Side Effects and Interactions of the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Febuxostat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What is known from scientific publications with regard to side effects and interactions during treatment with the xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat?
- Febuxostat’s safety profile in comparison and contrast to allopurinol.
2. Results
2.1. Findings in Original Works and Secondary Analyses
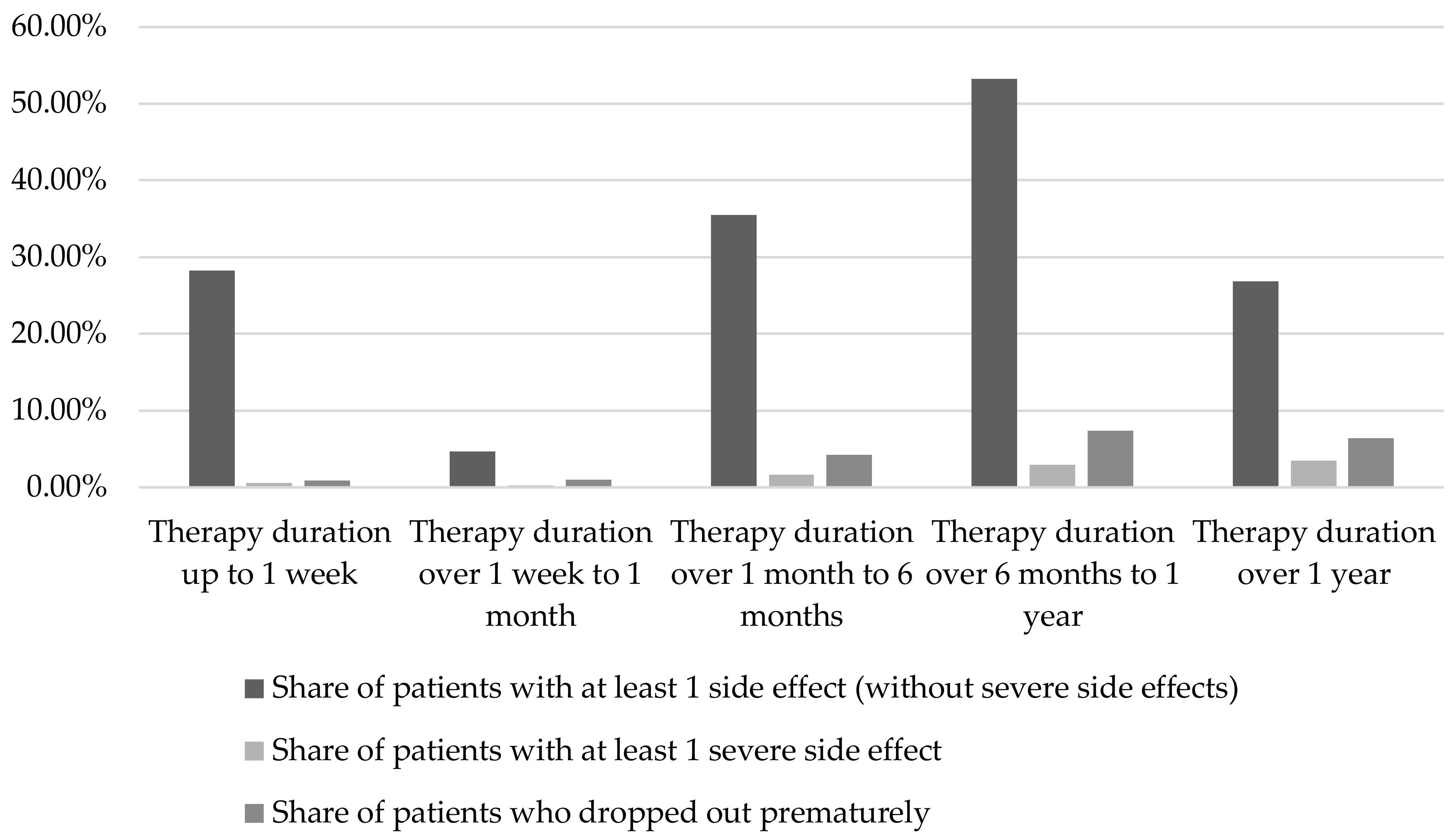
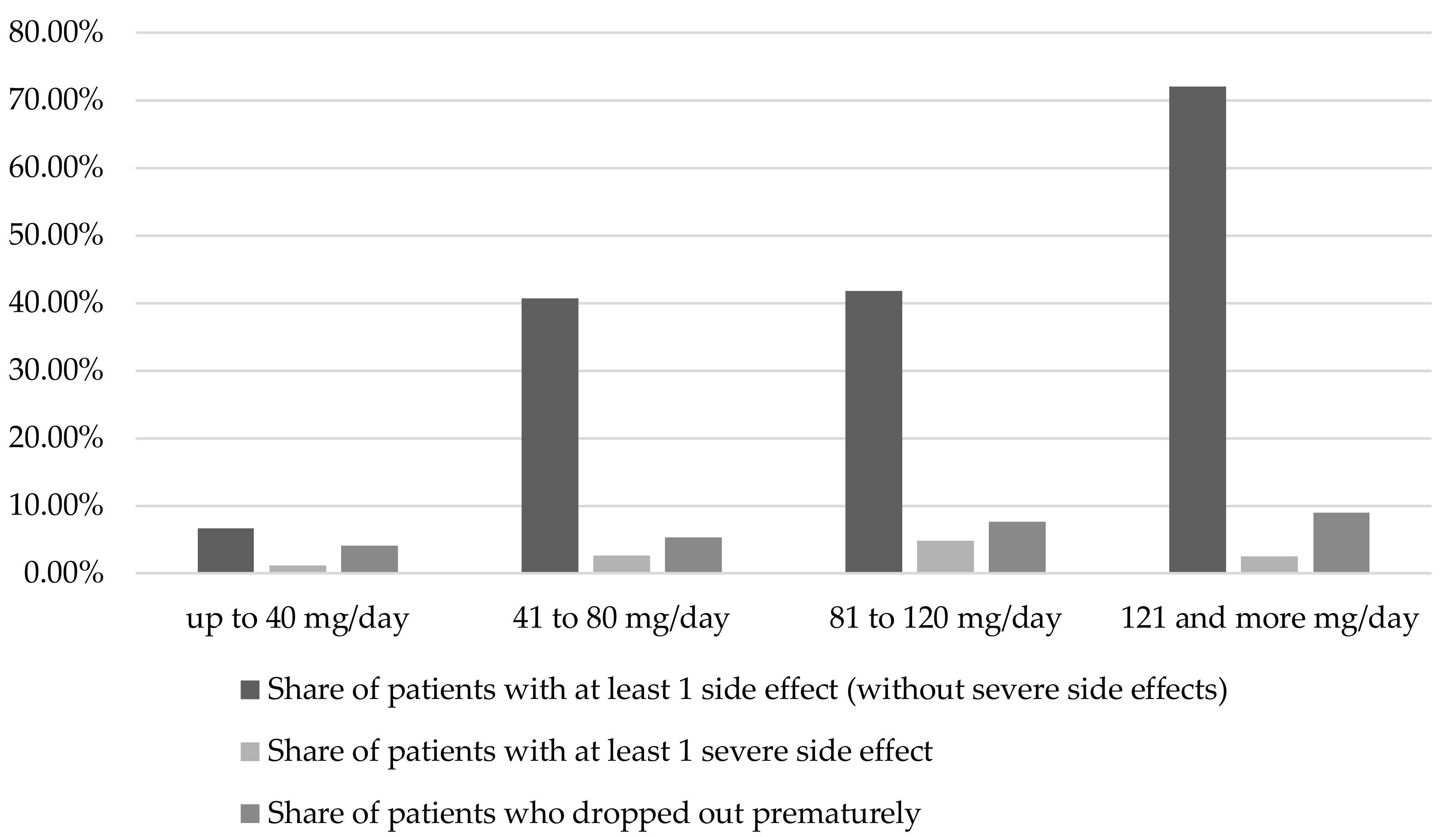
2.1.1. Duration of therapy and dosage
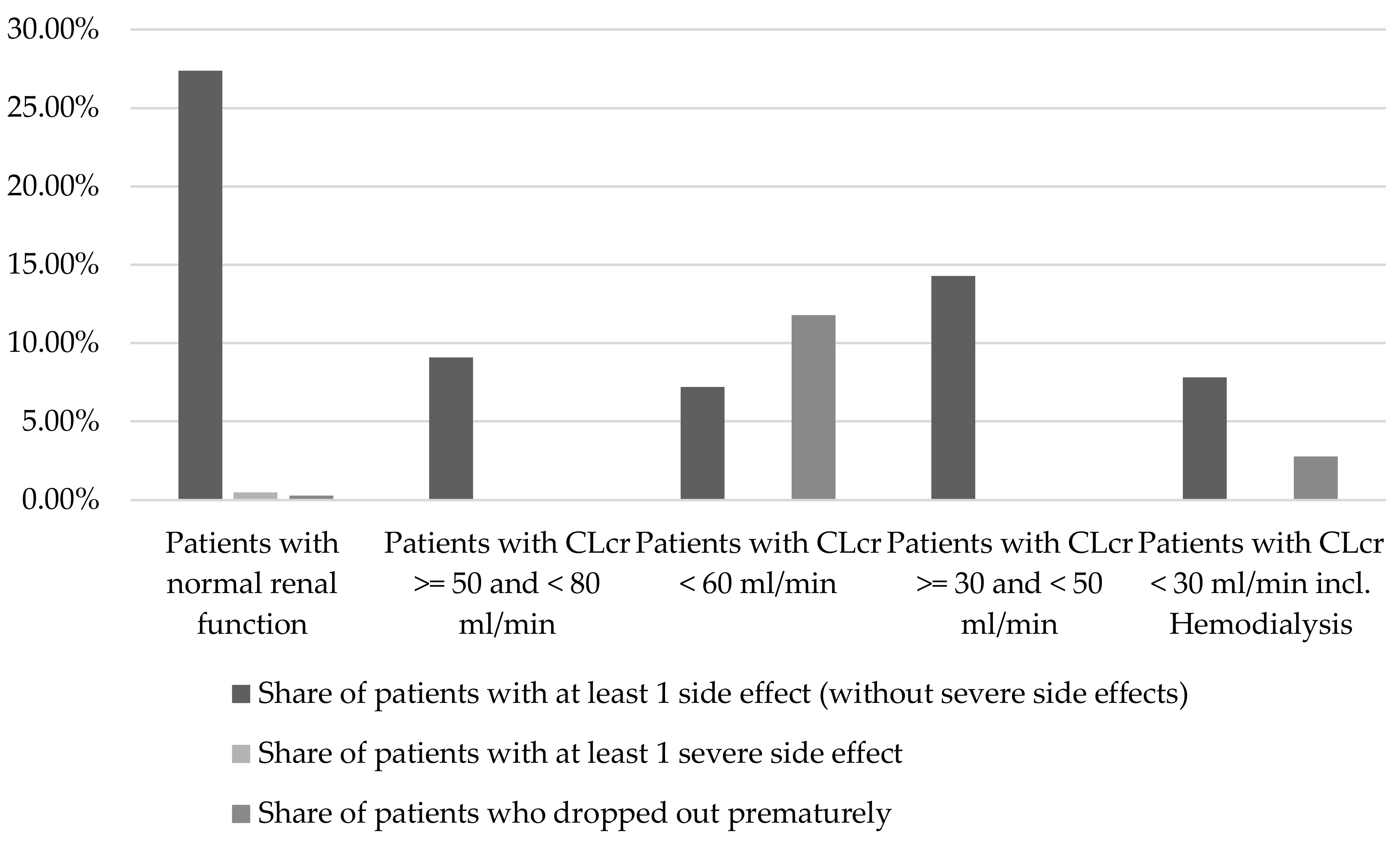
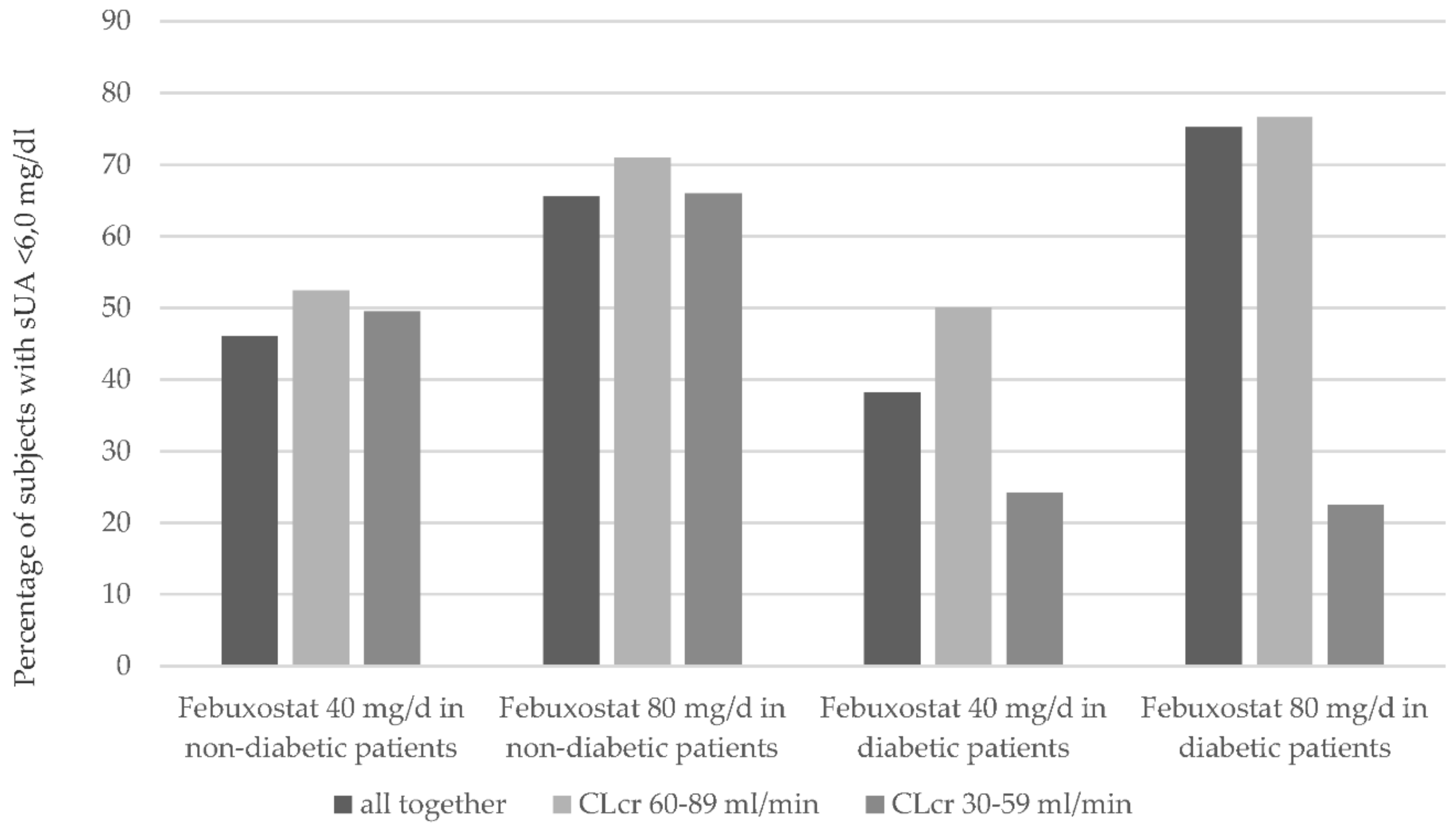
2.1.2. Renal Function
2.1.3. Liver Function
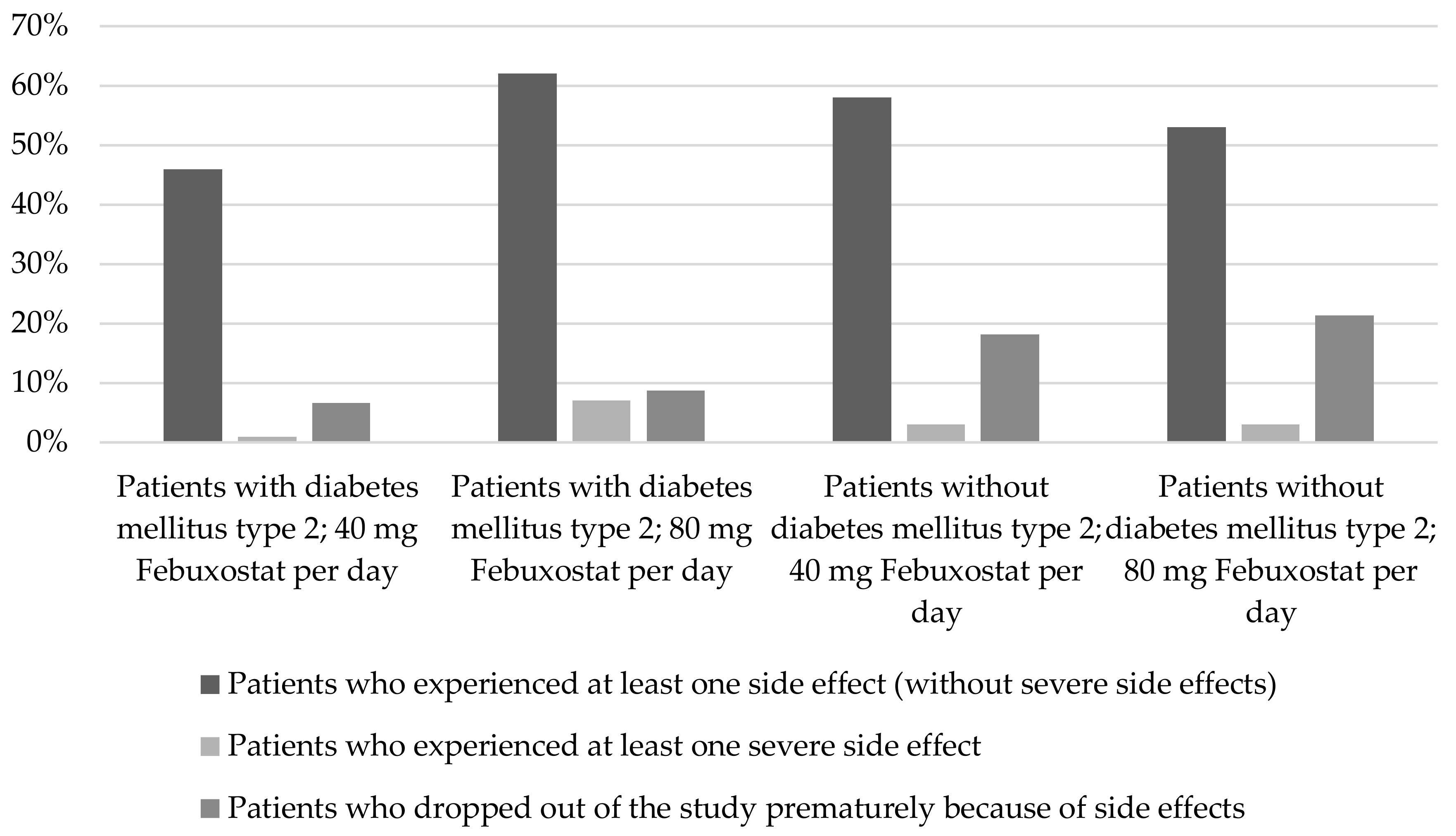
2.1.4. Diabetes mellitus type 2
2.1.5. Age Dependency
2.1.6. Pre-existing Allopurinol Intolerance
2.1.7. Combination of Febuxostat with NSAIDs
2.1.8. Combination of Febuxostat with Hydrochlorothiazide
2.1.9. Combination of Febuxostat with Uricosuric Drugs
2.1.10. Combination of Febuxostat with Azathioprine
2.1.11. Combination of Febuxostat with Theophylline
2.2. Findings of the Case Reports
2.2.1. Skin Reactions and DRESS Syndrome
2.2.2. Rhabdomyolysis
2.2.3. Agranulocytosis
2.2.4. Glomerulonephritis
2.2.5. Acute Liver Disease
3. Discussion
3.1. Renal Function
3.2. Liver Function
3.3. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
3.4. Age Dependence
3.5. Pre-Existing Allopurinol Intolerance
3.6. Combination of Febuxostat with NSAIDs
3.7. Combination of Febuxostat with Hydrochlorothiazide
3.8. Combination of Febuxostat with Uricosuric Drugs
3.9. Combination of Febuxostat with Azathioprine
3.10. Skin Reactions and DRESS Syndrome
3.11. Rhabdomyolysis
3.12. Agranulocytosis
3.13. Glomerulonephritis
3.14. Acute Liver Disease
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Number of Patients with Febuxostat Therapy | Number of Patients with at Least One Side Effect (Share in %) | Number of Patients with at Least One Severe Side Effect (Share in %) | Number of Patients to Drop out Prematurely (Share in %) | Number of Patients Who Died (Share in %) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 154 | 60 (38.9) | 0 | 9 (5.8) | 0 | [26] |
| 15 | 1 (6.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [23] |
| 507 | 123 (24.3) | 32 (6.3) | 39 (7.7) | 0 | [8] |
| 115 | 14 (12.2) | 3 (2.6) | 5 (4.3) | 0 | [49] |
| 32 | 10 (31.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [22] |
| 28 | 14 (50.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [50] |
| 118 | 57 (48.3) | 0 | 10 (8.5) | 0 | [51] |
| 51 | 9 (17.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [52] |
| 92 | 26 (28.3) | 2 (2.2) | 3 (3.3) | 0 | [20] |
| 48 | 21 (43.8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [21] |
| 670 | 462 (69.0) | 25 (3.7) | 61 (9.1) | 0 | [9] |
| 116 | 106 (91.0) | 0 | 13 (11.2) | 0 | [10] |
| 1513 | 839 (55.5) | 47 (3.1) | 110 (7.3) | 0 | [11] |
| 34 | 14 (41.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [12] |
| 13 | 1 (7.7) | 1 (7.7) | 0 | 0 | [32] |
| 6 | 3 (50.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [18] |
| 29 | 3 (10.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [17] |
| 20 | 8 (40.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [45] |
| 122 | 10 (8.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [46] |
| 171 | 63 (36.8) | 0 | 6 (3.5) | 0 | [47] |
| 161 | 39 (24.2) | 1 (0.6) | 0 | 0 | [48] |
| 69 | 11 (15.9) | 0 | 1 (1.5) | 0 | [13] |
| 39 | 12 (30.8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [25] |
| 12 | 2 (16.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [24] |
| 33 | 20 (60.6) | 0 | 2 (6.1) | 0 | [36] |
| 17 | 5 (29.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [37] |
| 100 | 1 (1.0) | 0 | 2 (2.0) | 0 | [27] |
| 344 | 113 (32.8) | 0 | 21 (6.1) | 0 | [41] |
| 38 | 1 (2.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [53] |
| 82 | 10 (12.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [33] |
