Microwave Foreign Object Detection in a Lossy Medium Using a Planar Array Antenna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method of Maximum Power Transmission Efficiency
3. Array Antenna Design
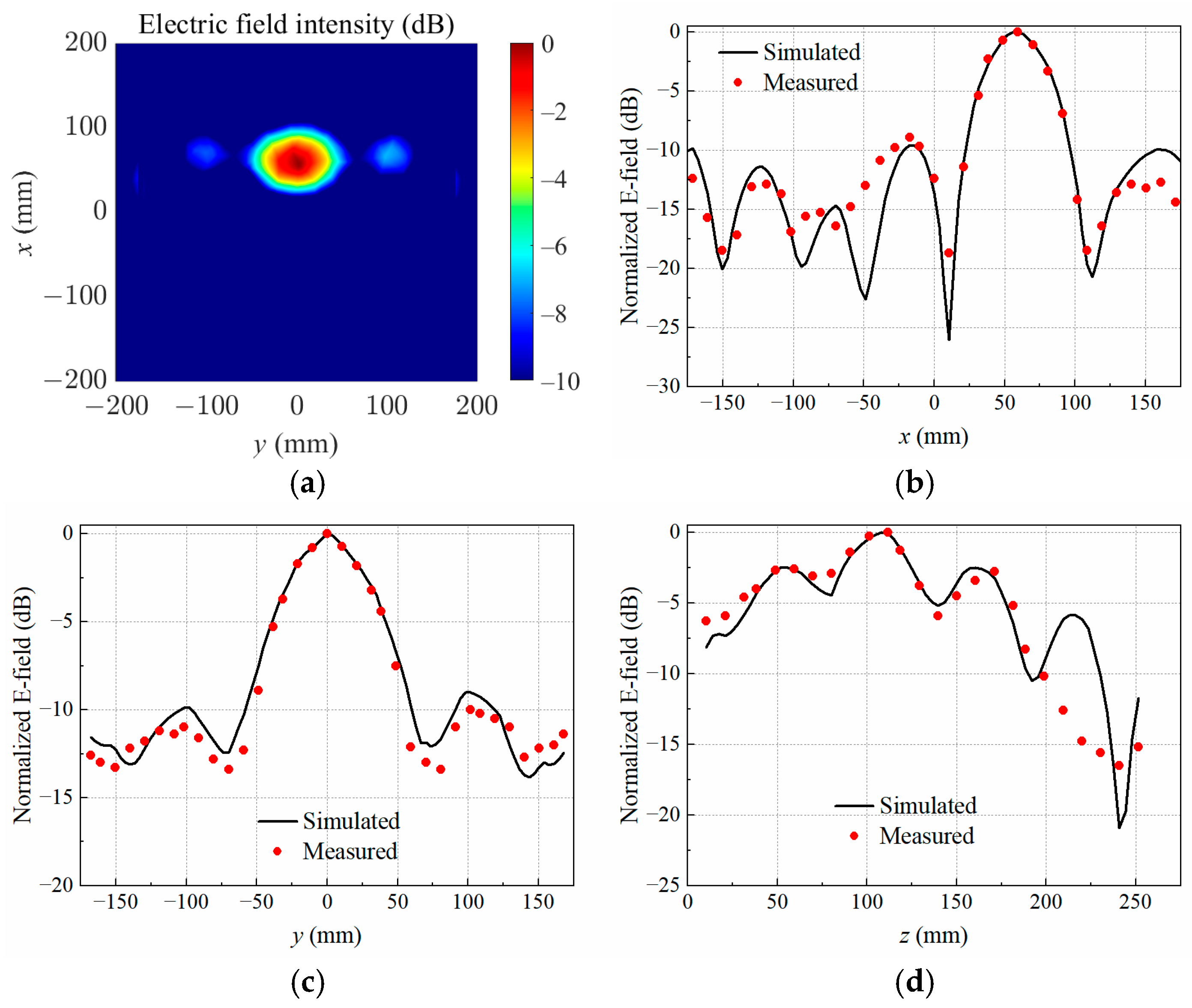
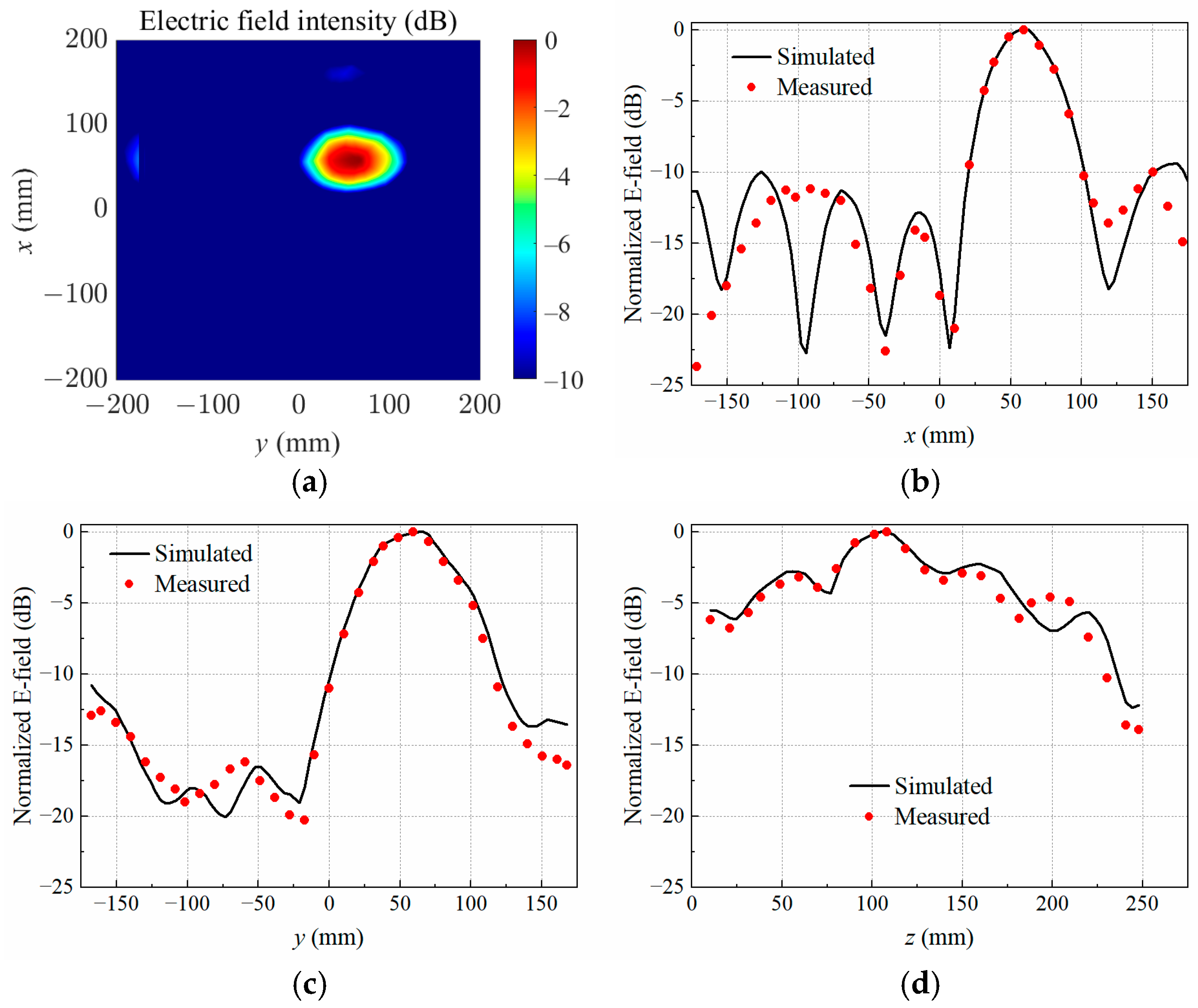
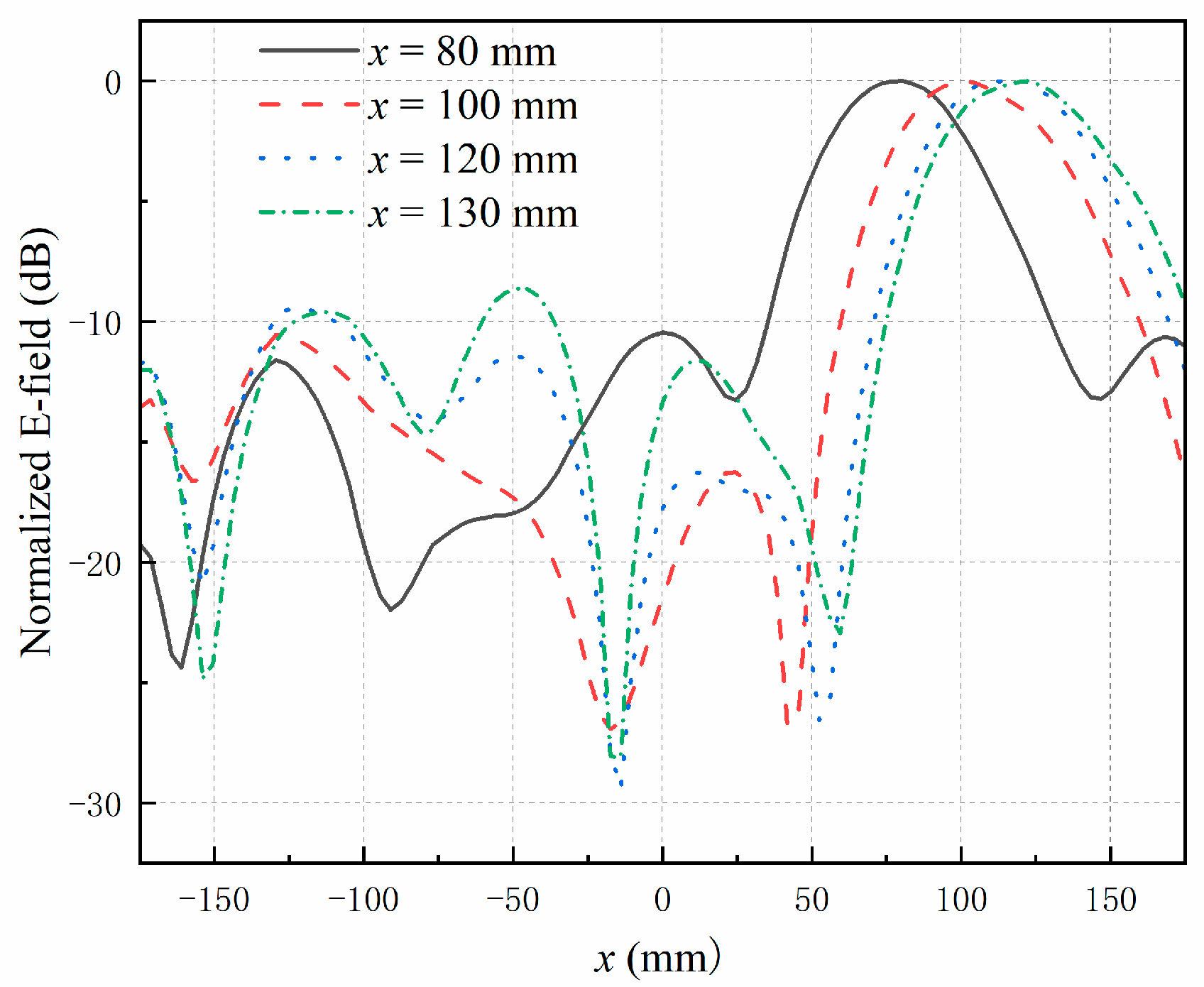
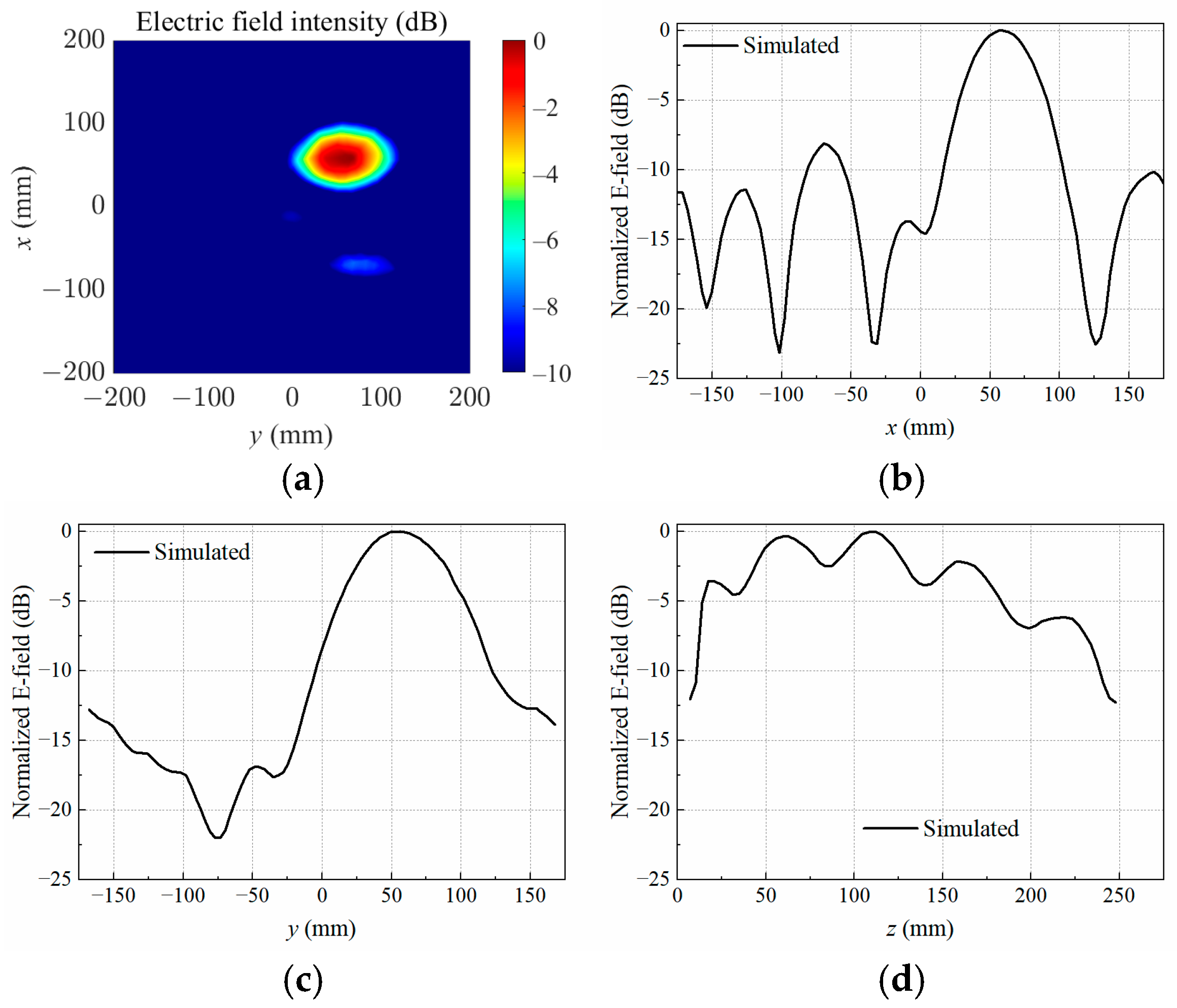
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buffi, A.; Serra, A.A.; Nepa, P.; Chou, H.T.; Manara, G. A Focused Planar Microstrip Array for 2.4 GHz RFID Readers. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siragusa, R.; Lemaitre-Auger, P.; Tedjini, S. Tunable Near-Field Focused Circular Phase-Array Antenna for 5.8-GHz RFID Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.T.; Hung, T.M.; Wang, N.N.; Chou, H.H.; Tung, C.; Nepa, P. Design of a Near-Field Focused Reflectarray Antenna for 2.4 GHz RFID Reader Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.T.; Lee, M.Y.; Yu, C.T. Subsystem of Phased Array Antennas With Adaptive Beam Steering in the Near-Field RFID Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motroni, A.; Pino, M.R.; Cecchi, G.; Nepa, P. A Near-Field Focused Array Antenna Empowered by Deep Learning for UHF-RFID Smart Gates. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 7946–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Meng, X.; Zhu, H.; Qi, Z. A Near-Field Focused Polling Antenna Array Working With 1-Bit Reflectarray for RFID Reader Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felaco, A.; Kapusuz, K.Y.; Rogier, H.; Ginste, D.V. Power-Efficient Near-Field Focusing for Upcoming 6G MIMO Networks. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Alomainy, A.; Hao, Y. Near-Field Millimeter-Wave Phased Array Imaging With Compressive Sensing. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18975–18986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Qu, S.W.; Yang, S. Two-Dimensional Imaging Based on Near-Field Focused Array Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutai, K.K.; Sato, H.; Chen, Q. Active Millimeter Wave Imaging Using Leaky-Wave Focusing Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, J.; Haynes, M.; Carson, P.; Moghaddam, M. A Preclinical System Prototype for Focused Microwave Thermal Therapy of the Breast. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofigh, F.; Nourinia, J.; Azarmanesh, M.; Khazaei, K.M. Near-Field Focused Array Microstrip Planar Antenna for Medical Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Abbosh, A.; Crozier, S. Three-Dimensional Microwave Hyperthermia for Breast Cancer Treatment in a Realistic Environment Using Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Geyi, W.; Wang, S. Optimal design of focused arrays for microwave-induced hyperthermia. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2015, 9, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Geyi, W.; Wang, S. A Hexagonal Focused Array for Microwave Hyperthermia: Optimal Design and Experiment. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, S.; Geyi, W. Optimal Design of a Hexagonal Antenna Array for Regional Microwave Breast Hyperthermia. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 4738–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Geyi, W.; Sun, H. Optimum Design of Wireless Power Transmission System Using Microstrip Patch Array antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1824–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Ayestarán, R.; León, G.; Pino, M.R.; Nepa, P. Wireless