ones [
37]. This was further supported by the ROC plot in
Figure 5. The AUC value of 0.92 shows that 92% of real positive findings were correctly identified by the docking method, underscoring its effectiveness in distinguishing active compounds from decoys. The RIE value was determined to be 11.54, a favorable outcome for validation. The BEDROC values at various tuning parameters were (α = 8.0/0.845), (α = 20.0/0.794), and (α = 160.9/0.657). The BEDROC metric indicates the probability that an active molecule is ranked higher than inactive compounds [
38]. These results confirm the reliability and effectiveness of the docking method for virtual screening.
Following validation via enrichment analysis, which yielded significant enrichment of potential therapeutic targets, we initiated molecular docking simulations to investigate the binding interactions between bioactive constituents of
R. officinalis and the ATP-binding domain of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90; PDB ID: 3OWD). These computational studies were designed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the potential inhibitory effects of the compounds on HSP90 function. The binding affinities, quantified as docking scores (XP GScore) for each derivative, are detailed in
Table 4.
To benchmark the binding efficacy of the
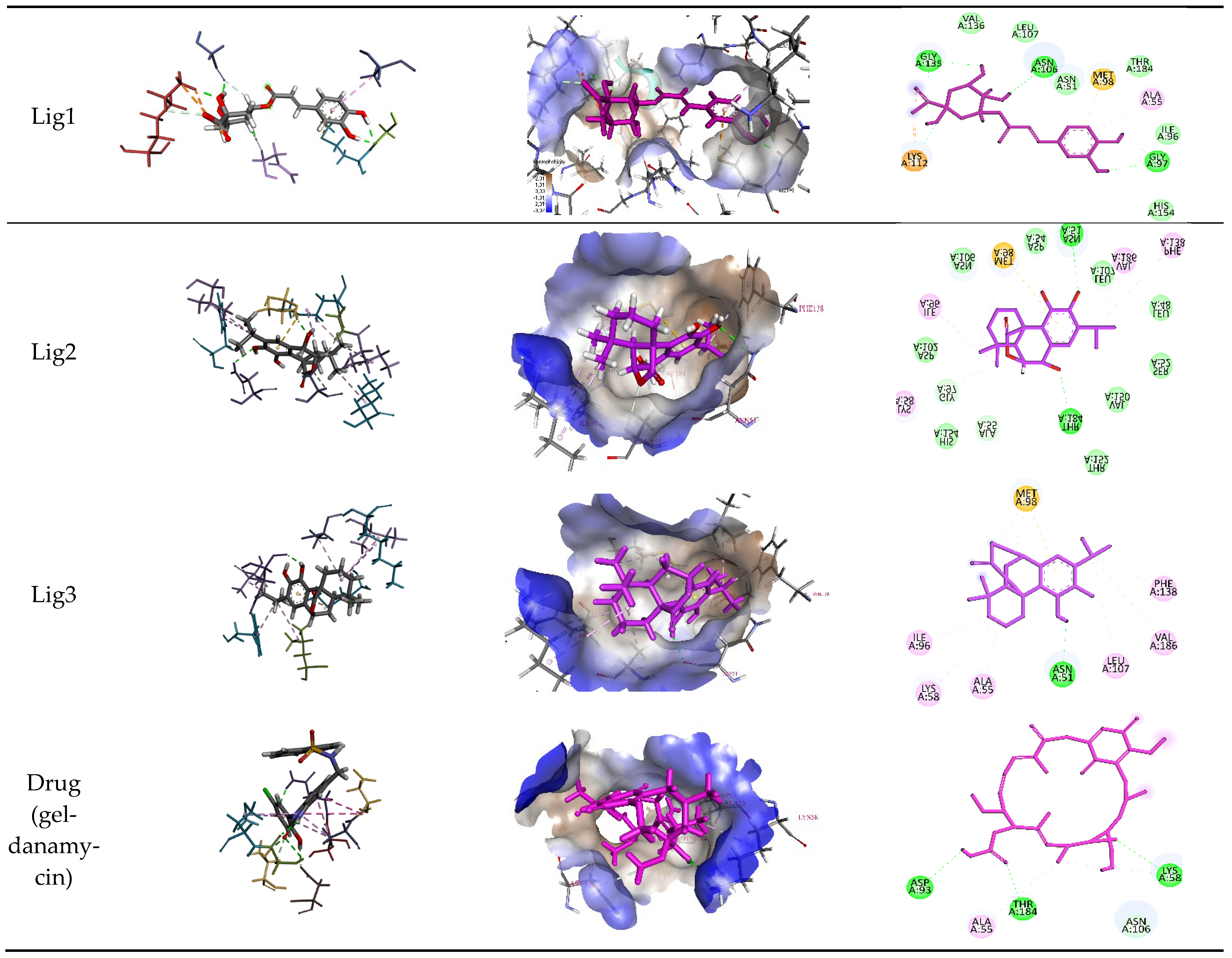
R. officinalis derivatives, molecular docking results were compared with two established reference inhibitors: (i) the co-crystallized ligand Mey (PDB: 3OWD), which serves as a structural and energetic benchmark for the HSP90 active site, and (ii) Geldanamycin (DB02424), a clinically validated HSP90 inhibitor. The docking scores (XP GScore) revealed distinct binding affinities: Mey exhibited a score of −7.25 kcal/mol, consistent with its moderate inhibitory potency, while Geldanamycin displayed a weaker interaction (−5.432 kcal/mol), likely reflecting its distinct binding mode or dynamic instability within the rigid docking framework. Strikingly, the tested derivatives demonstrated superior binding energetics, with Lig 1 achieving the highest affinity (−9.762 kcal/mol), followed by Lig 2 (−7.317 kcal/mol) and Lig 3 (−7.280 kcal/mol). These results suggest that Lig 1, in particular, may occupy the HSP90 binding pocket with enhanced complementarity compared to both reference compounds. Analysis of the ligand-protein interaction networks demonstrated that the bioactive derivatives form critical intermolecular contacts—including hydrogen bonds with conserved residues (e.g., Asp93, Asn51) and hydrophobic interactions with the ATP-binding pocket—mirroring the binding patterns observed for the reference inhibitors Mey and Geldanamycin (
Figure 6 and
Table 5).
