VIPS: Learning-View-Invariant Feature for Person Search
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel viewpoint-invariant person search (VIPS) framework leveraging CLIP’s semantic alignment for UAV and cross-camera scenarios;
- We propose a mask generator to suppress noise in UAV-captured images, enhancing text-guided feature learning and view prompts to encode camera perspectives into visual features, reducing viewpoint discrepancy;
- Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of VIPS, establishing a new state-of-the-art method in UAV-based person search tasks.
2. Related Work
2.1. Person Search
2.2. Prompt Learning
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Overview of CLIP-ReID
3.2. Overview of Faster R-CNN
3.3. Vision Transformer
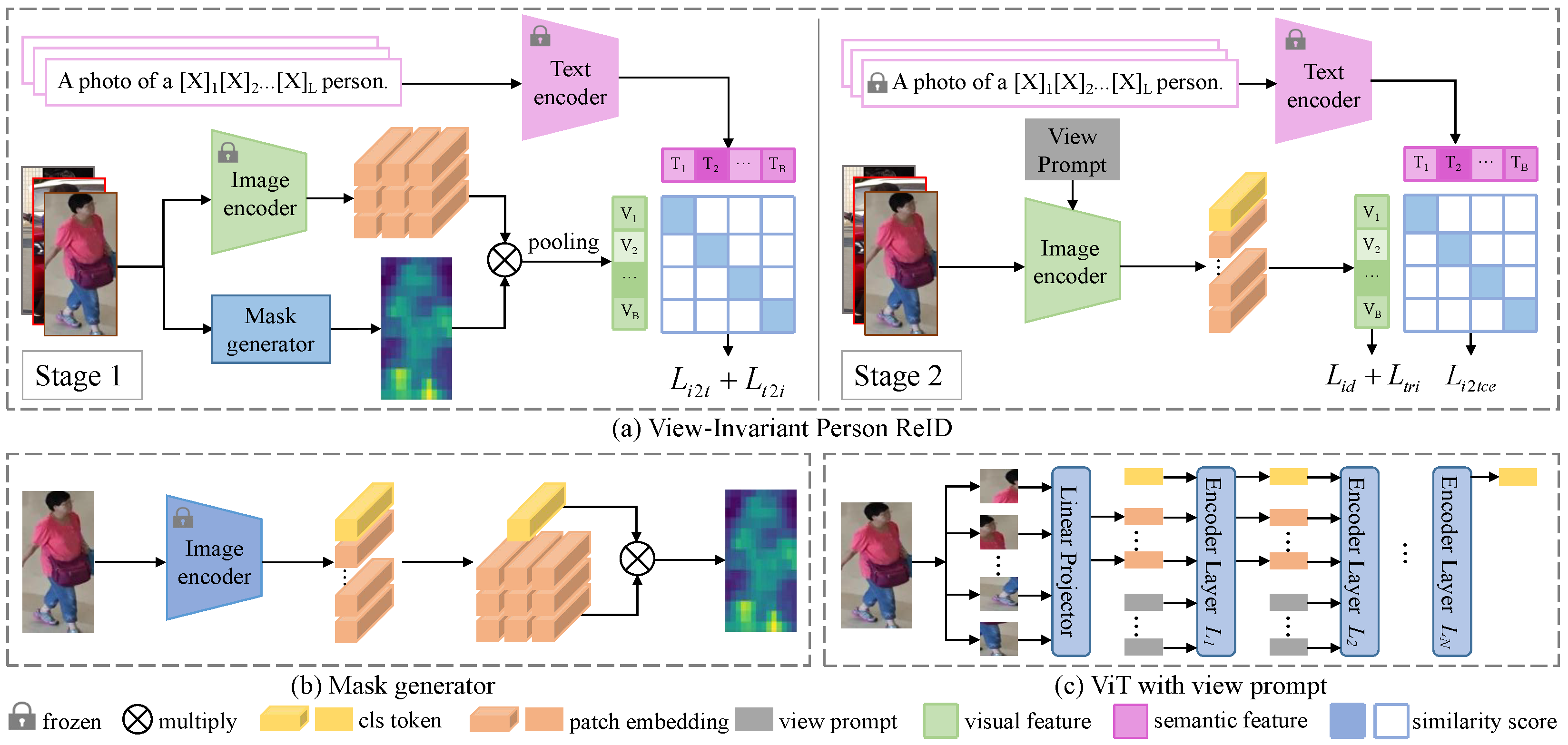
4. View-Invariant Person Search
4.1. View-Invariant Person ReID
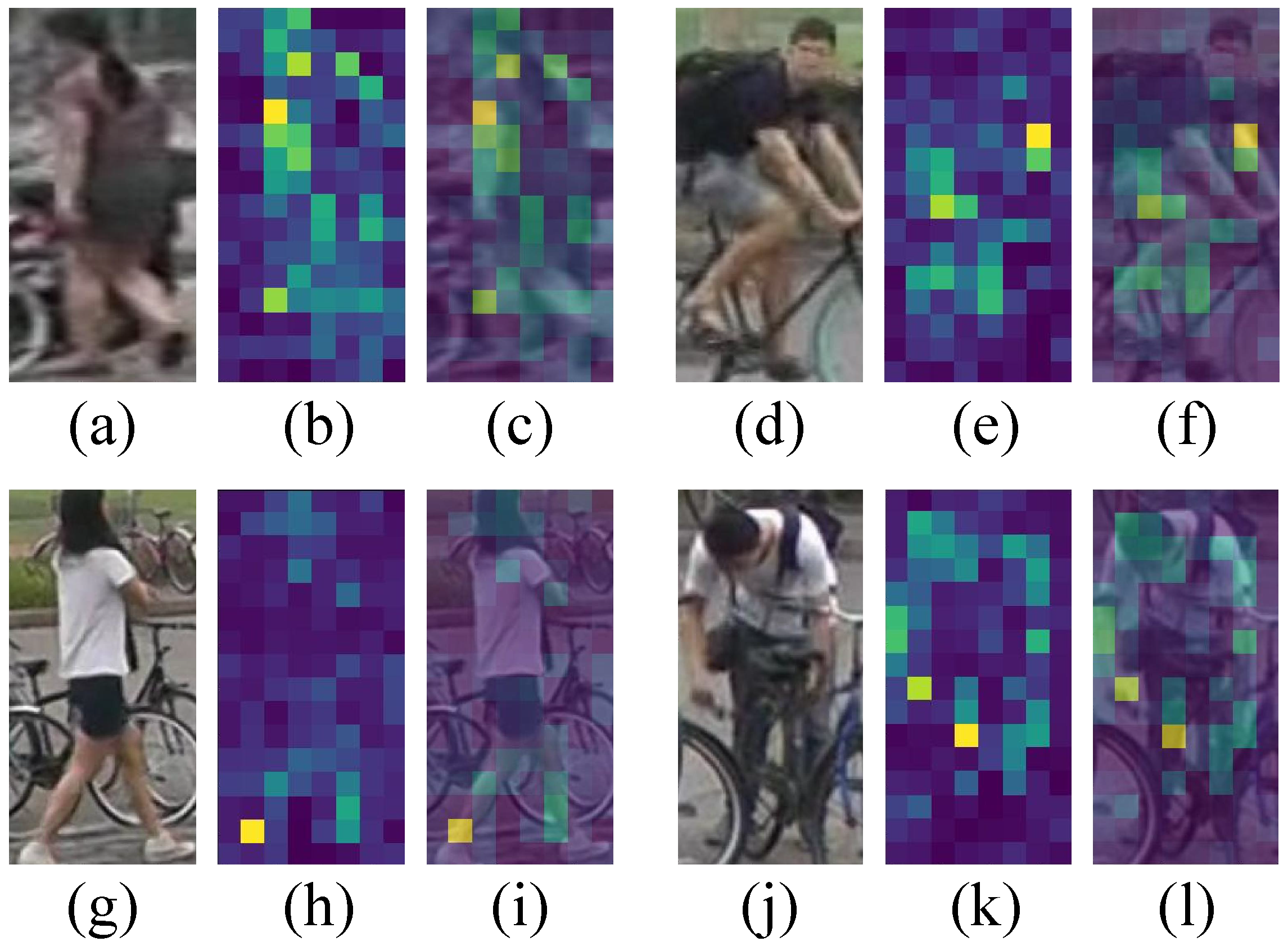
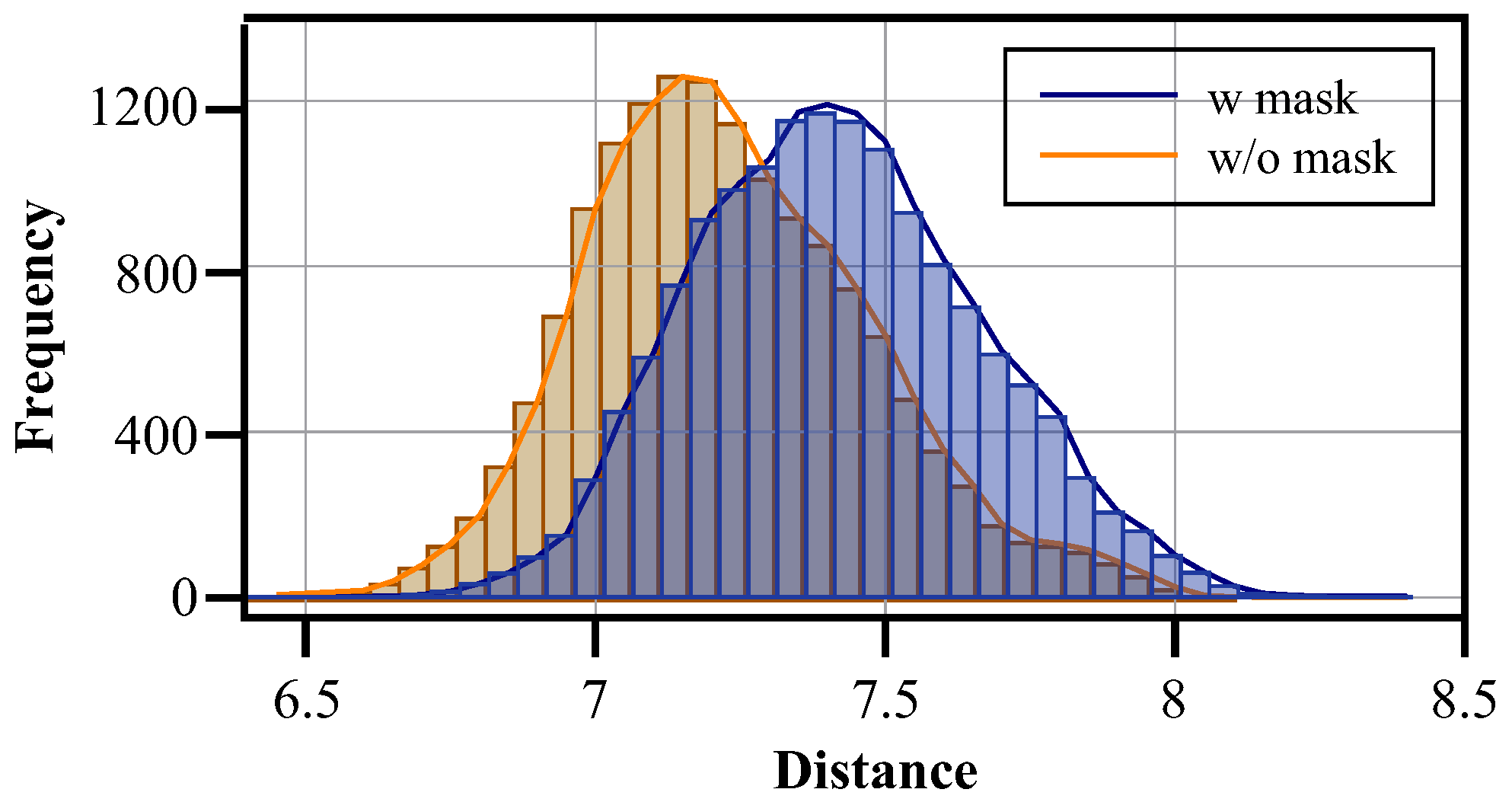
4.1.1. Mask Generator
4.1.2. View Prompt
4.2. Training
4.3. Relation to Prior Work
5. Experiments
5.1. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
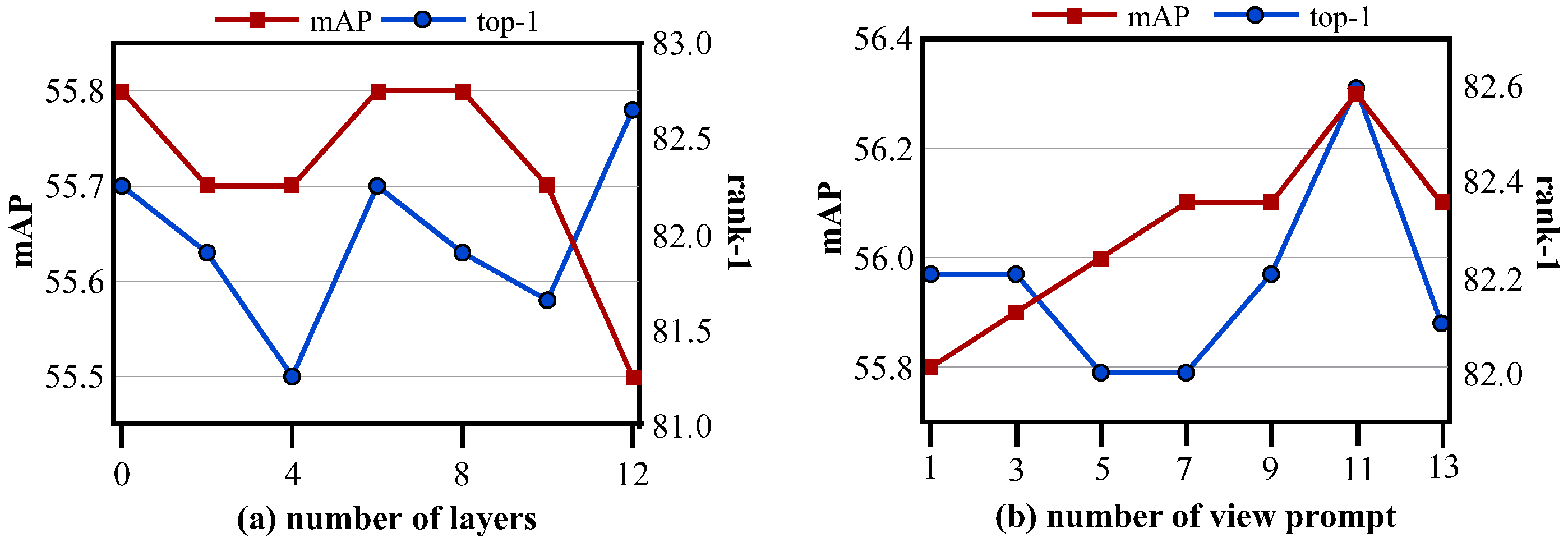
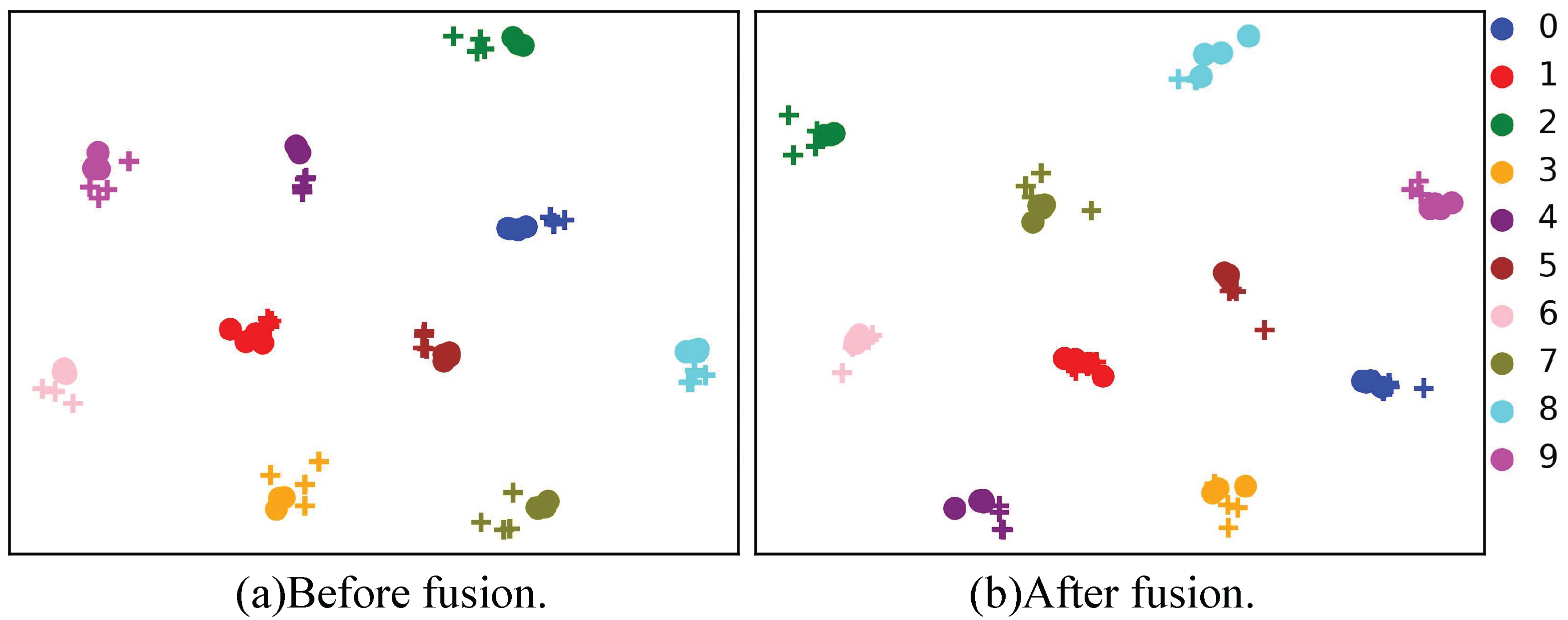
5.2. Ablation Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, S.; Chandraker, M.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q. Person re-identification in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1367–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Xing, Y.; Liang, G.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Ground-to-Aerial Person Search: Benchmark Dataset and Approach. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Lin, L.; Wang, X. Joint detection and identification feature learning for person search. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3415–3424. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Sun, L.; Li, Q. Clip-reid: Exploiting vision-language model for image re-identification without concrete text labels. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 1405–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ma, B.; Chang, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Tcts: A task-consistent two-stage framework for person search. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11952–11961. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Song, C.; Tan, T. Instance guided proposal network for person search. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2585–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Ye, J.; Zhong, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, C.; Gao, C.; Sang, N. Re-id driven localization refinement for person search. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9814–9823. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, C.; Sang, N.; Yang, Y. Decoupled and Memory-Reinforced Networks: Towards Effective Feature Learning for One-Step Person Search. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Bai, S.; Liao, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Shao, L. Anchor-free person search. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 7690–7699. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, K.; Pemasiri, A.; Liu, F.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. AG-VPReID: A Challenging Large-Scale Benchmark for Aerial-Ground Video-based Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Chongqing, China, 25–26 October 2025; pp. 1241–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Ge, Y.; Qi, X.; Sun, K.; Wan, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Y. SPL-PlaneTR: Lightweight and Generalizable Indoor Plane Segmentation Based on Prompt Learning. Sensors 2025, 25, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lu, J. Leveraging Vision Foundation Model via PConv-Based Fine-Tuning with Automated Prompter for Defect Segmentation. Sensors 2025, 25, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, H.; Ding, K.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y. Few-Shot Image Classification of Crop Diseases Based on Vision–Language Models. Sensors 2024, 24, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattak, M.U.; Rasheed, H.; Maaz, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S. Maple: Multi-modal prompt learning. In Proceedings of the the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19113–19122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, R.; Ren, X.; Su, G.; Perot, V.; Dy, J.; Pfister, T. Learning to prompt for continual learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Learning to prompt for vision-language models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Conditional prompt learning for vision-language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16816–16825. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Tang, L.; Chen, B.C.; Cardie, C.; Belongie, S.; Hariharan, B.; Lim, S.N. Visual prompt tuning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 709–727. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, P.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y. Pose-guided feature alignment for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 542–551. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, W.; Yang, J.; Tai, Y. Person search via a mask-guided two-stream cnn model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Person search by multi-scale matching. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 536–552. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Miao, D. Sequential end-to-end network for efficient person search. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 2011–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Oh, Y.; Baek, D.; Lee, J.; Ham, B. OIMNet++: Prototypical Normalization and Localization-Aware Learning for Person Search. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part X. pp. 621–637. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Pang, Y.; Anwer, R.M.; Cholakkal, H.; Xie, J.; Shah, M.; Khan, F.S. PSTR: End-to-end one-step person search with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9458–9467. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Du, D.; LaLonde, R.; Davila, D.; Funk, C.; Hoogs, A.; Clipp, B. Cascade transformers for end-to-end person search. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7267–7276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, G.; Zhou, E.; Sun, J. High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6449–6458. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, L.; Zakhor, A. Swap Path Network for Robust Person Search Pre-training. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.05433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, K. Unknown Instance Learning for Person Search. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Cheng, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. Learning disentangled representation implicitly via transformer for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Su, F.; Meng, H. LTReID: Factorizable Feature Generation with Independent Components for Long-Tailed Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 4610–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Tang, H.; Tang, J. Erasing, transforming, and noising defense network for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 4458–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, Q.; Schiele, B.; Hua, X.S.; Sun, Q. Learning comprehensive global features in person re-identification: Ensuring discriminativeness of more local regions. PAttern Recognit. 2023, 134, 109068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ke, W.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Tian, L.; Shan, Y. Dual cross-attention learning for fine-grained visual categorization and object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4692–4702. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Liu, H.; Song, P.; Guo, T.; Shi, W. Pose-guided feature disentangling for occluded person re-identification based on transformer. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Tang, M. Aaformer: Auto-aligned transformer for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 17307–17317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, K.; Luo, H.; Wang, F.; Jiang, W.; Ding, H. Region generation and assessment network for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 19, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Pu, S. PHA: Patch-Wise High-Frequency Augmentation for Transformer-Based Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 14133–14142. [Google Scholar]

| Dataset | Training Set | Test Set | #Cam | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #Image | #ID | #Image | #ID | ||
| CUHK-SYSU | 11,206 | 5532 | 6978 | 2900 | 2 |
| PRW | 5704 | 482 | 6112 | 450 | 6 |
| G2APS | 21,962 | 2077 | 9808 | 566 | 2 |
| Market-1501 | 12,936 | 751 | 19,732 | 750 | 6 |
| MSMT17 | 32,621 | 1041 | 93,820 | 3060 | 15 |
| Occluded-Duke | 15,618 | 702 | 19,871 | 1110 | 8 |