Power Transfer Through Simultaneous Near-Field Focusing and Far-Field Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5623–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.T. Conformal Near-Field Focus Radiation From Phased Array of Antennas to Enhance Power Transfer Between Transmitting and Receiving Antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 3567–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Gu, X.; Geyi, W. Optimal Design of Array antennas Focused on Multiple Targets. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4593–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Yue, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, H. Quantification Phase Gradient Near-Field Focusing Metasurface for Microwave Wireless Power Transfer System. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 1944–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Xu, M.; Shinohara, N.; Geyi, W. Optimal Design of Multitarget Wireless Power Transmission With Arbitrary Received Power Allocation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. 2024, 23, 3158–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogosanovic, M.; Williamson, A.G. Microstrip Array antenna With a Beam Focused in the Near-Field Zone for Application in Noncontact Microwave Industrial Inspection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.D.; Mead, J.B.; Pozar, D.M.; Wang, L.; Pearce, J.A. A Near Field Focused Microstrip Array for a Radiometric Temperature Sensor. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.J. Self-Progressive Near-Field Focusing 2-D Full Frequency Scanning Slot Array Antenna Based on Ridge-Gap Waveguide. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Y. An E-Plane-Focused Triple-Layer Multibeam Luneburg Lens Antenna for 5G Millimeter-Wave Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 21, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, P.; Nie, B.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X. E-Plane-Focused Partial Maxwell Fish-Eye Lens Antenna for Multibeam Wide-Angle Scanning. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 1853–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Si, L.; Zhu, W. Mechanically Reconfigurable Folded Reflectarray Antenna for Variable Near-Field Focusing. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 10038–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Geyi, W.; Tang, L.; Sun, H. Circularly-Polarized Focused Microstrip Antenna Arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffi, A.; Nepa, P.; Manara, G. Design Criteria for Near-Field-Focused Planar Arrays. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2012, 54, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, M. Generating Microwave Spatial Fields With Arbitrary Patterns. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyi, W. The Method of Maximum Power Transmission Efficiency for the Design of Antenna Arrays. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Geyi, W. Optimal Design of Focused Antenna Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 5565–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cai, X.; Geyi, W. A Pattern Shaping Method for Focused Antenna Arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Antenna No. | Re (Absence) | Im (Absence) | Re (P1) | Im (P1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | –0.0263 | 0.0196 | –0.0275 | 0.0344 |
| 2 | 0.0265 | 0.0074 | 0.0147 | 0.0077 |
| 3 | 0.0077 | 0.0316 | –0.0090 | 0.0032 |
| 4 | 0.0060 | –0.0164 | –0.0107 | –0.0141 |