Chlorogenic Acid (Lig 1) possesses a structure rich in hydroxyl groups (-OH), which contribute significantly to hydrogen bonding, both as donors and acceptors. This explains its formation of eight hydrogen bonds with residues such as Asn106, Gly97, Gly135, and Lys112. These interactions indicate a high affinity for the polar regions of the active site. However, the limited number of hydrophobic interactions (only two, involving Ala55 and Lys112) may reduce its stability in the hydrophobic pockets of HSP90, which play a crucial role in ligand docking. Consequently, despite strong polar interactions, Chlorogenic Acid may be less effective in engaging with the more hydrophobic regions of the protein.
Rosmanol (Lig 2) demonstrates a well-balanced interaction profile between hydrogen and hydrophobic interactions due to its diterpenic structure, which contains multiple rings and functional groups such as carbonyls and hydroxyls. It forms four hydrogen bonds with key residues like Asn51, Gly97, and Thr184, while also establishing seven hydrophobic interactions with residues such as Ile96, Lys58, Met98, and Phe138. These hydrophobic interactions enhance Rosmanol’s affinity for the non-polar regions of the active site, particularly around Met98, which appears to play a pivotal role in stabilizing this ligand.
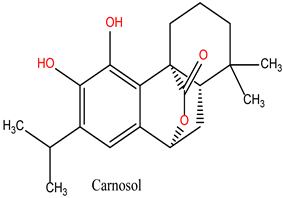
Carnosol (Lig 3), structurally similar to Rosmanol, displays a different binding behavior. It forms only one hydrogen bond (with Asn51), suggesting a lower affinity for the polar regions of the protein. However, it compensates for this with seven strong hydrophobic interactions involving Ala55, Ile96, Leu107, Lys58, Met98, and Phe138. The repeated involvement of Met98 as a key interacting residue for both diterpene ligands highlights its importance in ligand recognition and anchoring within the hydrophobic pockets of HSP90.
In comparison, the reference compound Geldanamycin exhibits a balanced profile, forming six hydrogen bonds with residues such as Asn106, Asp93, and Thr184, along with two hydrophobic interactions (Ala55 and Lys58). Although its hydrophobic interactions are moderate compared to the natural ligands, its well-distributed hydrogen bonds contribute to its established efficacy as an HSP90 inhibitor. However, its weaker performance in hydrophobic pockets suggests that the natural rosemary-derived ligands may offer superior stability and affinity.
These results suggest that the hydrophobic, ring-rich structures of natural ligands, such as Rosmanol and Carnosol, confer a significant advantage in terms of stability and affinity for HSP90. Multiple interactions with key hydrophobic residues, including Met98, Ile96, and Phe138, reinforce their ability to anchor firmly within the active site. Conversely, while Chlorogenic Acid demonstrates strong interactions with polar residues, it appears less suited for engaging with the critical hydrophobic pockets of HSP90.
3.4. Prediction of ADMET Profiles and Drug-likeness of the Lead Ligands
The evaluation of ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity) properties is crucial for predicting and mitigating potential risks associated with the administration of new therapeutic molecules. This analysis provides key insights to minimize failures during clinical trials by assessing the pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of drug candidates.
In this study, we examined the ADMET profiles of the identified lead ligands (Lig 1, Lig 2, and Lig 3), focusing on their pharmacokinetic behavior, toxicity, drug-likeness, and physicochemical properties. These assessments help determine the compounds’ potential efficacy and safety as drug candidates, ensuring they meet the necessary criteria for further pharmaceutical development.
