Propagation Regimes and Signal Enhancement Mechanisms of Collinear Double-Pulse Plasma with Varying Inter-Pulse Delays
Abstract
1. Introduction
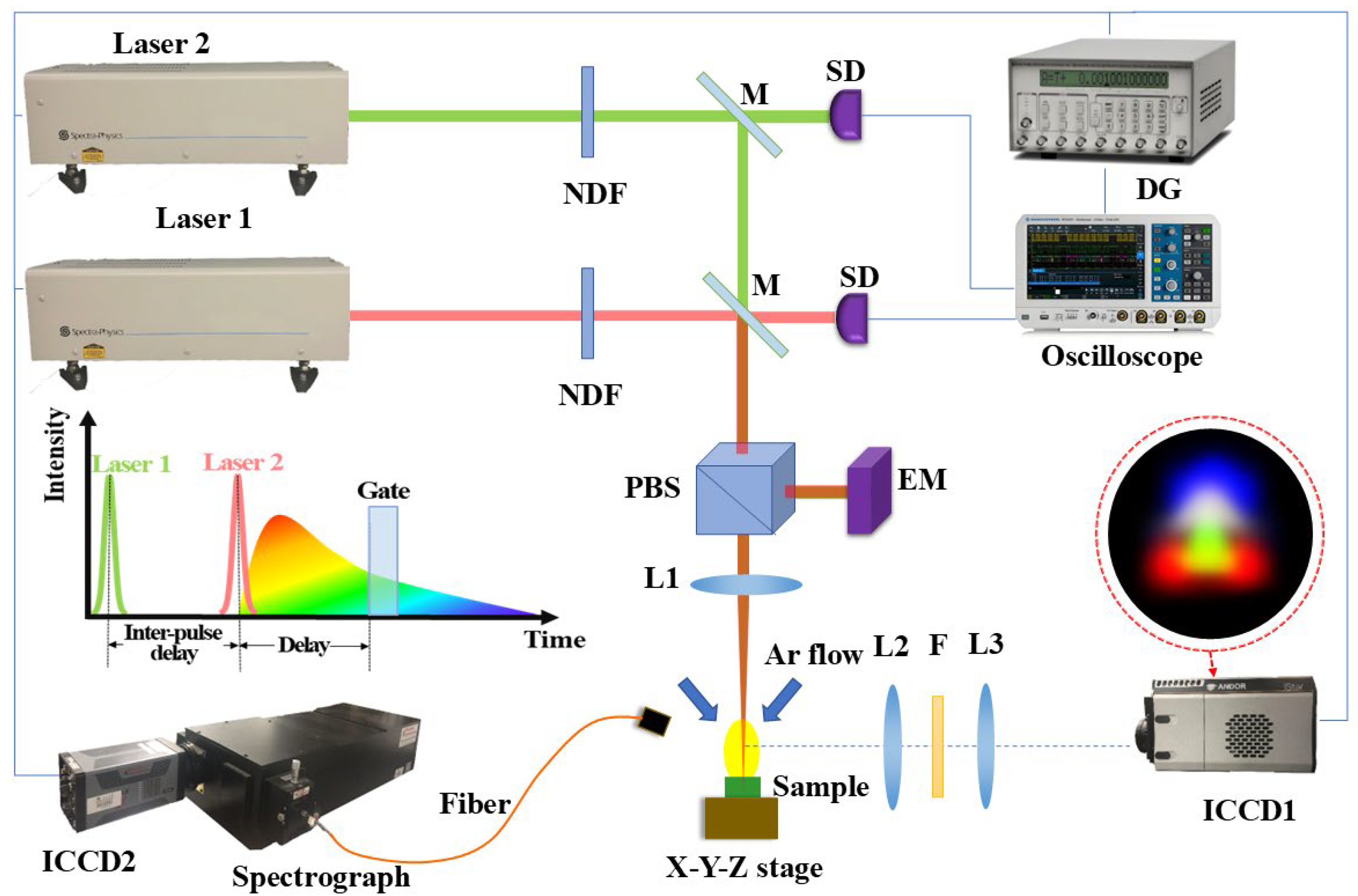
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of SP and DP LIBS Spectra
3.1.1. Effect of Spectral Acquisition Delays on Spectra
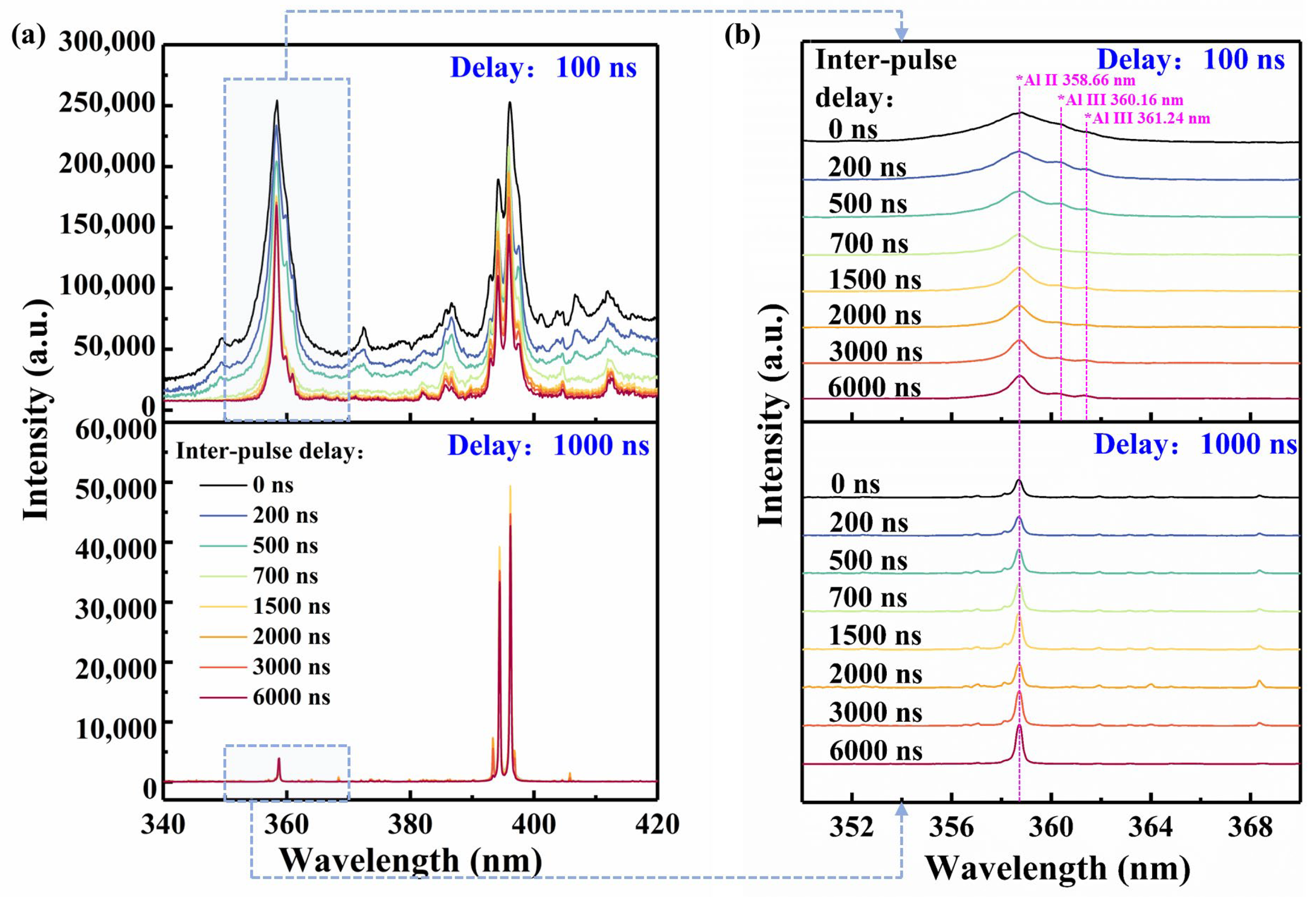
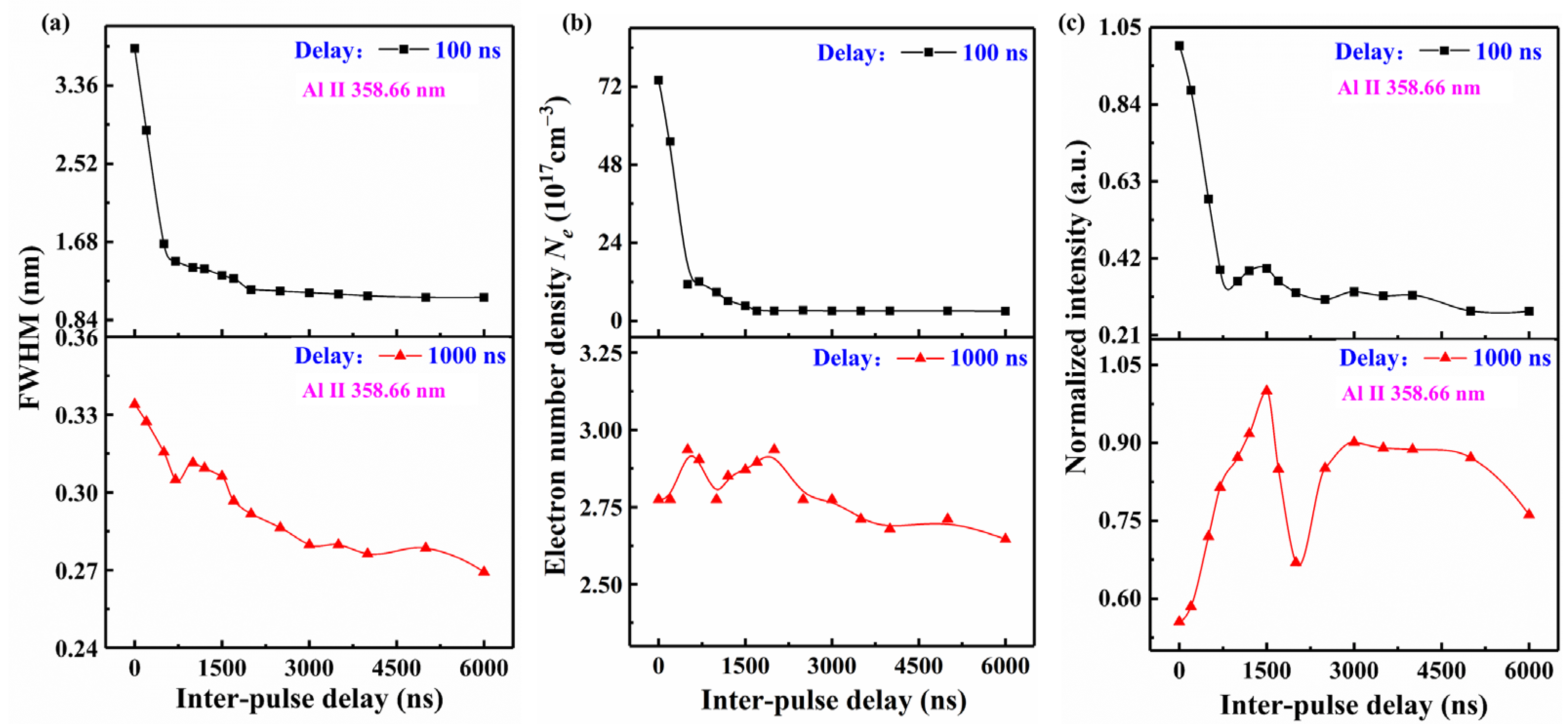
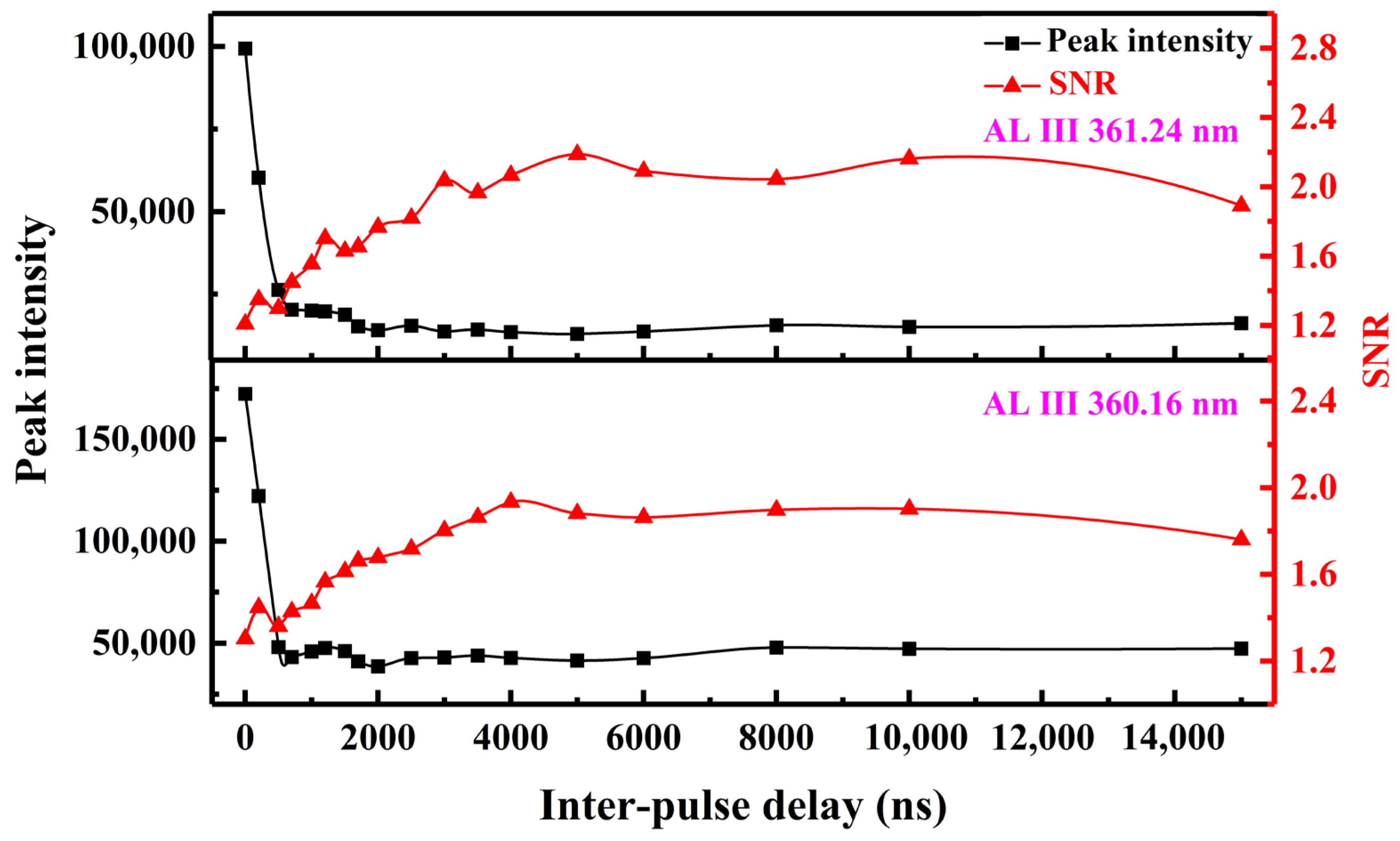
3.1.2. Effect of Inter-Pulse Delays on Spectra
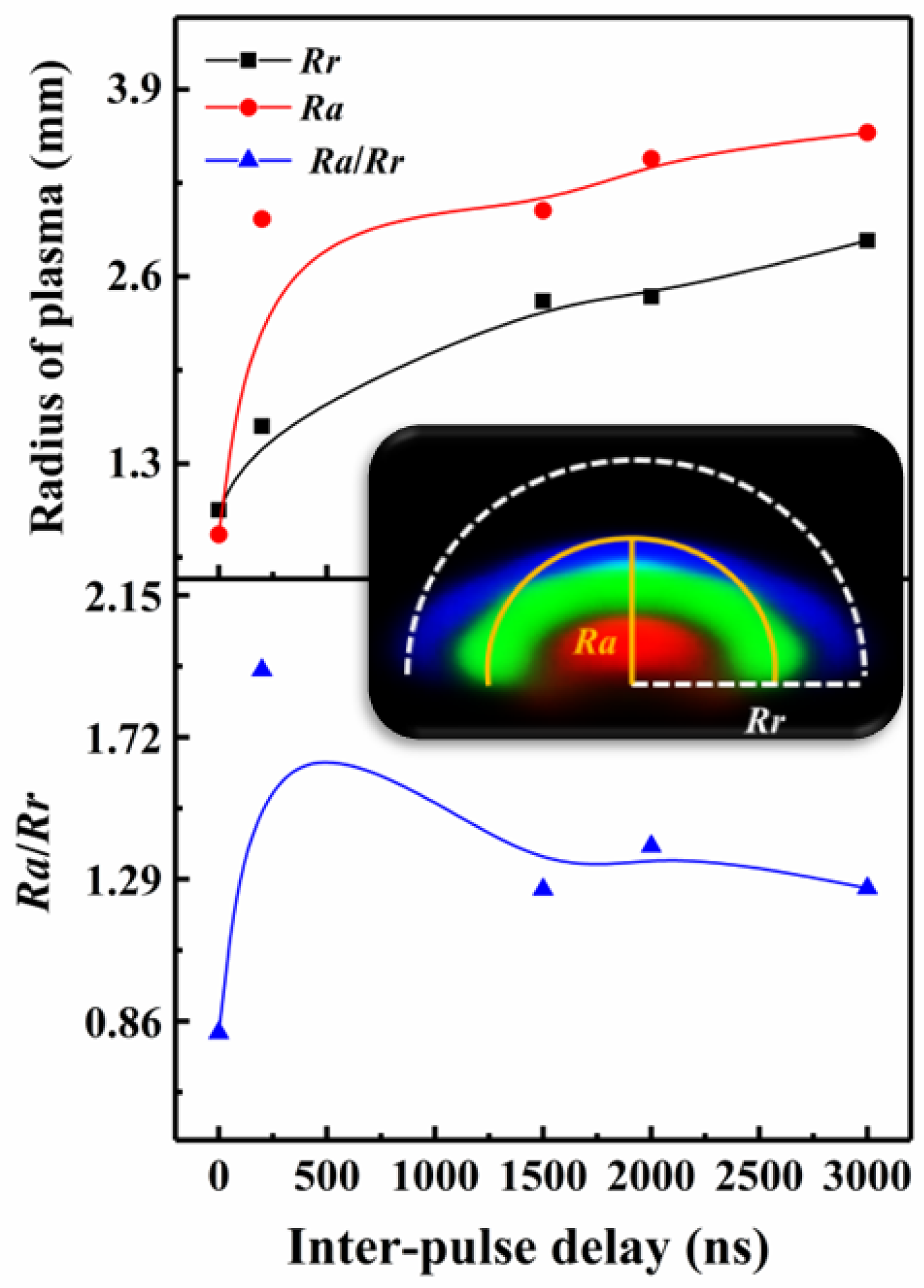
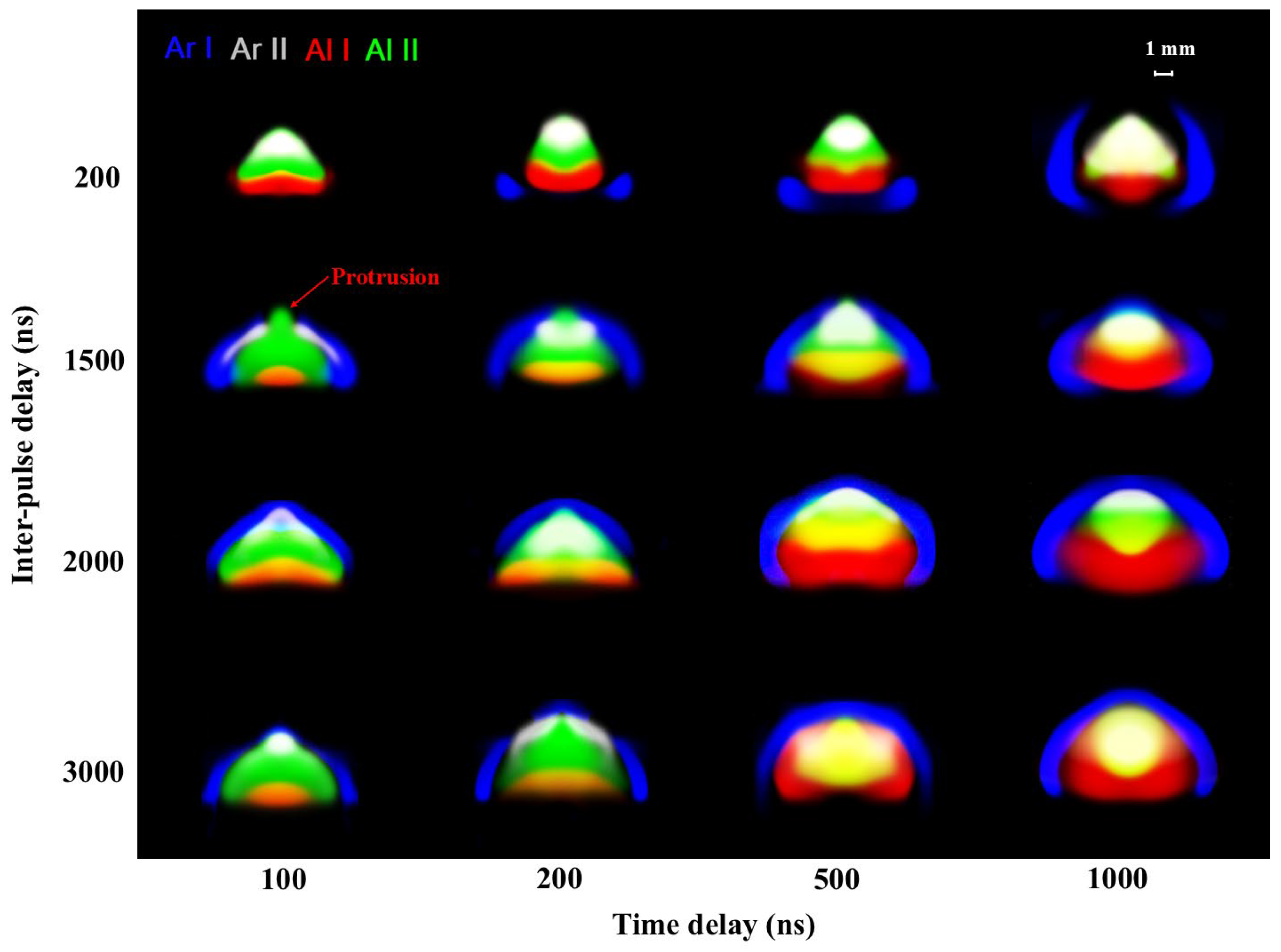
3.2. Comparison of Space-Time Evolution of SP and DP Plasma
3.2.1. Morphology and Structure of SP Plasma
3.2.2. Morphology and Structure of DP Plasma
3.3. Propagation Types of SP and DP Plasma
3.4. Signal Enhancement Mechanisms of DP-LIBS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LIBS | Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy |
| SP-LIBS | Single-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy |
| DP-LIBS | Double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy |
| SP | Single pulse |
| DP | Double pulse |
| LSA wave | Laser-supported absorption wave |
| LSC wave | Laser-supported combustion wave |
| LSD wave | Laser-supported detonation wave |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| FWHM | Full width at half maximum |
| LA-ICP-MS | Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence spectrometry |
| LIF | Laser-induced fluorescence |
References