| Method | Year | Param. (M) | PRW | CUHK-SYSU | G2APS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Top-1 | mAP(M) | Top-1 | mAP | Top-1 | |||
| MGTS [25] | 2018 | - | 32.6 | 72.1 | 83.0 | 83.7 | - | - |
| CLSA [26] | 2018 | - | 38.7 | 65.0 | 87.2 | 88.5 | - | |
| RDLR [9] | 2019 | - | 42.9 | 70.2 | 93.0 | 94.2 | - | - |
| IGPN [8] | 2020 | - | 47.2 | 87.0 | 90.3 | 91.4 | - | - |
| TCTS [7] | 2020 | - | 46.8 | 87.5 | 93.9 | 95.1 | - | - |
| SeqNet * [27] | 2021 | 48.4 | 46.7 | 83.4 | 93.8 | 94.6 | 34.0 | 44.5 |
| AlignPS [11] | 2021 | 42.2 | 45.9 | 81.9 | 93.1 | 93.4 | 27.0 | 34.7 |
| OIM++ * [28] | 2022 | - | 46.8 | 83.9 | 93.1 | 93.9 | 32.5 | 40.3 |
| PSTR * [29] | 2022 | - | 49.5 | 87.8 | 93.5 | 95.0 | 28.4 | 39.9 |
| COAT * [30] | 2022 | 37.0 | 52.5 | 86.0 | 93.7 | 94.1 | 40.3 | 50.5 |
| HKD * [2] | 2023 | 54.4 | 53.5 | 86.6 | 95.3 | 96.1 | 41.4 | 51.9 |
| Faster+HOreid [31] | 2023 | 95.6 | 55.6 | 98.3 | 97.4 | 98.0 | 52.6 | 62.2 |
| SPNet-L * [32] | 2024 | - | 54.2 | 89.0 | 95.8 | 96.3 | - | - |
| UIL * [33] | 2024 | - | 51.5 | 86.1 | 93.9 | 94.7 | - | - |
| VIPS (ours) | - | 168.2 | 56.3 | 82.6 | 98.2 | 98.6 | 57.0 | 66.1 |
| Method | References | Market-1501 | MSMT17 | Occluded-Duke | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Top-1 | mAP | Top-1 | mAP | Top-1 | ||
| CNN as the backbone | |||||||
| DRL-Net [34] | TMM 2022 | 86.9 | 94.7 | 55.3 | 78.4 | 50.8 | 65.0 |
| LTReID [35] | TMM 2022 | 89.0 | 95.9 | 58.6 | 81.0 | - | - |
| ETNDN [36] | TSCVT 2023 | 88.7 | 95.7 | 58.0 | 82.7 | 57.6 | 68.1 |
| CLIP-ReID [5] | AAAI 2023 | 89.8 | 95.7 | 63.0 | 84.4 | 53.5 | 61.0 |
| CGE [37] | PR 2023 | 90.1 | 95.6 | 65.9 | 85.1 | - | - |
| ViT as the backbone | |||||||
| DCAL [38] | CVPR 2022 | 87.5 | 94.7 | 64.0 | 83.1 | - | - |
| PFD [39] | AAAI 2022 | 89.6 | 95.5 | 64.4 | 83.8 | 60.1 | 67.7 |