| 5 | –0.0005 | 0.0374 | 0.0086 | 0.0494 |
| 6 | –0.0299 | 0.0029 | –0.0468 | 0.0008 |
| 7 | 0.0019 | –0.0272 | 0.0237 | 0.0019 |
| 8 | –0.0042 | –0.0282 | –0.0383 | 0.0138 |
| 9 | –0.0223 | –0.0341 | –0.0068 | –0.0101 |
| 10 | –0.0017 | 0.0288 | –0.0089 | 0.0276 |
| 11 | –0.0241 | –0.0099 | –0.0413 | –0.0282 |
| 12 | –0.0501 | 0.0453 | –0.0594 | 0.0923 |
| 13 | –0.0143 | 0.0320 | –0.0273 | 0.0765 |
| 14 | –0.0343 | 0.0053 | –0.0412 | –0.0058 |
| 15 | –0.0230 | 0.0031 | –0.0376 | 0.0037 |
| 16 | 0.0024 | –0.0279 | 0.0216 | –0.0066 |
| 17 | –0.0125 | –0.0143 | –0.0371 | 0.0222 |
| 18 | –0.0226 | –0.0324 | –0.0096 | –0.0153 |
| 19 | 0.0042 | 0.0320 | –0.0020 | 0.0311 |
| 20 | –0.0250 | 0.0250 | –0.0279 | 0.0359 |
| 21 | 0.0187 | 0.0099 | 0.0122 | 0.0119 |
| 22 | 0.0131 | 0.0250 | –0.0035 | 0.0023 |
| 23 | –0.0006 | –0.0176 | –0.0143 | –0.0132 |
| 24 | –0.0026 | 0.0404 | 0.0060 | 0.0495 |
| Antenna No. | Re (P2) | Im (P2) | Re (P3) | Im (P3) | Re (P4) | Im (P4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | –0.0262 | 0.0208 | –0.0312 | 0.0153 | –0.0288 | 0.0151 |
| 2 | 0.0221 | 0.0106 | 0.0294 | 0.0077 | 0.0278 | –0.0015 |
| 3 | 0.0050 | 0.0294 | 0.0094 | 0.0342 | 0.0035 | 0.0275 |
| 4 | 0.0127 | –0.0112 | 0.0031 | –0.0133 | 0.0061 | –0.0149 |
| 5 | –0.0025 | 0.0347 | 0.0002 | 0.0394 | 0.0014 | 0.0363 |
| 6 | –0.0216 | –0.0014 | –0.0314 | –0.0021 | –0.0266 | 0.0085 |
| 7 | 0.0145 | –0.0200 | 0.0021 | –0.0212 | 0.0058 | –0.0152 |
| 8 | 0.0046 | –0.0328 | –0.0060 | –0.0334 | –0.0007 | –0.0177 |
| 9 | –0.0260 | –0.0313 | –0.0165 | –0.0421 | –0.0178 | –0.0421 |
| 10 | –0.0012 | 0.0266 | –0.0041 | 0.0216 | –0.0025 | 0.0335 |
| 11 | –0.0162 | –0.0068 | –0.0192 | –0.0138 | –0.0380 | –0.0178 |
| 12 | –0.0524 | 0.0630 | –0.0531 | 0.0492 | –0.0522 | 0.0280 |