| 70 | 5 (7.1) | 0 | 4 (5.7) (included in pat. with ≥ 1 side effect) | 0 | [14] |
| 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | [43] |
| 5948 | 152 (2.6) | 15 (0.25) | 36 (0.6) | 0 | [2] |
| 22 | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 0 | 0 | [42] |
| 151 | 6 (4.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [34] |
| 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | [19] |
| 51 | 5 (9.8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [29] |
| 45 | 2 (4.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [38] |
| 336 | 91 (27.1) | 1 (0.3) | 6 (1.8) | 0 | [35] |
| 89 | 33 (37.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [30] |
| 101 | 4 (4.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | [28] |
| 160 | 27 (16.9) | 0 | 5 (3.1) | 0 | [39] |
| 294 | 18 (6.1) | 0 | 7 (2.4) | 0 | [44] |
| 83 | 0 | 0 | 6 (7.2) | 0 | [40] |
| 64 | 53 (82.8) | 13 (20.3) | 8 (12.5) | 1 (1.6) | [15] |
| 54 | 8 (14.8) | 2 (3.7) | 0 | 0 | [31] |
| 12,279 | 2462 (20.1) | 143 (1.2) | 354 (2.9) | 1 (0.008) | TOTAL |
Appendix B
| Number of Patients with Febuxostat Therapy | Number of Patients with at Least One Side Effect (Share in %) | Number of Patients with at Least One Severe Side Effect (Share in %) | Number of Patients to Drop Out Prematurely (Share in %) | Number of Patients Who Died (Share in %) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1513 | ND | 49 (3.2) | ND | 2 (0.7) | [57] |
| 116 | 106 (91.0) | 21 (18.0) | 13 (11.2) | 0 | [100] |
| 137 | 100 (71.9) | 9 (6.5) | ND | 1 (0.7) | [101] |
| 243 | 145 (59.7) | 17 (7.0) | 34 (14.0) | 0 | [102] |
| 1399 | 770 (55.0) | 44 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | [103] |
| 1462 | 812 (55.5) | 47 (3.2) | ND | 0 | [56] |
| 4870 | 1933 (39.7) | 187 (3.8) | 47 (1.0) | 3 (0.06) | Total |
References
- Tausche, A.-K.; Jansen, T.L.; Schroder, H.-E.; Bornstein, S.R.; Aringer, M.; Muller-Ladner, U. Gout—Current diagnosis and treatment. Deutsches Ärzteblatt Int. 2009, 106, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tausche, A.-K.; Reuss-Borst, M.; Koch, U. Urate lowering therapy with febuxostat in daily practice—A multicentre, open-label, prospective observational study. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 2014, 123105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, N.L. Febuxostat: A new treatment for hyperuricaemia in gout. Rheumatology 2009, 48 (Suppl. 2), ii15–ii19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiekermann, S. Electron spin resonance characterization of vascular xanthine and NAD(P)H oxidase activity in patients with coronary artery disease: Relation to endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Circulation 2003, 107, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.R.; Darley-Usmar, V.; Berrington, W.R.; McAdams, M.; Gore, J.Z.; Thompson, J.A.; Parks, D.A.; Tarpey, M.M.; Freeman, B.A. Circulating plasma xanthine oxidase contributes to vascular dysfunction in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8745–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, C.; Kilcoyne, C.M.; Cannon, R.O., 3rd; Quyyumi, A.A.; Panza, J.A. Xanthine oxidase inhibition with oxypurinol improves endothelial vasodilator function in hypercholesterolemic but not in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1997, 30 Pt 1, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tausche, A.-K.; Christoph, M.; Forkmann, M.; Richter, U.; Kopprasch, S.; Bielitz, C.; Aringer, M.; Wunderlich, C. As compared to allopurinol, urate-lowering therapy with febuxostat has superior effects on oxidative stress and pulse wave velocity in patients with severe chronic tophaceous gout. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Schumacher, H.R., Jr.; Wortmann, R.L.; MacDonald, P.A.; Eustace, D.; Palo, W.A.; Streit, J.; Joseph-Ridge, N. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2450–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, H.R.; Becker, M.A.; Wortmann, R.L.; MacDonald, P.A.; Hunt, B.; Streit, J.; Lademacher, C.; Joseph-Ridge, N. Effects of febuxostat versus allopurinol and placebo in reducing serum urate in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout: A 28-week, phase III, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, H.R.; Becker, M.A.; Lloyd, E.; MacDonald, P.A.; Lademacher, C. Febuxostat in the treatment of gout: 5-yr findings of the FOCUS efficacy and safety study. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Schumacher, H.R.; Espinoza, L.R.; Wells, A.F.; MacDonald, P.; Lloyd, E.; Lademacher, C. The urate-lowering efficacy and safety of febuxostat in the treatment of the hyperuricemia of gout: The CONFIRMS trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, B.; Khosravan, R.; Wu, J.-T.; Vernillet, L.; Lademacher, C. Effect of hydrochlorothiazide on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat, a non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 70, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, N.; Fujimori, S.; Hada, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kohri, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Matsuzawa, Y. Placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the non-purine-selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor Febuxostat (TMX-67) in patients with hyperuricemia including those with gout in Japan: Phase 3 clinical study. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17 (Suppl. 2), S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibagaki, Y.; Ohno, I.; Hosoya, T.; Kimura, K. Safety, efficacy and renal effect of febuxostat in patients with moderate-to-severe kidney dysfunction. Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 37, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saag, K.G.; Whelton, A.; Becker, M.A.; MacDonald, P.; Hunt, B.; Gunawardhana, L. Impact of febuxostat on renal function in gout patients with moderate-to-severe renal impairment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, W.B.; Saag, K.G.; Becker, M.A.; Borer, J.S.; Gorelick, P.B.; Whelton, A.; Hunt, B.; Castillo, M. Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat or Allopurinol in Patients with Gout. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, T.; Ohno, I. A repeated oral administration study of febuxostat (TMX-67), a non-purine-selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in patients with impaired renal function in Japan: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17 (Suppl. 2), S27–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, B.A.; Khosravan, R.; Vernillet, L.; Mulford, D.J. Metabolism and excretion of 14C febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in healthy male subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Di, X.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Song, L.; Xu, X. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat under fasting conditions in healthy individuals. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, R.; Grabowski, B.; Wu, J.-T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Vernillet, L. Effect of food or antacid on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, R.; Kukulka, M.J.; Wu, J.-T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Vernillet, L. The effect of age and gender on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 48, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.D.; Khosravan, R.; Vernillet, L.; Wu, J.-T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Mulford, D.J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat, a new non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase in subjects with renal impairment. Am. J. Ther. 2005, 12, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshide, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Kubo, J.; Tsuchimoto, M.; Komoriya, K.; Ohno, I.; Hosoya, T. PK/PD and safety of a single dose of TMX-67 (febuxostat) in subjects with mild and moderate renal impairment. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.; Wu, J.-T.; Gunawardhana, L.; Naik, H. The effects of xanthine oxidase inhibition by febuxostat on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 50, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, H.; Wu, J.-T.; Palmer, R.; McLean, L. The effects of febuxostat on the pharmacokinetic parameters of rosiglitazone, a CYP2C8 substrate. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Kisicki, J.; Khosravan, R.; Wu, J.; Mulford, D.; Hunt, B.; MacDonald, P.; Joseph-Ridge, N. Febuxostat (TMX-67), a novel, non-purine, selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, is safe and decreases serum urate in healthy volunteers. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramitsu, S.; Ishiguro, Y.; Matsuyama, H.; Yamada, K.; Kato, K.; Noba, M.; Uemura, A.; Matsubara, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Kani, A.; et al. Febuxostat (Feburic tablet) in the management of hyperuricemia in a general practice cohort of Japanese patients with a high prevalence of cardiovascular problems. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2014, 36, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, T.; Chales, G.; Pascart, T.; Flipo, R.-M.; Korng Ea, H.; Roujeau, J.-C.; Delayen, A.; Clerson, P. Risk of cutaneous adverse events with febuxostat treatment in patients with skin reaction to allopurinol. A retrospective, hospital-based study of 101 patients with consecutive allopurinol and febuxostat treatment. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, D.; Chisaki, Y.; Noda, S.; Araki, H.; Uzu, T.; Maegawa, H.; Yano, Y.; Morita, S.-Y.; Terada, T. Population pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of febuxostat in patients with severe renal impairment. Pharmacology 2015, 96, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Hidaka, Y.; Inaba, M.; Ishimura, E.; Ooyama, H.; Kakuta, H.; Moriwaki, Y.; Higami, K.; Ohtawara, A.; Hosoya, T.; et al. Effects of febuxostat on serum urate level in Japanese hyperuricemia patients. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.-H.; Lai, J.-H.; Hsu, P.-N.; Chen, D.-Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Lin, H.-Y. Safety and efficacy of oral febuxostat for treatment of HLA-B*5801-negative gout: A randomized, open-label, multicentre, allopurinol-controlled study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chohan, S. Safety and efficacy of febuxostat treatment in subjects with gout and severe allopurinol adverse reactions. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 1957–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Hayashi, T.; Hikosaka, S.; Shimabukuro, Y.; Murase, M.; Takahashi, K.; Hayashi, H.; Yuzawa, Y.; Nagamatsu, T.; Yamada, S. Efficacy and safety of febuxostat in elderly female patients. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.S.; Ng, S.P.; Kuo, L.H.; Chien, S.Y. The effectiveness and safety of febuxostat: An experience in medical center in Taiwan. Value Health 2014, 17, A776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Ming, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, J.; et al. A phase 3, multicenter, randomized, allopurinol-controlled study assessing the safety and efficacy of oral febuxostat in Chinese gout patients with hyperuricemia. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, D.S.; MacDonald, P.A.; Gunawardhana, L.; Chefo, S.; McLean, L. Randomized controlled trial of febuxostat versus allopurinol or placebo in individuals with higher urinary uric acid excretion and calcium stones. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, T.; Morishita, Y.; Ito, C.; Iimura, O.; Tsunematsu, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Kusano, E.; Nagata, D. Febuxostat for hyperuricemia in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Drug Target Insights 2014, 8, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sircar, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Waikhom, R.; Golay, V.; Raychaudhury, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Pandey, R. Efficacy of febuxostat for slowing the GFR decline in patients with CKD and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: A 6-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Antoku, S.; Abe, M.; Omoto, T.; Shinozaki, M.; Nishio, S.; Mifune, M.; Togane, M.; Nakata, M.; Yamashita, T. Comparison of the renoprotective effect of febuxostat for the treatment of hyperuricemia between patients with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective observational study. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 3247–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilis, N.; Andres, M.; Gil, S.; Ranieri, L.; Vela, P.; Pascual, E. Febuxostat for patients with gout and severe chronic kidney disease: Which is the appropriate dosage? Comment on the article by Saag et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2563–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Du, H.; Gu, J.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Zuo, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; et al. An allopurinol-controlled, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel between-group, comparative study of febuxostat in Chinese patients with gout and hyperuricemia. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojimbara, T.; Nakajima, I.; Yashima, J.; Fuchinoue, S.; Teraoka, S. Efficacy and safety of febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase for the treatment of hyperuricemia in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofue, T.; Inui, M.; Hara, T.; Nishijima, Y.; Moriwaki, K.; Hayashida, Y.; Ueda, N.; Nishiyama, A.; Kakehi, Y.; Kohno, M. Efficacy and safety of febuxostat in the treatment of hyperuricemia in stable kidney transplant recipients. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.-H.; Oh, J.S.; Ahn, S.M.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; Choi, S.W.; Yoo, B. Febuxostat in hyperuricemic patients with advanced CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 819–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, N.; Fujimori, S.; Hada, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kohri, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Matsuzawa, Y. An allopurinol-controlled, multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel between-group, comparative study of febuxostat (TMX-67), a non-purine-selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in patients with hyperuricemia including those with gout in Japan: Phase 2 exploratory clinical study. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17 (Suppl. 2), S44–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, N.; Fujimori, S.; Hada, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kohri, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Matsuzawa, Y. An allopurinol-controlled, randomized, double-dummy, double-blind, parallel between-group, comparative study of febuxostat (TMX-67), a non-purine-selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in patients with hyperuricemia including those with gout in Japan: Phase 3 clinical study. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17 (Suppl. 2), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, N.; Fujimori, S.; Hada, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kohri, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Matsuzawa, Y. Multicenter, open-label study of long-term administration of febuxostat (TMX-67) in Japanese patients with hyperuricemia including gout. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17 (Suppl. 2), S50–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, N.; Fujimori, S.; Hada, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kohri, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Matsuzawa, Y. Placebo-controlled double-blind dose-response study of the non-purine-selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat (TMX-67) in patients with hyperuricemia (including gout patients) in japan: Late phase 2 clinical study. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17 (Suppl. 2), S35–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Schumacher, H.R., Jr.; Wortmann, R.L.; MacDonald, P.A.; Palo, W.A.; Eustace, D.; Vernillet, L.; Joseph-Ridge, N. Febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: A twenty-eight-day, multicenter, phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response clinical trial examining safety and efficacy in patients with gout. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, R.; Grabowski, B.A.; Mayer, M.D.; Wu, J.-T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Vernillet, L. The effect of mild and moderate hepatic impairment on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, R.; Grabowski, B.A.; Wu, J.-T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Vernillet, L. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of febuxostat, a non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in a dose escalation study in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, R.; Wu, J.-T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Vernillet, L. Pharmacokinetic interactions of concomitant administration of febuxostat and NSAIDs. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maie, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kurita, N.; Minohara, H.; Yanagimoto, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Homma, M.; Chiba, S. Hypouricemic effect and safety of febuxostat used for prevention of tumor lysis syndrome. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Schumacher, H.R.; MacDonald, P.A.; Lloyd, E.; Lademacher, C. Clinical efficacy and safety of successful longterm urate lowering with febuxostat or allopurinol in subjects with gout. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmorski, S.; Doares, W.; Winfrey, S.; Al-Geizawi, S.; Farney, A.; Rogers, J.; Stratta, R. Gout and transplantation: New treatment option–Same old drug interaction. Transplantation 2011, 92, e13–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; MacDonald, P.A.; Hunt, B.J.; Jackson, R.L. Diabetes and gout: Efficacy and safety of febuxostat and allopurinol. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; MacDonald, P.A.; Hunt, B.; Gunawardhana, L. Treating hyperuricemia of gout: Safety and efficacy of febuxostat and allopurinol in older versus younger subjects. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2011, 30, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Kerr, B.; Yeh, L.-T.; Suster, M.; Shen, Z.; Polvent, E.; Hingorani, V.; Quart, B.; Manhard, K.; Miner, J.N.; et al. Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and tolerability evaluation of concomitant administration of lesinurad and febuxostat in gout patients with hyperuricaemia. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, A.S.; Vince, B.D.; Choi, Y.-J.; Martin, R.L.; McWherter, C.A.; Boudes, P.F. The pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and safety of arhalofenate in combination with febuxostat when treating hyperuricemia associated with gout. J. Rheumatol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, M.; Frenette, A.J.; Mansour, A.-M.; Troyanov, Y.; Begin, J. Febuxostat as a novel option to optimize thiopurines’ metabolism in patients with inadequate metabolite levels. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeles, A.M. Febuxostat hypersensitivity. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laura, A.; Luca, P.; Luisa, P.A. Interstitial granulomatous drug reaction due to febuxostat. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2014, 80, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Sawada, Y.; Ohmori, S.; Omoto, D.; Haruyama, S.; Yoshioka, M.; Nishio, D.; Nakamura, M. Fixed drug eruption-like macules caused by febuxostat. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2016, 26, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-B.