- Sheta, S.; Afgan, M.S.; Hou, Z.; Yao, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Coal analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A tutorial review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1047–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Li, T.; Yao, H.; Yan, G.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, H. Fast measurement of coking properties of coal using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2022, 191, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, N.; Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Song, X.; Su, W.; Yu, G. In-situ release characteristic of alkali metals during co-pyrolysis of coal and biomass in a visual fixed bed combined with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Fuel 2023, 331, 125868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erler, A.; Riebe, D.; Beitz, T.; Löhmannsröben, H.-G.; Leenen, M.; Pätzold, S.; Ostermann, M.; Wójcik, M. Mobile Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Future Application in Precision Agriculture—A Case Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleschi, V. Understanding the source of signal fuctuations in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analytical applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 16, 22503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yao, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, S.; Qin, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, J. Comparison of the matrix effect in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis of coal particle flow and coal pellets. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakaris, N.; Siozos, P.; Piñon, V.; Banerjee, S.P.; Sentis, M.; Pedarnig, J.D.; Anglos, D. UV femtosecond single-pulse and collinear double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for depth-resolved characterization of nano-scaled films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 640, 158354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wan, X.; Si, J.; Han, J.; Chen, A.; Jin, M. High-sensitivity analysis of trace elements in water using femtosecond LIBS with dry droplet pretreatment on a metallic substrate. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2024, 39, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, A.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, M. Highly sensitive analysis of trace Pb in aqueous solution using electro-deposition and spark-discharge assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, M.; Alwahabi, Z.T. Gated and non-gated silver detection using microwave-assisted laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, M.; Cristoforetti, G.; Giuffrida, M.; Hidalgo, M.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; Salvetti, A.; Tognoni, E.; Vallebona, C. Three-dimensional analysis of laser induced plasmas in single and double pulse configuration. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2004, 59, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Yin, C. Analysis of the trace elements in micro-alloy steel by reheating double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 123, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, C.R.; Hartzler, D.; Jain, J.C.; McIntyre, D.L. Evaluation of analytical performance of double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the detection of rare earth elements. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolodelli, G.; Senesi, G.S.; Ranulfi, A.; Watanabe, A.; Milori, D.M.B.P. Development of a double-pulse (DP) laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) setup in the orthogonal configuration for environmental applications. In Proceedings of the Latin America Optics & Photonics Conference, Medellin, Colombia, 22–26 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stratis, D.N.; Eland, K.L.; Angel, S.M. Dual-pulse LIBS using a pre-ablation spark for enhanced ablation and emission. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.N.; Yueh, F.Y.; Singh, J.P. Time-dependent single and double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of chromium in liquid. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, V.S.; Tarasenko, N.V.; Nedelko, M.I.; Kononov, V.A.; Vasilev, N.N.; Isakov, S.N. Analysis of lead and sulfur in environmental samples by double pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2009, 64, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, M.; Lu, Q.; Dong, C. Determination of the limits of detection for aluminum-based alloys by spatially resolved single- and double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Deguchi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fujita, Y.; Liu, R.; Shiou, F.J.; Zhao, S. Enhancement and stabilization of plasma using collinear long-short double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2018, 142, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Su, M.; Ma, P.; Wang, K.; Min, Q.; Sun, D.; Cheng, R.; Ying, Y.; Dong, C. Expansion dynamics and emission characteristics of nanosecond–picosecond collinear double pulse laser-induced Al plasma in air. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 242, 106773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Q. The effect of inter-pulse delay on the spectral emission and expansion dynamics of plasma in dual-pulse fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 083516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognoni, E.; Cristoforetti, G. Basic mechanisms of signal enhancement in ns double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in a gas environment. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2014, 29, 1318–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, C.; Cortez, J.; Silva, L.; Gonzaga, F.B. Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 463–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepes, E.; Gornushkin, I.; Porizka, P.; Kaiser, J. Tomography of double-pulse laser-induced plasmas in the orthogonal geometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagli, L.; Gaft, M.; Gornushkin, I. Comparison of single and double-pulse excitation during the earliest stage of laser induced plasma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3207–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hou, J.; Ma, W.; Dong, L.; Yin, W.; Xiao, L.; Jia, S.; Yu, J. Species distribution in laser-induced plasma on the surface of binary immiscible alloy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2019, 158, 105644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Han, J.; Xia, G.; Ma, W.; Dong, L.; Yin, W.; Xiao, L.; Jia, S.; et al. Species distribution in laser-induced plasma on the surface of binary miscible alloy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2020, 173, 105987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbini, A.M.E.; Hegazy, H.; Sherbini, T.M.E. Measurement of electron density utilizing the Hα-line from laser produced plasma in air. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2006, 61, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Cao, F.; Motto-Ros, V.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J. Morphology and characteristics of laser-induced aluminum plasma in argon and in air: A comparative study. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2015, 113, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ma, Q.; Perrier, M.; Motto-Ros, V.; Sabourdy, D.; Nguyen, L.; Jalocha, A.; Yu, J. Experimental study of laser-induced plasma: Influence of laser fluence and pulse duration. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2013, 87, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Motto-Ros, V.; Bai, X.; Yu, J. Experimental investigation of the structure and the dynamics of nanosecond laser-induced plasma in 1-atm argon ambient gas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 204101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, N.; Yin, W.; Hou, J.; Bai, C. Research on space-time evolutionary mechanisms of species distributionin laser induced binary plasma. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2023, 43, 2067–2073.32. [Google Scholar]
- Diwakar, P.K.; Harilal, S.S.; Freeman, J.R.; Hassanein, A. Role of laser pre-pulse wavelength and inter-pulse delay on signal enhancement in collinear double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2013, 87, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ma, Q.; Motto-Ros, V.; Lei, W.; Wang, X.; Bai, X. Generation and expansion of laser-induced plasma as a spectroscopic emission source. Front. Phys. 2012, 7, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Emission Line (nm) | Center Wavelength of Filter F1 (nm) | Center Wavelength of Filter F2 (nm) | ICCD Gain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP Plasma | DP Plasma | ||||
| Al I | 394.40 | 396 | 365 | 300 | 200 |
| 396.15 | |||||
| Al II | 358.66 | 358 | 365 | 300 | 200 |
| Ar I | 763.51 | 764 | 786 | 500 | 300 |
| Ar II | 484.78 | 488 | 530 | 500 | 300 |
| SP Plasma | DP Plasma with Different Inter-Pulse Delays | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 ns | 1500 ns | 2000 ns | 3000 ns | ||
| Propagation regime | LSC wave | LSD wave | LSC wave | LSC wave | LSC wave |
| Enhancement mechanism | - | Reheating | Reheating | Reheating | Increase in ablation mass |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bai, J.; Yin, W. Propagation Regimes and Signal Enhancement Mechanisms of Collinear Double-Pulse Plasma with Varying Inter-Pulse Delays. Sensors 2025, 25, 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113409
Zhao Y, Zhang L, Tian Z, Zhang X, Bai J, Yin W. Propagation Regimes and Signal Enhancement Mechanisms of Collinear Double-Pulse Plasma with Varying Inter-Pulse Delays. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113409
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yang, Lei Zhang, Zhihui Tian, Xiuqing Zhang, Jiandong Bai, and Wangbao Yin. 2025. "Propagation Regimes and Signal Enhancement Mechanisms of Collinear Double-Pulse Plasma with Varying Inter-Pulse Delays" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113409
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhang, L., Tian, Z., Zhang, X., Bai, J., & Yin, W. (2025). Propagation Regimes and Signal Enhancement Mechanisms of Collinear Double-Pulse Plasma with Varying Inter-Pulse Delays. Sensors, 25(11), 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113409