3.4.1. Physicochemical Properties
Table 6 presents the physicochemical and medicinal properties of the lead ligands, which exhibit molecular weights and volumes within an optimal range (330–355 Da), lower than that of Geldanamycin. This suggests their enhanced potential for favorable interactions with HSP90 and promising therapeutic characteristics.
The Total Polar Surface Area (TPSA) is a crucial parameter influencing a molecule’s ability to penetrate biological membranes and be effectively absorbed by the body [
39]. Compounds with a TPSA exceeding 140 Å
2 generally exhibit poor membrane permeability, whereas those with TPSA values ≤ 60 Å
2 are typically well absorbed. The analysis indicates that Lig 2 and Lig 3 have TPSA values within the optimal range, i.e., below 140 Å
2, which supports their favorable absorption and oral bioavailability. In contrast, Lig 1 possesses a significantly higher TPSA, surpassing the ideal threshold, which could compromise its gastrointestinal absorption and limit its oral therapeutic efficacy. This finding underscores the importance of optimizing physicochemical properties to improve pharmacokinetic profiles.
Regarding solubility (Log S), all ligands meet the required criteria, except for Lig 3, which slightly exceeds the optimal range (−4 to 0.5), potentially affecting its membrane permeability. The octanol–water partition coefficient (LogP) values of Lig 1 and Lig 2 fall within the ideal range (0–3), indicating a balanced hydrophilicity-lipophilicity profile and high bioavailability potential. Conversely, although the LogP of Lig 3 remains within an acceptable range, optimization may further enhance its pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy.
In drug discovery, adherence to established guidelines is essential for identifying compounds with high therapeutic potential while ensuring safety and efficacy. Several key principles contribute to this selection process, including Lipinski’s Rule of Five [
40], the Pfizer Rule, the GSK Rule [
41], and the Golden Triangle Concept [
42,
43]. Lipinski’s Rule of Five establishes key structural attributes that favor oral bioavailability, such as a molecular weight below 500 Da, LogP under 5, and defined limits on hydrogen bond donors and acceptors. The Pfizer Rule [
44], also known as the “3/75 Rule,” highlights potential toxicological risks associated with high lipophilicity (LogP greater than 3) and reduced TPSA (below 75 Å
2). GSK’s Rule suggests that compounds with a molecular weight above 400 Da and LogP exceeding 4 may present safety and pharmacokinetic concerns. The Golden Triangle Concept integrates molecular weight, lipophilicity, and TPSA into an optimal range to balance efficacy, bioavailability, and safety [
21]. These principles serve as critical selection criteria to streamline drug candidate identification and minimize development risks.
The synthetic accessibility assessment (SA) of the ligands yields values below 6, suggesting that their synthesis is feasible and straightforward. According to
Table 6, Lig 1 and Lig 2 comply with the Lipinski, Pfizer, and GSK rules, as well as the Golden Triangle criteria. These findings indicate a high bioavailability potential, favorable pharmacokinetics, and promising therapeutic efficacy, surpassing that of Geldanamycin, which adheres only to the Lipinski and Pfizer rules, thereby limiting its pharmacological potential.
3.4.2. Absorption
The results presented in
Table 7 show notable differences between the compounds in terms of their absorption and membrane permeability. Regarding human intestinal absorption (HIA), Lig1 (Chlorogenic Acid), Lig2 (Rosmanol), and Lig3 (Carnosol) all exhibit values above 30%, indicating their potential for efficient absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. This suggests that these compounds may be suitable for oral administration. In contrast, Geldanamycin has an HIA value below 30%, which indicates limited absorption and may hinder its efficacy as an oral drug.
When considering Caco-2 permeability, a critical parameter for predicting a compound’s ability to cross intestinal membranes, lower values (negative and close to zero) are associated with reduced permeability. Lig1 shows the lowest permeability (−6.426 cm/s), consistent with its highly polar structure that is rich in hydroxyl groups. On the other hand, Lig3 (−4.767 cm/s) and Lig2 (−5.256 cm/s) display significantly better permeability, which can be attributed to their lipophilic nature due to their hydrophobic diterpene structures. These compounds are thus more likely to cross biological membranes with ease.
Geldanamycin, with a Caco-2 permeability value of −5.246 cm/s, falls between Lig2 and Lig1 but still performs worse than Lig3. This difference could help explain why Geldanamycin has a lower overall bioavailability compared to the natural compounds derived from rosemary.
3.4.3. Distribution
Table 7 shows that all ligands exhibit low penetration through the blood–brain barrier (BBB) (<0.2), indicating limited potential for interaction with the central nervous system (CNS). Lig1 (Chlorogenic Acid) has a binding potential to plasma proteins (PPB) of less than 90%, which is similar to that of Geldanamycin, whereas the other ligands have higher PPB values (greater than 90%), suggesting a potentially limited systemic bioavailability for these compounds.