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-A.; Ng, C.Y.; Kuo, K.-L.; Chen, W.-L.; Chen, C.-H. Febuxostat-associated drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschou, E.; Gavriilaki, E.; Papaioannou, G.; Tsompanakou, A.; Kalaitzoglou, A.; Sabanis, N. Febuxostat hypersensitivity: Another cause of DRESS syndrome in chronic kidney disease? Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 48, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lien, Y.-H.H.; Logan, J.L. Cross-reactions between allopurinol and febuxostat. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, e67–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Jang, H.N.; Bae, E.J.; Yun, S.; Cho, H.S.; Chang, S.-H.; Park, D.J. Rhabdomyolysis associated with initiation of febuxostat therapy for hyperuricaemia in a patient with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; McGann, P.M.; Furlong, T.J.; Day, R.O. Febuxostat-associated rhabdomyolysis in chronic renal failure. Med. J. Aust. 2015, 203, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahine, G.; Saleh, K.; Ghorra, C.; Khoury, N.; Khalife, N.; Fayad, F. Febuxostat-associated eosinophilic polymyositis in marginal zone lymphoma. Jt. Bone Spine 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ogura, M.; Hosoya, T. Acute neutropenia associated with initiation of febuxostat therapy for hyperuricaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzedine, H.; Boulanger, H.; Gueutin, V.; Rouvier, P.; Deray, G. ANCA-positive pauci-immune glomerulonephritis and febuxostat treatment. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, M.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Chalasani, N. Febuxostat-induced acute liver injury. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrejon, I.; Toledano, E.; Rosario, M.P.; Loza, E.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Carmona, L. Safety of allopurinol compared with other urate-lowering drugs in patients with gout: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, R.; Kydd, A.S.R.; Buchbinder, R.; Bombardier, C.; Edwards, C.J. Allopurinol for chronic gout. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 10, CD006077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruque, L.I.; Ehteshami-Afshar, A.; Wiebe, N.; Tjosvold, L.; Homik, J.; Tonelli, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the safety and efficacy of febuxostat versus allopurinol in chronic gout. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardhana, L.; McLean, L.; Punzi, H.A.; Hunt, B.; Palmer, R.N.; Whelton, A.; Feig, D.I. Effect of Febuxostat on Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Subjects With Hyperuricemia and Hypertension: A Phase 2 Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wei, F.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Li, W.; Sun, L.; et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of urate-lowering therapy for the treatment of hyperuricemia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markel, A. Allopurinol-induced DRESS syndrome. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 7, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Stamp, L. Allopurinol dosing in renal impairment: Walking the tightrope between adequate urate lowering and adverse events. Semin. Dial. 2007, 20, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Veronesi, M.; Borghi, C. An evidence-based review on urate-lowering treatments: Implications for optimal treatment of chronic hyperuricemia. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, C.H.; Kim, H.; Yang, W.S.; Han, D.J.; Park, S.-K. Efficacy and Safety of Febuxostat in Kidney Transplant Patients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratiopharm GmbH. Fachinformation zu “Allopurinol-ratiopharm 100/300 mg Tabletten”. 2016. Available online: http://www.ratiopharm.de/index.php?eID=dumpFile&t=f&f=70732&g=-1&r=1894%2C1894&token=38cd525615b9b72e43152a6306fbb025793a5c41 (accessed on 5 March 2017).