| 13 | –0.0189 | 0.0327 | –0.0074 | 0.0348 | –0.0089 | 0.0403 |
| 14 | –0.0284 | 0.0043 | –0.0290 | –0.0002 | –0.0389 | 0.0028 |
| 15 | –0.0162 | –0.0010 | –0.0250 | –0.0020 | –0.0267 | –0.0141 |
| 16 | 0.0136 | –0.0210 | 0.0033 | –0.0229 | 0.0197 | –0.0399 |
| 17 | –0.0038 | –0.0191 | –0.0131 | –0.0194 | –0.0189 | –0.0311 |
| 18 | –0.0255 | –0.0291 | –0.0165 | –0.0395 | –0.0193 | –0.0210 |
| 19 | 0.0037 | 0.0290 | 0.0017 | 0.0246 | 0.0026 | 0.0243 |
| 20 | –0.0246 | 0.0254 | –0.0296 | 0.0205 | –0.0298 | 0.0219 |
| 21 | 0.0159 | 0.0120 | 0.0220 | 0.0099 | 0.0190 | 0.0021 |
| 22 | 0.0109 | 0.0237 | 0.0147 | 0.0282 | 0.0048 | 0.0200 |
| 23 | 0.0044 | –0.0128 | –0.0047 | –0.0148 | 0.0070 | –0.0105 |
| 24 | –0.0042 | 0.0378 | –0.0019 | 0.0417 | –0.0050 | 0.0390 |
| Antenna No. | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.113∠−48° | 0.034∠152.2° | 0.227∠−158.3° | 0.097∠−29.9° |
| 2 | 0.090∠−132.2° | 0.144∠95° | 0.099∠55.8° | 0.170∠−67.2° |
| 3 | 0.250∠167.1° | 0.092∠20.6° | 0.109∠5.7° | 0.110∠−13.1° |
| 4 | 0.127∠−125.6° | 0.223∠−158° | 0.146∠−70.6° | 0.029∠123.9° |
| 5 | 0.114∠−5.8° | 0.089∠5.4° | 0.072∠−7.3° | 0.042∠−117.9° |
| 6 | 0.129∠−140.7° | 0.247∠−92.7° | 0.181∠168.8° | 0.121∠152.6° |
| 7 | 0.276∠−6.6° | 0.383∠−150.3° | 0.210∠−26.1° | 0.236∠139.3° |
| 8 | 0.409∠−82.5° | 0.262∠−92.1° | 0.194∠171.7° | 0.207∠139.5° |
| 9 | 0.217∠−10.7° | 0.124∠97.2° | 0.342∠116.8° | 0.172∠−87.9° |
| 10 | 0.055∠−143° | 0.059∠−43.9° | 0.263∠171.3° | 0.089∠110.9° |
| 11 | 0.190∠179.8° | 0.223∠−141.8° | 0.216∠100.9° | 0.299∠1.6° |
| 12 | 0.363∠−54.5° | 0.469∠142.4° | 0.169∠−64.5° | 0.328∠−51.9° |
| 13 | 0.352∠−59.7° | 0.125∠68.4° | 0.257∠40.5° | 0.186∠154.2° |
| 14 | 0.099∠168.7° | 0.156∠−110.6° | 0.266∠108.4° | 0.099∠3.5° |