3.4.4. Metabolism and Excretion
Regarding metabolism and excretion, none of the compounds evaluated exhibit significant inhibition of major cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes [
45], which suggests a low risk of drug–drug interactions related to CYP inhibition. Lig2 (Rosmanol) and Lig3 (Carnosol) show moderate renal clearance values (5–15 mL/min/kg), with values of 12.456 and 12.709, respectively. In contrast, Lig1 has the lowest renal clearance value, indicating potentially reduced renal elimination. All ligands display relatively short half-lives (T½ < 3 h), with Lig3 having the shortest half-life, indicating faster elimination compared to Lig1 and Lig2.
3.4.5. Toxicity
In terms of toxicity, the results from the ADMETlab 3.0 server reveal that the three ligands have low hERG scores (<0.1), indicating no significant potential for inhibiting the hERG ion channel. This is consistent with the behavior of Geldanamycin and suggests that these ligands do not present a risk of cardiotoxicity, which is crucial for ensuring the safety of drug candidates [
46]. The mutagenic potential of Lig1 and Lig2 is considered moderate (0.3–0.7), while Lig3 is categorized as toxic. Similarly to Geldanamycin, the selected ligands exhibit a high potential for skin sensitization.
Further analysis using the Protox 3.0 platform (
Table 8) suggests that the compounds evaluated have a low potential for toxicity, including hepatotoxicity, carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and cytotoxicity. Geldanamycin does not show hepatotoxic, carcinogenic, or mutagenic potential but presents a moderate risk for cytotoxicity with an estimated probability of 0.67.
The ADMET properties and toxicity profiles of Lig3 highlight some limitations that may pose barriers to its use. These findings suggest the need for structural modifications to reduce potential risks and improve the safety and efficacy of Lig3 as a therapeutic candidate.
3.5. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Studies
The molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were conducted not only to validate the docking results but also to assess the stability, flexibility, and dynamic behavior of the ligand–HSP90AA1 complexes over time. This step is critical for understanding whether the predicted binding poses remain stable under physiological conditions and whether any significant conformational changes occur during the interaction.
In this analysis, the complexes (Lig1-Hsp90), (Lig2-Hsp90), and (Lig3-Hsp90), proposed as potential inhibitors of the HSP90 protein, were compared to the reference complex (MEY-Hsp90). The comparison was based on parameters such as RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation), RMSF (Root Mean Square Fluctuation), and interactions with key residues, which are critical for assessing the stability and binding efficacy of these ligands to HSP90.
RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) measures the average structural deviation and serves as a key indicator of complex stability. The MEY-Hsp90 complex (
Figure 7A), considered as a reference, shows moderate stability throughout the simulation. The protein RMSD (blue curve) fluctuates between 1.6 and 3.2 Å, with a gradual increase beyond 50 ns, suggesting global structural adjustments in the protein due to its interaction with the MEY ligand. In contrast, the ligand RMSD (red curve) remains highly stable, with an average value of around 1.4 Å, indicating that its position and orientation remain relatively constant despite some local fluctuations. These results highlight the strong affinity and stable interaction of the MEY ligand with Hsp90, justifying its use as a reference for further studies.
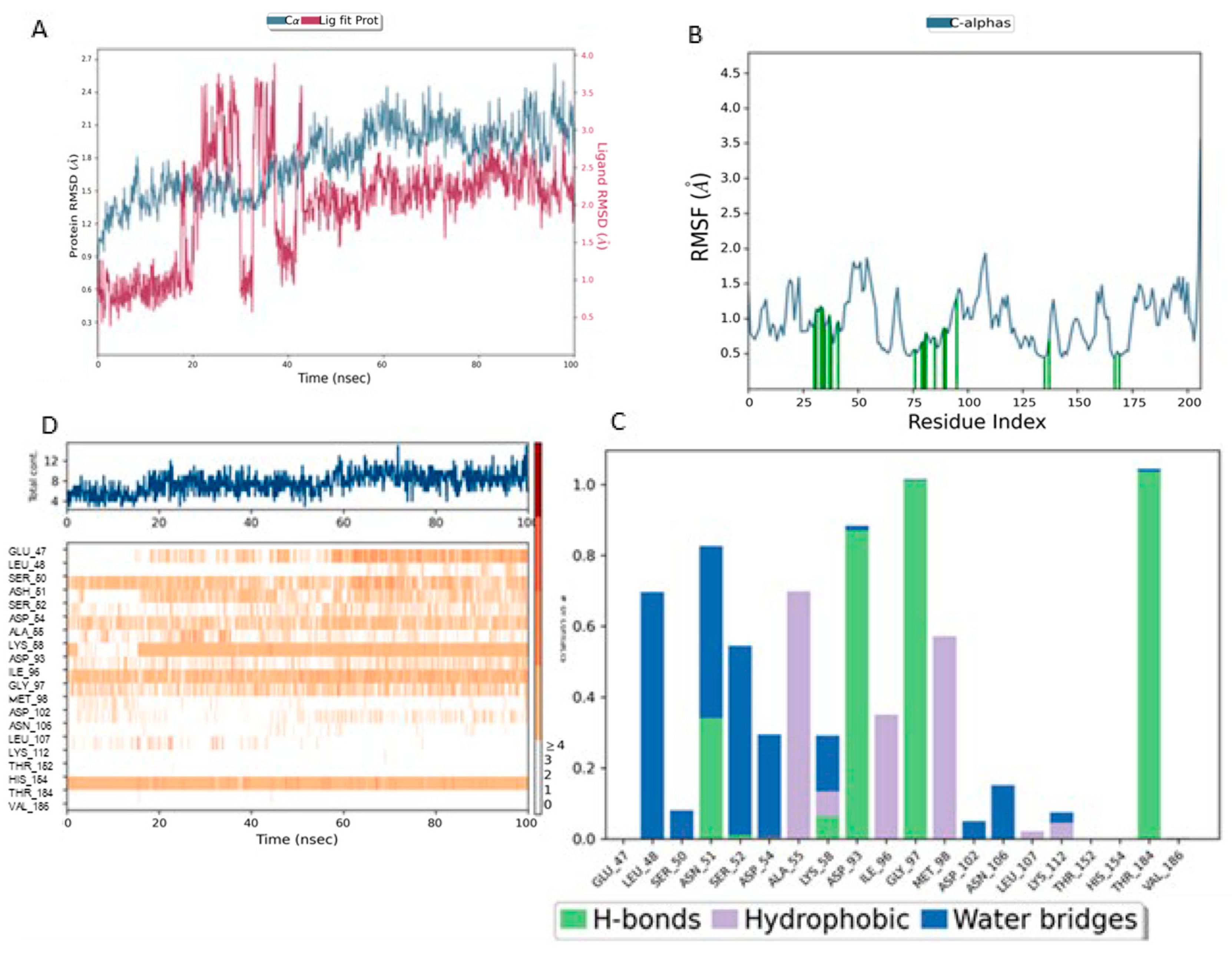
Figure 8 presents a detailed analysis of the molecular dynamics of the complex between Lig1 (Chlorogenic Acid) and the Hsp90 protein, highlighting its stability and key interactions. Plot (A) shows the evolution of the RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) of the protein (blue) and the ligand (red) over 100 ns. The RMSD of the protein fluctuates between 2 and 3.5 Å, indicating some flexibility, especially in specific regions. Meanwhile, the RMSD of the ligand remains more stable (~1–2 Å), suggesting that it stays well anchored in the active site without significantly disengaging.