- Berlin-Chemie, A.G. Fachinformation Adenuric. 2017. Available online: http://www.fachinfo.de/pdf/012335 (accessed on 18 March 2017).
- Pea, F. Pharmacology of drugs for hyperuricemia. Mechanisms, kinetics and interactions. Contrib. Nephrol. 2005, 147, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A.; Jordan, K.M. Use of febuxostat in the management of gout in the United Kingdom. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2017, 9, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Terkeltaub, R. A critical reappraisal of allopurinol dosing, safety, and efficacy for hyperuricemia in gout. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2009, 11, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Ruiz, F.; Sundy, J.S.; Miner, J.N.; Cravets, M.; Storgard, C. Lesinurad in combination with allopurinol: Results of a phase 2, randomised, double-blind study in patients with gout with an inadequate response to allopurinol. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, T.; Keenan, R.T.; Khanna, P.P.; Kopicko, J.; Fung, M.; Bhakta, N.; Adler, S.; Storgard, C.; Baumgartner, S.; So, A. Lesinurad in combination with allopurinol: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with gout with inadequate response to standard of care (the multinational CLEAR 2 study). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, L.K.; Jordan, S. The challenges of gout management in the elderly. Drugs Aging 2011, 28, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearry, R.B.; Day, A.S.; Barclay, M.L.; Leong, R.W.L.; Sparrow, M.P. Azathioprine and allopurinol: A two-edged interaction. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Chang, M.-T.; Chiu, H.-C. Colchicine-induced acute myopathy in a patient with concomitant use of simvastatin. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2002, 25, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.K.; Goodwin, S.; Sur, M.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Cytoskeletal myotoxicity from simvastatin and colchicine. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alayli, G.; Cengiz, K.; Canturk, F.; Durmus, D.; Akyol, Y.; Menekse, E.B. Acute myopathy in a patient with concomitant use of pravastatin and colchicine. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005, 39, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoyu, E.M.; Evrenkaya, T.R.; Solmazgul, E. Possible colchicine rhabdomyolysis in a fluvastatin-treated patient. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005, 39, 1368–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufan, A.; Dede, D.S.; Cavus, S.; Altintas, N.D.; Iskit, A.B.; Topeli, A. Rhabdomyolysis in a patient treated with colchicine and atorvastatin. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006, 40, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarullo, F.M.; Americo, L.; Di Franco, A.; Di Pasquale, P. Rhabdomyolysis induced by co-administration of fluvastatin and colchicine. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2010, 74, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, Y.Y.; Yao Hui, L.L.; Kraus, V.B. Colchicine—Update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, P.-H.; Lin, F.-Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J. Risk of Febuxostat-Associated Myopathy in Patients with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, J.Z.; Wallace, S.L. The allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome. Unnecessary morbidity and mortality. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, A.; MacDonald, P.A.; Zhao, L.; Hunt, B.; Gunawardhana, L. Renal function in gout: Long-term treatment effects of febuxostat. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chohan, S.; Becker, M.A.; MacDonald, P.A.; Chefo, S.; Jackson, R.L. Women with gout: Efficacy and safety of urate-lowering with febuxostat and allopurinol. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2012, 64, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.L.; Hunt, B.; MacDonald, P.A. The efficacy and safety of febuxostat for urate lowering in gout patients >= 65 years of age. BMC Geriatr. 2012, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, A.F.; MacDonald, P.A.; Chefo, S.; Jackson, R.L. African American patients with gout: Efficacy and safety of febuxostat vs allopurinol. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of Patients with Febuxostat Therapy | Liver Function | Number of Patients with at Least One Side Effect (Share in %) | Number of Patients with at Least One Severe Side Effect (Share in %) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | Normal | 3 (25.0) | 0 | [50] |
| 8 | Mildly limited | 5 (63.0) | 0 | |
| 8 | Moderately limited | 6 (75.0) | 0 |
| NSAID | Number of Patients Examined | Number of Patients with at Least One Side Effect (Share in % a Study Population) | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Febuxostat | Febuxostat + NSAID | NSAID | |||
| Indometacin | 27 | 2 (8.0) | 6 (22.0) | 7 (27.0) | [52] |
| Naproxen | 26 | 7 (28.0) | 9 (35.0) | 7 (26.0) | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jordan, A.; Gresser, U. Side Effects and Interactions of the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Febuxostat. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020051
Jordan A, Gresser U. Side Effects and Interactions of the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Febuxostat. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(2):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleJordan, Andreas, and Ursula Gresser. 2018. "Side Effects and Interactions of the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Febuxostat" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 2: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020051
APA StyleJordan, A., & Gresser, U. (2018). Side Effects and Interactions of the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Febuxostat. Pharmaceuticals, 11(2), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11020051