| AAformer [40] | TNNLS 2023 | 87.7 | 95.4 | 63.2 | 83.6 | 58.2 | 67.0 |
| CLIP-ReID [5] | AAAI 2023 | 89.6 | 95.5 | 73.4 | 88.7 | 59.5 | 67.1 |
| RGANET [41] | TIFS 2023 | 89.8 | 95.5 | 72.3 | 88.1 | - | - |
| PHA [42] | CVPR 2023 | 90.2 | 96.1 | 68.9 | 86.1 | - | - |
| VIReID (ours) | 90.3 | 96.1 | 74.9 | 89.2 | 60.2 | 67.9 | |
| Mask Generator | View Prompt | PRW | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Top-1 | ||
| × | × | 55.5 | 81.0 |
| ✓ | × | 55.8 | 82.1 |
| × | ✓ | 56.0 | 81.6 |
| ✓ | ✓ | 56.3 | 82.6 |
| Methods | Time of Day | Scene | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | Noon | Afternoon | Indoor | Outdoor | ||||||
| mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | |
| Baseline | 77.1 | 90.8 | 67.3 | 84.3 | 74.4 | 90.0 | 67.0 | 86.9 | 74.3 | 89.0 |
| VIReID (ours) | 78.5 | 91.1 | 69.1 | 85.1 | 76.0 | 90.4 | 69.8 | 87.9 | 75.6 | 89.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Luo, W.; Wu, W.; Xie, F.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. VIPS: Learning-View-Invariant Feature for Person Search. Sensors 2025, 25, 5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175362
Wang H, Luo W, Wu W, Xie F, Liu J, Li J, Zhang S. VIPS: Learning-View-Invariant Feature for Person Search. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175362
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hexu, Wenlong Luo, Wei Wu, Fei Xie, Jindong Liu, Jing Li, and Shizhou Zhang. 2025. "VIPS: Learning-View-Invariant Feature for Person Search" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175362
APA StyleWang, H., Luo, W., Wu, W., Xie, F., Liu, J., Li, J., & Zhang, S. (2025). VIPS: Learning-View-Invariant Feature for Person Search. Sensors, 25(17), 5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175362