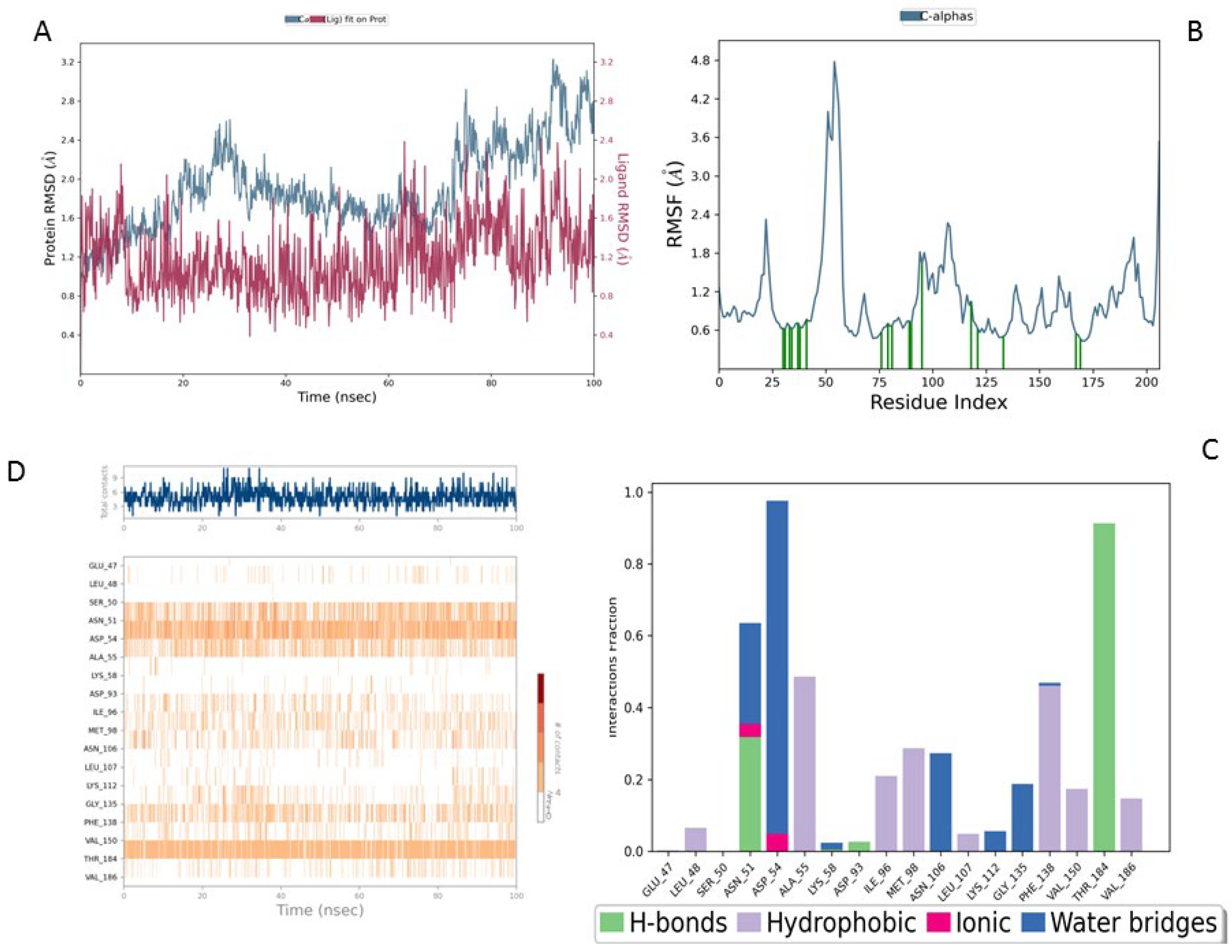
In comparison, the Lig2-HSP90 complex (
Figure 9A), representing Lig2 (Rosmanol) derived from Rosemary, shows improved stability, particularly for the ligand. The protein RMSD reaches similar values to the reference complex, with an oscillation between 1.2 and 2.8 Å over the 100 ns. However, the stability of the ligand is more pronounced, with fluctuations limited to a range below 1.6 Å, indicating a better fit in the binding cavity. This enhanced stability may reflect increased hydrophobic or hydrogen interactions, highlighting a potentially increased affinity compared to the MEY ligand.
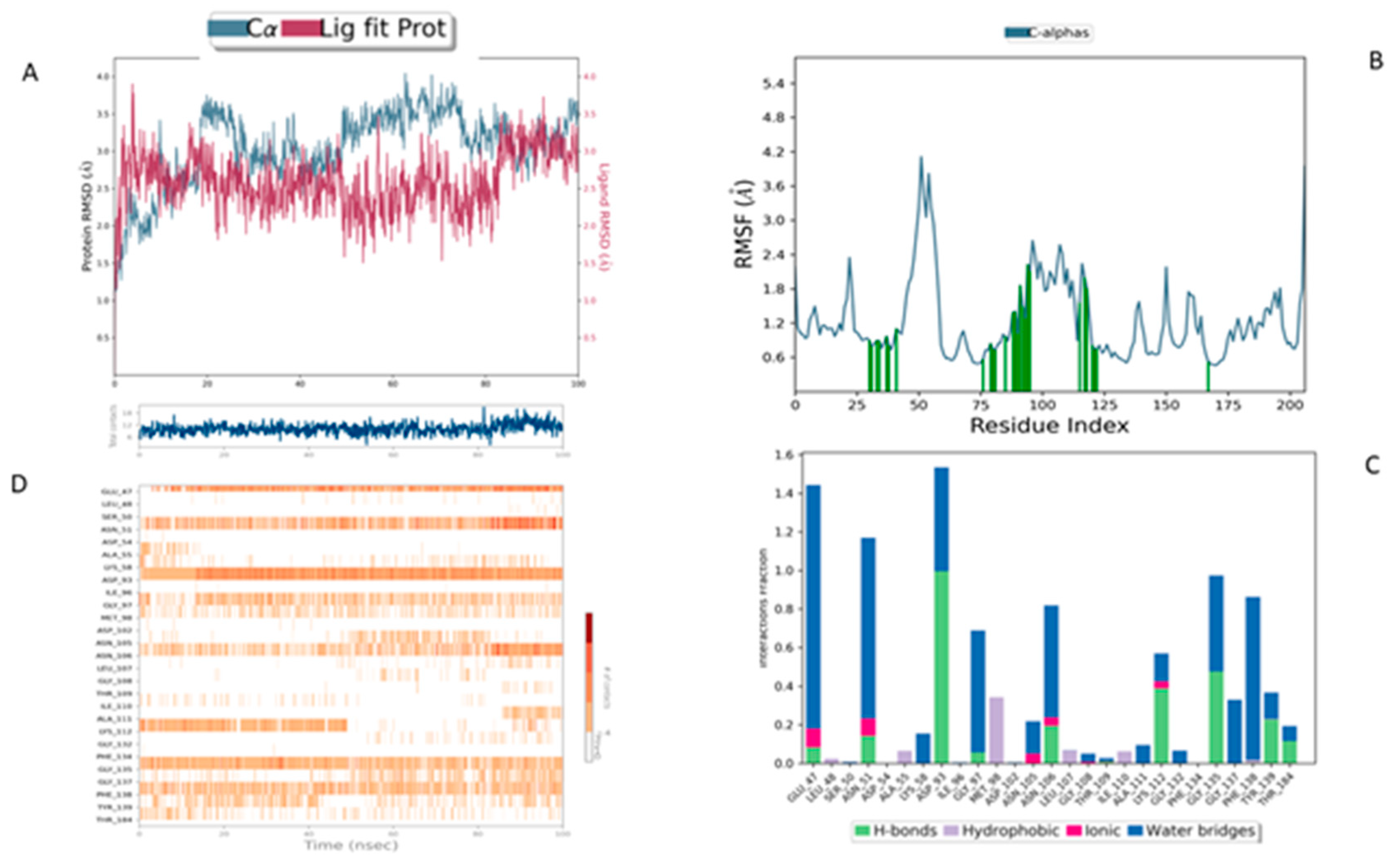
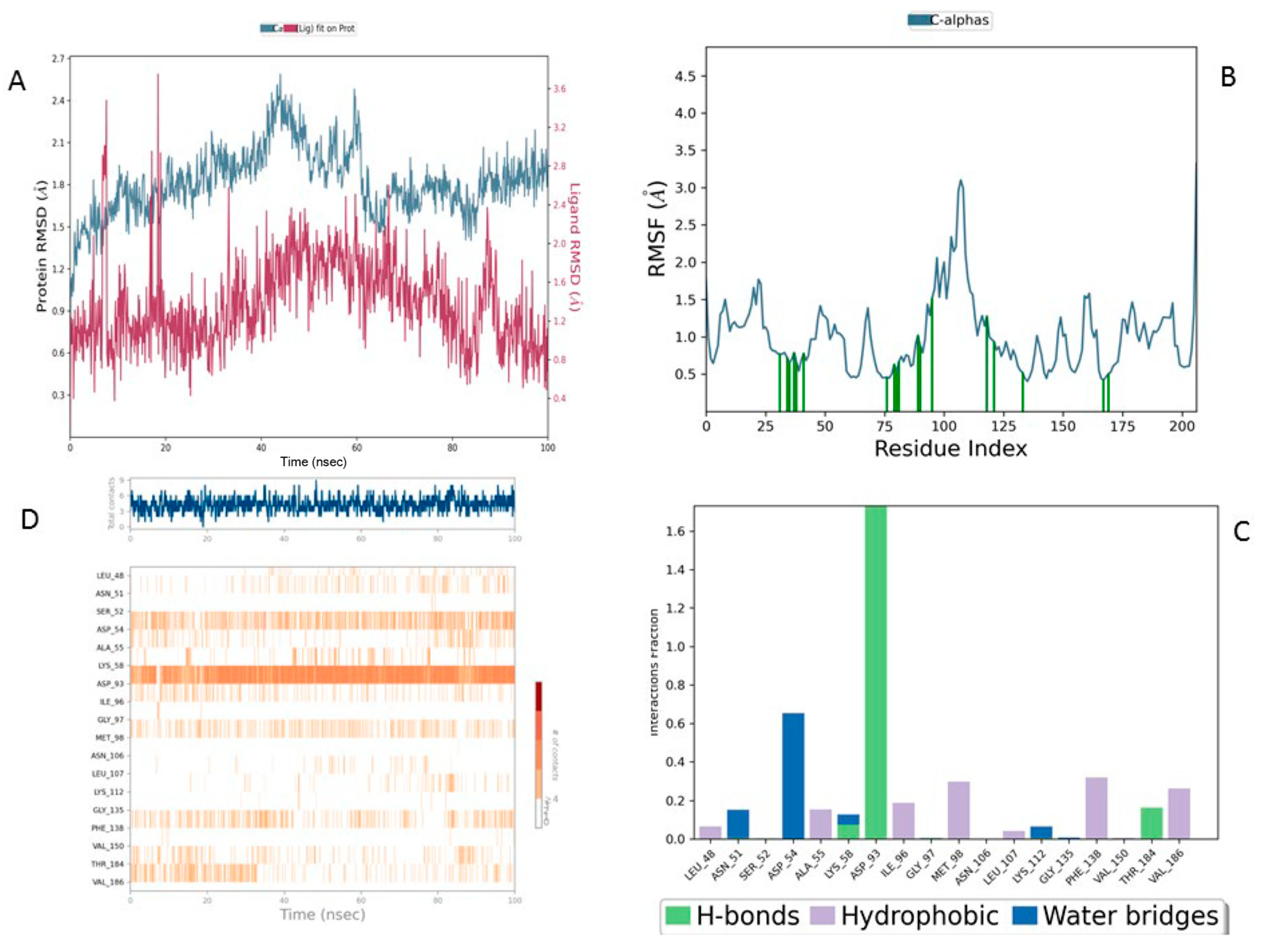
The Lig3-HSP90 complex (
Figure 10A), on the other hand, shows even more promising performance. The protein RMSD remains on average lower than that of the MEY-HSP90 and Lig2-HSP90 complexes, stabilizing around 2.1 Å after 50 ns. This overall stability suggests less perturbation of the protein structure, which may be beneficial for efficient interaction. The ligand, in turn, exhibits very low RMSD fluctuations, staying mostly below 1.6 Å. This enhanced stability could be attributed to additional specific interactions or better conformational compatibility with the active site of HSP90.