| 15 | 0.110∠−131° | 0.209∠−89.3° | 0.190∠173° | 0.330∠−46.9° |
| 16 | 0.218∠−1.4° | 0.348∠−151.7° | 0.176∠−17.3° | 0.395∠−114° |
| 17 | 0.333∠−77.4° | 0.262∠−91.3° | 0.176∠159° | 0.337∠−37.9° |
| 18 | 0.163∠−6.1° | 0.116∠108.7° | 0.325∠159° | 0.223∠137.6° |
| 19 | 0.048∠−141.4° | 0.081∠−21° | 0.271∠111.5° | 0.148∠−46.8° |
| 20 | 0.086∠−58.5° | 0.016∠−167.4° | 0.225∠170.6° | 0.108∠−1.9° |
| 21 | 0.052∠−116.2° | 0.095∠96.8° | 0.113∠−161.9° | 0.146∠−60.8° |
| 22 | 0.213∠172.8° | 0.068∠29.7° | 0.125∠61° | 0.181∠0.8° |
| 23 | 0.110∠−115.7° | 0.181∠−163.9° | 0.172∠−1.4° | 0.193∠168.2° |
| 24 | 0.095∠0° | 0.081∠0° | 0.050∠−84.2° | 0.053∠0° |
| Target Material | Conductivity (S/m) | Dielectric Value | Medium | Detection | Maximum Electric Field Intensity (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 5.8 × 107 | 1 | Colza oil | Yes | 30 |
| Non-metallic | 10−14 | 4.4 | Colza oil | Yes | 26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Xu, P.; Li, W.; Cai, X. Microwave Foreign Object Detection in a Lossy Medium Using a Planar Array Antenna. Sensors 2025, 25, 3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133965
Yu L, Xu P, Li W, Cai X. Microwave Foreign Object Detection in a Lossy Medium Using a Planar Array Antenna. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133965
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Longzheng, Peng Xu, Wenbo Li, and Xiao Cai. 2025. "Microwave Foreign Object Detection in a Lossy Medium Using a Planar Array Antenna" Sensors 25, no. 13: 3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133965
APA StyleYu, L., Xu, P., Li, W., & Cai, X. (2025). Microwave Foreign Object Detection in a Lossy Medium Using a Planar Array Antenna. Sensors, 25(13), 3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133965