Overall, RMSD analysis confirms that all three R. officinalis compounds form structurally stable complexes with HSP90, with Lig3 showing the most consistent behavior. This high degree of stability is indicative of effective binding and supports its potential as a lead compound for further investigation. Following the RMSD analysis, we next examined the RMSF profiles to identify flexible and stable regions and to pinpoint key residues involved in ligand interactions.
The reference MEY–HSP90 complex (
Figure 7B) shows moderate overall stability, with fluctuations not exceeding 2.5 Å, indicating a relatively rigid backbone. Interaction analysis (
Figure 7C) reveals moderate involvement of residues such as Leu41 and Glu47, with interaction frequencies around 0.6 and 0.5, respectively. The contact heat map (
Figure 7D) displays a uniform interaction distribution with no concentrated hot spots, suggesting that while functional, the reference ligand may not fully optimize key binding interactions.
For the Lig1–HSP90 complex (
Figure 8B), the RMSF profile shows distinct flexibility peaks around residues 50–75 and 100–125, which likely correspond to loop regions involved in ligand accommodation. Residues highlighted in green represent direct ligand interactions, confirming their contribution to stabilizing the complex. Interaction frequency analysis (
Figure 8C) shows hydrophobic contacts (blue) as the dominant stabilizing force, complemented by stable hydrogen bonds (green) with Asn51, Ala55, Asp93, and Tyr139. Ionic and π–π stacking interactions (red and purple) further enhance binding affinity. The contact map (
Figure 8D) demonstrates a consistent 10–15 contacts throughout the simulation, indicating robust and sustained ligand binding.
The Lig2–HSP90 complex (
Figure 9B) displays slightly increased dynamic flexibility, with RMSF peaks reaching 4.8 Å at Asp54 and Val186, suggesting adaptive motion that may improve ligand accommodation. These residues also exhibit high interaction frequencies (~0.9 and 0.8) (
Figure 9C,D), and the heat map shows prominent hot spots, underscoring stronger ligand–protein affinity compared to the reference complex.
The Lig3–HSP90 complex (
Figure 10B) demonstrates superior overall performance. RMSFs remain low across most regions, except for Asp95 and Gly97, which show peaks of ~4.5 Å (
Figure 10C,D), indicating localized flexibility that may facilitate binding. These residues exhibit very high interaction frequencies (up to 1.6), highlighting their critical roles in ligand stabilization. The heat map confirms these observations, displaying dense clusters and well-defined hot spots, which illustrate enhanced stabilization and strong ligand–protein interactions.
Collectively, these findings show that Lig2 and Lig3 form stronger and more persistent interactions with HSP90 than the reference ligand. Together with the RMSD results, this confirms that rosemary-derived compounds form stable, specific, and dynamically favorable interactions with HSP90AA1 under near-physiological conditions, providing strong computational evidence of their potential as effective inhibitors.
Beyond the computational data presented above, rosemary-derived phytochemicals—rosmanol, carnosol, and chlorogenic acid—have been extensively reported for their anticancer activities in diverse cancer models. These compounds modulate key signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin, and p53/p21, leading to apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, inhibition of metastasis, and suppression of tumor progression. Evidence from numerous in vitro and in vivo studies provides strong biological context to our computational predictions and further supports the rationale for targeting HSP90AA1 with these natural compounds.
While rosmanol, carnosol, and chlorogenic acid are known phytochemicals with previously reported anticancer properties, the novelty of this study lies in its integrative computational approach and its specific focus on HSP90AA1 as a molecular target—a critical chaperone in oncogenic signaling that has not been systematically explored in relation to these compounds. Unlike previous studies, which primarily investigated their general anticancer effects, our work combines network pharmacology, molecular docking, ADMET profiling, and molecular dynamics simulations to provide a detailed mechanistic and structural rationale for their potential as multi-target HSP90 inhibitors. This holistic approach not only offers new insights into how dietary phytochemicals can modulate HSP90-driven cancer pathways but also lays a strong foundation for future experimental validation and translational research.